-
应对全球气候变暖,对二氧化碳(CO2)实施控制与减排已成为所有国家的共同责任。2020年9月,习总书记在第七十五届联合国大会中提出,我国力争于2030年前使CO2排放达到峰值,努力争取2060年前实现碳中和。碳捕集和封存技术是实现碳中和目标的重要途径。CO2排放主要来源于燃煤电厂,对电厂烟气实施CO2捕集是实现碳减排的有效手段。化学吸收法是烟气CO2捕集最有效的方法之一[1-2]。以乙醇胺(MEA)为代表的有机胺是目前研究最为成熟的一类化学吸收剂,其具有CO2吸收迅速、选择性好等特点[3-4]。但传统有机胺吸收剂通常为水溶液,其存在解吸能耗高、设备腐蚀大等问题,工业化推广受到一定限制[5]。
对于传统有机胺水溶液而言,过高的解吸能耗主要是溶剂水较大的比热和蒸发焓所致[6]。同水相比,有机溶剂具有较低的比热和蒸发焓,在解吸方面有较大的节能优势。因此,用有机试剂作为溶剂构建无水吸收剂是降低CO2捕集能耗行之有效的手段。Yu等[7]构建了MEA/甲醇吸收剂用于CO2捕集,相比MEA水溶液,MEA/甲醇的解吸能耗可降低7%—24%。Rashidi等[8]利用吸收-解吸塔模拟MEA/甲醇和MEA/H2O的CO2捕集过程,发现MEA/甲醇的解吸能耗比MEA/H2O低12%。此外,研究者陆续开发了N-乙基乙醇胺(EMEA)/乙醇[9]、2-乙醇吡啶(2-PE)/乙二醇[10]等无水吸收剂,这些吸收剂均具有良好的节能潜力,同时对设备的腐蚀性低。但醇溶剂普遍存在沸点低、易挥发损失的缺陷。为避免醇类溶剂易损失的难题,研究者们用沸点高、蒸气压低的醇醚类试剂作为溶剂,开发了MEA/乙二醇单甲醚(2ME)[11]、2-乙基己烷-1-胺(EHA)/四乙二醇二甲醚(TGDE)[12]、EMEA/二乙胺基乙醇(DEEA)[13]等无水吸收剂。然而,上述无水吸收剂所使用的胺大多为一元胺(只含1个氨基),其CO2吸收负荷较低(约为0.5 mol·mol−1),CO2捕集效率欠佳。
胺溶液吸收CO2是基于胺分子中的氨基基团与CO2之间的化学反应,胺分子中氨基个数越多,其CO2负荷就越大。因此,利用二元或多元胺构建无水吸收剂可提高CO2负荷。陶梦娜[14]构建了三乙烯四胺(TETA)/聚乙二醇200(PEG200)吸收体系,发现TETA/PEG200的CO2吸收负荷可达1.63 mol·mol−1 (CO2/胺)。Zhang等[15]用二乙烯三胺(DETA)/N-甲基吡咯烷酮(NMP)无水吸收剂吸收CO2,发现DETA可与CO2发生等摩尔反应。但上述吸收剂吸收CO2后易产生固体不溶物甚至黏稠的胶状物质,可能会引起设备结垢、管道堵塞等问题。目前,关于CO2吸收负荷高且无固体不溶物析出的无水吸收剂仍鲜有报道。基于前期大量筛选工作,本研究小组发现二元胺羟乙基乙二胺(AEEA)/二甲基亚砜(DMSO)溶液吸收CO2过程中能始终保持均相状态,且其具有较高的CO2吸收负荷,是一种颇具应用潜力的CO2吸收剂。因此,本文拟对AEEA/DMSO捕集CO2的吸收和解吸性能进行全面研究,并通过核磁共振碳谱(13C NMR)分析其捕集CO2的反应机理。
全文HTML
-
羟乙基乙二胺(AEEA,纯度98.0%)、二甲基亚枫(DMSO,纯度99.8%)、一乙醇胺(MEA,纯度99.0%)等试剂均为分析纯,购买于上海阿拉丁生化科技有限公司。CO2气体(纯度99.999%)购买于桂林如一生物科技有限公司。
-
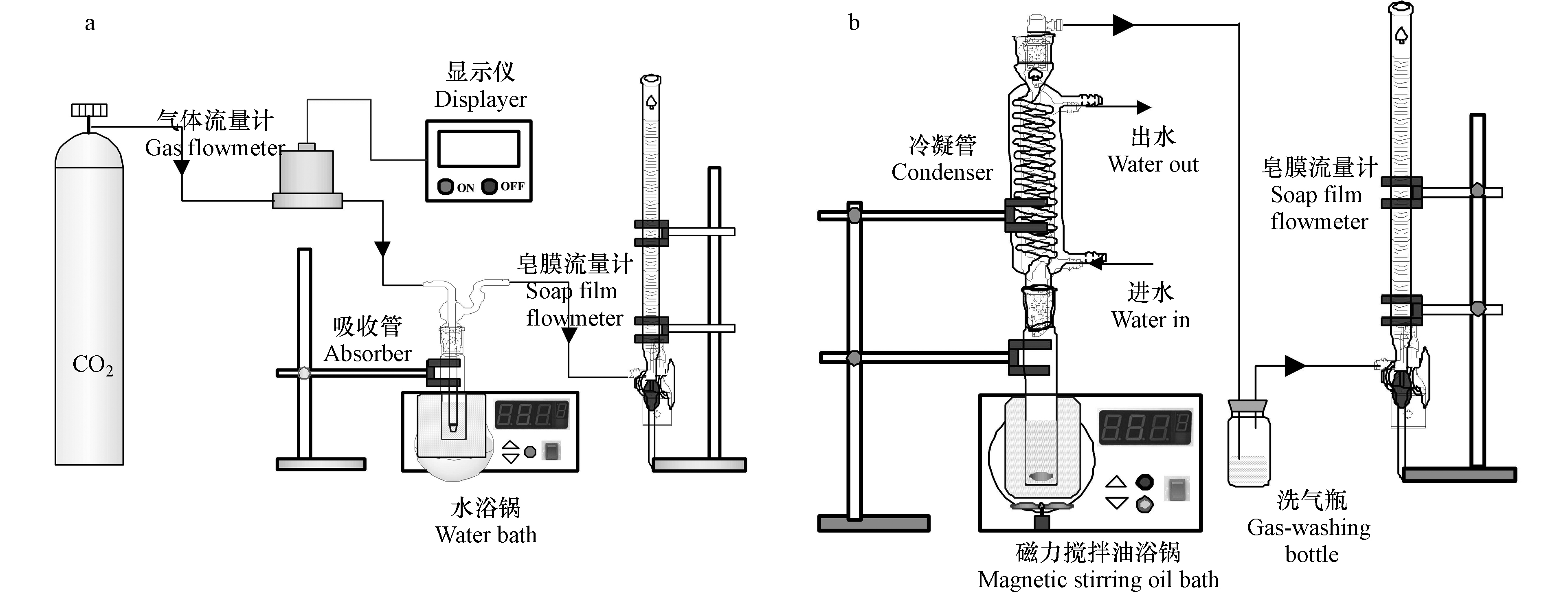
利用鼓泡吸收装置(图1(a))进行CO2吸收实验。简要步骤为:(1)以DMSO为溶剂,配制25 mL一定浓度的AEEA溶液;(2)将溶液置于鼓泡吸收管中,通过水浴锅加热到所需温度;(3)向鼓泡吸收管中通入恒定流速的CO2气体;(4)利用皂膜流量计测定不同时刻下吸收管出气口的CO2流速。基于吸收管进、出口的气体流量差,即可计算CO2吸收速率。对于无水吸收剂,为避免其吸收CO2后粘度过高,通常有机胺的质量分数不超过20%。因此,本研究设置AEEA浓度为2.0 mol·L−1(质量分数约为20%)。另一方面,为保证CO2较好的传质效率,实验中控制气体流速为80 mL·min−1。
需要说明的是,本研究采用纯CO2气体进行吸收实验,但在实际应用中,烟气中CO2分压较低且存在其他气体杂质,可能对吸收剂的吸收速率及使用寿命产生影响。在下一步工作中,有必要探究低CO2分压和气体杂质对AEEA/DMSO吸收CO2的影响。
-
利用常压油浴加热装置(图1(b))进行CO2解吸实验。简要步骤为:(1)将吸收饱和的溶液移至磁力搅拌油浴锅中加热至所需的解吸温度;(2)当溶液开始冒泡时开始解吸计时;(3)利用皂膜流量计测定不同时刻下溶液释放出的CO2流量。通过计算,即可得到溶液的CO2解吸速率。
此外,配制2.0 mol·L−1 AEEA水溶液(AEEA/H2O)和30%wt MEA(MEA/H2O)水溶液用于与AEEA/DMSO溶液进行CO2吸收-解吸性能对比。以上所有吸收-解吸实验均进行了重复实验。
-
吸收剂吸收CO2后,产物可通过13C NMR进行分析。首先,将0.4 mL的吸收剂溶液置于直径为5 mm的核磁管中,再加入0.2 mL氘代试剂与溶液混合均匀。随后,将制备的样品用核磁共振波谱仪(500 MHz Bruker Avance,德国)进行13C NMR测试,即可得到样品的13C NMR谱图。本研究选用DMSO-d6溶解AEEA/DMSO样品,而AEEA/H2O样品则用D2O溶解。
-
吸收过程中,吸收剂吸收CO2的瞬时速率可由式(1)计算得到:
式中,ra为CO2吸收速率(mol·min−1·L−1),Qin、Qout分别进、出口流量(mL·min−1),T0和P0分别为标准状态下的温度(K)和大气压(kPa),Tact和Pact分别为实际状态下的温度(K)和大气压(kPa),V为吸收剂体积(L)。
吸收剂的CO2吸收负荷由吸收速率对吸收时间积分求得,可由式(2)计算得到:
式中,α为CO2吸收负荷(mol·mol−1),t为吸收时间(min),C为胺的浓度(mol·L−1)。
解吸过程中,CO2的瞬时解吸速率可由式(3)计算得到:
式中,rd为CO2解吸速率(mol·min−1),
Q′out 为冷凝管出口气体流量(mL·min−1)。吸收剂的CO2解吸负荷由解吸速率对解吸时间积分求得,可由式(4)计算得到:
式中,
α′ 为CO2解吸负荷(mol·mol−1),t为解吸时间(min),C为胺浓度(mol·L−1),V为吸收剂体积(L)。
1.1. 试剂
1.2. 实验方法
1.2.1. 吸收实验
1.2.2. 解吸实验
1.2.3. 核磁共振测试
1.3. 计算方法
-
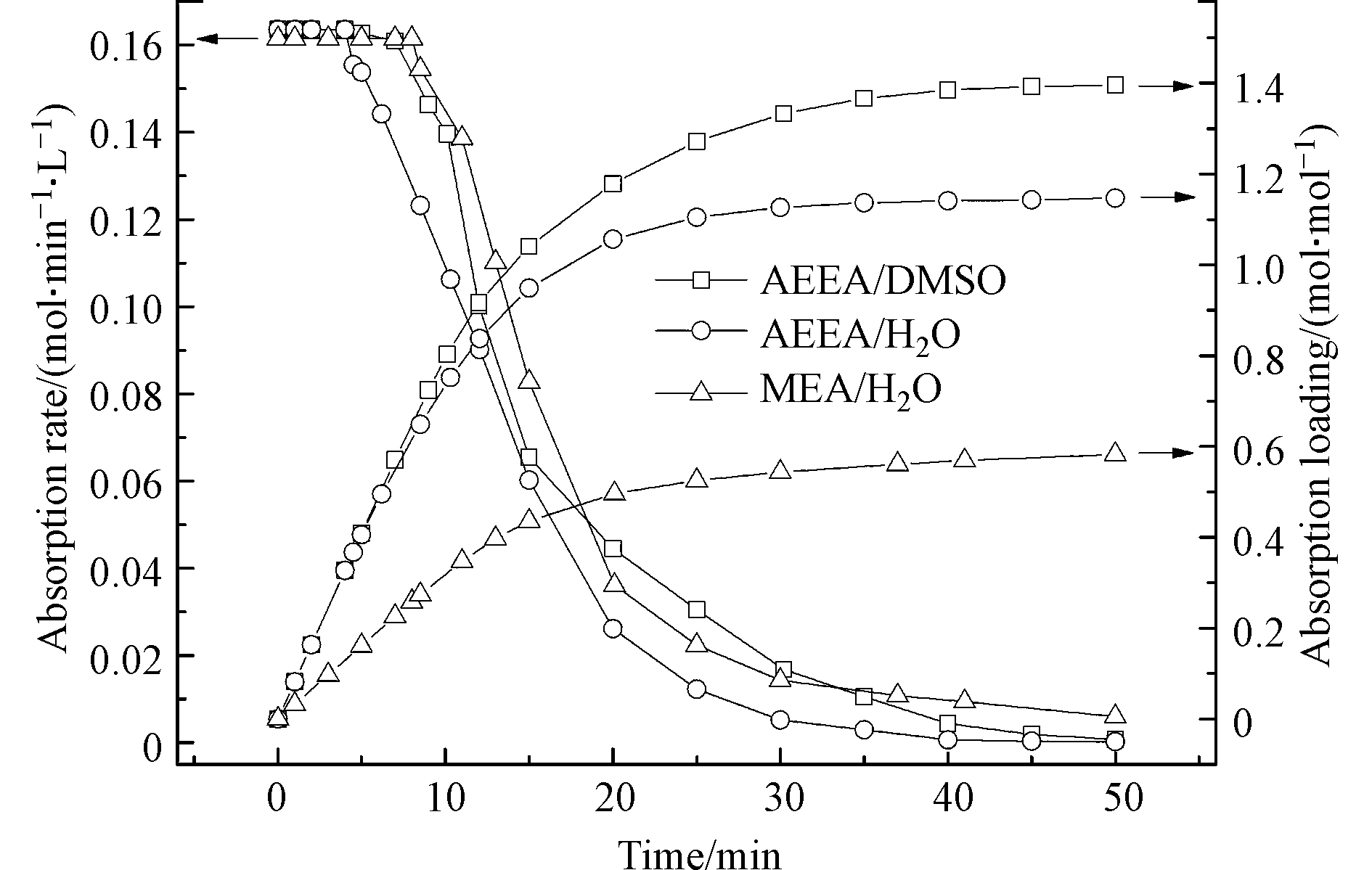
研究首先考察AEEA/DMSO吸收剂的CO2吸收性能,并以AEEA/H2O和MEA/H2O溶液的CO2吸收性能作为对比。图2为3种吸收剂的CO2吸收速率和吸收负荷随时间的变化曲线。由图2可知,3种吸收剂具有相近的初始吸收速率(0.16 mol·min−1·L−1)。随着吸收时间的增加,各吸收剂的吸收速率逐渐降低。经过50 min后,吸收速率趋近于零,说明吸收剂达到吸收饱和。值得注意的是,AEEA/H2O的吸收速率经历4 min率先下降,而AEEA/DMSO和MEA/H2O的吸收速率均在7 min后才呈现下降趋势。此结果说明AEEA/DMSO的CO2吸收效率与MEA/H2O相当。另外,从图2可以看出,3种吸收剂的CO2吸收负荷均随时间的增加而升高。达到CO2饱和后,AEEA/DMSO的负荷高达1.40 mol·mol−1,显著高于AEEA/H2O和MEA/H2O,这意味着AEEA/DMSO具有较强的CO2吸收能力。
-
经过脱硫,烟气的温度通常在40—55 ℃之间。AEEA/DMSO能否在较大的温度范围内保持良好的CO2吸收能力,对于其实际应用具有重要意义。因此,研究考察了AEEA/DMSO在40—60 ℃温度范围内的CO2吸收性能,结果如图3所示。由图3可知,在考察的温度范围内,吸收剂在各温度下的初始吸收速率相近。不过,随着吸收时间增加,温度越高,吸收速率的下降幅度越大。但总体来说,吸收温度的改变对AEEA/DMSO的CO2吸收速率并未有显著影响。另外,在不同温度下,AEEA/DMSO的CO2吸收负荷随着吸收的进行迅速升高并最终达到吸收饱和。AEEA/DMSO的CO2负荷随温度的升高有轻微的降低,但在60 ℃下依然能保持在1.21 mol·mol−1。以上结果表明,AEEA/DMSO具有稳定的CO2吸收能力,能适应烟气脱硫后的温度范围。
-
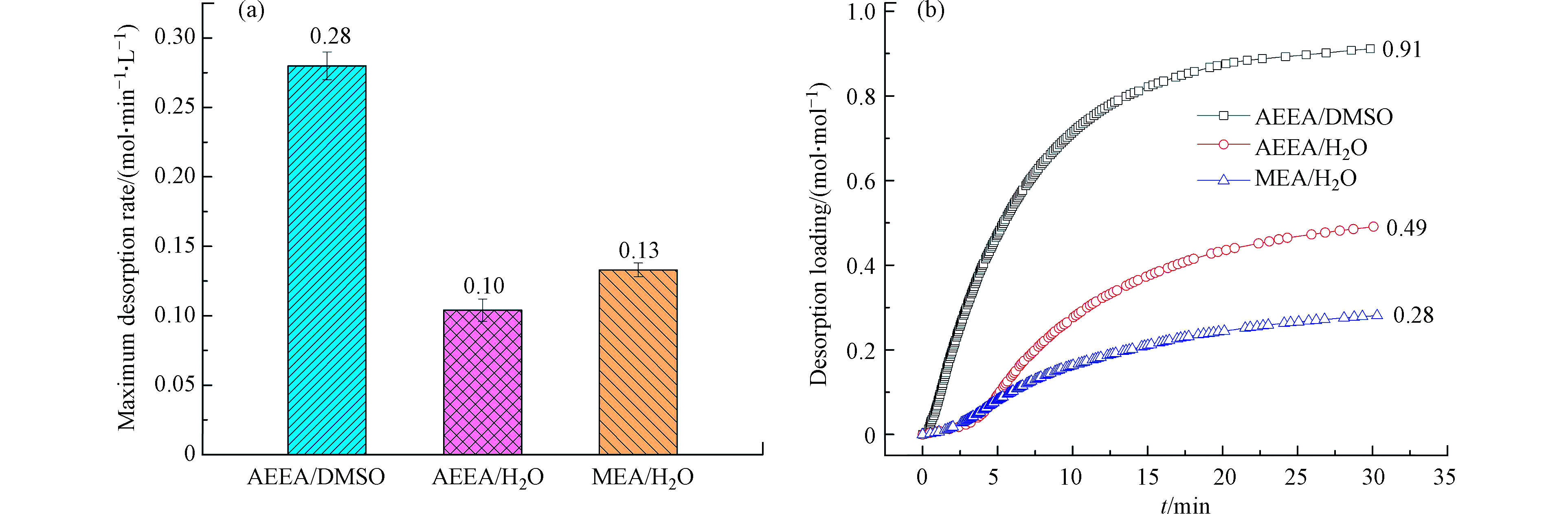
除了吸收性能,解吸性能也是评价吸收剂的重要指标。研究对比了AEEA/DMSO、AEEA/H2O和MEA/H2O等3种吸收剂在120 ℃下的解吸性能,结果如图4所示。在相同解吸条件下,相比于AEEA/H2O和MEA/H2O,AEEA/DMSO具有更优异的解吸效率,其最大CO2解吸速率高达0.28 mol·min−1·L−1,而AEEA/H2O和MEA/H2O的最大解吸速率分别只有0.10 mol·min−1·L−1和0.13 mol·min−1·L−1(图4(a)).
图4(b)为解吸负荷随时间的变化曲线。可以看出,在解吸前15 min,AEEA/DMSO的CO2解吸负荷迅速升高,而AEEA/H2O和MEA/H2O的解吸负荷则缓慢上升。这是因为AEEA/H2O具有较大的解吸速率,而AEEA/H2O和MEA/H2O的解吸速率较低。解吸结束后,AEEA/DMSO的解吸负荷可达0.91 mol·mol−1,分别是AEEA/H2O和MEA/H2O解吸负荷的1.86倍和3.25倍。以上结果表明,AEEA/DMSO具有优异的CO2解吸性能。较高的CO2解吸速率和解吸负荷,一方面能缩短吸收剂解吸CO2的时间,另一方面能降低气体的压缩功,最终能达到降低CO2捕集运行成本的目的[16]。
-
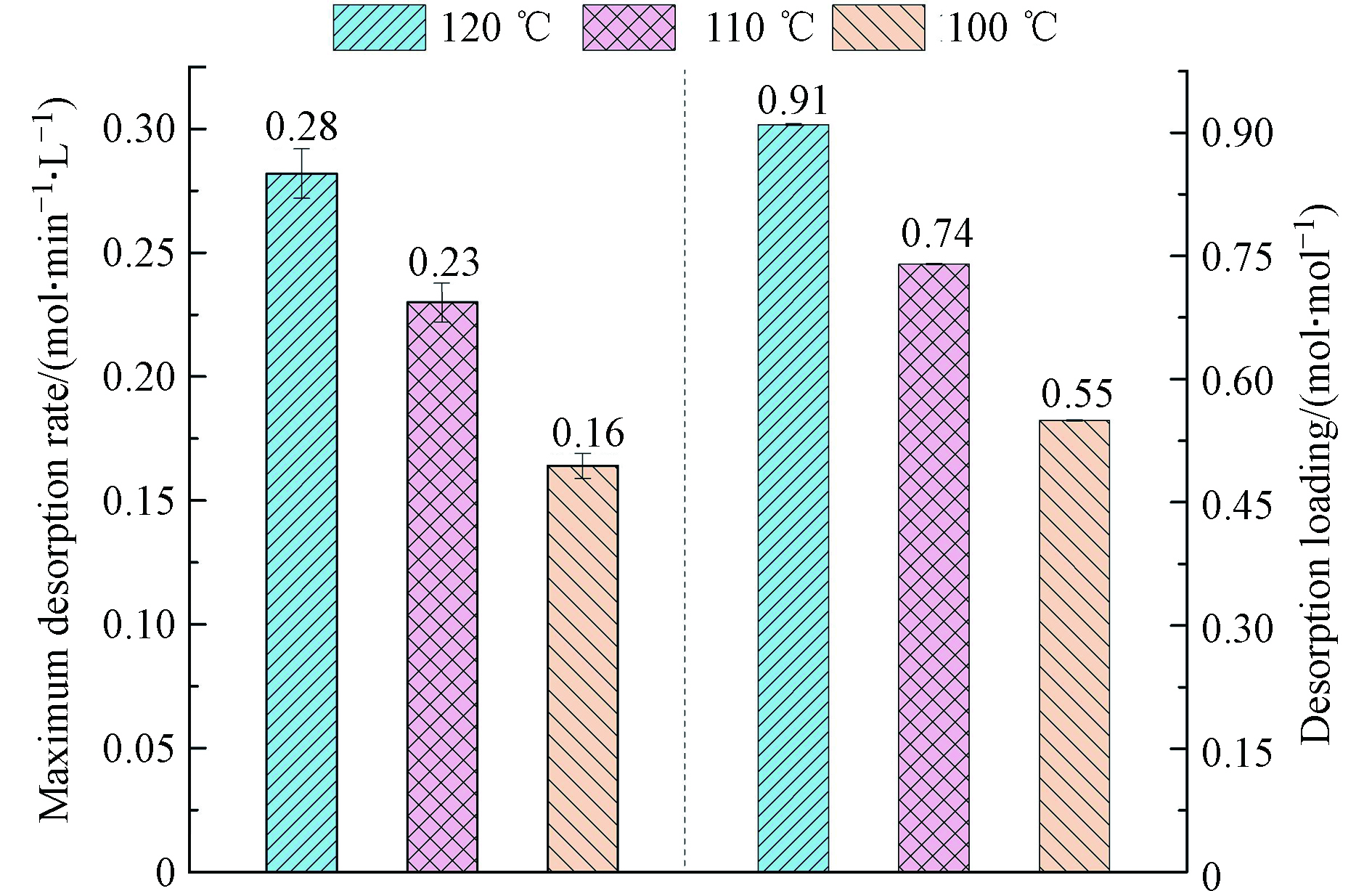
此外,研究考察了AEEA/DMSO在不同解吸温度下的CO2解吸性能,结果如图5所示。由图5可知,AEEA/DMSO的最大CO2解吸速率和解吸负荷均随解吸温度的降低而降低。
但解吸温度降至100 ℃时,AEEA/DMSO的最大解吸速率和解吸负荷仍可达0.16 mol·min−1·L−1和0.55 mol·mol−1,此结果优于AEEA/H2O和MEA/H2O在120 ℃时的解吸性能。此结果意味着AEEA/DMSO在较低的解吸温度下即可实现较为理想的CO2解吸。在较低温度下进行CO2解吸有利于降低CO2捕集过程中吸收剂的再生能耗,从而也可降低CO2捕集运行成本,从这方面来说,AEEA/DMSO是一种颇具潜力的CO2吸收剂。
-
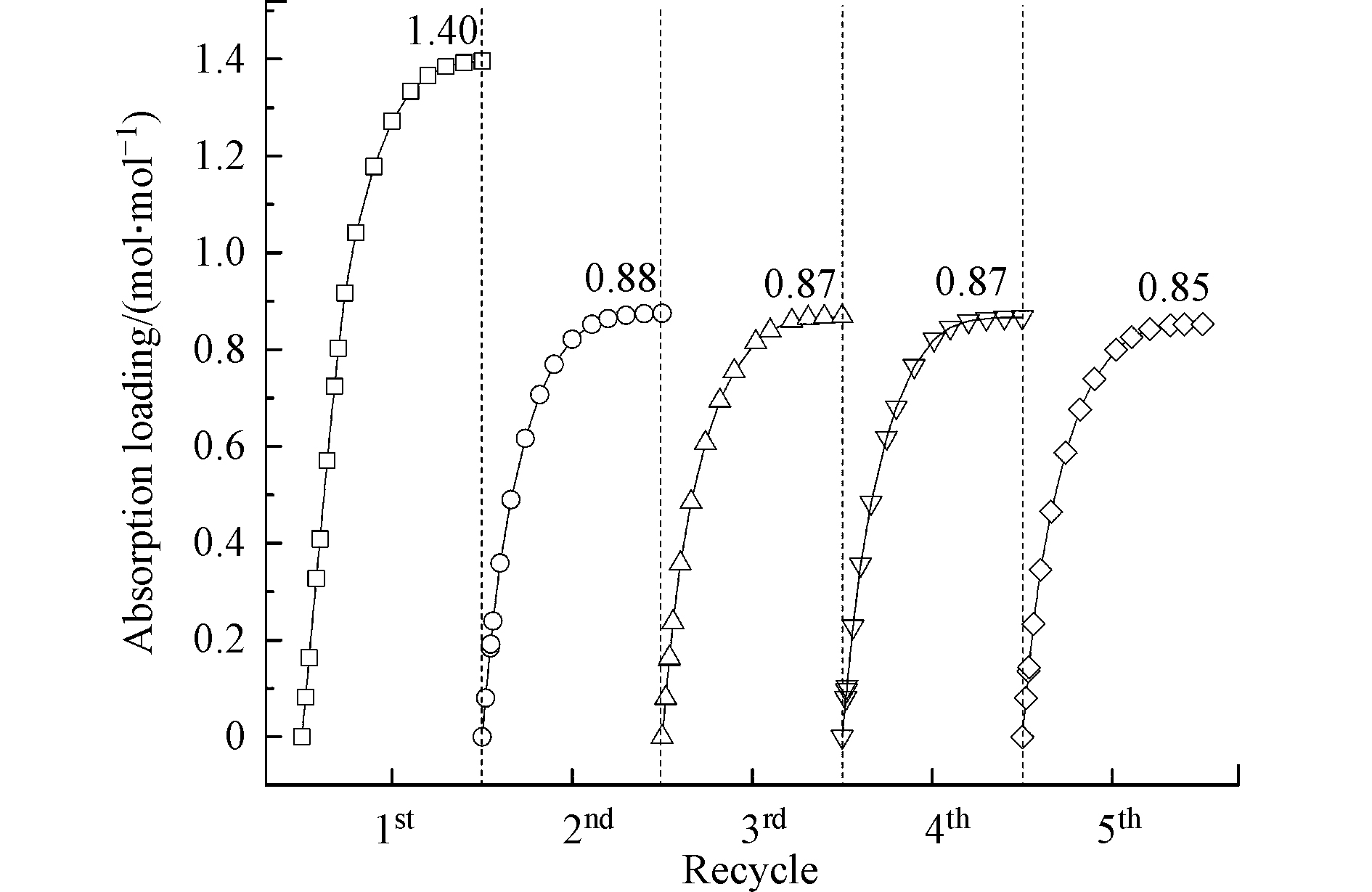
循环吸收-解吸性能可用于评估吸收剂在CO2捕集过程中的长期使用稳定性。研究考察了AEEA/DMSO吸收剂5次吸收-解吸循环性能,每次吸收时间为50 min,解吸时间为30 min。如图6所示,相比于第一次吸收,AEEA/DMSO第二次吸收CO2的负荷发生了较为明显的下降,由1.40 mol·mol−1降至0.88 mol·mol−1。这可能是由于AEEA/DMSO与CO2反应生成的伯氨基甲酸盐在解吸过程中难以分解,导致吸收剂的活性组分浓度降低,从而影响后续的CO2吸收。但从第二次吸收开始,随着循环次数的增加,吸收负荷仅呈现轻微的降低。经历5次吸收-解吸循环,AEEA/DMSO的CO2负荷仍可保持在0.85 mol·mol−1以上。此外,经测定,AEEA/DMSO吸收剂在5次循环后,溶剂损失不超过总质量的5%。以上结果说明AEEA/DMSO具有良好的吸收-解吸循环稳定性。
-
由上述实验结果可知,AEEA/DMSO的CO2吸收负荷明显高于AEEA/H2O,这意味着AEEA在DMSO中与其在水中同CO2的反应存在差异。为厘清AEEA/DMSO吸收CO2的反应机理,研究利用13C NMR表征手段分析了AEEA/DMSO与CO2反应的产物情况。作为对比,同时也对AEEA/H2O吸收CO2的产物情况进行考察。如图7所示,AEEA/H2O吸收CO2饱和后,在其核磁谱图中的化学位移164.3、163.9和160.3位置检测到了碳信号峰,这些峰分别对应的是氨基甲酸盐和碳酸氢盐/碳酸盐中的羰基碳信号[13,17]。
然而,AEEA/DMSO吸收CO2后,其核磁谱图与AEEA/H2O存在明显不同,碳信号峰出现在化学位移162.6、161.5、161.0和159.9。162.6和159.9处的碳信号峰可对应氨基甲酸盐和氨基甲酸中的羰基碳信号,而161.5和161.0处产生的信号峰是由氨基甲酸盐和氨基甲酸产物间发生快速的质子交换所致[18]。
-
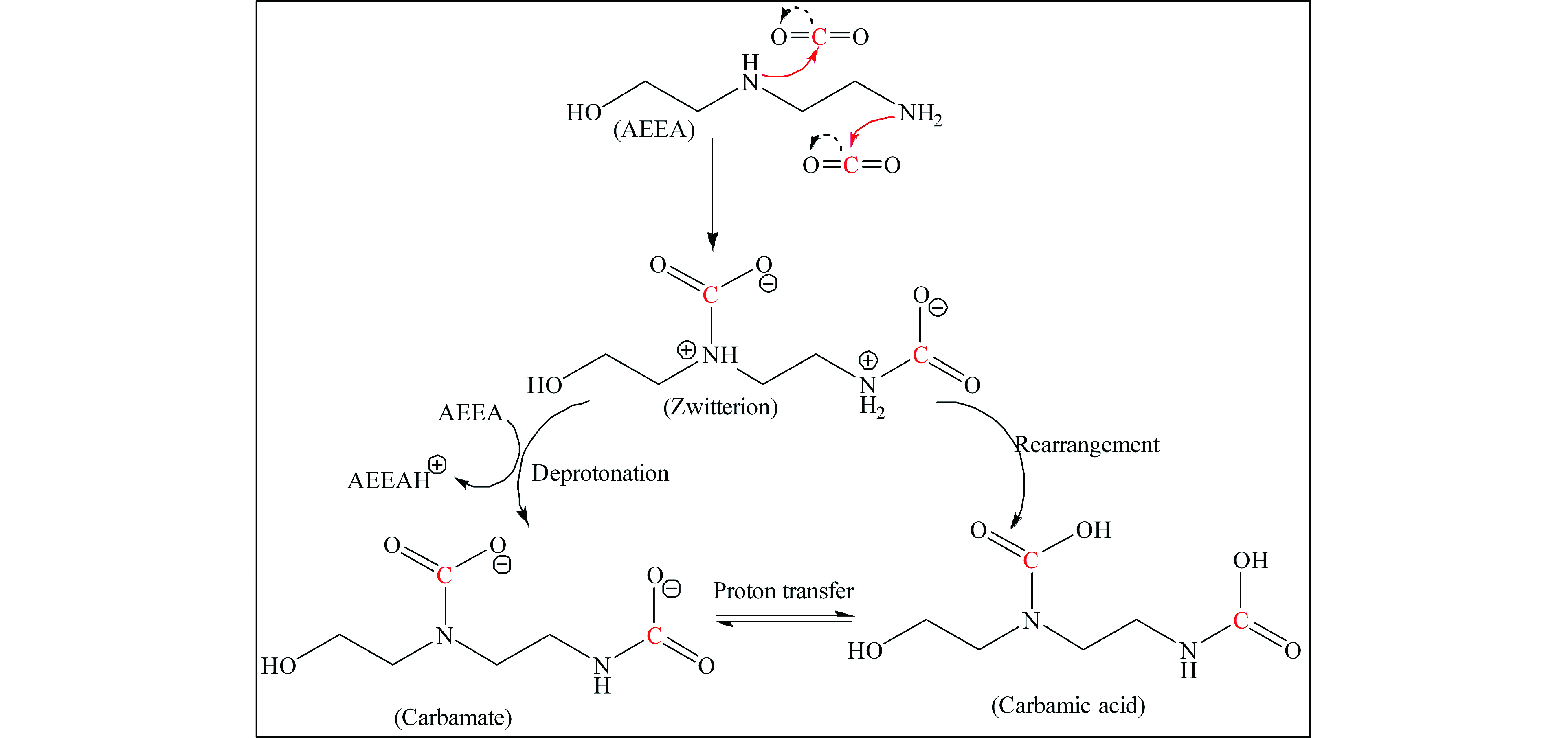
基于核磁结果,即可分析出AEEA/DMSO吸收CO2的反应机理。当往AEEA/DMSO中通入CO2,AEEA首先与CO2反应生成两性离子中间产物,遵循两性离子机理(RNH2代表AEEA)[18]:
生成的两性离子是不稳定的物质,在另外一个AEEA分子的攻击下很容易被去质子化,从而生成氨基甲酸盐:
此外,在CO2饱和的AEEA/DMSO溶液中检测到了氨基甲酸物质,这可能是两性离子通过分子内质子转移进而发生重排所致:
然而,和两性离子相似,氨基甲酸分子同样具有不稳定性,容易与氨基甲酸盐发生分子间质子转移:
综上所述,AEEA/DMSO吸收CO2首先生成不稳定的两性离子,其中一部分两性离子被AEEA分子去质子化生成氨基甲酸盐产物,另一部分则发生分子内质子转移形成氨基甲酸物质,而氨基甲酸可与氨基甲酸盐发生分子间的质子转移,如图8所示。值得注意的是,胺分子按照两性离子反应生成氨基甲酸盐时,理论上氨基基团和CO2的比例遵循0.5:1,而生成氨基甲酸时则遵循1:1的比例。AEEA分子有两个氨基基团(1个伯氨基和1个仲氨基),与CO2反应后,氨基全部转化成氨基甲酸根时,理论上AEEA的CO2负荷为1.0 mol·mol−1,氨基全部转化成氨基甲酸时,AEEA的CO2负荷则为2.0 mol·mol−1,而两种产物均生成时,AEEA的CO2负荷介于1.0 mol·mol−1至2.0 mol·mol−1之间。研究表明,AEEA的CO2负荷为1.40 mol·mol−1,这意味着其与CO2反应同时生成了氨基甲酸盐和氨基甲酸两种产物,这符合13C NMR的检测结果。
2.1. CO2吸收性能
2.1.1. 不同吸收剂的CO2吸收性能对比
2.1.2. 不同温度对AEEA/DMSO吸收CO2的影响
2.2. CO2解吸性能
2.2.1. 不同吸收剂的CO2解吸性能对比
2.2.2. 不同温度对AEEA/DMSO解吸CO2的影响
2.2.3. AEEA/DMSO的循环吸收-解吸性能
2.3. AEEA/DMSO吸收CO2反应机理分析
2.3.1. 13C NMR分析
2.3.2. 反应机理
-
本文以AEEA为吸收活性组分,DMSO为溶剂,构建了AEEA/DMSO无水吸收剂用于CO2捕集。吸收性能实验结果表明,AEEA/DMSO的吸收负荷可达1.40 mol·mol−1,远优于AEEA/H2O和MEA/H2O溶液,且其在40—60 ℃温度范围内对CO2有稳定的吸收能力。解吸性能测试表明,AEEA/DMSO的解吸负荷可达0.91 mol·mol−1,分别是AEEA/H2O和MEA/H2O解吸负荷的1.86倍和3.25倍。另外,AEEA/DMSO具有良好的重复使用性能,经过5次吸收-解吸循环,吸收负荷仍能保持在0.85 mol·mol−1以上。13C NMR结果表明,与AEEA/H2O体系不同,AEEA/DMSO吸收CO2后生成的产物为氨基甲酸盐和氨基甲酸,两种反应产物分子间可发生质子交换。



 下载:
下载: