-
磷是植物生长所必需的大量营养元素之一,植物生长发育所需的磷主要从土壤磷库中获得。在作物生产中,合适的磷肥来源尤为重要,施用由磷矿开采生产的磷肥是保障作物产量的重要措施之一。2013年,全国规模以上磷矿企业已有368个;2014年,中国磷肥生产量(P2O5)已接近1700万吨,磷矿石开采量约为12000万吨[1]。近年来,磷化工产品在人们的衣食住行方面的作用逐渐凸显,各种磷化工产品逐渐渗透到尖端科学和新兴产业等部门,使磷化工成为国民经济中的重要产业之一[2]。随着磷矿资源开发利用规模的扩大,矿石的需求量也逐渐增多,矿石运输量增加,运输过程中洒落的矿粉造成地面扬尘也会对周围环境造成污染[3]。磷矿石因其化学组成的特殊性,有害元素含量较高,磷矿加工也会产生大量的有毒有害重金属元素以及磷石膏废弃物,随着选矿工艺及“三废”进入土壤、水体、大气等,对人类的生活安全构成威胁[4-5]。
关于磷矿区重金属的污染问题鲜有报道,通过研究磷矿区木本植物对重金属的富集特征,筛选出有较强富集效应的木本植物,这对磷矿的生态恢复有重要意义。磷矿区产生的重金属经淋溶后随地表径流进入河道、农田等造成水源和作物污染,对周围居民的生活安全造成安全隐患。土壤中的重金属不易被察觉,通过根系在植物体内积累,直接或间接进入人体,对人体机能造成损伤[6]。重金属在土壤中不易被察觉,土壤环境的治理一直是严峻的问题。修复污染土壤中重金属的方法有物理修复、化学修复、生物修复等。植物修复是生物修复中的方法之一,即利用植物的根系吸收土壤中的金属元素,并将其转移到地上部分、收获植物地上部分从而移除植物体内的过程[7]。植被不同会对土地复垦和生态恢复产生影响,植物种类的选择尤为重要[8]。
本研究以贵州开阳磷矿马路坪矿区为研究区,对研究区土壤及植物中的重金属元素含量进行测定,了解植物营养状况,并对其进行富集特征分析,寻找和筛选适合当地气候及土壤条件的重金属耐受性植物,为后期矿区污染治理、植物修复和树种选择提供理论依据,为矿区范围内土壤安全、居民健康和预防潜在危险提供科学依据。
-
开阳磷矿洋水矿区(106°47′28″—106°52′48″ E、27°02′49″—27°10′40″ N))位于贵州省开阳县金钟镇,洋水矿区含:沙坝土矿段、马路坪矿段、牛赶冲矿段、两岔河矿段、用沙坝矿段以及极乐矿段等6个矿段。马路坪矿段位于开阳县城西29 km,总面积为8.269 km2,属北温带亚热带高原大陆性气候,雨量充沛,年平均降雨量962.5—1419.2 mm,年平均气温10.6—15.3 ℃。
马路坪矿段位于云贵高原东部中、低山带,土壤类型主要为黄壤,植被以灌木为主,常见植被有楸树、构树(Broussonetia papyrifera)、枫香(Liquidambar formosana)、八角枫(Alangium chinense(Lour.)Harms)、盐肤木、刺槐等。马路坪矿区土地利用类型有水田、旱地、有林地、灌木林地、草地、建设用地、采矿用地和风景区及特殊用地。马路坪矿区农作物以旱生作物为主,主要种植水稻(Oryza sativa L.)、玉米(Zea mays L.)、小麦(Triticum aestivum L.)、马铃薯(Solanum tuberosum L.),经济作物有油菜(Brassica napus L.)。
-
野外采样于2019年7月中旬完成,经实地调研统计发现,矿区范围内的植物种类较多,其中木本植物所占比例较大,几乎在整个矿区均有分布。因此在矿渣堆、废石场、工业场地、原充填站、居民区周边采集较为常见、数量较多且具代表性的10种植物:马尾松、杉木、构树、刺槐、楸树、八角枫、枫香、盐肤木、二球悬铃木、核桃(均为人工植被,林相为乔灌混交林,种植方法为实生苗栽植)的叶片及其表层土壤(采集的土壤样品均为原生土壤)。
划定20 m×20 m的采样范围,分别采集长势较为一致的马尾松、杉木、构树、刺槐、楸树、八角枫、枫香、盐肤木、二球悬铃木、核桃的3株样木(即3个重复样)混合[9],分别在每株样木的东、南、西、北的4个方向采集叶片[10];按“梅花形”布设5个分样点[11]采集表层0—20 cm的土壤做混合土样,约1 kg。
-
将采集叶片用自来水洗净,用去离子水冲洗2—3次,放于干净网袋中滤水4 h,在105 ℃的烘箱中杀青15 min,最后在65 ℃下烘至恒重,用不锈钢粉碎机将植物样品粉碎,过0.15 mm筛,置于有标签的自封袋中备用。植物叶片Cd、Cu、Zn、Pb利用HNO3消解,用原子吸收分光光度计(ICE–3500)测定,Pb用石墨炉测定,植物叶片As用HNO3–H2SO4–HClO4消解,用原子荧光光度计(LC–AFS 9700)测定。
将采集回来的土壤样品于聚乙烯膜上风干,期间将混在土样中的石块、植物残体等杂物剔除。土样风干后用玛瑙钵研磨,过0.15 mm尼龙筛,置于有标签的自封袋中备用。土壤重金属Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd利用HNO3–HF消解,用原子吸收分光光度计(ICE–3500)测定,土壤As利用1:3比例的HNO3–HCl来消解,用原子荧光光度计(LC–AFS 9700)测定。实验过程均使用优级纯药品和超纯水[12]。
-
采用Excel 2013、SPSS 20.0等软件统计数据,对植物叶片重金属含量进行富集能力等级划分[13],对土壤重金属含量进行相关性分析、主成分分析[14]。
采集距矿区15—20 km且未受人为干扰的4个林地土样,将测定的重金属含量作为无污染对照,该结果与文献报道的开阳当地的土壤重金属背景值(即未施猪粪肥的土壤剖面重金属含量)[15]进行比较,结果见表1,二者较为一致。因此,本研究以所测背景值数据作为开阳县土壤背景值,进行参照评价。
-
研究中Zn含量较高的有马尾松、楸树、二球悬铃木、杉木;Cu含量较高的有二球悬铃木、楸树;Pb含量较高的有杉木、马尾松、核桃。Cd含量较高的有马尾松、刺槐、盐肤木。As含量较高的有刺槐、二球悬铃木。分析表见表2。
-
不同环境下生长的不同植物对重金属元素的吸收能力不同,使得植物体内的重金属元素含量不同,重金属元素之间的相关性也存在差异[16]。对马路坪矿区中10种常见木本植物叶片重金属含量进行相关性分析,结果如表3所示,马路坪矿区的植物体中重金属元素之间的相关性不同,Cu与Zn、Zn与Pb之间分别存在正相关关系,相关系数分别为0.65、0.72,Zn与As、Pb与As之间也存在正相关关系,相关系数分别为0.51、0.52,Cd与Zn之间存在显著负相关关系,相关系数为−0.59。研究得出,植物叶片中Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、As之间存在显著相关性,表明植物叶片中重金属中的Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、As 5种元素之间联系相当密切,并且其来源可能具有相同的来源,Cd与Zn之间存在显著的负相关关系,其来源可能不同[9,17-18]。
-
对马路坪矿区范围内的植物重金属含量进行富集系数研究,结果如表4所示,楸树、杉木、马尾松等10种植物分别对Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、As等5种重金属元素的富集系数范围为0.19—0.64、0.11—0.45、0.07—0.47、1.09—4.95、0.01—0.17。除二球悬铃木、楸树、核桃Cu富集系数>0.4外,其余植物Cu富集能力都较小,均在0.3以下。马尾松Zn富集系数较高,其大小为0.45,其余植物Zn富集能力较小,均在0.3以下;杉木Pb富集系数较高,为0.47,其余植物Pb富集系数均在0.21及以下。盐肤木、马尾松、核桃、枫香、杉木Cd富集能力较强,均在3以上(杉木Cd富集能力为2.95,此部分将其视为0.3而统一描述分析),其余植物Cd富集能力均在1—2之间。二球悬铃木、核桃、杉木、盐肤木As富集能力均在0.1—0.2范围期间,其余植物As富集能力均小于0.1,说明所有植物中对As的富集能力较弱。
-
研究区土壤重金属含量的分布情况如表5所示,10种木本植物的土壤中Cu含量范围是28.11—127.94 mg·kg−1,Zn含量为118.41—193.67 mg·kg−1,Pb含量为5.75—35.76 mg·kg−1,Cd含量为0.10—0.82 mg·kg−1,As含量为4.09—31.77 mg·kg−1。所有样品中,二球悬铃木土壤中Cu含量最高,构树土壤的Zn、Cd含量最高,楸树土壤的Pb含量最高,刺槐土壤的As含量最高。
-
对马路坪矿区中土壤重金属含量进行相关性分析(表6),结果表明,马路坪矿区土壤重金属元素之间的相关性不同,其中Cd与As在0.05水平上存在显著相关关系,相关系数为0.597,Zn与Cd在0.05水平上存在显著性正相关关系,相关系数为0.667,Zn与Pb在0.05水平上存在显著性正相关关系,相关系数为0.508。
-
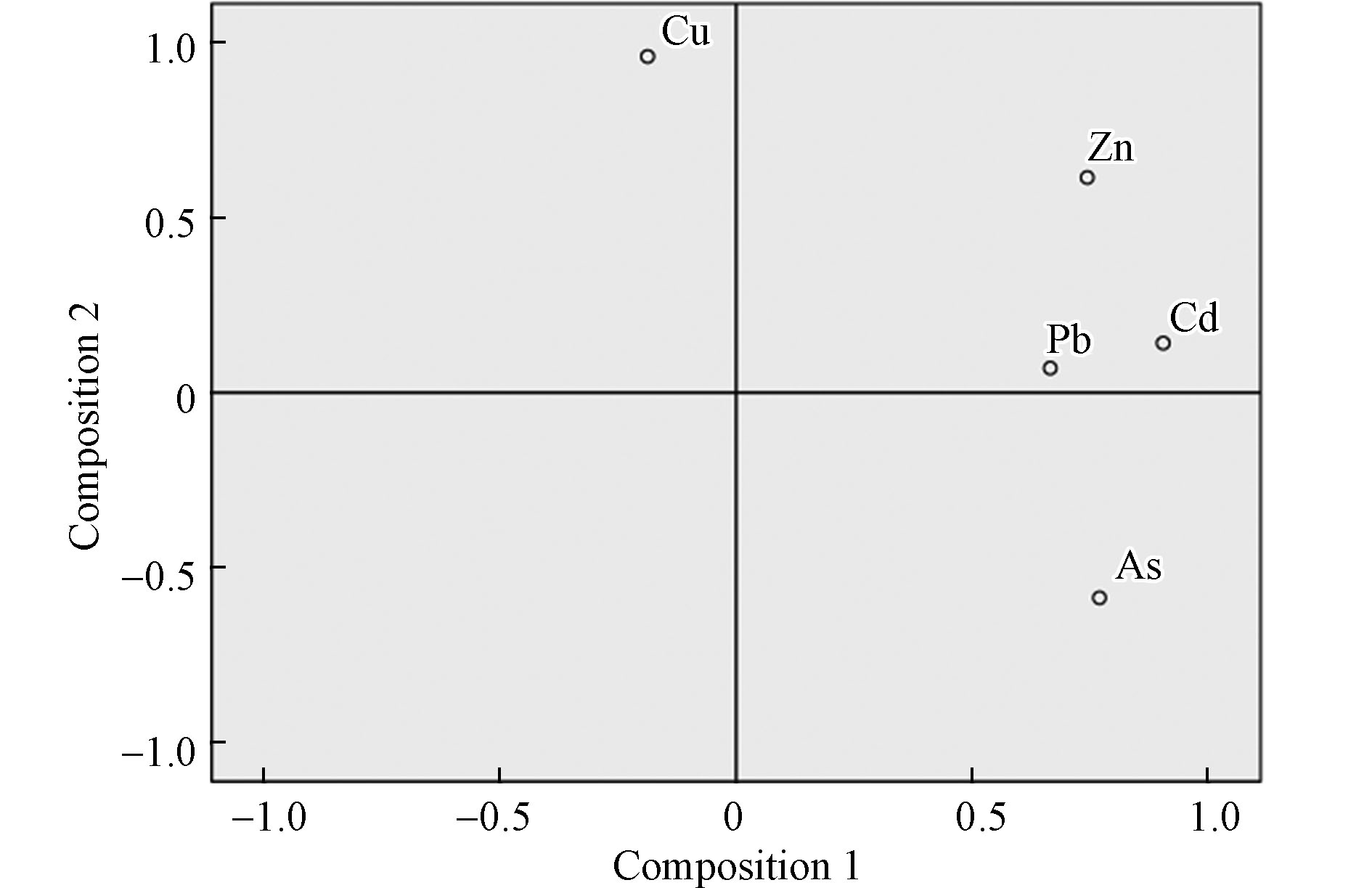
本研究对土壤中Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、As等5种重金属元素进行主成分分析,由表7结果显示,提取两个主成分可以反映5种重金属70.80%的信息,Zn、Pb、Cd、As在成分1中负荷较高(0.69—0.84),贡献率为47.94%,Cu在成分2中负荷较高(0.88),贡献率为22.87%。由图1可知,Cu、Pb、As的污染来源不同,Zn、Cd具有相似的污染来源。土壤中重金属元素的主成分分析结果表明,两个主成分的贡献率分别为47.94%、22.87%。成分1中Zn、Pb、Cd、As元素的载荷较高,成分2中Cu元素的荷载较高。采样点位于矿区范围内采矿点周围、工业厂区附近、道路周边、以及农田周围等,受工业活动、交通以及农业活动的强烈影响[19]。
-
为弄清土壤重金属元素与植物叶片重金属的关系,在此对两种类型重金属含量进行相关性分析,相关性分析结果见表8(S代表土壤,P代表植物)。相关性分析中,土壤中的Cu含量与植物叶片中Cu含量的存在极显著正相关关系,土壤中Zn含量与植物叶片中Cd含量存在显著正相关关系,土壤中Pb含量与植物中Pb含量存在显著正相关关系,土壤中的Cd含量与植物叶片中Cd含量存在较强的相关关系,与植物叶片中的Zn含量存在较强的负相关关系;土壤中As含量与植物叶片中Cd、As含量存在较显著的相关性。
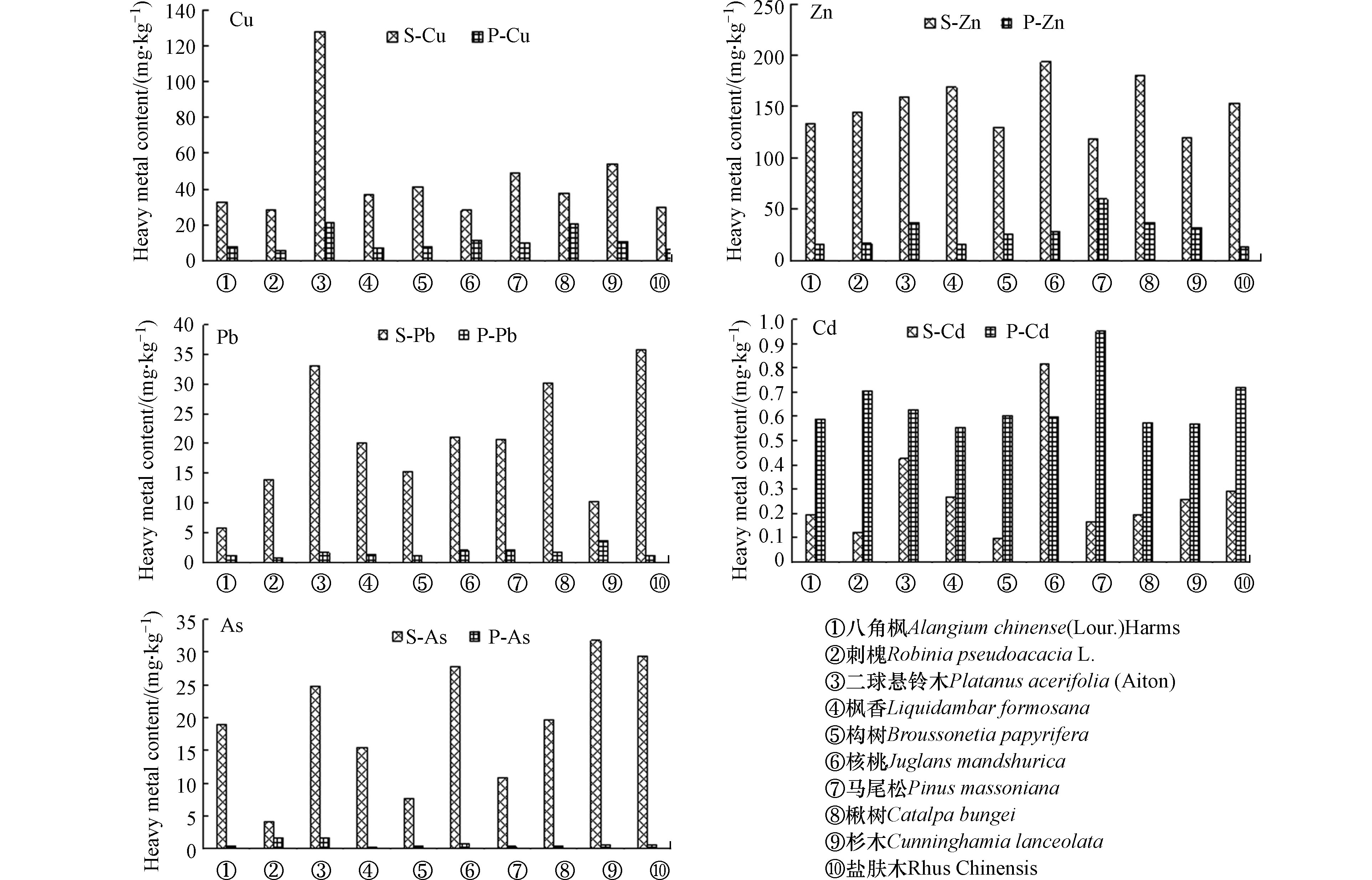
分析植物叶片、土壤中重金属含量,研究重金属元素的富集情况,得出柱状图2。
由图2可见部分土壤Cu含量和植物叶片Cu含量的变化趋势,Cu元素含量在植物及其土壤中的含量不同,在不同植物中表现出不同的富集特性,结果表明,Cu在二球悬铃木叶片中及其土壤的含量差异较大,表现出较弱的富集特性,所有植物类型中,楸树对Cu表现出较强的富集能力;部分土壤Zn含量和植物叶片Zn含量的变化趋势,Zn元素含量在植物及其土壤中的含量不同,在不同植物中表现出不同的富集特性,结果表明,Zn在马尾松叶片中及其土壤的含量差异较小,表现出较强的富集特性,其他植物种类对Zn的富集能力较弱。马尾松对Cu表现出较强的富集能力;部分土壤Pb含量和植物叶片Pb含量的变化趋势,Pb元素含量在植物及其土壤中的含量不同,在不同植物中表现出不同的富集特性,结果表明,Pb在八角枫、杉木叶片中及其土壤的含量差异较小,表现出较强的富集特性,其他植物种类对Pb的富集能力较弱。八角枫、杉木对Pb表现出较强的富集能力;部分土壤Cd含量和植物叶片Cd含量的变化趋势,Cd元素含量在植物及其土壤中的含量不同,在不同植物中表现出不同的富集特性,结果表明,除核桃外,其他植物种类叶片中重金属含量均高于对应土壤中的Cd含量;部分土壤As含量和植物叶片As含量的变化趋势,As元素含量在植物及土壤中的含量不同,在不同植物中表现出不同的富集特性。结果表明,As在刺槐、构树、马尾松叶片及土壤的含量差异较小,表现出较强的富集特性,其他植物种类对As的富集能力较弱。刺槐、构树、马尾松对As表现出较强的富集能力。
富集系数越大,表明地上部植物体内重金属富集质量分数大[20-21]。植物通过根系吸收土壤中的重金属,将其富集在可收割的部位(如根、茎、叶),经过收获后达到修复土壤污染效果[22]。本研究对10种木本植物叶片中重金属元素富集能力进行分析,所有植物叶片重金属均表现为对Cd的富集最明显,对As的富集能力最小,且每种植物种类中Cd的富集均大于其他4种元素。从10种木本植物叶片重金属的平均值含量看,植物叶片内Zn最高,5种重金属元素含量趋势为Zn>Cu>Pb>Cd>As。研究中Zn含量较高的植物有马尾松、楸树、二球悬铃木、杉木;Cu含量较高的有二球悬铃木、楸树;Pb含量较高的有杉木、马尾松、核桃。Cd含量较高的有马尾松、刺槐、盐肤木。As含量较高的有刺槐、二球悬铃木。所有植物体内的Zn含量都是最高,这一结果与张芹芹[23]的研究结果相对一致,该作者在研究中提出,土壤中Zn含量较大时,所生长植物体内的Zn含量也最高。Pb含量在杉木、马尾松、核桃中较高的研究结果与康薇等[24]的Pb污染区域可以选择栽植二球悬铃木和构树的研究结果不太一致,这有可能是研究中所选取的植物类型不一致,因此具有不同的评价标准,也可能和研究区环境不同有关。Cd的富集能力最大很可能是因为磷矿在加工过程中会产生大量含Cd的污染物,冶炼以及磷肥工业中的废水、废弃、废渣等也会造成Cd污染[25]。当木本植物富集系数大于0.4时,可认为该植物的修复能力强,富集系数在0.1—0.4之间时,可判断该植物对土壤重金属污染有一定的修复能力[26]。
-
为弄清土壤养分含量与植物叶片重金属的关系,在此对两种类型数据进行相关性分析,相关性分析结果见表9。相关性分析中,仅有土壤速效钾和植物中As元素含量存在较显著的负相关关系,与其它元素关系不明显;Cu、Zn、Pb元素之间,Cu、Pb均与Zn存在较显著的正相关关系;土壤有机质与土壤速效钾存在显著的负相关关系;其余养分含量与土壤中Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、As含量均不存在明显的相关性。
-
(1)植物叶片中Zn最高,5种重金属元素含量趋势为Zn>Cu>Pb>Cd>As。Zn含量较高的有马尾松、楸树、二球悬铃木、杉木;Cu含量较高的有二球悬铃木、楸树;Pb含量较高的有杉木、马尾松、核桃。Cd含量较高的有马尾松、刺槐、盐肤木。As含量较高的有刺槐、二球悬铃木。
(2)马尾松、楸树、二球悬铃木可以作为Zn污染严重区的修复树种;二球悬铃木、楸树可以作为Cu污染严重区的修复树种;马尾松、杉木、核桃可作为Pb污染严重区的修复树种;马尾松、刺槐、盐肤木可以作为Cd污染严重区的修复树种,刺槐、二球悬铃木可以作为As污染严重区的修复树种。
(3)土壤与植物中Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、As 的5种重金属之间的关系较为密切:土壤与植物中的Cu、Zn、As、Pb、Cd的 5种元素含量之间存在极显著正相关关系,土壤中Zn含量与植物叶片中Cd含量存在显著正相关关系,土壤中Pb含量与植物中Pb含量存在显著正相关关系,土壤中的Cd含量与植物叶片中Cd含量存在较强的相关关系,与植物叶片中的Zn含量存在较强的负相关关系;土壤中As含量与植物叶片中Cd、As含量存在较显著的相关性。说明研究区中5种重金属元素关系密切,具有相似的污染来源。
开阳磷矿10种木本植物叶片重金属富集特征
Enrichment characteristics of heavy metals in leaves and soil of 10 woody plants in Kaiyang phosphate mine
-
摘要: 植物对重金属具有一定的吸附能力,植物修复是生态修复不可或缺的一部分,利用植物减缓和治理重金属污染具有重要意义。选取开阳磷矿马路坪矿区生命周期较长的木本植物及其土壤作为研究对象,探究木本植物受Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、As 等5种重金属污染土壤的效应,对植物重金属含量及其富集特性进行研究分析,筛选出累积重金属的植物,作为矿区生态修复的优势植物,获得如下的主要研究结论:(1)植物叶片中Zn最高,5种重金属元素含量趋势为Zn>Cu>Pb>Cd>As。Zn含量较高的有马尾松(Pinus massoniana)、楸树(Catalpa bungei)、二球悬铃木(Platanus acerifolia (Aiton) Willdenow)、杉木(Cunninghamia lanceolata);Cu含量较高的有二球悬铃木、楸树;Pb含量较高的有杉木、马尾松、核桃(Juglans mandshurica)。Cd含量较高的有马尾松、刺槐(Robinia pseudoacacia L.)、盐肤木(Rhus Chinensis)。As含量较高的有刺槐、二球悬铃木。(2)马尾松、楸树、二球悬铃木可以作为Zn污染严重区的修复树种;二球悬铃木、楸树可以作为Cu污染严重区的修复树种;马尾松、杉木、核桃可作为Pb污染严重区的修复树种;马尾松、刺槐、盐肤木可以作为Cd污染严重区的修复树种,刺槐、二球悬铃木可以作为As污染严重区的修复树种。(3)土壤与植物中Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、As 等5种重金属之间的关系较为密切,具有相似的污染来源。Abstract: Plants can absorb heavy metals, phytoremediation is an indispensable part of ecological remediation, it is important to use plants to mitigate and control heavy metal pollution. To bridge the gap, the contents of copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), and arsenic (As) in soils and woody plants surrounding Maluping Base, Kaiyang Phosphorous Mining Corporation (Guiyang, China) were investigated. Then, phytoaccumulators were selected for providing reference for the phytoremediation of metal-contaminated soils. Our results suggest that based on determination of heavy metals in plant leaves arranged in descending order are Zn, Cu, Pb, Cd, As, and indicate a single source for them since their concentrations in either soils or plants are closely correlated. Besides, high contents of Zn for Pinus massoniana, Catalpa bungei, Platanus acerifolia (Aiton) Willdenow, and Cunninghamia lanceolata, large concentrations of Cu in Platanus acerifolia (Aiton) Willdenow, and Catalpa bungei, Pb accumulation within Cunninghamia lanceolate, Pinus massoniana, and Juglans mandshurica were measured. Additionally, it is shown that plants amassing Cd include Pinus massoniana and Robinia pseudoacacia L., and Rhus Chinensis, and that Robinia pseudoacacia L. and Platanus acerifolia (Aiton) Willdenow readily takes up As. Therefore, the aforementioned plants can be regarded as the accumulators of their corresponding contaminants in soils.
-
Key words:
- phosphorous mining area /
- heavy metal /
- soil /
- woody plant /
- enrichment characteristics
-

-
表 1 研究区土壤重金属背景值(mg·kg−1)
Table 1. Background values of heavy metals in soils of study area(mg·kg−1)
Cu Zn Pb Cd As 文献报道[15] 35.15 161.40 59.59 0.28 11.37 取样实测(土壤背景值) 35.97 148.67 33.47 0.23 15.16 表 2 木本植物叶片重金属的含量分布(g·kg−1)
Table 2. Distribution of heavy metals in leaves of 9 species of moody plants(g·kg−1)
植物种类Plant species Cu Zn Pb Cd As 楸树Catalpa bungei 20.80 37.07 1.71 0.57 0.16 杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata 10.60 32.14 3.74 0.57 0.61 马尾松Pinus massoniana 10.12 59.82 2.02 0.95 0.31 构树Broussonetia papyrifera 7.77 25.11 1.20 0.60 0.38 八角枫Alangium chinense(Lour.)Harms 7.61 16.02 1.22 0.59 0.13 枫香Liquidambar formosana 6.80 15.48 1.29 0.55 0.26 盐肤木Rhus Chinensis 6.29 13.36 1.22 0.72 0.47 刺槐Robinia pseudoacacia L. 5.77 16.61 0.66 0.70 1.63 二球悬铃木Platanus acerifolia (Aiton) 21.43 36.46 1.69 0.63 1.67 核桃Juglans mandshurica 11.63 28.07 2.01 0.60 0.75 表 3 植物重金属元素之间的相关性分析
Table 3. Correlation analysis of heavy metal elements in plants
Cu Zn Pb Cd As Cu 1 Zn 0.65 1 Pb 0.48 0.72 1 Cd −0.38 −0.59 −0.13 1 As 0.14 0.51 0.52 −0.03 1 表 4 植物叶片中重金属含量的富集系数
Table 4. Enrichment coefficient of heavy metals in plant leaves
植物种类Plant species 富集系数Enrichment coefficient Cu Zn Pb Cd As 楸树Catalpa bungei 0.64 0.29 0.11 1.58 0.02 杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata 0.24 0.22 0.47 2.95 0.17 马尾松Pinus massoniana 0.27 0.45 0.12 3.55 0.04 构树Broussonetia papyrifera 0.20 0.15 0.07 1.38 0.07 八角枫Alangium chinense(Lour.)Harms 0.26 0.11 0.10 1.09 0.01 枫香Liquidambar formosana 0.22 0.14 0.10 3.24 0.04 盐肤木Rhus Chinensis 0.22 0.11 0.21 4.95 0.12 刺槐Robinia pseudoacacia L. 0.19 0.17 0.07 1.86 0.05 二球悬铃木Platanus acerifolia (Aiton) 0.59 0.28 0.08 1.65 0.16 核桃Juglans mandshurica 0.46 0.23 0.19 3.24 0.16 表 5 土壤重金属的含量分布(g·kg−1)
Table 5. Distribution of heavy metals in soil(g·kg−1)
土壤Soil Cu Zn Pb Cd As 楸树土Catalpa bungei’s soil 37.84 158.89 33.04 0.43 24.78 杉木土Cunninghamia lanceolata’s soil 54.13 144.53 13.87 0.12 4.09 马尾松土Pinus massoniana’s soil 48.75 168.87 20.05 0.27 15.43 构树土Broussonetia papyrifera’s soil 41.36 193.67 20.99 0.82 27.73 八角枫土Alangium chinense(Lour.)Harms’s soil 32.53 153.20 35.76 0.30 29.40 枫香土Liquidambar formosana’s soil 36.61 118.41 20.75 0.16 10.85 盐肤木土Rhus Chinensis’s soil 29.78 133.26 5.75 0.19 18.97 刺槐土Robinia pseudoacacia L.’s soil 28.68 119.80 10.26 0.26 31.77 二球悬铃木土Platanus acerifolia (Aiton)’s soil 127.94 179.91 30.19 0.19 19.71 核桃土Juglans mandshurica’s soil 28.11 129.58 15.29 0.10 7.63 表 6 土壤重金属含量的相关系数
Table 6. Correlation coefficient of heavy metal content in soil
Cu Zn Pb Cd As Cu 1 Zn −0.065 1 Pb 0.358 0.508 1 Cd 0.128 0.667 0.258 1 As 0.223 0.277 0.319 0.597 1 表 7 研究区土壤重金属因子载荷和总方差解释
Table 7. Interpretation of factor load and total variance of heavy metals in soil of study area
PC1 PC2 Cu 0.33 0.88 Zn 0.78 −0.42 Pb 0.69 0.33 Cd 0.84 −0.30 As 0.72 0.07 特征值 2.40 1.14 方差贡献率/% 47.94 22.87 累计贡献率/% 47.94 70.80 表 8 土壤重金属与植物叶片重金属相关性分析
Table 8. Correlation analysis of heavy metals in soil and plant leaves
分析指标Analytic Index S-Cu S-Zn S-Pb S-Cd S-As P-Cu P-Zn P-Pb P-Cd P-As S-Cu 1 S-Zn 0.52 1 S-Pb 0.35 0.51 1 S-Cd −0.11 0.67 0.26 1 S-As −0.10 0.28 0.32 0.60 1 P-Cu 0.95 0.29 0.32 −0.40 −0.19 1 P-Zn 0.39 −0.15 0.28 −0.71 −0.23 0.65 1 P-Pb 0.33 0.11 0.84 −0.26 0.10 0.48 0.72 1 P-Cd −0.13 0.65 0.35 0.98 0.68 −0.38 −0.59 −0.13 1 P-As −0.04 −0.24 0.28 −0.19 0.63 0.14 0.51 0.52 −0.03 1 表 9 土壤养分与植物叶片重金属相关性分析
Table 9. Correlation between soil nutrients and heavy metals in plant leaves
分析指标Analytic Index P-Cu P-Zn P-Pb P-Cd P-As AN AP AK SOM P-Cu 1 P-Zn 0.65 1 P-Pb 0.48 0.72 1 P-Cd −0.38 −0.59 −0.13 1 P-As 0.14 0.51 0.52 −0.03 1 AN −0.05 0.00 0.61 0.23 0.03 1 AP 0.34 0.55 0.48 −0.02 0.05 0.31 1 AK −0.07 0.03 −0.08 −0.26 −0.71 −0.07 0.16 1 SOM 0.35 0.14 0.40 0.01 0.42 0.51 0.04 −0.71 1 -
[1] 杨威杉, 於方, 赵丹, 等. 滇池周边磷矿复垦区土壤重金属污染特征研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(6): 1145-1152. YANG W S, YU F, ZHAO D, et al. Characteristics of heavy metals in reclaimed soils of a phosphorite-mining area around Dianchi Lake [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 27(6): 1145-1152(in Chinese).
[2] 卢科. 磷矿和磷肥中微量元素Bi、Cd、Cr、Cu、Fe、Pb及常量元素Ca、P的测定研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2017. LU K. Study on the determination of micronutrients Bi, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb and major elements Ca, P in phosphate ores and phosphate fertilizers[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2017(in Chinese).
[3] 程馨, 施泽明, 张成江, 等. 贵州开阳磷矿开采对洋水河水体重金属污染与评价 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2015, 31(2): 78-83. CHENG X, SHI Z M ZHANG C J, et al. Evaluation of heavy metals pollution to Yangshui river water in mining of phosphate rock of Kaiyang Phosphate Mine in Guizhou [J]. Environmental Monitoring, 2015, 31(2): 78-83(in Chinese).
[4] 程馨, 施泽明, 张成江, 等. 开阳磷矿洋水矿区近地表大气降尘中重金属污染特征分析 [J]. 矿物学报, 2013, 33(S2): 690-691. CHENG X, SHI Z M, ZHANG C J, et al. Pollution characteristics of heavy metals in near-surface atmospheric dustfall in the yangshui mining area of the Kaiyang Phosphate Mine [J]. Journal of Mineralogy, 2013, 33(S2): 690-691(in Chinese).
[5] 刘雨曦, 刘志祥. 磷矿开采环境损伤调查与防治对策 [J]. 采矿技术, 2015, 15(4): 72-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2900.2015.04.025 LIU Y X, LIU Z X. Environmental damage investigation and prevention measures in phosphate rock mining [J]. Mining Technology, 2015, 15(4): 72-74(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2900.2015.04.025
[6] 王娟, 李玉成, 黄欣欣, 等. 铜陵矿区植物重金属富集行为及健康风险评估 [J]. 生物学杂志, 2020, 37(3): 76-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2020.03.076 WANG J, LI Y C, HUANG X X, et al. Enrichment of heavy metals and health risk assessment of plants in Tongling mining area [J]. Journal of Biology, 2020, 37(3): 76-80(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2020.03.076
[7] ALKORTA I, HERNÁNDEZ-ALLICA J, BECERRIL J M, et al. Recent findings on the phyoremediation of soils contaminated with environmentally toxic heavy metals and metalloids such as zinc, cadmium, lead, and arsenin of China [J]. Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 2004, 3(1): 71-90. doi: 10.1023/B:RESB.0000040059.70899.3d [8] 卞正富. 煤矿区土地复垦条件分区研究 [J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 1999, 28(3): 37-42. BIAN Z F. Study on regionalization of land reclamation conditions in coal mining area [J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 1999, 28(3): 37-42(in Chinese).
[9] 黄大伟. 宿南矿区土壤-玉米系统重金属含量特征及迁移规律研究[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2018. WANG D W. Study on concentration and transfer characteristics of heavy metals in soil-maize system from Sunan mining area[D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2018(in Chinese).
[10] 陈洁宜, 刘广波, 崔金立, 等. 广东大宝山矿区土壤植物体系重金属迁移过程及风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(12): 5629-5639. CHEN J Y, LIU G B, CUI J L, et al. Mobilization of heavy metals in soil-plant system and risk assessment in Dabaoshan mine area, Guangdong Province [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(12): 5629-5639(in Chinese).
[11] 图雅日拉, 黄道友, 许超, 等. 废弃冶炼厂重金属镉向周边的扩散及其风险评价 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(10): 3086-3092. TUYARILA, HUANG D Y, XU C, et al. Diffusion and risk assessment of cadmium from abandoned smelters [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(10): 3086-3092(in Chinese).
[12] 陆金, 赵兴青, 黄健等. 铜陵狮子山矿区尾矿库及周边17种乡土植物重金属含量及富集特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(1): 78-86. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018021302 LU J, ZHAO X Q, HUANG J, et al. Heavy metal contents and enrichment characteristics of 17 species indigenous plants in the tailing surrounding in Shizishan, Tongling [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(1): 78-86(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018021302
[13] 唐敏, 张欣, 王美仙. 北京37种园林植物对4种重金属的富集力及其分级评价研究 [J]. 西北林学院学报, 2019, 34(5): 263-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2019.05.40 TANG M, ZHANG X, WANG M X. Heavy metal enrichment ability and grade evaluation of 37 garden plants in Beijing [J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2019, 34(5): 263-268(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2019.05.40
[14] 陈小敏, 朱保虎, 杨文, 等. 密云水库上游金矿区土壤重金属空间分布、来源及污染评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(12): 2248-2256. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.12.2015071601 CHEN X M, ZHU B H, YANG W, et al. Sources, spatial distribution and contamination assessments of heavy metals in gold mine area soils of Miyun Reservoir upstream, Beijing [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(12): 2248-2256(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.12.2015071601
[15] 何腾兵, 黄会前, 付天岭, 等. 施用10年猪粪肥的黄壤剖面重金属分布及风险评价 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2018, 18(2): 789-794. HE T B, HUANG H Q, FU T L, et al. Distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in yellow soil profile after 10-year application of pig manure [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2018, 18(2): 789-794(in Chinese).
[16] 李晶, 徐玉玲, 黎桂英, 等. 兰州市交通道路主要乔灌木植物叶片重金属积累及生理特性的分析 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(5): 999-1006. LI J, XU Y L, LI G Y, et al. Analyses of heavy metal accumulation and physiological characteristics in leaves of main arbor and shrub plants in traffic roads of Lanzhou City of China [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(5): 999-1006(in Chinese).
[17] 于元赫, 吕建树, 王亚梦. 黄河下游典型区域土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6): 2865-2874. YU Y H, LU J S, WANG Y M. Source identification and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils in typical areas around the Lower Yellow River [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6): 2865-2874(in Chinese).
[18] 黄华斌, 林承奇, 胡恭任, 等. 基于PMF模型的九龙江流域农田土壤重金属来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1): 430-437. HUANG H B, LIN C Q, HU G R, et al. Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Jiulong River Basin based on Positive Matrix Factorization [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1): 430-437(in Chinese).
[19] 李艳玲, 卢一富, 陈卫平, 等. 工业城市农田土壤重金属时空变异及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(3): 1432-1439. LI Y L, LU Y F, CHEN W P, et al. Spatial-temporal variation and source change of heavy metals in the cropland soils in industrial city [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(3): 1432-1439(in Chinese).
[20] CHAMBERLAIN A C. Fallout of lead and uptake by crops [J]. Atmospheric Environment (1967), 1983, 17(4): 693-706. doi: 10.1016/0004-6981(83)90416-X [21] 王庆仁, 崔岩山, 董艺婷. 植物修复—重金属污染土壤整治有效途径 [J]. 生态学报, 2001(2): 326-331. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2001.02.024 WANG Q R, CUI Y S, DONG Y T. Phytoremediation an effective approach of heavy metal cleanup from contaminated soil [J]. Journal of Ecology, 2001(2): 326-331(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2001.02.024
[22] UNTERBRUNNER R, PUSCHENREITER M, SOMMER P, et al. Heavy metal accumulation in trees growing on contaminated sites in Central Europe [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 148(1): 107-114. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.10.035 [23] 张芹芹. 淮南矿区环境修复木本植物中重金属分布特征研究[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2011. ZHANG Q Q. Study on distribution characteristics of heavy metals in woody plants of environmental remediation in Huainan Mining area [D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2011(in Chinese).
[24] 康薇, 鲍建国, 郑进, 等. 湖北铜绿山古铜矿遗址区木本植物对重金属富集能力的分析 [J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2014, 23(1): 78-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2014.01.12 KANG W, BAO J G, ZHENG J, et al. Analysis on heavy metal enrichment ability of woody plants at ancient copper mine site in Tonglushan of Hubei Province [J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2014, 23(1): 78-84(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2014.01.12
[25] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2007. PAUSTIN. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House, 2007(in Chinese).
[26] 王旭旭, 黄鑫浩, 胡丰姣, 等. 4种木本植物对重金属铅、锌的积累及叶片养分含量特征研究 [J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2018, 38(6): 115-122. WANG X X, HUANG X H, HU F J, et al. Characteristics of Pb, Zn accumulation of and foliar nutrient in four kinds of woody species [J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2018, 38(6): 115-122(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: