-
高污染的石油烃泄漏点往往含有残留产物和非水相液体,将石油烃连续释放到地下水中,成为地下水污染源[1]。物理和化学修复技术是如今较为常见的修复方法。如物理法中,Yang等[2]使用吸油栏、吸油材料和撇油器等设备封堵地下水体油污的污染扩散。在最优条件下,采用上述物理方法处理石油烃污染地下水,最大回收率为30%上下。化学修复技术方面,经张兴等[3]研究发现,在地下水渗流中,高铁酸钾完全氧化分解低浓度石油烃类有机物效果较好。这些方法通常有较高的操作和维护费用,较高的能源消耗,并可能出现二次污染问题。
由于石油产品的主要成分在不同的环境条件下通常是可生物降解的,因此原位生物修复是一种经济有效的方法[4]。同时,使用微生物的方法处理石油污染物,具有去除效果好、成本低廉、无二次污染的优点,是较为理想的处理手段[5-6]。如Sathishkumar等[7]从石油污染土壤土著微生物中筛出57株石油烃降解菌,其中降解能力较强的4株单菌为IOS1-7、BPS2-6、HPS2-5和BPS1-8,分别属于芽胞杆菌属、棒状杆菌属和假单胞菌属。总体来说,如今国内大量的微生物修复石油烃的研究取得了不少的成果,但是主要集中在修复土壤石油烃的方面。而土壤环境相较地下水环境存在较大的差异性,主要由于地下水具有一定的特异性,如水温,pH以及其流动性等,土壤研究中筛选出的菌种很难适用于地下水中石油烃的降解。因此去研究一种用于地下水石油烃修复的微生物材料是十分具有意义的。
微生物处理法是如今高浓度石油烃地下水治理研究中较为常见的处理方法,处理效果高效并且无二次污染。但生物法在地下水环境中同时存在很多的局限性,如在水体环境中微生物为游离状态,导致部分局部浓度低、菌体易流失。此外,地下水的流动性也让微生物材料不易回收利用,难以进行后续监测以及重复利用。因此,微生物固定化技术成为了地下水生物修复法中研究的热点。为了解决这些问题,使用微生物固定化培养基的技术已经成为日本和欧洲等发达国家的替代技术。自20世纪60年代末以来,微生物固定化培养基开始应用于生物膜理论,人们一直在对微生物固定化技术进行研究,以达到稳定处理地下水中有机物的目的。主要由于微生物固定化技术可使地下水中修复区域的微生物保持所需的密度;同时减少微生物的流失,提高其耐毒害能力;并且可以保护微生物的活性不受水体环境的影响,从而增强降解微生物适应环境的能力,加快反应速度[8]。
在我国如今地下水处理的形式中,固定化微生物技术在处理水污染中有其特有的优势,主要体现在降解多组分的复杂有机污染物上[9-10]。近年来,生物炭应用于固定化微生物的制备受到越来越多的关注。主要因为生物炭来源广泛成本低廉,可以充分实现资源的再利用。从生物炭本身作为吸附材料性能来看,其具有空隙小、比表面积高和体表官能团丰富的特点,具有良好的吸附功能。可以为石油烃降解提供场地,同时微生物也能负载其中。其次,生物炭的物理吸附和微生物降解可同时存在并相互作用,对多种有机物具有清除吸附效果且去除率高。
本研究在地下水中筛选出土著高效石油降解菌,选用玉米生物炭为载体材料,采用吸附法固定石油烃复合降解菌。以柴油模拟石油烃C10—C40组分作为降解底物,研究地下水pH、固定化菌群投加量、石油烃浓度以及微生物固定化时间对地下水中石油烃降解率的影响。使用软件Design-Expert进行响应面法分析,通过4种环境因素的正交实验,分析不同环境因子对石油烃降解的影响程度,最终确定材料的最佳降解环境条件。
-
为了石油烃降解菌能够适用于地下水条件,本研究筛选的菌株全部来源于地下水土著微生物。模拟地下水条件,进行石油烃降解菌的低温驯化,确保降解菌能够适应15—18 ℃的温度条件。摇床实验中,使用封口膜封住瓶口,处于无光照状态,确保微生物在地下水低温、低溶解氧、无光照等特殊情况下能够高效降解石油烃。
配置石油烃培养基:选取250 mL锥形瓶倒入100 mL无机盐培养基,接入2 mL的地下水水样。使用柴油模拟石油烃C10—C40成分,接入0.1 g柴油,配置溶液石油烃浓度为1 g·L−1,富集培养土著微生物。在摇床中培养7 d,每周期按梯度增加培养基中石油烃浓度,浓度递增梯度为1 g·L−1。
经过4个周期的驯化,石油烃浓度达到5 g·L−1,此时石油降解菌的降解能力已经趋于稳定。在无菌操作台中,将筛选出的降解微生物菌液通过倍比稀释法,按照 10−1、l0−2、10−3、10−4、10−5、10−6、10−7的倍数依次稀释(如菌株在培养基太密集,可以增加稀释倍数)。
取30 µL稀释不同倍数的菌液,使用涂布棒使其均匀分布于固体富集培养基上。在恒温培养箱中,倒置培养1—2 d,设置温度为15 ℃。观测菌落生长情况,直至培养基中菌落形成。通过观察菌落的形貌及颜色,挑取体征不同的微生物进行划线分离,重复数次,得到纯菌落。随后进行石油降解实验,取降解率较高菌株进行生长曲线的测定,送去上海生物工程有限公司进行单株菌测序。
-
测定游离菌石油烃降解率时,取实验组的水样100 mL,用正己烷萃取后,经无水硫酸钠干燥,使用氮吹法吹脱萃取液,使正己烷转化为气相,得到石油烃成分。利用硅镁型净化柱对样品进行前处理。在测定生物炭固定化菌石油烃降解率时,使用过滤的方式使生物炭脱水,再将生物炭浸泡在正己烷中,以超声的方法分3次冲洗,使石油烃充分转移入液相,将正己烷转移回先前过滤分离的水相,重复先前游离菌水样的处理工作。
以正己烷作为溶剂,稀释石油烃标准溶液取,从而配制质量浓度分别为 0、0.25、0.5、1、2、4 mg·L−1的TPH标准样品。使用气相色谱的 DB-5毛细管色谱柱分离和以火焰离子检测器(FID)测定标准样品[11]。以保留时间在3.439—15.418 min的所有色谱峰总面积为纵坐标,质量浓度为横坐标绘制标准曲线。结果表明,两者之间存在良好的线性关系,相关系数 R2为0.9923。
-
将1.1节筛选出的石油烃降解单株测定生长曲线,紫外分光光度仪打开15 min预热,将波长调至OD600,以未接种的牛肉膏蛋白胨富集培养基校正分光光度仪调零。移液管从各瓶吸取1.5 mL菌液,取3个平行样,将OD600值在1.2—1.8(生长期)的菌悬液保存,作为备用菌悬液。
选取250 mL锥形瓶中,选取一定量的生物炭倒入100 mL固定化培养基中,在灭菌锅内高温高压灭菌20 min。随后将锥形瓶放入无菌操作台,紫外灭菌后待其冷却,接种定量的石油烃降解菌株。在恒温振荡箱中培养24 h,振荡条件为温度为15 ℃、转速为180 r·min−1,使降解菌完全附着在生物炭上。振荡后,使用离心机离心分离,倒出上清液。用10%的生理盐水冲洗生物炭表面2—3次,放入恒温培养箱常温干燥,最终获得生物炭固定化菌群。
-
为了进一步探索环境因素对固定化菌群的影响,确定其最佳使用条件,采用控制变量法,选取4个环境单因素,如pH 值(3—11)、固定化菌群投加量(0.5—10 g)、固定化时间(8—96 h)和石油烃质量浓度(1000—5000 mg),分别研究环境单因素变化对石油烃降解微生物游离状态和固定状态下,石油烃降解率的不同影响程度。另一反面,可以探索从而探索出复合菌剂处理地下水石油烃降解率达到最高时,所对应的环境条件。
在确定的石油烃降解最佳条件下,研究固定化菌群降解石油烃的动力学特点。于恒温摇床放置固定化菌群样品,设置温度为15 ℃,转速为160 r·min−1,每24 h取3个平行样,进行水样中所剩石油烃含量的测定。3个平行样取平均值,连续测定7 d,每天测得石油烃降解率,绘制石油烃降解曲线。使用origin软件线性拟合功能,绘制固定化菌群一级动力学及二级动力学拟合曲线。
-
响应面优化法是一种实验条件寻求方法,通过预测模型设计多因素多种组合的正交实验,对不同环境情况下石油烃降解率的进行分析,拟合出最佳降解率的模型方程,确定石油烃降解达到最高时所对应的实验条件[12]。将预测结果与实验结果进行比较,验证响应面实验在此研究中的适用性。并以此响应面模型作为研究方法,对固定化菌群处理石油烃效率的各个因素和各自变量的联合交互作用的影响进行探究。
-
根据上海生物工程公司送样要求,采用Ezup柱细菌基因组DNA提取试剂盒(中国上海生工生物工程有限公司)从过滤后的地下水样品中提取基因组DNA。提取的DNA储存在-80 ℃中冷藏直至样品送去分析。为保证地下水剖面微生物群落的完整提取,对16SrDNA基因片段进行了扩增和测序,每个样本用2套引物进行测序;细菌引物F(GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGG)和16S引物NS1(GTAGTCATATGCTTGTCTC)。PCR反应条件为:预变性,95 ℃,4 min;变性 94 ℃,45 s;退火,53 ℃,45 s;延伸72 ℃,1 min;重复变性到延伸流程进行30个循环,最终修复延伸温度为72 ℃进行10 min,等浓度的扩增产物混合,用Agencourt纯化。使用M13+引物扩增进行测序,对M13+/-引物进行测序,最后在核糖体数据库中比较16SrDNA序列。
-
实验所用的石油烃降解菌株是从受石油重度污染的地下水中驯化、筛选出的24株土著微生物。在游离条件下进行石油烃降解实验,通过对24株菌的生长曲线测定以及 7 d的石油降解实验,进行单株石油烃降解菌的初步筛选。其中,J2、J3、J5、J18的石油烃降解率达到了30%以上。
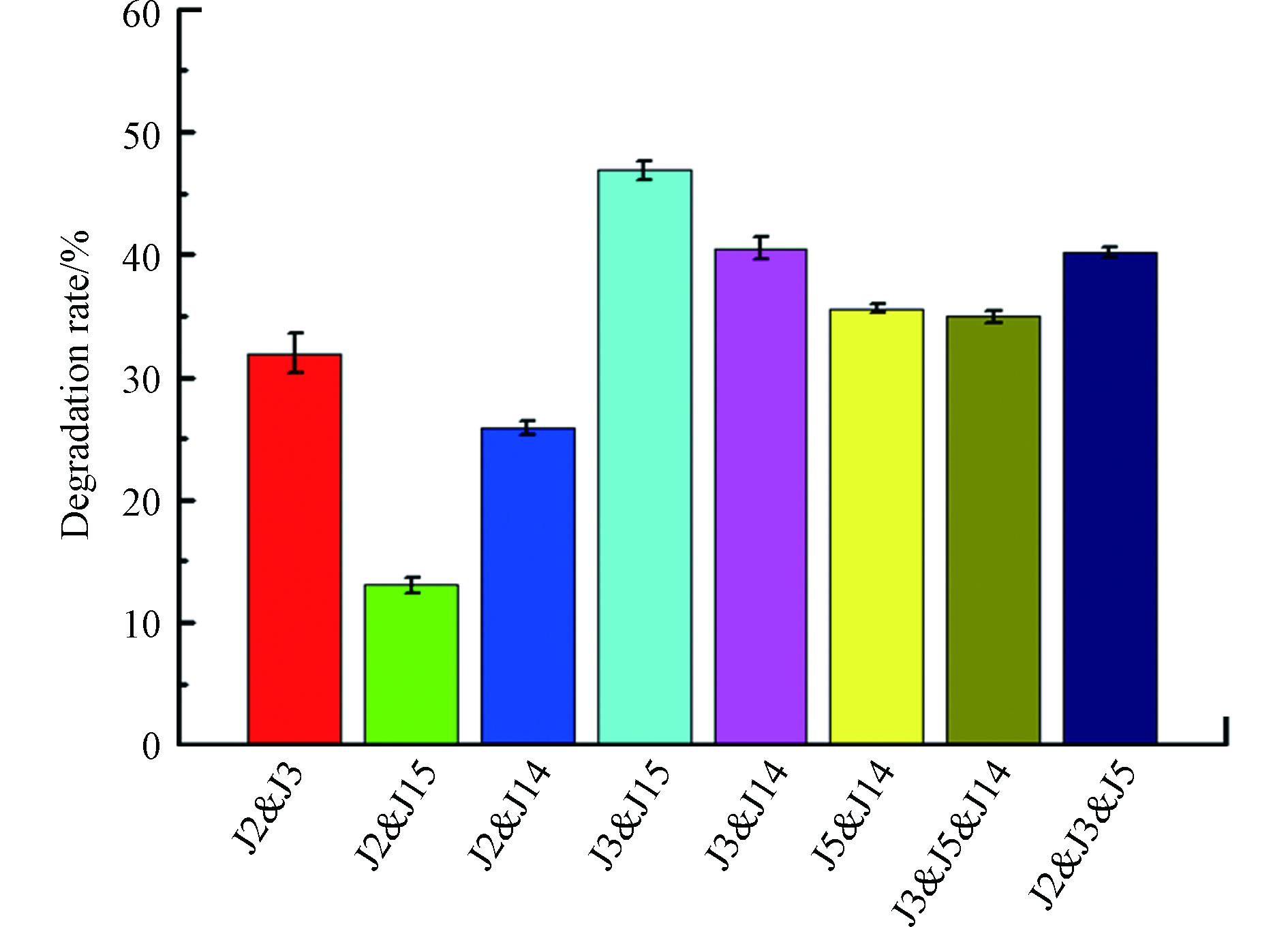
将石油烃降解率较高的3株菌株,两两组合进行复合菌的石油烃降解实验。单株菌按照1:1的接种比两两接入配置的模拟石油烃污染地下水的培养基中,游离态复合菌剂的石油烃降解效果如图1所示。由图1可以明显看到,由J2参与复配的复合菌剂石油烃降解能力普遍偏低,效果最好的组合为J2和J3,降解率为31.97%。 J2与其他菌株很难共生,不适用于制成复合菌剂,J14亦是如此。而J3、J5和J14两两复配制成复合菌剂的对石油烃都有一定的去除效果,尤其是J3和J5的组合,石油烃降解率最高,达到了46.86%。因此,选择J3和J5的复合菌株为后续实验目标菌。
-
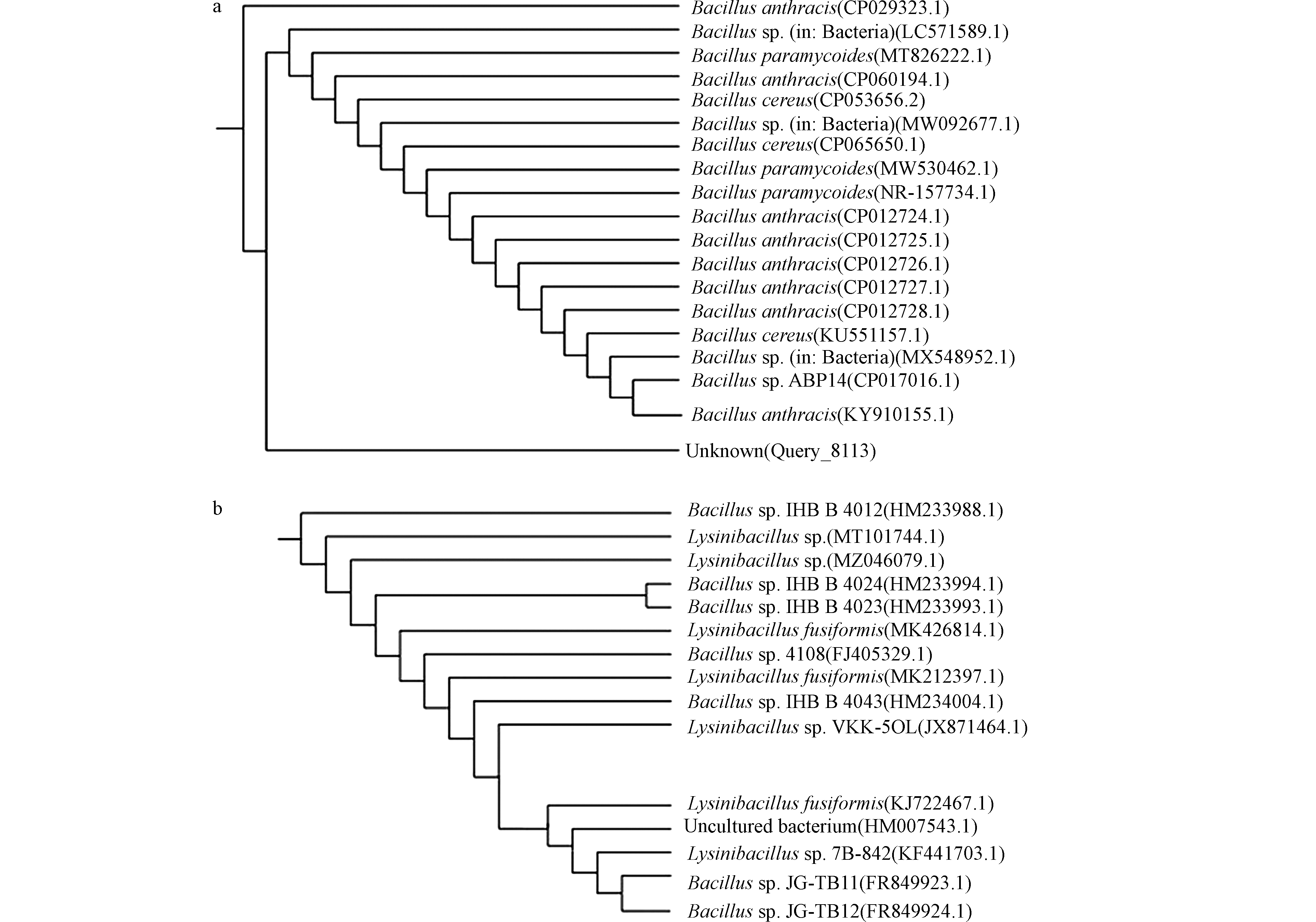
如图2所示,将J3、J5两菌株的16s rDNA核酸序列导入RDP与NCBI 数据库中,进行同源性比对。经系统发育树分析,发现菌株J5与杆菌属(Bacillus)聚类于同一簇,同源性为100%;菌株J3与赖氨酸芽孢杆菌属(Lysinibacillus.sp)聚类于同一簇,同源性为 100%。初步确定菌株 J3是赖氨酸芽孢杆菌属(Lysinibacillus),J5则为杆菌属(Bacillus)。
已有很多学者研究证明,许多杆菌能对石油烃有较强的的降解作用[13]。Parthipan等[14]研究发现,枯草芽孢杆菌能产生生物表面活性剂,可以降解石油烃 87%以上的组分。钟磊等[15]在天津大港油田筛选出的高效石油降解菌TDYN1T (Falsochrobactrum sp.) ,特定条件下能对石油烃的降解率达到90%以上。但以上研究大多针对土壤微生物条件,而地下水环境有其独特的温度及流动性条件,J3和J5制成的复合菌株能否在地下水环境高效降解石油烃,仍需后续的实验研究。
-
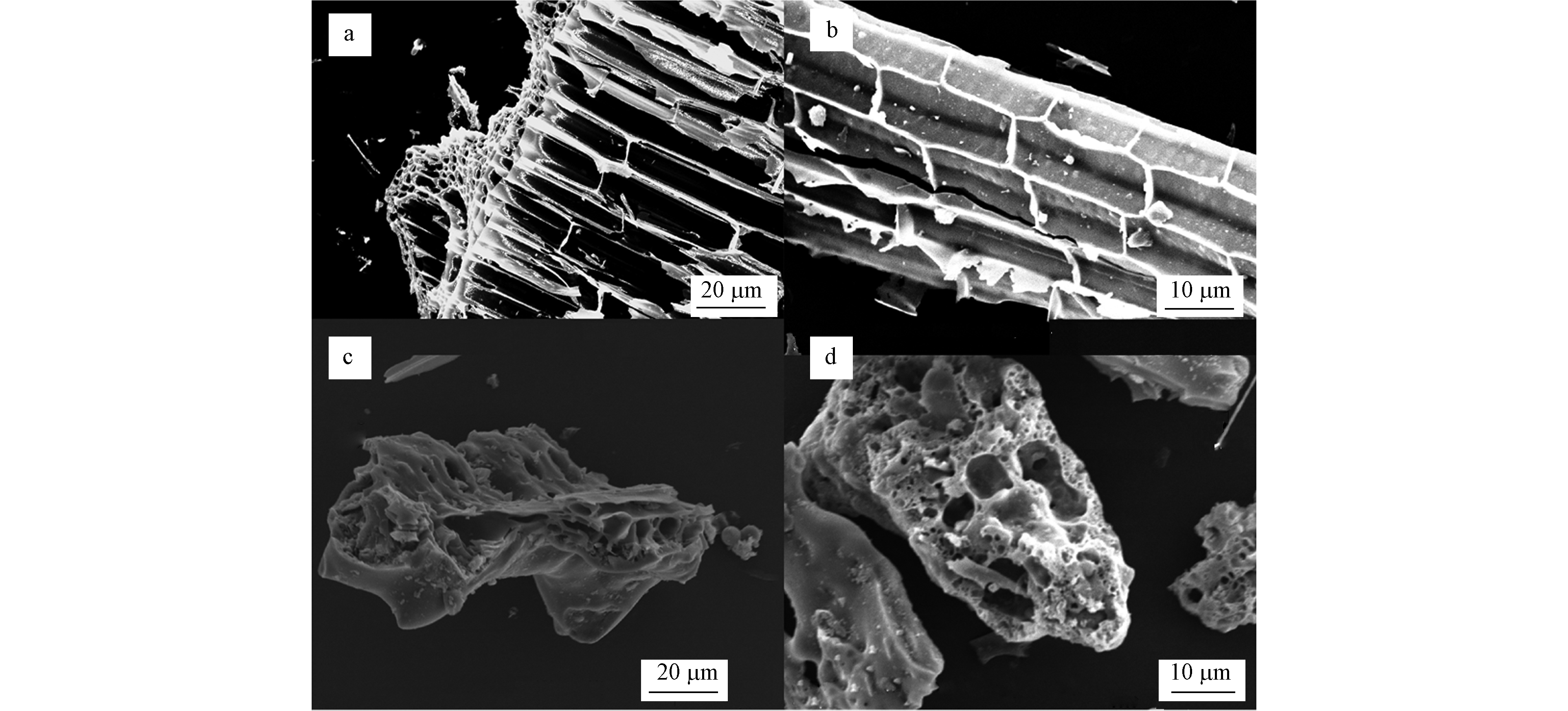
为观察生物材料的表面形貌,初步评估该微生物固定化材料的降解性能,采用扫描电镜对500 ℃玉米生物炭固定化前后和固定化菌群剂的表面结构进行观察。如图3a、b所示,未固定化微生物的玉米生物炭,其表面较平整,并且具有多孔结构,比表面积出色,可以为微生物提供较好的固定化条件。而进行固定化培养后,生物炭表面产生较多的褶皱,并且孔隙有明显缩小和堵塞,可以推断出有较多的石油烃降解菌附着在了生物炭上,固定化菌群的制作是成功的。
任静等[16]学者也成功制成生物炭固定化多环芳烃高效降解菌Martelella sp.材料,并且高度评价了此生物炭固定化材料的稳定性。白鹭等[17]学者研究不同材料作为固定化载体对石油烃降解率影响,发现生物炭固定化的降解效果明显高于花生壳、木屑和松针等,其分解产物还可以为石油降解微生物提供石油烃类物质的共代谢底物,使微生物量增加。可见,生物炭固定化微生物材料是一种良好的地下水石油烃生物修复功能材料。
-
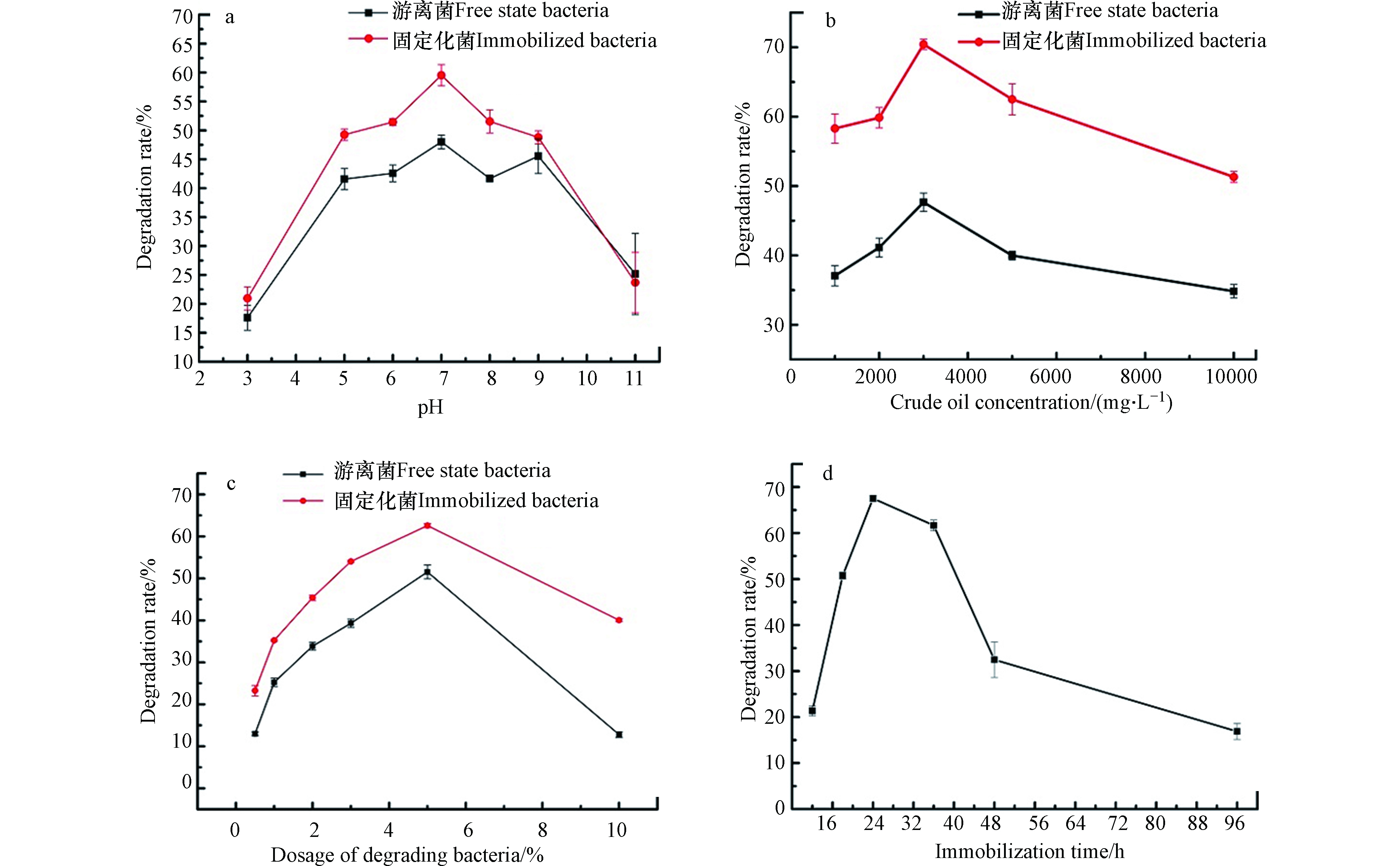
将微生物固定化24 h,制成固定化菌群材料。随后称取2 g,加入100 mL石油烃初始浓度为2000 mg·L−1的富集培养基中,将锥形瓶放入温度为15 ℃的摇床之中,7 d后,测定不同pH条件下石油烃的降解情况。重复上述实验步骤,依次改变石油烃浓度、微生物固定化时间和材料的投加量确定最佳单因素值,实验结果如图4所示。
pH实验一直是降解实验的重点,同时也是其他实验的前提条件。主要因为一般降解材料在不同的pH条件下,其材料的结构会发生很大的变化,从而影响其降解石油烃的能力。由图4a可知,当pH = 7时,石油烃降解菌活性达到最价,石油烃的降解率达到最高。当pH值小于7时,石油烃的降解率与pH值呈正相关趋势;而pH大于7时,降解率随pH值的持续升高而呈下降趋势。由此可见,pH对石油烃降解菌群的影响较大,特别是强酸强碱条件,会严重影响该材料的降解效率。采用固定化技术适当改善了此问题,但该固定化菌群仍不适用于极端pH环境下。
由图4b可知,当水体石油烃浓度小于3000 mg·L−1,石油烃降解率与石油烃浓度呈正比关系;而当水体石油烃浓度大于3000 mg·L−1,石油烃降解率随石油烃浓度提升呈下降趋势。主要由于微生物的生长繁殖必须的碳源,在培养基中只由石油烃供给。随着石油烃浓度的增加,液体培养基中的碳源丰富,从而改进微生物的成长环境,最终能够提高石油烃降解率。当石油烃初始浓度超过一定限度时,微生物液体培养基表面油层过厚,外部空气难以进入培养基,使得液体培养基中溶解氧下降,降解菌群的生物活性显著下降,从而降低石油烃降解率。
由图4c可知,适当增加固定化菌群投加量,石油烃降解率与固定化菌群的投加量呈正比关系;固定化菌群投加量大于5%时,石油烃降解率随投加量的提高呈下降趋势。主要由于,在固定化菌群投加量较少时,适当增加固定化菌群投加量,可以更充分地利用培养液中的碳源,从而加快微生物的生长繁殖。但是当降解复合菌群浓度过高时,培养液中的碳源消耗过快,从而使得微生物的后续生长碳源不足,微生物代谢速率减缓,导致固定化菌群降解石油烃效率下降。
由图4d可知,当固定化时间为24 h时,固定化菌的降解效果到达最佳;固定化时间小于24 h时,石油烃降解率与固定化时间呈正比;固定化时间大于24 h后,石油烃降解率上升趋势平缓并且逐渐开始下降。虽然生物炭拥有出色的比表面积和孔隙率,但随着微生物的不断繁殖,生物炭空隙中有限的营养物质不断消耗。当固定化时间超过24 h时,空隙中的微生物数量达到饱和程度,导致微生物新陈代谢开始减慢乃至停滞,最终导致石油烃降解率逐渐降低。
由单因素实验结果来看,固定化菌群的降解率及降解稳定性明显好于游离菌。并且固定化菌群的最佳条件为:pH=7,TPH浓度为3000 mg·L−1,投加量为3 g(3%),固定化时间为24 h。在此条件下进行验证实验,TPH降解率为70.14%。
该微生物固定化材料能够在pH = 5—9的情况之下,保持40%以上的微生物石油烃降解率,可见微生物固定化技术能提高菌株适应不同酸碱度的地下水水质环境,但不能适用于强酸强碱的条件。在一般的环境条件之下,最佳的石油烃微生物降解 pH 值范围为7.0—8.0。李敏等[18]对研究了生物炭固定化复合菌在pH = 7情况下对石油烃的降解效果,经过28 d,对石油烃的去除率为78.32%。
而就石油烃浓度而言,李琦等[19]开展的石油烃降解环境三因素的正交实验中,研究结果表明,相对于表面活性剂含量、投菌量,最强的环境影响因素为石油污染物浓度。,当石油烃浓度过高时,会限制地下水微生物所需的营养物质的传输,同时降低地下水中溶解氧浓度;而当地下水中石油烃浓度过低时,水中碳源又不足以维持石油烃降解菌的生长繁殖,从而降低降解效果。 而本实验结果,也符合这一结论,固定化菌群在石油浓度10000 g·L−1以下的地下水环境中,降解率能够达到50%以上的水平。由此可见,该固定化菌群能够适应绝大部分的地下水修复环境。
此外,该固定化菌群的最佳固定化时间为24 h,投加量为6%左右时,微生物固定化材料具有制作简易快捷,运用于工艺成本低廉的特点。如张利军[20]在地下水石油烃的PRB介质研究中,同样使用生物炭固定微生物材料作为反应介质,在固定化时间26 h,投加量4 g(4%)的情况下,其降解率达到最高。同样佐证以生物炭固定微生物材料处理地下水,在实际中是完全可行的。
-
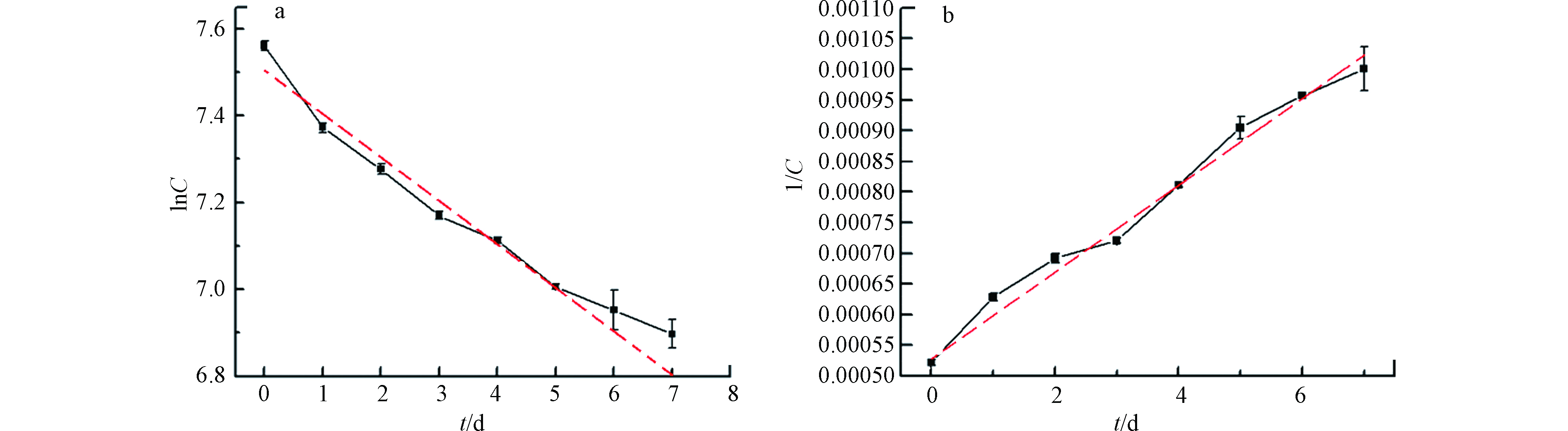
一般微生物降解有机物过程,大多符合零级或一级反应动力学模型[21]。Krishna等[22]利用废弃植物秸秆强化修复石油污染的土壤,研究表明石油烃微生物生物降解过程符合一级反应动力学,可以用方程(1)表示:
式中,C为水体污染物浓度,k 为反应速率常数,t为降解时间。 在之前的研究中,栾庆祥等[23]在土壤石油烃单因素实验的降解处理中,证明了处理的土壤石油含量自然对数(lnC)与微生物降解时间呈线性相关,且拟合优度高[24]。而本实验为了探索地下水中石油烃浓度与微生物处理时间的变化关系,同样进行了动力学的实验与分析,结果如下。
由图5可知,在单因素实验得出的最佳条件下,固定化菌群对石油烃降解过程更符合二级动力学模型, R2为0.963。由表1反应速率方程可见,微生物降解石油烃速率与石油烃浓度呈正比关系。不影响微生物生长繁殖的情况下,适当提高水体石油烃浓度,可加快微生物降解石油烃速率。
-
在单因素试验的基础之上,以单因素的最佳条件确定响应面法试验设计的因素和水平,即选取pH值( A) 、固定化时间( B) 、石油烃浓度( C) 和投加量(D)为因素。根据 Box -Behnken的中心组合实验设计原理[25],实验方案中的因素及水平如表2所示。以单因素实验结果的最优点的相邻区间作为研究水平,以固定化菌群在地下水中7 d时间对石油烃的最终降解率为评价指标,设计四因素三水平的响应面分析实验。由软件Design-Expert最终组合出29组实验,其中每个实验重复3次,减少实验误差,最终将实验结果进行响应面回归分析。
-
采用 Design-Expert统计软件对实验结果进行响应面回归分析,本次响应面分析的各环境因素水平结果如表3所示。响应面分析法实验中,其中当显著性系数P代表该研究项目对目标项目的影响程度,及该环境因素对固定化菌群降解地下水石油烃的贡献度大小;当P大于0.05时,表示该环境因素的变化引起固定化菌群对石油烃的降解率变化幅度较小;当显著性系数P在0.01与0.05之间时,影响的固定化菌群对石油烃的降解率变化幅度较大;当P小于0.01时,表示该环境因素变化引起固定化菌群对石油烃的降解率变化幅度非常大。
响应面分析法中得到下列归方程:
对该模型进行模型系数进行显著性检验以及方差分析,结果见表3。由表3可知,该回归模型显著系数P<0. 0001 ,说明建立的模型有意义;失拟项 P<0. 0001,具有良好的显著性系数,说明模型拟合度良好,总得来说,此模型和方程用于预测固定化菌群在地下水不同环境条件下其对石油烃降解率,是非常可信并且准确的。
由方差分析结果可知,模型的校正决定系数 R2为0. 9603,说明在不同环境因素条件下,96. 13% 响应值的变化与此模型相符。即此模型与实验数据具有出色的拟合度,实验误差。回归模型系数显著性检验结果中可以看出,模型的一次项中A因素(pH)影响程度最为显著,其次为B因素(原油浓度),较为显著。这一点在二次项显著性比较中更是得到了验证,A2( P<0. 0001)影响为极显著。而在各因素的交互关系中,AC较为显著(P = 0.0318)。由此可知,各影响因素对固定化菌群石油烃降解率的影响不是简单的线性关系。在所选取的各因素水平范围内,按照对结果的影响排序,由大到小分别为:pH值、石油烃浓度、固定化时间、固定化菌群投加量。
综上所述,方程的相关系数R2 = 0.9603,说明该回归方程模型可信度较高。所以,以此回归方程为基础进行分析计算,得到固定化菌群降解石油烃的最佳环境条件为:水体pH = 6.93、石油烃初始浓度2803.17 mg·L−1、复合菌群固定化时间为26.96 h、固定化菌群投加量为3.62 g。在此环境情况下,地下水中石油烃的降解率可以达到70.51%。
-
根据上文中得到的回归方程绘制响应面图,在四个环境因素变化交互作用下得到的响应值结果,以一个三维空间曲面的模型可视化。分析当pH值( A) 、固定化时间( B) 、原油浓度( C) 和投加量(D)其中有2个因素固定时,另外2个因素及其交互作用对地下水中石油烃降解率的影响。根据线性回归方程做出的模型的响应曲面,如图6所示。
由响应曲面图6可知,pH值趋近与7时,石油烃降解率达到峰值,酸碱条件都会影响固定化菌群的石油烃降解效果;随着石油烃浓度的增大,石油烃降解率也随之增加,但当石油烃浓度增大到一定程度后,降解率开始呈现较为明显下降的趋势;而然,固定化菌群的投加量和固定化时间的变化对石油烃降解率的影响,相对于前两个环境因素不显著。造成这种现象的可能原因是随着时间的延长,固定化菌群降解石油烃的能力趋于稳定,导致石油烃最终的降解率变化不大。并且,由响应曲面的陡峭程度可知,pH值的变化对石油烃的含量影响非常显著,其次是石油烃浓度和固定化时间,影响最小的为固定化菌群的投加量,这与方差分析结果一致。
-
(1)该实验筛选出了两株可以高效降解石油烃的菌株J3(Lysinibacillus)和J5(Bacillus),将其复配制成复合菌剂,随后采用生物炭固定化技术,将其制成了一种集吸附-降解功能为一体的石油烃生物降解材料。
(2)在单因素实验中,固定化菌群降解石油烃的最优条件分别为pH = 7、石油烃浓度3000 mg·L−1、固定化菌群投加量3 g(3%)和微生物固定化时间为28 h,在此最优条件下进行实验,TPH降解率达到70.14%;并且固定化菌群降解石油烃动力学模型更加符合二级动力学拟合曲线,拟合程度R2值达到0.963。
(3)采用响应面优化分析,结果表明固定化菌群对石油烃降解率影响的最为显著的因素为pH值,其次是石油烃初始浓度,固定化时间和固定化菌群投加量显著性较小。
(4) 响应面分析中得到最佳条件:pH为6.93、石油烃初始浓度为2803.17 mg·L−1、复合菌群固定化时间为26.96 h。在此条件下,石油烃降解率为70.51%,且与单因素最优条件下的实验结果70.14%非常接近。
生物炭固定化复合菌群修复石油烃污染地下水
Remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated groundwater by biochar immobilized bacterial consortia
-
摘要: 随着能源工业化的高速发展,如今地下水石油烃污染趋势日益严重。本实验以柴油模拟地下水环境中石油烃C10—C40成分,筛选出两株可以高效降解地下水石油烃的菌株,分别为赖氨酸芽孢杆菌属(Lysinibacillus)和杆菌属(Bacillus)。利用微生物固定化技术,把其制成了一种稳定性较高的基于吸附-降解功能为一体的石油烃降解材料。扫描电镜结果显示,该微生物固定化材料具有较为出色的吸附能力;降解动力学实验表明该材料降解石油烃符合二级动力学模型。采用单因素实验结合响应面法设计正交实验探索该材料最佳环境条件,结果表明,生物炭固定化石油烃降解菌在地下水中使用的最佳条件为:pH值6.93、石油烃初始浓度2803.17 mg·L−1、固定化时间为26.96 h,固定化菌群投加量3.62 g,经过7 d后石油烃降解率可达70.51%。该微生物固定化材料能够较好的适应地下水高浓度石油烃环境,并且显著降低石油烃浓度,研究可对地下水石油烃的修复提供重要的参考依据。Abstract: With the rapid development of energy industrialization, groundwater has been seriously contaminated by petroleum hydrocarbon. In this study, the C10—C40 components of petroleum hydrocarbons in the groundwater were simulated by diesel to screen two strains of efficient petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria, that is, Lysinibacillus and Bacillus. Then, the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation material with high stability of adsorption and degradation was prepared using microbial immobilization technology. Scanning electron microscopy results indicated that this material had excellent adsorption capacity. The degradation kinetics experiment showed that the degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon followed the second-order kinetic model. Single-factor experiments combined with the response surface method were used to design the orthogonal experiment to explore the optimal conditions for the degradation of this material. By controlling the pH being 6.93, initial concentration of petroleum hydrocarbon being 2803.17 mg·L−1, immobilization time being 26.96 h, and the immobilized microorganisms inoculum being 3.62 g, the best degradation rate of 70.51% was obtained after 7 days. In conclusion, the microbial immobilization material can adapt to the high concentration of petroleum hydrocarbons in groundwater, and significantly reduce the concentration of petroleum hydrocarbons. Our study provides important references for the remediation of petroleum hydrocarbons in groundwater.
-

-
表 1 固定化菌群石油烃降解动力学模型
Table 1. Kinetic model of petroleum hydrocarbon degradation by immobilized bacteria
反应动力学模型Kinetic model 反应速率方程Reaction rate equation K R2 零级 C=-130.8t+1787.134 −130.8 0.882 一级 lnC=-0.10042t+7.5153 −0.10042 0.925 二级 1/C=7.49×10-5t+5.32×10−5 7.49×10−5 0.963 表 2 固定化菌群实验设计的因素与水平
Table 2. Factors and levels of experimental design of immobilized bacteria
因素
FactorpH 固定化时间/h
Immobilization timeTPH浓度/(mg·L−1)
Concentration投加量/%
Dosage(A) (B) (C) (D) 等级
Level6 12 2000 2 7 24 3000 3 8 36 4000 4 表 3 固定化复合菌石油烃降解实验数据方差分析
Table 3. Variance analysis of the experimental data of petroleum hydrocarbon degradation of immobilized composite bacteria
项目
Project平方和
Square自由度
Degree of freedom均方差
Mean Square Error显著系数
Significance CoefficientModel 1488.23 14 106.30 < 0.0001 A 26.02 1 26.02 0.0290 B 18.93 1 18.93 0.0570 C 0.0456 1 0.0456 0.9203 D 41.44 1 41.44 0.0083 AB 4.43 1 4.43 0.3325 AC 25.00 1 25.00 0.0318 AD 0.2116 1 0.2116 0.8295 BC 2.39 1 2.39 0.4734 BD 7.26 1 7.26 0.2196 CD 1.22 1 1.22 0.6065 A² 1341.82 1 1341.82 < 0.0001 B² 79.93 1 79.93 0.0008 C² 17.53 1 17.53 0.0657 D² 21.34 1 21.34 0.0448 残差 61.57 14 4.40 失拟项 61.52 10 6.15 < 0.0001 净误差 0.0479 4 0.0120 总离差 1549.79 28 -
[1] 于艺彬, 杨四福, 侯愷. 近10年地下水中重金属与石油烃污染物修复研究进展 [J]. 江西化工, 2020(4): 64-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3103.2020.04.021 YU Y B, YANG S H, HOU K. Research Progress on remediation of heavy metals and petroleum hydrocarbons in groundwater in recent 10 years [J]. Jiangxi Chemical Industry, 2020(4): 64-69(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3103.2020.04.021
[2] YANG D, CHEN S. Use of a novel biopellet to treat total petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated groundwater [J]. Water, 2020, 12(9): 2512. doi: 10.3390/w12092512 [3] 张兴, 杨敏, 柯佳闻, 等. 地下水渗流中高铁酸钾氧化去除石油烃类污染物的试验研究[J]. 广东化工, 2020, 47(9): 159-162. ZHANG X, YANG M, KE J W , et al. Test study on removal of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants by oxidation of potassium ferrate in groundwater seepage[J]. 2020, 47(9): 159-162(in Chinese).
[4] 张小梅, 孔萌, 邢献杰, 等. 双效工程菌BBb对炼化油泥中总石油烃的降解特性 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(7): 2255-2264. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020031503 ZHANG X M, KONG M, XING SHAO JIE, et al. Degradation characteristics of total petroleum hydrocarbons in refinery sludge by the dual-acting engineering bacterium BBb [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(7): 2255-2264(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020031503
[5] MCGUIRE J T, COZZARELLI I M, BEKINS B A, et al. Toxicity assessment of groundwater contaminated by petroleum hydrocarbons at a well-characterized, aged, crude oil release site. [J]. Environmental science & technology, 2018, 52(21): 12172-12178. [6] 朱超飞, 杨文龙, 董亮, 等. 土壤中的石油类化合物(C10—C40)的快速测定[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(1): 224-227. ZHU C F, YANG W L, DONG L, et al. The rapid method to analyze petroleum hydrocarbons (C10—C40) in soil[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(1): 224-227(in Chinese).
[7] SHARMASARKAR S, JAYNES W F, VANCE G F. BTEX sorption by montmorillonite organo-clays: TMPA, Adam, HDTMA [J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2000, 119(1/2/3/4): 257-273. doi: 10.1023/A:1005167524630 [8] 韩嘉碧, 吴慧芳, 庄子孟, 等. 固定化微生物技术用于废水处理的研究进展[J]. 江西化工, 2020(4): 50-51. HAN J B, WU H F, ZHUANG Z M , et al. Research progress of immobilized microorganism technology in wastewater treatment[J]. 2020(4): 50-51(in Chinese).
[9] 张小雄. 固定化微生物技术在富营养化水体修复中的应用[J]. 化工管理, 2020(29): 21-22. ZHANG X X. Application of immobilized microorganism technology in eutrophic water remediation [J]. Chemical Enterprise Management, 2020(29): 21-22(in Chinese).
[10] 张鸿郭, 熊静芳, 李猛, 等. 固定化硫酸盐还原菌处理含铊废水效果及其解毒机制[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(3): 591-597. ZHANG H G, XIONG J F, LI M, et al. Effect and detoxification mechanism for treating wastewater containing thallium by immobilized sulfate reducing bacteria[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(3): 591-597(in Chinese).
[11] 杨励君. 石油烃测定方法和标准使用建议 [J]. 江西科学, 2019, 37(4): 501-503. doi: 10.13990/j.issn1001-3679.2019.04.006 YANG L J. Suggestions for the method and standard use of petroleum hydrocarbon determination [J]. Jiangxi Science, 2019, 37(4): 501-503(in Chinese). doi: 10.13990/j.issn1001-3679.2019.04.006
[12] 杨慧敏, 曾礼兰, 贺富强, 等. 响应面法优化超压肠杆菌利用黄水生产微生物絮凝剂[J]. 中国酿造, 2020, 39(2): 78-83. YANG H M, ZENG L L, HE F Q, et al. Optimization of microbial flocculant production by Enterobact nimipressualis with Huangshui by response surface methodology[J]. China Brewing, 2020, 39(2): 78-83(in Chinese).
[13] 邵栓, 党晓伟, 李慧娟, 等. 响应面法优化微生物除臭效果的研究[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2020, 47(8): 2684-2693. SHAO S, DANG X W, LI H J, et al. Study on optimizing the effectiveness of microbial deodorization by response surface methodology[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 47(8): 2684-2693(in Chinese).
[14] PARTHIPAN P, PREETHAM E, MACHUCA L L, et al. Biosurfactant and degradative enzymes mediated crude oil degradation by bacterium Bacillus subtilis A1[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017. [15] 钟磊, 卿晋武, 陈红云, 等. 微生物修复石油烃土壤污染技术研究进展 [J]. 生物工程学报, 2021: 1-17. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.210115 ZHONG L, QING J J, CHEN H Y, et al. Progress in microbial bioremediation of petroleum-hydrocarbon-contaminated soil [J]. Chinese journal of biotechnology, 2021: 1-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.210115
[16] 任静, 沈佳敏, 张磊, 等. 生物炭固定化多环芳烃高效降解菌剂的制备及稳定性[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(12): 4517-4523. REN J, SHEN J M, ZHANG L, et al. Preparation and stability of biochar for the immobilization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degradating-bacteria[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(12): 4517-4523(in Chinese).
[17] 白鹭, 吴春英, 谷风. 固定化微生物对石油污染土壤修复条件优化研究 [J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2021(3): 51-56. BAI L, WU C Y, GU F. Study on optimizing of immobilized microorganisms on remediation conditions of petroleum-contaminated soil [J]. Nonferrous Metals(Extractive Metallurgy), 2021(3): 51-56(in Chinese).
[18] 李敏, 李婷婷, 彭湃, 等. 石油烃降解菌降解性能及其对含油土壤的修复 [J]. 辽宁化工, 2021, 50(2): 127-130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0935.2021.02.001 LI M, LI T T, PENG P, et al. Degradation performance of petroleum hydrocarbon degrading bacteria and its remediation of oil-bearing soil [J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(2): 127-130(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0935.2021.02.001
[19] 李琦. 鼠李糖脂强化石油污染土壤植物—微生物联合修复研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2011. LI Q. The effect of rhamnolipid on phytoremediation and microbial remediation of petroleum contaminated soil[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2011(in Chinese).
[20] 张利军. 微生物渗透性反应墙原位修复石油烃污染地下水研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2016. ZHANG L J. The Study on the petroleum hydrocarbon contaminates the groundwater renovation by the permeable reactive barrier of microorganisms[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese).
[21] 张秀霞, 单宝来, 张剑杰, 等. 降解菌HJ-1降解石油动力学[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 33(5): 140-143. ZHANG X X, SHAN B L, ZHANG J J, et al. Kinetics on strain HJ-1 degrading petroleum[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2009, 33(5): 140-143(in Chinese).
[22] KRISHNA K K, KERYN L S, PAWEL P S, et al. A complementary approach to identifying and assessing the remediation potential of hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria [J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2012, 88(3): 348-355. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2011.12.006 [23] 栾庆祥, 赵杨, 周欣, 等. 单因素试验结合响应面分析法优化杜仲最佳提取工艺 [J]. 药物分析杂志, 2013, 33(5): 859-865. doi: 10.16155/j.0254-1793.2013.05.002 [24] LUAN Q X, ZHAO Y, ZHOU X, et al. Optimization on extraction technology for Eucommia ulmoides by single-factor experiment combined with response surface methodology [J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2013, 33(5): 859-865. [25] 赵颖, 王亚旻, 卫皇曌, 等. 响应面法优化污泥炭催化湿式过氧化氢氧化降解间甲酚模拟废水 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(3): 516-525. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.03.2015100801 ZHAO Y, WANG Y M, WEI H Z, et al. Optimization of m-cresol degradation by sludge-derived carbon in catalytic wet peroxide oxidation using response surface methodology [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(3): 516-525(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.03.2015100801
-



 下载:
下载: