-
重金属作为一种持久性污染物,具有难降解、易积累、毒性大等特性,可通过大气干湿沉降、污水排放及面源污染等途径进入环境[1-5]。环境中排放的重金属进入水体后,易通过生物积累和生物放大进入人体,从而危害人群健康[6]。因此有必要研究水环境系统水体和沉积物中重金属的污染特征及潜在生态风险。水库作为重要的淡水资源,在农业灌溉、区域防洪、饮用水供给以及水电清洁能源等方面都扮演着重要的角色[7-8]。随着社会经济的发展,水库水环境重金属污染问题日益突出,对水库生态环境安全提出了挑战。有研究表明,三峡水库、丹江口水库及山美水库等表层沉积物都呈现一定程度的Cd和Pb污染,处于较高的生态风险等级[9-13]。
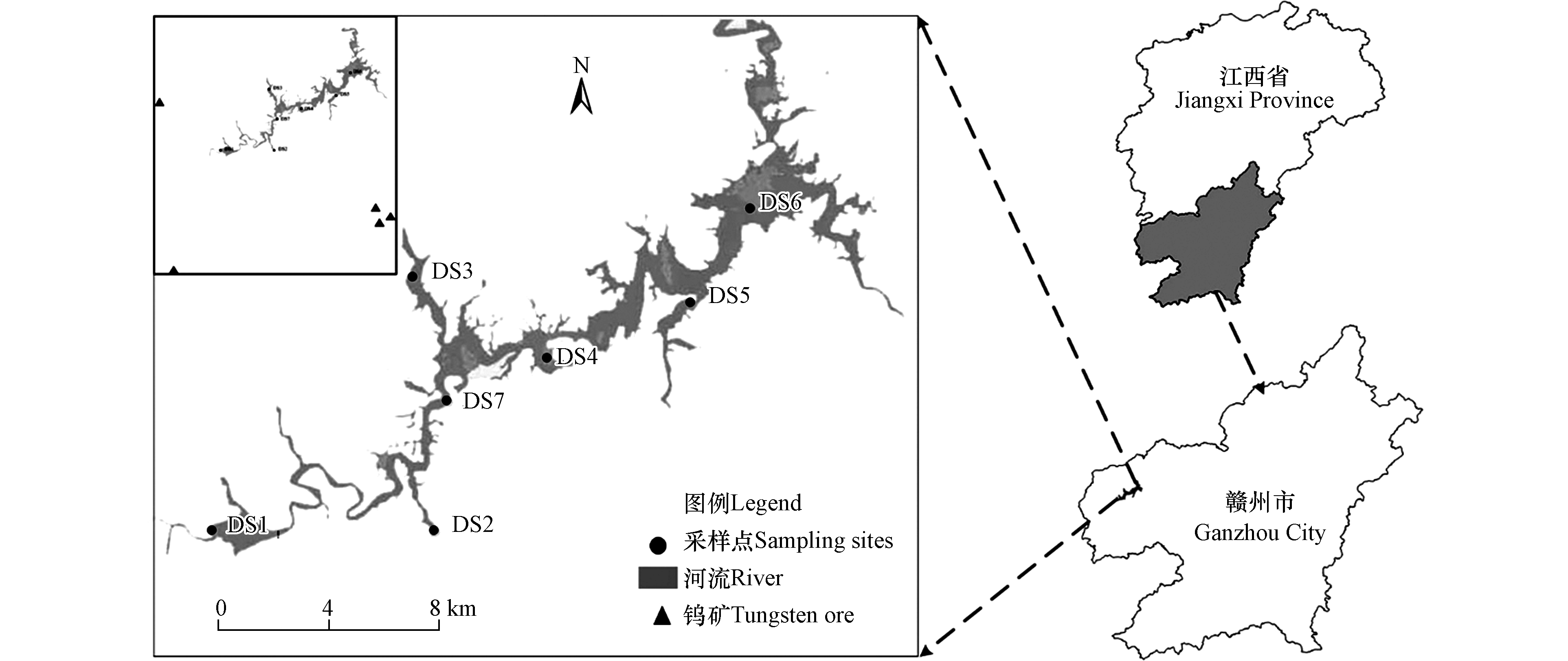
陡水水库位于江西省赣州市,横跨崇义县和上犹县,是一座以发电为主,结合渔业、航运、林业、城市供水、旅游等综合开发利用的大型水利工程[14]。有研究表明,崇义县矿产资源丰富,具有铜、铅、钨、钼等金属矿,但因历史上生产工艺落后,矿石回采率及选矿回收率不足八成,利用率仅为50%,加上多年的无序开采,矿区周围水质已被严重污染[15]。目前针对陡水水库水质方面的调查较少[14],尤其缺乏对整个库区重金属污染水平的研究。
本文以江西省赣州市陡水水库为研究对象,通过分析水库表层水体及沉积物中Cu、Zn、As、Hg、Pb和Cd等重金属的污染特征,阐述其时空分布特征及污染来源,评估重金属污染对生态环境的潜在风险,为水库水环境的综合治理提供科学指导和理论依据。
-
陡水水库建于1957年,距赣州市中心城区70 km,是一座重要的大型调节水库,库区人口达10万人之多。库区水域面积达3100万m2,蓄水量8×108 m3,森林面积2.27×108 m2。
该研究基于陡水水库地形及周边人口、农田和工矿企业分布的情况共设置7个采样点,见表1及图1。2018年2—11月,每月上旬在陡水水库采集水库表层水样,利用重力式抓斗采泥器采集水库表层沉积物样品,并使用便携式水质分析仪现场测定水体温度、pH及电导率。采集的水样装入500 mL聚乙烯塑料瓶中,并加入1∶1的硝酸调至pH值小于2.0,沉积物装入聚丙烯密封袋中,样品置于4℃保温箱中冷藏送至实验室分析。
-
采集的水样运至实验室后,过0.45 μm水系微孔滤膜,用硝酸酸化,王水消解。沉积物被剔除杂质后,研磨过100目筛,用HNO3-HF-HClO4消解。采用Agilen700X电感耦合等离子体质谱仪分析表层水和沉积物样品中Cu、Zn、As、Hg、Pb和Cd的含量。实验过程中使用的玻璃及聚丙烯容器均用15%硝酸溶液浸泡48 h;采用加标回收法,每隔10个样品添加2个有证标准物质(GBW-10020),设置10%的平行样。各元素的加标回收率范围为88.73%—108.41%,符合质量控制要求。
-
(1)单因子指数法
单因子指数法是将某种污染物实测浓度与该种污染物的评价标准进行比较,以确定水质类别的方法[16],单因子污染指数(Pi)计算公式为:
式中,Ci为水质指标i的实测浓度;Si为水质指标i的评价标准值,本次研究参考《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838-2002)Ⅲ类水质标准进行评价。
(2)内梅罗综合指数法
内梅罗综合指数法[17]是利用各污染因子的相对污染指数来评价水体的污染程度。内梅罗污染指数(P)计算公式为:
式中,Pi max为单因子污染指数最大值,Pi ave为各项单因子污染指数平均值,n为元素个数。内梅罗污染指数分级如表2所示。
-
(1)地积累指数法
地积累指数法[18]是国内外广泛应用的沉积物重金属污染评价方法之一,其计算公式为:
式中,Igeo为地积累指数;Bn为当地沉积物元素n的背景值(本文选取江西省赣州市土壤背景值[19]:Cu为20.7 mg·kg-1,Zn为68.1 mg·kg-1,As为8.32 mg·kg-1,Hg为75 mg·kg-1,Cd为157 mg·kg-1,Pb为51.65 mg·kg-1);Cn为元素n在待测沉积物中的实际含量;k为成岩作用引起的背景值波动参数,本研究取1.5。地积累指数分级如表3所示。
(2)潜在生态危害指数法
潜在生态危害指数法[20]既可以对单项重金属生态风险进行评价,又可以对多项重金属综合生态风险进行评价,其计算公式为:
Eir(单项重金属潜在生态危害指数):
RI(潜在生态风险指数):
式中,Eir为重金属i的潜在生态指数,Tir为重金属元素i的毒性系数。各元素的毒性系数:Cu为5,Zn为1,As为10,Hg为40,Cd为30,Pb为5。沉积物中重金属Eir和RI的分级标准如表4所示。
(3)生物毒性不利影响评价
生物毒性不利影响评价由Ingersoll等[21]提出,用于评价沉积物中重金属的混合生物效应。其计算公式为:
式中,Ci为沉积物中重金属i的实测浓度(mg·kg-1);PECi为重金属i可能效应浓度;n代表重金属种类。将单个重金属含量与相应的阈值效应浓度(TEC)和可能效应浓度(PEC)进行对比,若低于TEC表明生态毒性不可发生;若高于PEC则表明生态毒性会频繁发生[22]。重金属Cu、Zn、As、Hg、Cd和Pb的TEC值[23]分别为31.6、121、9.79、0.18、0.99和35.8,PEC值[23]分别为149、459、33、1.06、4.98和128,沉积物对生物毒性不利影响评价分级见表5。
-
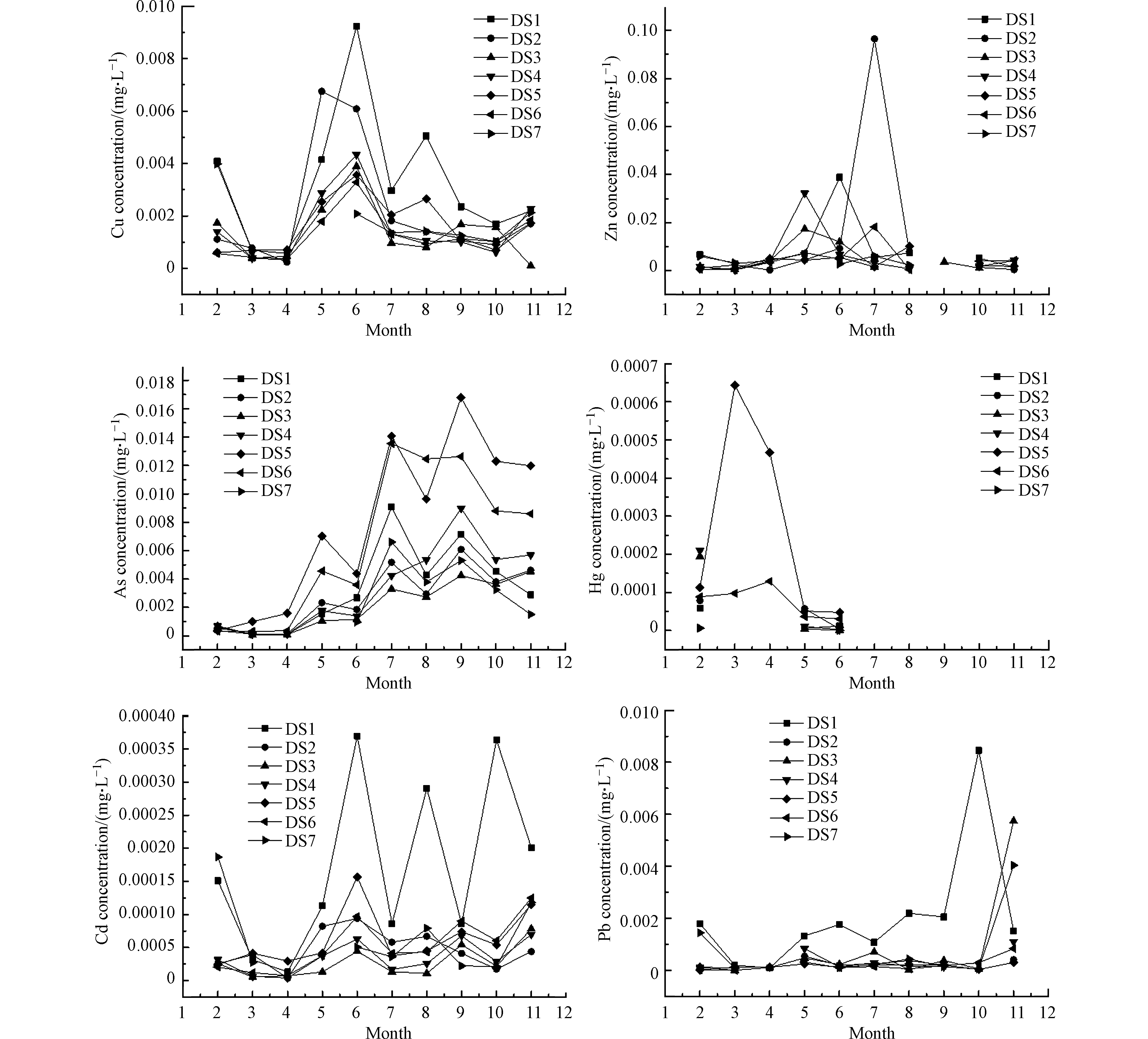
陡水水库表层水体中重金属浓度水平如图2所示,Cu、As和Cd元素在表层水体中均有检出,其浓度范围分别为0.10—9.24、0.06—16.8、0.004—0.37 μg L-1;Zn、Hg和Pb的浓度范围分别为nd—96.48、nd—0.64、nd—8.46 μg L-1,其中Hg在7—11月的水库表层水体中均未检出。从全年来看,表层水体重金属含量分布存在季节差异,其中As、Cd和Pb浓度在秋季最高,Cu和Zn浓度在夏季最高。从空间分布来看(见表6),表层水体重金属含量自南向北波动较大,其中Zn、As和Hg浓度呈现先升后降的趋势,而Cu、Cd和Pb浓度则呈现明显下降趋势。水库表层水体中Cu、Zn、As、Cd和Pb的浓度均低于《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838-2002)中的Ⅲ类标准,而Hg在DS3、DS4、DS5和DS6出现不同程度的超标,且主要集中在2—4月份,此时水库水位较低,污染物易聚集而造成水体污染。陡水水库表层水体中Hg的含量在不同季节表现出明显的差异性,可能源于矿山开采、大气沉降及污染废水排放等人为污染源。
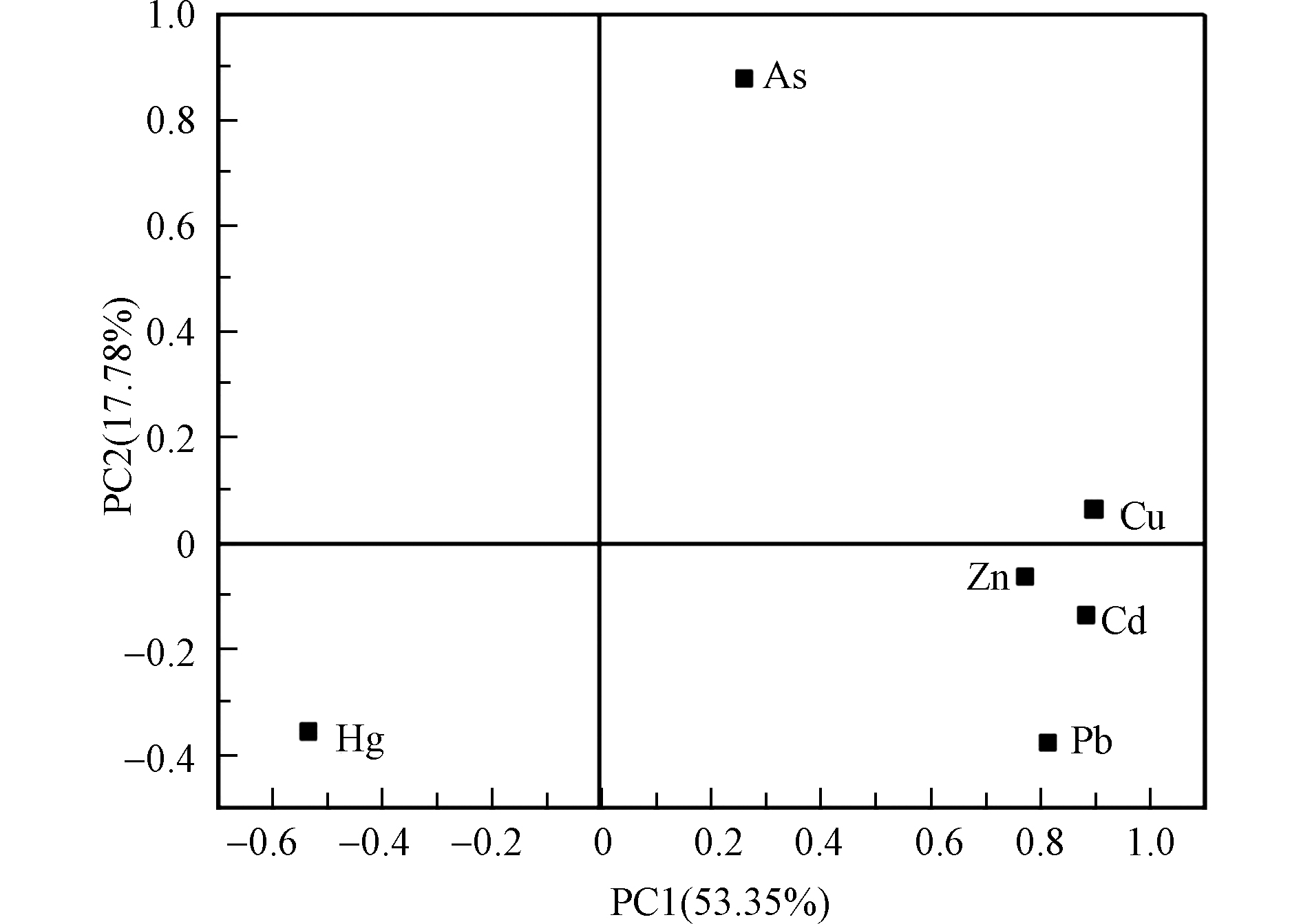
为探索陡水水库表层水体中重金属的主要来源,本研究采用主成分分析法对检出的6种重金属进行来源解析(Kaiseri-Meyer-Olkin 值为0.732),结果如图3所示。陡水水库表层水体中6种重金属可归纳为2个主成分,累积方差贡献率达到71.13%。从载荷系数来看,主成分1(PC1)主要由Cu、Cd和Pb这3种元素构成,其最高浓度均出现在DS1,大江流域于DS1处汇入陡水水库,流域周边的钨矿和稀土矿开采导致的河流污染,通过流域传送汇聚至DS1,因此可推断PC1源于陡水水库上游的矿山开采。主成分2(PC2)主要由As构成,其最高浓度出现在DS5,该点位离省道较近,其重金属污染可能源于采矿运输扬尘,因此可推断PC2由交通运输等人为活动所致。
-
陡水水库各采样点沉积物中重金属的含量水平如表7所示。各采样点沉积物中Zn的浓度水平最高,Hg和Cd的浓度水平较低,其中DS2和DS4沉积物中重金属浓度从大到小依次为:Zn>Cu>As>Pb>Hg>Cd;DS3和DS5沉积物中重金属浓度从大到小依次为:Zn>As>Cu>Pb>Hg>Cd;DS6和DS7沉积物中重金属浓度从大到小依次为:Zn>Cu>Pb>As>Hg>Cd。与江西省赣州市土壤背景值相比,陡水水库沉积物中Hg和Cd的浓度均低于当地土壤背景值,说明沉积物中Hg和Cd主要来源于成土母质,受地球化学成因的影响较大[24-25]。而Cu、Zn、As和Pb这4种元素分别超过当地土壤背景值的5.19—10.82倍、1.90—8.13倍、3.00—52.87倍和0.23—1.94倍,说明上述4种元素在沉积物中有明显的累积现象,反映了人为活动导致的环境污染。陡水水库附近工业企业较少,矿产资源多年的无序开采,已然造成周围水质的严重污染。有研究表明,崇义县最主要的矿产资源为钨锡矿,其主要伴生金属包括Cu、Pb和Zn等,且伴生金属的总储量大于钨矿总储量(比例为1.1:1)。因此陡水水库沉积物中超标重金属主要源于矿产资源的开采。
与国内外其他水库的沉积物相比,江西陡水水库沉积物中Cu、Zn、As、Hg和Cd的平均浓度均高于韩国、马塞卢、伊拉克及国内部分水库,Pb的平均浓度低于梅江清凉山水库而高于其他研究区域。总体而言,陡水水库沉积物中重金属的浓度处于较高水平。对陡水水库沉积物中重金属进行相关性分析,结果见表8。Pb与Zn、As呈极显著相关(P﹤0.01),表明其人为源与地球化学行为的相似性。Zn与As、Hg、Cd呈显著相关(P﹤0.05),Pb与Cu、Cd呈显著相关(P﹤0.05),Cd与Hg呈显著相关(P﹤0.05),说明其可能具有相似的来源、迁移和沉积过程。
-
陡水水库各采样点中重金属的单因子污染指数Pi和内梅罗综合污染指数P见表9。与地表水环境质量Ⅲ类标准相比,DS3—DS6表层水中Hg的Pi max值均大于1,而其余重金属的Pi值均小于1,说明陡水水库水体存在Hg污染。内梅罗综合污染指数表明,DS3—DS5表层水重金属的P值均大于1,其中DS5为重度污染,其余为轻度污染。DS5离省道较近,其重金属污染可能源于采矿运输扬尘。
-
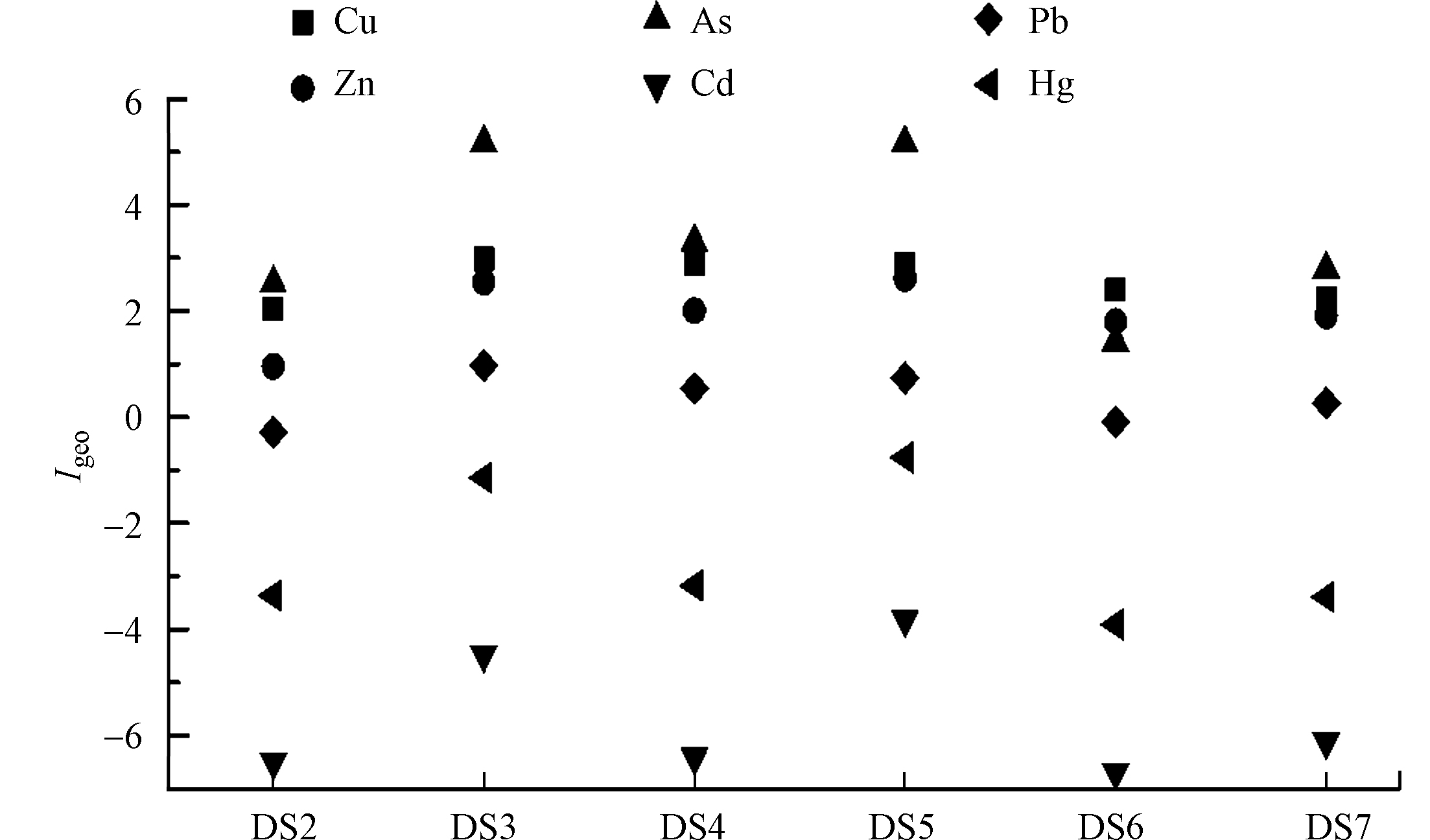
地累积指数评价结果见图4,陡水水库沉积物中除Cd和Hg外,其他元素均呈现不同程度的污染。DS2—DS5和DS7沉积物中重金属污染程度从大到小依次为:As>Cu>Zn>Pb>Hg>Cd;DS6沉积物中重金属污染程度从大到小依次为:Cu>Zn>As>Pb>Hg>Cd。陡水水库沉积物中As的污染较重,呈现偏中度-严重污染;其次为Cu和Zn,Cu呈中度污染,Zn呈轻度-中度污染;Pb在DS2和DS6沉积物中呈清洁状态,而在其他点位呈轻度污染。从沉积物受污染程度上看,DS3和DS5污染最重,可能源于居民生活排放、矿业开采及交通运输等人为活动;而DS2和DS6污染程度较轻,其中DS2为渔业捕捞码头,DS6离森林较近,其受矿业开采的的影响相对较小。
-
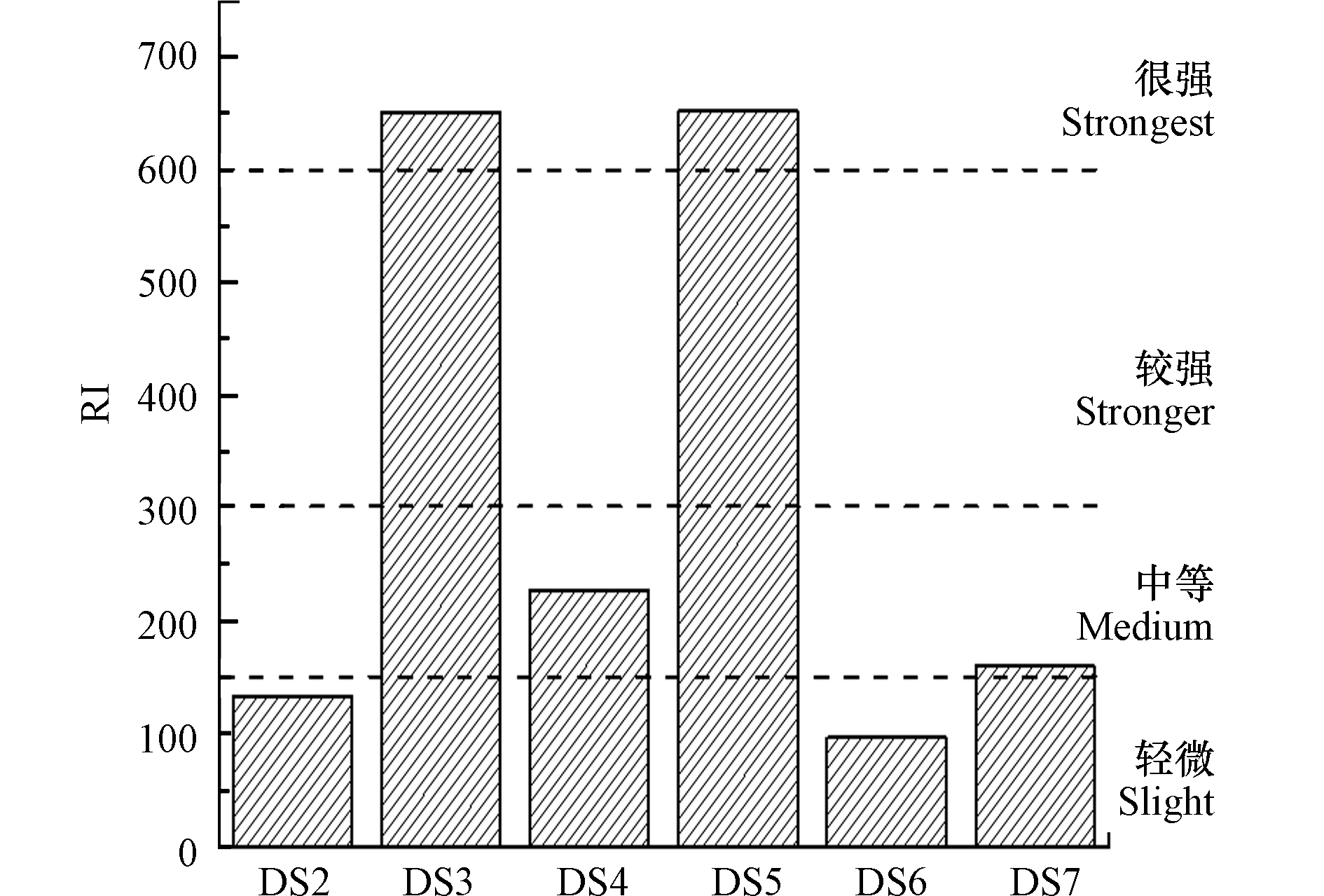
陡水水库表层沉积物潜在生态危害指数如图5所示,DS2、DS4和DS7各重金属潜在生态危害指数从大到小依次为:As>Cu>Pb>Hg>Zn>Cd;DS3和DS5各重金属潜在生态危害指数从大到小依次为:As>Cu>Hg>Pb>Zn>Cd;DS6各重金属潜在生态危害指数从大到小依次为:As>Cu>Pb>Zn>Hg>Cd。其中,As是最主要的生态风险贡献因子,在DS3和DS5表现为“极强生态危害”,在DS2、DS4和DS7表现为“较强生态危害”,在DS6表现为“轻微生态危害”。Cu的生态危害程度次之,在DS3、DS4和DS5表现为“中等生态危害”,其余表现为“轻微生态危害”。其他4种元素的Eir值均小于40,表现为“轻微生态危害”。潜在生态风险指数结果表明,DS3和DS5的RI值均高于600,属于“很强生态危害”;DS4和DS7重金属潜在生态危害程度属于“中等生态危害”;而DS2和DS6呈现“轻微生态危害”。
-
沉积物中DS3和DS5的mPEC-Q值均大于5,表明其发生生物毒性影响的可能性为75%—81%。其余4个调查点位的mPEC-Q值均介于1—5之间,表明其发生生物毒性不利影响的可能性为33%—58%。沉积物中重金属的生物毒性不利影响评价与地积累指数和潜在生态危害指数具有较高一致性。
由于不同评价方法考虑的影响因素不同,其评价结果侧重点也有所不同。地累积指数法侧重单一重金属在各调查点位的超标情况。潜在生态指数法综合考虑重金属毒性和浓度,反映单一重金属生态影响的同时体现多种重金属的综合潜在生态风险,但会忽略多种重金属复合污染时金属间的协同影响[34-36]。生态毒性不利影响评价反映重金属的相互作用,评价数值与相应沉积物毒性发生率高度相关[37-38]。总体而言,3种评价结果具有较高一致性,Igeo和RI均显示As为主要风险元素,DS3和DS5污染最严重。
-
(1)陡水水库表层水体中除部分点位(DS3—DS6)存在Hg超标外,其他点位均达到《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838-2002)Ⅲ类标准限值。DS5表层水污染程度较高,可能源于采矿及运输扬尘,其次为DS3和DS4,水质呈轻度污染。
(2)陡水水库沉积物中As、Cu和Zn污染较重,其中As为主要污染因子,可能源于矿产开采及农业面源排放;Hg和Cd含量水平低于当地土壤背景值。DS3、DS4和DS5沉积物中重金属含量较高。
(3)地累积污染指数、潜在生态风险指数及生态毒性不利影响评价均表明陡水水库DS3和DS5沉积物污染较严重,具有很强生态危害,发生生物毒性影响的可能性为75%—81%。
江西陡水水库水环境重金属时空分布特征及生态风险评价
Profiles of heavy metals pollution and potential influence to aquatic environment of Doushui Reservoir from Jiangxi Province
-
摘要: 本研究采用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)分析江西陡水水库表层水体及沉积物中Cu、Zn、As、Hg、Pb和Cd的含量水平,利用内梅罗综合污染指数评价法、地累积指数评价法、潜在生态风险指数法等方法对污染程度和生态风险进行评价。结果表明,陡水水库表层水体中Cu、Zn、As、Hg、Pb和Cd的浓度范围分别为0.10—9.24、nd—96.48、0.06—16.8、nd—0.64、nd—8.46、0.004—0.37 μg·L−1。陡水水库沉积物中Cu、Zn、As、Hg、Pb和Cd的含量水平分别为(190.59±45.95)、(426.70±144.65)、(201.43±175.79)、(26.49±23.23)、(103.75±30.88)、(6.38±5.42)mg·kg−1,其中Cu、Zn、As和Pb的最高浓度分别达到了江西省赣州市土壤背景值的11.82、9.13、53.87、2.94倍。综合污染指数评价法表明,陡水水库表层水体受到重金属污染,其中DS5为重度污染,DS3和DS4为轻度污染,主要污染物质为Hg;地累积指数评价法表明,陡水水库沉积物中As污染较重,其次为Cu和Zn;潜在生态风险指数法表明,DS3和DS5重金属具有很强生态危害,As为主要贡献因子;生物毒性不利影响评价表明,DS3和DS5重金属发生生物毒性影响的可能性为75%—81%。因此,在陡水水库重金属治理中要加强对Hg和As的防控。Abstract: Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) was used to qualify and quantify six commonly monitored heavy metals, Cu, Zn, As, Hg, Pb and Cd, in surface waters and sediments, at Doushui Reservoir from Jiangxi Province, China. Contamination degree and ecological risk of the heavy metals to aquatic ecosystem was further evaluated by comprehensive environmental pollution index (CEPI), geo-accumulation index (Igeo), potential ecological risk index (ERI) and so on. The results showed that concentrations of Cu, Zn, As, Hg, Pb and Cb in the surface waters ranged at 0.10—9.24, not detected (nd)—96.48, 0.06—16.8, nd—0.64, nd—8.46 and 0.004—0.37 μg·L−1, respectively. Concentrations (mean±standard deviation) of Cu, Zn, As, Hg, Pb and Cd in the sediments were at (190.59±45.95), (426.70±144.65), (201.43±175.79), (26.49±23.23), (103.75±30.88) and (6.38±5.42) mg·kg−1, respectively. The maximum concentrations of Cu, Zn, As and Pb in the sediments were 11.82, 9.13, 53.87 and 2.94 times, respectively, of the soil background values of those metals in Ganzhou City, Jiangxi Province. CEPI evaluation indicated that the surface water at DS5 was the most heavily polluted site especially by Hg whereas results from Igeo demonstrated that the sediments were mainly polluted by As, followed by Cu and Zn. The ERI assessemnt indicated that sites of DS3 and DS5 suffered a higher risk driven by the heavy metals with As as the main contributor. The adverse biological effects (ABE) data pointed out that the probability of toxic effects posed by the heavy metals ranged from 75% to 81% at the sites of DS3 and DS5. Therefore, aquatic contaminations of Hg and As in Doushui Reservoir deserved more attention for their further control and regulation.
-

-
表 1 采样点信息
Table 1. Sampling point information
编号
Number采样点
Sampling site电导率/(μs·cm−1)
Electrical conductivity水温/℃
TemperaturepH 经度(E)
Longitude (E)纬度(N)
Latitude (N)水深/m
DepthDS1 过埠大桥 60.4—117.3 6.1—21.7 7.0—9.6 114.215692 25.758442 0.5 DS2 水口码头 69.2—111.0 6.9—23.0 6.3—9.4 114.276335 25.759198 20.3 DS3 社官弯 70.7—112.4 6.2—23.0 5.7—9.8 114.271984 25.829949 11.8 DS4 泥坑 70.7—105.2 6.1—21.9 6.1—9.3 114.307384 25.805980 22.1 DS5 半坑口 92.6—168.0 6.4—22.4 5.8—9.6 114.354313 25.821869 31.5 DS6 树木园 88.6—140.0 6.6—21.4 6.2—9.2 114.370391 25.845120 40.0 DS7 蛇坑子湾 62.8—105.1 6.4—22.1 7.2—9.5 114.285652 25.792450 10.5 表 2 重金属内梅罗污染指数分级
Table 2. Pollution index and classification of heavy metal Nemero
水质综合污染等级
Comprehensive pollution gradeⅠ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ 水质综合污染指数 P≤0.7 0.7<P≤1.0 1.0<P≤2.0 2.0<P≤3.0 P>3.0 污染程度 清洁 尚清洁 轻污染 中污染 重污染 表 3 沉积物中重金属地积累指数分级
Table 3. Geological Accumulation Index and Classification of Heavy Metals in Sediments
Igeo Igeo<0 0≤Igeo<1 1≤Igeo<2 2≤Igeo<3 3≤Igeo<4 4≤Igeo<5 Igeo>5 级别 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 污染程度 清洁 轻度污染 偏中污染 中度污染 偏重污染 重度污染 严重污染 表 4 沉积物中重金属Eir和RI的分级标准
Table 4. Classification of Eir and RI for heavy metals in sediments
Eir Eir<40 40≤Eir<80 80≤Eir<160 160≤Eir<320 Eir≥320 RI RI<150 150≤RI<300 300≤RI<600 RI≥600 潜在生态危害程度 轻微 中等 较强 很强 极强 表 5 沉积物生物毒性不利影响评价分级标准
Table 5. Adverse effects evaluation and grading standards for sediment biotoxicity
mPEC-Q mPEC-Q≤0.1 0.1<mPEC-Q≤1 1<mPEC-Q≤5 mPEC-Q>5 发生生物毒性不利影响的可能性 PTP<14% 15%<PTP≤29% 33%<PTP≤58% 75%<PTP≤81% 表 6 不同采样点水样中重金属元素含量(μg·L−1)
Table 6. Heavy metal elements in water samples at different sampling points (μg·L−1)
编号
Number项目
ProjectCu Zn As Hg Cd Pb DS1 范围 0.57—9.24 nd—38.85 0.10—9.08 nd—0.06 0.01—0.37 0.09—8.46 平均值 3.30 8.82 3.30 0.03 0.17 2.05 标准偏差 2.42 10.78 2.86 0.02 0.12 2.24 DS2 范围 0.24—6.75 nd—96.48 0.13—6.08 nd—0.08 0.004—0.09 nd—0.54 平均值 2.17 13.74 2.74 0.05 0.05 0.27 标准偏差 2.17 29.41 2.05 0.03 0.03 0.14 DS3 范围 0.10—3.89 nd—17.31 0.06—4.53 nd—0.19 0.01—0.08 0.01—5.74 平均值 1.38 5.25 2.14 0.07 0.03 0.78 标准偏差 1.06 5.71 1.64 0.09 0.02 1.67 DS4 范围 0.32—4.34 nd—32.21 0.10—8.97 nd—0.21 0.004—0.07 nd—1.10 平均值 1.56 6.05 3.37 0.07 0.04 0.40 标准偏差 1.20 9.43 2.84 0.10 0.02 0.37 DS5 范围 0.60—3.56 nd—10.20 0.38—16.79 nd—0.64 0.02—0.16 0.02—0.30 平均值 1.65 3.56 7.91 0.26 0.06 0.16 标准偏差 0.97 2.91 5.60 0.24 0.04 0.09 DS6 范围 0.36—3.28 nd—18.18 0.32—13.55 nd—0.13 0.01—0.13 nd—0.84 平均值 1.27 4.85 6.52 0.08 0.05 0.22 标准偏差 0.83 5.22 5.08 0.04 0.04 0.24 DS7 范围 0.67—3.98 nd—6.12 0.13—6.61 nd—0.01 0.02—0.19 0.05—4.04 平均值 1.74 3.93 2.77 0.004 0.07 0.81 标准偏差 0.96 1.51 2.21 0.003 0.05 1.29 地表水环境质量标准
(GB3838-2002,Ⅲ类)1000 1000 50 0.1 5 50 表 7 不同采样点沉积物中重金属元素含量(mg·kg-1)
Table 7. Heavy metal elements in sediment samples at different sampling points (mg·kg-1)
编号
NumberCu Zn As Hg Cd Pb DS2 128.09 (5.19) 197.72 (1.90) 71.79 (7.63) 10.94 (0) 2.61 (0) 63.47 (0.23) DS3 244.63 (10.82) 593.70 (7.72) 448.21 (52.87) 50.91 (0) 10.58 (0) 151.70 (1.94) DS4 230.50 (10.14) 409.25 (5.01) 123.12 (13.80) 12.43 (0) 2.77 (0) 112.86 (1.19) DS5 230.29 (10.13) 621.44 (8.13) 446.28 (52.64) 66.40 (0) 16.67 (0) 128.88 (1.50) DS6 163.48 (6.90) 355.78 (4.22) 33.26 (3.00) 7.51 (0) 2.27 (0) 72.65 (0.41) DS7 146.56 (6.08) 382.34 (4.61) 85.95 (9.33) 10.74 (0) 3.39 (0) 92.95 (0.80) 平均值 190.59 426.70 201.43 26.49 6.38 103.75 北运河沙河水库[26] 40.65 125.78 35.75 — — 24.55 贵州啊哈水库[27] 75.03 217.50 54.58 — 1.43 28.45 嘉陵江亭子口水库[28] 63.84 140.77 — — 1.42 96.79 梅江清凉山水库[29] 17.83 143.78 — — 0.93 105.08 上海青草沙水库[30] 33.20 78.12 18.29 0.03 0.12 35.04 Hoedong reservoir, Korea (韩国) [31] 29.90 172.40 — — 2.80 71.20 Maqalika Reservoir, Maseru (马塞卢) [32] — 78.33 2.40 — — 0.29 Al-Najaf sea depression reservoir, Iraq (伊拉克) [33] — 177.63 — — 0.06 18.16 注:括号内数值为沉积物超过当地土壤背景值的超标倍数.
Notes: The values in brackets were the exceed multiple of concentrations in sediment samples, comparing with the values of the local soil background in Ganzhou City, Jiangxi Province.表 8 沉积物中重金属元素的相关性系数
Table 8. Correlation coefficient of heavy metal elements in sediments
Cu Zn As Hg Cd Pb Cu 1.000 Zn 0.771 1.000 As 0.771 0.886* 1.000 Hg 0.600 0.829* 0.886* 1.000 Cd 0.486 0.886* 0.886* 0.829* 1.000 Pb 0.886* 0.943** 0.943** 0.771 0.829* 1.000 注:*.在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关,**.在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关.
Notes: * Significant correlation at the 0.05 level (both sides), **. Significant correlation at the 0.01 level (both sides).表 9 陡水水库地表水污染统计表
Table 9. Statistics on surface water pollution of the steep water reservoir
编号
Number采样点
Sampling sitePi P Cu Zn As Hg Cd Pb DS1 过埠大桥 0.0006—0.0092 nd—0.04 0.002—0.182 nd—0.6 0.002—0.074 0.002—0.169 0.428 DS2 水口码头 0.0002—0.0068 nd—0.10 0.003—0.122 nd—0.8 0.001—0.018 nd—0.011 0.570 DS3 社官弯 0.0001—0.0039 nd—0.02 0.001—0.091 nd—1.9 0.002—0.016 0.0002—0.115 1.347 DS4 泥坑 0.0003—0.0043 nd—0.03 0.002—0.179 nd—2.1 0.001—0.014 nd—0.022 1.488 DS5 半坑口 0.0006—0.0036 nd—0.01 0.008—0.336 nd—6.4 0.004—0.032 0.0004—0.006 4.537 DS6 树木园 0.0004—0.0033 nd—0.02 0.006—0.271 nd—1.3 0.002—0.026 nd—0.017 0.926 DS7 蛇坑子湾 0.0007—0.0040 nd—0.01 0.003—0.132 nd—0.1 0.004—0.038 0.001—0.081 0.095 -
[1] SINGH U K, KUMAR B. Pathways of heavy metals contamination and associated human health risk in Ajay River basin, India [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 174: 183-199. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.103 [2] 汤洁, 韩维峥, 李娜, 等. 哈尔滨市城区大气重金属沉降特征和来源研究 [J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2011, 31(11): 3087-3091. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2011)11-3087-05 TANG J, HAN W Z, LI N, et al. Multivariate analysis of heavy metal element concentrations in atmospheric deposition in Harbin city, northeast China [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2011, 31(11): 3087-3091(in Chinese). doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2011)11-3087-05
[3] 李小虎, 汤中立, 初凤友. 白银矿山水体和沉积物中重金属及其化学形态分布特征 [J]. 地球与环境, 2008, 36(3): 218-224. LI X H, TANG Z L, CHU F Y. Analysis on speciation and transportation of heavy metals in water and sediment in Baiyin mine [J]. Earth and Environment, 2008, 36(3): 218-224(in Chinese).
[4] 廖柏寒, 曾敏, 郭朝晖, 等. 模拟酸雨下自然红壤与污染红壤中Cd, Cu, Zn的释放特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2009, 28(3): 343-349. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2009.03.005 LIAO B H, ZENG M, GUO Z H, et al. Release characteristics of Cd, Cu and Zn from the natural and contaminated red soils under simulated acid rain [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2009, 28(3): 343-349(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2009.03.005
[5] 旷攀, 李秋华, 金爽, 等. 贵州高原普定水库水环境重金属的时空分布特征及风险评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(3): 576-588. KUANG P, LI Q H, JIN S, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of heavy metals in water environment of Puding Reservoir in Guizhou Province and risk assessment[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 34(3): 576-588.
[6] 石志芳. 太湖沉积物中重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2010. SHI Z F. The characteristics of pollution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Taihu lake[D]. Yangling, China: Northwest A & F University, 2010 (in Chinese).
[7] 李佳璐, 姜霞, 王书航, 等. 丹江口水库沉积物重金属形态分布特征及其迁移能力 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(4): 1207-1217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.04.037 LI J L, JIANG X, WANG S H, et al. Heavy metal in sediment of Danjiangkou Reservoir: chemical speciation and mobility [J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(4): 1207-1217(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.04.037
[8] 李晋鹏, 成登苗, 赵爱东, 等. 澜沧江梯级水坝库区沉积物重金属和营养盐污染特征及评价 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(8): 2791-2799. LI J P, CHENG D M, ZHAO A D, et al. The characteristics and the assessment of heavy metal and nutrient pollution in sediments of cascading hydropower dams in Lancang River [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(8): 2791-2799(in Chinese).
[9] 张文慧, 许秋瑾, 胡小贞, 等. 山美水库沉积物重金属污染状况及风险评价 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2016, 29(7): 1006-1013. ZHANG W H, XU Q J, HU X Z, et al. Pollution and potential ecological risks of heavy metals in sediment of Shanmei Reservoir [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2016, 29(7): 1006-1013(in Chinese).
[10] 王闯, 单保庆, 唐文忠, 等. 官厅水库主要入库河流(洋河)表层沉积物重金属污染特征及风险水平 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(5): 1632-1640. WANG C, SHAN B Q, TANG W Z, et al. Pollution and ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments from input river (Yang River) of Guanting Reservoir [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(5): 1632-1640(in Chinese).
[11] 张伯镇, 王丹, 张洪, 等. 官厅水库沉积物重金属沉积通量及沉积物记录的生态风险变化规律 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(2): 458-465. ZHANG B Z, WANG D, ZHANG H, et al. The flux of sedimentary heavy metals and variation of ecological risks recorded by sediments from Guanting Reservoir [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(2): 458-465(in Chinese).
[12] 李冰, 王亚, 郑钊, 等. 丹江口水库调水前后表层沉积物营养盐和重金属时空变化 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(8): 3591-3600. LI B, WANG Y, ZHENG Z, et al. Temporal and spatial changes in sediment nutrients and heavy metals of the Danjiangkou Reservoir before and after water division of the mid-route project [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(8): 3591-3600(in Chinese).
[13] 张茜, 冯民权, 郝晓燕. 漳泽水库沉积物重金属污染特征与生态风险评价 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(1): 11-17. ZHANG Q, FENG M Q, HAO X Y. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Zhangze Reservoir [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(1): 11-17(in Chinese).
[14] 曾明昱, 曾泽国, 曾学平, 等. 陡水水库吻鰕虎鱼栖息环境及其优势种群形成原因的初步调查与分析 [J]. 江西水产科技, 2017(3): 9-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3188.2017.03.004 ZENG M Y, ZENG Z G, ZENG X P, et al. Preliminary investigation and analysis of formation reasons on habitat environment and dominant population of Scyphus chinensis in Doushui Reservoir [J]. Jiangxi Fisheries Science and Technology, 2017(3): 9-12(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3188.2017.03.004
[15] 江玮. 基于生态环境敏感性评价的生态功能分区研究——以崇义县为例[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2013. JIANG W. Ecological function zoning based on ecological environment sensitivity—a case syudy of Chongyi County[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2013.
[16] 叶素桃, 张思佳, 彭亚绵, 等. 单因子指数法在土壤重金属污染模型的应用研究 [J]. 数学学习与研究, 2016(11): 141. YE S T, ZHANG S J, PENG Y M, et al. Application of single factor index method on heavy metal pollution model in soil [J]. Mathematics Study and Research, 2016(11): 141(in Chinese).
[17] XIE L, ZHU W J, ZHANG J T, et al. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in the soil of brownfield based on improved Nemero index method[C]//中国土壤学会土壤环境专业委员会第二十次会议暨农田土壤污染与修复研讨会. [18] 王倩倩, 王祖伟, 侯迎迎, 等. 改进的地累积指数法在重金属生态风险评价中的应用 [J]. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 38(5): 47-51. WANG Q Q, WANG Z W, HOU Y Y, et al. Application of improved geo-accumulative index method in the ecological assessment of heavy metals [J]. Journal of Tianjin Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 38(5): 47-51(in Chinese).
[19] 邹勇军, 胡小娟, 汪成钵, 等. 江西省赣县沙地土壤重金属的来源及环境等级评价 [J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2018, 30(11): 66-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2018.11.14 ZOU Y J, HU X J, WANG C B, et al. Study on soil heavy metal source and environmental grade assessment in Shadi Township, Ganxian County, Jiangxi Province [J]. Coal Geology of China, 2018, 30(11): 66-73(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2018.11.14
[20] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [21] INGERSOLL C G, MACDONALD D D, WANG N, et al. Predictions of sediment toxicity using consensus-based freshwater sediment quality guidelines [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2001, 41(1): 8-21. doi: 10.1007/s002440010216 [22] LACEY E M, KING J W, QUINN J G, et al. Sediment quality in Burlington harbor, lake champlain, U. S. A. [J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2001, 126(1-2): 97-120. [23] 边博, 周燕, 张琴. 太湖西岸河网沉积物中重金属污染特征及风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(4): 1442-1450. BIAN B, ZHOU Y, ZHANG Q. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals from river network sediment in western area of Taihu Lake [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(4): 1442-1450(in Chinese).
[24] MEENA N K, PRAKASAM M, BHUSHAN R, et al. Last-five-decade heavy metal pollution records from the Rewalsar Lake, Himachal Pradesh, India [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6304-z [25] 郭云, 陈都, 王铭, 等. 阿哈水库沉积物中重金属分布特征及潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 水生态学杂志, 2018, 39(4): 24-30. GUO Y, CHEN D, WANG M, et al. Distribution and ecological hazard risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediment of Aha Reservoir [J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2018, 39(4): 24-30(in Chinese).
[26] 杨颖, 孙文, 刘吉宝, 等. 北运河流域沙河水库沉积物重金属分布及生态风险评估 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(1): 217-227. YANG Y, SUN W, LIU J B, et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Shahe Reservoir in Northern Canal Basin [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(1): 217-227(in Chinese).
[27] 张伟, 张丽丽. 贵州啊哈水库不同季节水体及沉积物重金属分布特征及其污染评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(6): 1753-1765. ZHANG W, ZHANG L L. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of heavy metals in water and sediments of different seasons in Aha Reservoir of Guizhou[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(6): 1753-1765.
[28] 可华明, 杨清伟, 刘守江, 等. 嘉陵江亭子口水库沉积物重金属分布特征及风险评价 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2020, 20(6): 2389-2397. KE H M, YANG Q W, LIU S J, et al. Distribution of the heavy metal contaminants and the corresponding eco-hazard risk assessment in the sediment of Tingzikou Reservoir of Jialing River [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2020, 20(6): 2389-2397(in Chinese).
[29] 江涛, 林伟稳, 曹英杰, 等. 梅江流域清凉山水库沉积物重金属污染、生态风险评价及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12): 5410-5418. JIANG T, LIN W W, CAO Y J, et al. Pollution and ecological risk assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments of Qingliangshan Reservoir in the Meijiang Basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(12): 5410-5418(in Chinese).
[30] 朱宜平, 李小飞, 梁霞. 上海青草沙水库表层沉积物重金属含量水平及其生态风险评价 [J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021(2): 54-62. ZHU Y P, LI X F, LIANG X. Content and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Qingcaosha Reservoir in Shanghai [J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 2021(2): 54-62(in Chinese).
[31] LEE P K, KANG M J, YU S, et al. Enrichment and geochemical mobility of heavy metals in bottom sediment of the Hoedong reservoir, Korea and their source apportionment [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 184: 74-85. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.124 [32] GWIMBI P, KOTELO T, SELIMO M J. Heavy metal concentrations in sediments and Cyprinus carpio from Maqalika Reservoir –Maseru, Lesotho: An analysis of potential health risks to Fish consumers [J]. Toxicology Reports, 2020, 7: 475-479. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.03.005 [33] HUSSEIN A M, JABBAR D N, ALI A R. Spatial distribution and evaluation of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Al-Najaf sea depression reservoir, Iraq [J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2020, 59(6): 5197-5206. doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2020.09.049 [34] CHEN C X, ZHENG B H, JIANG X, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of mercury in sediments of Lake Taihu, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2013, 25(2): 316-325. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60033-3 [35] 陈明, 蔡青云, 徐慧, 等. 水体沉积物重金属污染风险评价研究进展 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(6): 1069-1074. CHEN M, CAI Q Y, XU H, et al. Research progress of risk assessment of heavy metals pollution in water body sediments [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(6): 1069-1074(in Chinese).
[36] EL-SAYED S A, MOUSSA E M M, EL-SABAGH M E I. Evaluation of heavy metal content in Qaroun Lake, El-Fayoum, Egypt. Part I: Bottom sediments [J]. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 2015, 8(3): 276-285. doi: 10.1016/j.jrras.2015.02.011 [37] LI C, SONG C W, YIN Y Y, et al. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Shuangtaizi estuary, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 98(1-2): 358-364. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.05.051 [38] YU G B, LIU Y, YU S, et al. Inconsistency and comprehensiveness of risk assessments for heavy metals in urban surface sediments [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 85(6): 1080-1087. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.039 -



 下载:
下载: