-
溴系阻燃剂(BFRs)阻燃效率高、耐热性好、适应性强,能有效阻止高分子材料燃烧,广泛用于电子元件、塑料制品等产品中,是目前世界上使用的阻燃剂中产量最高、消耗量最大、阻燃效率最好的有机阻燃剂之一[1]。目前常用的溴系阻燃剂主要有四溴双酚A(tetrabromobisphenol A,TBBPA)、多溴联苯醚(polybrominated diphenyl ethers,PBDEs)和六溴环十二烷(hexabromocyclododecane,HBCD)等,其中TBBPA约占世界溴系阻燃剂总使用量的60%[2]。中国是TBBPA类溴代阻燃剂的主产国,2020年TBBPA类溴代阻燃剂的年产量超过了18万吨。TBBPA及其衍生物既可用作反应型阻燃剂,亦可用作添加型阻燃剂,溴科学与环境论坛(BSEF)报告称,58%的TBBPA作为反应型阻燃剂,以共价键与其他分子结合成为聚合物,应用于印刷电路板的环氧树脂、聚碳酸酯和酚醛树脂中;约18%的TBBPA作为添加型阻燃剂用于丙烯腈-丁二烯-苯乙烯(ABS)树脂或高抗冲聚苯乙烯(HIPS)的生产[3]。添加型阻燃剂与产品的结合力不强,它们在使用处置过程中容易滤出,进入环境[4],进而吸附在室内灰尘、土壤、沉积物等介质中,具有潜在的环境危害性[5]。据报道,武汉某垃圾填埋场附近TBBPA的平均浓度高达24030 ng·g−1dw(干重)[6],TBBPA生产地之一山东寿光的土壤中TBBPA的浓度在1.64—7758 ng·g−1dw之间[7],安徽巢湖水样中TBBPA浓度为4.8 μg·L−1,远高于世界环境水中TBBPA的浓度[8],同时,巢湖沉积物中也检测到518 ng·g−1dw的TBBPA[9],虽然TBBPA工业衍生物在TBBPA类阻燃剂中占比仅为约18%[3],但它们在多种环境介质中的污染水平却明显高于TBBPA,例如,室内灰尘中检测到四溴双酚A双(2,3-二溴丙基)醚(TBBPA-BDBPE)含量为9.96 μg·g−1dw,而TBBPA的检出量为3.44 μg·g−1dw[10- 11];浏阳河河流沉积物中四溴双酚A双烯丙基醚(TBBPA-BAE)的浓度为13 μg·g−1dw,约为TBBPA浓度(0.132 μg·g−1dw)的100倍[12]。TBBPA及其衍生物的生物累积性和潜在毒性,特别是内分泌干扰效应,引起了人们的广泛关注[5]。此外,进入环境中的TBBPA类BFRs也可能在环境条件下,发生转化,通过结构转变生成新型环境污染物,产生未知的环境风险[13]。
光解是环境中有机污染物的主要转化方式,也是常用的环境有机污染物的消除途径[14]。在直接光解中,有机物吸收辐照光中的能量变为激发态,发生光转化;在间接光解过程中,有机物可能与另一种受激物接触,获得转移能量,或者与光照状态下生成的活性氧物种(如羟基自由基、单线态氧等)反应而发生转化[14]。TBBPA极易发生光降解,在太阳光(或模拟日光)、紫外光等条件下均会发生转化,且TBBPA的光转化过程受多种因素的影响,如体系pH值、TBBPA初始浓度、溶解氧、催化剂、有机质等。TBBPA的光转化产物结构多样,主要通过脱溴、β-断裂、羟基化等过程产生。TBBPA衍生物的环境浓度显著高于TBBPA,但因分析方法和商品化标准品的缺失,其相关的环境降解过程研究很少[15]。因此研究TBBPA及其衍生物在环境中的光转化过程、机理以及产物,对评估其潜在的环境危害和健康风险至关重要。
-
模拟自然环境条件下TBBPA光降解的研究中,光源有太阳光(或模拟日光)、紫外灯等不同的选择。模拟日光照射操作简单、成本低,有利于最大程度模拟TBBPA在自然环境状态下的光转化过程;紫外光的能量比日光强,实验室内采用紫外灯辐照可以大幅缩短实验时间。
-
TBBPA是一种疏水性可电离有机化合物,其pKa1和pKa2分别为7.5和8.5[15],在不同条件下,由于TBBPA的离子化,TBBPA会以分子态和离子态TBBPA−、TBBPA2-的形式存在。在光解实验中,溶液的pH会对TBBPA的降解速度产生影响,这可能与不同pH条件下,TBBPA的离子状态有关。
Eriksson等[16]研究了溶液pH值对TBBPA降解速率的影响,发现当溶液pH低于TBBPA的pKa2时,反应速率常数随着pH的升高而升高,当溶液pH高于TBBPA的pKa2时,反应速率常数随pH的升高保持相对恒定,在pH=10时观察到最快的降解速率,在紫外线照射下,TBBPA(0.77 μmol·L−1)的半衰期(t1/2)为16 min。Han等[17]在腐殖酸存在条件下,318 nm时测得TBBPA的吸收光谱值随着pH(pH<pKa2时)的增加而增加,绘制成pH-吸收光谱图发现曲线与Eriksson等[16]获得的pH-反应速率常数图曲线相似,Han等[17]的实验结果与Eriksson等[16]的观察结果相似,认为TBBPA的光降解速率随着pH的增加而增加是因为TBBPA对光的吸收值随pH的增加而增加[17]。反应机理的不同导致不同pH条件下TBBPA降解效率的差异,TBBPA离子化的程度随pH的升高而扩大,形成更多的负离子态,同时吸收光谱的红移,使反应加快[18]。TBBPA在酸性条件下主要发生苯环断裂,碱性条件下主要发生水解反应,而苯环断裂的速度要小于水解的速度,因此随pH的升高(2、4、6、8、10),TBBPA的反应速率常数逐渐升高[18]。而Bao等[15]测得当非缓冲体系的初始pH大于pKa2时,随着初始pH值增加TBBPA的反应速率常数有略微下降的趋势,这可能是因为在光转化过程中产生的偏酸性的中间产物(溴化氢)、小分子羧酸等物质,导致反应体系pH的降低,较低的溶液pH反过来限制偏酸性中间产物的累积,进一步阻碍TBBPA的转化,造成反应速率减慢[15]。可见在缓冲体系中,TBBPA的反应速率常数会随着pH的增加而增加,当pH值超过TBBPA的pKa2时,TBBPA的反应速率常数随pH值增加变化幅度较小。
-
TBBPA溶液的初始浓度会对TBBPA的降解产生影响,TBBPA的反应速率常数随初始浓度的增加而减小。在TBBPA含量较低的情况下,TBBPA的半衰期较短,例如,在pH值为10时,紫外线照射下,TBBPA(0.77 μmol·L−1)的t1/2为16 min[16],模拟太阳光照射15 min,TBBPA(1.8 μmol·L−1)转化率可达48.6%[19],随着溶液初始浓度的增加,TBBPA的降解率会降低[20],在pH 12时,紫外线照射240 min,少于20%的TBBPA(100 μmol·L−1)发生降解,这可能与较高浓度的TBBPA使溶液不透光,或者与反应生成的中间产物对光源的竞争有关[21]。当浓度超过0.15 mmol·L−1时,TBBPA的反应速率常数随浓度升高不再显著降低,对反应速率常数与TBBPA的初始浓度进行相关性研究发现在较大的初始浓度下,伪一级动力学可能不成立[20]。
-
为探究自然界水环境中溶解氧的存在是否会对TBBPA的降解产生影响,王晓雯[18]分别研究了有氧和无氧环境下TBBPA的光降解过程。TBBPA在有氧和无氧条件下的反应速率常数分别是7.66×10−3 min−1和6.95×10−3 min−1,说明TBBPA在两种环境下均可进行降解反应且降解效率差异不大,但进行电子顺磁共振检测后发现空气中的氧气对反应体系是有影响的,采取添加氧自由基捕获剂的方式,证实在有氧条件下氧气主要通过产生单线态氧活性物种对TBBPA光降解产生影响[18]。氧气作为电子受体,经过一系列变化生成单线态氧,攻击TBBPA中的C-Br键和异丙基,使得TBBPA通过脱溴和β-断裂发生降解。在自然环境中,TBBPA自敏化产生单线态氧的量子产率较低,而环境中存在的腐殖酸会产生单线态氧,对TBBPA的光降解产生影响[17]。Han等[17]用紫外可见光照射腐殖酸悬浮溶液中的TBBPA,检测到单线态氧是在波长大于400 nm时产生的关键活性氧物种,且TBBPA降解速率随着腐殖酸浓度和pH值的增加而增加[22]。
-
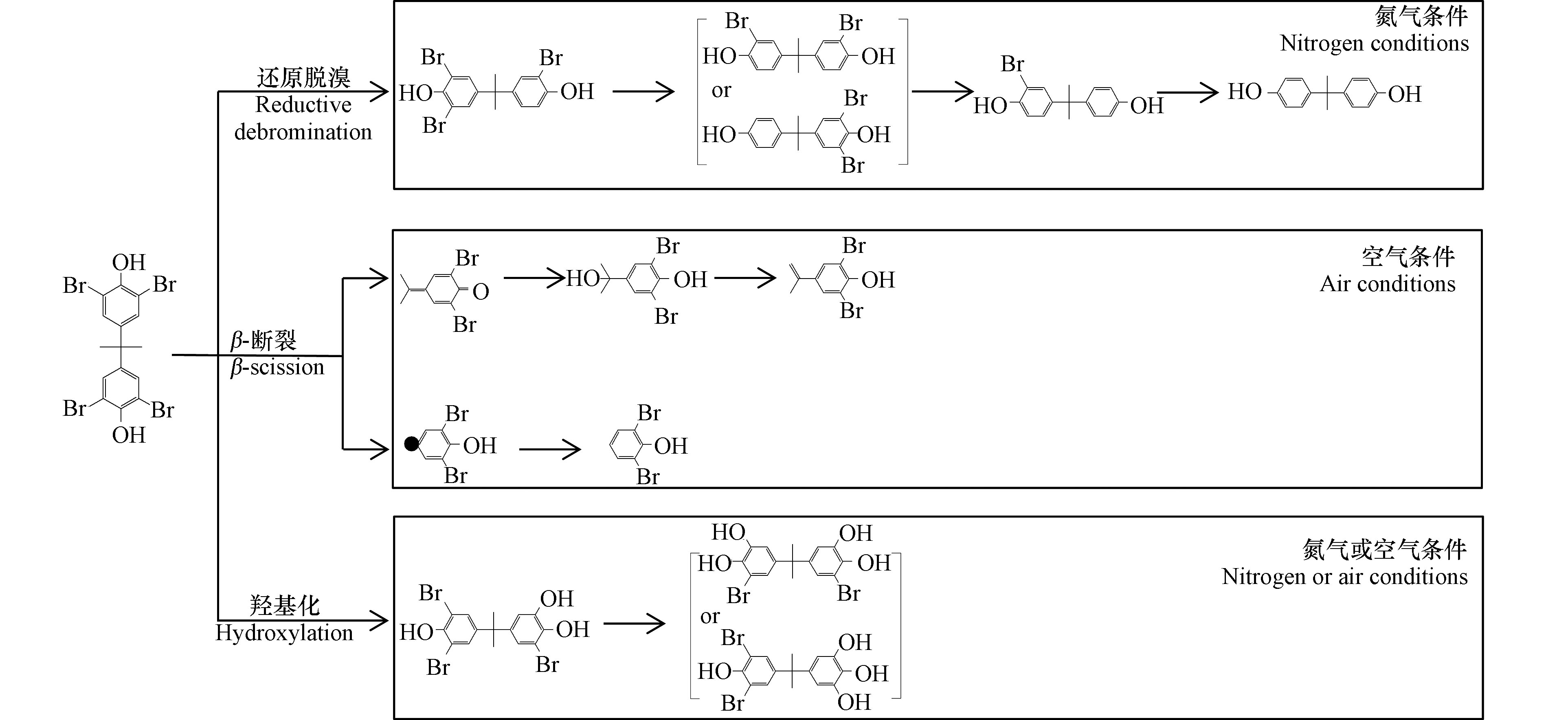
TBBPA接受光照发生光降解的主要途径可以归纳为还原脱溴、β-断裂和羟基化[21, 23-24](图1):
(1)在通入氮气条件下,TBBPA的C-Br键遭到电子攻击,主要发生脱溴反应,生成三溴双酚A,随光照时间的增加,逐步还原脱溴生成二溴双酚A和双酚A。
(2)在通入空气条件下,O2作为电子受体可以减少脱溴过程,O2经过一系列变化生成单线态氧,使得TBBPA生成超氧自由基和苯氧自由基,苯氧自由基发生C-C键的断裂后形成两种不稳定的中间体,其中一种可水解生成4-异丙醇基-2,6-二溴苯酚,再经过水解生成4-异丙烯基-2,6-二溴苯酚;另一种可通过去质子转化成2,6-二溴苯酚。
(3)在通入氮气或空气条件下,TBBPA吸收太阳光发生水解反应,生成羟基化三溴双酚A,该产物持续发生水解生成羟基化二溴双酚A。
-
自然光的条件下,TBBPA降解较为缓慢,但改变一定的条件,如加入催化剂、光敏剂等会使情况发生改变,如加快反应速度、提高反应效率等[25] ,表1总结了几种常用光催化剂对TBBPA的降解效率及机理。
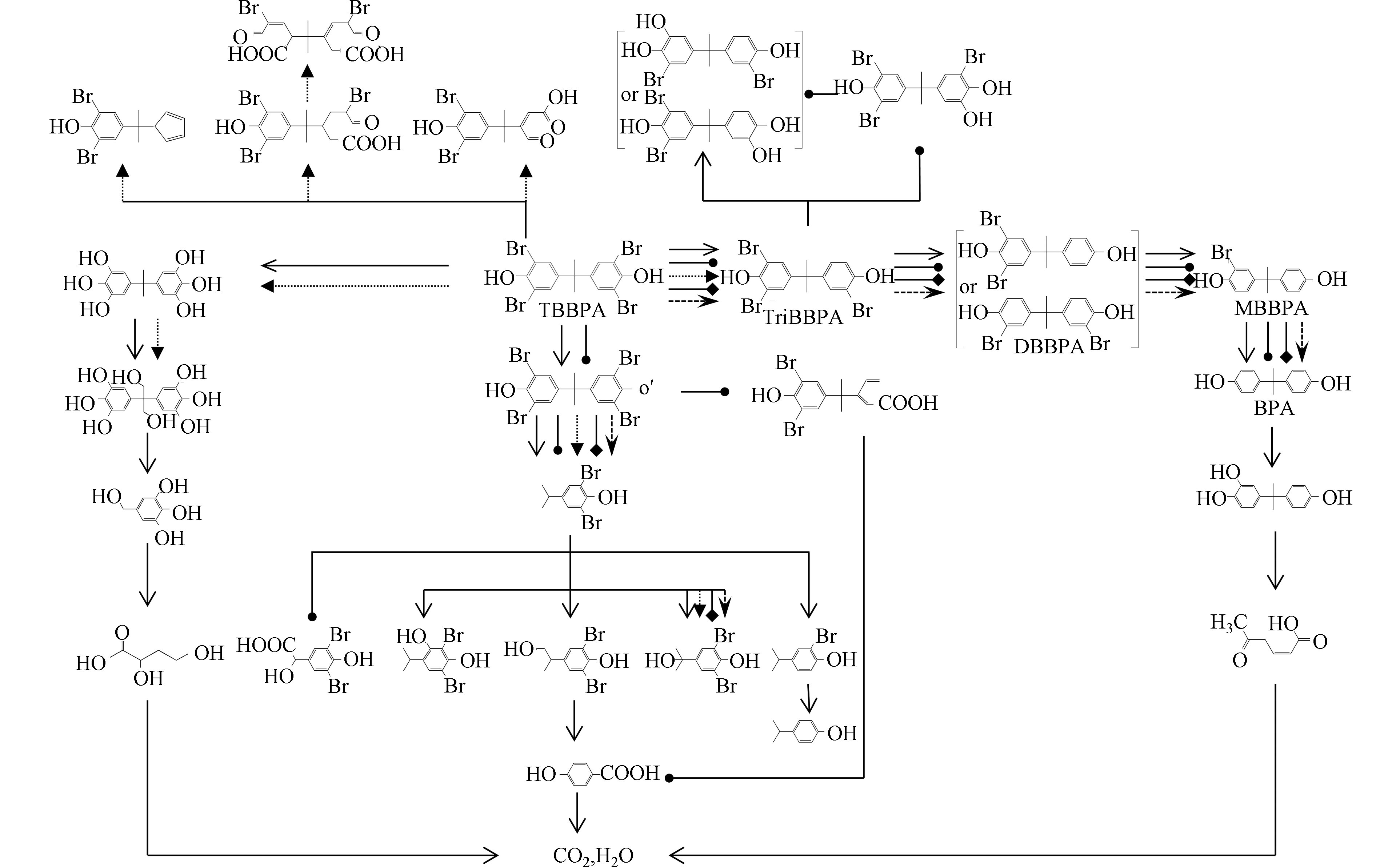
光催化材料接受太阳光的照射过程中,产生电子(e−)和空穴(h+),伴随着电子和空穴的产生、迁移和消除,在电荷分离过程中生成了一些活性物质,如电子和溶解氧反应生成的超氧自由基(·O2−)、单线态氧(1O2),空穴和OH−、H2O反应生成羟基自由基(·OH)等。空穴、·O2−、·OH可以攻击TBBPA中的C—Br键和异丙基,使其通过脱溴、β-断裂、羟基化等过程生成降解产物,如脱溴产物三溴双酚A、二溴双酚A、一溴双酚A和双酚A,羟基化产物羟基-三溴双酚A、二羟基-二溴双酚A和四羟基双酚A,此外,也会产生4-异丙烯基-2,6-二溴苯酚、4-(2-羟丙基)-2,6-二溴苯酚、2,6-二溴-4-异丙基苯酚等产物[26] (图2).
-
二氧化钛具有优异的光电特性和化学稳定性,在光催化领域备受关注,广泛应用于环境修复、自清洁涂层、自杀菌材料、纺织工业中染料的降解等领域。但因其光生载流子复合率较高,对太阳光的利用率较低,极大的限制了它的应用,开发新型高效复合二氧化钛光催化剂,如金属掺杂、非金属掺杂、共掺杂、半导体复合、染料敏化、表面阴离子修饰等一直是光催化领域研究的热点[27-28]。
用0.05 g Cu-TiO2@HQ作催化剂,可见光照射下降解18.4 μmol·L−1的TBBPA溶液,10 min内降解率达99.4%[29],紫外光照射10 min,2%-银/二氧化钛将TBBPA(7.4 μmol·L−1)完全降解,表观反应速率常数(kapp)达到0.63 min−1[30]。可见金属掺杂后的二氧化钛对TBBPA的催化性能有了很大提升,掺杂金属在二氧化钛带隙中引入掺杂能级,致使价带电子跃迁到导带所需能量降低,因而有利于提高二氧化钛对可见光的吸收。Zhou等[26]将g-C3N4(石墨相氮化碳)和聚苯胺共修饰的二氧化钛纳米管材料作为催化剂,在pH=3的条件下,可见光照射120 min时TBBPA(18.4 μmol·L−1)的光转化效率超过94%[26],1 g·L−1的电气石(20%)-二氧化钛作催化剂降解TBBPA(18.4 μmol·L−1)时,一级反应速率常数为0.0748 min−1[31],磁性石墨烯TiO2的复合材料MG-TiO2-3%(3%的磁性石墨烯TiO2复合材料)对TBBPA(18.4 μmol·L−1)也具有高效的降解效率,体系在230 W汞灯照射60 min后,TBBPA降解率达99.5%[32],改性后的二氧化钛催化材料具有窄带隙、大的比表面积和较低的光致电子和空穴复合速率,光生电子产生、迁移、消除过程中与O2、OH−等反应生成的活性物质如·O2−、·OH等攻击TBBPA的C—Br键和异丙基,使TBBPA经过脱溴、β-断裂和羟基化等过程发生降解,极大地提升了催化剂对光的利用率。
-
纳米材料(NMs)具有高表面积、超硬度、超导性以及耐腐蚀性等特征优势[33]。例如银纳米颗粒(AgNPs)在表面等离子共振效应下,产生光生电子(e−)-空穴对(h+),光生电子与溶解氧反应生成1O2、O2•−,与OH−反应生成·OH,1O2和·OH通过氧化作用使TBBPA 的β键断裂而导致其整体结构被破坏,而O2•−通过还原路径使TBBPA脱溴,pH值为7.5,Ag+浓度为2 mmol·L−1条件下,AgNPs能在1 h内降解74.9%的TBBPA(3.7 μmol·L−1)[34]。金属与多孔骨架物质构建的复合光催化材料对TBBPA具有更高的降解性能,可见光光源下Tang等[35]用10 mg·L−1 CoO@石墨烯催化120 min后,TBBPA(7.4 μmol·L−1)降解率为73.4%,这是由于可见光照射下电子(e−)-空穴(h+)在CoO上分离,随后又快速地转移到具有巨大表面积的石墨烯材料上,电子和溶解氧结合形成的超氧阴离子自由基,与吸附在CoO@石墨烯表面的TBBPA分子反应使其降解[35]。
-
铋基半导体材料BiOX(X = Cl,Br,I),因其独特的开放式层状结构、间接光跃迁特性、高化学稳定性和催化活性,已经成为高性能光催化剂的主要研究方向[36-37]。
Xu等[19]首次探索用BiOBr催化降解TBBPA(1.8 μmol·L−1),紫外-可见光照射15 min后,计算出BiOBr和市售光催化剂P25二氧化钛的表观速率常数kapp分别为0.388 min−1和0.101 min−1,P25二氧化钛的降解率为75.5%,相同条件下,BiOBr的加入使得TBBPA几乎完全降解,证实了BiOBr优异的光催化性能[19]。负载铂纳米粒子的微球状BiOBr具有较强的光捕获能力,模拟太阳光照射5 min,Pt-BiOBr对TBBPA(18.4 μmol·L−1)的去除率达到100%;可见光条件下,15 min时Pt-BiOBr对TBBPA(18.4 μmol·L−1)的去除率为98.4%,铂纳米粒子作为光生电子的储库,使得光生电子-空穴对在Pt-BiOBr的界面上快速分离和传输[38]。因此,与BiOBr相比,Pt-BiOBr的光催化活性进一步增强。将50 mg合成的BiOBr/BiOI/Fe3O4(2∶2∶0.5)加入到TBBPA(73.5 μmol·L−1)溶液中,模拟可见光光源照射60 min时,降解率能达到90%。可见光下三元复合催化剂性能的提升主要归因于BiOBr和BiOI之间价带能级差与独特的异质结构,这使得电荷有效分离并且阻止了电子空穴对的复合,Fe3O4的加入增强了催化材料的磁分离性和可回收性[39]。在异质结构金属银-层状铌酸铋(Ag/Bi5Nb3O15)双组分体系中,Bi5Nb3O15负载Ag含量为20%时,73.5 μmol·L−1的TBBPA暴露于模拟太阳光照射下,30 min内转化率高达95.7%[40]。改良后的铋系光催化复合材料的光生电子分离率提高、对可见光的吸收范围变宽、光生电子-空穴复合率降低,催化活性不断增强。
-
硫酸根自由基(SO4•−)高级氧化技术是一种新兴的环境治理技术,它通过紫外线照射、碱性条件、过渡金属及其氧化物、高温、超声波等方式激活过硫酸盐(PS)化合物,活化产生SO4•−,SO4•−是一种单电子氧化剂,具有很强的氧化能力,同时对苯环类有机物具有一定的选择性,广泛用于各种环境介质中有机污染物的降解去除。过硫酸盐活化材料是决定过硫酸盐高级氧化体系性能的关键因素,因此开发高活性、绿色、低成本的过硫酸盐活化材料是目前的研究热点[41-42]。
在紫外/碱/过硫酸盐体系中,240 min内80%以上的初始浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1的TBBPA发生降解,而相同条件下的水溶液体系内,TBBPA仅降解了15%左右,可能是SO4•−和·OH的联合氧化作用促进了TBBPA的降解[20],且该体系pH越高,TBBPA的降解速率越快,这与Furman等[43]的发现一致,即碱活化的PS体系的反应性能随碱∶过硫酸盐的物质的量比的增加而增强。在91.9 μmol·L−1的TBBPA溶液中加入1 g·L−1单原子Mn负载氮化碳(SA-Mn/g-C3N4)活化0.2 g·L−1的过一硫酸盐,当pH值为10时,氙灯照射下,TBBPA在30 min内的去除率为100%[44]。
-
类芬顿法产生的羟基自由基(·OH)和单线态氧(1O2)的氧化作用是TBBPA光降解主要原因[45]。在UV/Fenton环境下,以钛铁矿石为催化剂,可使TBBPA快速降解,例如在pH值为6.5条件下,0.125 g·L−1 Fe2.02Ti 0.98O4和10 mmol·L−1 H2O2体系中,紫外线照射下,TBBPA(36.8 μmol·L−1)溶液在240 min内几乎完全降解[46]。在25 ℃、pH 6.5时,紫外照射0.50 g·L−1 Fe2.04Cr0.96O4和10 mmol·L−1 H2O2体系,120 min时TBBPA(36.8 μmol·L−1)的降解率达到90%[47]。紫外照射下,磁铁矿表面的氧可以快速还原Fe(Ⅲ)为Fe(Ⅱ),同时产生·OH,生成的Fe(Ⅱ)还可以继续与H2O2反应产生·OH,大量·OH攻击TBBPA分子的C—Br键和异丙基,使得TBBPA分子发生脱溴和β-断裂,因此添加了催化剂的UV/Fenton体系对TBBPA降解表现出高效的催化活性。
-
Gao等[48]通过简单易行的沉淀工艺制备了具有光催化性能的AgCl/AgBr复合光催化剂,测得在最优化条件即pH=10,材料投加量为0.6 g·L−1,光照强度为5700 lm时,9.19 μmol·L−1的TBBPA溶液30 min内降解效率可达98.49%,可见光激发复合银基材料,产生光生电子和光生空穴,光生电子与空气中的氧气反应生成·O2−,空穴与空气中的水、OH−反应生成·OH,这两种自由基可以与TBBPA反应达到降解的效果[48]。
-
与TBBPA相似,TBBPA衍生物也是水体、土壤表层、沉积物及生物样品中检出的高浓度污染物,但目前很少有研究集中在TBBPA衍生物的光转化方面。虽然TBBPA衍生物的结构相似,但它们的转化过程往往存在显著差异,在含有甲醇钠、甲醇和二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)的溶液中,四溴双酚A-双(2,3-二溴丙基)醚在亲核试剂的辅助下可以通过脱卤作用快速降解,而在60℃ 99.5% DMF的条件下不能去除四溴双酚A双烯丙基醚[49]。在紫外线照射下,三溴双酚A的光转化效率约为TBBPA的两倍且经过不同的降解过程,三溴双酚A和TBBPA的主要产物往往不同[16]。TBBPA 衍生物的降解产物多为未知物质,且缺少相关的商品化标准物质,致使同时分析衍生物和降解产物的有效方法仍处于缺失状态。因此,TBBPA衍生物在环境中降解转化过程及机理的多样化,在未来的研究中值得更多的关注[5]。
-
TBBPA产量不断增大,可在生产、使用、处置等环节进入环境,且目前已在多种环境介质中检测到TBBPA的存在。TBBPA光解可发生在自然光照和模拟光照条件下,在模拟TBBPA环境光解实验中发现,在缓冲体系中,TBBPA的反应速率常数会随着pH的增加而增加,当pH值超过TBBPA的pKa2时,TBBPA的反应速率常数随pH值增加变化幅度较小;TBBPA的反应速率常数随初始浓度的增加而减小;体系中的溶解氧主要通过产生单线态氧促使TBBPA发生光降解。当体系中存在光催化剂时,光解速率更快,目前常用的几种催化剂主要是通过形成超氧自由基(·O2−)、单线态氧(1O2),空穴等几种活性物质,攻击TBBPA中的C—Br键和异丙基,使其通过脱溴、β-断裂、羟基化等过程发生降解。
光照辐射是卤代污染物的主要环境降解途径之一,在光解过程中促使母体化合物产生结构复杂的中间产物和终产物,如TBBPA脱溴产物三溴双酚A、二溴双酚A等是常见的中间产物,光照辐射中产生的自由基可促使TBBPA通过β-断裂或羟基化产生单苯环的小分子产物如4-异丙烯基-2,6-二溴苯酚、4-(2-羟丙基)-2,6-二溴苯酚等。
与TBBPA相比,TBBPA衍生物具有和TBBPA相似的结构,但环境浓度水平更高,结构更复杂,反应位点和转化路径更多,由此可以预测其环境转化产物的数量更多,但目前有关TBBPA工业衍生物的光降解转化结果鲜有报道,其潜在的生态风险更难掌控。在TBBPA及衍生物光降解过程的研究中,通过控制反应条件使降解更彻底,减少或避免中间有毒物质的产生,以及揭示危害较高的衍生物光解过程及机理,将为准确评估 TBBPA 类溴代阻燃剂的环境风险提供重要的基础数据。
四溴双酚A的光转化过程及机理
Photodegradation process and mechanism of Tetrabromobisphenol A
-
摘要: 四溴双酚A(Tetrabromobisphenol A,简称TBBPA)作为目前使用最广泛的溴系阻燃剂,通过生产、使用、处置等环节进入到环境中,并通过环境降解过程转化为新型的有机污染物,产生未知环境风险。光转化是环境中有机污染物降解的主要方式之一,转化效率高、速度快。本文综述了TBBPA及其衍生物在光照条件下的模拟环境光转化和光催化过程及机理。TBBPA及其衍生物在光辐射条件下易发生转化,转化效率和速率受到pH、初始浓度、溶解氧等环境条件的影响,光催化剂会显著提升TBBPA的转化速率。TBBPA的光转化机理包括脱溴、β-断裂、羟基化等,产物主要包括三溴双酚A、二溴双酚A、4-异丙烯基-2,6-二溴苯酚、2,6-二溴苯酚、羟基化三溴双酚A等。相较于TBBPA,针对TBBPA衍生物的光降解过程和机理尚不明晰,未来需要进一步对TBBPA及衍生物光转化过程进行研究,为其迁移转化过程的机理和相关未知污染物的监控提供理论支持,为综合评估TBBPA类溴代阻燃剂的环境风险提供科学依据。Abstract: As the most widely used brominated flame retardant (BFR) at present, tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) enters the environment during the process of production, usage and disposal. TBBPA and its derivatives could transform into new organic substances through environmental degradation process, resulting in unknown environmental risks. Photodegradation is one of the main pathways to eliminate organic substances in the environment with high efficiency and fast speed. In this paper, the simulative environment photodegradation and photocatalysis process and mechanism of TBBPA and its derivatives under light conditions were reviewed. TBBPA and its derivatives are easily transformed under the condition of light radiation. The photodegradation efficiency and rate are affected by pH, initial concentration, dissolved oxygen and other environmental conditions. The photocatalysts can significantly improve the conversion rate of TBBPA. The photodegradation mechanism includes debromination, β-scission, hydroxylation, etc, and the products mainly include tribromobisphenol A, dibromobisphenol A, 4-isopropyl-2,6-dibromophenol, 2,6-dibromophenol, hydroxylated tribromobisphenol A and so on. Compared with TBBPA, the photodegradation process and mechanism of TBBPA derivatives are still unclear, and further studies on the photodegradation process of TBBPA and its derivatives are needed in the future. It will provide theoretical support for the mechanism of their migration and transformation process and the monitoring of related unknown pollutants, and provide a scientific basis for the comprehensive assessment of environmental risks of brominated flame retardants.
-

-
表 1 TBBPA的光催化降解条件
Table 1. Photocatalytic degradation conditions of TBBPA
光催化剂
Photocatalyst反应条件
Reaction condition降解效率
Degradation efficiency反应机理
Reaction mechanism参考文献
ReferencesCu-TiO2@HQ Xe灯( < 420 nm),
10 mg·L−1 TBBPA10 min,
99.4%光照Cu-TiO2@HQ 生成的光生eCB−和hVB+快速消耗,生成活性物质攻击TBBPA使其发生脱溴、β-断裂和羟基化等过程 [29] 2%-Ag/TiO2 紫外-可见光(>360 nm),
4 mg·L−1 TBBPA,pH=8.010 min,
100%光生eCB−与O2反应生成的·O2−与hVB+是TBBPA降解的主要原因 [30] g-C3N4和聚苯胺共修饰的TiO2 氙灯模拟可见光,
10 mg·L−1 TBBPA,pH=3.0120 min,
>94%光生eCB−与hVB+的产生、迁移和消除的过程中生成的氧化性物质如hVB+、·OH和·O2−是TBBPA降解
主要原因[26] 电气石(20%)-二氧化钛 汞灯(λmax=365 nm),
10 mg·L−1 TBBPA,
循环水控制反应温度60 min,
100%光生eCB−被电气石阳极吸附,hVB+与OH−和H2O反应生成·OH [31] MG-TiO2-3%(3%的磁性石墨烯TiO2复合材料) 230 W汞灯,
10 mg·L−1 TBBPA,r.t.60 min,
99.5%光生eCB−与O2反应生成的·O2−、hVB+与OH−和H2O反应生成的·OH外加hVB+使TBBPA发生脱溴、取代和脱羟基过程 [32] AgNPs 350 W氙灯模拟太阳光,1 mg·L−1
HA 溶液,2 mg·L−1 TBBPA,
pH=7.51 h,
74.9%AgNPs光激发后可产生eCB−与hVB+,eCB−与溶解氧反应生成1O2、O2•−,hVB+与OH−反应生成·OH [34] CoO@石墨烯 氙灯模拟可见光,
4 mg·L−1 TBBPA,
pH=8.0± 0.1120 min,
73.4%可见光照射下,eCB−和hVB+在CoO上分离,eCB−和溶解氧生成·O2−,hVB+与OH−和H2O反应生成·OH [35] BiOBr Xe灯模拟太阳光照射,1 mg·L−1 TBBPA,r.t. 15 min,
100%光照BiOBr变为激发态后,eCB−将O2还原生成·OH,·OH使TBBPA发生脱溴、β-断裂和羟基化 [19] Pt–BiOBr Xe灯模拟太阳光照射/可见光
10 mg·L−1 TBBPA,r.t.Xe灯5min,100%;
可见光15min,98.4%Pt使得光照后BiOBr形成的eCB−和hVB+快速分离,eCB−与O2接触生成O2•−,O2•−与hVB+使TBBPA降解 [38] BiOBr/BiOI/Fe3O4 氙灯模拟可见光,
40 mg·L−1 TBBPA,r.t.60 min,
90%BiOBr和BiOI之间的价带能级差使光生eCB−快速转移,与O2反应生成·O2− [39] Ag/Bi5Nb3O15 氙灯模拟可见光
(320 nm <λ< 680 nm),
40 mg·L−1 TBBPA
(303±2)K30 min,
95.7%光照Ag/Bi5Nb3O15后,产生eCB−和hVB+ 、eCB−与O2生成O2•−,进一步反应生成OH•,共同作用使TBBPA降解 [40] 碱和过硫酸盐溶液 紫外光(<350 nm), 过硫酸盐溶液,
0.1mmol·L−1 TBBPA,
(28±2) oC,pH=12.00± 0.05240 min,
>80%过硫酸盐被碱和紫外活化生成SO4•−,同时SO4•−与OH−反应生成·OH,SO4•−和·OH共同作用 [20] 单原子Mn负载氮化碳(SA-Mn/g-C3N4) 可见光(>400 nm),过硫酸盐溶液,
50 mg·L−1 TBBPA,pH=1030 min,
100%SO4•−、·OH、1O2和光生电子空穴是主要的活性氧化物,可与TBBPA反应
使其降解[44] Fe2.02Ti 0.98O4 紫外光,芬顿反应,
20 mg·L−1 TBBPA,
25 oC,pH=6.5240 min,
> 97%Fe3+、Fe2+与H2O2反应生成·OH ,·OH攻击TBBPA的C-Br键和β键 [46] Fe2.04Cr0.96O4 紫外光,芬顿反应,
20 mg·L−1 TBBPA,
25 oC,pH=6.5120 min,
约90%Fe3+、Fe2+与H2O2反应生成·OH ,·OH攻击TBBPA的C-Br键和β键 [47] AgCl/AgBr复合光
催化剂自发光二极管,
5 mg·L−1 TBBPA,
pH=1030 min,
98.49%可见光激发复合银基材料,产生光生电子和光生空穴,与空气中的水、OH−、O2反应生成·OH、·O2− [48] -
[1] 田凤麟, 杨金水. 我国溴系阻燃剂的现状及发展方向 [J]. 盐业与化工, 2007, 36(4): 46-48. TIAN F L, YANG J S. The present situation and developing direction of the bromide flame retardants in China [J]. Journal of Salt and Chemical Industry, 2007, 36(4): 46-48(in Chinese).
[2] LAW R J, ALLCHIN C R, de BOER J, et al. Levels and trends of brominated flame retardants in the European environment [J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 64(2): 187-208. [3] COVACI A, VOORSPOELS S, ABDALLAH M A E, et al. Analytical and environmental aspects of the flame retardant tetrabromobisphenol-A and its derivatives [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2009, 1216(3): 346-363. [4] LIU K, LI J, YAN S J, et al. A review of status of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in China [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 148: 8-20. [5] LIU A F, ZHAO Z S, QU G B, et al. Transformation/degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A and its derivatives: A review of the metabolism and metabolites [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 243: 1141-1153. [6] YU C H, HU B. Novel combined stir bar sorptive extraction coupled with ultrasonic assisted extraction for the determination of brominated flame retardants in environmental samples using high performance liquid chromatography [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2007, 1160(1-2): 71-80. [7] ZHU Z C, CHEN S J, ZHENG J, et al. Occurrence of brominated flame retardants (BFRs), organochlorine pesticides (OCPs), and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in agricultural soils in a BFR-manufacturing region of North China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 481: 47-54. [8] YANG S W, WANG S R, LIU H L, et al. Tetrabromobisphenol A: Tissue distribution in fish, and seasonal variation in water and sediment of Lake Chaohu, China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2012, 19(9): 4090-4096. [9] FENG A H, CHEN S J, CHEN M Y, et al. Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) and tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in riverine and estuarine sediments of the Pearl River Delta in Southern China, with emphasis on spatial variability in diastereoisomer- and enantiomer-specific distribution of HBCD [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2012, 64(5): 919-925. [10] WU Y Y, LI Y Y, KANG D, et al. Tetrabromobisphenol A and heavy metal exposure via dust ingestion in an e-waste recycling region in Southeast China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 541: 356-364. [11] ALI N, HARRAD S, GOOSEY E, et al. "Novel" brominated flame retardants in Belgian and UK indoor dust: Implications for human exposure [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 83(10): 1360-1365. [12] QU G B, LIU A F, WANG T, et al. Identification of tetrabromobisphenol A allyl ether and tetrabromobisphenol A 2, 3-dibromopropyl ether in the ambient environment near a manufacturing site and in mollusks at a coastal region [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(9): 4760-4767. [13] LIU A F, SHI J B, QU G B, et al. Identification of emerging brominated chemicals as the transformation products of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) derivatives in soil [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(10): 5434-5444. [14] ZHOU S S, PAN X X, TANG Q Z, et al. Photochemical degradation of polyhalogenated carbazoles in hexane by sunlight [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 671: 622-631. [15] BAO Y P, NIU J F. Photochemical transformation of tetrabromobisphenol A under simulated sunlight irradiation: Kinetics, mechanism and influencing factors [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 134: 550-556. [16] ERIKSSON J, RAHM S, GREEN N, et al. Photochemical transformations of tetrabromobisphenol A and related phenols in water [J]. Chemosphere, 2004, 54(1): 117-126. [17] HAN S K, BILSKI P, KARRIKER B, et al. Oxidation of flame retardant tetrabromobisphenol A by singlet oxygen [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(1): 166-172. [18] 王晓雯. 模拟太阳光作用下水中四溴双酚A的光转化研究[D]. 烟台: 中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所, 2015. WANG X W. Study on the phototransformation of TBBPA in aqueous solution under solar light irradiation[D]. Yantai: Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015(in Chinese).
[19] XU J, MENG W, ZHANG Y, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A by mesoporous BiOBr: Efficacy, products and pathway [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2011, 107(3-4): 355-362. [20] GUO Y G, ZHOU J, LOU X Y, et al. Enhanced degradation of Tetrabromobisphenol A in water by a UV/base/persulfate system: Kinetics and intermediates [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 254: 538-544. [21] WANG X W, HU X F, ZHANG H, et al. Photolysis kinetics, mechanisms, and pathways of tetrabromobisphenol A in water under simulated solar light irradiation [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(11): 6683-6690. [22] HAN S K, de YAMASAKI T, YAMADA K I. Photodecomposition of tetrabromobisphenol A in aqueous humic acid suspension by irradiation with light of various wavelengths [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 147: 124-130. [23] GUO Y G, LOU X Y, XIAO D X, et al. Sequential reduction-oxidation for photocatalytic degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A: Kinetics and intermediates [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 241-242: 301-306. [24] XIONG J K, LI G Y, PENG P A, et al. Mechanism investigation and stable isotope change during photochemical degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in water under LED white light irradiation [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 258: 127378. [25] 晋艺聪, 刘丽华, 罗贤丽, 等. 四溴双酚-A的降解性和毒性研究进展 [J]. 中央民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 19(2): 5-10. JIN Y C, LIU L H, LUO X L, et al. Progress in study of degradability and ecotoxicology of TetrabromobisphenolA [J]. Journal of Minzu University of China (Natural Sciences Edition), 2010, 19(2): 5-10(in Chinese).
[26] ZHOU Q X, ZHAO D C, SUN Y, et al. g-C3N4- and polyaniline-co-modified TiO2 nanotube arrays for significantly enhanced photocatalytic degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A under visible light [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 252: 126468. [27] BUAMA S, JUNSUKHON A, NGAOTRAKANWIWAT P, et al. Validation of energy storage of TiO2 NiO/TiO2 film by electrochemical process and photocatalytic activity [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 309: 866-872. [28] 张晓燕. 有机小分子或无机酸修饰Cu-TiO2以提升其光催化性能的研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2020. ZHANG X Y. Studies on Cu-TiO2 modified by organic small molecule or inorganic acid to improve its photocatalytic performance[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2020(in Chinese).
[29] ZHANG X Y, CHEN Y N, SHANG Q K, et al. Copper doping and organic sensitization enhance photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide: Efficient degradation of phenol and tetrabromobisphenol A [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 716: 137144. [30] ZHANG Y H, ZHOU S X, SU X, et al. Synthesis and characterization of Ag-loaded p-type TiO2 for adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A [J]. Water Environment Research, 2020, 92(5): 713-721. [31] LI N, ZHANG J Q, WANG C P, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A by tourmaline-TiO2 composite catalyst [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2017, 52(12): 6937-6949. [32] CAO M H, WANG P F, AO Y H, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A by a magnetically separable graphene-TiO2 composite photocatalyst: Mechanism and intermediates analysis [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 264: 113-124. [33] 李文杰. 银纳米颗粒与脂质体及腐殖酸的相互作用及其原位合成与光催化应用[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2020. LI W J. Interaction of silver nanoparticles with liposome or humic acid and their in situ synthesis and photocatalytic applications[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2020(in Chinese).
[34] 李文杰, 虞盛松, 陈洁洁. 银纳米颗粒的绿色合成及其对四溴双酚A光催化降解的性能研究[J/OL]. 中国科学技术大学学报: 1-18. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1054.N.20210204.0848.002.html. LI W J, YU S S, CHEN J J. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their photocatalytic degradation performance of tetrabromobisphenol A[J/OL]. Journal of University of Science and Technology of China: 1-18. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1054.N.20210204.0848.002.html. (in Chinese).
[35] TANG Y L, DONG L F, MAO S, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic removal of tetrabromobisphenol A by magnetic CoO@graphene nanocomposites under visible-light irradiation [J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018, 1(6): 2698-2708. [36] ZHANG J, YUAN X Z, JIANG L B, et al. Highly efficient photocatalysis toward tetracycline of nitrogen doped carbon quantum dots sensitized bismuth tungstate based on interfacial charge transfer [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 511: 296-306. [37] ZHANG X, AI Z H, JIA F L, et al. Generalized one-pot synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic activity of hierarchical BiOX (X = Cl, Br, I) nanoplate microspheres [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(3): 747-753. [38] GUO W, QIN Q, GENG L, et al. Morphology-controlled preparation and plasmon-enhanced photocatalytic activity of Pt-BiOBr heterostructures [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 308: 374-385. [39] GAO S W, GUO C S, HOU S, et al. Photocatalytic removal of tetrabromobisphenol A by magnetically separable flower-like BiOBr/BiOI/Fe3O4 hybrid nanocomposites under visible-light irradiation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 331: 1-12. [40] GUO Y N, CHEN L, YANG X, et al. Visible light-driven degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A over heterostructured Ag/Bi5Nb3O15 materials [J]. RSC Advances, 2012, 2(11): 4656. [41] GHANBARI F, MORADI M. Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants: Review [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 310: 41-62. [42] 饶中庭. 废弃物衍生的nZVI/CuO@BC活化过二硫酸盐降解TBBPA研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020. RAO Z T. Research on degradation of TBBPA by waste-derived nZVI/CuO@BC activated peroxodisulfate system[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2020(in Chinese).
[43] FURMAN O S, TEEL A L, AHMAD M, et al. Effect of basicity on persulfate reactivity [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2011, 137(4): 241-247. [44] 柯倩. 过渡金属单原子负载石墨相氮化碳的制备及其降解污染物的应用研究[D]. 金华: 浙江师范大学, 2020. KE Q. Preparation of graphitic carbon nitride supported by transition mental single atom and application of pollutants degradation[D]. Jinhua: Zhejiang Normal University, 2020(in Chinese).
[45] 胡山, 王蒋镔, 郭耀广. 溴代阻燃剂四溴双酚A在环境中的降解转化研究进展[C]//《环境工程》2019年全国学术年会论文集. 北京, 2019: 785-790. [46] ZHONG Y H, LIANG X L, ZHONG Y, et al. Heterogeneous UV/Fenton degradation of TBBPA catalyzed by titanomagnetite: Catalyst characterization, performance and degradation products [J]. Water Research, 2012, 46(15): 4633-4644. [47] ZHONG Y H, LIANG X L, HE Z S, et al. The UV/Fenton degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A catalyzed by nanocrystalline chromium substituted magnetite [J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2014, 14(9): 7307-7314. [48] 高大方, 张刚. 复合光催化剂AgCl/AgBr降解水中四溴双酚A的研究 [J]. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 51(2): 50-55. GAO D F, ZHANG G. Photocatalytic degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A with composite AgCl/AgBr [J]. Journal of South China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 51(2): 50-55(in Chinese).
[49] RAHM S, GREEN N, NORRGRAN J, et al. Hydrolysis of environmental contaminants as an experimental tool for indication of their persistency [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(9): 3128-3133. -



 下载:
下载: