-
我国受镉(Cd)、砷(As)、汞(Hg)、铜(Cu)、锌(Zn)等重金属污染的耕地约有1000万ha,每年因重金属污染的粮食(如“镉米”、“砷米”等)达1000多万t,造成的直接经济损失200余亿元[1]。吉林省农田土壤重金属污染状况表明,玉米田中Cu、Cd含量超标率分别为1.39%和5.56%,大豆田土壤中重金属Cd含量的超标率为6.67%,而水稻田中各重金属元素含量均高于相同pH条件下的土壤环境标准限制[2]。陈亚华等[3]调查发现南京某地区田地土壤Cd、Pb、Zn和Cu等重金属元素含量比国家《土壤环境质量标准》中二级标准值分别高出58%、12%、18%及56%。杨丽等[4]调查和分析衡阳市珠晖区居民绿地土壤Cd、Pb、Zn和Cu总量及其形态,发现Cu、Cd、Pb的含量是国家土壤环境质量二级标准的1—5倍。可见,土壤受重金属Cd、Pb、Zn和Cu复合污染问题日益凸显,对全球土壤质量、土壤生态和人类健康产生重大影响[5-6]。由于土壤固有基质的复杂性,多种重金属之间、重金属与土壤界面之间存在复杂的相互作用,为污染修复和固化剂选择带来了挑战。如何妥善修复土壤重金属污染,尤其是多种重金属复合污染土壤引起了社会的广泛关注。
生物炭具有多孔、比表面积大且富含多种官能团等特性,已被广泛应用于土壤改良、作物增产、污染物治理、固氮及缓解全球气候变化[7-11]。近年来,国内外学者围绕生物炭材料的特性表征、重金属污染修复效果与吸附固持机制方面进行了大量的研究[12-14]。在土壤中施加生物炭不仅能减少土壤中的N、P等营养元素的流失,提高其利用率,同时能增加土壤持水能力[15-16]。生物炭的疏松多孔结构以及巨大的表面积和阳离子交换量(CEC)可以改善土壤理化性质,提高作物产量,还能吸附土壤中的污染物,降低土壤中砷的生物有效性和迁移转化能力[17-18]。陈再明等[19]通过缺氧裂解制备了水稻秸秆生物炭,发现其对重金属Pb2+的吸附量是原秸秆生物质的5—6倍。许超等[20]在污染土壤中施用生物炭,可降低重金属Zn、Cd、Pb、Cu的有效性和生态风险,提高土壤养分含量起到改良土壤作用。为了提高生物炭的物理化学性质,进而提高其对土壤重金属污染的修复能力,改性生物炭成为目前研究的热点。
锰及其氧化物是土壤的重要组分,主要包括软锰矿、斜方锰矿和水锰矿等。近年来,锰氧化物在污染土壤修复方面发挥了重要作用。锰氧化物特有的表面化学性质,影响着土壤对重金属的吸附(沉淀)作用,主要是通过改善土壤的理化性质(pH、氧化还原电位、含水量、孔隙、黏度等),改变重金属或类金属在土壤中的淋溶、移动性、迁移转化[21]。将锰氧化物作为改性材料应用于复合材料的制备一直是国内外学者研究的热点,如锰氧化物-活性炭复合材料用于固化土壤Pb、Cu污染的研究已取得良好的效果[22]。生物炭经锰氧化物负载后,能够显著增加表面的羟基、羧基和酚羟基等官能团的数量,提高对重金属的吸附能力[23-28]。于志红等[21]制备了玉米秸秆生物炭-锰氧化物复合材料,测试了其对红壤吸附Cu的影响表明,复合材料能增加红壤对Cu的吸附能力,降低Cu的可移动性和生物有效性。MnOx/生物炭复合材料对水体中重金属的吸附效果会明显好于单一生物炭[29-30],然而,将其应用于土壤重金属修复时,MnOx/生物炭固化重金属的效果和机理及是否会带来土壤Mn污染鲜见报道。另外,以往的研究大多处理单一重金属污染土壤[31-32],实际污染土壤中往往是多种重金属共存,因此,MnOx/生物炭复合材料对土壤中多种重金属的固化能力及机制需要进一步研究。
本文采用高锰酸钾溶液改性生物炭,研究不同MnOx负载浓度对MnOx/生物炭复合材料的性能影响;通过批量吸附实验和表征分析,探讨MnOx/生物炭复合材料对土壤重金属Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu的固化效果及其机理,以期为利用MnOx/生物炭复合材料环保功能修复重金属复合污染土壤提供科学依据。
-
本实验所用的生物质原料取自天津市北辰区农田小麦秸秆,将小麦秸秆自然风干后,磨碎过100目尼龙筛,将得到的小麦秸秆粉末装在自封袋中备用。实验药品Pb(NO3)2、Cu(NO3)2、Cd(NO3)2、Zn(NO3)2购买于天津江天化工试剂有限公司,皆为分析纯试剂,溶液用蒸馏水配制。
-
本实验所采用的土壤取自天津市北辰区河北工业大学绿化带表层(0—20 cm)土壤,在用于稳定化实验前,将土壤自然风干,剔除杂物,研磨过2 筛,均匀混合后,测得其理化性质:pH 7.48(土水比为1∶2.5,依据《中华人民共和国农业行业标准-土壤pH的测定》NY/T1377-2007),有机质8.26 g·kg−1,将按照美国环保署(USEPA)对土壤中总重金属含量测定方法的规定(USEPA method 3051A),测得土壤中重金属Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu含量均低于检测限(0.1 mg·kg−1)。
为研究MnOx/生物炭复合材料对污染土壤中重金属的固化效果,取浓度0.02 g·L−1的Cd(NO3)2、1.3 g·L−1的Pb(NO3)2、7.8 g·L−1的Zn(NO3)2和2.6 g·L−1的Cu(NO3)2溶液各1 L加入到5.2 kg上述备好的土样中,边添加重金属溶液边搅拌混匀。土壤风干后,老化6个月,过2 mm筛,为供试重金属复合污染土壤。经测定,复合污染土壤中Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu的实际测定值分别为3.8、248、1451、511 mg·kg−1,分别达到《土壤环境质量标准》(GB15618—2008)农业用地(pH>7.5,菜地)无机污染物的环境质量第二级标准值(0.6、50、300、100 mg·kg−1)的6.3、5.0、4.8、5.1倍。
-
通过浸渍-热解法制备高锰酸钾改性生物炭,将20 g小麦秸秆粉末分别浸泡在100 mL浓度为0.05、0.1、0.2 mol·L−1的KMnO4溶液中,磁力搅拌2 h后,将混合物放置烘箱中于80 ℃条件下烘干24 h。将KMnO4处理后的生物质在N2中于600 ℃的管式炉中热解1 h,得到MnOx负载生物炭,按照Mn在复合材料中的质量分数分别记为1.38%MnOx/生物炭、2.76%MnOx/生物炭和5.52%MnOx/生物炭。将其用蒸馏水冲洗3次以去除杂质,在80 ℃条件下烘干12 h,放在密封容器中备用。同时,以未经KMnO4处理的生物质为原料,在相同条件下制备未经改性的小麦秸秆生物炭(biochar),用于对照实验。
表征研究上述制备的固化剂的理化性质。通过X射线衍射(X-ray diffraction, XRD)进行物相分析,在5°—90°的2θ范围内,以6(°)·min−1的扫描速度和0.02°的步长测试5.52%MnOx/生物炭和未改性的小麦秸秆生物炭的晶型,以判断MnOx是否成功负载到生物炭上;材料的比表面积采用Brunauer-Emmett-Tuller(BET)N2吸附方法测定,孔容积和孔径采用Barrett-Joyner-Halenda(BJH)方法计算。采用扫描电子显微镜(Scanning Electron Microscope, SEM)观察材料的表面形貌结构。材料改性前后及固定化实验结束后土壤表面元素及变化通过X射线光电子能谱(X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy,XPS)进行分析。
-
称取被污染土壤200 g置于500 mL烧杯中。设置5组实验进行固定化实验研究,每种处理设置3个重复。第一组不加固化剂作为对照实验(CK),第二、三、四、五组分别加入2 g的未改性生物炭、1.38%MnOx/生物炭、2.76%MnOx/生物炭和5.52%MnOx/生物炭。将复合材料与受污染土壤按上述比例充分混匀后,每个烧杯都用扎过孔的保鲜膜封口,放在室温条件下进行固定化反应。反应过程中每隔5 d向烧杯中补充去离子水,以保持土壤含水量在20%左右。
为了研究复合材料添加量对土壤重金属的固化效果,选取上一实验中得到的效果最优的复合材料,将材料在土壤(200 g)中的添加量分别设置为1、2、4、8 g(即0.5%、1%、2%和4%)。为了研究固定化时间对固化效果的影响,分别在反应进行第3 d、7 d、14 d、29 d、46 d时,从烧杯中取出一定质量的土壤,进行TCLP(Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure)重金属毒性浸出测试。
采用TCLP法评估MnOx/生物炭对土壤重金属的固定化效果。TCLP测定采用中华人民共和国环境保护行业标准(HJ/T300-2007)中的方法,即采用醋酸和氢氧化钠缓冲溶液浸提,浸提过程为:在1.5 g土壤中加入30 mL的TCLP提取液(固液比1∶20),在30 r·min−1的翻转式振荡器上反应18 h,然后在2000 r·min−1速度下离心20 min,过0.45 μm滤膜,采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP)测定其上清液中重金属浓度。其中上述TCLP提取液的制备方法为:加5.7 mL冰醋酸至蒸馏水中,采用1 mol·L−1的NaOH和HNO3溶液调节其pH值为4.9,定容至1 L备用。
在46 d实验结束后,参照Tessier的形态分级分析方法,测定土壤重金属的赋存形态。该方法将土壤重金属形态分为可交换态(EX)、碳结合态(CB)、锰氧化物结合态(OX)、有机物结合态(OM)和残渣态(RS),具体操作步骤按照参考文献进行[33]。
-
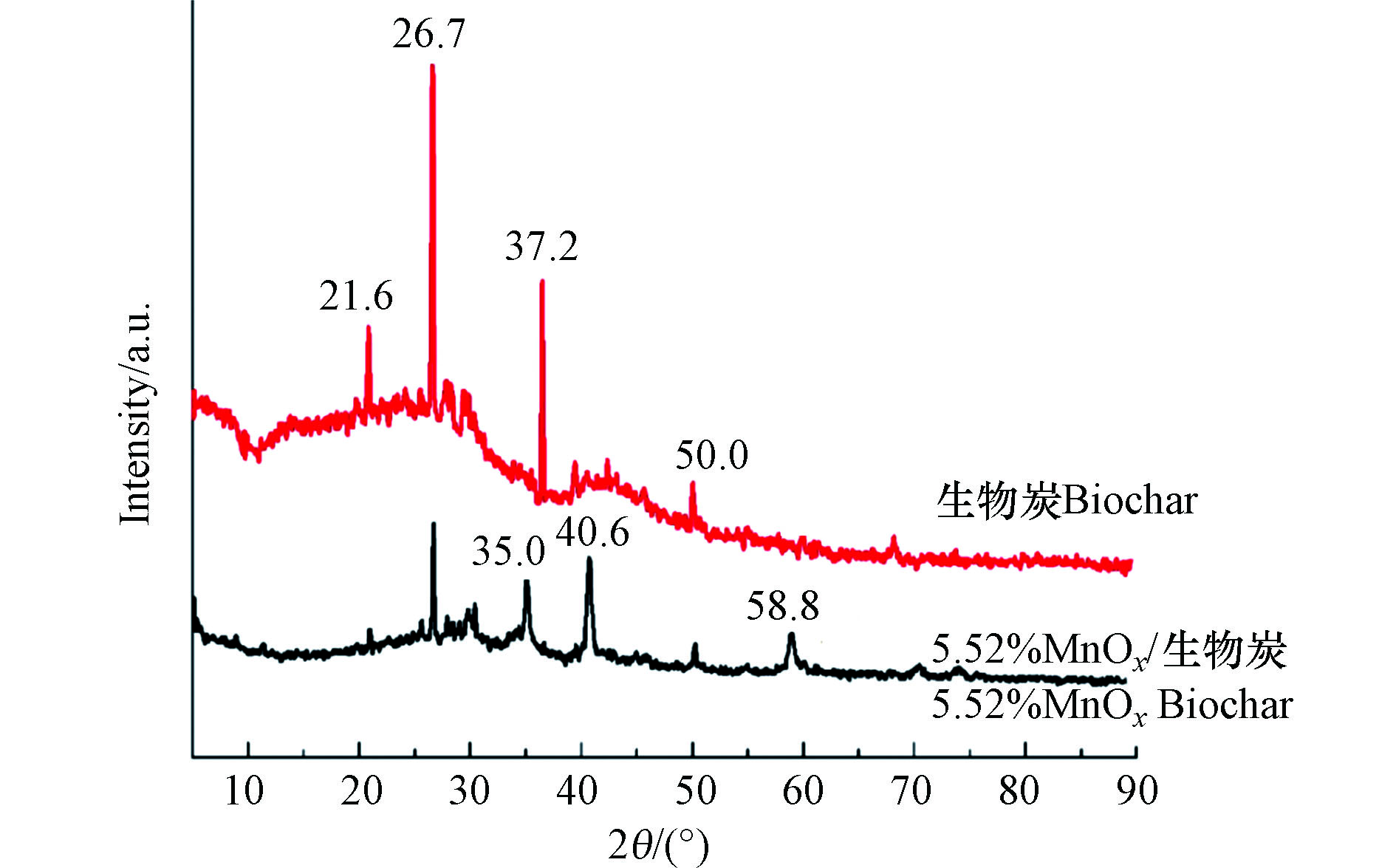
未改性生物炭和5.52%MnOx/生物炭的XRD谱图如图1所示。XRD分析表明,对于原始生物炭来说,位于21.6°的特征峰表示生物质原材料在碳化热解过程中生成的无定形碳,26.7°和37.2°的特征峰对应石墨结构的特征峰(JCPDS01–0640),50.0°表示方解石的特征峰(JCPD41-1475)[34-35]。5.52% MnOx/生物炭表面保留了生物炭在21.6°、26.7°和50.0°处的特征峰,而锰以MnOx的形式存在,比如:2θ为35.0°的衍射峰代表MnO2(JCPD 42-1316)[36],40.6°和58.8°处属于Mn3O4的特征峰(JCPD 24-0734/18-0803)[37]。以上结果说明高锰酸钾处理的生物质热解后生成了MnOx/生物炭复合材料。
-
生物炭及MnOx/生物炭的比表面积、孔容积和孔径如表1所示。MnOx/生物炭的比表面积和孔容积比单一生物炭增加了近一倍,其中2.76%MnOx/生物炭的比表面积和孔容积分别为26.5 m2·g−1和0.032 cm3·g−1,远高于原始生物炭,说明KMnO4的活化过程利于打开生物炭的孔隙结构,从而增加其比表面积[21]。随着MnOx 负载量从2.76%提升到5.52%,5.52%MnOx/生物炭的比表面积和孔容积有所降低,这是由于锰氧化物含量增加填充了生物炭中部分介孔和微孔。整体来看,高锰酸钾改性能够提高生物炭的比表面积和孔容积,增加了更多吸附点位,从而利于其对重金属的固化。与生物炭相比,MnOx/生物炭的孔径呈现先降低后增大的趋势,证明了KMnO4的强氧化性能可能导致微孔结构的破坏和微孔向中/大孔的变形。
-
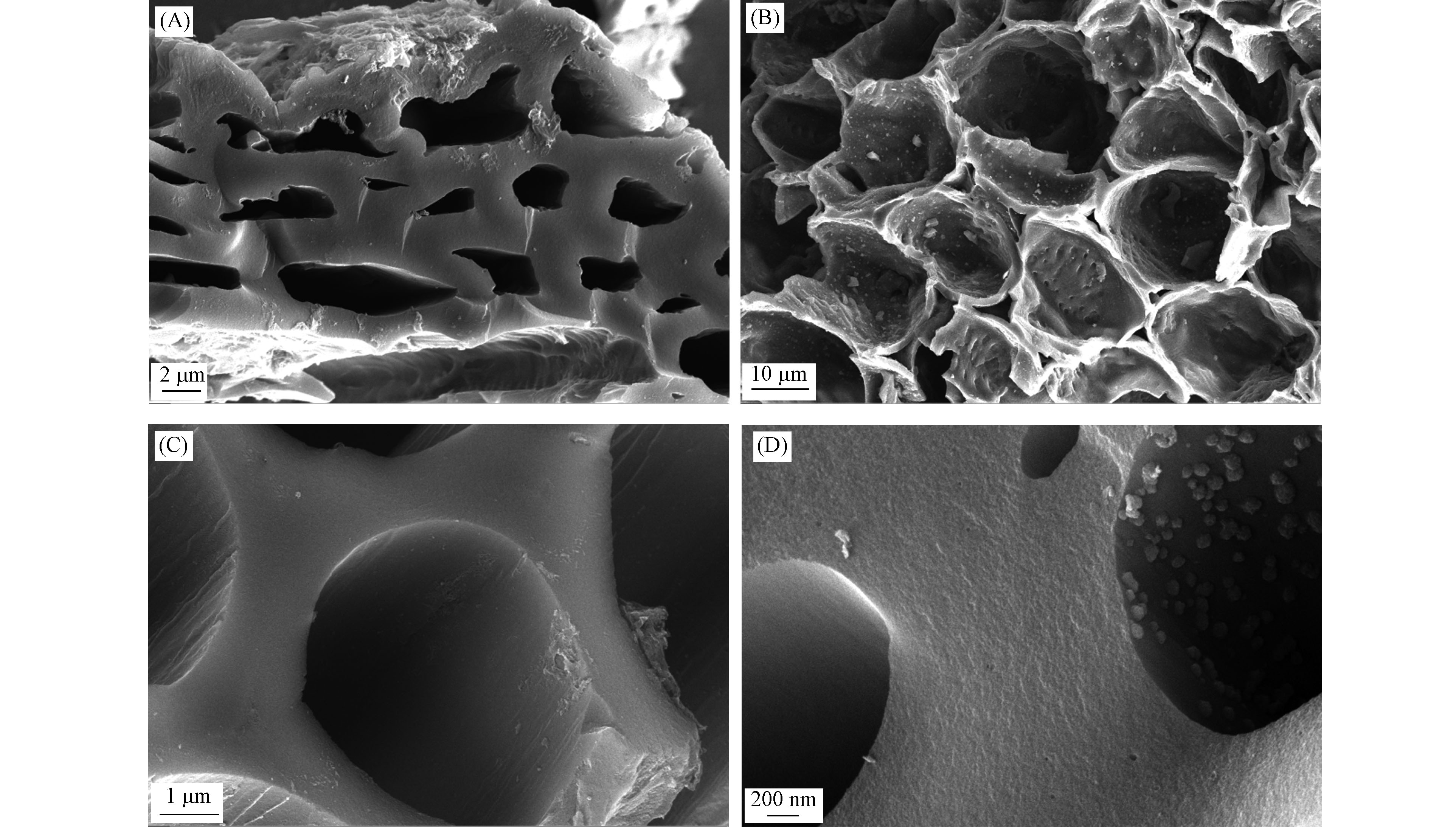
从图2可以看到,MnOx/生物炭复合材料保持了未改性生物炭的多孔结构,但表面有锰氧化物的存在。当锰氧化物负载量为5.52%时,大量的锰氧化物可能会占据生物炭的中孔和微孔,使复合材料的比表面积有所下降,这与BET的分析结论一致。虽然较多锰氧化物的引入降低了复合材料的比表面积,但是复合材料对Pb、Cu、Zn和Cd的最大吸附量依旧提高,这是由于锰氧化物增加了复合材料表面的吸附位点[27]。通过XPS图(图3)可知,MnOx/生物炭复合材料中形成较多的Mn−O键和Mn−OH键(详细分析见2.1.4部分),可见虽然与2.76%MnOx/生物炭相比,5.52%MnOx/生物炭的比表面积降低,但是平均孔径增大,增强了锰氧化物的负载,使得复合材料含氧官能团含量增加,为重金属的吸附提供了有利条件。
-
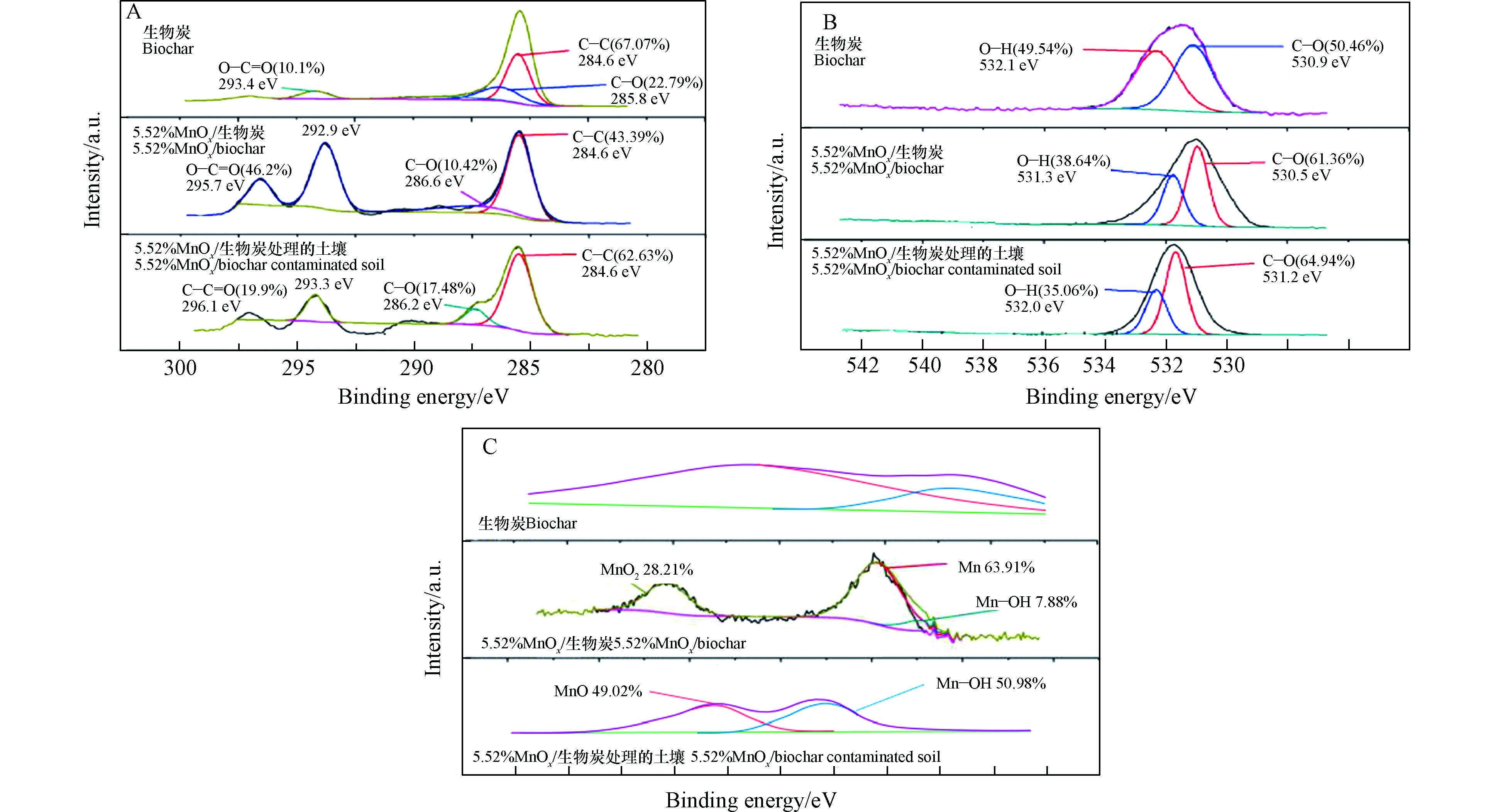
MnOx/生物炭表面C、O和Mn元素的形态分析如XPS图谱所示(图3)。对于生物炭来说,C1s的光谱在284.6 eV、285.8 eV和293.4 eV的特征峰分别代表官能团C—C、C—O和 O—C=O的振动峰(图3A)。当被改性后,与生物炭相比,复合材料表面C—C和C—O官能团的比例分别从67.07%和22.79%降至43.39%和10.42%,说明C—C和C—O在MnOx和生物炭的结合中起到重要作用。O—C=O的比例从10.1%上升至46.2%。这可能是由于KMnO4与生物炭之间发生了氧化还原作用,使得材料表面生成了更多的O—C=O[38]。
图3B中O1s的光谱在530.9 eV和532.1 eV处的结合能分别归因于C—O和O—H。与生物炭相比,MnOx/生物炭表面的C—O官能团比例由50.46%上升到61.36%,O−H的比例由49.54%下降到38.64%,这些变化进一步表明生物炭经KMnO4处理后,两者发生了氧化还原反应。改性后的生物炭表面C—O和O—C=O的含量增加,说明生物炭表面羟基和羧基官能团的增加是由于KMnO4的氧化作用。
对于Mn2p来说,未经改性的生物炭表面没有出现Mn2p的特征峰,说明生物炭不存在锰元素(图3C)。将生物炭负载5.52%MnOx后,图3C中Mn2p的能谱峰分为3个峰,分别为:MnO2、MnO和MnOH,这说明KMnO4能够成功将MnOx负载于生物炭表面,实际上是两者发生了化学反应,产生了新的化学键。
与5.52%MnOx/生物炭相比,复合材料与土壤固化反应后表面O—C=O和O—H的比例分别下降26.30%和3.58%(图3A和B),说明O—C=O和O—H与重金属的络合和氧化还原对复合材料对重金属的固化起到促进作用。另外,经固化处理后,MnO2的特征峰消失,MnO的比例下降,说明5.52%MnOx/生物炭中的MnO和MnO2对重金属的固化发挥了较大的作用。由此可知MnOx/生物炭固定土壤中重金属Pb、Cu、Zn和Cd的过程受吸附和氧化共同作用。
-
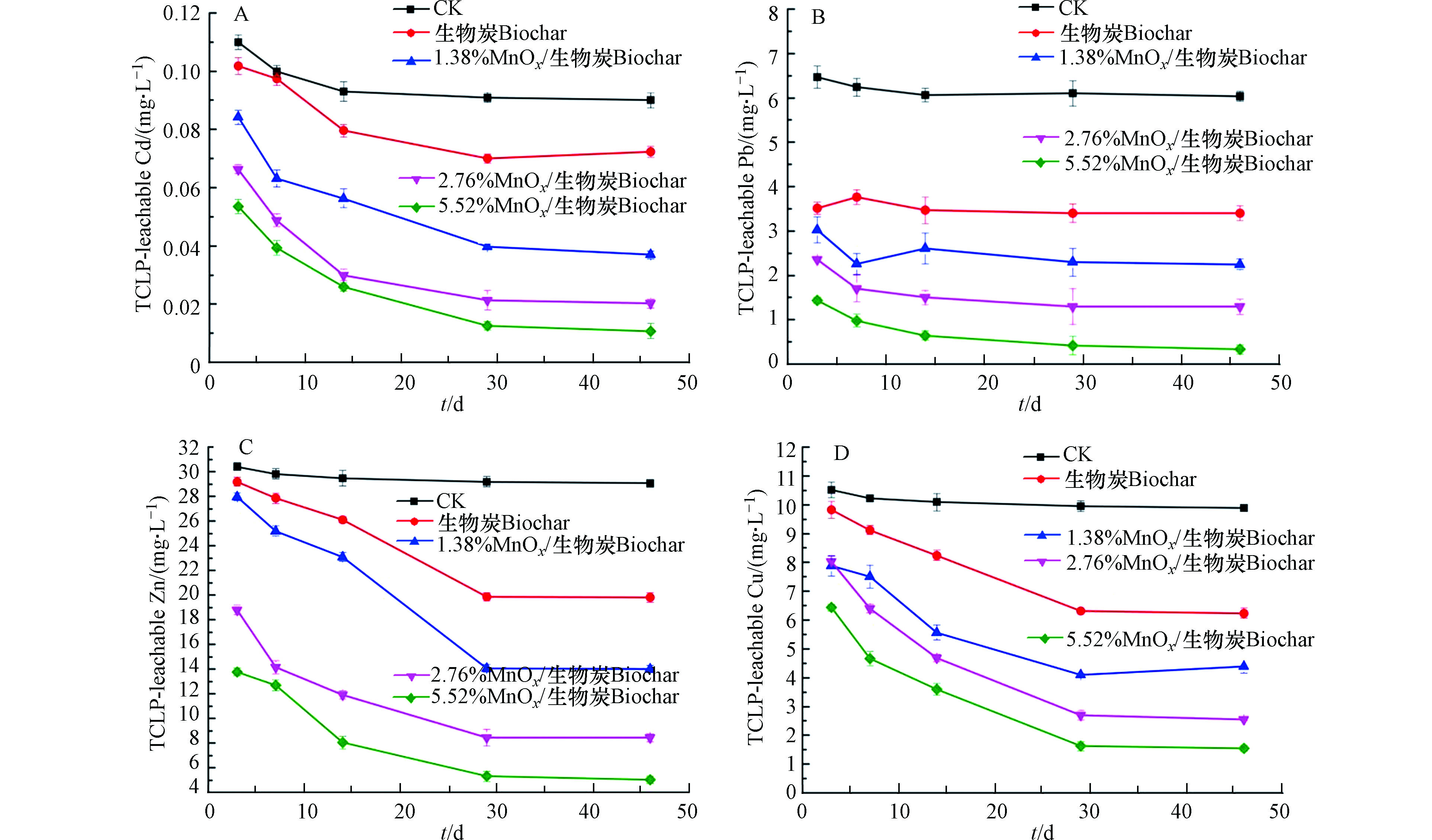
TCLP已被广泛用于评估土壤中重金属的固化效果。随着固化时间从3 d增加到46 d,未添加的受污染土壤TCLP可浸出的Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu的浓度分别保持在0.11—0.09 、6.47—6.04 、30.41—29.06、10.51—9.89 mg·L−1。随着MnOx的负载浓度增加,复合材料对重金属的固化效果提升。例如,当固化时间为46 d时,生物炭、1.38%MnOx/生物炭、2.76%MnOx/生物炭和5.52%MnOx/生物炭处理后土壤TCLP可浸出Cd的浓度分别降低了27.7%、63.1%、79.8%和89.3%(图4A)。MnOx/生物炭复合材料固化土壤重金属比生物炭更有效,这是因为锰氧化物能够显著增加生物炭表面的羟基、羧基和酚羟基等官能团的数量(图3A和B),增加的官能团和MnOx为复合材料提供更多活性点位,因此MnOx/生物炭比未改性生物炭具有更高的重金属固定化能力。
图4结果还表明,在相同添加量(1%)下,添加固化剂的处理组中重金属的固化效果都随着固化时间的增加而提高。例如,对于5.52%MnOx/生物炭来说,当固化时间从3 d增加到29 d时,Cd、Pb、Zn 和Cu的去除率分别从46.5%、77.0%、52.7%、36.9%升高到87.5%、93.3%、82.2%、84.1%。将固化时间继续延长到46 d,去除率没有明显增加,说明29 d时已达到复合材料固化效能的最佳时间。经过46 d的固定,复合材料对这四种重金属的固定效率依次是Pb>Cd>Cu>Zn。这可能是由于TCLP可浸出重金属的浓度不仅取决于土壤中的总含量,而且还取决于重金属的化学形态,即游离态与无机配体(OH−、CO32-、PO4−、SO42-、NO3−)络合的物种以及与有机化合物络合的物种,对于Pb而言,与有机化合物复合的化学物种更稳定,且形成的沉淀物溶度积(Ksp)最大,因此其活性最低,固化效果最好[39]。
-
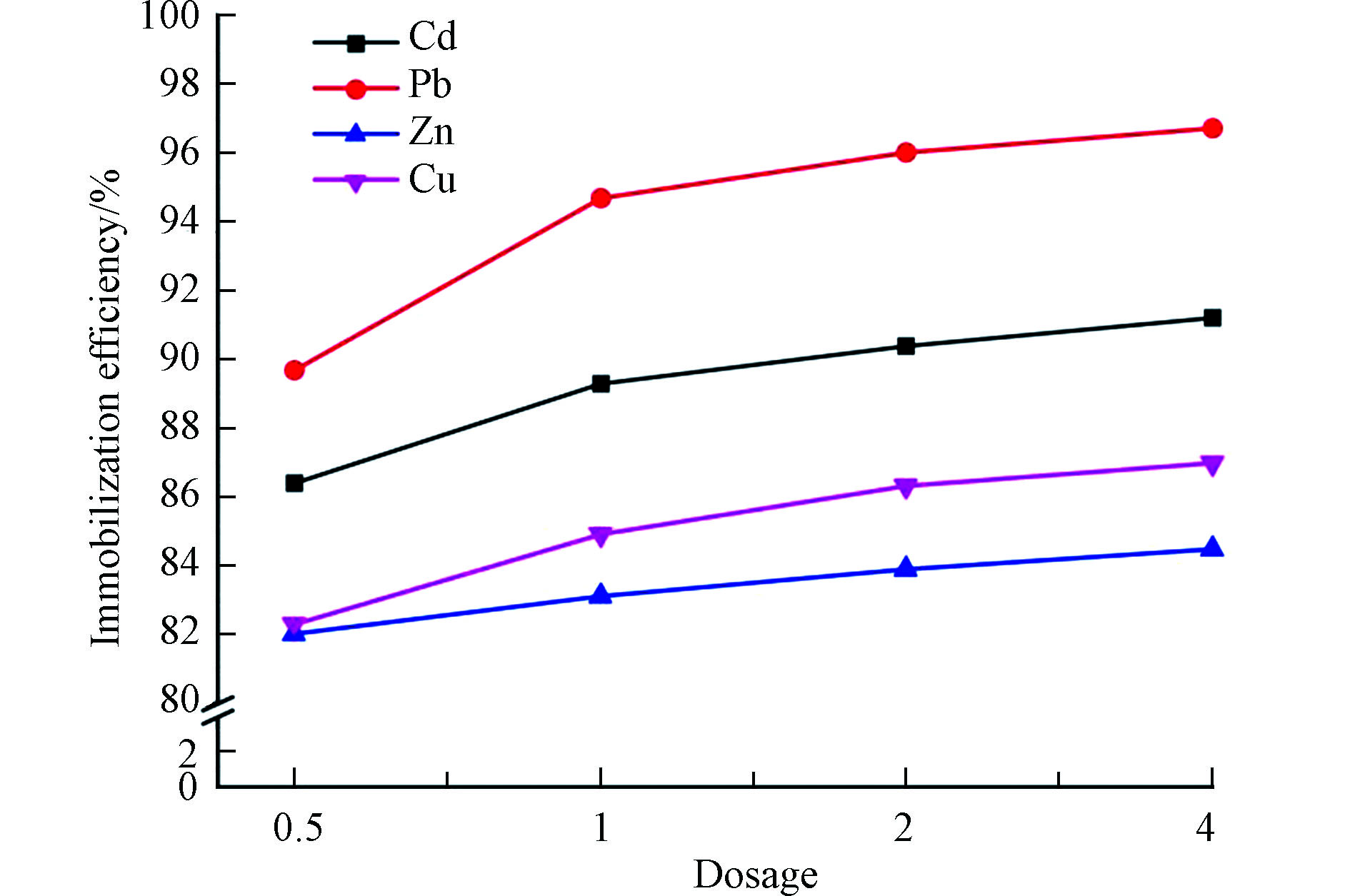
为了研究复合材料添加量对土壤重金属的固定化效果的影响,选取上一实验室得到的效果最优的复合材料(即5.52%MnOx/生物炭复合材料),将添加量设置为0.5%、1%、2%、和4%。结果如图5所示,重金属固化效率随着5.52%MnOx/生物炭复合材料添加量的增加而提升。当添加量为0.5%时,Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu的固定化效率分别为86.4%、89.7%、82.0%、82.3%,当添加量升高到4%时,相应的重金属固化效率分别升高至91.2%、96.7%、84.5%、87.0%。值得注意的是,此时的TCLP可浸出重金属Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu浓度分别为0.009、0.206、4.61、1.33 mg·L−1,Cd和Pb浓度满足《污水综合排放标准》(GB 8978-1996)中第一类污染物最高允许排放浓度(0.1 mg·L−1和1.0 mg·L−1),Zn和Cu满足第二类污染物最高允许排放浓度的三级标准(5.0 mg·L−1和2.0 mg·L−1)。
-
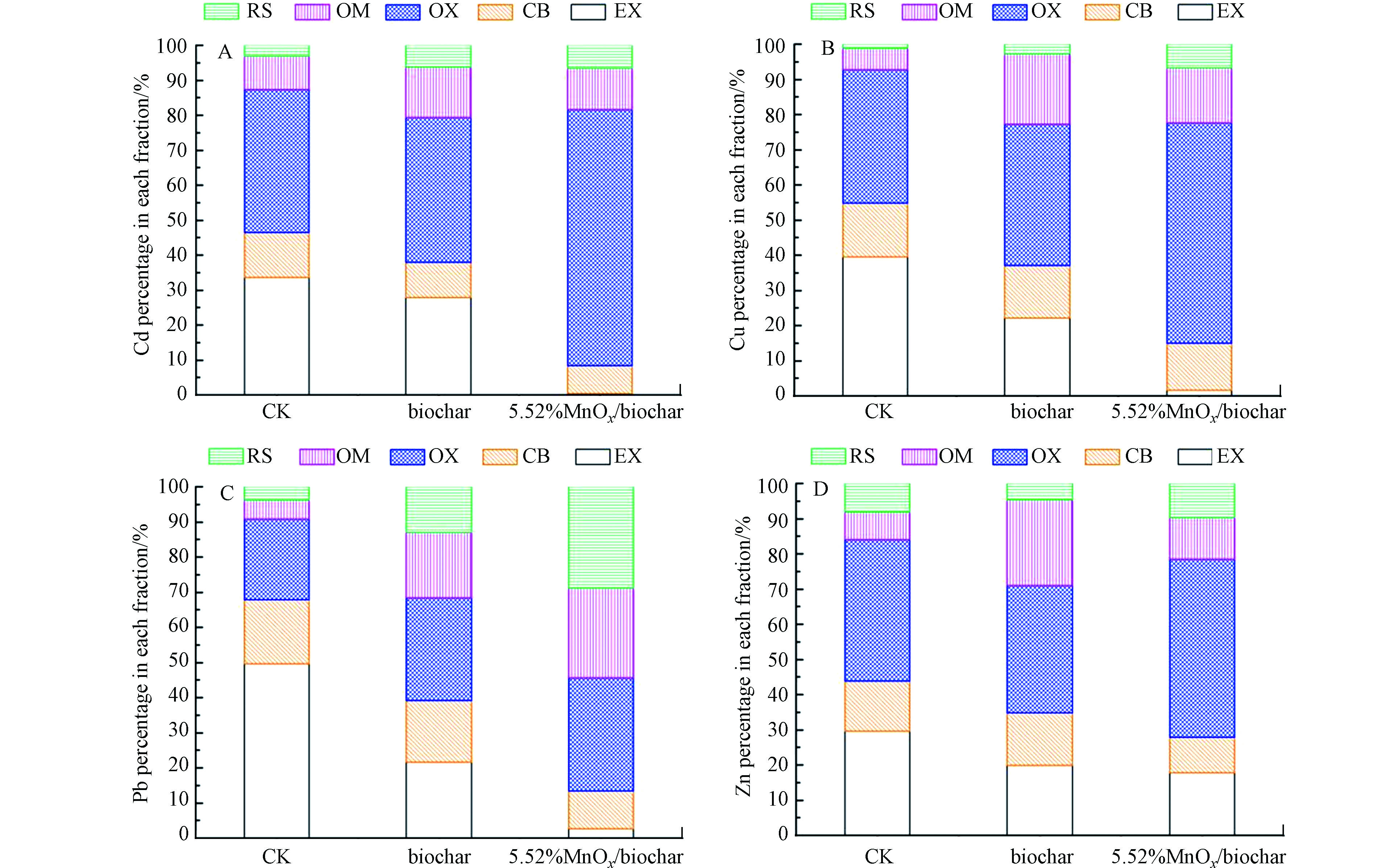
通过形态分级实验研究固化结束后土壤中重金属的赋存形态变化(图6)。MnOx/生物炭复合材料的添加可促进重金属Cd、Pb、Zn和Cu由EX和CB向更加稳定的OX、OM和RS转化,从而降低污染土壤重金属的活性态比例。比如,对Cd来说(图6A),与未加固化剂的土壤相比,经5.52%MnOx/生物炭处理后,土壤中Cd的EX含量由33.6%降低至0.3%,OX由40.8%显著增加至73.1%,OM由9.5%增加至11.9%,CB由12.9%下降到8.1%。其他3种重金属的形态变化与Cd的总体趋势一样,与原始生物炭相比,5.52%MnOx/生物炭更能促进活跃态重金属向稳定态转化,从而降低污染土壤重金属的毒性效应。
-
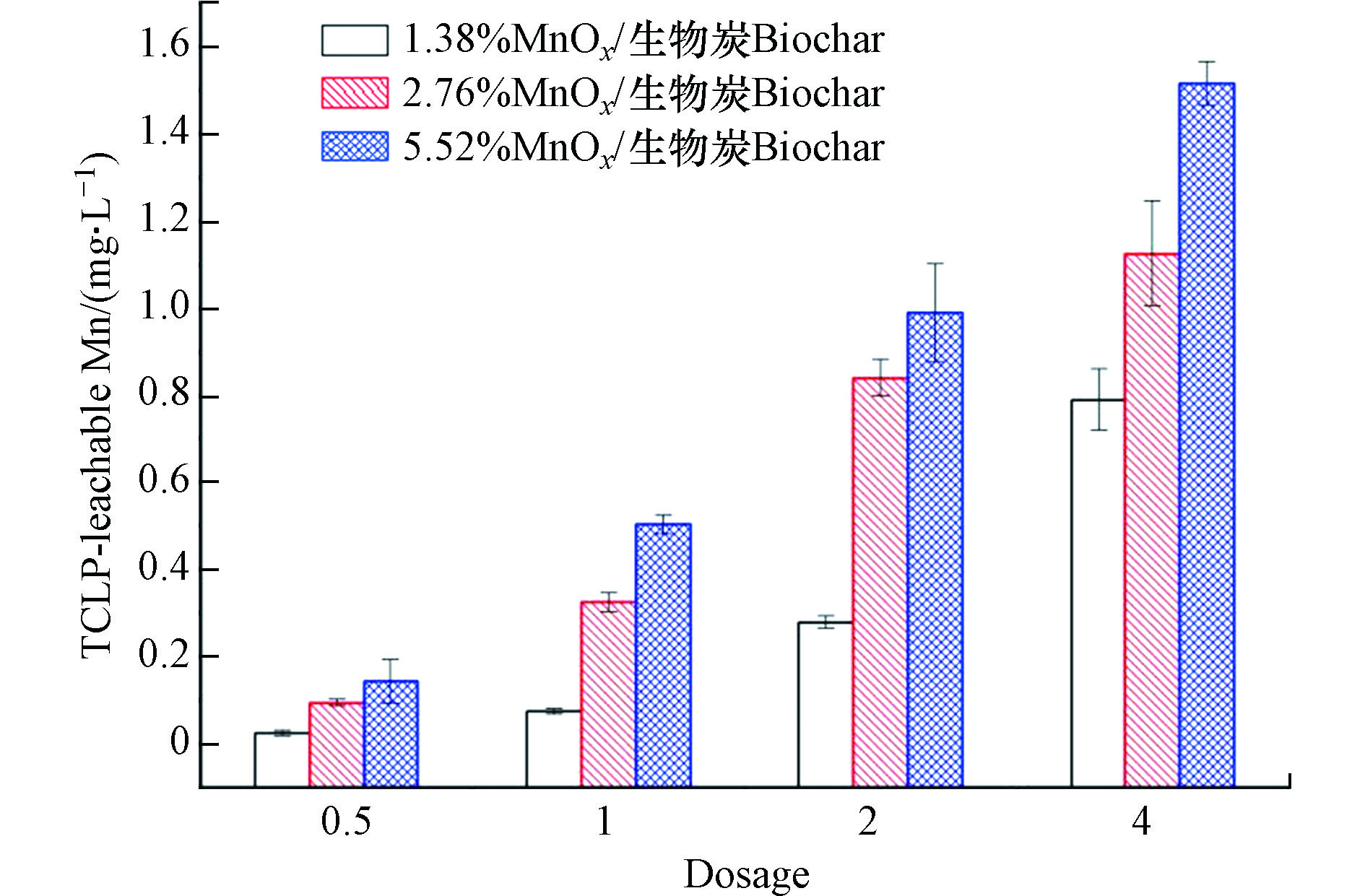
为了判断采用MnOx/生物炭复合材料固定土壤重金属是否会造成土壤锰污染,测定了不同MnOx/生物炭处理后土壤的TCLP浸出液中Mn的浓度,如图7所示。从图7可以看出,在MnOx/生物炭复合材料添加量相同的条件下,Mn元素浸出浓度随MnOx负载率的增大而升高;在MnOx负载率相同的条件下,Mn元素浸出浓度随MnOx/生物炭复合材料添加量增加而升高;但Mn元素浸出浓度最高仅为1.52 mg·L−1(复合材料MnOx负载率为5.52%,添加量为4%),满足污水综合排放标准(GB 8978-1996)中第二类污染物最高允许排放浓度的一级标准(2.0 mg·L−1),因此,采用MnOx/生物炭复合材料固定土壤重金属时,不会造成土壤锰污染。
-
本文通过高锰酸钾溶液浸渍-热解改性小麦秸秆生物炭,成功制备了MnOx/生物炭复合材料,并将其应用于土壤重金属Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu污染修复,取得以下结论:
(1)高锰酸钾改性能够提升MnOx/生物炭复合材料的比表面积、孔容积,增加其表面官能团数量。
(2)当固化剂添加量为1%时,MnOx/生物炭对土壤中Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu固化效果是未改性生物炭的2—4倍。
(3)复合材料对重金属的固化效果随着MnOx负载浓度、固化时间和复合材料添加量的增加而提高,5.52%MnOx/生物炭在固化时间为29 d的条件下,对重金属固化效率最高。处理后土壤TCLP可浸出重金属Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu浓度分别为0.009、0.206、4.61、1.33 mg·L−1,Cd和Pb浓度满足《污水综合排放标准》(GB 8978-1996)中第一类污染物最高允许排放浓度,Zn和Cu满足第二类污染物最高允许排放浓度的三级标准。
(4)MnOx/生物炭固定土壤中重金属Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu的过程受吸附和氧化共同作用。
综上,MnOx/生物炭复合材料在修复土壤重金属复合污染中具备较大的应用前景,且固定处理之后不会造成土壤锰污染。
MnOx/生物炭复合材料对土壤重金属的固化效果及其机理研究
Immobilization of heavy metals in contaminated soils using MnOx/biochar composites
-
摘要: 为了探究高锰酸钾改性生物炭(MnOx/生物炭)对土壤重金属的固化效果与生物炭的差异,本文采用高锰酸钾溶液改性小麦秸秆生物炭,研究不同MnOx负载浓度、复合材料添加量和固化时间对MnOx/生物炭复合材料固化土壤重金属Cd、Pb、Zn和Cu性能的影响及其机理。结果表明,锰氧化物负载能够显著增加生物炭表面的羟基、羧基和酚羟基等官能团的数量。土壤毒性浸出液(TCLP)中重金属浓度变化表明,当固化剂添加量为1%时,MnOx/生物炭对土壤中Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu固化效果是未改性生物炭的2—4倍;在相同固化时间内,MnOx/生物炭复合材料对重金属固定化效果随着添加量和MnOx负载的浓度升高而增大。MnOx/生物炭复合材料的添加可促进重金属Cd、Pb、Zn和Cu由可交换态(EX)和碳结合态(CB)向更加稳定的锰氧化物结合态(OX)、有机物结合态(OM)和残渣态(RS)转化,从而降低污染土壤重金属的活性态比例。MnOx/生物炭主要通过吸附和氧化的共同作用,实现对土壤中重金属的高效固定。固化处理后土壤TCLP浸出液中Mn浓度均低于1.52 mg·L-1,说明使用复合材料不会造成土壤锰污染。MnOx/生物炭复合材料在修复重金属污染土壤中具有较大的应用潜力。Abstract: In this work, potassium permanganate solution was used to modify wheat straw biochar to explore the difference between manganese-modified biochar (MnOx/biochar) and biochar in the immobilization of soil heavy metals. The effect of different MnOx loading concentration, MnOx/biochar dosage, and reaction time on the heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Zn, and Cu) immobilization ability of MnOx/biochar composites and its mechanism were studied. The results showed that manganese oxide loading could significantly increase the number of functional groups on the surface of biochar. The changes in the concentration of heavy metals in the soil toxicity leachate (TCLP) showed that, the immobilization rate of MnOx/biochar on Cd, Pb, Zn, and Cu in the soil was 2—4 times that of unmodified biochar at a MnOx/biochar dosage of 1%. The immobilization ability of MnOx/biochar composite materials on heavy metals increased with the increase of the MnOx/biochar dosage and the concentration of MnOx loading. The addition of MnOx/biochar composite materials promoted the conversion of more accessible Cd, Pb, Zn and Cu (EX and CB) into the less accessible forms (OX, OM, and RS) to reduce the activeness of Cd, Pb, Zn and Cu. Surface sorption and oxidation were dominant mechanisms for heavy metals immobilization. After solidification, the Mn concentration in the soil TCLP leaching solution was lower than 1.52 mg·L-1, indicating that the application of MnOx/biochar would not cause soil manganese pollution. The MnOx/biochar composite material has great application potential in the remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils.
-
Key words:
- biochar /
- manganese oxide /
- soil /
- heavy metals
-

-
表 1 生物炭及MnOx/生物炭的理化性质
Table 1. Physiochemical properties of biochar and MnOx/ biochars
生物炭
BiocharBET比表面积/(m2 ·g−1)
BET surface areaBJH孔容积/(cm3 ·g−1)
BJH pore volumeBJH孔径/nm
BJH pore size生物炭 7.26 0.011 6.11 1.38%MnOx/生物炭 11.2 0.015 5.41 2.76%MnOx/生物炭 26.5 0.032 4.83 5.52%MnOx/生物炭 11.8 0.025 8.66 -
[1] 周建军, 周桔, 冯仁国. 我国土壤重金属污染现状及治理战略 [J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2014, 29(3): 315-320, 350, 272. ZHOU J J, ZHOU J, FENG R G. Status of China's heavy metal contamination in soil and its remediation strategy [J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014, 29(3): 315-320, 350, 272(in Chinese).
[2] 梁烜赫, 曹铁华, 张磊, 等. 吉林省农田重金属含量及其在作物中的累积 [J]. 吉林农业科学, 2011, 36(6): 59-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8701.2011.06.018 LIANG X H, CAO T H, ZHANG L, et al. Content of heavy metals in farmland soil and accumulation in crops in Jilin province [J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 36(6): 59-62(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8701.2011.06.018
[3] 陈亚华, 黄少华, 刘胜环, 等. 南京地区农田土壤和蔬菜重金属污染状况研究 [J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2006, 15(3): 356-360. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2006.03.017 CHEN Y H, HUANG S H, LIU S H, et al. Study of the heavy metal contamination in soils and vegetables in Nanjing area [J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2006, 15(3): 356-360(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2006.03.017
[4] 杨丽, 毛祖莉. 衡阳市绿地Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb形态分布及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(S1): 227-231. YANG L, MAO Z L. Study on the Speciation of Cu and Zn and Risk Assessment in Urban Green Space in Hengyang City [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 42(S1): 227-231(in Chinese).
[5] 宋志政, 周润声. 我国重金属污染土壤的治理与修复研究进展 [J]. 化工设计通讯, 2020, 46(2): 216-217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2020.02.144 SONG Z Z, ZHOU R S. Research progress in remediation and remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil in China [J]. Chemical Engineering Design Communications, 2020, 46(2): 216-217(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2020.02.144
[6] 王丽娟. 土壤重金属污染的危害及修复 [J]. 现代农业, 2017(1): 73-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0708.2017.01.061 WANG L J. Harm and remediation of heavy metal pollution in soil [J]. Modern Agriculture, 2017(1): 73-75(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0708.2017.01.061
[7] 吕宏虹, 宫艳艳, 唐景春, 等. 生物炭及其复合材料的制备与应用研究进展 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(8): 1429-1440. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.08.001 LV H H, GONG Y Y, TANG J C, et al. Advances in preparation and applications of biochar and its composites [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(8): 1429-1440(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.08.001
[8] 朱灵峰, 何怡雪, 张昊, 等. 锰改性玉米秸秆生物炭吸附去除1, 4-苯醌 [J]. 江苏农业学报, 2016, 32(3): 570-574. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2016.03.013 ZHU L F, HE Y X, ZHANG H, et al. Adsorptive removal of 1, 4-benzoquinone by Mn-modified cornstalk biochar [J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 32(3): 570-574(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2016.03.013
[9] 陈温福, 张伟明, 孟军, 等. 生物炭应用技术研究 [J]. 中国工程科学, 2011, 13(2): 83-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2011.02.015 CHEN W F, ZHANG W M, MENG J, et al. Researches on biochar application technology [J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2011, 13(2): 83-89(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2011.02.015
[10] 何振嘉. 生物炭对土壤重金属污染修复研究 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2019, 47(21): 12-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2019.21.004 HE Z J. Study on biochar’s remediation of heavy metal pollution in soil [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(21): 12-13(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2019.21.004
[11] LV H H, ZHAO H, TANG J C, et al. Immobilization of hexavalent chromium in contaminated soils using biochar supported nanoscale iron sulfide composite [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 194: 360-369. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.182 [12] 吴诗雪, 王欣, 陈灿, 等. 凤眼莲、稻草和污泥制备生物炭的特性表征与环境影响解析 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(12): 4021-4032. WU S X, WANG X, CHEN C, et al. Characterization of biochar derived from water hyacinth, rice straw and sewage sludge and their environmental implications [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(12): 4021-4032(in Chinese).
[13] 孟梅, 华玉妹, 朱端卫, 等. 生物炭对重金属污染沉积物的修复效果 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 35(12): 4021-4032. MENG M, HUA Y M, ZHU D W, et al. Remediation effect of biochar on sediment contaminated by heavy metals [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 35(12): 4021-4032(in Chinese).
[14] 尹光彩, 陶琳, 宋小旺, 等. 不同原料生物炭的改性及其吸附/钝化Cd(Ⅱ)效果 [J]. 土壤通报, 2020, 51(3): 748-756. YIN G C, TAO L, SONG X W, et al. A review on the modification, Cd(Ⅱ) adsorption/passivation of biochars prepared by different raw materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 51(3): 748-756(in Chinese).
[15] 吴蔚君, 徐云连, 邢素林, 等. 生物炭对土壤氮磷转化和流失的影响 [J]. 农学学报, 2018, 8(9): 20-26. doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas17050013 WU W J, XU Y L, XING X L, et al. Effect of Biochar on soil nitrogen and phosphorus transformation and loss [J]. Journal of Agriculture, 2018, 8(9): 20-26(in Chinese). doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas17050013
[16] ZHENG H, WANG Z, DENG X, et al. Impacts of adding biochar on nitrogen retention and bioavailability in agricultural soil [J]. Geoderma, 2013, 206: 32-39. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.04.018 [17] 武玉, 徐刚, 吕迎春, 等. 生物炭对土壤理化性质影响的研究进展 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2014, 29(1): 68-79. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.01-0068 WU Y, XU G, LV Y C, ey al. Effects of biochar amendment on soil physical and chemical properties: current status and knowledge gaps [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2014, 29(1): 68-79(in Chinese). doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.01-0068
[18] BEESLEY L, MORENO-JIMENEZ E, GOMEZ-EYLES J L, et al. A review of biochars'potential role in the remediati on, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(12): 3269-3282. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.07.023 [19] 陈再明, 方远, 徐义亮, 等. 水稻秸秆生物碳对重金属Pb2+的吸附作用及影响因素 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(4): 769-776. CHEN Z M, FANG Y, XU Y L, et al. Adsorption of Pb2+ by rice straw derived-biochar and its influential factors [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2012, 32(4): 769-776(in Chinese).
[20] 许超, 林晓滨, 吴启堂, 等. 淹水条件下生物炭对污染土壤重金属有效性及养分含量的影响 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2012, 26(6): 194-198. XU C, LIN X B, WU Q T, et al. Impacts of biochar on availability of heavy metals and nutrient content of contaminated soil under waterlogged conditions [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 26(6): 194-198(in Chinese).
[21] 于志红, 谢丽坤, 刘爽, 等. 生物炭-锰氧化物复合材料对红壤吸附铜特性的影响 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(5): 897-903. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.05.026 YU Z H, XIE L K, LIU S, et al. Effects of biochar-manganese oxides composite on adsorption characteristics of Cu in red soil [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(5): 897-903(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.05.026
[22] 杨永军. 生物炭负载铁锰氧化物对铅、铜污染土壤的稳定化研究[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2018. YANG Y J. Study of modified biochar on the stabilization of heavy metals lead and copper contaminated soil[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2018 (in Chinese).
[23] O′REILLY S E, HOCHELLA JR M F. Lead sorption efficiencies of natural and synthetic Mn and Fe-oxides [J]. Geochim Cosmochim Ac, 2003, 67(23): 4471-4487. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00413-7 [24] 于志红, 黄一帆, 廉菲, 等. 生物炭-锰氧化物复合材料吸附砷(Ⅲ)的性能研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(1): 155-161. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.01.022 YU Z H, HUANG Y F, LIAN F, et al. Adsorption of arsenic(Ⅲ) on biochar-manganese oxide composites [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(1): 155-161(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.01.022
[25] 樊伟, 卞战强, 田向红, 等. 固载化纳米MnO2对砷的吸附性能研究 [J]. 水处理技术, 2013, 39(1): 60-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3770.2013.01.013 FAN W, BIAN Z Q, TIAN X H, et al. Study on absorption of arsenic by immobilized nano-manganese oxide [J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2013, 39(1): 60-64(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3770.2013.01.013
[26] 董爱琴, 谢杰, 刘佳, 等. 土壤重金属钝化材料生物炭的研究进展 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2017, 39(3): 319-325. DONG A Q, XIE J, LIU J, et al. Advances on heavy metal passivation material of biochar in soils [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2017, 39(3): 319-325(in Chinese).
[27] SONG Z G, LIAN F, YU Z H, et al. Synthesis and characterization of a novel MnOx-loaded biochar and its adsorption properties for Cu2+ in aqueous solution [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 242: 36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.12.061 [28] LI B, YANG L, WANG C Q, et al. Adsorption of Cd(Ⅱ) from aqueous solutions by rape straw biochar derive d from different modification processes [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 175: 332-340. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.061 [29] 杨兰, 李冰, 王昌全, 等. 改性生物炭材料对稻田原状和外源镉污染土钝化效应 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(9): 3562-3574. YANG L, LI B, WANG C Q, et al. Effect of modified biochars on soil cadmium stabilization in paddy suffered from original or exogenous contamination [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(9): 3562-3574(in Chinese).
[30] 孙彤, 付宇童, 李可, 等. 锰基改性生物炭对弱碱性Cd污染土壤团聚体结构以及Cd含量特征的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(7): 3426-3433. SUN T, FU Y T, LI K, et al. Effect of Mn-modified biochar on the characteristics of aggregate structure and the content of Cd in weakly alkaline Cd-contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(7): 3426-3433(in Chinese).
[31] 蒲生彦, 上官李想, 刘世宾, 等. 生物炭及其复合材料在土壤污染修复中的应用研究进展 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(3): 629-635. PU S Y, SHANGGUANG L X, LIU S B, et al. A review of the application of biochar and its composites in soil remediation [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(3): 629-635(in Chinese).
[32] 于志红. 锰氧化物—生物炭复合材料对砷的生物有效性的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2015. YU Z H. A Effects of biochar-manganese oxide composites on bio-availability of arsenic[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2015 (in Chinese).
[33] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G, BISSON M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51: 844-851. doi: 10.1021/ac50043a017 [34] HE R Z, PENG Z Y, LYU H H, et al. Synthesis and characterization of an iron-impregnated biochar for aqueous arsenic removal [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 612: 1177-1186. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.016 [35] FU H, MA S, ZHAO P, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by graphitized hierarchical porous biochar and MnFe2O4 magnetic nanoarchitecture for organic pollutants degradation: Structure dependence and mechanism [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 360: 157-170. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.207 [36] 张志军, 胡佳伟, 程萍. 生物炭载铁锰氧化物催化H2O2氧化含油废水 [J]. 水处理技术, 2019, 45(8): 61-66. ZHANG Z J, HU J W, CHENG P. Treatment of oily wastewater by charcoal supported iron-manganese oxides catalytic H2O2 oxidation [J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2019, 45(8): 61-66(in Chinese).
[37] LIU L, WANG B, YAO X, et al. Highly efficient MnOx/biochar catalysts obtained by air oxidation for low-temperature NH3-SCR of NO [J]. Fuel, 2021, 283: 119336. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119336 [38] LYU H, TANG J, HUANG Y, et al. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by a novel biochar supported nanoscale iron sulfide composite [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 322: 516-524. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.058 [39] LYU H H, GONG Y Y, TANG J S. Immobilization of heavy metals in electroplating sludge by biochar and iron sulfide [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(14): 14472-14488. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6621-5 -



 下载:
下载: