-
我国每年生产抗生素约21万吨,其中10万吨用于畜禽养殖业[1-2]. 畜禽养殖业大量使用抗生素主要用于疾病预防治疗及促生长[3]. 由于抗生素在动物肠道中吸收较差,约有30%—90%抗生素以原药或代谢产物的形式通过排泄排放到环境[4],导致环境中耐药水平提高,严重危害生态环境安全和人类健康[5]. 研究表明,生猪粪便中可检测出多种抗生素,如四环素类、氟喹诺酮类、磺胺类、大环内酯类、林可霉素和杆菌肽等[5-7]. 尽管单一种类抗生素的检测准确度较高,但针对养殖粪污抗生素污染的削减与控制,开展多种抗生素同步检测更为迫切.
猪粪基质复杂,不同抗生素辛醇-水分配系数(Kow值)差异较大,加大了猪粪中多种抗生素同步分析检测的难度. 已有研究中主要针对浓度较高的单一类别抗生素,主要集中在四环素类抗生素[8-11],Pan等[12]建立了同步检测方法,调查了猪场粪污中残留的9种抗生素,磺胺类抗生素、四环素类和泰勒菌素抗生素的含量范围为5.5—36271.1 μg·kg−1;An等[4]用固相萃取-高效液相色谱-串联质谱固相萃取法,用外标法定量测定了猪粪中4种四环素类和4种磺胺类抗生素,发现金霉素残留含量最高为143.97 mg·kg−1. 受复杂基质影响,无论是外标法、内标法定量都具有一定的局限性[13];不同猪粪样品的内标是否会受基质影响尚不清晰[14-15].
建立快速准确的多种类抗生素同步检测方法是评价与控制畜禽粪便中残留抗生素污染的重要环节,本研究以猪粪中抗生素为对象,以内标-外标法建立五类(四环素类、β-内酰胺类、大环内酯类、磺胺类大类、喹诺酮类)常见的21种抗生素同步的定量分析方法,以期为畜禽粪便中残留抗生素污染评价与控制提供科技支撑.
-
1290高效液相色谱仪和6460三重四极杆质谱仪(安捷伦科技有限公司);超临界固相萃取装置(美国Supelco公司);Oasis HLB型固相萃取柱(6 cc/300 mg,美国Waters公司);SE812型氮吹仪(北京帅恩科技有限责任公司);2-16P高速离心机(Sigma公司).
甲醇、乙腈和乙酸乙酯(色谱纯,美国Fisher公司);Na2EDTA、甲酸和盐酸(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司);超纯水(Milli-Q系统(Advantage A10,Millipore)制取).
四环素类抗生素(TCs):四环素(tetracyclines,TC,97%)、4-差向四环素(4-epi-tetracycline hydrochloride,ETC,99%)、金霉素(chlorotetracycline,CTC,99%)、土霉素(oxytetracycline,OTC,97%)、4-差向土霉素(4-epioxytetracycline,EOTC,97%)等购自于德国Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH.
β-内酰胺类抗生素(β-lactam):青霉素(Penicillin,PCN,99%)、头孢噻肟(Cefotaxime Sodium,CFX,97%)等购自于德国Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH.
大环内酯类抗生素(MLs):罗红霉素(roxithromycin,ROX,97%)、克拉霉素(clarithromycin,CLR,99%)、螺旋霉素(spiramycin,SPM,96%)、新螺旋霉素(neo spiramycin I,NSPM,97%)、替米考星(tilmicosin,TIL,97%)、泰乐菌素(tylosin,TYL,98%)等购自于德国Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH.
喹诺酮类抗生素(FQs):氧氟沙星(ofloxacin,OFX,97%)、诺氟沙星(norfloxacin,NOR,97%)、恩诺沙星(enrofloxacin,ENR,97%)、环丙沙星(ciprofloxacin,CIP,97%)、等购自于德国Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH.
磺胺类抗生素(SAs):磺胺嘧啶(sulfadiazine,SD,97%)、磺胺二甲嘧啶(sulfamethazine,SMN,99%)、磺胺间甲氧嘧啶(sulfamonomethoxine sodium,SMX,97%)、磺胺甲噻二唑(sulfamethizole,SML,99%)等购自于德国Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH.
内标:氧氟沙星-D3(ofloxacin-D3,OFX-D3,99%)、环丙沙星-D8(ciprofloxacin-D8,CIP-D8,95%)、磺胺二甲嘧啶(sulfamethazine,PHENYL-13C6,99%)、去甲基金霉素(demethylchlortetracycline,DMCTC,97%)、四环素-D6(tetracycline-D6,TC-D6,80%)等购自于德国Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH.
-
精确称取各标准品0.010 g,用甲醇溶解并定容至10 mL棕色容量瓶中,配成质量浓度1000 mg·L−1的标准储备液,置于−20 ℃冰箱内保存. 使用前取各标准储备溶液10 μL至10 mL棕色容量瓶中,用甲醇稀释定容,配制成1.0 mg·L−1的混合标准中间溶液.
-
称取60.5 g Na2EDTA,溶解于1000 mL 0.1 mol·L−1柠檬酸溶液和625 mL 0.2 mol·L−1磷酸氢二钠的混合液中,并用1 mol·L−1盐酸调节pH=(3.85±0.1).
-
在2018年9—10月,猪粪样品分别采集于山东一个集约化生猪养殖场(猪场1)和北京两个集约化生猪养殖场(猪场2和猪场3). 猪场1和猪场2样品为畜舍鲜猪粪,猪场3为畜舍水冲猪粪. 样品采集后冷藏保存,猪场3样品在8000 r·min−1下离心15 min,采集离心后的固体样品. 每个样品置于−20℃预冻48 h,然后将预冻后的样品冷冻干燥48 h,碾磨过筛(100目)后储存于棕色玻璃瓶. 3个猪场猪粪的常规理化指标测定方法参照《水和废水监测方法(第四版)》[16],具体参数见表1,剩余部分置于−20℃冰箱保存用于抗生素测定. 本研究使用猪场2猪粪进行方法优化研究,猪场1和猪场3样品进行分析验证.
-
分别准确称取0.5000 g猪场1的不同畜舍的3个干燥样品,置于50 mL聚四氟乙烯管中,分别加入20 mL下列不同组的提取液:pH=4的Na2EDTA-McIlvaine缓冲溶液、甲醇、乙腈、1%甲酸乙腈和甲醇与Na2EDTA-McIlvaine缓冲溶液(1∶1,V∶V),每组样品设置3个平行. 将样品放在振荡器中涡旋振荡1 min,置于20 ℃水浴锅中超声30 min,并在8000 r·min−1、4 ℃下离心15 min,取上清液转移至干净的60 mL聚四氟乙烯管中,重复上述步骤3遍,将3次上清液混合,并取5 mL上清液稀释10倍后(用pH=4的纯水稀释),加入100 μL饱和Na2EDTA溶液,取10 mL进行固相萃取.
-
固相萃取使用固相萃取柱,预先采用5 mL乙酸乙酯、5 mL甲醇、5 mL pH=3.85纯水依次淋洗活化. 开启真空泵,控制流速约为3—5 mL ·min-1,将过膜上清液上柱,上样量为10 mL. 过柱完成后,分别用5 mL 5%甲醇水、5 mL超纯水冲洗小柱,对HLB柱抽真空干燥30 min,最后用9 mL 50%甲醇+50%乙酸乙酯洗脱(1∶1,V∶V),收集洗脱液并在室温下用N2吹扫至近干,用10%甲醇在自动进样瓶中定容至1 mL,待测.
-
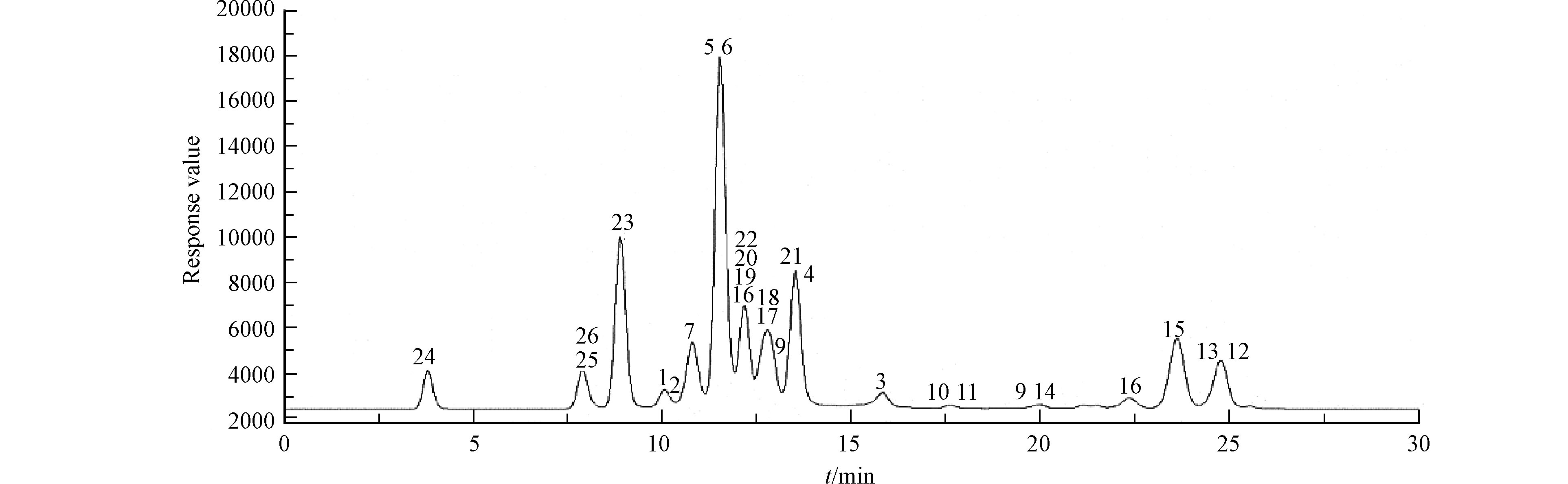
色谱柱:Agilent ZORBAX Eclipse Plus C18 (2.1 mm×100 mm,1.8 μm);流动相A为乙腈,流动相B为0.1% 甲酸溶液;柱温:35 ℃;流速:0.3 mL·min−1;梯度洗脱程序:0—1 min,90%A,1—10 min,90%—80% A,10—20 min,80%—50% A,20—25 min,50%—50%A,25—26 min,50% —90%A,26—35 min,90%—90% A;进样量:10 μL. 目标抗生素总离子流图(TIC)如图1所示.
-
电喷雾离子源:正离子扫描;雾化气、脱溶剂气和锥孔气:氮气,碰撞气:氩气;源温度:90 ℃,脱溶剂气温度:350 ℃;脱溶剂流速:500 L·h−1,锥孔气流速:70 L·h−1;毛细管电压:4 kV. 检测方式为MRM模式,采用ESI-MS/MS正离子检测,用注射泵直接进入的方式,测定每个化合物的母离子、子离子,并优化锥孔电压、碰撞能. 目标抗生素质谱条件以及辛醇水分配常数见表2.
-
对于抗生素的痕量分析,本研究采取选择与待测物性质相似的内标物,用于明确样品处理过程中待测物的损失以及检测过程中干扰物的影响[17]. 配制一系列浓度范围的抗生素标准溶液,经过LC-MS测定,以抗生素的质谱信号响应值对浓度得到标准曲线. 加入不同浓度的目标抗生素混标储备液,使样品成为20、50、100 μg·L−1的加标猪粪样品,同样按上述方法前处理后经SPE-LC-MS /MS(Agilent 1260超高效液相色谱、Agilent 6420三重四极杆质谱)测定,记录各化合物及内标色谱峰面积. 计算加标样品及空白样品中的抗生素浓度. 回收率计算方法如下:
将抗生素混标储备液配制成0.1、1、2、5、10、20、50.0、100、200 μg·L−1等9个浓度,对所测样品进行内标定量分析. 以标准偏差除以标准曲线的斜率乘以信噪比3和10计算仪器检出限(limits of detection,LOD)和定量限(limit of quantitation,LOQ)[18]. 整个流程重复3次,计算不同样品的方法精密度.
-
五种提取液的优化研究结果表明,乙腈对21种目标抗生素的平均提取率最低(约24%),且CTC、NOR和AMP等未被提取出来. 1%甲酸乙腈对目标物的提取效率也偏低,平均回收率42%左右. 单独用甲醇提取时,大多数抗生素均可被提取,其中FQs抗生素的提取效率较高(OFX、CIP、ETM的回收率分别为96%、65%和92%),TCs抗生素的提取效率较低(TC、OTC、CTC的回收率分别为29%、73%和40%),但E-TC和AMP和CFX等未能提取. Na2EDTA-McIlvaine缓冲溶液的提取效率较高,平均回收率68%,其中TCs抗生素的提取效率较高(TC、OTC、CTC的回收率分别在70%、109%和112%),FQs抗生素的提取效率较低(OFX、CIP、ERX的回收率分别在62%、31%和0%).
为了提高TCs和FQs抗生素回收率,本研究采用甲醇和Na2EDTA-McIlvaine缓冲溶液(V∶V=1∶1)的混合液提取目标抗生素,目标抗生素的回收率见图2. 结果表明,混合提取的回收率(平均83%)高于单独提取(61%和68%),尤其是TCs抗生素的回收率提高较大(TC、OTC、CTC的回收率分别在110.15%、116.36%和93.28%).
由于样品成分复杂,基质干扰效应较强,抗生素种类繁多,为此选取了5种分别与目标抗生素化学性质相似的内标抗生素消除可能存在的系统误差,并用甲醇和Na2EDTA-McIlvaine缓冲溶液(V∶V=1∶1)的混合液进行提取,发现5种内标抗生素的回收率除PCN外,其他目标抗生素回收率在51.85%—116.36%之间. 本研究最终选取20 mL甲醇和Na2EDTA-McIlvaine缓冲溶液(V∶V=1∶1)的混合液,超声15 min,重复提取3次,合并上清液后取5 mL稀释,进行固相萃取.
-
在0.1、1、2、5、10、20、50.0、100、200 μg·L−1等9个浓度范围,计算各待测目标抗生素在猪粪中的加标回收率(表3),除PCN和SML外,21种目标抗生素的回收率均大于51.85%;在0.5—200 μg·L−1浓度范围内,标准曲线的线性良好,检出限在0.90—26 μg·kg−1,定量限在2.91—85.20 μg·kg−1,内标定量回收率29.53%—116.36%,相关系数R2均大于0.997.
-
为了验证针对不同来源猪粪样品分析的准确性,本研究采用内标法,分别将猪场2不同畜舍的3个样品的内标回收率进行显著性分析. 每个样品做5个平行(n=5). 内标回收率的F检验(F-test)[19]结果表明(表4),不同猪场猪粪的P值(除TC-D6)均大于0.05,这表明不同猪粪样品使用内标法标定回收率时,在不同来源的猪粪抗生素回收率分析中没有显著性影响,TC-D6用作内标法定量时,受基质作用影响较大,不适宜作为内标定量猪粪中抗生素浓度. 根据保留时间和线性关系内控分析后发现DMCTC、CIP-D8、OFX-D3和SMZ-13C6分别可以标定TCs与CFX、MLs、FQs和SAs抗生素(文中所述抗生素种类). 此方法适用不同猪粪样品的分析,回收率满足分析要求.
-
在猪场1和猪场3猪粪样品按上述方法进行前处理并通过SPE-LC-MS/MS分析. 结果如表5所示,5大类抗生素均有被检出,2个猪场的猪粪均含有TCs抗生素,以TC、CTC、OTC、E-TC、E-OTC和TIL等6种抗生素为主. 猪场1和3的猪粪中抗生素浓度范围分别为ND—2055.95 μg·kg−1 DS和ND—52.06 mg·kg−1 DS. 万位宁等[15]使用固相萃取-超高效液相色谱串联质谱同时检测出畜禽粪便中17种抗生素,包括6种磺胺类(SAs)、4种四环素类(TCs)、3种氟喹诺酮类(FQs)、3 种大环内酯类(MLs)等,回收率在42.3%—79.6%之间,残留抗生素含量在0.60—13 μg·kg−1,与本研究的结果相似. 张丽丽等[20]的研究选择了京郊35家规模化养猪场的猪粪进行TCs抗生素分析,TCs抗生素浓度范围在0.48—29.2 mg·kg−1 DS,本研究高于其结果. 猪场1和猪场3抗生素含量和Hou等[21]的研究对比,FQs的浓度与其结果相似(411.3±1453.4)μg·kg−1). 通过以上研究分析,发现本方法适用于复杂基质下猪粪中抗生素的同步检出,且通过回收率验证发现本研究中的方法更适用于同步检测TCs 、MLs和FQs抗生素.
-
本研究对快速实现多种抗生素在猪粪等复杂基质下的同步检测进行了探索,在猪粪中不同抗生素的回收率不同,检测猪粪中5种TCs、2种β-lactams、6种MLs、4种FQs和4种SAs抗生素,检测限在0.5—200 μg·kg−1浓度范围内,标准曲线的线性良好,相关系数R2均大于0.997,检出限在0.90—26 μg·kg−1,定量限在2.91—85.20 μg·kg−1. SML和PCN回收率较低(38.34%和29.53%),在实际应用时可尝试其它优化提取条件以提高回收率. 此方法用四种内标(CIP-D8、DMCTC、OFX-D3、SMZ-13C6)标定,不同猪粪样品内标的回收率无显著性差异,并且根据保留时间和线性关系内控分析后发现DMCTC、CIP-D8、OFX-D3和SMZ-13C6分别可以标定TCs与CFX、MLs、FQs和SAs抗生素,通过以上研究分析,发现本方法适用于复杂基质下猪粪中抗生素的同步检出,且通过回收率验证发现本研究中的方法更适用于检测TCs 、MLs和FQs抗生素.
猪粪中21种常见抗生素的同步提取检测方法研究及应用
Research and application of detection method of simultaneous extraction and detection of 21 common antibiotics from pig manure
-
摘要: 为实现猪粪中抗生素的有效削减及控制,迫切需要开发快速、同步兽用抗生素的检测分析方法,明确猪粪中多种类抗生素赋存特征。本研究建立并优化了猪粪中21种常见抗生素的同步分析方法。该方法采用甲醇和Na2EDTA-McIlvaine缓冲溶液(1∶1,V/V)提取,提取液经固相萃取净化后高效液相色谱串联质谱检测。猪粪样品中5种四环素类、2种β-内酰胺类、6种大环内酯类、4种磺胺类和4种喹诺酮类抗生素的内标定量回收率29.53%—116.36%,检出限0.90—26 μg·kg−1 DS,定量限2.91—85.20 μg·kg−1 DS,相关系数R2均大于0.997。采用该方法对单个猪场不同畜舍样品加标回收率的单因素方差分析发现,除了四环素-D6(TC-D6)有显著性影响之外,其它内标回收率在不同样品中无显著性影响。分别采集不同地区2个猪场的猪粪样品进行验证分析,发现猪粪样品中单个抗生素含量范围在ND—99.37 mg·kg−1 DS。结果表明,该方法可用于猪粪中多种类抗生素的同步检测。
-
关键词:
- 猪粪 /
- 内标法 /
- 兽用抗生素 /
- 高效液相色谱-质谱联用法 /
- 固相萃取
Abstract: In order to achieve effective reduction and control of antibiotics in pig manure, there is an urgent need to develop rapid and simultaneous detection and analysis methods for veterinary antibiotics, and to clarify the characteristics of the occurrence of multiple antibiotics in pig manure. In this study, a simultaneous analytical method was developed and optimized for the determination of 21 common antibiotics in swine manure. The method used methanol and Na2EDTA-McIlvaine buffer solution (1∶1, V/V) for extraction, and the extracts were cleaned up by solid phase extraction and detected by high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. The recoveries of the internal standard quantification of five tetracyclines, two β-lactams, six macrolides, four sulfonamides and four quinolones antibiotics in pig manure samples ranged from 29.53% to 116.36%, the limits of detection (LODs) were 0.90—26 μg·kg−1 DS, and the limits of quantification (LOQs) were 2.91—85.20 μg·kg−1 DS, with the correlation coefficients R2 were greater than 0.997. Using this method to analyze the single-factor analysis of variance for the recovery rates of samples from different houses of a single pig farm, it was found that except for the significant effect of tetracycline-D6 (TC-D6), the recovery rates of other internal standards were not significant in different samples. Pig manure samples from two pig farms in different regions were collected for verification and analysis. It was found that the content of a single antibiotic in the pig manure samples ranged from ND—99.37 mg·kg−1 DS. The results show that this method can be used for simultaneous detection of multiple antibiotics in pig manure. -

-
表 1 3个猪场猪粪的基本理化参数
Table 1. Characteristics of three samples of manure of three pig farm
参数 Parameter 猪场1 Sample 1 猪场2 Sample 2 猪场3 Sample 3 COD /(g·kg−1) 170 288 96 NH4+-N/ (mg·kg−1) 2770 3947 2280 NO3—N/(mg·kg−1) 1145 2275 535 TOC/ (mg·kg−1) 6045 7528 3288 表 2 目标抗生素的质谱参数
Table 2. Mass spectrometric parameters of target antibiotics
序号 类别
Category目标分析物
Compounds辛醇水分配常数lgKow
Octanol-water partition coefficient母离子(m/z)
Parent ions子离子(m/z)
Product ions定量离子(m/z)
Quantitive ions碰撞能/eV
Collision energy保留
时间/min
Retention time1 TCs TC 0.54 445.1 427.3 410.3 6,10 10.8 2 E-TC — 445.8 428.5 411.2 6,10 10.81 3 CTC −0.62 479.3 462.3 444.3 8,12 15.82 4 *DMCTC — 465.3 448 430 6,15 13.44 5 OTC −0.9 461.3 443.3 426.1 5,12 11.58 6 E-OTC — 461.5 443.3 426.1 5,12 11.58 7 *TC-D6 — 451.3 416.2 433.9 12,16 10.7 8 β- lactam PCN −3.29 335 217 91 5,45 21.5 9 CTX 0.64 456 324 167 5,15 12.62 10 MLs SPM −2.04 843.4 174.1 142.1 35,30 17.68 11 NSPM — 699.3 174 142 20,25 17.58 12 CLA 3.16 748.3 158.1 126.9 25,20 24.79 13 TYL 1.63 916.9 145.1 173.8 50,35 24.57 14 TIL 3.8 869.6 696.4 174 40,40 19.96 15 ROX 2.75 837.4 679.3 158.1 15,20 23.65 16 FQs NOR −1.03 320.1 302 276.1 10,15 12.17 17 CIP 0.28 332.1 314.1 288.2 9,12 12.89 18 *CIP-D8 — 340.3 296.3 249.2 12,22 12.84 19 *OFX-D3 — 365.3 321.3 261.2 14,24 11.48 20 OFX −2 362.1 344 318.1 15,15 11.54 21 ERX 0.7 360.1 342.2 316.1 15,15 13.51 22 SAs SMX 0.7 281.1 156 92 10,25 12.17 23 SML 0.54 271 156 92 5,20 9.01 24 SD −0.09 251 156 108 9,17 3.83 25 SMN 0.19 279.1 156 124 10,25 8.91 26 *SMN-13C6 −0.07 285.1 124 186 20,22 8.9 *为DMCTC、TC-D6、CIP-D8、OFX-D3、SMN-13C6-同位素内标(Isotope Internal Standard). 表 3 目标抗生素的线性范围、线性回归方程、检出限、定量限和回收率
Table 3. Linear detection range, linear regression equations, limit of detection, limit of quantity and recoveries for the target antibiotics
类别Category 抗生素Compounds 线性回归方程
Linear regression equation检出限/(μg·kg−1)
Limit of detection定量限/(μg·kg−1)
Limit of quantity回收率/%
Recovery rateRSD/% R2 TCs TC y = 1.2419x − 6.7764 0.90 3.04 110.15 10.46 0.9952 ETC y = 0.9317x + 0.9728 15.00 51.50 94.29 2.79 0.9986 CTC y = 1.1215x − 2.1872 5.97 19.90 93.28 7.26 0.9996 DMCTC y = 1.0674x − 0.3681 4.64 15.46 105.06 1.75 0.9999 OTC y = 1.2335x − 8.288 12.00 39.30 116.36 11.75 0.9954 EOTC y = 1.0522x − 4.3296 6.91 23.05 55.47 3.85 0.9974 TC-D6 y = 1.0666x − 5.5293 2.10 7.03 99.17 8.55 0.9958 β− lactam PCN y = 1.046x − 6.9819 2.90 9.63 29.53 7.61 0.9953 CFX y = 1.0059x − 0.4935 1.93 6.44 87.99 6.94 0.9998 MLs SPM y = 1.0172x − 2.2896 5.40 18.00 80.68 4.23 0.9986 NSPM y = 0.946x + 2.3059 8.40 27.90 84.52 6.10 0.9999 CLA y = 0.9973x + 0.7278 6.00 19.90 113.72 7.85 0.9999 TYL y = 0.9915x + 0.7085 8.67 28.91 83.45 6.72 0.9998 TIL y = 1.0243x − 3.2394 13.00 44.90 105.97 6.89 0.9973 ROX y = 1.0015x − 0.1942 2.00 6.70 89.21 5.23 0.9999 FQs NOR y = 0.8307x + 1.4863 2.00 6.62 63.01 2.53 0.9994 CIP y = 1.0352x + 2.382 2.26 7.55 75.94 8.68 0.9990 CIP-D8 y = 1.0448x − 0.7331 1.96 6.52 70.41 3.65 0.9992 OFX-D3 y = 1.096x − 1.7729 1.60 5.31 85.42 11.20 0.9994 OFX y = 1.0299x − 0.1603 0.90 2.91 114.12 4.10 0.9998 ERX y = 0.8981x − 1.5119 6.90 23.10 86.25 2.73 0.9983 SAs SMX y = 0.9317x + 0.9728 12.00 38.90 51.85 5.14 0.9999 SML y = 0.946x + 2.3059 9.90 33.10 38.34 8.31 0.9984 SD y = 1.0125x − 0.7419 15.00 48.90 76.71 2.79 0.9992 SMN y = 1.0771x + 0.0393 26.00 85.20 67.29 2.15 0.9984 SMN-13C6 y = 24.538x + 289.43 1.80 5.85 75.16 8.55 0.9975 表 4 内标回收率的F检验(F-test)
Table 4. Single factor analysis of variance of internal antibiotics
序号
Number抗生素内标名称
Internal standard of antibioticsP 1 CIP-D8 0.333164 P>0.05 2 DMCTC 0.083809 P>0.05 3 TC-D6 0.0092 *P<0.05 4 OFX-D3 0.848074 P>0.05 5 SMN-13C6 0.091021 P>0.05 * P<0.05水平差异显著(The differences in levels were significant.). 表 5 不同规模化养猪场猪粪中的抗生素含量(μg·kg−1)
Table 5. Residues of antibiotics in pig manure from different pig farms
样品
Sample猪场1
Pig farm1猪场3
Pig farm3TC 65.69 751.3 E-TC 149.86 853.42 CTC 60.16 1653.34 OTC 219.35 52057.2 E-OTC 145.71 37013.86 PCN ND ND CTX ND ND SPM ND ND NSPM ND ND CLA 17.38 ND TYL 39.87 117.48 TIL 2055.95 4641.27 ROX ND ND NOR ND ND CIP 121.56 476.23 OFX 16.59 85.97 ERX 3.36 ND SMX 3.86 8.66 SML ND ND SD ND ND SMN 20.04 ND -
[1] 印遇龙, 杨哲. 天然植物替代饲用促生长抗生素的研究与展望 [J]. 饲料工业, 2020, 41(24): 1-7. YIN Y L, YANG Z. Research and prospect of natural plant substitute for antibiotic growth promoters in feed [J]. Feed Industry, 2020, 41(24): 1-7(in Chinese).
[2] 王怀禹. 减抗、限抗、禁抗及其替代方案对生猪养殖的影响 [J]. 猪业科学, 2020, 37(1): 42-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5358.2020.01.014 WANG H Y. Effects of reducing, estricting and prohibiting antibiotics and their alternatives on pig breeding [J]. Swine Industry Science, 2020, 37(1): 42-44(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5358.2020.01.014
[3] RAMASWAMY J, PRASHER S O, PATEL R M, et al. The effect of composting on the degradation of a veterinary pharmaceutical [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(7): 2294-2299. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.10.089 [4] 高立红, 史亚利, 厉文辉, 等. 抗生素环境行为及其环境效应研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(9): 1619-1633. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.09.004 Gao L H, Shi Y L, Li W H, et al. Environmental behavior and impacts of antibiotics [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(9): 1619-1633(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.09.004
[5] ZHAO L, DONG Y H, WANG H. Residues of veterinary antibiotics in manures from feedlot livestock in eight provinces of China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 408(5): 1069-1075. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.11.014 [6] ZHOU L J, YING G G, ZHANG R Q, et al. Use patterns, excretion masses and contamination profiles of antibiotics in a typical swine farm, South China [J]. Environmental Science:Processes & Impacts, 2013, 15(4): 802. [7] CHEN Y S, ZHANG H B, LUO Y M, et al. Occurrence and assessment of veterinary antibiotics in swine manures: A case study in East China [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(6): 606-614. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4830-3 [8] 钟冬莲, 丁明, 汤富彬, 等. 高效液相色谱-电喷雾串联质谱法测定畜禽粪便中四环素类抗生素 [J]. 分析科学学报, 2014, 30(3): 433-436. ZHONG D L, DING M, TANG F B, et al. Determination of tetracyclines antibiotics residues in animal manure by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Analytical Science, 2014, 30(3): 433-436(in Chinese).
[9] 罗庆, 孙丽娜, 胡筱敏. 固相萃取-高效液相色谱法测定畜禽粪便中罗红霉素和3种四环素类抗生素 [J]. 分析试验室, 2014, 33(8): 885-888. LUO Q, SUN L N, HU X M. Simultaneous determination of roxithromycin and three tetracyclines in manure by high-performance liquid chromatography with a diode-array detector [J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2014, 33(8): 885-888(in Chinese).
[10] 吴晓凤, 郑嘉熹, 魏源送, 等. 超高效液相色谱串联质谱法同时检测复杂基质中四环素类抗生素及其代谢产物 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(11): 2293-2301. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2013.11.027 WU X F, ZHENG J X, WEI Y S, et al. Simultaneous determination of tetracyclines and their degradation products in complicated matrix by ultra performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(11): 2293-2301(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2013.11.027
[11] 沈颖, 魏源送, 郭睿, 等. 超高效液相色谱串联质谱检测猪粪中残留的四环素类抗生素 [J]. 环境化学, 2009, 28(5): 747-752. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2009.05.027 SHEN Y, WEI Y S, GUO R, et al. Determination of tetracyclines residues in swine manure by uplc/ms [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2009, 28(5): 747-752(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2009.05.027
[12] PAN X, QIANG Z M, BEN W W, et al. Simultaneous determination of three classes of antibiotics in the suspended solids of swine wastewater by ultrasonic extraction, solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23(10): 1729-1737. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60590-6 [13] 李艳霞, 李帷, 张雪莲, 等. 固相萃取-高效液相色谱法同时检测畜禽粪便中14种兽药抗生素 [J]. 分析化学, 2012, 40(2): 213-217. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(11)60529-X LI Y X, LI W, ZHANG X L, et al. Simultaneous determination of fourteen verterinary antibiotics in animal manure using solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 40(2): 213-217(in Chinese). doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(11)60529-X
[14] 郭欣妍, 王娜, 郝利君, 等. 超高效液相色谱/串联质谱法同时测定水、土壤及粪便中25种抗生素 [J]. 分析化学, 2015, 43(1): 13-20. GUO X Y, WANG N, HAO L J, et al. Simultaneous detection of 25 kinds of veterinary antibiotics in soil, manure and water samples using liquid ChromatographyTandem mass spectrometry [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 43(1): 13-20(in Chinese).
[15] 万位宁, 陈熹, 居学海, 等. 固相萃取-超高效液相色谱串联质谱法同时检测禽畜粪便中多种抗生素残留 [J]. 分析化学, 2013, 41(7): 993-999. WAN W N, CHEN X, JU X H, et al. Simultaneous determination of residual antibiotics in livestock manure by solid phase extraction-ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tantem mass spectrometry [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 41(7): 993-999(in Chinese).
[16] 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 中国环境科学出版社, 国家环境保护总局, 水和废水监测分析方法编委会编, 2002. Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis methods[M]. Compilation by China Environmental Science Press, State Environmental Protection Administration, Editorial Board of Water and Waste water Monitoring and Analysis Methods, 2002(in Chinese).
[17] YUAN X J, QIANG Z M, BEN W W, et al. Rapid detection of multiple class pharmaceuticals in both municipal wastewater and sludge with ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 26(9): 1949-1959. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2014.06.022 [18] PAN X, QIANG Z M, BEN W W, et al. Residual veterinary antibiotics in swine manure from concentrated animal feeding operations in Shandong Province, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 84(5): 695-700. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.03.022 [19] 张秀英. 抗生素微生物检定中的常见问题分析 [J]. 中国兽药杂志, 2004, 38(3): 45-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1280.2004.03.015 ZHANG X Y. Analysis on common problems in testing antibiotics by microbiological method [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Drug, 2004, 38(3): 45-46(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1280.2004.03.015
[20] 张丽丽, 直俊强, 张加勇, 等. 北京地区猪粪中四环素类抗生素和重金属残留抽样分析 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30(35): 74-78. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2014-1494 ZHANG L L, ZHI J Q, ZHANG J Y, et al. Study on tetracyclines and heavy metals residues in pig feces from Beijing area [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014, 30(35): 74-78(in Chinese). doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2014-1494
[21] HOU J, WAN W N, MAO D Q, et al. Occurrence and distribution of sulfonamides, tetracyclines, quinolones, macrolides, and nitrofurans in livestock manure and amended soils of Northern China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(6): 4545-4554. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3632-y -



 下载:
下载:


