-
重金属是一类对生态环境系统和人体健康危害性极大的污染物[1]. 随着经济社会的快速发展,由工农业生产等人类活动产生的各类型重金属污染物进入到土壤等不同环境介质当中[2-3]. 土壤是农业生产的基础,赋存在土壤中的重金属污染物,通过根系富集等途径进入到农作物的不同部位,影响作物的生长发育,经不同层级食物链的累积作用最终危害到人体健康[4-6]. 目前粮食安全问题日益凸显,食用受污染的农作物已成为重金属摄入的主要方式[7-8].
农作物重金属污染评价已成为环境科学领域研究的热点问题之一. 受土壤中重金属污染物累积程度、土壤理化特征、不同作物对重金属元素富集能力等因素影响,不同作物或同一作物不同部位中重金属的污染特征和健康风险存在较大差异. 已有学者针对不同农作物对重金属的富集能力强弱、土壤理化特征对重金属富集程度的影响等方面进行了相关研究,如水稻对Pb的富集能力强于小麦[9],而小麦富集Cd的能力强于水稻[10]. Ding和王怡雯发现[11-12],土壤Cd含量、pH值、有机质等对作物吸收Cd具有显著的影响. 孙亚芳对比分析了天津市污灌区和清灌区小麦、水稻子实中重金属的含量,结果表明污水灌溉会增加重金属在植物体内的累积[13]. 小麦是我国第二大作物,受土壤污染影响,部分地区已经出现小麦重金属超标现象,如江苏省某地震带小麦籽粒Pb、Cr、Hg、Ni、As超标率分别为100%、58.97%、33.33%、10.26%、2.56%[14],天津市某污灌区冬小麦籽粒中As、Pb、Hg、Cr、Cd、Se均有不同程度的超标[15]. 已有研究对小麦重金属污染评价大多针对污灌区、矿区周边农田等具有明显污染源的区域,而对一般农业生产区域中的小麦籽粒重金属研究较少.
河南省是我国重要粮食大省和后备资源储粮基地,小麦是该地区主要粮食作物,在人们日常饮食中占有较大比重. 2017年河南省发布的《关于河南省重金属污染防治工作指导意见》中,安阳市龙安区被列入国家重金属污染防控重点区域[16],但针对该区域作物重金属污染研究未有报道. 基于此,本文以安阳市龙安区为研究区域,对该区域小麦籽粒重金属进行系统的污染评价,旨在为粮食作物重金属的风险管控和安全生产提供依据.
-
研究区地处河南省北部,地势西高东低,地形以平原为主,面积约58.17 km2,土壤pH值为8.27,土壤As、Pb、Cd、Cr含量均值分别10.59、22.76、0.16、74.84 mg·kg−1. 该区域属暖温带季风气候,年平均气温为14.3 ℃,年平均降水量558.3 mm,全年无霜期215 d,盛行东南风. 京广线、107国道自北向南穿过,交通网络发达,附近建有钢铁、机械、化工、建材、冶炼等企业.
-
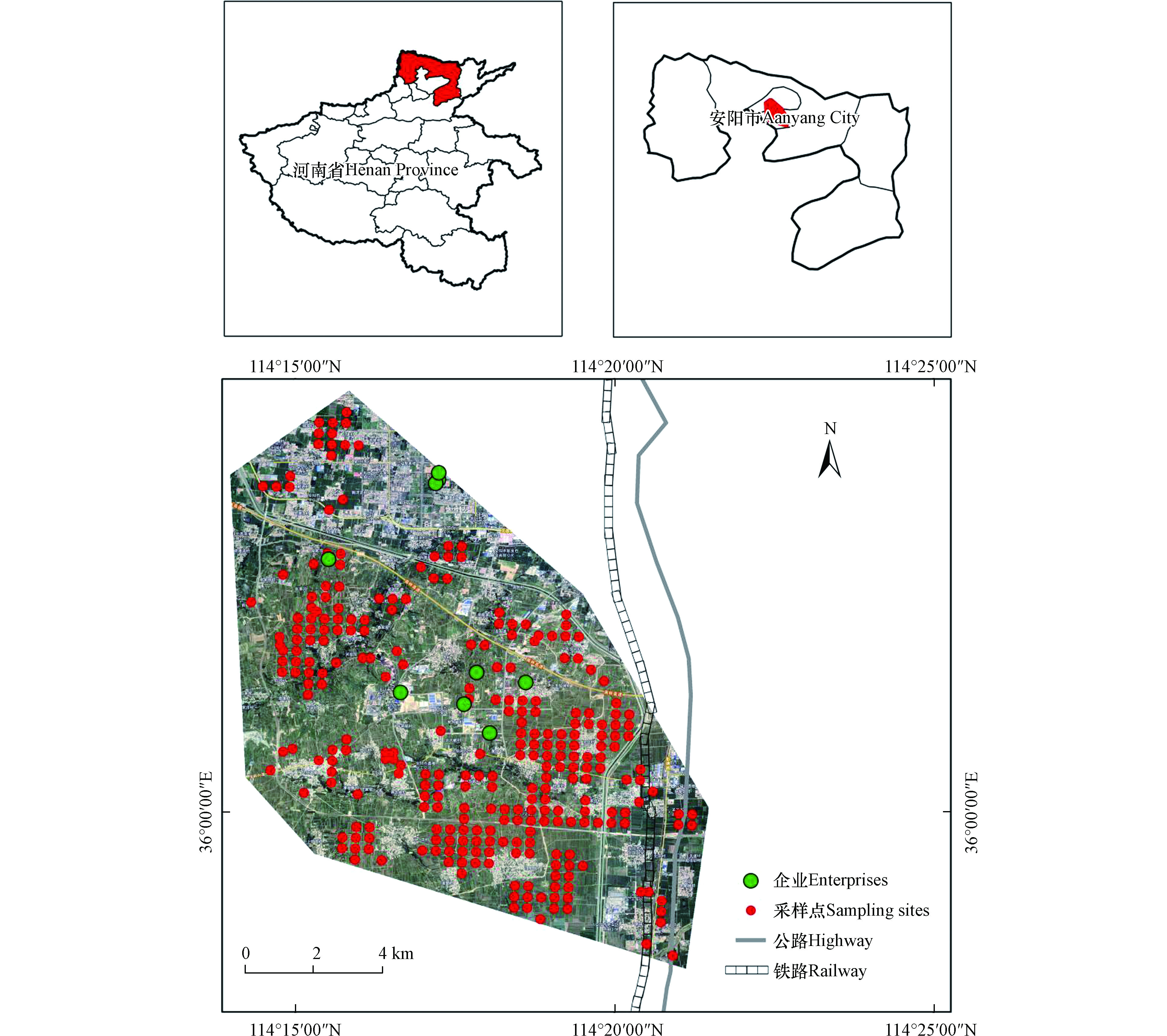
根据研究区耕地、建设用地、道路等分布特征,按照近似网格布点方法,共布设样点283个(图1),样点间距约100 m. 采样时,从每个采样单元随机挑选5棵小麦植株,采集重量约150 g的麦穗,将采集的样品放入密封袋中,做好标签.
-
小麦样品在室内自然风干后,手工脱壳,用超声波清洗籽粒,之后再用蒸馏水清洗3次,70 ℃烘干至恒重,粉碎后放于塑封袋内,注明编号. 样品中的Pb、Cd、Cr含量使用石墨炉-原子吸收光谱法测定,As含量采用原子荧光法测定,每个样品均反复测定3次后取平均值,以便消除误差,实验所用试剂均为优先纯,分析测试过程中采用生物成分分析标准物质(GBW10011)进行控制,回收率均在80%—100%.
-
本文以《食品安全国家标准—食品中污染物限量》(GB 2762—2017)为标准,利用单因子污染指数法和内梅罗综合污染指数法来评价小麦籽粒中重金属风险程度[17].
单因子污染指数常用于对某单一污染物的评价,计算公式为:
式中,Pi为作物中重金属i的单因子污染指数,Ci为重金属i的实测质量分数(mg·kg−1),Si为重金属i的评价参考值(mg·kg−1).
内梅罗综合污染指数计算公式为:
式中,P为农作物综合污染指数;
$ \overline P_i $ 为各项重金属污染指数平均值,Pimax为各项重金属污染指数最大值. -
采用美国环境保护署推出的健康风险评价模型评估研究区不同人群食用区域小麦的健康风险,通过计算饮食摄入的小麦籽粒重金属来评估重金属对人体造成的潜在健康风险[18]. 依据重金属是否为致癌物,可从非致癌风险和致癌风险两个方面进行评价. 本文研究的Pb属于非致癌重金属,As、Cd、Cr属于致癌重金属.
农作物摄入途径下重金属的日摄入量(ADD):
式中,ADD为摄入途径下重金属的日摄入量[mg·(kg·d)−1],Ci为作物中重金属i的浓度(mg·kg−1);I为农作物日摄入量(kg·d−1);EF代表暴露频率(d·a−1);ED为暴露年限(a);BW表示人均体重(kg);AT为人体接触时间(d). 具体见表1.
(1)非致癌风险评价
单项重金属的健康风险系数(HQ):
式中,HQ为风险系数;RfD代表重金属暴露途径下的参考剂量[mg·(kg·d)−1],As、Pb、Cd、Cr的暴露参考剂量分别为0.0003[21]、0.0035[22]、0.001[23]、0.003[20]. 当HQ≤1时,表示重金属对人体健康没有风险;当HQ>1时,表示重金属对人体健康存在风险,系数值越大,风险等级越高.
(2)致癌风险评价
式中,RI为重金属i的致癌风险,SF为致癌斜率因子[(kg·d)·mg−1],As、Cd、Cr的致癌斜率因子分别为1.5、6.1、0.5[24-25],R为致癌总风险. 当RI(R)≤1×10−6,表明无明显风险;当1×10−6<RI(R)≤1×10−4,表明风险可以接受;当RI(R)>1×10−4,表明存在显著风险.
-
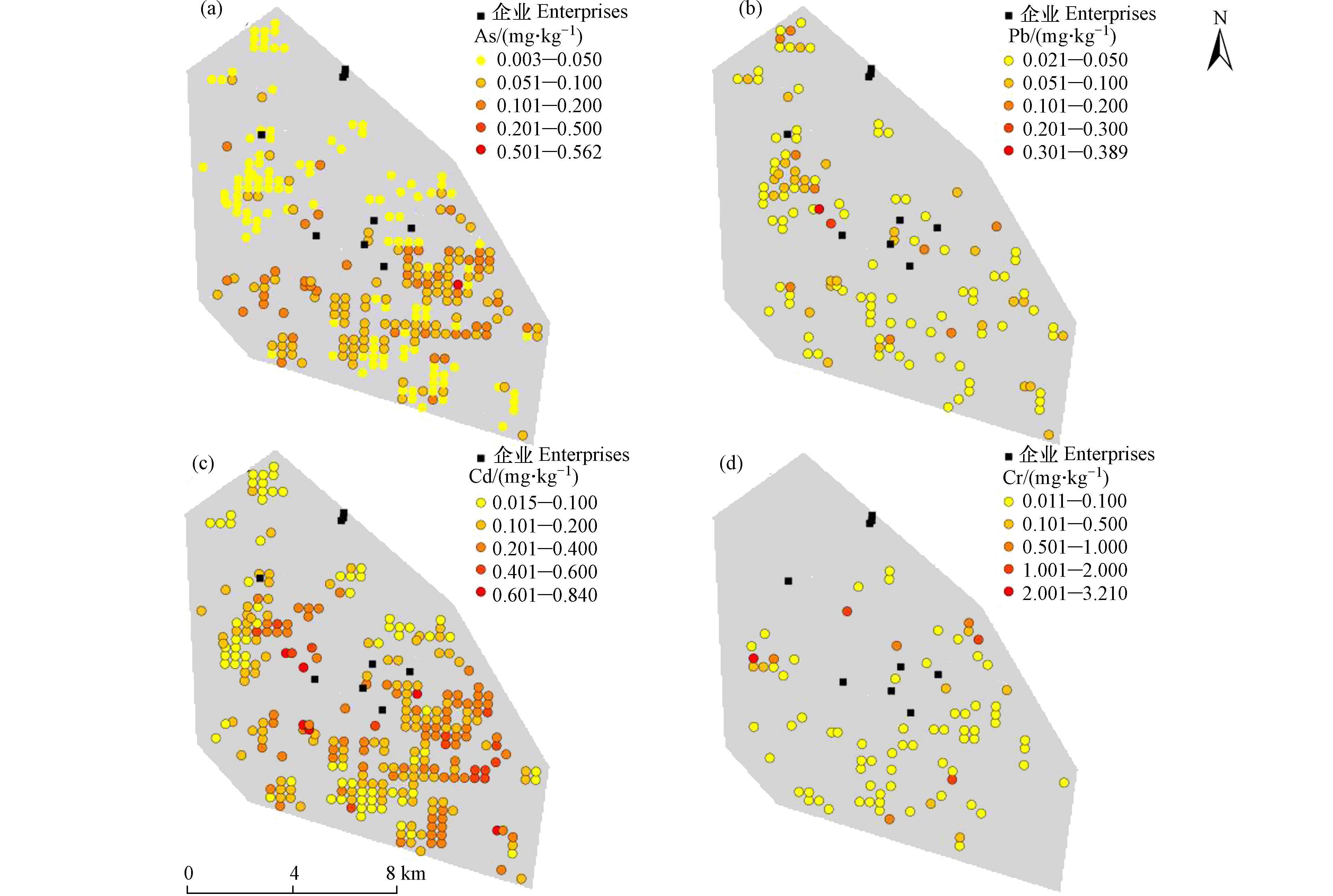
研究区小麦籽粒样品中重金属含量频数分布见图2. 小麦籽粒中As、Pb、Cd、Cr含量分别在0.003—0.562 mg·kg−1、0.021—0.389 mg·kg−1、0.0056—0.840 mg·kg−1、0.011—3.210 mg·kg−1之间,极差较大,平均含量分别为0.063、0.053、0.193、0.177 mg·kg−1. 参照《食品安全国家标准—食品中污染物限量》(GB 2762-2017),As、Pb、Cd、Cr的超标率分别为0.30%、1.50%、73.15%和5.06%,Cd的超标率高达73.15%,说明绝大多数小麦籽粒样品中的Cd含量超出国家标准,存在较大的粮食安全问题,应当引起足够重视,其余3种重金属的超标率均处于6%以下,表明在小麦籽粒中存在一定程度的累积. As、Pb、Cd、Cr的变异系数分别为78.2%、90.0%、70.6%、272.9%,均达到了重变异程度(CV>35%),表明研究区小麦籽粒重金属含量空间分异明显,受人为因素影响较大. K-S正态分布检验显示4种重金属均不符合正态分布,部分地区分布有高值点. Cd平均含量最高,Cr、As次之,Pb最低,这与内蒙古河套地区以及北京市小麦种植区的污染特征不同[26-27]. 4种重金属中Cd的点位超标率高达73.15%,且平均含量超出国家标准限值,远高于苏中地区Cd的4.65%以及某厂区34.3%的样点超标率[28-29]. 通过比较发现研究区Cd污染较为严重,这可能是因为不同区域污染来源、污染物释放程度、小麦品种不同等原因所致.
-
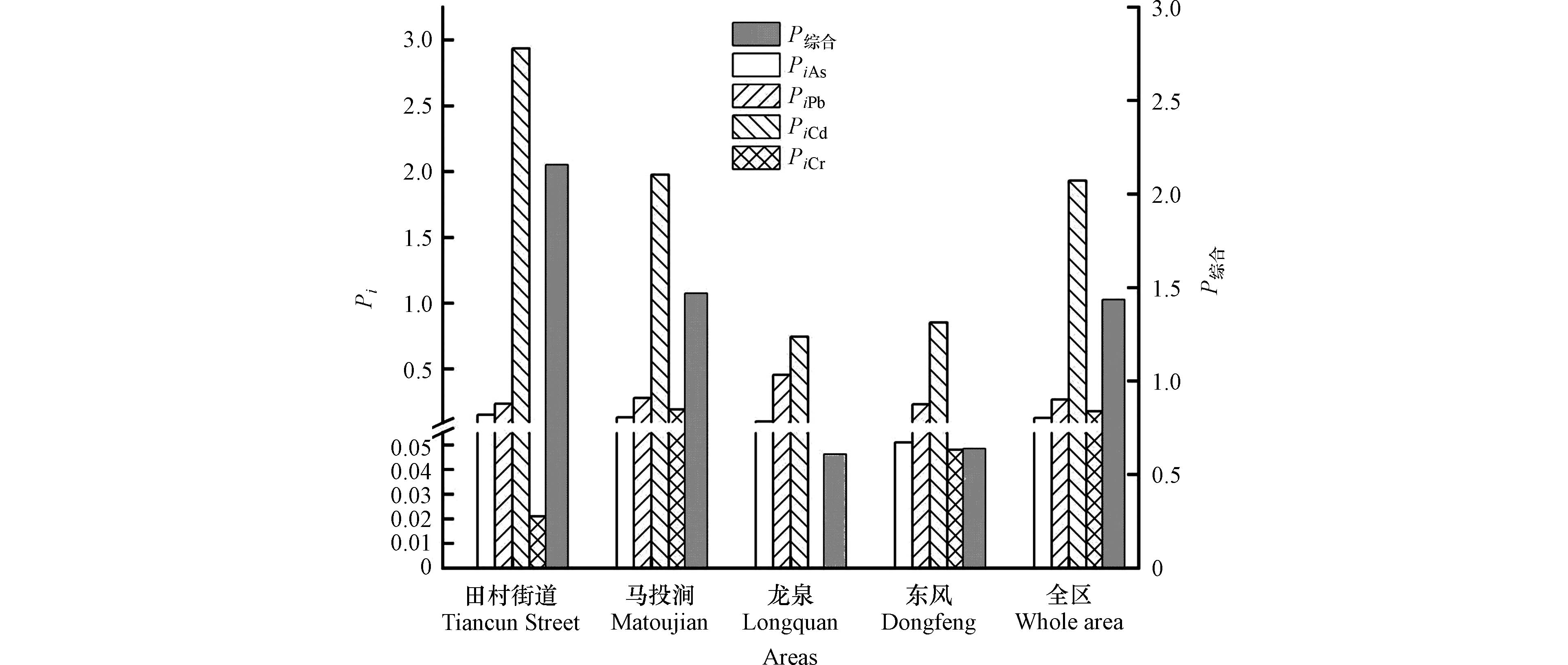
研究区各分区小麦籽粒重金属污染等级见表2. 单因子污染指数评价结果表明,Cd是对研究区小麦籽粒污染程度最高的重金属元素. 田村街道和马投涧镇的Cd污染指数平均值均>1,且田村街道样点中重度污染占比超过50%,表明这两个乡镇小麦籽粒存在不同程度的Cd污染,田村街道较马投涧镇污染更严重. 不同乡镇As、Pb和Cr的污染指数均<1,研究区上述重金属元素污染尚在清洁范围内. 除马投涧镇以外,其它乡镇As、Pb和Cr的无污染占比皆为100%.
综合污染指数评价结果如图3所示. 研究区小麦综合污染指数为1.435,属轻污染程度;各乡镇小麦综合污染指数从小到大依次为龙泉镇(0.608)<东风乡(0.637)<马投涧镇(1.469)<田村街道(2.157),田村街道属中度污染,马投涧镇属轻度污染,龙泉镇和东风乡属无污染. 田村街道东邻京广铁路线和107国道,交通流量大,且该地工业以有色金属冶炼和加工为主,Cd污染尤为严重,是综合污染指数最高的区域. 马投涧镇农业发达,工业以金属、煤炭、铁合金为主,经济发展速度较快,综合污染程度较田村街道次之. 龙泉镇和东风乡与上述两个乡镇相比,工业发展程度相对较弱,综合污染指数较低. 不同乡镇小麦籽粒污染状况存在差异,这可能是受地理位置、社会经济发展水平、产业分布、汽车尾气排放等污染源的因素影响[30-31].
-
样点重金属含量分级统计结果见图4. As整体上从西北部向东南部逐渐递增,含量低值点主要分布在西北部,最高值点和大部分较高值点主要分布在京广线和107国道西北部,小部分较高值点分布在西部. Cd整体上呈南北两端向中部递增,西北部多为低值点,东南部分布有大部分较高值点. Pb和Cr分布相对均匀,主要的高值点分部在中西部. 可以看出,研究区污染相对较重的两个区域,一是在两条交通干线附近,分布在该区域的样点As和Cd含量相对较高,Pb和Cr含量相对较低,可能是受到汽车尾气、固废堆积、化石燃料燃烧等因素影响[32-33],而这些因素对Pb和Cr的影响相对较小;另一个污染严重区域在中西部,Pb、Cr和Cd的大部分高值点均分布于此,可能是因为该地企业密集,受到周边钢铁、化工等企业的排废污染影响较大. 上述两个区域均在污染源的西北方,分析安阳市2019年8月—2020年6月风向数据发现,小麦生长期间,该地盛行风向为东南风,说明工业废气和粉尘会随风扩散沉降,造成小麦籽粒中重金属含量增加. 4种重金属中,Cd污染还可能与当地农业生产中施用化肥、喷洒农药等因素有关[34].
-
利用公式(3)—(6)计算得到成人和儿童摄食当地小麦可能产生的非致癌风险和致癌风险,结果见表3和表4. 由表3可知,成人和儿童对Pb的平均日摄入量(ADD)均低于暴露参考剂量(RfD),单项健康风险系数分别为1.08×10−1、1.67×10−1,均小于1,表明Pb对研究区居民不存在健康风险,但儿童的风险值要大于成人.
从表4可以看出,成人和儿童对Cr的平均日摄入量(ADD)均低于暴露参考剂量(RfD),而对As和Cd的平均日摄入量(ADD)均高于暴露参考剂量(RfD),说明从重金属日均摄入量来看,当地居民通过食用小麦所摄入的Cr尚未对人体健康造成威胁,As和Cd已经开始对人体健康造成威胁. As、Cd、Cr对成人的健康风险系数均值分别为6.75×10−4、8.40×10−3、6.32×10−4,儿童的风险系数平均值为1.04×10−3、1.30×10−2、9.79×10−4,均超出USEPA推荐的最大可接受风险临界值,且儿童的风险值均大于成人,表明存在致癌风险的可能性较高,应当引起人们的重视. 3种重金属致癌风险系数排序为Cd>As>Cr,Cd对成人和儿童的致癌风险远高于最大可接受风险临界值,As对儿童的致癌风险超出最大可接受风险临界值一个数量级. 而在小麦籽粒单项重金属污染评价结果中,当地As污染并不严重,这与健康风险评价结果存在差异,可能是由于As的致癌因子较高所导致的[35]. 研究区小麦籽粒健康风险评价结果与鲁北平原引黄灌区和华北某污灌区较为相似[35-36]. 从粮食安全角度考虑,应在保障产量的前提下,调整种植结构和布局,规避高污染区,培育Cd低积累小麦品种,或者在Cd高值区改种其他粮食作物.
-
(1)研究区小麦籽粒中As、Pb、Cd、Cr的平均含量分别为0.063、0.053、0.193、0.177 mg·kg−1,超标率分别为0.30%、1.50%、73.15%和5.06%. 各重金属的变异系数均达到了重变异程度.
(2)研究区小麦籽粒中Cd污染最为严重,As、Pb和Cr的污染指数皆小于1. 综合污染指数为1.435,属于轻污染程度. 4个乡镇中,田村街道的小麦综合污染指数最高,属中污染程度.
(3)研究区内重金属含量高值点主要集中在钢铁化工企业密集区以及两条交通干线附近,企业生产、交通运输产生的工业废气和汽车尾气等对该地小麦籽粒重金属含量有很大影响.
(4)非致癌重金属Pb对成人和儿童的健康风险系数均小于1,尚无健康风险. 致癌重金属As、Cd、Cr对成人和儿童的健康风险系数皆超出了USEPA推荐的最大可接受标准,存在致癌风险的可能性较高.
小麦籽粒重金属含量特征及人体健康风险评价——以河南省北部某县为例
Characteristics of heavy metal content in wheat grains and human health risk assessment — A county in northern Henan Province
-
摘要: 为评价小麦籽粒重金属含量污染特征及其健康风险,以河南省北部某县为研究区,采集小麦籽粒样品283个,测定样品中As、Pb、Cd、Cr含量,采用污染指数法、健康风险评价等方法分析研究区小麦籽粒中重金属污染程度,揭示空间分布特征,并评价人体健康风险. 结果表明,小麦籽粒中As、Pb、Cd、Cr的平均含量分别为0.063、0.053、0.193、0.177 mg.kg−1,Cd的超标率最高;小麦籽粒中重金属综合污染指数为1.435,达到轻污染程度;空间分级特征结果表明,附近交通和钢铁化工企业等因素是产生高污染的主要原因; As、Cd、Cr对成人和儿童健康风险系数最小值为6.32×10−4,均超出USEPA推荐的最大可接受标准,存在较高的致癌风险.Abstract: In order to evaluate the pollution characteristics and health risk of heavy metals in wheat grain, 283 wheat grain samples were collected from a county in northern Henan Province, and the contents of As, Pb, Cd and Cr in the samples were determined. The pollution degree of heavy metals in wheat grain in the study area was analyzed by pollution index method and health risk assessment, and the spatial distribution characteristics were revealed, and the human health risk was evaluated. The results showed that the average contents of As, Pb, Cd and Cr in wheat grains were 0.063, 0.053, 0.193 and 0.177 mg·kg−1, respectively, and the exceeding rate of Cd was the highest. The comprehensive pollution index of heavy metals in wheat grains was 1.435, reaching the level of light pollution. The spatial classification results show that the factors such as nearby traffic and steel chemical enterprises are the main causes of high pollution. The minimum health risk indexes of As, Cd and Cr for adults and children were 6.32×10−4, which exceeded the maximum acceptable risk range recommended by USEPA, and there was a high carcinogenic risk.
-
Key words:
- wheat grains /
- heavy metals /
- pollution assessment /
- health risk
-

-
表 1 健康风险模型评价参数
Table 1. Evaluation parameters of health risk mode
表 2 研究区各乡镇小麦污染指数及污染等级占比
Table 2. Wheat pollution index and pollution grade proportion in townships of the study area
区域
Areas样品数
Sample numbers元素
Elements单因子污染指数
Single factor contaminant index不同污染等级占比/%
Proportion of different pollution levels/%最大值 平均值 最小值 无污染 轻度污染 中度污染 重度污染 田村街道 26 As 0.286 0.150 0.010 100 田村街道 26 Pb 0.347 0.235 0.115 100 Cd 6.2 2.935 0.150 11.54 26.92 15.39 46.15 Cr 0.032 0.021 0.016 100 马投涧镇 225 As 1.124 0.133 0.006 99.53 0.47 Pb 1.945 0.279 0.108 97.78 2.22 Cd 8.400 1.976 0.240 21.78 42.67 22.67 12.88 Cr 3.210 0.191 0.011 94.44 4.17 1.39 龙泉镇 4 As 0.262 0.101 0.017 100 Pb 0.66 0.456 0.253 100 Cd 1.4 0.744 0.056 50 50 Cr — — — — 东风乡 28 As 0.156 0.051 0.014 100 Pb 0.575 0.231 0.110 100 Cd 2.200 0.852 0.330 75 21.43 3.57 Cr 0.080 0.048 0.014 100 “—”表示数据缺失. 表 3 小麦摄入途径下重金属摄入量及非致癌风险
Table 3. Heavy metal intake and non-carcinogenic risk under wheat intake pathway
重金属
Heavy metalADD HQ 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 Pb 3.78×10−4 5.86×10−4 1.08×10−1 1.67×10−1 表 4 小麦摄入途径下重金属摄入量及致癌风险
Table 4. Heavy metal intake and carcinogenic risk under wheat intake pathway
人群
PopulationADD RI R As Cd Cr As Cd Cr 成人
Adults4.50×10−4 1.37×10−3 1.26×10−3 6.75×10−4 8.40×10−3 6.32×10−4 9.71×10−3 儿童
Children6.96×10−4 2.13×10−3 1.95×10−3 1.04×10−3 1.30×10−2 9.79×10−4 1.50×10−2 -
[1] BRADL H B. Sources and origins of heavy metals[M]//Heavy Metals in the Environment: Origin, Interaction and Remediation. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2005. 1-27. [2] 刘剑飞, 胡留杰, 廖敦秀, 等. 食用菌生物修复重金属污染研究进展 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(2): 543-548. LIU J F, HU L J, LIAO D X, et al. Bioremediation of heavy metal pollution by edible fungi: A review [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(2): 543-548(in Chinese).
[3] 强承魁, 秦越华, 丁永辉, 等. 徐州地区麦田土壤和小麦籽实重金属污染特征分析 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(6): 1032-1038. QIANG C K, QIN Y H, DING Y H, et al. Pollution characteristics of heavy metals in soils and wheat grains in Xuzhou area [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(6): 1032-1038(in Chinese).
[4] CHEN H Y, TENG Y G, LU S J, et al. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 512/513: 143-153. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.025 [5] JOSEPH T, DUBEY B, MCBEAN E A. Human health risk assessment from arsenic exposures in Bangladesh [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 527/528: 552-560. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.05.053 [6] SEYED A M, REZA S A, FAEZEH H. Heavy mental concentration and availability of different soils in Sabzevar area, NE of Iran [J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2017, 134(10): 106-112. [7] KHAN S, CAO Q, ZHENG Y M, et al. Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2008, 152(3): 686-692. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.056 [8] ZARCINAS B A, PONGSAKUL P, MCLAUGHLIN M J, et al. Heavy metals in soils and crops in Southeast Asia 2. Thailand [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2004, 26(3/4): 359-371. [9] 蔡燕子, 谢湉, 于淑玲, 等. 黄河三角洲农田土壤-作物系统重金属污染风险评估 [J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(1): 48-55. CAI Y Z, XIE T, YU S L, et al. Assessment of the heavy metal pollution risks in soil-crop systems of farmlands in the Yellow River Delta [J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 2018, 54(1): 48-55(in Chinese).
[10] 范健, 廖启林, 许宏铭, 等. 稻米与小麦吸收土壤重金属的基本特征 [J]. 地质学刊, 2016, 40(4): 701-709. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2016.04.701 FAN J, LIAO Q L, XU H M, et al. General characteristics of heavy metals absorbed by rice and wheat seeds within topsoil of farmland [J]. Journal of Geology, 2016, 40(4): 701-709(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2016.04.701
[11] DING C F, ZHANG T L, WANG X X, et al. Prediction model for cadmium transfer from soil to carrot (Daucus carota L.) and its application to derive soil thresholds for food safety [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2013, 61(43): 10273-10282. doi: 10.1021/jf4029859 [12] 王怡雯, 芮玉奎, 李中阳, 等. 冬小麦吸收重金属特征及与影响因素的定量关系 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(3): 1482-1490. WANG Y W, RUI Y K, LI Z Y, et al. Characteristics of heavy metal absorption by winter wheat and its quantitative relationship with influencing factors [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(3): 1482-1490(in Chinese).
[13] 孙亚芳, 王祖伟, 孟伟庆, 等. 天津污灌区小麦和水稻重金属的含量及健康风险评价 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(4): 679-685. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.04.011 SUN Y F, WANG Z W, MENG W Q, et al. Contents and health risk assessment of heavy metals in wheat and rice grown in Tianjin sewage irrigation area, China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(4): 679-685(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.04.011
[14] 陈京都, 戴其根, 许学宏, 等. 江苏省典型区农田土壤及小麦中重金属含量与评价 [J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(11): 3487-3496. doi: 10.5846/stxb201105080598 CHEN J D, DAI Q G, XU X H, et al. Heavy metal contents and evaluation of farmland soil and wheat in typical area of Jiangsu Province [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(11): 3487-3496(in Chinese). doi: 10.5846/stxb201105080598
[15] 马传鑫, 汪志荣, 高琼, 等. 天津市典型污灌区冬小麦各生育期的重金属分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2010, 29(1): 44-47. MA C X, WANG Z R, GAO Q, et al. Heavy metal analysis of winter wheat at each stage in typical sewage irrigated area of Tianjin [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2010, 29(1): 44-47(in Chinese).
[16] 河南省重金属污染防治工作指导意见[Z]. 河南省环境保护厅, 2017. Guidance on Prevention and Control of Heavy Metal Pollution in Henan Province [Z]. Henan Provincial Department of Environmental Protection, 2017.
[17] CAO C, CHEN X P, MA Z B, et al. Greenhouse cultivation mitigates metal-ingestion-associated health risks from vegetables in wastewater-irrigated agroecosystems [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 560/561: 204-211. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.044 [18] 康国华, 张鹏岩, 李颜颜, 等. 黄河下游开封段引黄灌区小麦中重金属污染特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(8): 3917-3926. KANG G H, ZHANG P Y, LI Y Y, et al. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in wheat grains cultivated in Kaifeng irrigation area of the Yellow River [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(8): 3917-3926(in Chinese).
[19] 段小丽. 中国人群暴露参数手册概要-儿童卷 [M]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2016.1-1107. DUAN X L. Highlights of the Chinese exposure factors handbook 分辑名: 儿童卷 Children[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Press, 2016.1-1107(in Chinese). [20] USEPA. Superfund public health exaluation manual [R]. EPA/540/1-86/060. Washington, DC: Environmental Protection Agency, 986, 1-52. [21] 张江华, 徐友宁, 吴耀国. 小秦岭金矿区小麦和玉米重金属的健康风险评价 [J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(2): 501-508. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.02.016 ZHANG J H, XU Y N, WU Y G. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in wheat and maize in the Xiaoqinling gold mining Area [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(2): 501-508(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.02.016
[22] CASRN 7439-92-1, Lead and compounds (inorganic) [S]. [23] CASRN 7440-43-9, Cadmium [S]. [24] 王世玉, 吴文勇, 刘菲, 等. 典型污灌区土壤与作物中重金属健康风险评估 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(4): 1550-1560. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.04.043 WANG S Y, WU W Y, LIU F, et al. Assessment of human health risks of heavy metals in the typical sewage irrigation areas [J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(4): 1550-1560(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.04.043
[25] 杨文晓. 陕西主要麦区小麦籽粒中重金属含量调查及对人体健康的风险评价[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2019: -82 YANG W X. Inverstigation of heavy metal concentrtaion in wheat grain and human health risk assessment in Shaanxi Province[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2019.1-82.
[26] 张青, 段海龙, 廖蕾, 等. 内蒙古河套地区小麦重金属含量与土壤质量的关系研究 [J]. 安全与环境工程, 2010, 17(1): 36-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2010.01.009 ZHANG Q, DUAN H L, LIAO L, et al. Research on the relationship between the heavy metal content of wheat and the quality of soil in Hetao area, Inner Mongolia [J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2010, 17(1): 36-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2010.01.009
[27] 李晓燕, 陈同斌, 谭勇壁, 等. 北京市小麦籽粒的重金属含量及其健康风险分析 [J]. 地理研究, 2008, 27(6): 1340-1346. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2008.06.013 LI X Y, CHEN T B, TAN Y B, et al. Concentrations and risk of heavy metals in grain of wheat grown in Beijing [J]. Geographical Research, 2008, 27(6): 1340-1346(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2008.06.013
[28] 朱昊, 吴春发, 陈宜. 苏中地区小麦籽粒重金属含量水平及健康风险 [J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2017, 29(1): 35-38,56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2017.01.008 ZHU H, WU C F, CHEN Y. Concentrations of heavy metals in wheat grains and their potential health risk in the central region of Jiangsu [J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2017, 29(1): 35-38,56(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2017.01.008
[29] 赵多勇, 魏益民, 魏帅, 等. 区域小麦籽粒重金属分布及暴露评估 [J]. 中国粮油学报, 2016, 31(7): 6-10,18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2016.07.002 ZHAO D Y, WEI Y M, WEI S, et al. Spatial distribution of heavy metal in wheat kernal and dietary exposure assessment of local residents in an industrial area [J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2016, 31(7): 6-10,18(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2016.07.002
[30] 阳小成, 赵桂丹, 熊曼君, 等. 川西北高原路侧土壤重金属分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2018, 24(2): 239-244. YANG X C, ZHAO G D, XIONG M J, et al. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of soil heavy metal contamination along roadsides of the northwestern Sichuan Plateau, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2018, 24(2): 239-244(in Chinese).
[31] FÉLIX O I, CSAVINA J, FIELD J, et al. Use of lead isotopes to identify sources of metal and metalloid contaminants in atmospheric aerosol from mining operations [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 122: 219-226. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.11.057 [32] 王学锋, 姚远鹰. 107国道两侧土壤重金属分布及潜在生态危害研究 [J]. 土壤通报, 2011, 42(1): 174-178. WANG X F, YAO Y Y. Spatial distribution and ecological hazard of heavy metals in roadside soils along the 107th national highway [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2011, 42(1): 174-178(in Chinese).
[33] 任福民, 汝宜红, 许兆义, 等. 铁路旅客列车垃圾中重金属元素调查及防治对策的研究 [J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2002, 12(3): 74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2002.03.019 REN F M, RU Y H, XU Z Y, et al. Investigation on heavy metal content in garbage from passenger trains and study on countermeasures [J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2002, 12(3): 74-78(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2002.03.019
[34] FILZEK P D B, SPURGEON D J, BROLL G, et al. Pedological characterisation of sites along a transect from a primary cadmium/lead/zinc smelting works [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2004, 13(8): 725-37. doi: 10.1007/s10646-003-4472-6 [35] 王娟娟. 鲁北平原引黄灌区土壤-小麦系统重金属分布特征及污染风险评价[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2019.1-89. WANG J J. Distribution characteristics and pollution risk assessment of heavy metals in soil-wheat system of Yellow River irrigation district in lubei plain[D]. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2019.1-89.
[36] 肖冰, 薛培英, 韦亮, 等. 基于田块尺度的农田土壤和小麦籽粒镉砷铅污染特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(6): 2869-2877. XIAO B, XUE P Y, WEI L, et al. Characteristics of cd, as, and Pb in soil and wheat grains and health risk assessment of grain-Cd/as/Pb on the field scale [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(6): 2869-2877(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: