-
重金属是环境中普遍存在的一类污染物,具有难降解性、生物富集性等特性[1]。重金属污染物经由“三废”即废渣、废水及废气等途径排放到周围环境中,并通过雨水冲刷、海陆间循环等汇聚于江河湖海中[2]。水体中的重金属通过吸附、络合和沉降等途径富集到沉积物中[3]。当水体理化性质发生改变时,吸附在河流沉积物中的重金属会向上水体中缓慢释放,造成水体的“二次污染”,沉积物已成为河流重金属污染的汇集地和重要内源[4]。因此,着手这方面的研究,有助于人们把握污染来源和改善城市水环境,具有实际意义和学术价值。
淮河位于中国东部,是中国七大江河之一。淮河江苏段作为淮河流域的重要组成部分,是南水北调东线的主线河流,在江苏省境内延伸至宿迁、淮安、盐城、扬州等8个省辖市。淮河江苏段主要包括洪泽湖和苏北灌溉总渠两大区域,水域面积为6.53万 km2,约占淮河流域的四分之一[5]。随着淮河两岸经济的发展,未处理的生活污水与工业废水的大量排放,致使淮河江苏段的重金属污染日趋严重[6]。余辉等在洪泽湖采集10个点位的表层沉积物并分析Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、Cr、Hg和As等重金属的含量,发现洪泽湖中的Cd达到中污染水平,且存在较重的Cd生态风险[7]。最近的研究也发现,洪泽湖表层沉积物中重金属Cd的生态危害依然较大[8]。此外,陈孝杨等对淮河流域安徽段水系沉积物中的重金属开展调查,发现沉积物出现Cd和Mn重金属污染现象[9]。然而,关于淮河江苏段表层沉积物的重金属的研究相对较少。
本研究以江苏省内主要淮河江苏段为研究对象,调查表层沉积物8种重金属的含量,着重探讨沉积物中重金属空间分布特征及其来源,并对淮河江苏段主要污染现状作出评价,进一步完善淮河污染综合评价体系,以期为淮河水环境治理提供依据。
-
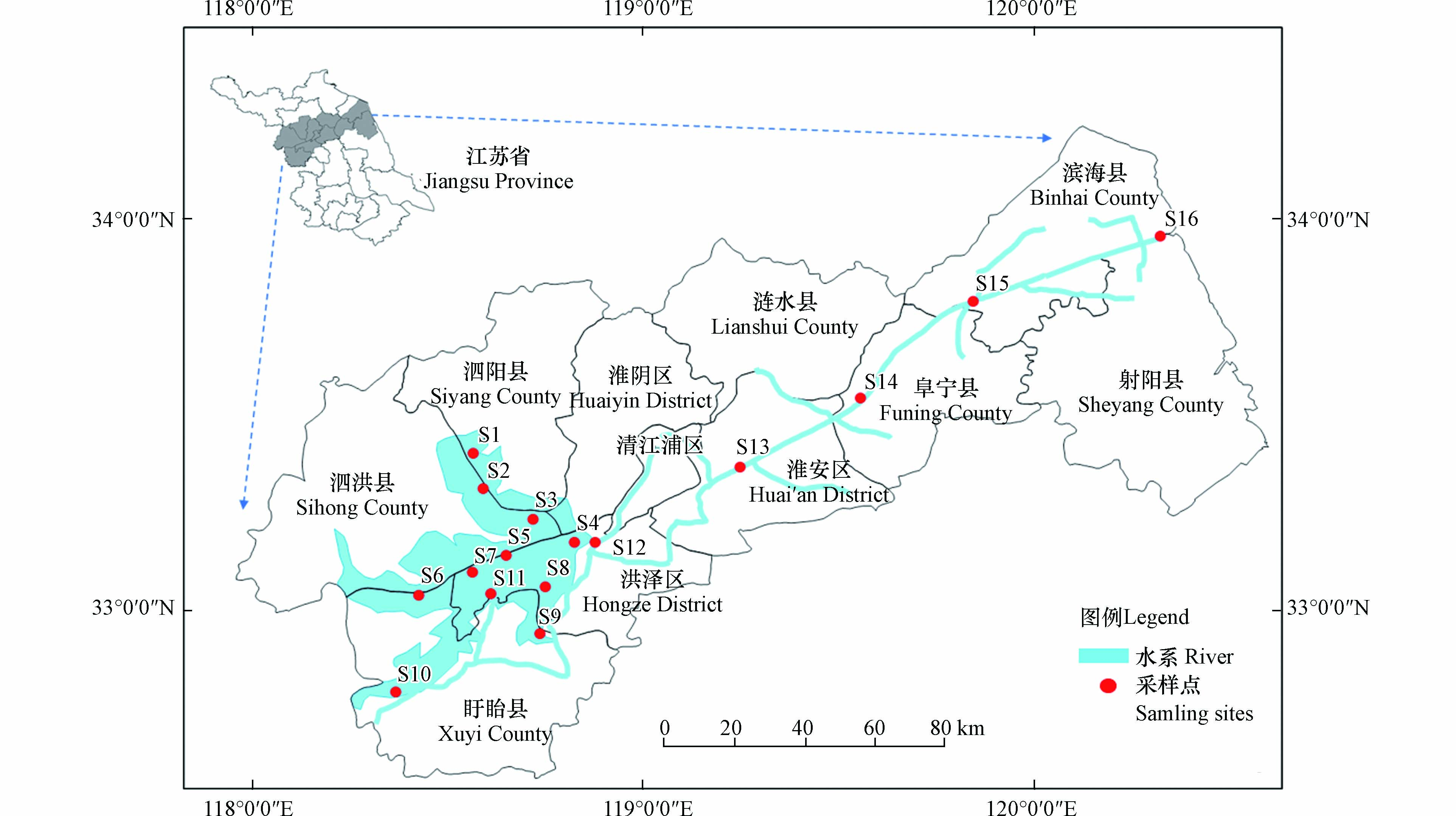
2019年12月—2020年1月,根据潮汐、水流的特征结合近岸排污口的分布情况,对淮河江苏段进行综合调查和样品采集。本次在研究区域设置了16个采样点,调查水域采样点共划分为2个区:洪泽湖和苏北灌溉总渠。流域内洪泽湖水流平稳,布设10个点位;苏北灌溉总渠共布设6个点位。采样过程中采样点的位置由GPS确定,采集16个采样点底泥,并对周边环境特征进行详细记录,采样点分布见图1。采样具体操作为:每个采样点使用抓斗式底泥采样器,在点位附近多点组合采样,充分混匀后用自封袋封装后冷藏(4 ℃)保存。
-
沉积物样品在实验室中通过电热恒温干燥箱干燥后,去除杂物,研磨过孔径为100目(0.15 mm)尼龙筛,并采用王水对其予以微波消解(CEM Mars6),其浓度用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)测定。ArcGis10.0绘制采样点位图,利用 SPSS Statistics 26软件对采样点重金属含量予以Spearman相关系数检验。运用了Origin 、Excel软件绘制图表。
-
本实验中所用试剂均为优级纯,试剂溶液均用二次去离子水配制。沉积物中Cd、Mn、Cu、Zn、As、Ni、Pb和Cr的方法检出限的范围为0.04—2 mg·kg−1,定量限的范围为0.16—8 mg·kg−1。加标回收率为70%—125%。采用标准土壤样品(ERM-S-510203、ERM-S-510202)进行实验过程质量控制。平行样品测量值相对偏差都小于20%,空白样中目标重金属均远低于样品浓度。
-
富集系数(Enrichment Factor,EF)是用来评估土壤和沉积物中重金属富集水平受人为影响效应的重要参变量[10-12],其背景值用江苏省表层土壤元素地球化学基准值[13]。根据富集系数的大小可以区分土壤中重金属富集的自然的和人为的环境影响。富集因子计算公式如下:
式中, (Ci /Cn)sediment是沉积物中金属 i 与参比元素 n 的检测含量比,(Ci/Cn)background是底泥中金属 i 与参比元素 n 的环境背景值含量比。重金属Ti性质较稳定,不易受所在环境与分析测试过程的影响。因此,本研究采用 Ti 作为参比元素。
Sutherland[14]以富集系数( EF 值) 的大小为划分依据,将富集污染程度分为 6 个水平,如表1 所示。
-
生物毒性不利影响评价利用生物毒性不利影响 (mean probable effect concentrations quotients,mPEC-Q) 评价表层沉积物重金属的混合生物效力[15], 计算公式如下式:
式中,n为重金属的种类;
$ {C}_{\mathrm{r}}^{i} $ 为第i种重金属的实测浓度(mg·kg−1);PECi表示第i种重金属的可能作用毒性浓度; mPEC-Q包含2 个临界值,划分为阈值效应浓度(threshold effect concentration, TEC)和可能效应浓度(probable effect concentration, PEC)[16]。重金属的TEC值与PEC值如表2,关于Mn的生态毒性研究还不够,尚缺乏相关的毒性系数以及 TEC、PEC值[17-18],故生物毒性不利影响与潜在生态风险指数评价均不包含Mn。计算后以 mPEC-Q值的大小为依据,生物毒性不利影响划分成 3个等级[10,19],见表3。单个重金属浓度与2个临界值比较,可以更深刻得对样品重金属的生态危害毒性进行评价。若
${C}_{r}^{i}$ <TEC,则重金属对底栖动物没有危害作用;若PEC<${C}_{r}^{i}$ <TEC,重金属可能会对底栖动物形成危害风险;若${C}_{r}^{i}$ >PEC,则重金属对底栖动物发生危害影响[20]。 -
潜在生态风险指数(RI)是Hakanson首次提出的一种用来评估沉积物中重金属污染水平的评价方式[21-22]. 计算公式如下式:
式中,n代表重金属的种类;
${E}_{r}^{i}$ 表示第i种重金属的潜在危害环境指数;${C}_{r}^{i}$ 为样品中第i种重金属的实测浓度(mg·kg−1),${C}_{n}^{i}$ 为对应重金属的环境背景参照值(mg·kg−1),${T}_{r}^{i}$ 为重金属i的毒性系数(TCd = 30 > TAs = 10 > TCu = TNi = TPb =5 > TCr =2 > TZn =1[23]。 -
淮河江苏段河流沉积物的重金属含量特征如表4所示,表层沉积物中重金属的含量平均大小顺序为:Mn> Zn> Cr > Ni > Cu > Pb > As> Cd,除Cd、Cr外,其他重金属含量均不同程度超过江苏省土壤背景值,其中 Zn与Mn含量分别是背景值的1.49 倍和1.25倍。调查结果表明,淮河江苏段沉积物重金属含量相对较高,特别是Zn与Mn。变异系数(CV)反映人类活动的影响程度,一般受人为污染越大,其污染物在地理位置上分散程度越高,即CV越高[24]。从表4可以看出,Cr、Ni、Pb、Cu、As、Mn、Zn重金属的变异系数较小,暗示了空间分散比较均匀与空间离散性较小,且受外源污染较小。但是Cd的变异系数最大,达到2.74,表明Cd在各点位不均匀分布,离散程度较大。结合变异系数及相关性分析,可知Cd某些点位受人类活动扰动因素及外源污染因素的干扰较大,有可能是水土流失严重导致。研究表明长江中下游地区土壤侵蚀状况变化与水土流失会对湖库水质的造成一定程度的影响[25]。Luo等研究发现,长江流域湖泊沉积物中含有高浓度的Cd,且水土流失是影响长江流域中Cd含量的重要因素之一[26]。据报道,湖泊沉积物中Cd、Cu与Cr等重金属的含量会受到淤泥和黏土的迁移等因素的影响[27]。
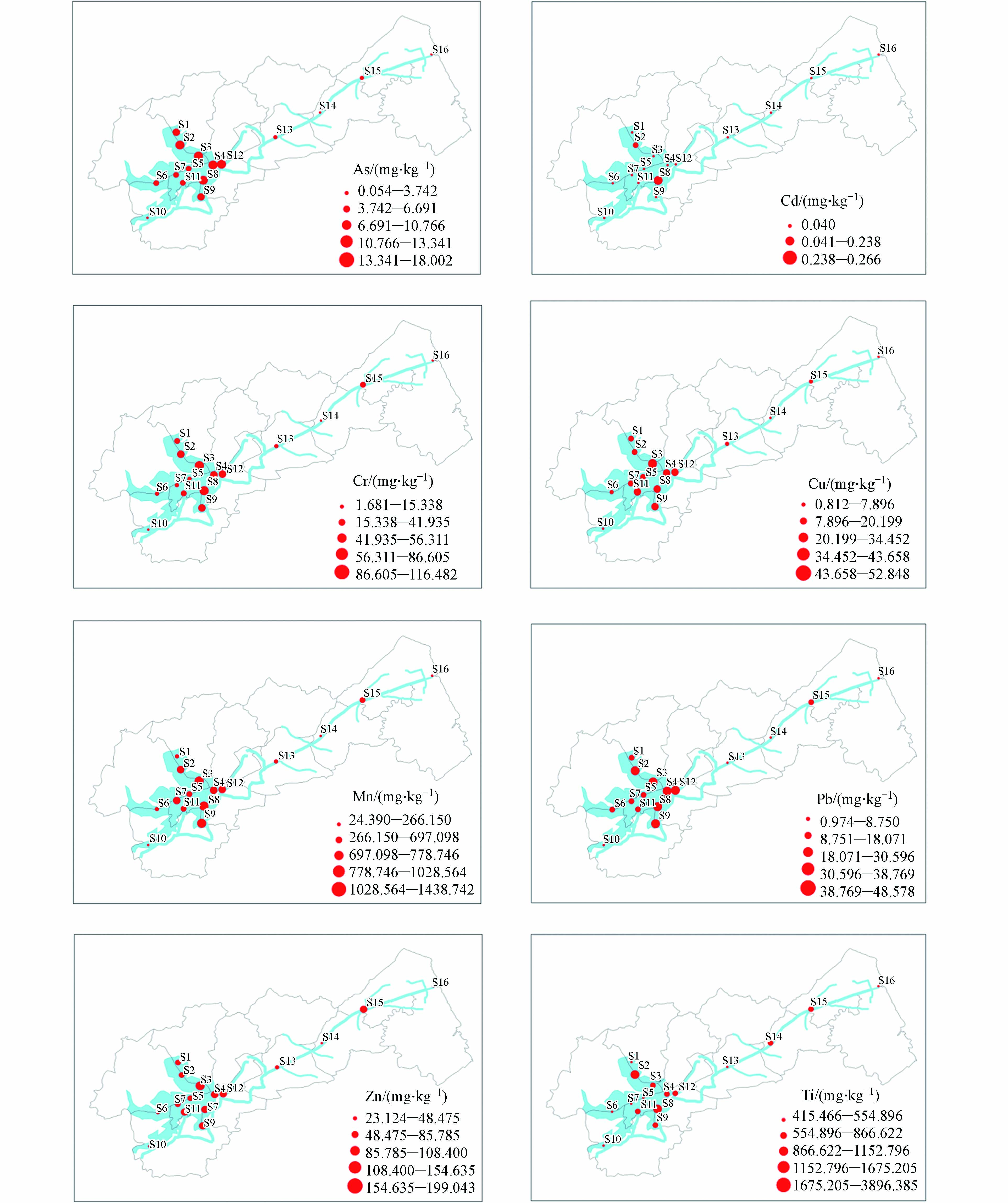
表层沉积物重金属空间分布特征如图2所示。结果显示,表层沉积物中Cd、Mn、Cu、Zn、As、Ni、Pb和Cr含量空间分布差异明显。其中,S1、S2、S3、S4、S8、S9、S11、S12和S15各点重金属含量较高,主要聚集在洪泽湖北部及围湖地区,洪泽湖北部(S1、S2、S3)污染状况最严重,东部围湖(S4、S8、S12)较严重,南部围湖(S9、S12)次之,苏北灌溉总渠采样点重金属污染程度较低。
根据水流及周边情况进行分析,其污染原因可能为:首先,洪泽湖北部存在多个污水处理厂,处理后污水虽然已符合城镇污水处理厂排放标准,却未达到河道的Ⅲ类标准,给洪泽湖北部底泥带来了污染压力。第二,洪泽湖是南水北调东线工程的重要节点湖泊。而长江江苏段重金属污染程度较为严重,调水过程可能将高浓度的重金属转移至洪泽湖。因此南水北调也是淮河江苏段重金属污染的重要来源之一[28]。第三,洪泽湖附近大量化肥和农药的使用也是导致淮河江苏段重金属污染的另一个重要因素[8]。最后,洪泽湖的入湖河道集中于洪泽湖西部,受水流冲刷影响,西部污染状况重金属含量不高,污水直排河道带来了重金属污染。加上采样时间为12月及1月,冬季降雨量较少且河道流动性差,给东部和北部围湖水体中沉积物造成重金属污染。综上,沉积物中重金属污染主要受污染源影响,但河道特性、泥沙淤积及水流特性等因素在一定程度上影响了沉积物中重金属污染物的空间分布。
-
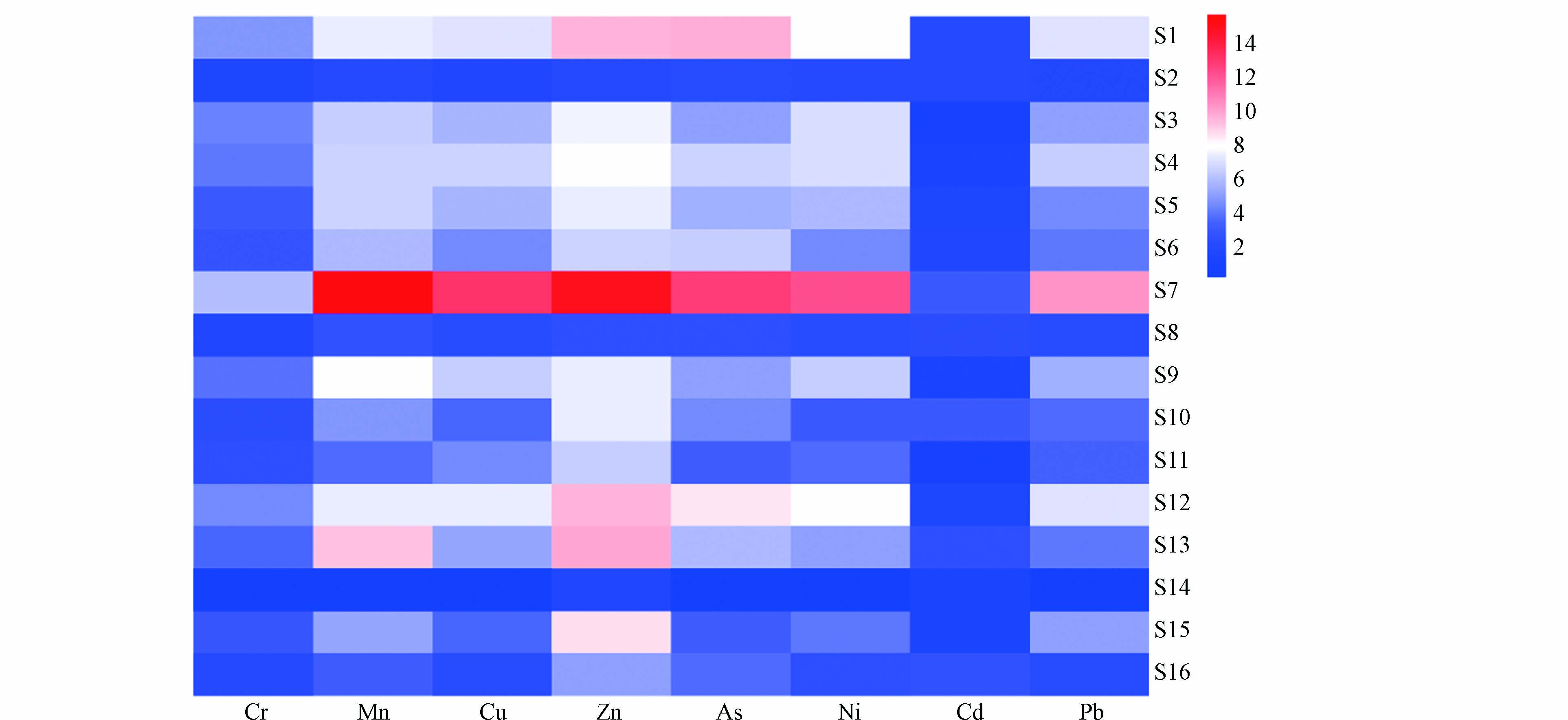
根据各重金属相关性分析显示,Cd 与Cr、Mn、Cu、Zn、Ni、Pb等重金属没有显著相关性,表明其来源的特殊性。然而,Cr与Mn、Cu、Zn、As、Ni、Pb等重金属存在显著的正相关关系(P < 0.01); Mn与Cu、Zn、As、Ni、Pb显著正相关(P < 0.01); Cu与Zn、As、Ni、Pb存在显著的正相关关系(P < 0.01);Zn与As、Ni、Pb显著正相关(P < 0.01);As与Ni、Pb显著正相关(P < 0.01)。部分重金属含量之间没有相关性,表明金属含量不是受单一因素控制,而是受多种因素控制。两种重金属含量之间的关系相关系数高,说明这两种金属来源相同,并且一起运输[27]。Cr、Mn、Cu、Zn、As、Ni、Pb等重金属在淮河江苏段沉积物中可能具有相同来源,可能吸附在沉积物中的粉砂和黏粒上。
淮河江苏段沉积物的重金属进行KMO 度量值检验,结果表明各元素间适合进行主成分分析。Ni、Pb、 Cr 、Cu 、Mn 、As、Zn的第一主成分达到0.9以上,第一主成分的贡献率为83.508%。8种重金属元素仅提取出一个成分,结果表明淮河江苏段沉积物的Ni、Pb、 Cr 、Cu 、Mn 、As与Zn等重金属污染可能具有同源性,来自相近污染源。据报道,洪泽湖表层沉积物中Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、Fe、Al 之间有很好的相关性, 这些元素污染具有同源性[7]。訾鑫源等发现,洪泽湖表层沉积物中Cr、Ni、Zn与As具有显著相关性,说明具有相同的来源或者产生了复合污染[8]。洪泽湖表层沉积物中Cr、Zn、Pb与Cd污染来源基本一致,对重金属潜在生态危害综合指数影响较大[29]。研究表明重金属污染源来自于工业污水,含有 Cu、Cr、Pb与As重金属的采矿、电子以及电镀和冶炼等行业废水,与江苏省产业结构中的支柱行业类型相符[30]。
-
如图3所示,淮河江苏段河流表层沉积物中重金属的平均富集水平排序为Zn>Mn>As>Ni>Cu>Pb>Cr>Cd。其中Zn、Mn 和As 的平均富集系数分别达到7.01、5.79、和5.16,为显著富集,而Cd基本无富集,其他重金属基本为中度富集;空间上看,点位S2、S14、S16富集程度较不明显,呈现无富集或轻微富集状态。而点位S7(围湖点位)的重金属Mn、Zn富集程度较为明显,其他元素为部分显著富集和中度富集状态。总体上,淮河江苏段河流表层沉积物中Zn、Mn和As的富集程度相对较高,点位S7(围湖点位)存在一定重金属富集。訾鑫源等调查发现,洪泽湖中表层沉积物富集因子排序为Cd>As>Pb>Zn>Cu> Ni>Cr [8]。在太湖与杭州湾等地表层沉积物中也发现Zn、Mn和As等重金属存在一定程度的富集。任杰等对太湖表层沉积物的重金属进行分析,重金属富集程度结果显示Mn、Zn 与Ni等重金属显著富集[31]。姜文博等也发现,杭州湾表层沉积物中Pb 和 Zn 的富集程度相对较高[32]。
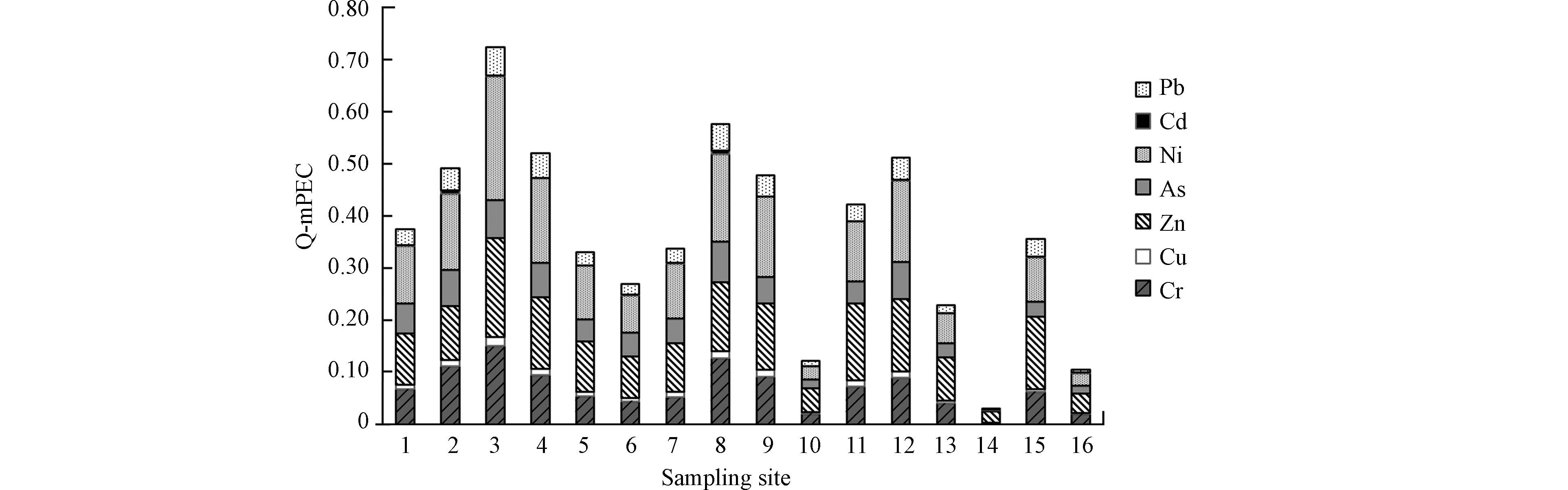
淮河江苏段表层沉积物中重金属生物毒性不利影响评价结果见图4。研究区域中除采样点14,其他各采样点重金属的mPEC-Q值均在0.1—1之间,S14生物毒性不利影响处于低风险状态,其他点位处于中风险状态,并且由贡献率可知各点位重金属的组成具有相似性,Ni、Zn贡献率较大。 将重金属的浓度与TEC值和PEC值比较, Cu、Cd、Pb浓度数值低于TEC值,表明Cu、Cd、Pb对底栖动物不产生危害; Ni、Zn、Cr、As的浓度值介于TEC值与PEC值之间,表明 Ni、Zn、Cr和As可能会对底栖动物产生危害作用。
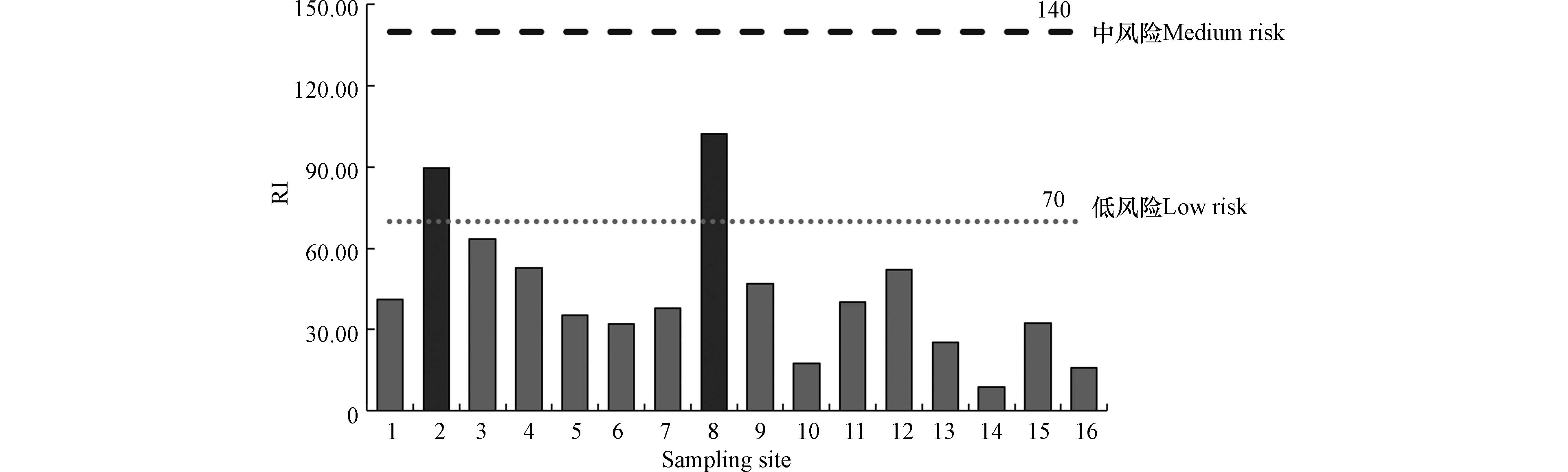
潜在生态风险指数如图5, S2、S8的 RI值较高,根据风险等级划分,属于中风险,其余采样点风险等级均为低风险。上述结果表明淮河江苏段沉积物重金属整体表现为较重生态风险水平。余辉等对洪泽湖表层沉积物重金属进行生态风险评价,结果发现洪泽湖中Cd的生态风险程度达到较重风险程度, 其余重金属污染状况相对较轻[7]。訾鑫源等也发现类似的现象,洪泽湖表层沉积物中 Cd 存在严重的潜在生态风险,其他元素污染程度较轻[8]。周德山等调查发现,洪泽湖表层沉积物中重金属的潜在生态危害处于轻微水平[29]。此外,李星谕等研究汤逊湖表层沉积物重金属的生态风险评价,发现汤逊湖表层沉积物Hg 和 Cd 处于偏中度污染,总体处于较重的重金属潜在生态风险[33]。陈斌等发现,珠江口表层沉积物重金属的潜在生态风险属于中等范畴[34]。研究发现太湖湖区部分区域的生态风险仍处于中等或较高生态风险等级[31]。
-
(1)在淮河江苏段表层沉积物中Cr、Mn、Cu、Zn、As、Ni、Cd与Pb重金属中,除 Cr、Cd、Pb均值低于或靠近于其相对应背景值外,其他重金属浓度均不同程度地高于江苏省土壤背景值,实测值与背景值比值从高到低依次为Zn、Mn、As、Ni、Cu,表明Zn、Mn污染最严重,重金属污染主要聚集在洪泽湖北部及围湖地区,苏北灌溉总渠采样点重金属污染程度较低。
(2)16个采样点的富集水平排序为Zn >Mn >As >Ni>Cu >Pb >Cr>Cd,其中,重金属Mn、Zn富集程度较为明显,S7点位Mn、Zn重金属呈显著富集状态;
(3)生物毒性不利影响评价结果显示,重金属Cu、Cd、Pb对底栖动物不产生危害;Ni、Zn、Cr、As可能会对底栖动物产生危害作用;而这16个点的生物毒性不利影响总体处于中风险状态,主要贡献来源于Ni、Zn。
(4)各采样点的潜在生态风险指数RI除采样点S2、S8外,均小于70 ,为轻微生态风险,采样点S2、S8(70<RI<140)为中等生态风险。
综上,淮河江苏段表层沉积物重金属Zn、Mn、As、Ni、Cu等重金属的含量均高于其背景,其中Mn和Zn富集程度较为明显。表层沉积物重金属对生物不利影响较大,且整体表现为较重生态风险水平。
淮河江苏段沉积物重金属的分布特征、来源解析及其生态风险
Pollution characteristics, potential sources, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Jiangsu section of Huaihe River
-
摘要: 为了解淮河江苏段沉积物重金属的污染特征、空间分布及其生态风险,对其表层沉积物中重金属(Cd、Mn、Cu、Zn、As、Ni、Pb和Cr)的含量进行检测,利用相关性和主成分进行重金属来源分析,并采用富集系数与生物毒性不利影响对表层沉积物重金属进行污染评价。结果表明,除Cd与Cr外,Zn、Mn、As、Ni、Cu等重金属的含量均高于江苏土壤背景值。重金属含量空间分布差异明显,其中洪泽湖北部及围湖地区等地重金属污染状况最严重,来源可能来自城镇污水、工业废水等复合污染。富集水平排序为Zn >Mn >As >Ni>Cu >Pb >Cr>Cd,其中Mn、Zn富集程度最为明显。生物毒性不利影响评价总体处于中风险状态,主要贡献来源于Ni、Zn。除了Cu、Cd、Pb外,Ni、Zn、Cr、As重金属可能会对底栖动物产生危害作用。因此,淮河江苏段沉积物重金属整体表现为较重生态风险水平。Abstract: In order to understand the pollution characteristics, spatial distribution, potential sources, and ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Huaihe river basin, the contents of heavy metals (Cd, Mn, Cu, Zn, As, Ni, Pb, and Cr) were analyzed. The potential sources of heavy metal were analyzed by correlation and principal component analysis. Using enrichment factor and mean Probable Effect Concentrations Quotients (mPEC-Q), the potential ecological risk degree of heavy metals in the sediments were evaluated. The results showed that except Cd, Cr, and As, the contents of Zn, Mn, As, Ni, and Cu were higher than their background values. The contents of heavy metals are higher in the north of Hongze, which may come from the combined pollution of domestic sewage and sewage discharge. The mPEC-Q are at medium risk level, and Ni, Zn, Cr, and As result in the damage to benthos. Thus, the heavy metals in surface sediments of Huaihe river basin showed a high ecological risk level.
-

-
表 1 富集系数评价指标
Table 1. Enrichment factors of Evaluation index
等级
GradeEF值
Enrichment factors富集(污染)程度
Pollution gradeⅠ ≤1 无富集(无污染) Ⅱ 1—2 轻微富集(轻微污染) Ⅲ 2—5 中度富集(中度污染) Ⅳ 5 —20 显著富集(强污染) Ⅴ 20 —40 强烈富集(较强污染) Ⅵ >40 极强富集(极强污染) 表 2 各种重金属的 TEC、PEC 和
$ {T}_{\mathrm{r}}^{i} $ Table 2. TEC, PEC, and
$ {T}_{\mathrm{r}}^{i} $ Cr Cu Zn As Ni Cd Pb Mn TEC 43.4 121 31.6 9.79 22.7 0.99 35.8 — PEC 111 459 149 33 48.6 4.98 128 — $ {T}_{r}^{i} $ 2 5 1 10 5 30 5 — 表 3 mPEC-Q及RI风险等级划分
Table 3. Risk classification of mPEC-Q and RI
mPEC-Q及RI值 危害程度
Risk classificationmPEC-Q≤0.1或RI≤70 低风险或轻微生态风险 0.1<mPEC-Q≤1或70<RI≤140 中风险或中等生态风险 mPEC-Q>1或RI >140 高风险或强生态风险 表 4 重金属含量描述统计
Table 4. Descriptive statistics of each metal content
元素
Element含量变化范围
Content range平均值
Average value变异系数
Coefficient of variation江苏土壤背景值
Baseline values of elements
in soil of Jiangsu ProvinceCr 1.68—116.48 53.05 0.59 76.00 Mn 24.39—1438.74 786.42 0.50 629.00 Cu 0.81—52.85 27.83 0.54 26.00 Zn 23.12—199.04 109.17 0.43 73.00 As 0.05—18.00 10.55 0.51 9.40 Ni 0.19—80.86 36.60 0.58 32.90 Cd 0.04—0.27 0.07 2.74 0.15 Pb 0.97—48.58 26.80 0.54 26.80 -
[1] 刘敏, 邓玮, 赵良元, 等. 长江源区主要河流表层沉积物及沿岸土壤重金属分布特征及来源 [J]. 长江科学院院报, 2021, 38(7): 143-149,154. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20201371 LIU M, DENG W, ZHAO L Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in surface sediments and bank soils of major rivers in source region of Yangtze River [J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2021, 38(7): 143-149,154(in Chinese). doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20201371
[2] 王利娜, 周俊丽, 赵艳芳, 等. 海河流域中部表层沉积物中重金属分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 水资源保护, 2021, 37(5): 147-152. WANG L N, ZHOU J L, ZHAO Y F, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments in the middle of Haihe River Basin [J]. Water Resources Protection, 2021, 37(5): 147-152(in Chinese).
[3] 王韬轶, 潘保柱, 韩谞, 等. 黄河沉积物重金属时空分布与污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(5): 2467-2475. WANG T T, PAN B Z, HAN Y, et al. Spatial-temporal distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Yellow River[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(5): 2467-2475 (in Chinese).
[4] 邓瑜衡, 赵军. 沉积物中重金属的迁移转化影响机制研究 [J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(4): 179-182. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201704037 DENG Y H, ZHAO J. Influence of sediment properties on migration and bioavailability of heavy metals [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2017, 35(4): 179-182(in Chinese). doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201704037
[5] 白传颂. 淮河流域红色文化阐释与研究: 基于淮河流域范围内红色基地的调查分析 [J]. 淮南师范学院学报, 2021, 23(3): 30-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9530.2021.03.007 BAI C S. Interpretation and research of red culture in the Huai River Basin [J]. Journal of Huainan Normal University, 2021, 23(3): 30-34(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9530.2021.03.007
[6] 郝永飞, 金光球, 唐洪武, 等. 淮河干流典型污染物时空分布特性分析 [J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(4): 291-299. HAO Y F, JIN G Q, TANG H W, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution analysis of typical contaminants in mainstream of Huaihe River [J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2020, 48(4): 291-299(in Chinese).
[7] 余辉, 张文斌, 余建平. 洪泽湖表层沉积物重金属分布特征及其风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(2): 437-444. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2011.02.035 YU H, ZHANG W B, YU J P. Distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hongze Lake [J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(2): 437-444(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2011.02.035
[8] 訾鑫源, 张鸣, 谷孝鸿, 等. 洪泽湖围栏养殖对表层沉积物重金属含量影响与生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(11): 5355-5363. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202012131 ZI X Y, ZHANG M, GU X H, et al. Impact of enclosure culture on heavy metal content in surface sediments of Hongze Lake and ecological risk assessment [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(11): 5355-5363(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202012131
[9] 陈孝杨, 严家平, 况敬静, 等. 淮河流域安徽段水系沉积物中重金属的分布与赋存形态 [J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 32(3): 299-304. CHEN X Y, YAN J P, KUANG J J, et al. Distribution and occupied state of heavy metals in sediment of rivers of the Anhui Section in the Huaihe River Basin [J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2009, 32(3): 299-304(in Chinese).
[10] 陈明, 郑小俊, 陶美霞, 等. 桃江流域河流沉积物中重金属污染特征与风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(10): 2784-2791. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019072902 CHEN M, ZHENG X J, TAO M X, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment from Taojiang River Basin [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(10): 2784-2791(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019072902
[11] 王毅, 崔健, 李师. 近海沉积物及悬浮物重金属污染评价方法综述 [J]. 广东石油化工学院学报, 2020, 30(6): 87-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2562.2020.06.020 WANG Y, CUI J, LI S. Review on the assessment methods of heavy metal pollution in offshore sediments and suspended matter [J]. Journal of Guangdong University of Petrochemical Technology, 2020, 30(6): 87-92(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2562.2020.06.020
[12] 张宪军, 蓝先洪, 赵广涛, 等. 苏北浅滩表层沉积物中重金属元素Cd、As、Hg、Se分布及污染评价 [J]. 海洋地质动态, 2007, 23(2): 9-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2007.02.002 ZHANG X J, LAN X H, ZHAO G T, et al. Distribution of heavy metal elements Cd, As, Hg and Se in the surface sediments of shallow beaches in northern Jiangsu Province and evaluation of their pollution [J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2007, 23(2): 9-13(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2007.02.002
[13] 廖启林, 刘聪, 许艳, 等. 江苏省土壤元素地球化学基准值 [J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(5): 1363-1378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.05.023 LIAO Q L, LIU C, XU Y, et al. Geochemical baseline values of elements in soil of Jiangsu Province [J]. Geology in China, 2011, 38(5): 1363-1378(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.05.023
[14] BERGAMASCHI L, RIZZIO E, VALCUVIA M G, et al. Determination of trace elements and evaluation of their enrichment factors in Himalayan lichens [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2002, 120(1): 137-144. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00138-0 [15] INGERSOLL C G, MACDONALD D D, WANG N, et al. Predictions of sediment toxicity using consensus-based freshwater sediment quality guidelines [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2001, 41(1): 8-21. doi: 10.1007/s002440010216 [16] NIU H Y, DENG W J, WU Q H, et al. Potential toxic risk of heavy metals from sediment of the Pearl River in South China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21(8): 1053-1058. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62381-5 [17] 唐聪, 钱宝, 李炜钦, 等. 洞庭湖区表层沉积物重金属污染特征与风险评价 [J]. 人民长江, 2020, 51(6): 49-56,62. doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2020.06.010 TANG C, QIAN B, LI W Q, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk evaluation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Dongting Lake [J]. Yangtze River, 2020, 51(6): 49-56,62(in Chinese). doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2020.06.010
[18] MACDONALD D D, INGERSOLL C G, BERGER T A. Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2000, 39(1): 20-31. doi: 10.1007/s002440010075 [19] 边博, 周燕, 张琴. 太湖西岸河网沉积物中重金属污染特征及风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(4): 1442-1450. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201608078 BIAN B, ZHOU Y, ZHANG Q. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals from river network sediment in western area of Taihu Lake [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(4): 1442-1450(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201608078
[20] LACEY E M, KING J, QUINN J, et al. Sediment quality in Burlington harbor, lake Champlain, USA [J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2001, 126: 97-120. doi: 10.1023/A:1005271101398 [21] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [22] SADIQ R, HUSAIN T, BOSE N, et al. Distribution of heavy metals in sediment pore water due to offshore discharges: An ecological risk assessment [J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2003, 18(5): 451-461. [23] 李一蒙, 马建华, 刘德新, 等. 开封城市土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(3): 1037-1044. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.03.037 LI Y M, MA J H, LIU D X, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of urban soils in Kaifeng City, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(3): 1037-1044(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.03.037
[24] 赵晓亮, 李响, 卢洪斌, 等. 东江湖表层沉积物重金属污染特征与潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(6): 3048-3057. ZHAO X L, LI X, LU H B, et al. Analysis of heavy metal pollution characteristics and potential ecological risks of surface sediments in Dongjiang Lake[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(6): 3048-3057 (in Chinese).
[25] HOU X J, SHAO J H, CHEN X L, et al. Changes in the soil erosion status in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Basin from 2001 to 2014 and the impacts of erosion on the water quality of lakes and reservoirs [J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(8): 3175-3196. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2019.1699974 [26] LUO M K, YU H, LIU Q, et al. Effect of river-lake connectivity on heavy metal diffusion and source identification of heavy metals in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 416: 125818. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125818 [27] LIU J J, WANG P F, WANG C, et al. Heavy metal pollution status and ecological risks of sediments under the influence of water transfers in Taihu Lake, China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2017, 24(3): 2653-2666. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7909-1 [28] 朱陈名, 朱咏莉, 韩建刚, 等. 洪泽湖重金属污染现状与防控技术 [J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 41(3): 175-181. ZHU C M, ZHU Y L, HAN J G, et al. The heavy metal pollution situation and control in Hongze Lake [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2017, 41(3): 175-181(in Chinese).
[29] 周德山, 张晴, 宋向明, 等. 洪泽湖表层沉积物中重金属的分布特征及潜在生态危害 [J]. 淮海工学院学报(自然科学版), 2012, 21(2): 39-43. ZHOU D S, ZHANG Q, SONG X M, et al. Distribution of heavy metals and potential ecological risk in the surface sediment of Hongze Lake [J]. Journal of Huaihai Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 21(2): 39-43(in Chinese).
[30] 成末红. 城市污水处理厂污泥重金属污染状况探讨 [J]. 资源节约与环保, 2020(2): 61,82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2251.2020.02.057 CHENG M H. Exploration of heavy metal contamination in sludge of urban wastewater treatment plants [J]. Resources Economization & Environmental Protection, 2020(2): 61,82(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2251.2020.02.057
[31] 任杰, 白莉, 李军, 等. 太湖表层沉积物重金属污染评价与来源分析 [J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(4): 416-427. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2021.49.027 REN J, BAI L, LI J, et al. Pollution evaluation and source apportionment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Taihu Lake [J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, 49(4): 416-427(in Chinese). doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2021.49.027
[32] 姜文博, 梁斌, 高范, 等. 杭州湾表层沉积物中重金属空间分布特征与污染状况评价 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021, 40(4): 555-561. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20200164 JIANG W B, LIANG B, GAO F, et al. Concentration distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments in Hangzhou Bay [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2021, 40(4): 555-561(in Chinese). doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20200164
[33] 李星谕, 李朋, 苏业旺, 等. 汤逊湖表层沉积物重金属污染与潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(2): 859-866. LI XY, LI P, SU YW, et al. Pollution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Tangxun Lake[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(2): 859-866 (in Chinese).
[34] 陈斌, 吕向立, 王中瑗, 等. 珠江口表层沉积物重金属潜在生态风险及生物富集评价 [J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 51(7): 73-82. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20200260 CHEN B, LV X L, WANG Z Y, et al. Assessment of the potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments and biological accumulation in Pearl River Estuary [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2021, 51(7): 73-82(in Chinese). doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20200260
-



 下载:
下载: