-
土壤重金属污染是人类面临的重要环境问题之一,已影响到农产品质量安全和农田生态系统健康[1],进而危害到人类健康。所以,土壤重金属污染评价、源解析及治理的研究越来越多。研究者采用单因子污染指数法[2]、内梅罗综合污染指数法[3]、潜在生态风险指数法[4]以及2018年制定的针对农用地和企业用地的污染物风险管控标准[5]对土壤环境质量进行评估,受重金属污染的风险水平评判不再局限于简单的含量特征描述,而是从某种重金属元素污染研究过渡到重金属复合污染研究,尤其在近年土壤污染风险评价中,更强调了不同重金属元素的毒性[6]、研究地的土壤重金属背景值与实测值,使得土壤重金属污染等级评价更趋科学,为受重金属污染土壤的防控及治理提供了科学依据。
在探究土壤重金属污染特征及其影响因素时,研究者发现土壤重金属来源主要受工业[7]、农业[8]及其成土母质[9]等诸多因素影响。段淑辉等[10]利用UNIMX模型对农田重金属污染源解析发现,土壤表层Zn、Cu均主要来源于施肥和灌溉等农业活动。沈洪艳等[11]对湖南某典型流域农用地土壤重金属的污染源解析显示,流域农田土壤中Cd、As、Pb污染受工业生产活动、交通运输、农业活动的综合影响,Hg、Cr主要来源于成土母质等自然因素。大多数研究针对特定区域土壤重金属污染评价及来源解析,比如采矿区[12-13]、某流域[14-15]、重点污染企业[16]、农产品产地[17]、公园[18]等周边土壤重金属污染评价及来源探究。然而在不同的环境体系中不同重金属元素含量会受到多种因素的影响[19],进而导致不同区域重金属污染具有一定差异性,其中农田土壤重金属污染差异尤为明显[20-22]。因此研究金属采选与冶炼企业周边农田土壤重金属污染特征及来源解析对了解土壤重金属富集规律和防治重金属污染有重要意义。
本研究以湖南30家典型有色金属采选与冶炼企业周边表层土壤为研究对象,采用单因子污染指数法、内梅罗综合污染指数法及《农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》(GB15618-2018)评价重金属污染程度,应用潜在生态风险指数法评价重金属的潜在生态风险,利用主成分分析法与相关性法对污染区重金属来源进行解析。以期为湖南典型有色金属采选与冶炼企业周边土壤重金属污染控制及其治理提供科学依据。
全文HTML
-
选取湖南省30家典型金属采选与冶炼企业周边土壤为研究对象,依据企业废气、废水排放特征与废渣堆积区所在位置,并结合企业周围土地利用现状,在每个企业所在地年主导风向下风口和企业废水排放下游布设土壤采集点(表1)。
每个土壤样品采集点位区域为30 m×30 m(长×宽),采用5点蛇形采样法采集5个点的表层0—20 cm土壤样品混合均匀,保留2 kg,为1个污染监测点土壤样品,共采集污染点土壤样品112个,其中耕地72个(旱地54个、水田18个)、荒草地21个、林地19个。在距离工厂周边 2000 m以外主导上风向布设25个对照点,对照点与监测点土地利用类型、土壤类型尽量一致。其中耕地19个(旱地13个、水田6个)、荒草地1个、林地5个。
-
土壤样品带回实验室后采用自然风干、粗磨和分样、细磨和分样、过粒径0.15 mm(100目)筛处理。土壤样品pH测定采用《土壤元素近代分析测试方法》(NY/T 1121.2-2006);镉采用原子吸收分光光度法(GB/T 17141-1997),汞采用微波消解/原子荧光法(HJ 680-2013),砷、铅、铬、铜、锌、镍采用波长色散X射线荧光光谱法(HJ 780-2015)。以不少于10%的比例实施精密度和准确度控制,覆盖全部监测项目,重金属项目和pH项目实验室内部平行样的总合格率均为100%,带标的总合格率均为100%。质控平行样理化3项合格率75.2%、常规8项重金属合格率96.3%、重金属项目带标的总合格率均为100%。质量控制样品的测试结果准确性满足《土壤环境监测质量监督检查技术规定》中合格率不低于85%的要求,实验室内测试结果的精密度和准确度满足该规定中合格率达到100%的要求。
-
内梅罗污染指数评价法为常用的土壤污染评价法,考虑了不同重金属元素含量对土壤环境的影响,突出了污染最严重重金属的污染危害,比较全面、客观地反映土壤的污染状况[23]。
单因子污染指数和内梅罗污染指数计算方法见公式(1)和公式(2)。评价污染等级见表2。
式中,
$ {P}_{i} $ 为土壤中重金属i的单项污染指数,$ {C}_{i} $ 为土壤中重金属i的含量,$ {S}_{i} $ 为土壤中重金属i含量的评价标准[24]。$ {P}_{{\rm{ave}}} $ 为单因子指数的平均值,$ {P}_{{\rm{max}}} $ 为单因子污染指数中的最大值,$ {P}_{{\rm{N}}} $ 为土壤中重金属的内梅罗污染指数。 -
Hakanson潜在生态风险指数法[25]综合考虑了重金属性质、环境行为特点、含量水平、生物毒性、生态效应等因素,可用于评价土壤和沉积物中重金属的潜在生态风险,其计算方法见公式(3)—(5),Hakanson生态风险指数分级见表3。
式中,
$ {C}_{d}^{i} $ 为样品实测浓度,mg.kg−1,$ {C}_{r}^{i} $ 为土壤中i元素的背景值,为湖南省重金属背景值(Cd、Hg、As、Cu、Pb、Cr、Zn、Ni背景值分别为0.142、0.09、12.8、25.0、30、58.3、84.2、27.8 mg.kg−1)[26],$ {T}_{r}^{i} $ 为第i种重金属元素的毒性响应系数,$ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 为第i种重金属元素潜在生态风险系数,$ {C}_{f}^{i} $ 为第i种重金属元素的污染系数,$ \mathrm{R}\mathrm{I} $ 为多种重金属污染物潜在生态风险指数。毒性影响因子采用Hakanson制定的标准化重金属响应系数为评价依据(Cd为30、Hg为40、As为10、Pb为5、Cr为2、Cu为5、Ni为5、Zn为1)[27]。 -
采用《土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB 15618—2018)(见表4)对污染区农用地土壤样品进行风险管控评价[28]。当样品中8种重金属元素含量全部小于或等于风险筛选值时,土壤属于优先保护类(用A表示),土壤风险可以忽略;当土壤中Cd、Hg、As、Pb、Cr的任意一种含量高于风险筛选值并且小于等于风险管制值时,土壤存在污染风险,但属于安全利用类(用B表示);当土壤中Cd、Hg、As、Pb、Cr的任意一种含量大于风险管制值时,土壤污染风险高,属于严格管控类(用C表示)[29]。
-
采用Excel对重金属含量数据进行统计分析;相关性分析和主成分分析由SPSS 20.0完成。
1.1. 土壤样品采集
1.2. 样品测定与质量控制
1.3. 评价方法
1.3.1. 内梅罗综合污染指数法
1.3.2. 潜在生态风险指数法
1.3.3. 农用地土壤污染风险管控评价
1.4. 数据处理与分析
-
企业周边污染监测点所有土壤样品中Cd、Hg、As、Pb、Cr、Cu、Ni、Zn的含量见表5。从表5可知,金属采选与冶炼企业周边112个污染监测点样品中Cd、Hg、As、Cu、Pb、Cr、Zn、Ni均值分别为3.221、0.985、65.6、67.4、165.5、94、329、43.9 mg·kg−1,与湖南省土壤背景值[26]对比发现,监测点样品中8种元素均值都超过背景值,分别为对应重金属元素背景值的22.7、11、5.1、2.7、5.5、1.6、3.9、1.6倍;对照点样品中Cd、Hg、As、Cu、Pb、Cr、Zn、Ni均值分别为背景值的11.3、2.9、2.7、1.4、2.77、1.4、2.5、1.1倍,间接说明了金属采选与冶炼企业生产活动对周边表层土壤形成为Cd、Hg、As、Zn、Pb的污染。从变异系数看,污染监测点样品中Cd、Hg、As、Cu、Pb、Zn、Ni均属于强变异,Cr为中等变异。25个对照点土壤样品中Cd、As、Pb、Zn均属于强变异,Hg、Cu、Cr、Ni属于中等变异。从表5还可知,除Cr、Ni外,污染监测点样品中Cd、Hg、Cu、Pb、Zn均值都明显高于对照点,说明金属采选与冶炼企业生产活动对周边土壤形成了Cd、Hg、Cu、Pb、Zn的污染。从各用地类型样品中Cd、Hg、As、Cu、Pb、Cr、Zn、Ni含量看,不同用地类型土壤中Cd、Hg、As等均存在一定差异性。
-
不同用地现状土壤重金属单因子污染指数(
$ {P}_{i} $ )评价结果见表6。从表6可知,旱地土壤样品重金属元素$ {P}_{i} $ 均值大小依次为Cd>As>Pb>Zn>Cu>Ni>Cr>Hg,Cd的$ {P}_{i} $ 均值达到重度污染,As处于中度污染,Pb和Zn为轻度污染,Hg、Cu、Cr、Ni为无污染;水田样品重金属元素$ {P}_{i} $ 均值大小依次为Cd>Hg>Pb>As>Zn>Ni>Cu>Cr,Cd的$ {P}_{i} $ 均值达到重度污染,Hg处于中度污染,As、Pb、Zn为轻度污染,Cr、Cu、Ni为无污染;在荒草地样品中重金属元素$ {P}_{i} $ 均值大小依次为Cd>Zn>As>Pb>Cu>Cr>Ni>Hg,Cd的$ {P}_{i} $ 均值达到重度污染,Zn处于中度污染,As和Pb为轻度污染,Hg、Ni、Cu、Cr均为无污染;在林地样品中重金属元素$ {P}_{i} $ 均值大小顺序与旱地一致,Cd的$ {P}_{i} $ 均值达到重度污染,As为轻度污染,其余6种重金属元素均为无污染。综上可知,污染区所有土壤样品均受到Cd污染,应引起政府和企业的高度关注与重视。 -
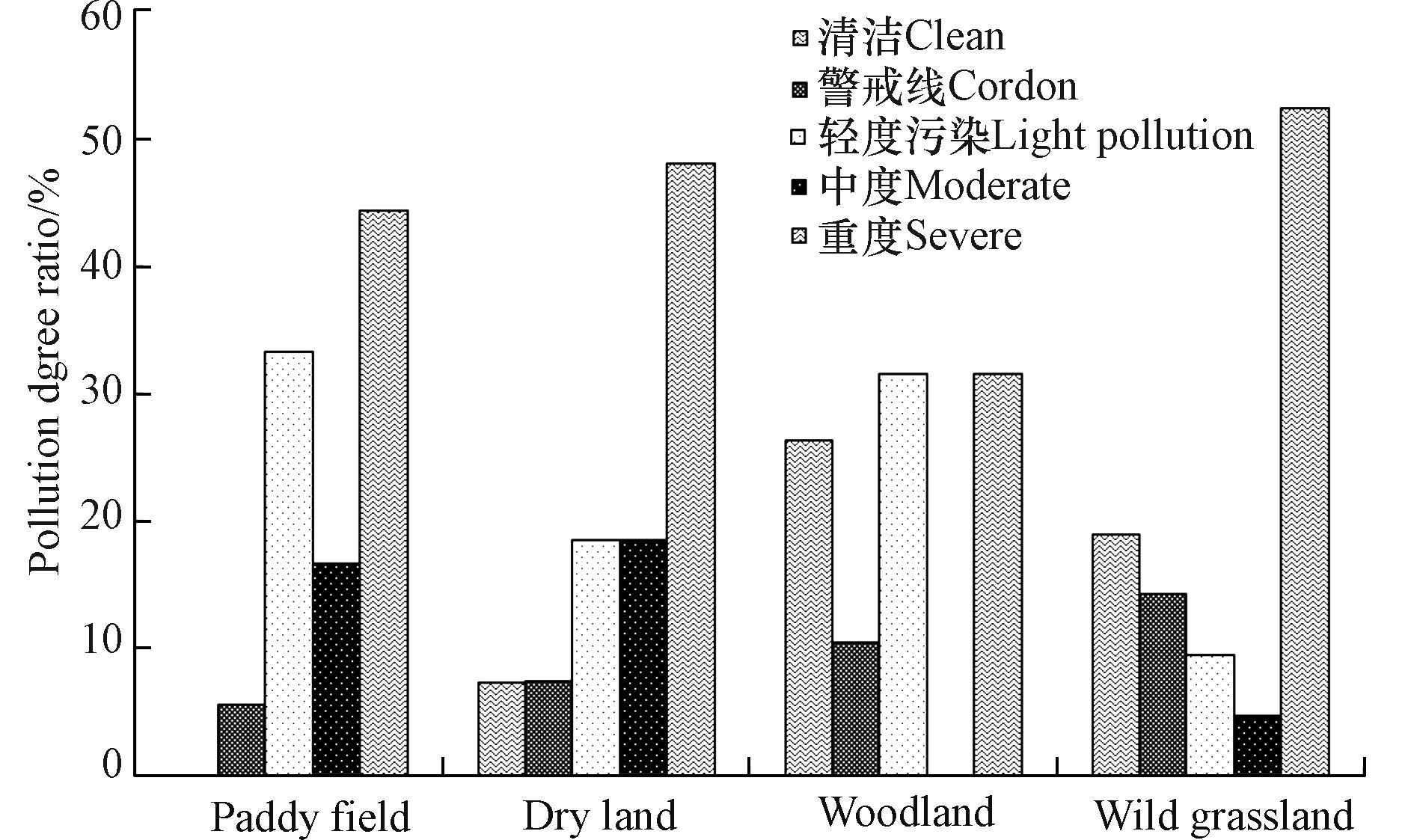
污染区土壤重金属内梅罗综合污染指数评价结果见图1。从图1可知,水田样品中重金属内梅罗综合污染指数处于清洁、警戒限、轻度污染、中度污染、重度污染等级的点位比例分别为0、5.6%、33.3%、16.7%、44.4%;旱地为7.4%、7.5%、18.5%、18.5%、48.1%;荒草地为19%、14.3%、9.5%、4.8%、52.4%;林地为26.3%、10.5%、31.6%、0、31.6%。在各用地类型样品中,60.1%的水田样品受到重金属中度及以上污染,主要为Cd、Hg污染;66.6%的旱地样品受到重金属中度及以上污染,主要为Cd、As污染;荒草地和林地分别有67.2%、31.6%的样品受到重金属中度及以上污染,其中荒草地主要受Cd、Zn污染,而林地受Cd污染。
-
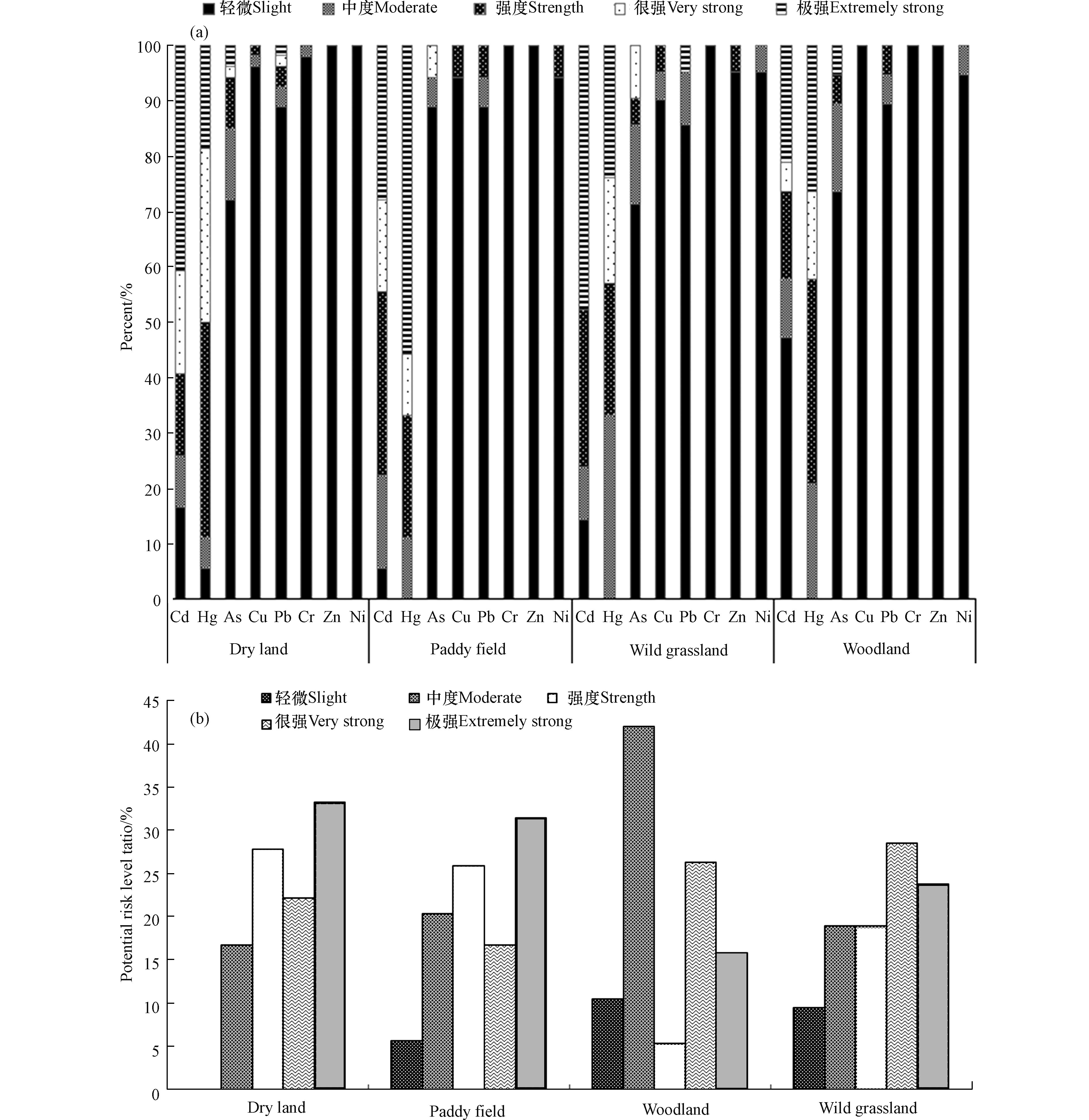
污染区各用地现状样品潜在生态风险指数结果见图2。从图2可知,Cd和Hg在旱地、水田、荒草地、林地土壤中处于强风险及以上危害水平点位的占比均较高,其余6种重金属主要处于轻微危害水平;旱地样品综合潜在生态风险处于轻微、中度、强度、很强、极强等级点位的比例分别为0、16.7%、27.8%、22.2%、33.3%;水田样品处于轻微、中度、强度、很强、极强等级点位的比例分别为5.6%、20.4%、25.9%、16.6%、31.5%;林地样品处于轻微、中度、强度、很强、极强等级点位的比例分别为10.5%、42.1%、5.3%、26.3%、15.8%;荒草地样品处于轻微、中度、强度、很强、极强等级点位的比例分别为9.6%、19%、19%、28.6%、23.8%。综上可知,污染区各用地类型样品综合潜在生态风险处于很强及以上等级所占比例的大小顺序依次为旱地>荒草地>水田>林地。
-
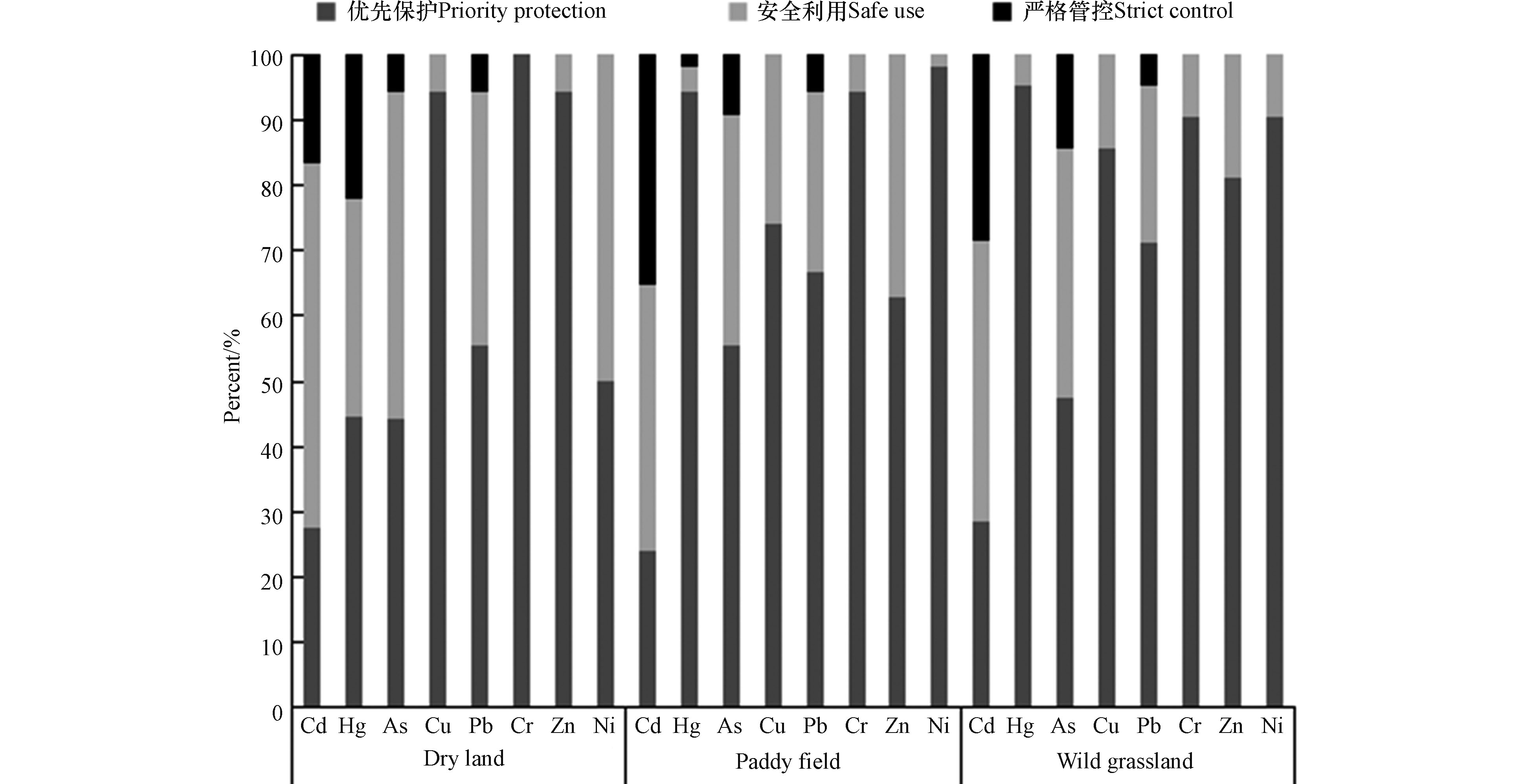
污染区旱地、水田及荒草地重金属含量风险管控标准[28]评价结果见图3。从图3可知,在54个旱地样品中,Cd、Hg、As、Cu、Pb、Cr、Zn、Ni含量超筛选值的样品比例分别为40.7%、3.7%、35.2%、25.9%、27.8%、5.6%、37%、1.9%;Cd、Hg、As、Pb含量超管制值样品比例分别35.2%、1.9%、9.3%、5.6%;A、B、C类比例分别为9.2%、35.2%、55.6%。在18个水田样品中,Cd、Hg、As、Pb、Cu、Zn、Ni含量超筛选值的样品比例分别为55.6%、33.3%、50%、38.9%、5.6%、50%、11.1%;Cd、Hg、As、Pb含量超管制值样品的比例分别为16.7%、22.2%、5.6%、5.6%;Cr含量未超筛选值;A、B、C类比例分别为0、44.4%、55.6%。在21个荒草地样品中,Cd、As、Pb、Hg、Cr、Cu、Zn、Ni含量超筛选值样品比例分别为42.9%、38.1%、23.85%、4.8%、9.5%、14.3%、19%、9.5%;Cd、As、Pb含量超管制值样品的比例分别为28.6%、14.3%、4.8%;A、B、C类比例分别为23.8%、38.1%、38.1%。综上可知,93个农用地样品中,Cd含量超筛选值和管制值样品的比例分别为44.1%、30.1%,Hg分别为9.7%、5.4%,As分别为38.7%、9.7%,Pb分别为29%、5.4%;Cr、Cu、Zn、Ni含量超筛选值样品的比例分别5.4%、19.4%、35.5%、5.4%。所有样品中,A、B、C类比例分别为10.8%、50.5%、38.7%,其中C类样品比例大小顺序依次为:水田=旱地>荒草地。
新邵云翔矿业、湖南柿竹园有色金属、湖南三立集团、湖南博隆矿业、保靖县锌业、郴州云湘矿冶、宝山有色金属矿业、湖南鑫海锌品8家企业周边监测点土壤样品重金属评价结果均属于C类;五矿湖南铁合金、衡阳市远景钨业2家企业周边监测点土壤样品重金属评价结果均属于B类;湖南辰州矿业(沅陵)和桃江县久通锑业2家企业周边监测点位均为A类;湖南安化渣滓溪矿业、花垣民乐锰矿区、溆浦江龙锰业、永州福嘉有色金属4家企业B、C类样点比例为2:1;湖南安圣电池、湖南证大予捷矿业、临湘湘岳矿业、邵阳市鼎盛矿业4家企业B、C类样点比例为1:2;湖南金石矿业(沅陵)和湖南金旺铋业2家企业B、C类样点各占一半;湖南水口山有色金属(柏坊铜矿)B、C类样点比例为1:3;冷水江锡矿山采矿区A、B、C类样点比例为1:4:5;湘潭锰矿红旗矿区A、B、C类样点比例为1:3:2;新邵县辰州锑业A类、B类、C类样点比例为1:1:2;湖南省星月颜料A、B、C类样点比例为1:1:1。综上所述,80%企业周边土壤重金属污染风险属于严格管控类。
-
研究重金属之间的相关性可以推测重金属的来源是否相同。若它们之间存在相关性,则它们的来源可能相同,否则来源可能不同[30]。污染区土壤重金属含量Pearson相关性分析结果见表7。由表7可知,Cu与Cd、As、Pb、Zn均存在极显著相关关系,因此推断Cu与Cd、As、Pb、Zn具有较大的同源性。Ni与Zn存在极显著关系,说明他们可能有相同来源。Cr和Hg与各元素之间无较显著的相关性,可以推断与其他重金属元素来源途径不同。
-
主成分分析可以将多个指标转化为几个综合指标来反映原始数据的信息,在土壤研究中用来区分各重金属来源。通过KMO检验(KMO值为0.607)和Bartlett球形检验P=0.000说明变量可以为因子分析提供合理基础。由表8可知,污染区前3个主成分反映61.540%的贡献率,因此对前3个主成分进行分析。由表9可知,第一主成分Cd、As、Cu、Pb、Zn具有较高的载荷,分别为0.609、0.706、0.701、0.786、0.577;第二主成分Cr的载荷为0.839;第三主成分主要反映了Hg和Ni的富集信息,载荷分别为0.747和0.651。
-
由主成分分析可知,该结果与相关性分析具有较好的一致性。第一主成分的贡献率为33.516%,其中Cd、As、Cu、Pb、Zn具有较高的载荷,且这5种重金属含量都严重超标,主成分1反映以上5种重金属的作用。由于污染区处于铅锌、铁、金矿等采选业企业周边,土壤易受到企业废气、堆放的固体废物中Cd、Cu、As、Pb、Zn等重金属污染[31]。而且在化合物生产及合金加工过程中会有Cd、As、Cu、Pb、Zn等金属配合物和催化剂的使用,这些也是导致污染区重金属富集的原因。在冶炼金属的过程中会有预脱砷处理过程,这个过程必然导致As元素进入土壤,使As元素超标。张晓文等[32]研究指出,湖南省土壤中Cd、Zn、Pb主要来源于冶炼和尾矿废水排放,车辆尾气也会导致Pb的富集。在交通运输方面,Pb常被作为机动车污染源的指示性元素[33]。研究区周边有水稻、玉米、蔬菜等农作物的种植,农药和化肥中含有的Cu、As等元素会在土壤中残留,仅就磷肥而言,As的含量一般在20—50 mg·kg−1,其不合理施用会使土壤中As含量升高[34]。化肥、农药的使用会导致污染区耕地As、Cu的大量积累。根据以上分析可以推断主成分1为工业、交通和农业的混合源。
第二主成分的贡献率为15.161%,Cr是主要的贡献因子。本研究中Cr与其他元素的相关性均不显著,变异系数为中等变异,说明受人为干扰程度比其他几种重金属低。同时,Cr的平均值也略高于湖南省背景值。大多数Cr的含量与自然背景接近,Cr可能受成土母质的控制[35]。徐源等[36]经过研究也确定了湖南Cr主要来自于土壤母质源。因此推断主成分2为土壤母质源。
第三主成分的贡献率为12.864%,主要贡献来源于Hg和Ni。大多数研究认为土壤中Ni的人为污染源贡献较小,主要受母质的控制,但是也有学者提出Ni除受自然来源外,人为活动输入对Ni的含量也有一定影响[37]。综合2种统计方法可以得出Zn和Ni相关性极显著,具有同源性,因此推断Ni受到工业活动影响。陈雅丽等[38]通过近十年我国土壤源解析统计结果得知,Hg主要来源于工业活动及其产生的大气沉降。煤炭的燃烧对Hg元素的积累作用非常明显,研究区内存在大量的冶炼厂,煤炭作为冶炼的燃料之一,会不可避免的进入研究区内[39]。因此,推断主成分3为工业源。
2.1. 土壤样品中重金属含量特征
2.2. 土壤重金属污染状况
2.2.1. 污染区土壤重金属单因子污染指数评价
2.2.2. 污染区土壤重金属内梅罗综合污染指数评价
2.2.3. 污染区土壤重金属潜在生态风险指数评价
2.2.4. 污染区农用地表层土壤重金属风险管控评价
2.3. 污染区土壤重金属来源解析
2.3.1. 土壤重金属的相关性分析
2.3.2. 土壤重金属元素的主成分分析
2.3.3. 土壤重金属来源解析
-
(1)湖南省采选与冶炼企业已对周边土壤重金属呈现出一定的富集,其中土壤中Cd、As、Pb污染严重。不同土地利用类型重金属含量存在差异,As在旱地中含量较高,Cu、Hg、Ni在水田中含量较高,Cd、Pb、Zn、Cr在荒草地中含量较高。
(2)Cd在污染区土壤处于重度污染水平,达到了极强的生态危害。林地土壤重金属含量在一定程度上低于其他土地利用类型,受到污染最小。在农用地土壤中,水田样品重金属含量超筛选值和管制值的样品比例达100%。
(3)综合相关性分析和主成分分析,推断Cd、As、Cu、Pb、Zn为农业、工业和交通的混合源,Cr主要来自于自然源,Ni受到工业活动影响,Hg主要来源于大气沉降。
(4)湖南典型金属冶炼与采选行业企业已对其周边土壤形成了Cd、Hg、As、Pb、Zn的污染,应加强湖南金属冶炼与采选行业企业外排Cd、Hg、As、Pb、Zn的污染控制,并治理企业周边土壤重金属污染。



 下载:
下载: