-
当前,湖泊、湖库型河道和池塘等缓流水体的富营养化已成为全球一个十分严重的水环境污染问题,而引发缓流水体富营养化的关键营养元素之一是磷[1]。缓流水体中的磷有两个来源:外源和内源。在外源性磷的输入得到有效控制后,控制底泥中磷向上覆水的释放便成为了缓流水体富营养化防治的关键。目前内源磷释放控制技术主要包括底泥疏浚[2]、曝气增氧[3]、硝酸钙添加[4]、铝盐化学钝化[5]、物理惰性覆盖[6]和活性覆盖[7-19]等。其中,活性覆盖技术,也就是将钝磷能力强的固体材料投加到底泥-上覆水界面上方形成一层活性覆盖层以降低底泥内源磷向上覆水体释放风险的技术,近年来受到国内外研究学者的广泛青睐,被认为是一种极具应用前景的底泥内源磷释放控制技术[7-19]。
运用活性覆盖技术控制底泥磷释放的一个关键问题就是寻找到合适的活性覆盖材料。目前国内外的研究人员已经考察了铁改性方解石[7]、铁铝污泥[8]、热改性凹凸棒土[9]、锆改性沸石[10-11]、镧改性黏土[12]、镧改性沸石[13-16]、氢氧化镧[17-18]和氢氧化镁[19]等作为固体吸附材料对底泥内源磷释放的控制效果。其中,氢氧化镧对水中磷酸盐的吸附能力强,并且对底泥中潜在可移动态磷和生物可利性磷的钝化能力好,极具应用前景[17]。但是,单纯使用氢氧化镧控制底泥中磷释放存在成本高、镧的有效利用率低等问题。镁是自然界广泛存在的碱土金属元素,是人体必须的金属元素之一。氢氧化镁是一种无毒无味的白色晶体粉末,对水中的磷酸盐具有良好的去除能力,对水体内源磷释放的控制效果较好[19]。目前国内外关于利用镁镧复合材料控制水体内源磷释放的研究却鲜见报道。过硫酸氢钾(PMS)是一种常见、高效和安全的抑菌剂和氧化剂,可与水发生氧化反应生成不稳定的臭氧,进而生成新生态氧,可用于水体底泥的改良[20-22]。将PMS添加和Mg/La复合材料覆盖进行联用,可能也可以用于水体底泥中磷释放的控制。但是,目前国内外关于PMS添加和Mg/La复合材料覆盖组合技术控制水体底泥磷释放的研究却鲜见报道。
本研究采用共沉淀法制备Mg/La复合材料,通过批量吸附实验和X射线光电子能谱分析技术(XPS)考察Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的吸附特性及相关吸附机理。通过构建实验室模拟反应体系,考察Mg/La复合材料覆盖、PMS添加与联用对水体内源磷释放的控制效果,探讨相关的控磷机制。本文旨在为应用Mg/La复合材料及其与过硫酸氢钾联用控制缓流水体底泥内源磷释放提供科学依据。
全文HTML
-
本实验所用的化学试剂包括六水合氯化镁(MgCl2·6H2O)、七水合氯化镧(LaCl3·7H2O)、NaOH、HCl、NaCl、CaCl2、KCl、NaHCO3、Na2SO4、KH2PO4、钼酸铵、酒石酸锑钾和抗坏血酸等,均购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司,均为分析纯试剂。PMS购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司。实验用水均为去离子水。本实验所用底泥均采自上海海洋大学临港校区的校园景观水体。
-
Mg/La复合材料按照MgCl2和LaCl3的物质的量比为3:1进行制备,具体的制备步骤为:称取83.55 g MgCl2·6H2O和50.9 g LaCl3·7H2O放于1 L锥形瓶中,移取300 mL去离子水进行溶解,在磁力搅拌下向混合溶液中缓慢滴加1 mol·L−1的NaOH溶液,调节溶液的pH值为10.0;继续搅拌30 min后采用离心分离的方法进行固液分离,所得固体用去离子水清洗5遍,将固体放置于105 ℃的烘箱内进行烘干,所得固体经过研磨破碎后放于自封袋内备用。
采用日本株式会社理学生产的型号为Smartlab9的X射线衍射仪(XRD)对吸附磷酸盐前后的Mg/La复合材料进行表征,XRD分析采用Cu靶,Kα射线源,操作电压为40 kV和150 mA,λ=0.154056 nm,扫描范围为2θ=5°—80°。采用X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS,ESCALAB250Xi,赛默飞世尔科技公司,美国)对吸附磷酸盐前后的Mg/La复合材料进行表征。
-
采用吸附实验考察Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的吸附性能。首先准确称取一定质量的Mg/La复合材料置于50 mL锥形瓶中,然后配制一定质量浓度的磷酸盐溶液,并采用1 mol·L−1的NaOH溶液和1 mol·L−1的HCl溶液将磷酸盐溶液的pH值调至所需数值,然后再准确移取一定体积磷酸盐溶液放入装有Mg/La复合材料的锥形瓶中。将该混合液放置于25 ℃的恒温振荡器中以150 r·min−1进行振荡,反应一段时间后采用离心分离的方法对混合反应液进行固液分离,上清液中残留的磷酸盐浓度采用钼锑抗分光光度法进行测定,然后根据计算公式(1)计算得到Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的平衡吸附量。所有实验均设置2个平行。
式中,qe为Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的平衡吸附量(mg·g−1);c0和ce为初始和反应结束后的磷质量浓度(mg·L−1);V为磷酸盐溶液体积(mL);m为Mg/La复合材料的质量(mg)。采用Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附模型对吸附等温实验进行拟合。Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附方程分别为[23-24]:
式中,qe和qmax分别为Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的平衡单位吸附量和最大单位吸附量(mg·g−1),ce为吸附平衡时磷的浓度(mg·L−1),KL为Langmuir常数(L·mg−1),KF和1/n均为Freundlich常数。
采用准一级(PFO)、准二级(PSO)和Elovich模型对吸附动力学实验数据进行拟合,这三种模型的数学表达式分别见公式(4)、(5)和(6)[24]。
式中,t为反应时间(min);qt和qe分别为t时和平衡时Mg/La复合材料对水中磷的单位吸附量(mg·g−1),k1为准一级动力学模型速率常数(min−1),k2为准二级动力学模型速率常数[g·(mg·min) −1];a和b均为Elovich模型参数。
-
将底泥过筛后充分混合均匀,取8份质量均为1 kg的湿底泥放入透明圆柱形有机玻璃容器(直径为10 cm,高度为25 cm)内并铺平,然后对这8个容器进行以下处理(每2个容器为1组,即每个处理设置2个平行):① 对底泥不做任何处理,作为对照组;② 将10 g Mg/La复合材料均匀覆盖在底泥上方,作为Mg/La复合材料覆盖组(单位面积的水土界面上覆盖材料的投加量为1274 g·m−2);③ 向底泥中注入5 mL 200 g·L−1的PMS溶液,混匀3 cm表层底泥后,作为PMS添加组;④ 首先向底泥中注入5 mL 200 g·L−1的PMS溶液,混匀3 cm表层底泥后,再将10 g Mg/La复合材料均匀覆盖在底泥上方,作为PMS添加和Mg/La复合材料覆盖组合组。然后配置含10 mmol·L−1 NaCl、1 mmol·L−1 NaHCO3、1 mmol·L−1 CaCl2和1 mol·L−1 MgCl2溶液,再采用亚硫酸盐氧化脱氧法对该溶液进行脱氧,制备得到缺氧的上覆水样,然后将其加入到上述8个容器中,使上覆水充满底泥上方空间,随后用橡胶塞盖住,并用白凡士林密封培养。在底泥培养期间,每周分别采用溶解氧仪、pH计和钼锑抗分光光度法测定上覆水的DO浓度、pH值和溶解性活性磷(SRP)浓度,结果以平均值±标准偏差的方式进行展示。每次采集水样后补充等体积的水样,以维持每个容器中上覆水体积在一个固定的值。待底泥培养进行至22 d和44 d的时候,分别再次将5 mL 200 g·L−1的PMS溶液均匀注射至表层的3 cm底泥中。待底泥培养至119 d,取出1个覆盖组反应器和1个联合组反应器,将其中的覆盖材料移除出来,再采用连续分级提取法对所采集覆盖材料中磷赋存形态进行分析。 本研究中,覆盖材料的磷形态分为5级,分别为易解吸态磷(Labile-P)、氧化还原敏感态磷(BD-P)、金属氧化物结合态无机磷(NaOH-IP)、盐酸提取态磷(HCl-P)和残渣态磷(Res-P)。提取步骤为:将一定质量的覆盖材料依次与1 mol·L−1的NH4Cl溶液(pH=7)、0.11 mol·L−1 Na2S2O4和0.11 mol·L−1 NaHCO3的混合溶液、1 mol·L−1 NaOH溶液(298 K)、1 mol·L−1 HCl溶液和1 mol·L−1 NaOH溶液(358 K)进行反应,所提取的磷分别为Labile-P、BD-P、NaOH-IP、HCl-P和Res-P[17]。磷的形态分析设置3个平行。采用以下公式计算确定各种底泥处理方法对上覆水中SRP的削减率(RE,%):
式中,LCK和LTR分别为对照组和处理组上覆水中SRP的浓度(mg·L−1)。采用公式(8)对底泥磷释放速率[JD,mg·(m2·d)−1]进行计算[25]。
式中,k为采样次数;n为总的采样次数;tk为第k次采样时实验的持续时间(d);tn为第n次采样时实验的持续时间;L0、Lk和Ln分别为初始时刻、tk和tn时上覆水中SRP浓度(mg·L−1);Vn为第n次采样后上覆水的体积(L);Vk为tk时采集水样的体积(L);A为底泥-水界面的面积(m2)。
1.1. 实验材料
1.2. 吸附剂制备及表征
1.3. 吸附实验
1.4. 底泥培养实验
-
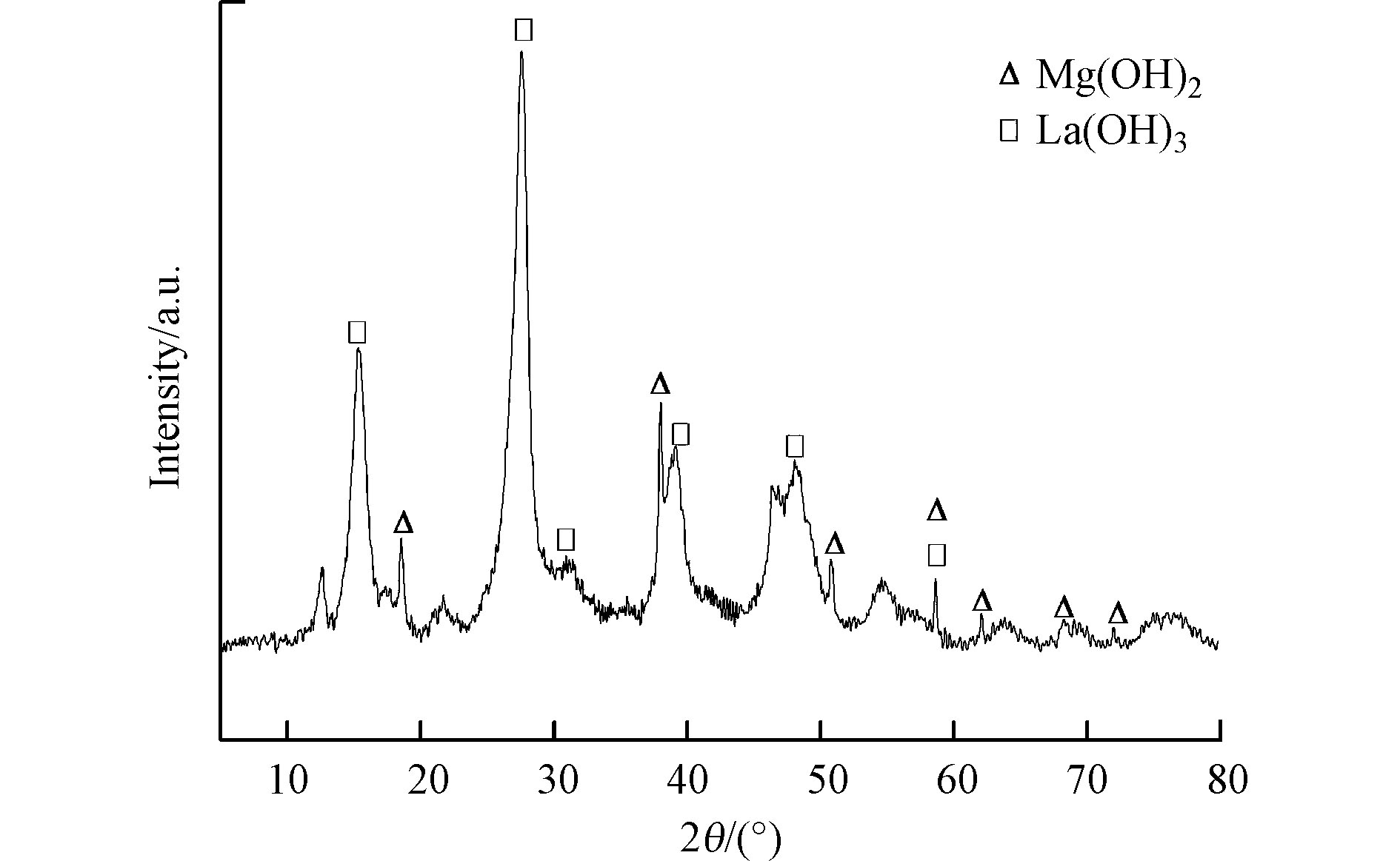
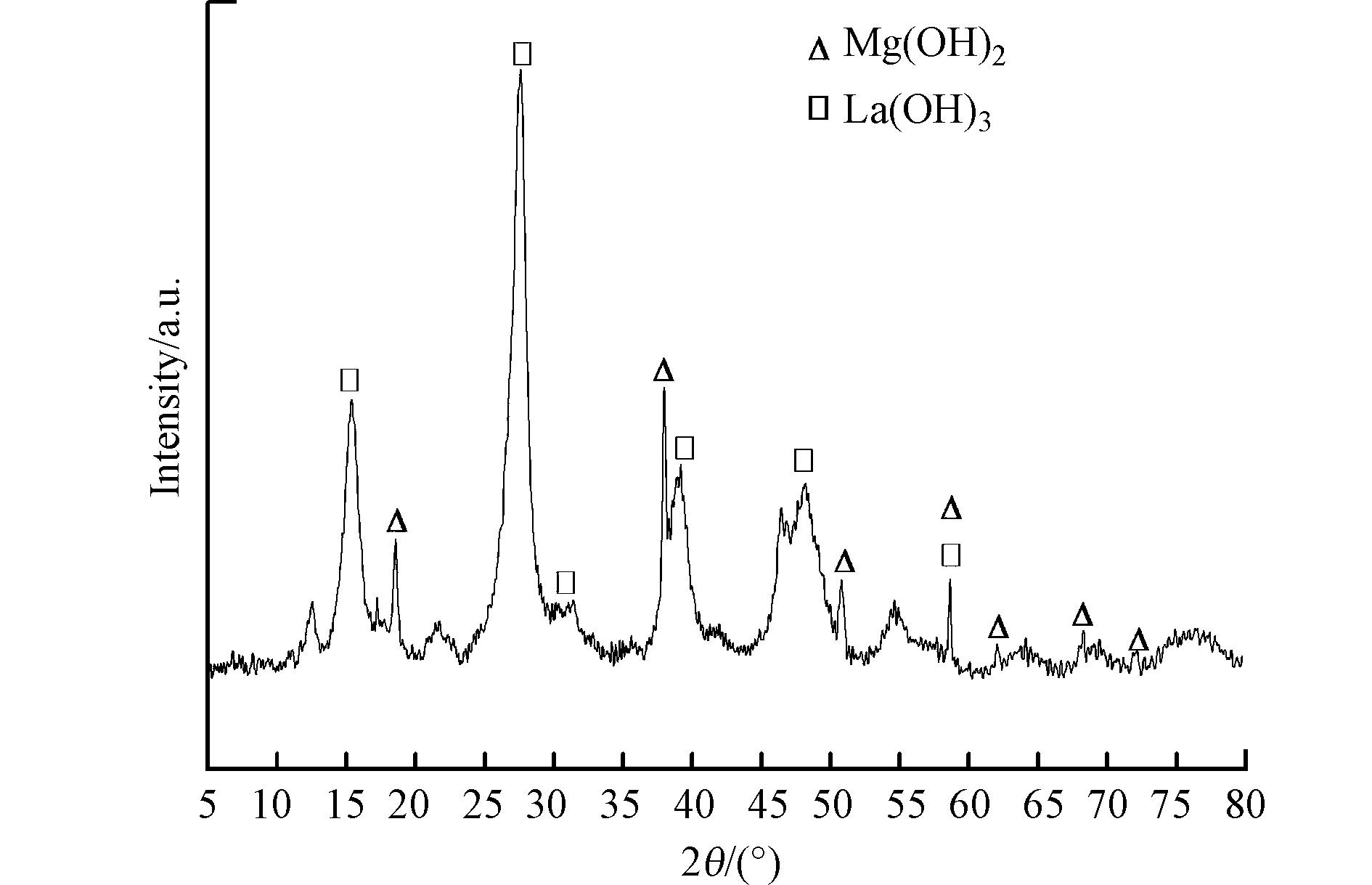
本研究所制备得到的Mg/La复合材料为白色的粉末状材料。图1为Mg/La复合材料的XRD图谱。由图1可以发现,Mg/La复合材料的XRD图谱中于2θ为18.6°、39.0°、50.8°、58.6°、62.0°和68.3°等处出现了氢氧化镁晶体的特征峰(JCPDS 44-1482)[19]。另外,由图1还可以发现,Mg/La复合材料的XRD图谱中于2θ为15.4°、27.6°、39.5°和48.2°等处出现了氢氧化镧晶体的特征峰(JCPDS 36-1481)[17]。Mg/La复合材料的主要X射线衍射峰均与氢氧化镁晶体或氢氧化镧晶体特征峰一致,说明本研究所制备的Mg/La复合材料的主要成分为氢氧化镁和氢氧化镧。
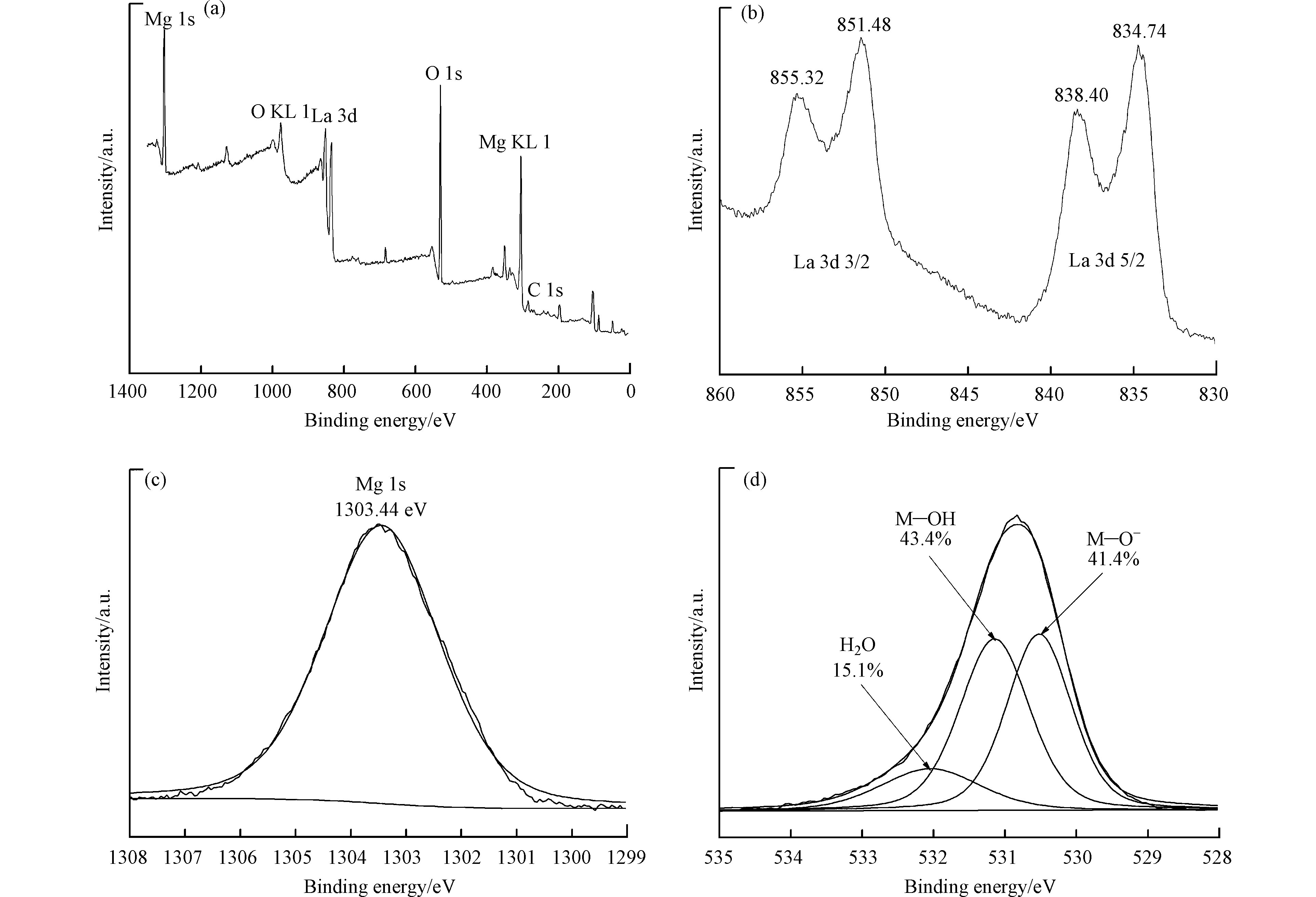
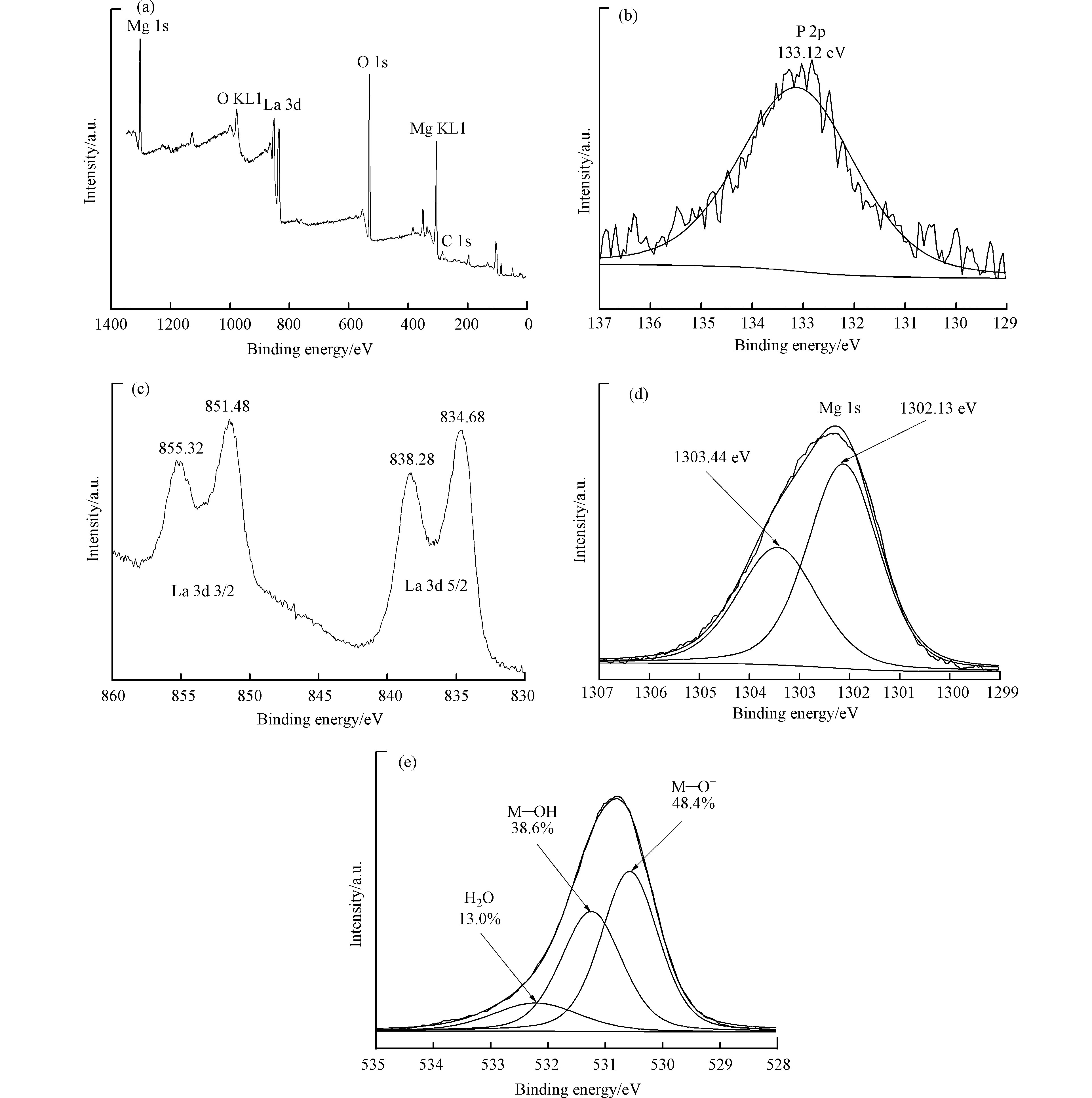
图2为 Mg/La 复合材料的 XPS 分析结果. 从图2中可见,XPS谱图中出现了La 3d、Mg 1s和O 1s峰。这进一步证明了Mg/La复合材料中存在Mg(OH)2和La(OH)3。从图2中还可见,Mg/La复合材料表面的氧基团可细分为3种不同类型的基团,即结合水(H2O)、金属结合态羟基基团(M—OH)和金属结合氧(M—O−)。其中,43.4%的氧基团以M—OH形式存在。
-
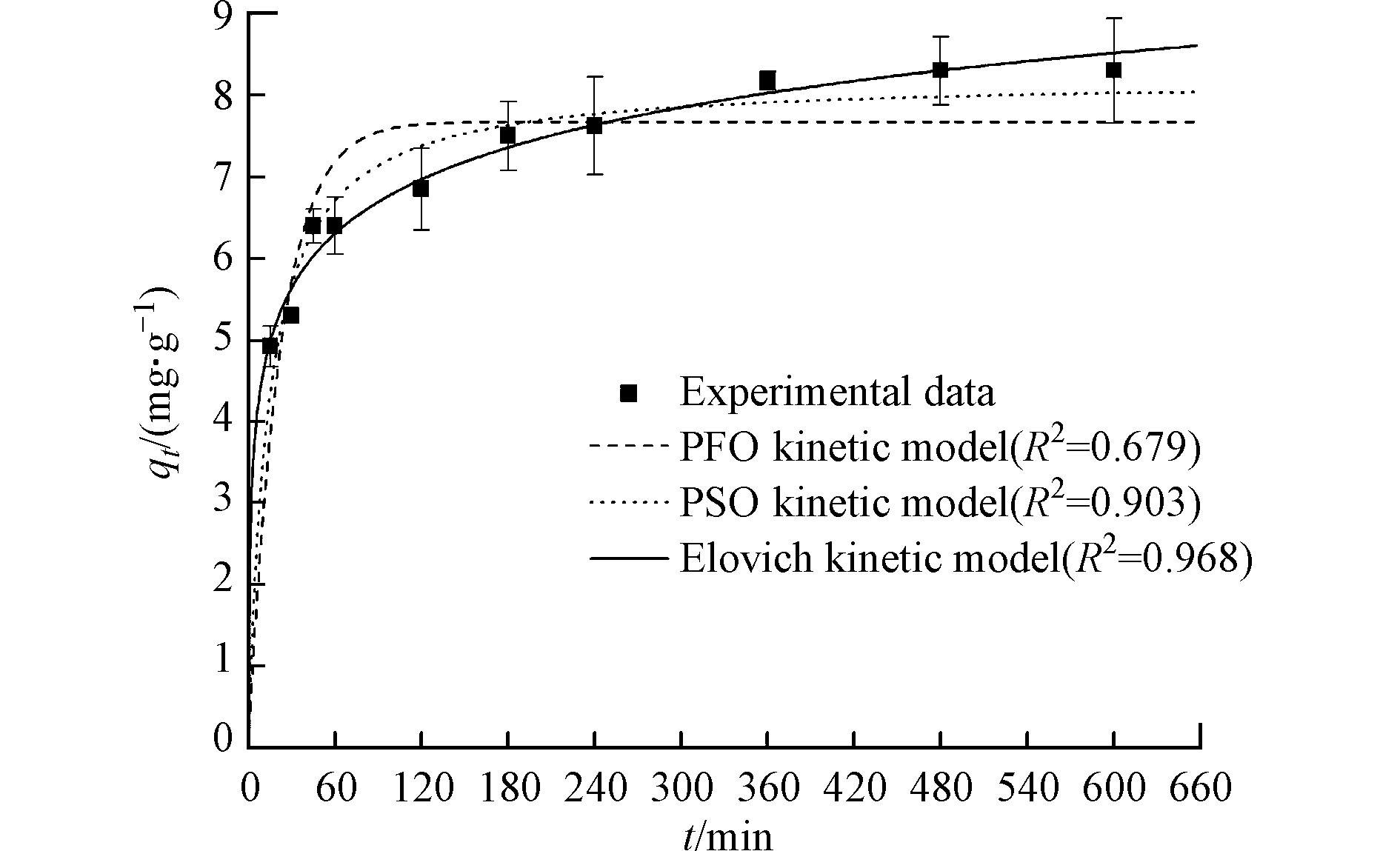
图3为Mg/La复合材料吸附水中磷酸盐的动力学曲线(吸附剂投加量为25 mg,溶液体积为25 mL,溶液pH值为7.0,反应温度为25 ℃,初始磷浓度为10 mg·L−1,反应时间为15—600 min)。由图3可以发现,Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的单位吸附量随着反应时间的增加而增加,直至达到吸附平衡。为进一步了解Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的吸附动力学过程,采用PFO、PSO和Elovich动力学模型对图3中的吸附动力学实验数据进行拟合,结果也列于图3中。从图3可见,与准一级动力学模型相比,准二级动力学模型和Elovich模型更适合用于描述Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的吸附过程。这说明Mg/La复合材料吸附水中磷酸盐的过程属于化学吸附过程[24,26]。这个结论将进一步根据XPS分析结果确定。
-
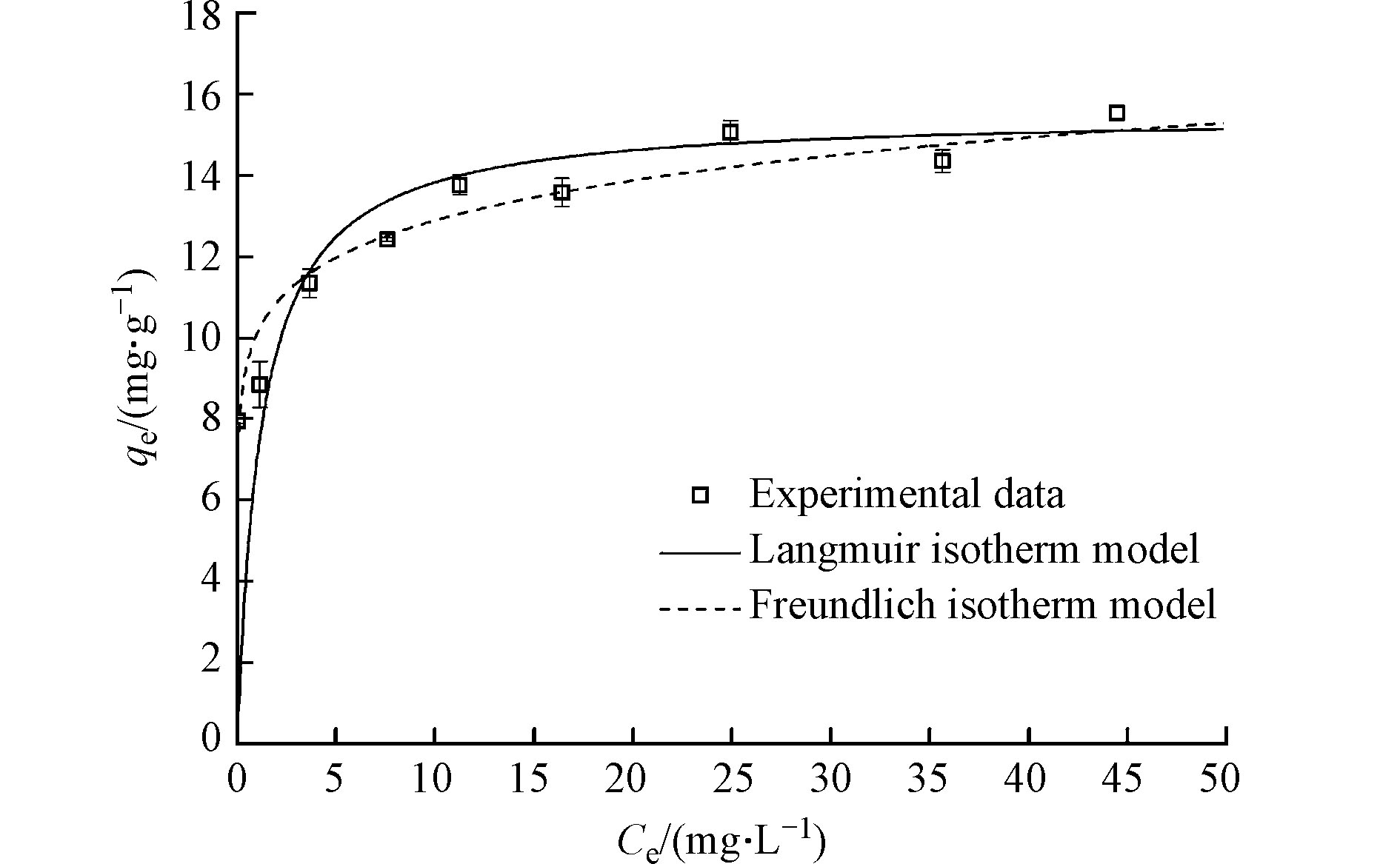
图4是溶液磷平衡浓度对Mg/La复合材料吸附水中磷酸盐的影响(吸附剂投加量为25 mg,溶液体积为25 mL,pH值为7.0,反应温度为25 ℃,反应时间为24 h,磷初始浓度为8—60 mg·L−1)。由图4可以发现,Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的单位吸附量随水中磷酸盐平衡浓度的增加而增加,直至达到吸附饱和。根据模型参数值计算得到的Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附线也列于图4,表1为Langmuir 和Freundlich 等温吸附模型参数的拟合值.。
由表1和图4可以发现,Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附模型均适合用于描述Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的等温吸附行为。通过Freundlich等温吸附模型计算得到的1/n为0.106,介于0—1之间,说明Mg/La复合材料吸附磷为优惠型吸附,吸附容易发生[24]。从表1还可以发现,根据Langmuir等温吸附模型计算得到Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的最大单位吸附量可以达到15.5 mg·g−1(以元素P计)。Haghseresht等发现,目前国内外常用的一种底泥磷钝化材料——镧改性膨润土(锁磷剂)对水中磷的最大吸附量为9.5—10.5 mg·g−1[27]。本研究所制备的Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的最大吸附容量远大于锁磷剂,从吸附容量角度看,利用Mg/La复合材料控制水体内源磷释放比常用的底泥磷钝化材料——锁磷剂更有优势。杨春懿等发现,氢氧化镁对水中磷酸盐的最大吸附量为2.38 mg·g−1[19],远低于本研究所制备的Mg/La复合材料。利用Mg/La复合材料控制水体内源磷释放比单纯的氢氧化镁更具优势。
-
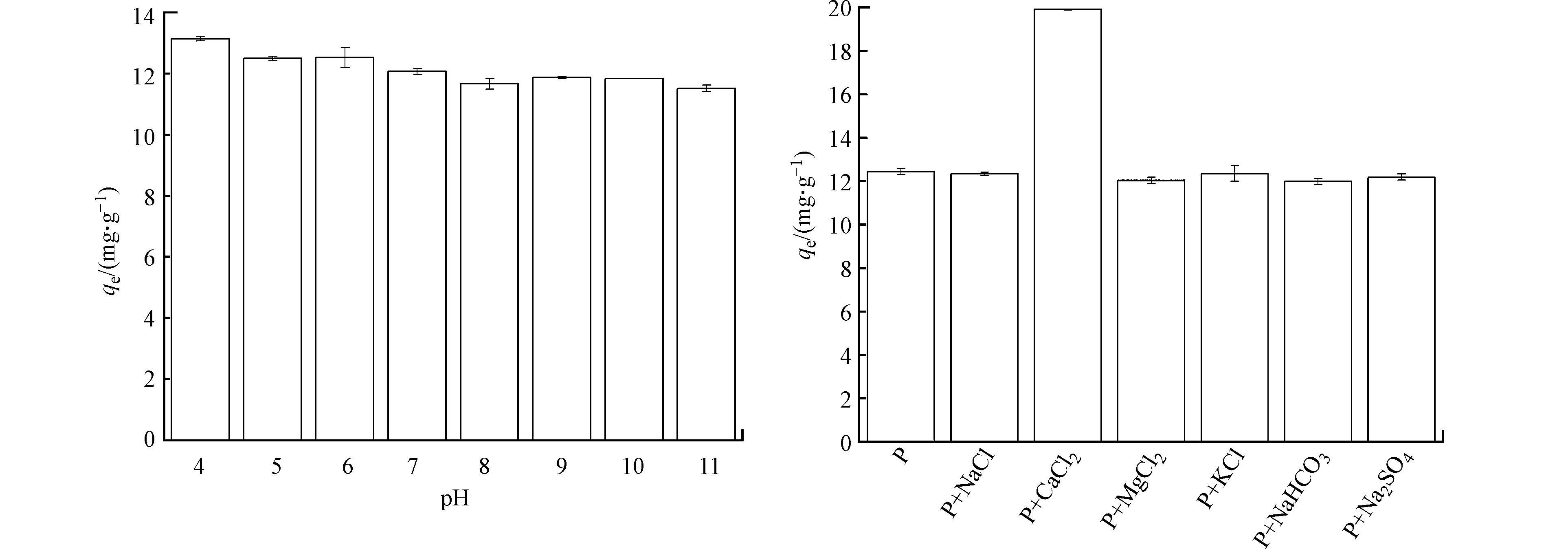
图5是溶液初始pH对Mg/La复合材料吸附水中磷酸盐的影响(吸附剂投加量为25 mg,溶液体积为25 mL,初始磷浓度为20 mg·L−1,反应温度为25 ℃,反应时间为24 h,溶液pH值为4.0—11.0)。由图5可以发现,当溶液初始pH值由4增加至5时,Mg/La复合材料的单位吸附量由13.1 mg·g−1略微降低至12.5 mg·g−1,下降率仅为5.0%;当pH值由5增加到6时,Mg/La复合材料的单位吸附量保持不变;当pH值由6增加到11时,Mg/La复合材料的单位吸附量由12.5 mg·g−1缓慢下降至11.5 mg·g−1,下降率仅为8.0%。这说明Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的吸附去除具有较为广阔的pH值适应性。
-
天然水体中通常存在Na+、K+、Ca2+和Mg2+等阳离子以及Cl−、HCO3−和SO42-等阴离子。揭示它们对Mg/La复合材料吸附水中磷酸盐的影响,对于了解Mg/La复合材料吸附水中磷酸盐的性能是至关重要的。溶液共存NaCl、CaCl2、MgCl2、KCl、NaHCO3和Na2SO4等电解质对Mg/La复合材料吸附水中磷酸盐的影响也列于图5中(吸附剂投加量为25 mg,溶液体积为25 mL,初始磷浓度为20 mg·L−1,溶液pH值为7.0,反应温度为25 ℃,反应时间为24 h,共存离子浓度均为2 mmol·L−1)。由图5可以发现,溶液共存NaCl、KCl、MgCl2、NaHCO3和Na2SO4条件下Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的单位吸附量均接近于不存在共存电解质条件下的单位吸附量,而共存CaCl2条件下Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的单位吸附量则远远高于不存在共存电解质条件下的单位吸附量。这说明,溶液共存的Na+、K+、Cl−、Mg2+、HCO3−和SO42-对Mg/La复合材料吸附水中磷酸盐的影响可以忽略不计。这也进一步说明Mg/La复合材料对共存Na+、K+、Mg2+、Ca2+、Cl−、HCO3−和SO42-等阴阳离子的水体中的磷酸盐具有高度的选择性吸附。另外,上述结果也说明了,共存的Ca2+极大地促进了Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的吸附,这对于利用Mg/La复合材料去除天然水体中的磷酸盐是有利的,因为天然水体中往往存在一定浓度的Ca2+。
-
为了揭示Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的吸附机理,本研究采用XRD对吸附磷酸盐后Mg/La复合材料进行表征,并采用XPS对吸附磷酸盐前后的Mg/La复合材料进行对比表证,结果见图6和图7。从图6中可见,吸附磷酸盐后Mg/La复合材料中的主要晶体成分仍为Mg(OH)2和La(OH)3,没有发现新的晶型物质的生成。这可能是因为磷酸盐被Mg/La复合材料吸附后所生成的物质是无定形的缘故。从图7中可见,吸附磷酸盐后Mg/La复合材料的XPS图谱中不仅存在La 3d、Mg 1s和O 1s峰,而且存在P 2p峰。这说明将Mg/La复合材料与磷溶液接触之后,磷酸盐已经被成功地负载到了Mg/La复合材料表面上。从图7(b)中可见,吸附磷酸盐后Mg/La复合材料的P 2p峰位于133.12 eV。这个值高于NaH2PO4·2H2O的P 2p峰的结合能(132.9 eV)[28]和通过静电吸引作用被磁性阳离子水凝胶-N+(CH3)3基团所吸附磷酸盐的P 2p峰的结合能(131.9 eV)[17]。这说明磷酸盐与Mg/La复合材料之间的相互作用强于静电吸引作用,Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的吸附主要归功于化学吸附作用。从图7(c)中可见,吸附磷酸盐后,Mg/La复合材料的La 3d 5/2峰发生了轻微的偏移。这说明Mg/La复合材料中的La(OH)3与磷酸盐之间发生了配位体交换反应并形成了LaPO4[29]。从图7(d)中可见,吸附磷酸盐后,Mg/La复合材料的Mg 1s峰发生了偏移,出现了新的含镁物质的峰。这说明Mg/La复合材料中Mg(OH)2与磷酸盐之间发生化学反应并生成MgHPO4和Mg3(PO4)2等镁磷化合物,也是 Mg/La复合材料吸附水中磷酸盐的重要机制[30]。对比图2和图7可以发现,吸附磷酸盐后,Mg/La复合材料表面的羟基基团数量下降(M-OH的占比从吸附之前的43.4%下降到吸附之后的38.6%)。这说明Mg/La复合材料表面的羟基基团对其吸附水中磷酸盐会起到非常重要的作用,配位体交换作用是Mg/La复合材料吸附水中磷酸盐的重要机制。综上所述,Mg/La复合材料吸附水中磷酸盐的机制主要为:La(OH)3与磷酸盐之间的配位体交换并生成LaPO4,以及Mg(OH)2和磷酸盐之间的化学反应并生成MgHPO4和Mg3(PO4)2等镁磷化合物。
-
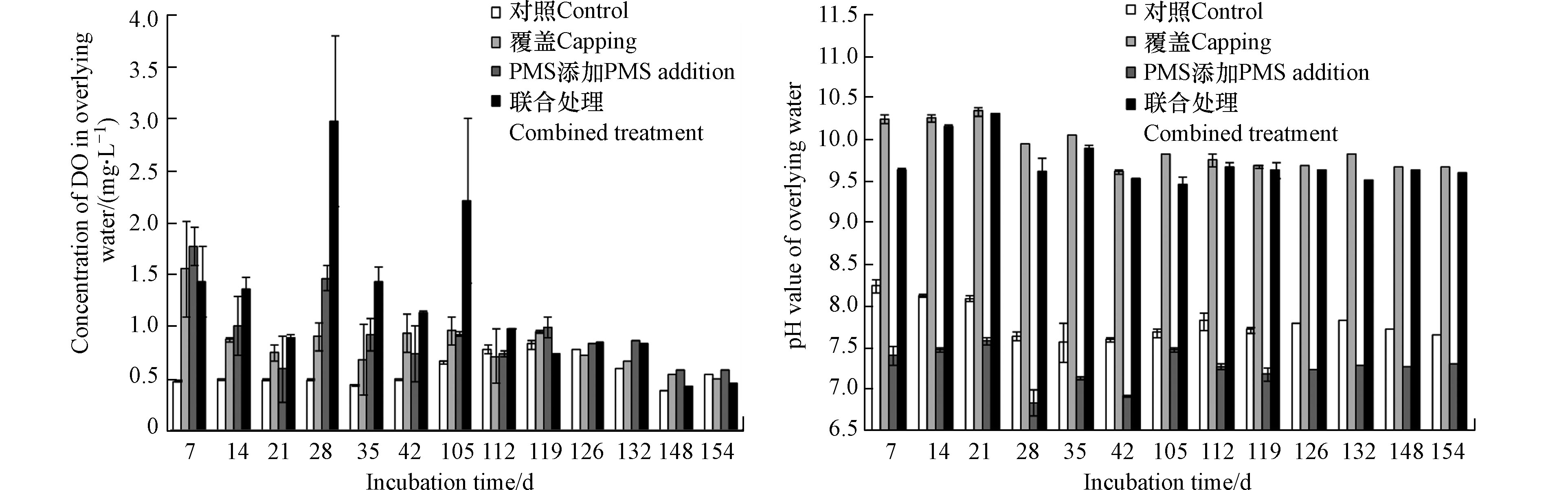
图8是对照组、Mg/La复合材料覆盖组、PMS添加组和组合组上覆水中DO浓度和pH值随时间变化而变化的规律。由图8中可以发现,对照组上覆水中DO浓度位于0.38—0.83 mg·L−1,说明对照组中底泥在其培养期间处于缺氧状态。对于Mg/La复合材料覆盖组,上覆水中DO浓度除了刚开始时稍微有点高外(1.56 mg·L−1),大部分时间上覆水DO浓度均处于较低的水平(当培养时间为14—154 d时,上覆水中DO浓度位于0.49—0.97 mg·L−1)。这说明培养一定时间后,Mg/La复合材料覆盖组中的底泥会处于缺氧状态。当底泥培养时间为7—105 d时,Mg/La复合材料覆盖组上覆水中DO浓度略微高于对照组。这可能是因为覆盖层阻止了上覆水中DO向底泥的扩散,从而阻止了底泥对上覆水中DO的消耗。另外,当底泥培养时间为7—105 d时,PMS添加组上覆水中DO浓度也略微高于对照组。这可能是由于PMS自身分解产生新生态氧,使得上覆水中DO浓度升高[20-22]。需要指出的是,向底泥中添加PMS一段时间之后,上覆水中DO浓度仍然会变得很低。这说明向底泥中添加PMS对上覆水中DO浓度的影响是有时效性的。当底泥培养时间为7—105 d时,组合组上覆水中DO浓度高于对照组(图8)。这可能归功于覆盖层的阻挡效应和PMS的增氧效应。但是,在底泥培养的后期,组合组上覆水中DO浓度仍然会处于很低的水平,此时底泥会处于缺氧状态。
-
由图8中还可以发现,对照组、Mg/La复合材料覆盖组、PMS添加组和组合组上覆水pH值分别位于7.58—8.25、9.62—10.4、6.85—7.58和9.55—10.33。这说明,对照组和PMS添加组上覆水的pH值在整个底泥培养期间比较稳定,仅发生轻微的波动,且在中性pH值附近波动。以上结果也说明,Mg/La复合材料的覆盖导致了上覆水pH值的升高。这主要归咎于Mg/La复合材料中Mg(OH)2的溶解。
-
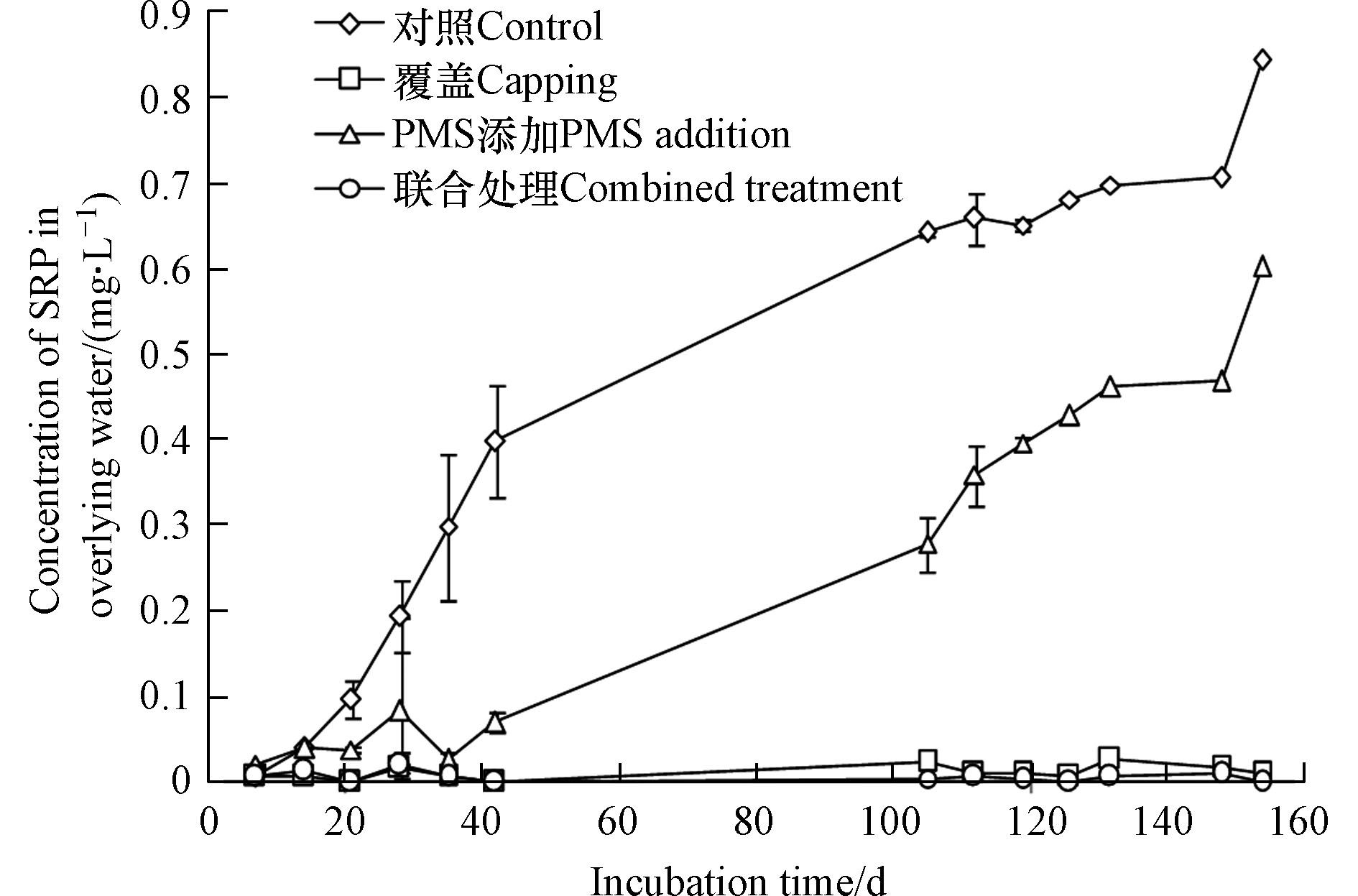
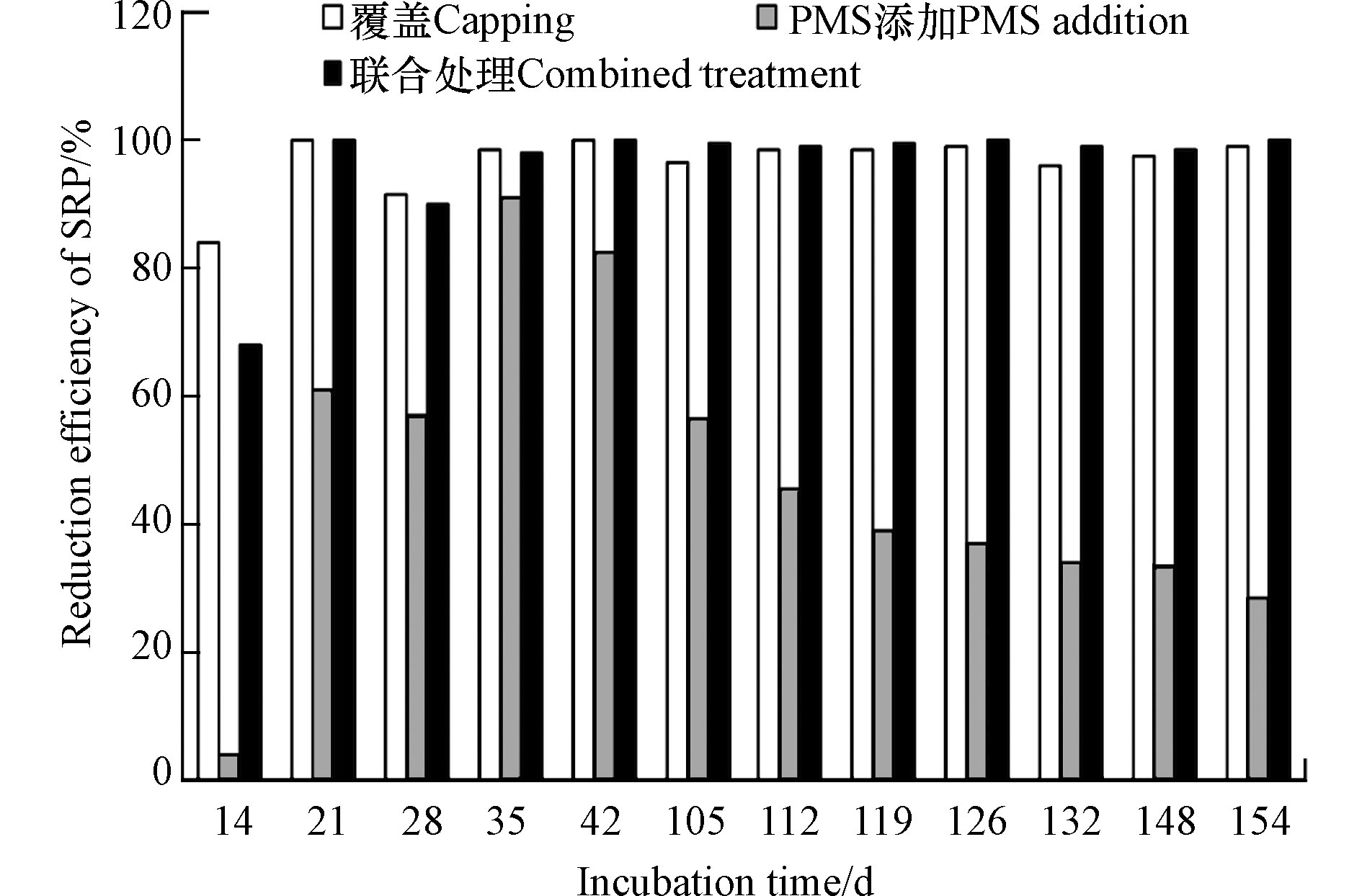
图9是对照组、Mg/La复合材料覆盖组、PMS添加组和组合组上覆水中SPR浓度随时间的变化而变化的规律。图10为Mg/La复合材料覆盖、PMS添加以及二者的组合对上覆水中SRP的削减率。由图9中可以发现,对于对照组,上覆水中SRP浓度总体上随着底泥培养时间的延长而上升。当底泥培养进行到第154 d时,对照组上覆水中SRP浓度达到了0.841 mg·L−1。根据公式(8)计算得到对照组中底泥磷的平均释放速率为0.868 mg·(m2·d)−1。这说明,在缺氧条件下,底泥中的磷可释放进入上覆水体。文献研究表明,在缺氧条件下,底泥中的三价铁氧化物/氢氧化物可被铁异化还原菌所转化为二价铁氧化物/氢氧化物,进而被溶解释放,与此同时被铁氧化物/氢氧化物所吸附的磷也会被释放[31]。因此,磷铁同步释放机制是缺氧条件下底泥中磷向上覆水体中释放的重要机制。
从图9还可见,Mg/La复合材料覆盖组上覆水中SRP浓度均小于等于0.027 mg·L−1。当底泥培养时间为14—154 d时,Mg/La复合材料覆盖组上覆水中SRP浓度远远小于对照组(图9),根据计算得到的Mg/La复合材料覆盖对上覆水体中SRP的削减率位于84%—100%(图10)。这说明Mg/La复合材料覆盖可有效控制底泥中磷向上覆水体中释放。底泥中的磷可通过静态释放或动态释放向上覆水迁移[32]。对于静态释放,间隙水中溶解态磷主要通过浓度梯度扩散机制穿越底泥-水界面向上覆水迁移[32]。动态释放是由表层底泥再悬浮引起的磷迁移[32]。在无扰动且缺氧条件下,底泥中的磷会首先释放出来进入间隙水中,继而通过分子扩散机制穿过底泥-水界面进入上覆水体中。将Mg/La复合材料覆盖到底泥-水界面上方后,所形成的覆盖层会通过La(OH)3与磷酸盐之间的配位体交换作用和Mg(OH)2与磷酸盐之间的化学反应作用机制吸附间隙水中的SRP,从而导致间隙水中SRP浓度的下降,进而降低了上覆水和底泥间隙水之间SRP浓度差,底泥-水界面SRP扩散通量随之下降,最终导致上覆水中SRP浓度处于非常低的浓度水平。
从图9还可见,PMS添加组上覆水中SRP会随之底泥培养时间的延长而逐渐增加,到第154 d时上覆水中SRP浓度达到了0.601 mg·L−1。这说明,在缺氧条件下,经PMS处理后的底泥仍然会向上覆水体中释放磷。但是,当底泥培养时间为21—154 d时,PMS添加组上覆水中SRP的浓度小于对照组(图9),根据计算确定的PMS添加对上覆水中SRP的削减率为28.6%—91.0%(图10)。这说明,PMS添加可以有效地降低底泥中磷向上覆水体中释放的风险。这可能归功于这样一个事实:PMS释放出来的新生态氧会抑制底泥中三价铁氧化物/氢氧化物的还原溶解,从而抑制了铁结合态磷的释放。
另外,当底泥培养时间为14—154 d时,Mg/La复合材料覆盖和PMS添加的组合组上覆水中SPR浓度也始终明显低于对照组,甚至低于PMS添加组(图9),联合使用对上覆水中SRP的削减率为68.0%—100%(图10)。这说明Mg/La复合材料覆盖和PMS添加的联合使用也同样可以有效抑制底泥内源磷的释放,并且其抑制效果优于单独添加PMS。特别需要指出的是,单独的Mg/La复合材料覆盖技术对底泥磷释放的控制效率与Mg/La复合材料覆盖-PMS添加组合技术差别不明显。这可能归功于Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐吸附能力卓越的缘故。
-
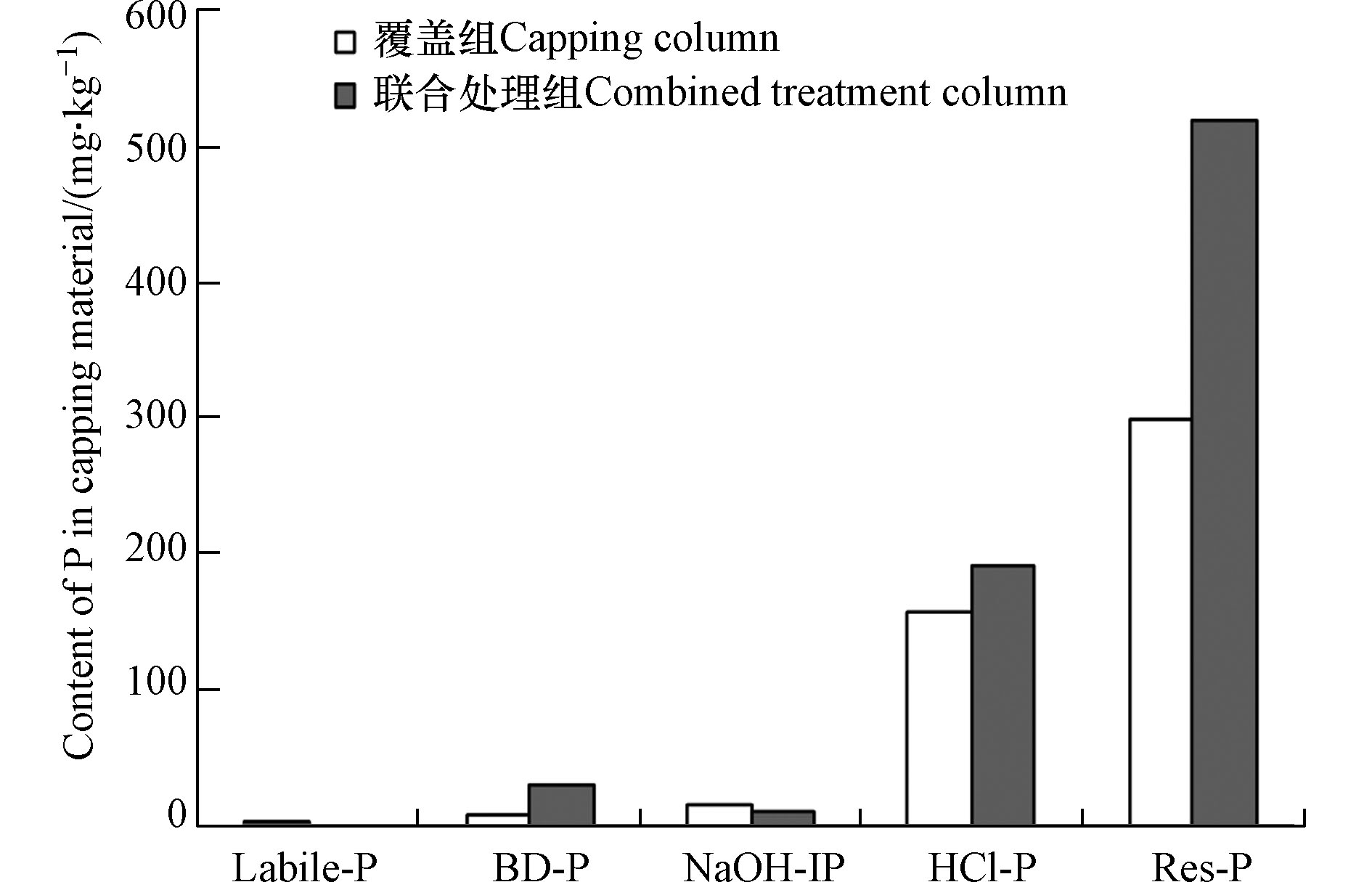
如果被Mg/La复合材料覆盖层所吸附磷的稳定性差,那么利用Mg/La复合材料覆盖控制水体底泥磷释放的长期效果将难以得到保证。通常,被固体材料所吸附磷的稳定性与它的赋存形态是密切相关的[33]。分析被Mg/La复合材料覆盖层所吸附磷的形态分布特征,对于Mg/La复合材料的实际应用是至关重要的。从图11可见,对于单纯的覆盖组,Mg/La复合材料中Labile-P、BD-P、NaOH-IP、HCl-P和Res-P含量分别为1.66、6.45、12.7、157、300 mg·kg−1,分别占总可提取态磷(TEP)的0.3%、1.4%、2.7%、32.9%和62.7%。对于联合处理组,Mg/La复合材料中Labile-P、BD-P、NaOH-IP、HCl-P和Res-P含量分别为0.691、29.3、11.1、190、519 mg·kg−1,分别占TEP的0.1%、3.9%、1.5%、25.4%和69.2%。Labile-P的释放风险很高[33-34]。BD-P在缺氧条件下很容易被释放出来[33-34]。Labile-P和BD-P均属于潜在可移动态磷[33]。NaOH-IP和HCl-P属于较为稳定的磷,它们在缺氧且通常pH(5—9)条件下不容易被释放出来[33]。Res-P是非常稳定的,很难被重新释放出来[33]。进一步计算得到单独覆盖组中Mg/La复合材料覆盖层的潜在可移动态磷占比仅为1.7%,联合处理组中Mg/La复合材料覆盖层的潜在可移动态磷占比仅为4.0%。这说明,绝大多数被Mg/La复合材料覆盖层所吸附的磷在缺氧且通常pH(5—9)条件下难以被重新释放出来。
2.1. Mg/La复合材料的表征
2.2. Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的吸附行为和机理
2.2.1. 吸附动力学
2.2.2. 吸附等温线
2.2.3. 溶液pH的影响
2.2.4. 共存阴阳离子的影响
2.2.5. 吸附机理
2.3. Mg/La复合材料及其与PMS联用对水体内源磷释放的控制效果与机制
2.3.1. 上覆水中DO浓度的动态变化
2.3.2. 上覆水pH值的动态变化
2.3.3. 上覆水中SRP浓度的动态变化
2.3.4. 被覆盖材料所吸附磷的形态分布特征
-
(1)Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附模型均可用于描述Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的等温吸附行为,根据Langmuir模型确定的最大吸附量为15.5 mg·g−1。与准一级动力学模型相比,准二级和Elovich动力学模型更适合用于描述Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的吸附动力学过程。Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的吸附去除具有较为广阔的pH值适应性。溶液共存Ca2+极大地促进了Mg/La复合材料对水中磷酸盐的吸附,而共存的Na+、K+、Mg2+、Cl−、
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的影响则可忽略不计。(2)Mg/La复合材料吸附水中磷酸盐的机理为La(OH)3与磷酸盐之间的配位体交换作用和Mg(OH)2与磷酸盐之间的化学反应作用。
(3)Mg/La复合材料单独覆盖以及联合使用PMS添加和Mg/La复合材料覆盖均可以有效抑制缺氧条件下水体底泥内源磷的释放,使得上覆水体中SPR浓度处于很低水平,并且它们的控磷效果均优于单独添加PMS。绝大多数被Mg/La复合材料覆盖层所吸附的磷以HCl-P和Res-P形式存在,在缺氧且通常pH(5—9)条件下难以被重新释放出来。
(4)Mg/La复合材料是一种有希望的用于控制水体底泥磷释放的活性覆盖材料。







 下载:
下载: