-
碳、氮、磷等营养元素是生物系统中最重要的基础生命元素,是构成生态系统初级生产力和物质循环的重要载体[1]。水域生态系统中氮、磷营养盐的分布、变化特征对水生生物的生长、群落演替等有决定性作用[2]。水生态系统中的氮、磷营养盐变化是由生物和非生物因素共同作用影响[3]。网箱养殖是一种集约化、高密度的投饵型养殖方式[4]。鱼类养殖过程中投饵、吸收、排泄和同化,浮游生物和水生植物的吸收和利用以及细菌等微生物的分解等是养殖水域生态系统中氮、磷等营养元素物质循环和能量流动的主要方式[5-6]。因此了解网箱养殖过程中的氮、磷营养元素的分布形式、变化规律等时空演替特征对新时代环保压力下水产养殖业的健康可持续发展有重要指导意义。
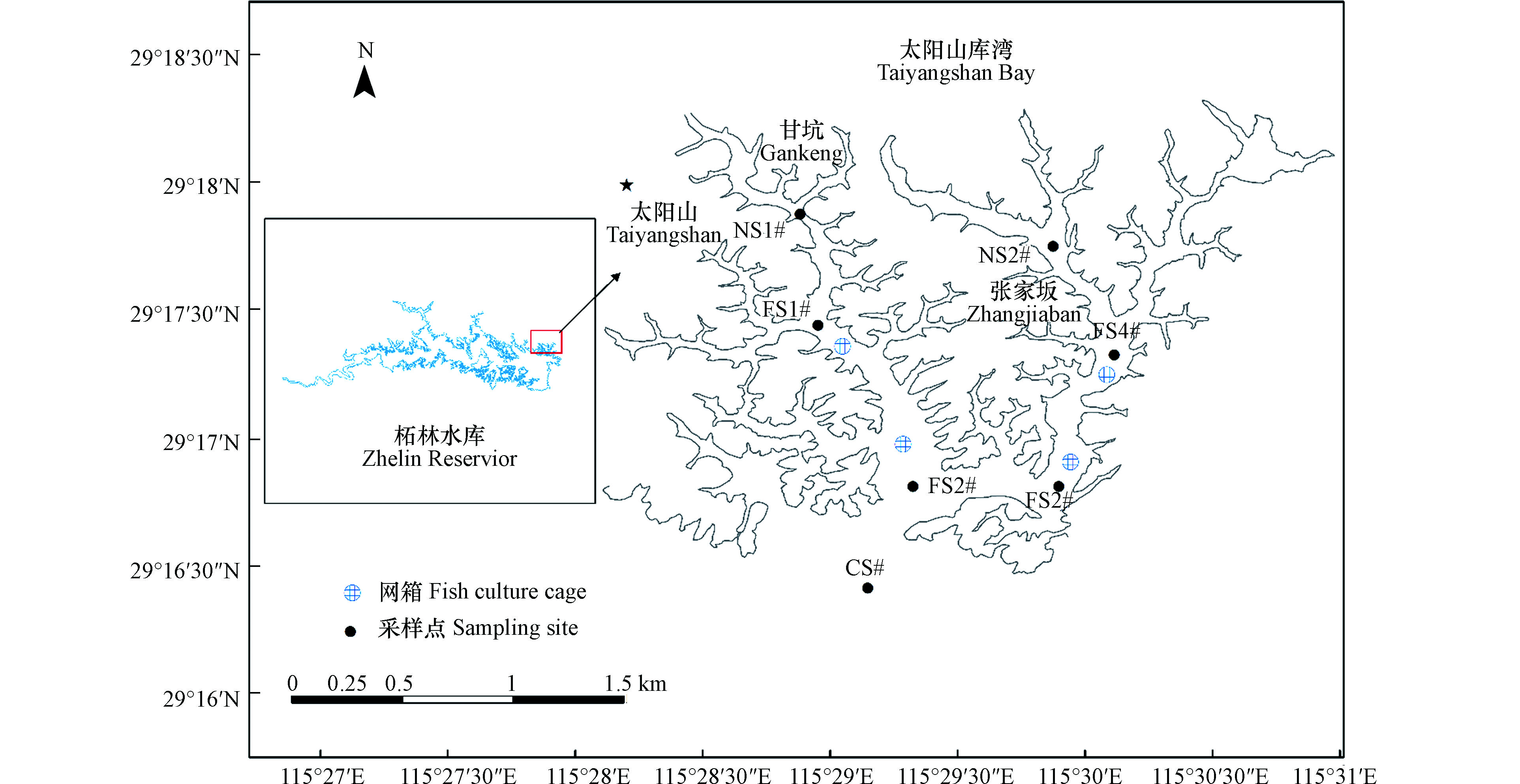
柘林水库位于长江中游鄱阳湖流域,是江西省最大的人工湖,通过人工拦截鄱阳湖五大支流之一“修河”形成。流域内有大小支流600余条,坝址以上汇水区域面积9340 m2,湖区水域面积308 km2,总库容79.2×108 m3。柘林水库太阳山库湾位于九江市永修县三溪桥镇黄岭村(E: 115°28′—115°31′, N:29°16′—29°18′),库湾水域总面积约265.33 hm2。目前库湾内有网箱3.1×103个,规格为5 m×5 m,网箱养殖总面积约为7.96 hm2,主要养殖对象有加州鲈(Micropterus salmoides)、长吻鮠(Leiocassis longirostris)、匙吻鲟(Polyodon spathula)、大鳞鲃(Luciobarbus capito)等特色淡水鱼,2018—2019年成鱼年产量在9.0×104—1.1×104 kg。
本研究通过监测养殖期间太阳山库湾水体中的水质理化因子含量变化,分析了网箱养殖对其水环境的影响,并以单因子、综合营养状态指数法和潜在性营养法对水环境质量进行健康评价,重点分析和探讨了网箱养殖对氮、磷营养盐的时空变化的影响,为养殖水域污染物控制和新型生态网箱系统研发等技术提供科学依据。
-
根据柘林水库太阳山库湾网箱养殖渔排的数量和分布,将研究区域分为3个不同的采样区域即:近岸区(nearshore area, NS)、养殖区(fish cage area, FS)、和对照区(control area, CS),其中近岸区靠近库区居民生活和农业生产,无网箱养殖活动,设2个采样点(NS1#、NS2#);养殖区为网箱养殖活动集中区域,设4个采样点(FS1#、FS2#、FS3#、FS4#);对照区为远离近岸区和养殖区的水库中心区域,设1个采样点(CS1#),采样点坐标信息如表1所示,网箱分布与采样点布设如图1所示。
-
于2018年10月—2019年7月分季度采样即秋季(2018年10月)、冬季(2019年1月)、春季(2019年4月)和夏季(2019年7月)。水温(WT)、溶解氧(DO)、pH和电导率(conductivity)采用美国哈希HQ40D多参数水质分析仪现场测定,透明度(SD)采用塞式盘现场测定。水样用5 L不锈钢采水器现场采集,取1 L低温保存带回实验室分析。
-
总氮(TN)、氨氮(
${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $ -N)、硝酸盐氮(${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ -N)、亚硝酸盐氮(${\rm{NO}}_2^{-} $ -N)、总磷(TP)、磷酸盐(${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ -P)、高锰酸盐指数(CODMn)等水质指标的测定方法参照金相灿等[7]的方法进行。以水体TN、TP、
${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $ -N和CODMn等4个参数作为水质评价关键因子,参照《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838—2002)对柘林水库太阳山库湾水质进行评价。分别采用综合营养状态指数(TLI)法[7]和潜在性富营养评价法[8]对太阳山库湾水体富营养化状态进行综合评价。 -
运用SPSS 22.0软件进行数据统计和单素方差分析(One-way ANOVA),进行方差齐性检验(Homogeneity of variance test),差异显著性采用多重比较(Multiple comparison)邓肯(Duncan)检验,差异水平设为0.05(P<0.05)。统计数值以“平均值±标准差(
$ \stackrel{-}{X} $ ±SD)”表示,并运用Origin 9.1软件进行科学绘图. -
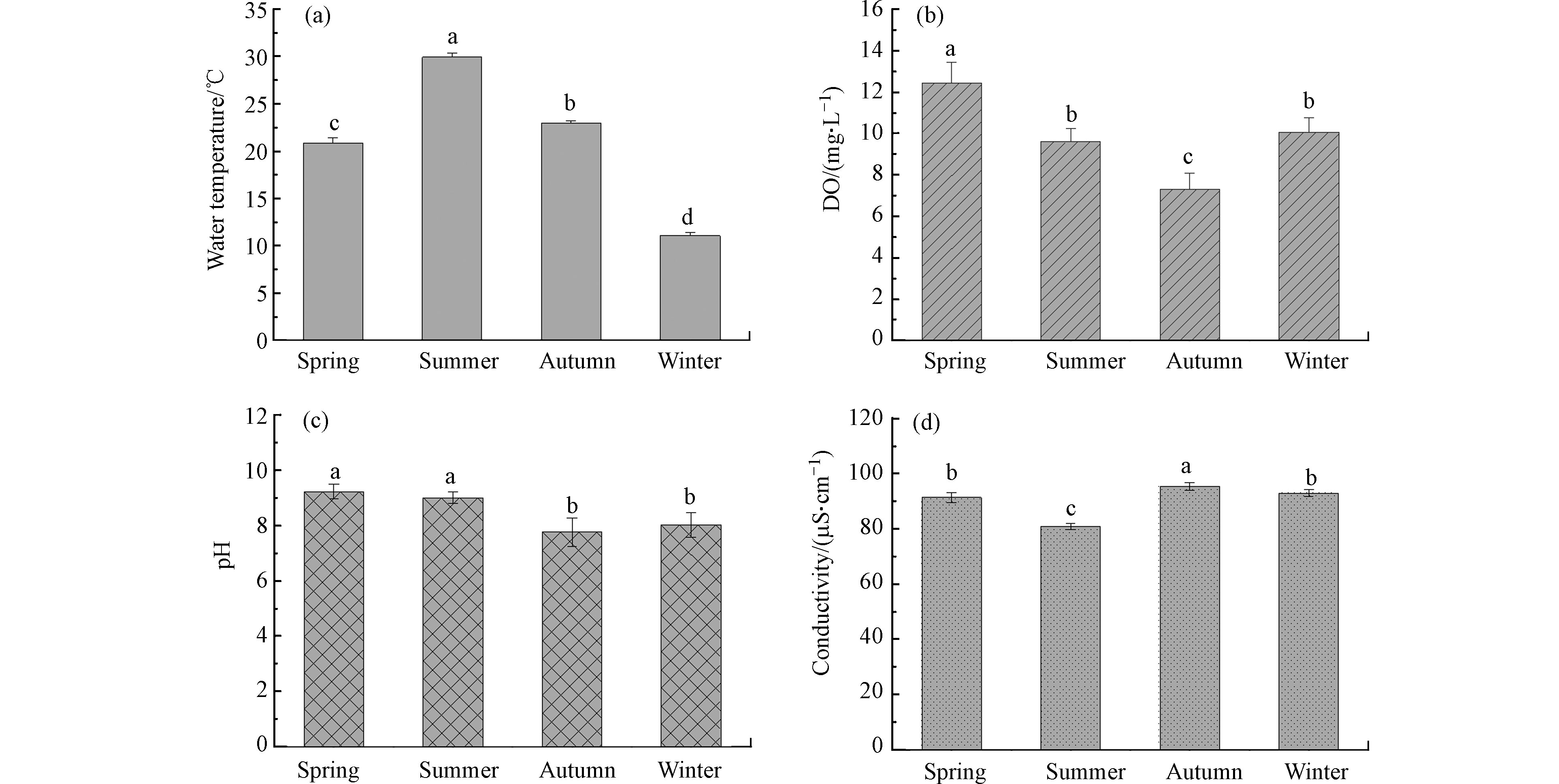
网箱养殖作为一种重要的养殖活动,对养殖水域的理化性质诸如水温、溶解氧、pH和电导率的变化有重要影响[4]。太阳山库湾养殖区、近岸区与对照区间的水温、溶解氧、pH和电导率均无显著性差异(P > 0.05)(表2)。不同季节表层水体的水温、溶解氧、pH和电导率时空变化特征如图2所示。不同季节间水温均具有显著差异(P < 0.05),且夏季的水温显著高于其他季节(P < 0.05),分析认为水温主要受气候变化影响。溶解氧含量的变化与细菌微生物、浮游生物、鱼类等水生生物的呼吸活动紧密相关[9]。溶解氧含量为春季显著高于其他季节,秋季最低并显著低于其他季节(P < 0.05),冬季和夏季差异不显著(P > 0.05)。秋季是太阳山库湾网箱养殖投饵的高峰期,鱼类粪便残饵等有机质大量积累,有机质的分解会大量消耗水体中的溶解氧,这可能是导致秋季太阳山库湾溶解氧含量显著低于其他季节的主要原因,这与Huang等[10]研究结果一致。春与夏季、秋与冬季两两间的pH差异不显著(P > 0.05),但春夏两季显著高于秋、冬两季(P < 0.05)。养殖区与非养殖区的水质理化因子差异不显著(P > 0.05),表明适当的网箱养殖活动对养殖水域水温、pH等影响较小,王毛兰等[11]有关网箱养殖对鄱阳湖都昌水域水环境影响的研究同样表明网箱养殖对湖水的水温、pH影响较小。
-
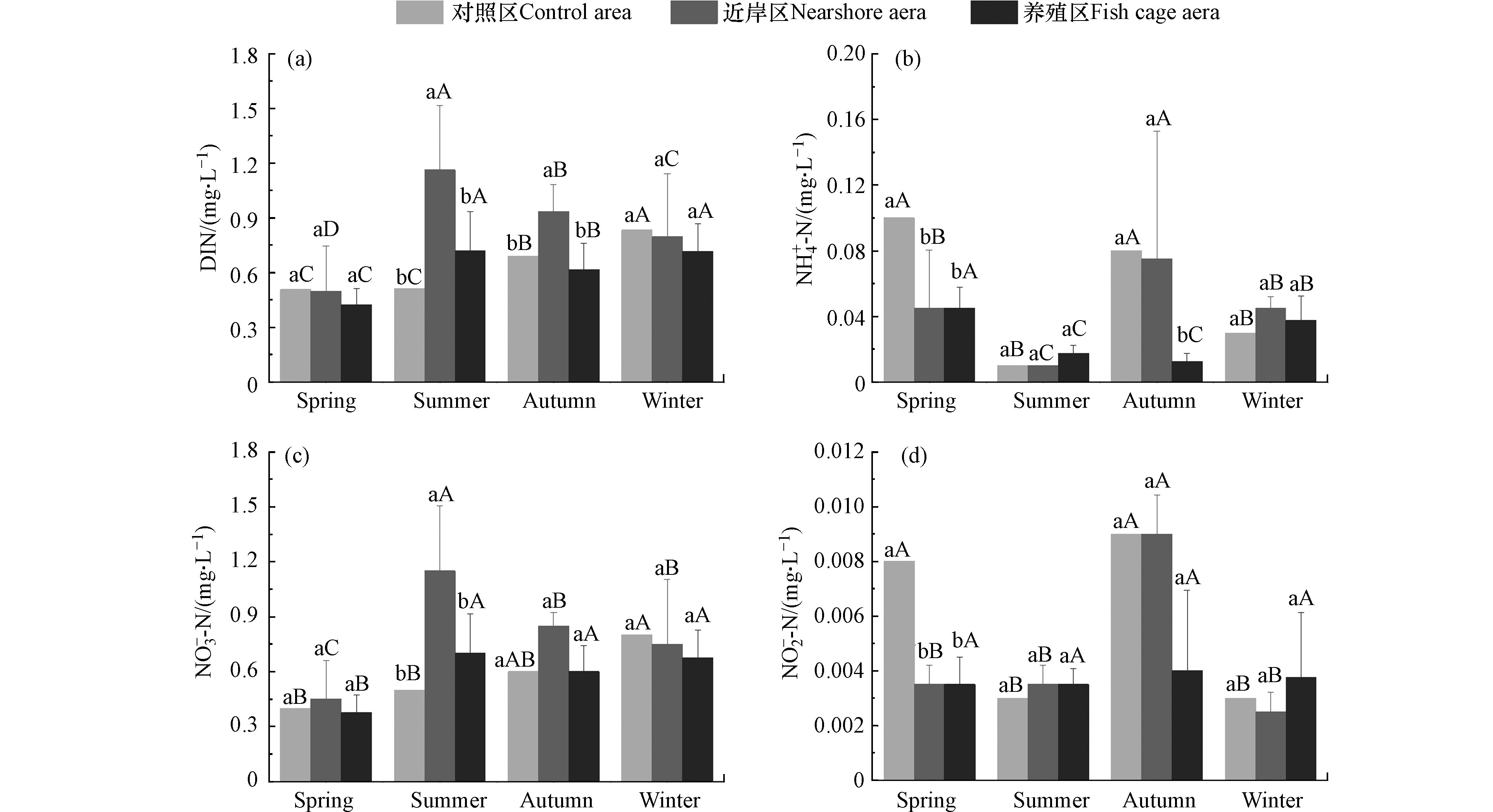
网箱养殖过程的饵料中仅有少部分的氮磷被养殖鱼类吸收利用[12],这会导致在养殖区及其附近水域大量积累粪便、残饵等有机质,并被以细菌为主的微生物进行消化分解为硝酸盐、亚硝酸盐、磷酸盐等,最后再被藻类、浮游生物等同化利用而移除水体[13]。太阳山库湾不同季节的近岸区和养殖区的DIN和
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ -N含量显著高于对照区(P < 0.05),但${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $ -N和${\rm{NO}}_2^{-} $ -N显著低于对照区(P < 0.05);养殖区和近岸区的DIN春季和冬季差异不显著(P > 0.05),近岸区秋季和夏季的DIN含量均显著高于养殖区(P < 0.05)(图3)。养殖区和近岸区的DIN和
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ -N含量显著高于对照区(P < 0.05),${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $ -N和${\rm{NO}}_2^{-} $ -N则显著低于对照区(P < 0.05),表明太阳山库湾水体中氮的时空分布与网箱养殖和人类活动密切相关。曾涛[14]、贾后磊等[15]对樟湖库湾和哑铃湾网箱养殖的研究得到了类似的结果。不同的是太阳山库湾养殖区和近岸区的DIN春季和冬季差异不显著(P > 0.05),但近岸区秋季和夏季的DIN含量均显著高于养殖区(P < 0.05),这可能是春季和冬季处于养殖活动间歇期,养殖废物排放减少而近岸区因人类活动的影响,DIN含量仍保持在较高水平。而秋季和夏季水温较高,硝化与反硝化细菌分解有机质的速度加快,导致水体中的DIN含量升高。太阳山库湾的不同形态DIN的比例有明显的差异(表3),但均以${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ -N形式为主,而${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ -N是有机氮硝化过程的最终产物,是热力学最稳定的化合氮形式[16],说明太阳山库湾的氮营养盐达到了热力学平衡状态。太阳山库湾${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ -N含量冬季较高,此时${\rm{NO}}_2^{-} $ -N含量最低,分析认为这可能是因为冬季水温较低,反硝化细菌等微生物的代谢活动减弱,造成${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ -N的累积,此外,冬季浮游生物繁殖活动减弱,对水体中氮营养盐的利用减少也是冬季${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ -N含量较高的原因之一。${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ -P的时空变化规律表明(图4),养殖区的${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ -P含量春季(0.0325 mg·L−1)最低且显著低于其他季节(P < 0.05),夏、秋和冬季间无显著差异(P > 0.05);近岸区和对照区均为秋季最低,${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ -P含量分别为0.025 mg·L−1、0.04 mg·L−1且秋季显著低于其他季节(P < 0.05),春、夏和冬季间差异不显著(P > 0.05)。养殖区与非养殖区在春、夏和冬季的${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ -P含量均无显著差异(P > 0.05),而秋季养殖区和对照区均显著高于近岸区(P < 0.05),表明网箱养殖和其他人类活动对太阳山库湾的${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ -P均没有显著影响。 -
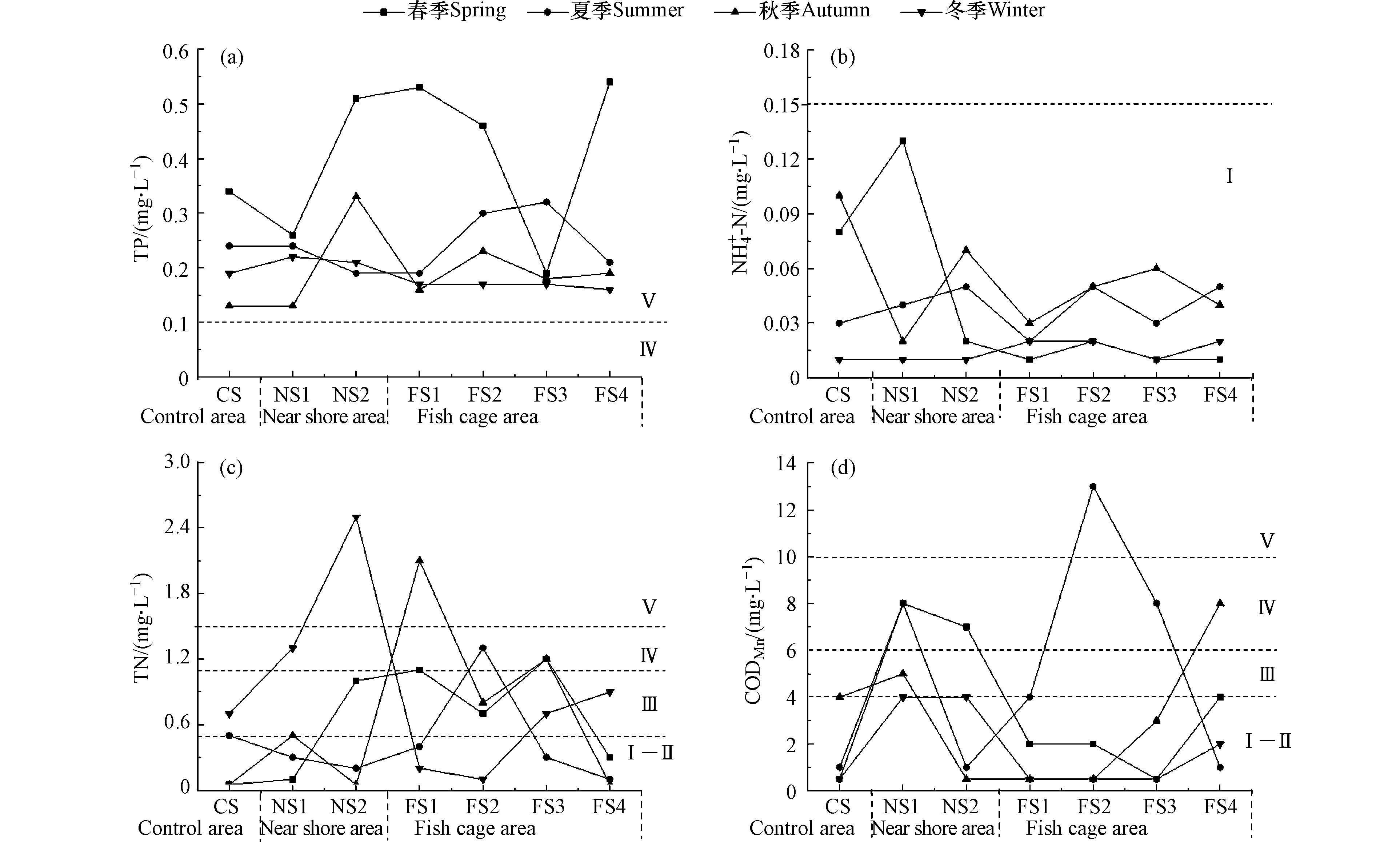
单个水质指标分析结果表明(图5),太阳山库湾养殖区、近岸区和对照区的NH+4-N含量均低于0.15 mg·L−1,达到Ⅰ类标准但TP含量均超过0.1 mg·L−1,属Ⅴ类-劣Ⅴ类标准,且养殖区、近岸区TP含量高于对照区,表明网箱养殖和人类活动均对TP含量的变化影响显著。TN和CODMn含量季节和采样区域波动较大,但对照区不同季节的TN含量均低于1.0 mg·L−1,属Ⅰ—Ⅲ类标准;CODMn含量最大值为13 mg·L−1(Ⅴ类),出现在夏季的养殖区FS2采样点,低于4 mg·L−1(Ⅱ类及以上)的采样点占比为75%。TN和CODMn含量则表现为近岸区高于养殖区和对照区,这与胡春华等[17]、李栋梁等[18]对鄱阳湖的研究结果一致,说明相比网箱养殖活动,其他人类活动如生活污水无序排放、不规范农业用药、施肥等造成的面源污染对太阳山库湾TN、TP和CODMn含量影响作用更大。
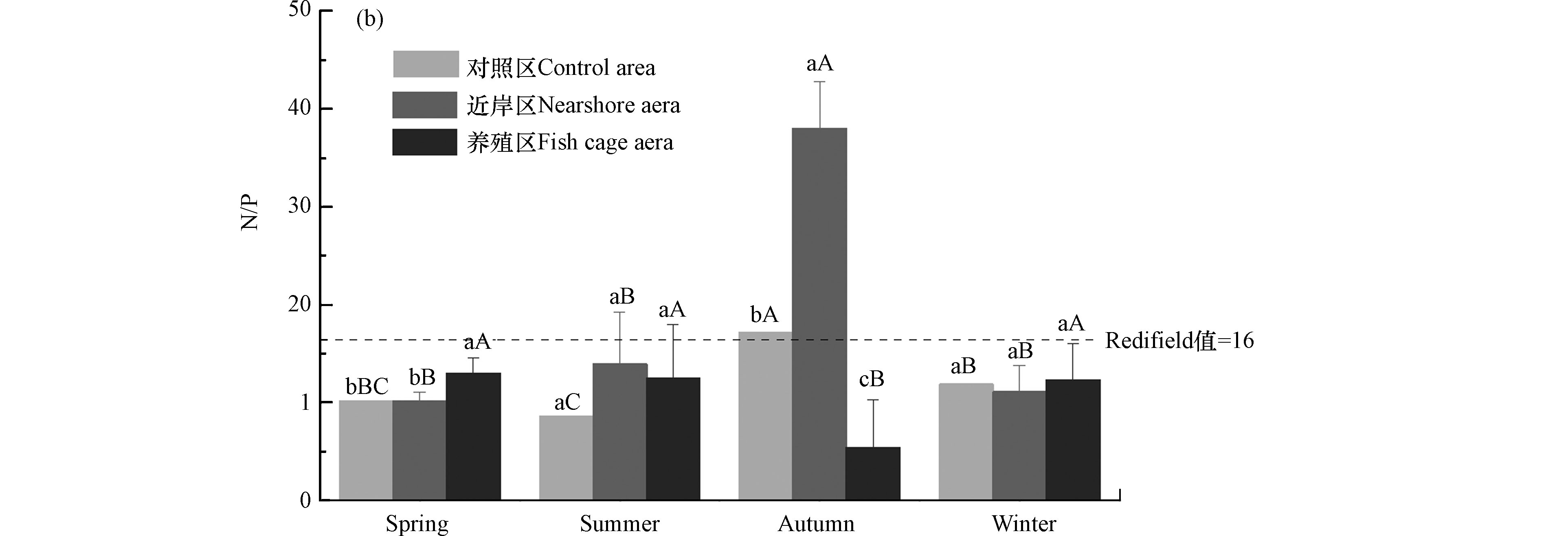
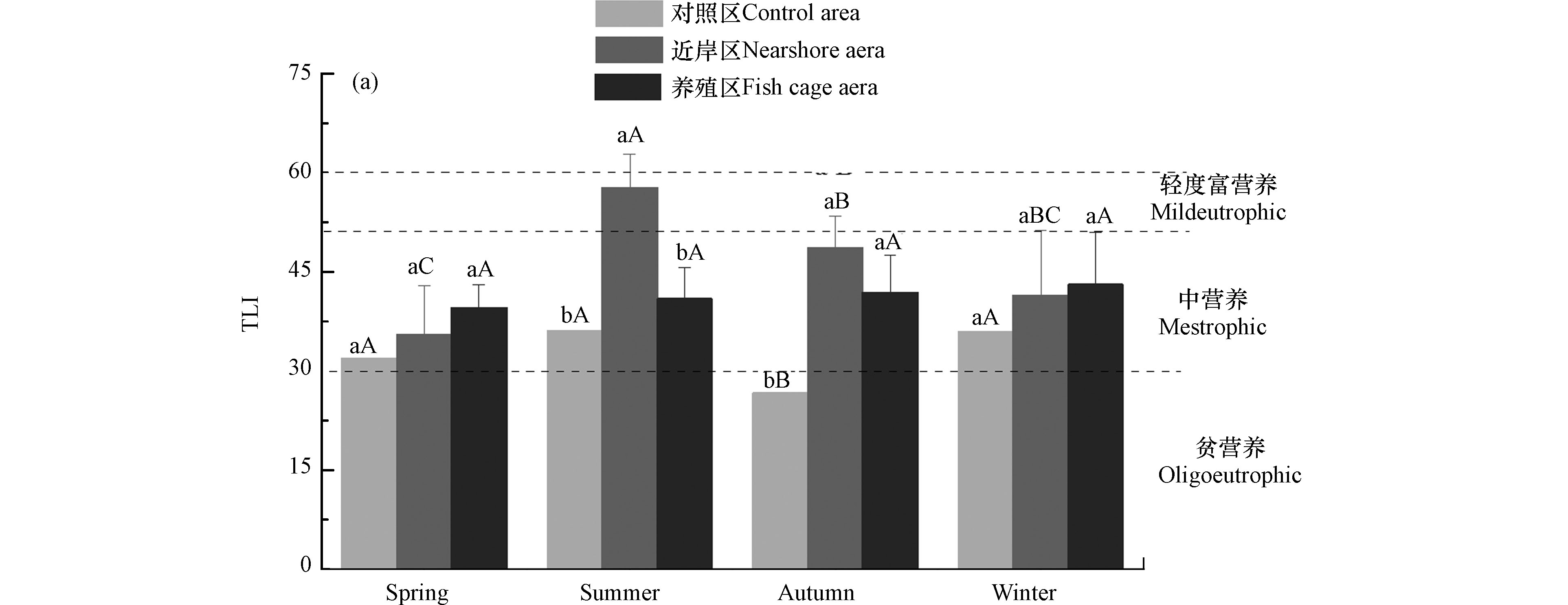
综合营养状态指数法和潜在性富营养化法作为评价水体富营养化状态的方法被广泛应用于水库、湖泊、海洋等大水面水体[17-23]。综合营养状态指数是以Chl. a为基准参数,同时选取TN、TP、SD和CODMn 的4个参数,并根据不同参数的相关权重计算得出[7]。结果显示(图6),不同采样区域的综合营养状态指数变化范围为26.7—57.9,除秋季对照区最低为贫营养和夏季近岸区最高为轻度富营养外,太阳山库湾水体总体呈中营养状态,且近岸区综合营养状态指数高于养殖区和对照区,表明相比于生活污水、农业用药施肥等造成的面源污染,网箱养殖对养殖水域的富营养化影响作用不大,这与乌梁素海的相关研究结果一致[24]。氮磷比(N/P)是考察水体潜在性营养结构状态的关键指标,对水中浮游生物的生长有重要影响[25-27],且浮游植物对氮磷吸收利用的最佳比例是16:1即N/P=16:1,而此时的N/P即为Redfield值[28]。太阳山库湾秋季各采样区域间的氮磷比差异显著,且近岸区高于对照区和养殖区。夏季和冬季不同采样区域间差异均不显著,春季养殖区显著高于对照区和近岸区。除秋季对照区和近岸区2个点氮磷比值高于Redfield值外,其余22个点次均低于16,占所有点次91.7%。表明太阳山库湾水体为潜在氮限制。养殖区与对照区差异不显著,表明网箱养殖活动对太阳山库湾潜在性富营养状态没有显著性影响。
综上所述,网箱养殖活动对养殖水域的水环境产生一定的影响,主要表现为养殖区夏季溶解氧含量低于近岸和对照区,这与夏季养殖活动密集,残饵粪便等污染物大量增加,导致有机物的分解耗氧有关。养殖水域除夏季近岸区外,整体处于中营养状态,这可能与近岸区的人类活动诸如农业生产、生活污水排放等有关。此外,太阳山库湾的N/P值整体低于16,表现为潜在氮限制,养殖区的N/P值与对照区差异不显著,表明现状养殖规模下的网箱养殖对水体的潜在性营养状态影响并不显著。
-
通过对柘林水库太阳山库湾水域不同区域的水环境因子和氮磷营养盐的时空变化特征分析,主要得到以下结论:
(1)太阳山库湾的水温、溶解氧、pH和电导率呈明显季节变化,水温夏季最高,溶解氧春季最高,电导率秋季最高,pH春夏高于秋冬,但养殖区与近岸区和对照区无显著差异。
(2)近岸区和养殖区的无机氮显著高于对照区;除秋季养殖区与对照区显著高于近岸区外,其他季节养殖区、近岸区和对照区磷酸盐含量无显著异。不同形态的无机氮的比例有明显的差异,硝酸盐氮占比最大(93.35%),其次为氨氮(6.00%),亚硝酸盐氮占比最小(0.65%),说明太阳山库湾的氮营养盐达到了热力学平衡状态。
(3)综合营养状态指数表明,太阳山库湾水体总体呈中营养状态;潜在营养化结果表明,除秋季对照区和近岸区2个点次氮磷比值高于Redfield值外,其余22个点次均低于16,占所有点次91.7%。表明太阳山库湾水体为潜在氮限制;养殖区与对照区差异不显著,表明现状养殖规模下的网箱养殖活动对太阳山库湾潜在性富营养状态没有显著性影响。
网箱养殖对柘林水库氮磷营养盐时空分布的影响-以太阳山库湾为例
Influence of cage fish-farming on tempo-spatial distribution of nitrogrn and phosphorus in Zhelin Reservior: A case study of Taiyangshan Bay
-
摘要: 为探究网箱养殖对柘林水库氮磷营养盐时空分布的影响,以太阳山库湾为例,于2018年10月—2019年7月分别对网箱养殖区、近岸区和对照区的水温(WT)、溶解氧(DO)、电导率(conductivity)、无机氮(DIN)、磷酸盐(
${{\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} }$ -P)等指标监测分析,并对水体的富营养状态进行综合评价。结果显示,太阳山库湾的WT、DO、pH和电导率呈明显季节变化,WT夏季最高,DO春季最高,Conductivity秋季最高,pH春夏高于秋冬,但养殖区与近岸区和对照区无显著差异(P > 0.05)。近岸区和养殖区的DIN显著高于对照区(P < 0.05),除秋季养殖区与对照区显著高于近岸区外(P < 0.05),其他季节养殖区、近岸区和对照区${{\rm{PO}}_4^{3-}} $ -P含量无显著异(P > 0.05)。不同形态的DIN的比例有明显的差异,硝酸盐氮(${{\rm{NO}}_3^{-}} $ -N)占比最大(93.35%),其次为氨氮(${{\rm{NH}}_4^{+}} $ -N)(6.00%),亚硝酸盐氮(${{\rm{NO}}_2^{-}} $ -N)占比最小(0.65%),说明太阳山库湾的氮营养盐达到了热力学平衡状态。太阳山库湾除夏季近岸区为轻度富营养状态外,整体呈中营养状态,表明相较于生活污水无序排放、不规范农业用药和施肥等产生的面源污染,网箱养殖对水环境的富营养化影响较小。此外,太阳山库湾的N/P值整体低于16(Redfield值),表现为潜在氮限制,养殖区的N/P值与对照区差异不显著(P > 0.05),表明现状下的网箱养殖投饵对水体的潜在性营养状态影响并不显著。Abstract: To investigate Influence of cage fish-farming on tempo-spatial distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in Taiyangshan Bay of Zhelin Resverior, water temperature (WT), dissolved oxygen (DO), dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN), phosphate (${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ -P) other physical & chemical factors were determined and analyzed in three different sampling area: control area(CS), nearshore area(NS) and fish cage area(FS) with different seasons from October 2018 to July 2019. The concentration and distribution of WT、DO、pH and Conductivity showed obvious seasonal variation and reached their maximum values in summer, spring and autumn, respectively. However, there were no significant difference between FS、NS and CS (P > 0.05). DIN concentration in FS and NS were significant higher than CS (P < 0.05),${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ -P concentration of FS and CS in autumn were significant higher than NS (P < 0.05). DIN was dominated by nitrate nitrogen (${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ -N) with percentages of 93.35%, followed by ammonia nitrogen (${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $ -N) with percentages of 6.00%, and nitrite nitrogen (${\rm{NO}}_2^{-} $ -N) was lowest with percentages of 0.65%, indicating that the thermodynamic equilibrium of N was reached. The trophic level of Taiyangshan Bay was moderate overall except that of nearshore in summer, indicating that compared with non-point source pollution caused by human production activities such as disorderly discharge of domestic sewage, irregular agricultural medicine and fertilization, cage culture had a smaller impact on the eutrophication of the water environment. In addition, The N/P value of Taiyangshan Bay was lower than 16 (Redfield value) as a whole, which mean there was a potential nitrogen limitation. The N/P value of Fish cage area was not significantly different from the control area (P > 0.05), indicating that the impact of cage culture on the potential nutritional status of water was not significant with the current cage culture scale. -

-
表 1 柘林水库太阳山库湾采样点坐标
Table 1. The Sampling sites coordinate in Taiyangshan Bay of Zhelin Reservior
采样区域
Sampling area采样点编号
Sampling Number采样点坐标Sampling sites coordinate 纬度(N)Latitude 经度(E)Longitude 近岸区
Nearshore areaNS1 115°30′15.96" 29°17′41.46" NS2 115°28′39.50" 29°18′02.57" 养殖区
Fish cage areaFS1 115°29′59.04" 29°17′11.65" FS2 115°29′52.28" 29°16′48.29" FS3 115°29′20.33" 29°16′54.33" FS4 115°28′58.48" 29°17′26.31" 对照区Control area CS 115°29′04.06" 29°16′06.13" 表 2 柘林水库太阳山库湾水环境因子空间变化特征
Table 2. Spatial variation in enviromental in Taiyangshan Bay of Zhelin Reservior
区域
Sampling area水温/℃
Water Temperature溶解氧/(mg·L−1) DO pH 电导率/(μS·cm−1) Conductivity 对照区(CS) 21.3±7.2 9.43±1.28 8.11±0.85 89.9±6.1 近岸区(NS) 21.2±7.1 10.26±2.47 8.64±0.69 89.4±6.2 养殖区(FS) 21.0±7.6 9.76±1.97 8.54±0.73 90.5±5.8 表 3 柘林水库太阳山库湾无机氮中不同形态氮的占比(%)
Table 3. Seasonal variation of dissolved inoganic nirigen composition in Taiyangshan Bay of Zhelin Reservior
季节Sampling time 氨氮 ${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $ 硝酸盐氮 ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 亚硝酸盐氮 ${\rm{NO}}_2^{-} $ 春季 5.57 93.57 0.86 夏季 5.10 94.46 0.43 秋季 11.57 87.53 0.91 冬季 1.75 97.83 0.42 平均值±标准差 6.00±4.08 93.35±4.29 0.65±0.26 -
[1] STEVENS C J. Nitrogen in the environment [J]. Science, 2019, 363(6427): 578-580. doi: 10.1126/science.aav8215 [2] ZEHR J P, KUDELA R M. Nitrogen cycle of the open ocean: From genes to ecosystems [J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2011, 3(1): 197-225. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-120709-142819 [3] 高勤峰, 张恭, 董双林. 网箱养殖生态学研究进展 [J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 49(3): 7-17. GAO Q F, ZHANG G, DONG S L. Reviews on cage-culture ecology [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2019, 49(3): 7-17(in Chinese).
[4] 李学梅, 孟子豪, 胡飞飞, 等. 网箱养鱼的氮磷排放 [J]. 淡水渔业, 2020, 50(4): 39-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2020.04.006 LI X M, MENG Z H, HU F F, et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus emissions from cage fish culture [J]. Freshwater Fisheries, 2020, 50(4): 39-46(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2020.04.006
[5] 徐淑敏, 齐占会, 史荣君, 等. 水产养殖对亚热带海湾氮磷营养盐时空分布的影响: 以深澳湾为例 [J]. 南方水产科学, 2019, 15(4): 29-38. doi: 10.12131/20190049 XU S M, QI Z H, SHI R J, et al. Influence of mariculure on tempo-spatial distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in subtropical zone: A case study of Shen'ao Bay [J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2019, 15(4): 29-38(in Chinese). doi: 10.12131/20190049
[6] 杜岩岩, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 等. 网箱养殖对刘家峡水库浮游细菌群落组成及影响因素分析 [J]. 淡水渔业, 2018, 48(5): 11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2018.05.002 DU Y Y, LOU Z Y, ZHANG Y P, et al. Effect of cage culture on community structure and influencing factors of bacterioplankton in Liujiaxia Reservoir [J]. Freshwater Fisheries, 2018, 48(5): 11-16(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2018.05.002
[7] 金相灿, 屠清瑛. 湖泊富营养化调查规范[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990. JIN X C, TU Q Y. The standard methods in lake eutrophication (Second Edition)[M]. Beijing: China Environment Science Press, 1990(in Chinese).
[8] 王明翠, 刘雪芹, 张建辉. 湖泊富营养化评价方法及分级标准 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2002, 18(5): 47-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2002.05.018 WANG M C, LIU X Q, ZHANG J H. Evaluate method and classification standard on lake eutrophication [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2002, 18(5): 47-49(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2002.05.018
[9] 杨美兰, 林钦, 黄洪挥, 等. 大鹏澳养殖水域溶解氧的变化及其与生态结构的关系 [J]. 中国水产科学, 2005, 12(3): 357-361. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2005.03.021 YANG M L, LIN Q, HUANG H H, et al. Variation characteristics of DO levels in cage-culture waters of Dapengao Cove, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2005, 12(3): 357-361(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2005.03.021
[10] HUANG Y C A, HUANG S C, MENG P J, et al. Influence of strong monsoon winds on the water quality around a marine cage-culture zone in a shallow and semi-enclosed bay in Taiwan [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2012, 64(4): 851-860. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.01.012 [11] 王毛兰, 刘景景. 鄱阳湖网箱养殖对水环境的影响: 以都昌水域为例 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(10): 2348-2355. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018112615 WANG M L, LIU J J. The impact of cage fish-farming on the aquatic environment in Poyang Lake, China: A case study of Duchang water area [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(10): 2348-2355(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018112615
[12] BOUWMAN L, GOLDEWIJK K K, van der HOEK K W, et al. Exploring global changes in nitrogen and phosphorus cycles in agriculture induced by livestock production over the 1900-2050 period [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,, 2013, 110(52): 20882-20887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1012878108 [13] VERDEGEM M C J. Nutrient discharge from aquaculture operations in function of system design and production environment [J]. Reviews in Aquaculture, 2013, 5(3): 158-171. doi: 10.1111/raq.12011 [14] 曾涛. 樟湖库湾鱼类网箱养殖区水体氮的时空变化特征 [J]. 渔业研究, 2018, 40(3): 177-185. ZENG T. Characteristics on spatial and temporal variations of nitrogen in water of cage culture areas of Zhanghu reservoir bay [J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2018, 40(3): 177-185(in Chinese).
[15] 贾后磊, 温琰茂. 哑铃湾网箱养殖水体中N的含量特征 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2004, 23(2): 8-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2004.02.003 JIA H L, WEN Y M. Content and character of nitrogen in water environment of cage culture, Yaling Bay [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2004, 23(2): 8-11(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2004.02.003
[16] 丘耀文. 珠江口水体的三氮特征 [J]. 热带海洋, 1992, 11(3): 84-88. QIU Y W. The characteristics of dissolved inorganic nitrogen in the water body of Zhujiang estuarine [J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1992, 11(3): 84-88(in Chinese).
[17] 胡春华, 周文斌, 王毛兰, 等. 鄱阳湖氮磷营养盐变化特征及潜在性富营养化评价 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2010, 22(5): 723-728. HU C H, ZHOU W B, WANG M L, et al. Inorganic nitrogen and phosphate and potential eutrophication assessment in Lake Poyang [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2010, 22(5): 723-728(in Chinese).
[18] 李栋梁. 鄱阳湖氮磷营养盐特征研究[D]. 抚州: 东华理工大学, 2014. LI D L. The research on nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients characteristic of Poyang lake[D]. Fuzhou: East China Institute of Technology, 2014(in Chinese).
[19] 全栋, 史小红, 赵胜男, 等. 2006—2017年乌梁素海夏季水体营养状态及影响因子 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2019, 31(5): 1259-1267. doi: 10.18307/2019.0503 QUAN D, SHI X H, ZHAO S N, et al. Eutrophication of Lake Ulansuhai in 2006-2017 and its main impact factors [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2019, 31(5): 1259-1267(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2019.0503
[20] 郭诗琪, 步秀芹, 廖洁, 等. 南宁市大王滩水库水质评价及富营养化分析 [J]. 环境保护科学, 2019, 45(5): 63-68. GUO S Q, BU X Q, LIAO J, et al. Water quality evaluation and eutrophication analysis of Dawangtan reservoir in Nanning [J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2019, 45(5): 63-68(in Chinese).
[21] ZHAO C Y, LIU S L, JIANG Z J, et al. Nitrogen purification potential limited by nitrite reduction process in coastal eutrophic wetlands [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 694: 133702. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133702 [22] MEI L L, YANG X, ZHANG S Q, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviate phosphorus limitation by reducing plant N: P ratios under warming and nitrogen addition in a temperate meadow ecosystem [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 686: 1129-1139. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.035 [23] 魏潇, 李凡, 马元庆, 等. 2014年山东近岸海域海水氮磷营养盐含量特征及富营养化评价 [J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2019(5): 103-109. WEI X, LI F, MA Y Q, et al. Characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient concentrations and eutrophication evaluation of Shandong coastal waters in 2014 [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2019(5): 103-109(in Chinese).
[24] 巴达日夫. 乌梁素海水环境因子时空分布特征及富营养化评价 [J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2019(4): 108-114. BA D. Characterization of spatial and temporal distribution of environmental factors of wuliangsuhai lake and evaluation of its eutrophication [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2019(4): 108-114(in Chinese).
[25] 李付宽, 郑剑锋, 贾泽宇, 等. 海河干流天津段氮磷对藻类生长的影响及动力学分析 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(2): 959-964. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201509154 LI F K, ZHENG J F, JIA Z Y, et al. Impact of nitrogen and phosphorus on algal growth and kinetics in Haihe River of Tianjin [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(2): 959-964(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201509154
[26] WEBER T S, DEUTSCH C. Ocean nutrient ratios governed by plankton biogeography [J]. Nature, 2010, 467(7315): 550-554. doi: 10.1038/nature09403 [27] SPILLING K, CAMARENA-GÓMEZ M T, LIPSEWERS T, et al. Impacts of reduced inorganic N: P ratio on three distinct plankton communities in the Humboldt upwelling system [J]. Marine Biology, 2019, 166(9): 1-17. [28] REDFIELD A C. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment [J]. Science Progress, 1960, 11: 150-170. -













 下载:
下载: