-
铬(Cr)化合物是制革、电镀、冶金、颜料、印染以及纺织品生产等行业不可缺少的工业原料,涉及国民经济商品品种的15%[1]. Cr被广泛运用于皮革鞣制、金属加工电镀、磁带和颜料生产、电气或电子设备以及催化等领域,从而产生大量含Cr废水[2]. 在这些废水中,Cr主要以三价铬(Cr(Ⅲ))和六价铬(Cr(Ⅵ))两种形式存在. Cr(Ⅲ)在水中溶解度较小,不易扩散,在pH>5时易形成沉淀,毒性较小,是人体必须的微量元素之一. Cr(Ⅵ)具有强氧化性、致癌性和高毒性(其毒性约为Cr(Ⅲ)的100倍),会引起支气管炎、哮喘、皮肤溃烂、急性肾衰竭等,严重威胁人类健康[3];同时Cr(Ⅵ)易溶于水,在水中主要以CrO42-和Cr2O72-的形式存在,难以形成沉淀除去,也难以自然分解,具有很强的流动性和很长的污染周期[4]. 美国环保署(EPA)将Cr(Ⅵ)列为首要治理的污染物之一;国家生态环境部将Cr(Ⅵ)列为一类污染物,规定工业废水中Cr(Ⅵ)的最高允许排放浓度为0.5 mg·L−1[5].
为了减少Cr(Ⅵ)的危害,必须对其进行无害化处理. 目前含Cr(Ⅵ)废水的无害化处理方法主要分为物理法和化学法. 物理法是利用具有高比表面积和多孔结构的生物炭[6]、有机聚合物[7]以及氧化石墨烯[8]等吸附剂来吸附Cr(Ⅵ),或使用具有Cr(Ⅵ)选择透过性的壳聚糖和聚乙烯醇[9]等渗透膜将其从水体中分离,常用的吸附沉淀法、离子交换法和膜分离法等均属于物理法. 物理法处理Cr(Ⅵ)操作简单、工艺成熟,但是并没有从根本上对Cr(Ⅵ)进行彻底解毒,仍然存在危害人类健康和污染环境的风险,且沉淀剂和渗透膜制备工艺复杂、成本较高且易对环境产生二次污染[10]. 化学法是利用亚硫酸盐[11]等还原性试剂、电化学反应、生物降解作用和催化反应等将Cr(Ⅵ)还原为毒性较弱且易形成沉淀的Cr(Ⅲ),是对Cr(Ⅵ)进行彻底解毒的有效途径,试剂还原法、电化学还原法、微生物还原法和催化还原法等均属于化学法[12].
虽然化学法可以从根本上对Cr(Ⅵ)进行解毒,但是也存在一些问题需要解决. 如传统的化学试剂还原法需要消耗大量的化学试剂,且会产生大量难以从水体中分离的污泥,若处理不当可能造成二次污染[13];电化学还原法虽然处理Cr(Ⅵ)效果好,但其成本过高,难以大规模应用[14];微生物还原法处理Cr(Ⅵ)依赖于微生物的生长繁殖,效率有限,同时高毒性的Cr(Ⅵ)可能杀死微生物,因此处理Cr(Ⅵ)的浓度有限[15]. 催化还原法是近年新发展起来的Cr(Ⅵ)处理方法,包括光催化还原法、电催化还原法以及微波催化还原法等,与其它化学方法相比,催化还原法具有处理效率高、试剂消耗量低以及不易产生二次污染等优点,被认为是处理Cr(Ⅵ)污染最有前景的一类方法,但是催化还原法需要用到各类催化剂,Cr(Ⅵ)的处理效果严重依赖催化剂的催化能力和可重复利用性能[16].
-
尖晶石型铁氧体(化学式MFe2O4)拥有立方晶系的晶体结构,其中O2-作面心立方最紧密堆积,形成四面体空隙和八面体空隙两种可容纳阳离子的位置,分别被M2+和Fe3+占据,且M2+和Fe3+的位置可以相互替换,使铁氧体呈现不同的性质[17]. 尖晶石型铁氧体是一种典型的磁性非金属材料,具有高磁晶各向异性、高饱和磁化强度和强介电性能,可通过调整结构对其性能进行调控[18-19].
尖晶石型铁氧体可应用于不同领域,如具有高饱和磁化强度、低表面粗糙度和稳定化学性质的钴铁氧体是良好的磁记录材料[20];在较弱磁场下易磁化也易退磁的软磁性镍铁氧体是各类电感元件和电子设备的优选材料[21];具有吸波能力强、吸波频带宽和抗蚀能力强等优点,且高频下的磁导率和电阻率高的锌/锰铁氧体是最早的电磁波吸收剂,在传感器、吸波材料和微波催化等领域发挥着重要作用[22];锰铁氧体可沿外加磁场的磁场梯度方向将所需药物精确释放到机体特定部位,常在生物、医药等方面作为靶向药物载体使用[23]. 而近年的研究结果表明,尖晶石型铁氧体可对废水中的Cr(Ⅵ)进行无害化处理,如图1所示.
-
吸附法是当前处理含Cr(Ⅵ)废水最常用的一种方法,其原理是利用固体吸附剂的高比表面积和丰富表面官能团特性,在分子引力或化学键力作用下将Cr(Ⅵ)束缚在吸附剂表面,之后随着吸附剂的分离而从废水中除去[24]. 吸附法去除Cr(Ⅵ)具有操作简单、处理效率高、处理效果好和适用性强等优点[25]. 为获得优异的Cr(Ⅵ)吸附效果,吸附剂的选择至关重要,合适的吸附剂需要具有:吸附容量大、吸附速率快、容易解吸和再生、制备简单、价格低廉和环境友好等特点. 常用的Cr(Ⅵ)吸附剂有活性炭、硅藻土、硅胶和树脂等,虽然这些吸附剂具有较好的吸附去除Cr(Ⅵ)能力,但是存在分离回收困难的突出缺点[26]. 鉴于此,制备简单、成本低且易于通过简单的磁吸工艺从溶液中分离的尖晶石型铁氧体吸附剂被广泛应用于废水中Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附去除[27].
Nasrallah等[28]采用共沉淀法制备了CuFe2O4粉体并将其用于吸附去除水中Cr(Ⅵ),发现在用量为1 g·L−1且连续搅拌1 h的条件下,其对浓度为3×10−4 mol·L−1的Cr(Ⅵ)溶液的离子去除率约为23%. Jovanovic等[29]采用醇热法制备了直径为100—250 nm的球形CoFe2O4粉体,经研究发现其吸附去除Cr(Ⅵ)的过程符合准二级动力学模型,且吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力随着比表面积的增大而增强,在吸附剂添加量为0.8 g·L−1、温度为25 ℃、pH=5.5、Cr(Ⅵ)浓度为10 mg·L−1以及搅拌速度和时间分别为230 r·min−1和30 min的条件下,溶液中Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附去除率随着CoFe2O4粉体的比表面积由45.1 m2·g−1升至46.4 m2·g−1而由38%升高至88%;吸附饱和后的CoFe2O4粉体可通过磁吸方式从溶液中进行快速分离. Jovanovic等指出:活性位点数量是影响CoFe2O4粉体吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力的主要因素,而吸附位点数量随着比表面积的增大而增加,因此CoFe2O4粉体吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力随着比表面积的增大而增强.
虽然单相尖晶石型铁氧体可以吸附去除溶液中的Cr(Ⅵ)并很容易分离回收,但是其吸附能力有限,难以满足工业生产需求. 由于吸附剂的吸附能力随着其比表面积的增大而增强,因此研究者们开发了各种方法来提高单相尖晶石型铁氧体的比表面积以增强其吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的能力. Bhowmik等[30]采用共沉淀法制备了MnFe2O4/Mn3O4复合纳米粉体吸附剂,然后以1 g·L−1的比例将其加入温度30 ℃、pH=2和Cr(Ⅵ)浓度50 mg·L−1的溶液中,在250 r·min−1的转速下搅拌1 h可以吸附溶液中96.6%的Cr(Ⅵ). Bhowmik等指出,由于MnFe2O4和Mn3O4的晶体结构和晶格常数不同,在制备MnFe2O4/Mn3O4复合材料过程中会产生应力,进而抑制了晶粒的长大,使MnFe2O4/Mn3O4复合粉体的比表面积高达100.62 m2·g−1,远大于单相MnFe2O4粉体,使得复合粉体具有更强的吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力. 除此之外,MnFe2O4/Mn3O4复合粉体还具有比单相MnFe2O4粉体更大的饱和磁化强度,也更容易分离回收.
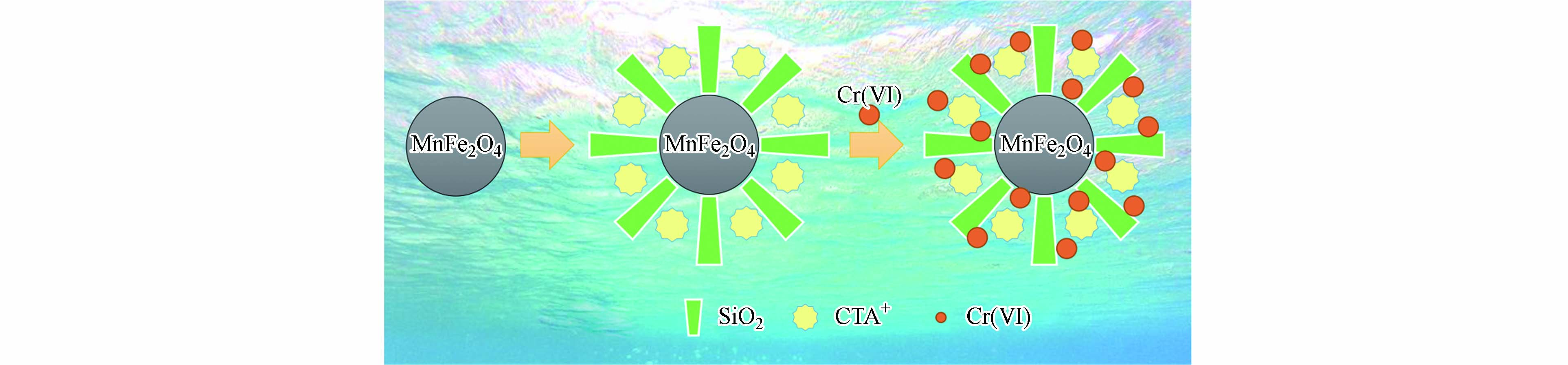
尽管尖晶石型铁氧体吸附剂优异的磁性使其易于从溶液中分离,但是尖晶石型铁氧体直接与Cr(Ⅵ)接触易被腐蚀,导致其去除Cr(Ⅵ)能力和磁分离性能降低,因此,研究人员对尖晶石型铁氧体进行表面包覆以解决该问题. Li等[31]首先采用水热法制备了MnFe2O4纳米颗粒,之后以十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB)和SiO2为修饰材料,采用一步修饰法制备了具有核壳结构的MnFe2O4@SiO2-CTAB磁性介孔材料,并研究其吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的能力(图2). 实验结果表明:1)MnFe2O4@SiO2-CTAB复合材料吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的能力随着溶液pH值的减小而增强,其原因是改性后的复合材料在酸性条件下表面有大量的CTA+,而此时Cr(Ⅵ)以HCrO4−的形式存在,两者可相互结合形成离子对C16H33(CH3)3N+. 当溶液pH值升高时,溶液中OH−的量也随之增多,OH−与含Cr(Ⅵ)阴离子竞争MnFe2O4@SiO2-CTAB复合材料表面的吸附位点,导致Cr(Ⅵ)吸附量下降. 2)MnFe2O4@SiO2-CTAB复合材料对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附行为符合Freundlich等温吸附模型和准二级动力学模型,是非均质吸附过程且吸附速率受化学吸附作用的控制,机理是吸附剂与被吸附物质之间的电子共用或电子转移. 3)SiO2-CTAB外壳可以在一定程度上保护内部的MnFe2O4不被溶液腐蚀,有利于保持其磁性,因而MnFe2O4@SiO2-CTAB复合材料具有良好的重复使用性能,即使在第6次循环使用时仍能保持高达92.4%的Cr(Ⅵ)去除效率.
还原氧化石墨烯(rGO)表面含有大量对重金属离子具有较强吸附能力的离域π电子和含氧官能团. 此外,包含N或S原子的导电高分子材料含有大量可通过络合作用或氧化还原作用吸附重金属离子的氨基和亚氨基功能基团. 因此,研究人员利用以上两种材料对尖晶石型铁氧体进行表面功能化改性,以提高其吸附溶液中Cr(Ⅵ)能力. Wang等[32]首先采用水热法制备了平均粒径约为15 nm的NiFe2O4(NFO)纳米颗粒,之后以聚间苯二胺(PmPD)和rGO为修饰材料,通过原位氧化聚合法制备了一种新型聚间苯二胺/氧化石墨烯/纳米NiFe2O4(PmPD/rGO/NFO)复合吸附剂,并研究了其吸附溶液中Cr(Ⅵ)行为. 显微结构分析表明PmPD包覆在片状的rGO表面,而NFO纳米颗粒则嵌在片层状的rGO和PmPD之间,这种特殊结构可以提供更多的吸附位点,增强了复合吸附剂吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的能力. 实验结果表明在吸附剂投加量为0.1 g·L−1和溶液pH=3时,PmPD/rGO/NFO复合吸附剂对Cr(Ⅵ)的最高吸附量可达322.5 mg·g−1,远大于单相NFO的80 mg·g−1. PmPD/rGO/NFO复合吸附剂优异的Cr(Ⅵ)吸附能力除了与其独特的结构有关外,也受到了PmPD和rGO表面基团的影响. PmPD的引入提供了具有还原能力的苯胺基团(—NH—)和带正电的醌亚胺基团(—N=+),rGO则提供了羟基、羧基和不饱和C=C键,醌亚胺基团可通过静电引力吸附带负电的含Cr(Ⅵ)基团,而苯胺基团、羟基、羧基和不饱和C=C键则可以将吸附的Cr(Ⅵ)还原为Cr(Ⅲ),之后将其吸附在PmPD/rGO/NFO复合吸附剂表面;因此PmPD/rGO/NFO复合吸附剂吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的过程包括对Cr(Ⅵ)的直接吸附,以及首先将Cr(Ⅵ)还原为Cr(Ⅲ)之后再对其进行吸附的间接吸附两个过程. 吸附动力学和热力学分析表明PmPD/rGO/NFO复合吸附剂对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附行为符合准二级动力学模型和Langmiur等温吸附模型,为受化学吸附作用控制的单分子层吸附.
尖晶石型铁氧体材料兼具吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力和磁分离性能,常被用于改性其它Cr(Ⅵ)吸附剂,以提高其吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力和分离回收能力. Ahmadi等[33]首先采用共沉淀法制备了膨润土/MnFe2O4吸附剂,之后研究了其吸附Cr(Ⅵ)行为. 发现在吸附剂用量为1 g·L−1、温度为25 ℃、pH=3和搅拌60 min的条件下,其对浓度为10 mg·L−1 Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附率和吸附容量分别可达98.65%和178.6 mg·g−1,均高于单相膨润土(98.65% vs 92.75 %,178.6 mg·g−1 vs 161.3 mg·g−1). 出现这种现象的原因是负载MnFe2O4颗粒后,膨润土的比表面积提高了至少6%,表面活性位点增多. 另一方面,膨润土/MnFe2O4复合材料的饱和磁化率为13.28 emu·g−1,可以简单地利用磁铁将其从溶液中进行分离回收,极大地提高了膨润土吸附剂的重复使用性能.
大部分吸附剂在酸性条件下具有良好的吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力,然而工厂实际排放的废水可能呈酸性、中性或碱性,因此需要研究吸附剂在不同酸碱环境下对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除情况. Verma等[34]先采用溶胶-凝胶法合成了粒径约为29 nm的磁性MgFe2O4纳米颗粒,再通过超声处理将其负载在多壁碳纳米管(MWCNTs)上制得MgFe2O4/碳纳米管复合吸附剂(MMFNCs),之后研究了其吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力. 实验结果表明,相较于其它吸附剂仅适用于酸性环境的局限,MMFNCs在碱性条件下也具有良好的吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力,当溶液pH值从2升高至12时,MMFNCs在1 h内的Cr(Ⅵ)吸附率仍可保持在75.4%,其原因是Cr(Ⅵ)与Fe3+发生了反应:
$ \text{—}\text{(FeOH}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}\text{+Cr}{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{2-}}\stackrel{\text{yields}}{\to }\text{—}\text{(Fe}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}\text{—}\text{Cr}{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}\text{+2O}{\text{H}}^{\text{-}} $ . 将达吸附平衡后的MMFNCs进行分离、清洗之后再用于Cr(Ⅵ)吸附,经7次循环后其仍保留80%的吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力,说明MMFNCs的结构牢固不易破坏,具有优异的可重复使用性能. 当以工业电镀废水为处理对象时,MMFNCs可吸附去除其中98%的Cr(Ⅵ),说明共存杂质离子对MMFNCs吸附Cr(Ⅵ)行为影响较小.大量研究结果表明,尖晶石型铁氧体及其复合材料可被用于废水中Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附去除(表1). 单相尖晶石型铁氧体吸附剂吸附溶液中Cr(Ⅵ)存在着吸附效率低、吸附容量有限以及再生和重复使用性能差等缺点. 通过引入其它材料进行结构调控和表面功能化改性可以显著提高尖晶石型铁氧体吸附剂的Cr(Ⅵ)吸附去除能力和重复使用性能,但是也存在工艺复杂、成本高以及难以量化生产的不足,同时其它物相的引入也削弱了尖晶石型铁氧体材料的磁性,在一定程度上增加了其磁分离的难度. 因此,为了增强尖晶石型铁氧体吸附去除废水中Cr(Ⅵ)的能力,今后不仅要研发比表面积大、表面功能化、制备工艺简单和成本低廉的新型吸附剂,同时也要重视尖晶石型铁氧体吸附剂吸附Cr(Ⅵ)后的脱附,提高其重复使用性能.
-
虽然吸附法处理废水中Cr(Ⅵ)具有吸附效率高、操作简单、成本低等优点,但是该方法仅对Cr(Ⅵ)进行吸附和富集,没有从根本上对Cr(Ⅵ)进行解毒,并且吸附产生的大量污泥可能造成二次污染[39]. 此外,吸附剂使用后通常难以再生,需要进行清洗处理,在脱附释放被吸附的污染物后才能被再次重复使用[40].
研究表明,Cr(Ⅵ)在光照、电场、微生物介质和微波场的作用下可被还原为Cr(Ⅲ),该过程相应地需要光催化剂、电催化剂、微生物催化剂和微波催化剂[41]. 尖晶石型铁氧体具有带隙窄、可见光响应范围宽、微波响应频率低以及化学稳定性和热稳定性好等优点,常被用于Cr(Ⅵ)的光催化还原、电催化还原和微波催化还原等;其中,尖晶石型铁氧体光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)的报道最多[42].
-
光催化具有能耗低、反应条件温和、操作简便以及可减少二次污染等优点[43],被广泛用于甲酸、苯、亚甲基蓝、罗丹明B等有机污染物以及汞、铬、铅等重金属离子的还原[44].
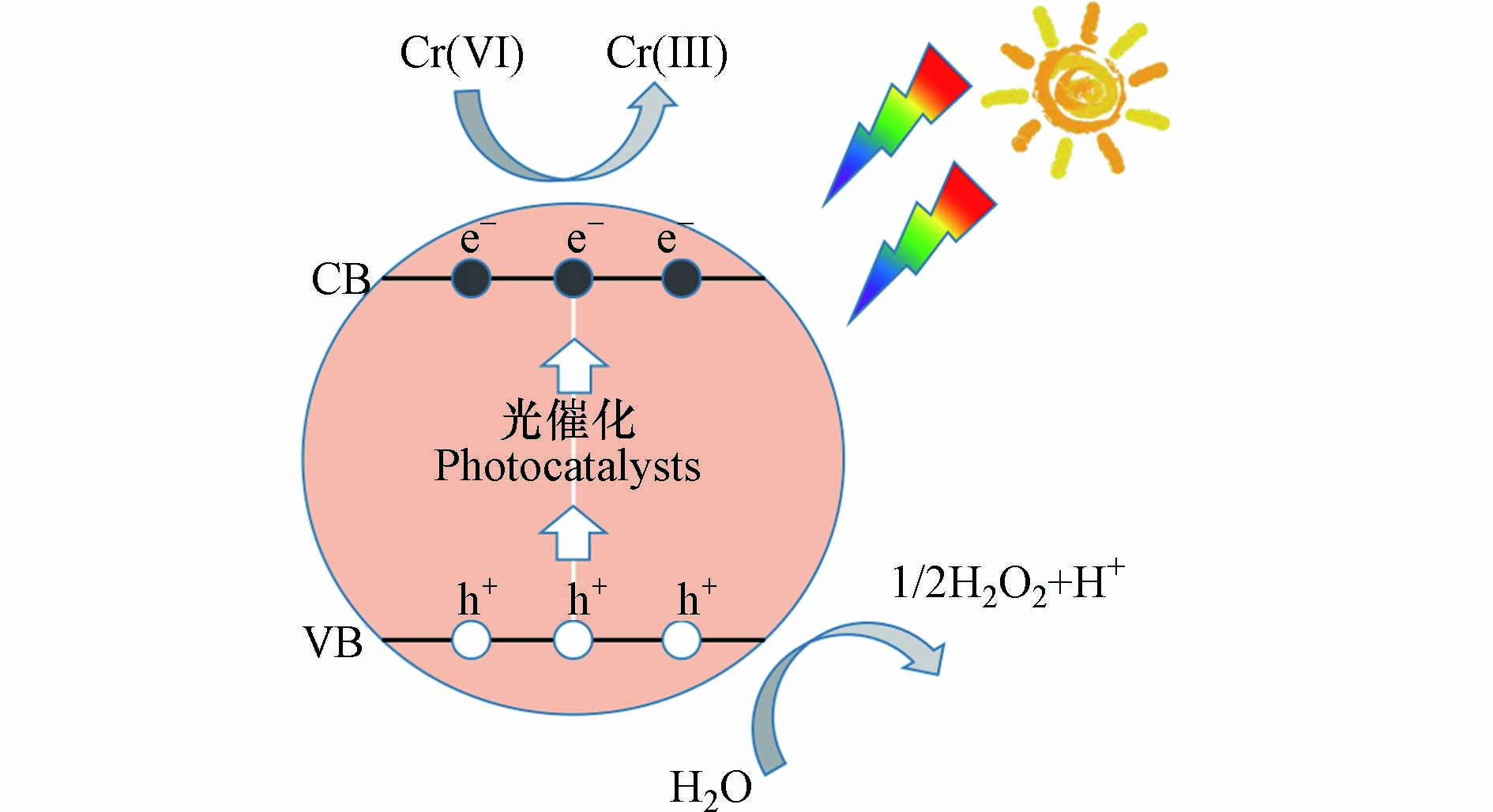
一般情况下,光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)的过程需经历3个阶段[45]:首先,催化剂吸收大于禁带宽度的光子能量,导致其价带(VB)上的电子(e−)被激发跃迁到导带(CB)上形成具有强还原能力的光生e-,同时在VB上形成具有强氧化能力的光生空穴h+. 然后,e−和h+迁移到催化剂表面. 最后,e−将吸附在催化剂表面的Cr(Ⅵ)还原为Cr(Ⅲ),而h+则与H2O发生氧化反应生成O2和H+. Cr(Ⅵ)的光催化还原过程如图3所示,可用下列化学方程式表示[46]:
由以上方程式可以看出,光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)反应整体上是一个消耗H+的过程,在酸性条件下更容易进行[47]. Cr(Ⅵ)在水中的存在形式取决于溶液的pH值[48]:pH<6时主要以HCrO4−的形式存在;pH>6时则主要以CrO42-的形式存在,而CrO42-浓度较高(>520 mg·L−1)时会发生二聚反应生成Cr2O72-,由于Cr2O72-中O原子的电子云密度较大,故其中的Cr(Ⅵ)难以与e−接触发生反应[49],因此光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)反应在中性或碱性条件下不易进行. 除溶液pH外,催化剂用量也是影响光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)效果的重要因素[50]. 一般而言,催化剂用量越多,催化反应活性位点也越多,光催化反应越容易进行. 但是,催化剂用量过多一方面会引起催化剂团聚,使表面活性位点减少;另一方面会使溶液变浑浊,降低溶液的透光度,催化剂无法吸收足够的光能而使催化效率降低. 因此,溶液的pH值和催化剂用量是光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)过程的两个重要影响因素[51].
光催化剂的禁带宽度决定了其对入射光的响应范围和光生e−-h+对的产生及分离效率,不同禁带宽度的光催化剂适用于不同的光催化体系[52]. 太阳光中红外光(E:0.23—1.59 eV)、可见光(E:1.59—3.1 eV)和紫外光(E > 3.1 eV)分别占比49%、46%和5%[53],由于紫外光的能量较高,所以大部分的光催化剂只能在紫外光作用下才有催化能力,如TiO2光催化剂(Eg=3.2 eV)[54]. 尖晶石型铁氧体的禁带宽度较窄(1.38—2.21 eV)[55],可以利用更多的太阳光能量,同时其具有优异的磁性能,易于分离回收,因此在紫外光、可见光和太阳光照射下利用尖晶石型铁氧体对Cr(Ⅵ)进行催化还原的工作已经大量开展[56].
-
紫外光波长较短(10—400 nm),光子能量较高(3.10—124 eV),能激发较宽带隙的光催化剂产生光生e−-h+对,紫外光催化技术是研究最多、应用最广的光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)技术. 尖晶石型铁氧体带隙较窄(< 2.21 eV),易被紫外光激发产生e−-h+对,单相、双相和多相尖晶石型铁氧体基催化剂均可在紫外光照射下催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)为Cr(Ⅲ).
Islam等[57]将粒度< 100 nm的ZnFe2O4纳米粉体以0.4 g·L−1的比例投入pH=3、浓度为10 mg·L−1的Cr(Ⅵ)溶液,发现在紫外灯(15 W,352 nm)照射下溶液中Cr(Ⅵ)的浓度几乎不发生变化,其原因是ZnFe2O4的带隙较窄(Eg=1.92 eV),产生的e−-h+对极易复合,没有多余的e-还原Cr(Ⅵ). 在将h+捕获剂EDTA加入催化反应体系后,发现溶液中的Cr(Ⅵ)在3 h内被全部还原,其原因是EDTA捕获了产生的光生h+,使得体系中有充足的光生e-与溶液中的Cr(Ⅵ)发生氧化还原反应,并将其还原为Cr(Ⅲ).
单相尖晶石型铁氧体催化剂在紫外光照射下还原溶液中Cr(Ⅵ)往往存在着效率较低且还原能力有限的局限. 其原因是:1)尖晶石型铁氧体吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力有限;2)光生e−-h+对的产生和分离效率较低;3)产生的光生e-不能及时转移到催化剂表面. 将尖晶石型铁氧体与其它材料复合制备复合光催化剂,借助材料间的协同效应可增强其光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)的能力.
Du等[38]制备了MgFe2O4/硅藻土复合光催化剂并将其以1 g·L−1的比例加入温度为25 ℃、pH=4和浓度为20 mg·L−1的Cr(Ⅵ)溶液,紫外光照射3 h后发现溶液中几乎检测不到Cr(Ⅵ). 其原因一方面是MgFe2O4/硅藻土复合材料吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力强,有利于后续光生e-对Cr(Ⅵ)的还原;另一方面是MgFe2O4/硅藻土复合材料的禁带宽度较窄(1.2 eV),在紫外光照射下产生大量光生e−-h+对,当光生h+被草酸捕获后,剩余的光生e-将吸附在复合材料表面的Cr(Ⅵ)还原为Cr(Ⅲ). 虽然MgFe2O4/硅藻土复合材料具有优异的处理Cr(Ⅵ)能力,但其磁分离能力和重复使用性能较差.
银(Ag)等贵金属纳米颗粒独特的表面共振效应可以增强对光的吸收,同时又可作为e−陷阱捕获e−,因此可用于增强尖晶石型铁氧体的光催化还原能力. Ibrahim等[58]制备了Ag/TiO2/CoFe2O4 (Ag/TCF)复合光催化剂,并研究了其紫外光催化还原溶液中Cr(Ⅵ)的能力. 实验结果表明当Ag/TCF复合光催化剂投加量为0.1 g·L−1时,经150 min的紫外光照射可将pH=2、浓度为10 mg·L−1的Cr(Ⅵ)还原95.1%. Ag/TCF复合光催化剂优异的紫外光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)能力来源于:1)Ag/TCF复合光催化剂的等电点为8.22,远大于Cr(Ⅵ)溶液的初始pH值,因此Ag/TCF复合光催化剂分散在Cr(Ⅵ)溶液中时表面带正电,很容易通过静电作用吸附含Cr(Ⅵ)的阴离子基团,吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力强. 2)Ag/TCF复合光催化剂的禁带宽度较窄(<1.37 eV),因此在紫外光的激发下很容易产生光生e−-h+对. 3)复合光催化剂中的Ag粒子可起到e−诱捕剂的作用,促进了光生e−-h+对的分离,并加速e−的迁移. 此外,虽然Ag/TCF复合光催化剂的饱和磁化强度相较于单相CoFe2O4有所下降,但是仍然可以通过外加磁场的方式将其从溶液中分离进行重复使用. Ag/TCF复合光催化剂具有较强的结构稳定性,经5次循环还原Cr(Ⅵ)实验后,其晶体结构及反应速率基本不发生变化.
研究表明掺杂可在基体材料能带结构中形成杂质能级,使禁带的实际宽度Eg变窄,引发带隙变窄效应[59]. 由于光催化剂的催化能力受其禁带宽度的影响较大,因此可通过掺杂改善其光催化能力. Othman等[60]研究了掺杂Cd2+对MnFe2O4光催化性能的影响,在催化剂用量为1 g·L−1、温度为25 ℃和pH=2的条件下,MnFe2O4和Cd0.2Mn0.8Fe2O4粉体在紫外光照射30 min后可分别将浓度为15 mg·L−1的Cr(Ⅵ)还原86%和96%. 造成这种现象的原因是掺杂Cd2+使MnFe2O4的禁带宽度由2.16 eV降至1.46 eV,因此Cd0.2Mn0.8Fe2O4可以吸收利用更多的可见光,量子效率更高,具有更强的催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)能力.
单相尖晶石型铁氧体催化剂用于紫外光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)时具有还原效率低和容量有限等缺点,通过与其它材料复合制备复合光催化剂以及掺杂改性均可提高光生e−-h+对的分离以及e−的迁移能力,进而显著提高尖晶石型铁氧体催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)活性(表2). 但是,这两种方法都不同程度存在着工艺复杂、成本高以及磁分离能力低等缺点[61]. 此外,虽然大多数催化剂均可在紫外光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)体系中使用,但紫外光只占太阳光的5%左右,对太阳光的利用率低,不利于大范围应用.
-
可见光波长介于紫外光和红外光之间,波长范围为400—780 nm,光子能量为1.59—3.1 eV,大于部分尖晶石型铁氧体的带隙宽度(1.38—2.21 eV)[62],因此尖晶石型铁氧体在可见光照射下也具有催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)的能力.
异质结结构可以有效促进光生e−-h+对的分离和传输[63],将尖晶石型铁氧体与其它材料复合制备异质结催化剂可以有效提高其光催化活性[64]. Xu等[65]首先采用三步法制备了具有核/壳结构的ZnFe2O4/氯化聚氯乙烯(ZFO/CPVC)异质结复合光催化剂,而后研究了其可见光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)能力. 结果发现当ZFO/CPVC复合光催化剂投加量为1 g·L−1时,pH=3.1、浓度为100 mg·L−1的Cr(Ⅵ)经可见光照射240 min的还原率为55.8%,远高于相同条件下单相ZFO对Cr(Ⅵ) 23.2%的还原率. ZFO的价带电位和导带电位分别为0.38 eV和−1.54 eV,CPVC的最高占据分子轨道和最低占据分子轨道电位分别为0.46 eV和−1.02 eV,ZFO被可见光激发产生的光生e−在电势差的作用下由导带迁移到CPVC的最低占据分子轨道,而CPVC受激产生的光生h+则在电势差的作用下由最高占据分子轨道迁移到ZFO的价带,使ZFO/CPVC复合光催化剂具有比单相ZFO更高的光生e−-h+对分离效率,因此ZFO/CPVC复合光催化剂具有更强的可见光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)能力.
金属硫化物是光催化剂使用过程中常用的助催化剂,由于其与光催化剂的导带电位存在电势差,光催化剂受激产生的光生e−被传输到金属硫化物,可以提高光生e−-h+对的分离效率,进而表现出优异的光催化能力[67-70]. Nasrallah等[28]用共沉淀法制备了异质结构CuFe2O4/CdS光催化剂,将其以1 g·L−1的用量加入pH=3、温度为30 ℃和HCrO4−浓度为3×10−4 mol·L−1的Cr(Ⅵ)溶液,经波长为650 nm的可见光照射6 h后使Cr(Ⅵ)的还原率达到了72%,远高于单相CuFe2O4不到3%的还原率. CuFe2O4禁带宽度较窄(1.48 eV),受可见光激发产生的e−-h+对在自然状况下极易发生复合,因此其催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)的能力较差. 当引入n型半导体CdS与p型半导体CuFe2O4复合制备具有p-n结结构的CuFe2O4/CdS复合光催化剂后,虽然CdS的禁带宽度较大(2.37 eV),在可见光照射下产生的e−-h+对数量较少,但是CuFe2O4受可见光激发产生的光生e−在电势差的作用下迁移到CdS,抑制了光生e−-h+对的复合,同时延长了光生e−的寿命,进而促进了Cr(Ⅵ)的还原,因此CuFe2O4/CdS复合光催化剂表现出优于单相CuFe2O4的可见光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)能力.
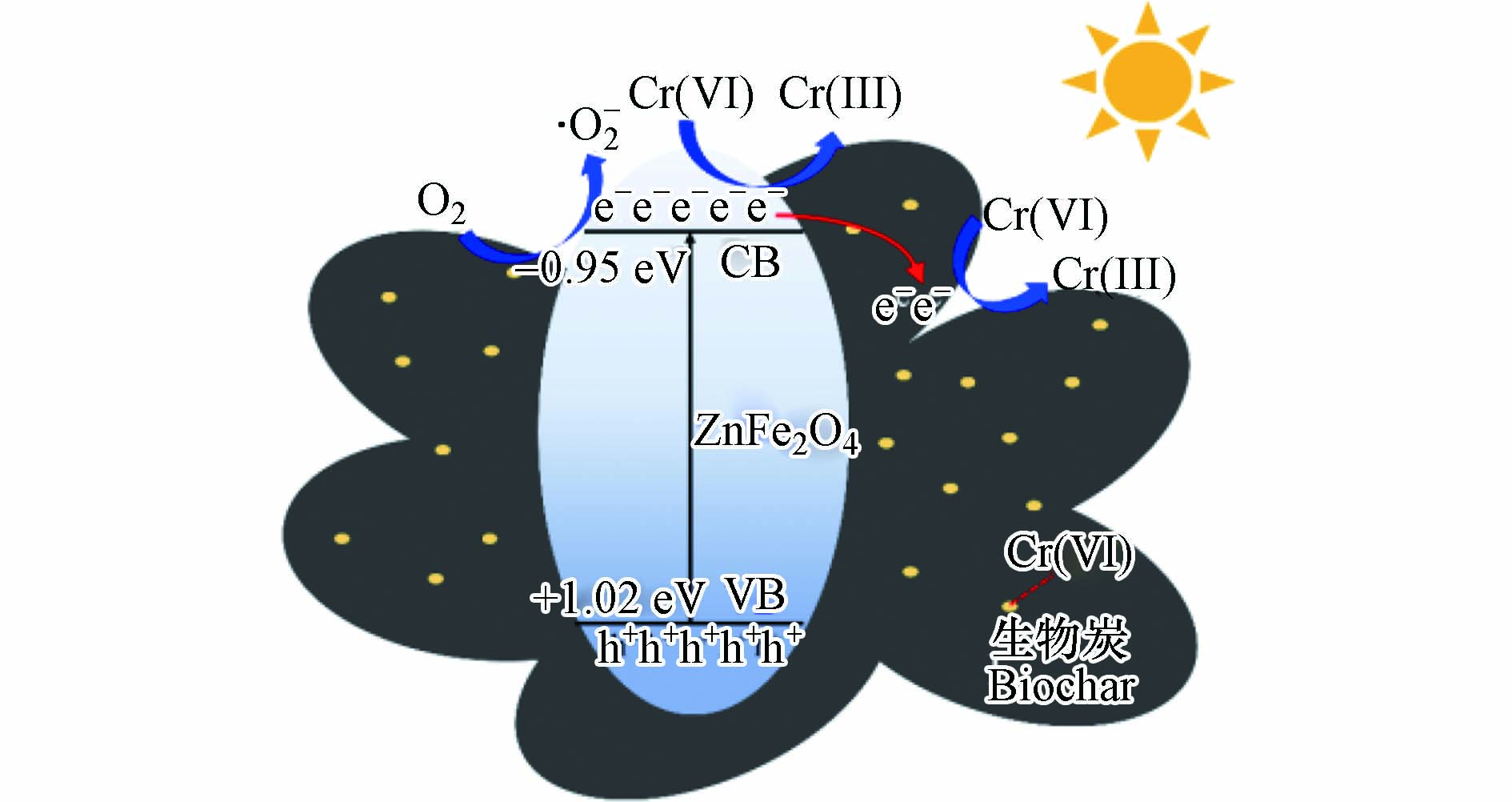
碳材料一方面具有较大的比表面积,光催化剂与其复合可以提高对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附能力;另一方面具有优良的导电性,与光催化剂复合后可促进其受激产生的光生e−的迁移,提高光生e−-h+对的分离效率,从而提高其光催化活性. Shen等[71]将制备的生物炭/ZnFe2O4纳米复合光催化剂以1 g·L−1的比例加入浓度为20 mg·L−1、pH=3和温度为22 ℃的Cr(Ⅵ)溶液,发现其经λ > 400 nm的可见光照射160 min后可实现80%的Cr(Ⅵ)还原率,远高于同样条件下单相生物炭和ZnFe2O4的Cr(Ⅵ)还原率(80% vs 0% vs 44%),其还原机理如图4所示. 该复合光催化剂还具有良好的稳定性,经5次重复使用后仍能保持89%的Cr(Ⅵ)还原能力. ZnFe2O4可见光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)能力差的原因是其光生e−-h+对的复合效率高以及量子效率低;引入生物炭制备生物炭/ZnFe2O4复合光催化剂一方面可提供更多活性位点,增强对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附,为Cr(Ⅵ)的还原提供了前提条件;另一方面增强对可见光的吸收,提高了光生e−-h+对的分离效率,增大了光生e−的迁移速率,使更多光生e−参与Cr(Ⅵ)的还原反应.
类似于紫外光催化,也可通过掺杂的方法提高尖晶石型铁氧体材料的可见光催化能力. Thomas等[72]研究了Co掺杂对ZnFe2O4纳米粉体可见光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)的影响,发现将直径为5—10 nm的介孔Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4纳米球以0.52 g·L−1的比例加入pH=5.36和浓度为20 mg·L−1的Cr(Ⅵ)溶液后,在可见光照射下其具有比ZnFe2O4纳米催化剂更大的还原Cr(Ⅵ)速率常数(2.94 min−1 vs 2.36 min−1). 出现这种现象的原因是:1)Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4具有比ZnFe2O4更窄的禁带宽度(2.07 eV vs 1.97 eV),因此可以吸收利用更多的可见光;2)介孔Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4纳米球具有比ZnFe2O4纳米球更大的比表面积(110.43 m2·g−1 vs 107.38 m2·g−1)、孔容(0.3325 cm3·g−1 vs 0.2489 cm3·g−1)和孔径(7.2849 nm vs 5.8375 nm),大的比表面积可以提供更多的Cr(Ⅵ)吸附位点,而大尺寸的孔有利于吸附过程中Cr(Ⅵ)的传输,二者的协同作用使介孔Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4纳米球具有更优异的吸附和还原Cr(Ⅵ)能力. 磁滞回线测量结果表明制备的介孔Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4纳米球具有超顺磁性,极易进行磁分离回收,说明掺杂Co对ZnFe2O4的分离回收性能影响不大.
由于单相尖晶石型铁氧体仅可吸收利用部分可见光,因此其可见光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)能力有限. 同时,有限的Cr(Ⅵ)吸附能力也在一定程度抑制了其催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)行为. 如表3所示,通过与其它物质复合构建异质结构可以达到以下目的:1)有效减小禁带宽度,增强对可见光的吸收;2)提高光生e−-h+对的分离效率;3)强化吸附Cr(Ⅵ)能力. 因此,构建异质结构可以提高尖晶石型铁氧体可见光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)性能. 另一方面,通过元素掺杂可以使尖晶石型铁氧体的禁带宽度显著变窄,提升其对可见光的响应能力,提高量子效率,增强其可见光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)能力. 但是,构建异质结构工艺复杂、成本高,且异质结构的引入可能导致尖晶石型铁氧体的磁性减弱而削弱催化剂的磁分离性能;掺杂改性会引入缺陷,而缺陷的引入会形成更多的载流子捕获中心(复合中心),显著影响光生载流子的传输和寿命,进而限制了光生载流子的实际催化效率,同时也缺乏相关理论指导掺杂金属离子的合理选择.
综上,尖晶石型铁氧体可见光催化剂未来的研究方向应该集中在改性工艺的优化和改性思路的突破上,实现Cr(Ⅵ)吸附能力、可见光吸收响应能力和光生e−-h+对分离能力强且性能稳定的新型可见光催化剂的简单、低成本制备,同时可引入材料计算学等先进理论研究方法,建立改性尖晶石型铁氧体光催化剂的理论指导体系.
-
太阳能具有丰富、安全和可持续的优点,太阳光取之不尽用之不竭,具有比紫外光和可见光更广阔的应用前景,太阳光催化还原技术在Cr(Ⅵ)无害化处理领域引起了越来越多研究者的兴趣[77].
Oladoja等[78]将CaFe2O4纳米粉体以0.1 g·L−1的比例加入浓度为105.38 mg·L−1的Cr(Ⅵ)溶液,在添加浓度为1 g·L−1草酸的情况下,经辐射强度为618.2 W·m−2的太阳光照射2 h后还原了98.65%的Cr(Ⅵ),远高于其9.20%的Cr(Ⅵ)吸附容量,表明所制备的CaFe2O4纳米粉体具有优异的太阳光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)能力. 但是,当不添加h+捕获剂草酸时,CaFe2O4纳米粉体在太阳光照射下还原Cr(Ⅵ)的效率最高仅为56.39%,其原因是CaFe2O4的禁带宽度太窄,吸收太阳光能量后产生的e−-h+对极易复合,没有足够的e-还原Cr(Ⅵ). 虽然添加h+捕获剂草酸可以提高CaFe2O4纳米粉体光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)的活性,但是残留的草酸可能会引起有害微生物繁殖,造成水体二次污染. 为了克服上述问题,Anthony等[79]制备了p-n异质结构CaFe2O4/ZnO复合光催化剂,由于CaFe2O4与ZnO的费米能级不同,CaFe2O4/ZnO复合材料界面处形成内建电场,光生e−和光生h+受内建电场力的作用分别迁移并富集到ZnO和CaFe2O4表面,从而被有效分离,进而增强了其光催化活性. 将CaFe2O4/ZnO复合光催化剂以1 g·L−1的比例加入浓度为2.91 mg·L−1的Cr(Ⅵ)溶液,经辐射强度为618.21 W·m−2的太阳光照射210 min后,Cr(Ⅵ)的还原效率达到了45.84%.
碳纳米管(CNT)、氧化石墨烯(GO)及富勒烯(Fullerene)等碳同素异构材料独特的π骨架结构可以帮助捕获半导体材料受激产生的光生e−,促进e−的分离和迁移,提高激子寿命,进而增强半导体/碳复合材料的光催化活性[80]. Behera等[81]采用一步水热结合煅烧的方法制备了ZnFe2O4/CNT纳米复合光催化剂,经光照强度为100000 lm的太阳光照射1 h后,发现其在投加量为1 g·L−1的条件下可将pH=3和浓度为10 mg·L−1的Cr(Ⅵ)还原82%,而单相ZnFe2O4光催化剂在相同条件下仅可还原48%的Cr(Ⅵ). 此外,一级动力学拟合结果表明,复合光催化剂催化反应的速率常数更大(27×10−3 min−1 vs 10×10−3 min−1). ZnFe2O4/CNT纳米复合光催化剂具有优于单相ZnFe2O4光催化剂催化Cr(Ⅵ)还原能力的原因是其光生电流密度更大、光生e−-h+对复合率更低和激子分离效率更高. 产生这些现象的原因如下:1)CNT的吸光能力强,ZnFe2O4/CNT纳米复合光催化剂可以利用更宽波长范围的太阳光,量子效率更高,可以产生更多的e−-h+对;2)光生e−被CNT捕获并沿着其π骨架结构提供的通道迁移,抑制了光生e−-h+对的复合. 循环实验结果表明经重复使用4次后,ZnFe2O4/CNT纳米复合光催化剂太阳光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)的能力几乎不发生变化,说明该材料具有优异的重复使用性能.
太阳能是一种无污染、易获得和可持续利用的绿色能源,但是尖晶石型铁氧体光催化剂仅能吸收部分波长范围的太阳光,对太阳能的利用率低. 将尖晶石型铁氧体与其它材料复合构建异质结构可以有效抑制光生e−-h+对的复合,增强其太阳光催化还原溶液中Cr(Ⅵ)的能力(表4),但是存在复合工艺复杂和复合后磁性降低的问题. 同时太阳光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)所需时间较长,还原效率低. 因此,未来的研究工作需要集中在提高尖晶石型铁氧体光催化剂对太阳光的吸收以及其太阳光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)效率上,比如设计新的异质结结构、寻找更合适的可与尖晶石型铁氧体复合的物质以及制备禁带宽度可调的尖晶石型铁氧体光催化剂等.
-
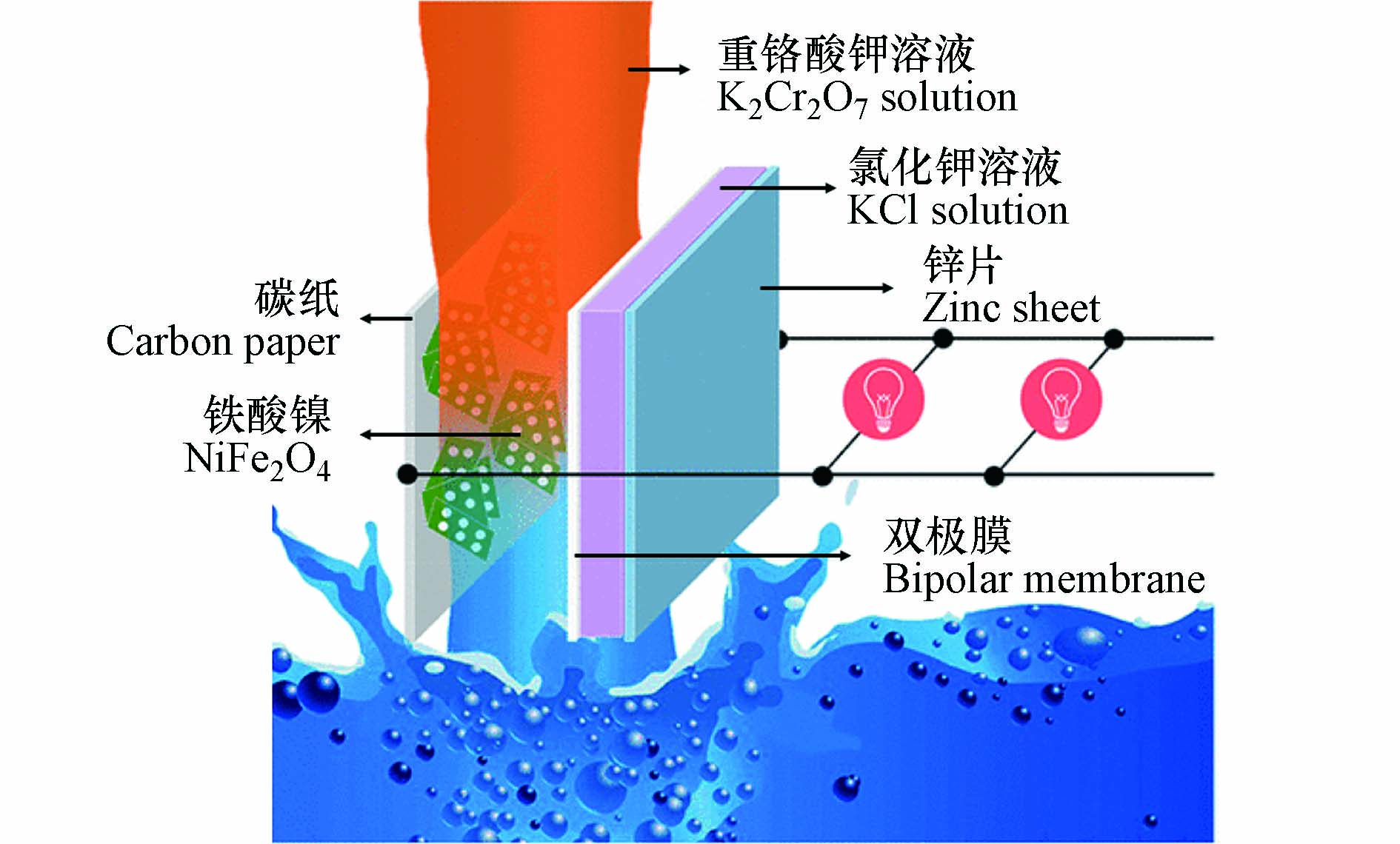
相较于光催化技术,采用电化学还原的方法将溶液中的Cr(Ⅵ)还原为Cr(Ⅲ)具有处理效率高和易实现自动化等优点[82-83]. Luo等[84]将水热法制备的NiFe2O4纳米粉体作为催化剂加入由K2Cr2O7阴极和金属Zn阳极组成的Cr-Zn氧化还原电池,其结构如图5所示. 实验结果表明:1)当Cr-Zn氧化还原电池完全放电后,初始浓度为30 mg·L−1的Cr(Ⅵ)几乎完全被还原;2)催化反应前后NiFe2O4催化剂的晶体结构和微观形貌基本不发生变化,稳定性优异;3)NiFe2O4催化剂除了可以促进溶液中Cr(Ⅵ)的还原,还可以提高Cr-Zn氧化还原电池的能量输出,使Cr-Zn氧化还原电池的平台电压和输出能量值分别由1.46 V和2500 Wh·kg−1升高至1.5 V和2660 Wh·kg−1. 显微结构分析表明纳米NiFe2O4呈由平均厚度为20—40 nm的纳米片组成的大小为3—5 μm的花状结构,比表面积大,可以为Cr(Ⅵ)的还原提供更多活性位点. 在Cr-Zn氧化还原电池体系中,Cr2O72-在离子交换和静电引力的共同作用下被吸附在NiFe2O4催化剂表面,NiFe2O4中存在的Ni3+和Ni2+两种离子可作为e−传输的中间体,促使e−转移到表面与吸附的Cr(Ⅵ)发生还原反应,促进Cr(Ⅵ)的还原. 另一方面,添加NiFe2O4催化剂还可使Cr(Ⅵ)的还原电位由0.56 V增至0.8 V,因此Cr(Ⅵ)的还原反应更易进行. 虽然电化学还原法具有较强的还原Cr(Ⅵ)能力,但是该方法成本过高,难以实现含Cr(Ⅵ)污水的大规模在线处理
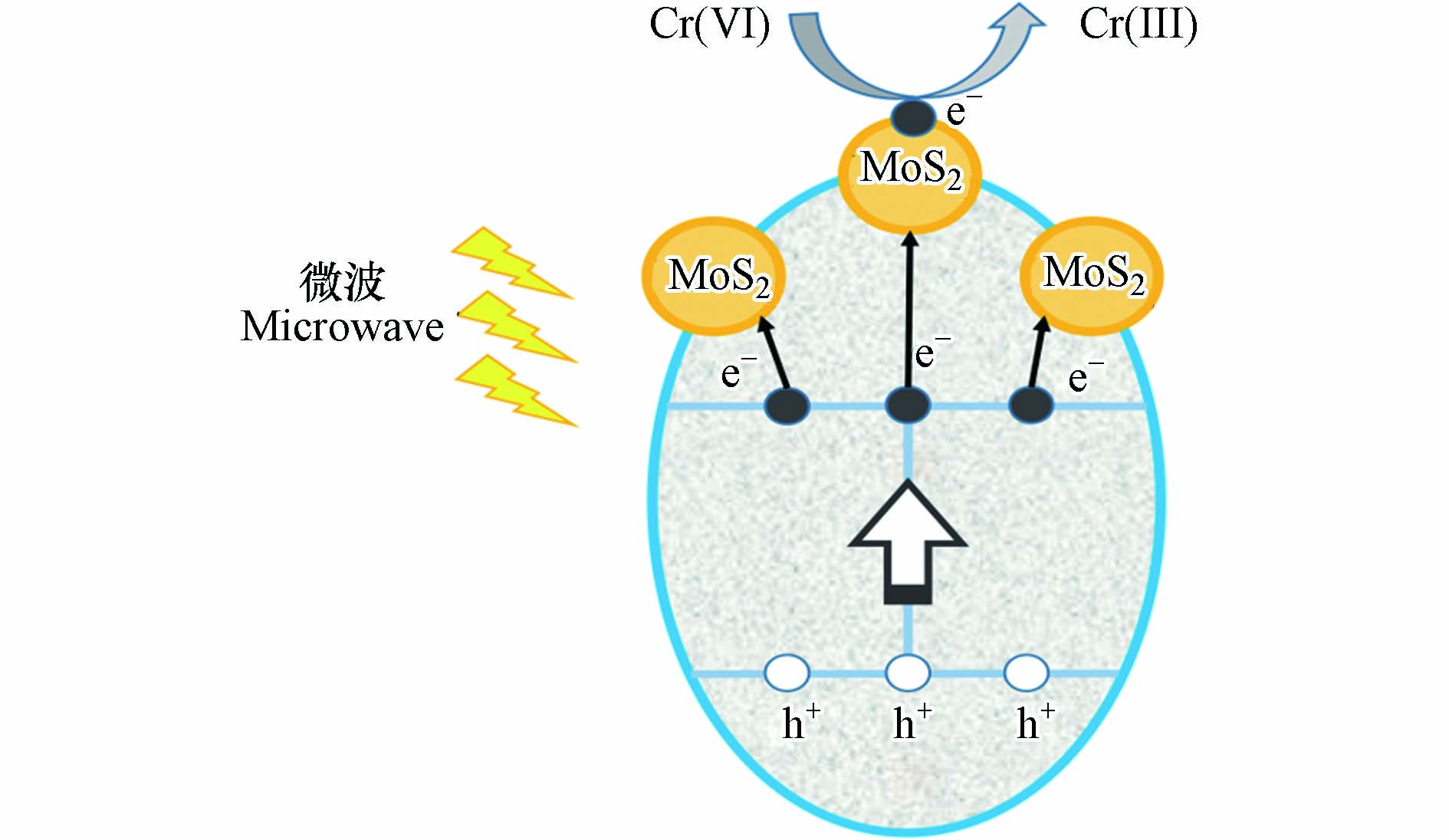
微波诱导催化是另一种应用广泛的催化技术,已被成功应用于污水处理、空气净化及固废处理等领域[85-87],其基本原理是利用具有微波响应能力的吸波材料在微波场作用下产生的强烈耦合作用将微波能转化为热能,引发持续的高温,形成“热点效应”[88-90],以这些“热点”为活性位点产生e−跃迁并生成h+,从而使微波响应材料具有很强的氧化还原能力[91]. 尖晶石型铁氧体具有较高的电阻率(108—1012 Ω)[92]和磁导率、较好的阻抗匹配性能,且易于制备和回收,被认为是最有前途的微波响应催化剂[93],已被成功应用于多种有机污染物和Cr(Ⅵ)的还原[85, 94]. Pang等[95]采用水热法合成了MoS2/MnFe2O4纳米颗粒微波催化剂,将其以2 g·L−1的用量加入50 mL浓度为10 mg·L−1和pH=5.5的Cr(Ⅵ)溶液,发现经功率为200 W的微波辐照16 min后,Cr(Ⅵ)的还原率可达85.8%,其还原Cr(Ⅵ)所需时间远低于大多数已报道的光催化反应. MoS2/MnFe2O4具有优异微波诱导催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)活性的原因是MnFe2O4吸收微波能量后产生大量的e−-h+对. 如图6所示,由于MoS2与MnFe2O4的能带结构不同,受激产生的e−快速迁移到MoS2表面,加强了e−-h+对的分离,因此有更多e−与Cr(Ⅵ)发生还原反应. 微波诱导尖晶石型铁氧体催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)具有效率高、操作方便和设备简单等优点,在Cr(Ⅵ)无害化处理领域显示出巨大的应用潜力[96]. 但目前关于尖晶石型铁氧体微波诱导催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)的报道还较少,微波催化具体过程的研究还不够深入,且微波“热点效应”激发产生e−-h+对的机理尚不明确[97-99]. 因此,今后的工作应着重研究微波诱导催化作用的机理,并开发具有更宽微波响应频率和更高微波吸收能力的微波催化剂.
-
皮革鞣制、金属加工电镀、磁带和颜料生产以及电气或电子设备生产等工业领域排放的含Cr(Ⅵ)废水具有成分复杂、水质波动大、排放量大、危害严重、管理难度大和处理难度高等特点[2,100]. 目前国内外污水处理厂主要采用加碱沉淀法和吸附法对工业排放的含Cr(Ⅵ)废水进行处理,虽然具有工艺成熟、成本低、操作简单和适用性广等优点[101],但是存在含铬污泥产生量大的问题,通常需要与氧化沟处理工艺或序批式活性污泥法处理工艺等相结合使用[102]. 而近年来发展起来的离子交换法和膜分离法虽然具有可实现选择性吸附、处理效果好和铬酸可回收利用等优点,但其工艺复杂且操作管理水平要求高,因此主要适用于具有一定技术水平和管理水平的现代大型企业,中小型企业使用难度大[103]. 化学还原法(如硫酸亚铁石灰法、亚硫酸盐法、二氧化硫法、亚铁盐法、硫化碱法和铁屑法等)也被广泛用于含Cr(Ⅵ)废水的工业化处理,具有原理简单和易于操作的优点,但是其出水水质差,不能回用,在处理混合废水时易造成二次污染,而且还需解决通用氧化剂的供货和毒性的问题. 虽然引入催化剂可以促进Cr(Ⅵ)的还原反应,但是因催化剂制备和回收成本高以及催化条件严苛等而表现出较差的普遍适用性[73],目前尚难以大规模应用于含Cr(Ⅵ)废水的工业化处理. 但随着国家节能减排工作的推进和催化还原技术的发展,未来在实现催化剂产业化制备和开发催化条件温和的新型催化技术后,将含Cr(Ⅵ)废水的传统处理技术与催化还原技术相结合,有望实现含Cr(Ⅵ)废水的大规模绿色无害化处理.
-
随着工业的发展和社会的进步,日益严重的Cr(Ⅵ)污染问题引起了人们的深切关注. 尖晶石型铁氧体因具有比表面积大、易分离、带隙窄、光响应范围宽、制备简单、兼具磁性和介电性等众多优异性能而被广泛用于Cr(Ⅵ)的无害化处理. 虽然以尖晶石型铁氧体为吸附剂和催化剂可以实现Cr(Ⅵ)的无害化,但是仍然存在一系列问题:
(1) 尖晶石型铁氧体独特的磁性使其克服了传统吸附剂难以从水体中分离的缺点,避免了二次污染的产生. 但是,单相尖晶石型铁氧体吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的能力有限,往往需要与其它材料复合以提高吸附能力. 而吸附能力强的复合吸附剂通常存在制备工艺复杂、成本高、脱附困难和磁分离性能差等缺点.
(2) 尖晶石型铁氧体较窄的带隙使其易被光激发,但是同时存在光生e−-h+对易复合的问题,抑制了其光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)活性. 此外,尖晶石型铁氧体光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)过程普遍存在反应时间过长和还原效率低等不足.
(3) 虽然可以利用尖晶石型铁氧体的磁介电性能促进Cr(Ⅵ)还原,但是电化学还原法难以实现Cr(Ⅵ)的大规模处理,而微波催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)的反应机理尚不明晰.
基于上述情况,尖晶石型铁氧体在Cr(Ⅵ)无害化处理中未来可能的研究重点为:
(1) 对Cr(Ⅵ)吸附和脱附机理进行深入研究,选择具有合适的表面结构和官能团的材料与尖晶石型铁氧体复合,研发同时具有比表面积大、表面功能化、制备工艺简单、原料便宜易得的新型吸附剂,同时也应注重尖晶石型铁氧体的脱附.
(2) 结合材料计算和反应动力学等研究方法对尖晶石型铁氧体催化剂进行改性和优化,设计和制备具有更高催化活性和稳定性的尖晶石型铁氧体基催化剂. 同时,可引入原位表征和元素追踪等先进的研究方法,将理论计算与实验结果相结合,在深入研究催化反应具体反应机理的基础上进一步提升尖晶石型铁氧体的光生e-分离效率、寿命和迁移速率.
(3) 深入开展对尖晶石型铁氧体磁介电性能的研究,在研究微波催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)机理的基础上,探索尖晶石型铁氧体微波还原Cr(Ⅵ)的影响因素和最佳反应条件,丰富尖晶石型铁氧体在微波催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)领域的应用.
(4) 建立尖晶石型铁氧体催化剂结构-吸波性能-催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)能力间的关联模型,为尖晶石型铁氧体应用于其它微波催化还原领域提供理论借鉴.
(5) 目前对尖晶石型铁氧体处理Cr(Ⅵ)的研究尚处于实验室阶段,通常以仅含有Cr(Ⅵ)的溶液为目标污染物,而实际污染除含有Cr(Ⅵ)之外,往往还含有其它重金属离子和有机污染物,复杂的污染物成分对尖晶石型铁氧体还原Cr(Ⅵ)能力的影响仍待研究. 因此将来的研究应该逐渐过渡到以实际排放的含Cr(Ⅵ)废水为处理对象.
尖晶石型铁氧体处理废水中Cr(Ⅵ)研究现状与进展
Current status and prospects of aqueous Cr(Ⅵ) removal by spinel ferrites
-
摘要: 六价铬(Cr(Ⅵ))具有生物积累性、生物持久性和剧毒性三大特性,是致癌、致畸、致突变的“三致”污染物,严重危害生态环境和人类健康. 随着工业化的迅速发展,含Cr(Ⅵ)废水的排放日益增多,Cr(Ⅵ)污染日趋严重,必须对其进行无害化处理. 尖晶石型铁氧体具有吸附/催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)的能力和特殊的磁分离性能,是一种重要的Cr(Ⅵ)无害化处理材料. 本文综述了尖晶石型铁氧体在Cr(Ⅵ)无害化处理领域的应用现状,并展望了今后的研究重点和发展方向,以期为含Cr(Ⅵ)废水的无害化处理及绿色工业的发展提供建议.Abstract: Hexavalent chromium (Cr(Ⅵ)) is a highly toxic inorganic pollutant with the characteristics of bioaccumulation, biopersistence and high toxicity, and has strong carcinogenic, teratogenic and mutagenic effects on ecological environment and human health. With the rapid development of industrialization, the discharge of Cr(Ⅵ)-containing wastewater is gradually increasing, causing more and more serious Cr(Ⅵ) pollution, which has become a great threat to the human society. Removal of the toxic Cr(Ⅵ) is becoming an urgently task to be solved and has attracted more and more attention. Spinel ferrites, which possess adsorption and catalytic degradation ability of Cr(Ⅵ) and magnetic separation nature, are considered as the most promising candidates for harmless treatment of Cr(Ⅵ)-containing wastewater. Some research results and development directions of spinel ferrites used for Cr(Ⅵ) removal in the future are prospected in present paper. We hope this review will provide some useful guidance for the harmless treatment of Cr(Ⅵ)-containing wastewater, and arouse more attention to the development of green industry.
-
Key words:
- Cr(Ⅵ) pollution /
- spinel ferrites /
- adsorption /
- catalytic reduction.
-

-
表 1 部分尖晶石型铁氧体吸附剂吸附Cr(Ⅵ)性能对比
Table 1. Comparison of Cr(Ⅵ) adsorption properties of some spinel ferrite adsorbents
吸附剂
Adsorbent初始Cr(Ⅵ)浓度/(mg·L−1)
Initial Cr(Ⅵ) concentrationpH 处理时间/min
TimeCr(Ⅵ)吸附容量/(mg·g−1)
Cr(Ⅵ) adsorption capacity参考文献
ReferencesCoFe2O4 10 5.5 30 11 [29] CuFe2O4 88.2 3 60 20.286 [28] MnFe2O4/SiO2-CTAB 20 3 180 25.044 [31] CoFe2O4/Activated carbon 10 3 60 70 [35] MnFe2O4/Mn3O4 50 2 60 91.24 [30] CoFe2O4/MMFNCs 100 2 180 100 [36] NiFe2O4/MMFNCs 100 2 60 129.83 [37] MgFe2O4/MWCNTs 100 2 60 175.43 [34] MnFe2O4/bentonite 10 6 60 178.6 [33] NiFe2O4/PmPD/rGO 250 3 30 502.5 [32] MgFe2O4/diatomite 20 4 60 570 [38] 表 2 部分尖晶石型铁氧体紫外光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)性能对比
Table 2. Comparison of photocatalytic reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) by some spinel ferrite photocatalysts under UV irradiation
光催化剂
Photocatalyst初始Cr(Ⅵ)
浓度/(mg·L−1)
Initial Cr(Ⅵ)
concentration催化剂用量/
(mg·L−1)
Dosage of
catalystpH 还原效率/%
Reduction
efficiency处理时间/
min
Time还原动力学常数/min−1
Kinetics parameters
of reduction(k)循环性/活性
保持率/%
Circularity/
Activity
maintenance参考文献
ReferencesCoFe2O4/TiO2/Ag 10 0.1 2 95.1 150 4.88×10−2 5/100 [58] MnFe2O4
Cd0.2Mn0.8Fe2O415 1 2 86
9630 9.52×10−1
1.06×10−1— [60] NiFe2O4/SiO2/TiO2 10 2 4 96.5 300 1.05×10−2 3/71.42 [66] MgFe2O4/diatomite 20 1 4 99 180 — — [38] ZnFe2O4(with EDTA) 10 0.4 3 100 180 2.6×10−2 — [57] 表 3 部分尖晶石型铁氧体可见光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)性能对比
Table 3. Comparison of photocatalytic reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) by some spinel ferrite photocatalysts under visible light
光催化剂
Photocatalyst初始Cr(Ⅵ)
浓度/(mg·L−1)
Initial Cr(Ⅵ)
concentration催化剂用量/
(mg·L−1)
Dosage of
catalystpH 还原效率/%
Reduction
efficiency处理时间/
min
Time还原动力学
常数/min−1
Kinetics
parameters of
reduction(k)循环性/活性
保持率/%
Circularity/
Activity
maintenance参考文献
ReferencesZnFe2O4
ZnFe2O4/CPVC100 1 3.1 23.2
55.8240 — — [65] Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 20 0.52 5.4 60 60 2.94×10−2 6/90 [72] CuFe2O4/CdS 10.6 1 3 72 360 — — [28] ZnFe2O4/g-C3N4/PANI 20 10 5 75 120 1.12×10−2 4/95.1 [73] ZnFe2O4/BC 20 1 3 80 160 — 5/89 [71] CoFe2O4/ZrO2 10 0.4 2 83 180 9.45×10−3 — [74] Ion imprinted
ZnFe2O410 0.5 — 92.67 120 — 5/100 [75] MnFe2O4/ZnFe2O4 50 0.5 5 99 180 1.44×10−2 3/99 [76] 表 4 部分尖晶石型铁氧体太阳光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ)性能对比
Table 4. Comparison of photocatalytic reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) by some spinel ferrite photocatalysts under solar light
光催化剂
Photocatalyst初始Cr(Ⅵ)
浓度/(mg·L−1)
Initial Cr(Ⅵ)
concentration催化剂用量/
(mg·L−1)
Dosage of
catalystpH 还原效率/%
Reduction
efficiency处理时间/min
Time还原动力学常数/min−1
Kinetics parameters
of reduction(k)循环性/活性
保持率/%
Circularity/
Activity maintenance参考文献
ReferencesCaFe2O4
CaFe2O4 (with oxalic acid)105.38 0.1 4 56.39
98.65120 1.83×10−3
1.96×10−2— [78] CaFe2O4/ZnO 2.91 1 6 45.84 210 2×10−3 — [79] ZnFe2O4
ZnFe2O4/CNT10 1 3 48
8260 2.7×10−2 4/100 [81] CoFe2O4/TiO2/Ag 10 0.1 2 92.1 150 4.51×10−2 5/100 [58] -
[1] CHEN L F, ZHANG J, ZHU Y X, et al. Interaction of chromium(Ⅲ) or chromium(Ⅵ) with catalase and its effect on the structure and function of catalase: An in vitro study [J]. Food Chemistry, 2018, 244: 378-385. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.062 [2] 刘炜珍, 郑嘉毅, 吴智诚, 等. 表界面调控晶体变化微观机制探索与铬渣治理研究的结合 [J]. 化学进展, 2017, 29(9): 1053-1061. doi: 10.7536/PC170513 LIU W Z, ZHENG J Y, WU Z C, et al. The application of micro-mechanism of crystal changes under the surface/interface control in treating chromium-containing residues [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2017, 29(9): 1053-1061(in Chinese). doi: 10.7536/PC170513
[3] 李茹霞, 钟文彬, 谢林华, 等. 金属有机框架材料对Cr(Ⅵ)离子的吸附去除研究进展 [J]. 无机化学学报, 2021, 37(3): 385-400. doi: 10.11862/CJIC.2021.068 LI R X, ZHONG W B, XIE L H, et al. Recent advances in adsorptive removal of Cr(Ⅵ) ions by metal-organic frameworks [J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2021, 37(3): 385-400(in Chinese). doi: 10.11862/CJIC.2021.068
[4] GRACEPAVITHRA K, JAIKUMAR V, KUMAR P S, et al. A review on cleaner strategies for chromium industrial wastewater: present research and future perspective [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 228: 580-593. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.117 [5] GB8978—1996. 中华人民共和国污水综合排放标准[S]. GB8978—1996. Integrated wastewater discharge standard[S].
[6] RAJAPAKSHA A U, ALAM M S, CHEN N, et al. Removal of hexavalent chromium in aqueous solutions using biochar: chemical and spectroscopic investigations [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 625: 1567-1573. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.195 [7] AKRAM M, BHATTI H N, IQBAL M, et al. Biocomposite efficiency for Cr(Ⅵ) adsorption: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamics studies [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2017, 5(1): 400-411. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2016.12.002 [8] ZHAO D L, GAO X, WU C N, et al. Facile preparation of amino functionalized graphene oxide decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 384: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.05.022 [9] HABIBA U, AFIFI A M, SALLEH A, et al. Chitosan/(polyvinyl alcohol)/zeolite electrospun composite nanofibrous membrane for adsorption of Cr6+, Fe3+ and Ni2+ [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 322: 182-194. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.06.028 [10] 席改红, 石国荣, 李强, 等. 木本泥炭对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附性能 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(1): 202-208. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018082304 XI G H, SHI G R, LI Q, et al. Adsorption performance of woody peat for Cr(Ⅵ) [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(1): 202-208(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018082304
[11] XIE B H, SHAN C, XU Z, et al. One-step removal of Cr(Ⅵ) at alkaline pH by UV/sulfite process: reduction to Cr(Ⅲ) and in situ Cr(Ⅲ) precipitation [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 308: 791-797. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.123 [12] ZOU Y D, WANG X X, KHAN A, et al. Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: a review [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(14): 7290-7304. [13] MEENA A H, ARAI Y. Effects of common groundwater ions on chromate removal by magnetite: importance of chromate adsorption [J]. Geochemical Transactions, 2016, 17: 1. doi: 10.1186/s12932-016-0033-9 [14] ZHOU R, LIU F Y, WEI N, et al. Comparison of Cr(Ⅵ) removal by direct and pulse current electrocoagulation: implications for energy consumption optimization, sludge reduction and floc magnetism [J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2020, 37: 101387. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101387 [15] BIANCHI E, BIANCALANI A, BERARDI C, et al. Improving the efficiency of wastewater treatment plants: bio-removal of heavy-metals and pharmaceuticals by azolla filiculoides and lemna minuta [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 746: 141219. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141219 [16] WANG H, YUAN X Z, WU Y, et al. Facile synthesis of amino-functionalized titanium metal-organic frameworks and their superior visible-light photocatalytic activity for Cr(Ⅵ) reduction [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 286: 187-194. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.11.039 [17] KHARISOV B I, DIAS H V R, KHARISSOVA O V. Mini-review: ferrite nanoparticles in the catalysis [J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 12(7): 1234-1246. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.10.049 [18] 高卫国, 钱林波, 韩璐, 等. 锰铁氧体吸附及催化柠檬酸还原六价铬的过程及机理 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(7): 1525-1533. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017101302 GAO W G, QIAN L B, HAN L, et al. Iron manganese minerals catalyzed Cr(Ⅵ) reduction by citric acid and its mechanism [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(7): 1525-1533(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017101302
[19] ROCA A G, COSTO R, REBOLLEDO A F, et al. Progress in the preparation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine [J]. Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics, 2009, 42(22): 224002. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/42/22/224002 [20] PRAVEENA K, CHEN H W, LIU H L, et al. Enhanced magnetic domain relaxation frequency and low power losses in Zn2+ substituted manganese ferrites potential for high frequency applications [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2016, 420: 129-142. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.07.011 [21] BINDU K, SRIDHARAN K, AJITH K M, et al. Microwave assisted growth of stannous ferrite microcubes as electrodes for potentiometric nonenzymatic H2O2 sensor and supercapacitor applications [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 217: 139-149. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.09.083 [22] LIANG P L, YUAN L Y, DENG H, et al. Photocatalytic reduction of uranium(Ⅵ) by magnetic ZnFe2O4 under visible light [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 267: 118688. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118688 [23] KEFENI K K, MSAGATI T A M, MAMBA B B. Ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis, characterisation and applications in electronic device [J]. Materials Science and Engineering:B, 2017, 215: 37-55. doi: 10.1016/j.mseb.2016.11.002 [24] CHEN B, ZHAO X S, LIU Y, et al. Highly stable and covalently functionalized magnetic nanoparticles by polyethyleneimine for Cr(Ⅵ) adsorption in aqueous solution [J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(2): 1398-1405. doi: 10.1039/C4RA10602D [25] 秦艳敏, 王敦球, 梁美娜, 等. 桑树杆活性炭/铁锰氧化物复合吸附剂的制备及其对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(4): 783-792. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.04.2015101902 QIN Y M, WANG D Q, LIANG M N, et al. Preparation of mulberry stem activated carbon/Fe-Mn oxide composite sorbent and its effects on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(4): 783-792(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.04.2015101902
[26] OWLAD M, AROUA M K, DAUD W A W, et al. Removal of hexavalent chromium-contaminated water and wastewater: a review [J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2009, 200(1-4): 59-77. doi: 10.1007/s11270-008-9893-7 [27] REDDY D H K, YUN Y S. Spinel ferrite magnetic adsorbents: alternative future materials for water purification [J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2016, 315: 90-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2016.01.012 [28] NASRALLAH N, KEBIR M, KOUDRI Z, et al. Photocatalytic reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) on the novel hetero-system CuFe2O4/CdS [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 185(2): 1398-1404. [29] JOVANOVIĆC S, KUMRIĆC K, BAJUK-BOGDANOVIĆC D, et al. Cobalt ferrite nanospheres as a potential magnetic adsorbent for chromium(Ⅵ) ions [J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2019, 19(8): 5027-5034. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2019.16803 [30] BHOWMIK K L, DEBNATH A, NATH R K, et al. Synthesis of MnFe2O4 and Mn3O4 magnetic nano-composites with enhanced properties for adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ): artificial neural network modeling [J]. Water Science and Technology, 2017, 76(11): 3368-3378. [31] LI N, FU F L, LU J W, et al. Facile preparation of magnetic mesoporous MnFe2O4@SiO2−CTAB composites for Cr(Ⅵ) adsorption and reduction [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 220: 1376-1385. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.097 [32] WANG W, CAI K, WU X F, et al. A novel poly(m-phenylenediamine)/reduced graphene oxide/nickel ferrite magnetic adsorbent with excellent removal ability of dyes and Cr(Ⅵ) [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 722: 532-543. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.06.069 [33] AHMADI A, FOROUTAN R, ESMAEILI H, et al. The role of bentonite clay and bentonite clay@MnFe2O4 composite and their physico-chemical properties on the removal of Cr(Ⅲ) and Cr(Ⅵ) from aqueous media [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 27(12): 14044-14057. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-07756-x [34] VERMA B, BALOMAJUMDER C. Magnetic magnesium ferrite-doped multi-walled carbon nanotubes: an advanced treatment of chromium-containing wastewater [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 27(12): 13844-13854. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-07988-x [35] FOROUTAN R, MOHAMMADI R, RAMAVANDI B, et al. Removal characteristics of chromium by activated carbon/CoFe2O4 magnetic composite and Phoenix dactylifera stone carbon [J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2018, 35(11): 2207-2219. doi: 10.1007/s11814-018-0145-2 [36] VERMA B, BALOMAJUMDER C. Fabrication of magnetic cobalt ferrite nanocomposites: an advanced method of removal of toxic dichromate ions from electroplating wastewater [J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2020, 37(7): 1157-1165. doi: 10.1007/s11814-020-0516-3 [37] VERMA B, BALOMAJUMDER C. Synthesis of magnetic nickel ferrites nanocomposites: an advanced remediation of electroplating wastewater [J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2020, 112: 106-115. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2020.07.006 [38] DU Y C, WANG X K, WU J S, et al. Mg3Si4O10(OH)2 and MgFe2O4 in situ grown on diatomite: highly efficient adsorbents for the removal of Cr(Ⅵ) [J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2018, 271: 83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.04.036 [39] SAMUEL M S, SHAH S S, SUBRAMANIYAN V, et al. Preparation of graphene oxide/chitosan/ferrite nanocomposite for chromium(Ⅵ) removal from aqueous solution [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2018, 119: 540-547. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.07.052 [40] WANG X, LIANG Y H, AN W J, et al. Removal of chromium (Ⅵ) by a self-regenerating and metal free g-C3N4/graphene hydrogel system via the synergy of adsorption and photo-catalysis under visible light [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2017, 219: 53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.07.008 [41] 王洪红, 雷文, 李孝建, 等. 催化还原降解Cr(Ⅵ) [J]. 化学进展, 2020, 32(12): 1990-2003. WANG H H, LEI W, LI X J, et al. Catalytic reductive degradation of Cr(Ⅵ) [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2020, 32(12): 1990-2003(in Chinese).
[42] YUAN G Q, LI F L, LI K Z, et al. Research progress on photocatalytic reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) in polluted water [J]. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 2021, 94(4): 1142-1155. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.20200317 [43] FUJISHIMA A, HONDA K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode [J]. Nature, 1972, 238(5358): 37-38. doi: 10.1038/238037a0 [44] CHONG M N, JIN B, CHOW C W K, et al. Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: a review [J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(10): 2997-3027. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.02.039 [45] TONG H, OUYANG S X, BI Y P, et al. Nano-photocatalytic materials: possibilities and challenges [J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(2): 229-251. doi: 10.1002/adma.201102752 [46] YUAN R R, YUE C L, QIU J L, et al. Highly efficient sunlight-driven reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) by TiO2@NH2-MIL-88B(Fe) heterostructures under neutral conditions [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2019, 251: 229-239. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.03.068 [47] WANG C C, DU X D, LI J, et al. Photocatalytic Cr(Ⅵ) reduction in metal-organic frameworks: a mini-review [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 193: 198-216. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.04.030 [48] BARRERA C E, LUGO-LUGO V, BILYEU B. A review of chemical, electrochemical and biological methods for aqueous Cr(Ⅵ) reduction [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 223: 1-12. [49] BARAKAT M A. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater [J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2011, 4(4): 361-377. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.07.019 [50] FUJISHIMA A, ZHANG X T, TRYK D A. TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena [J]. Surface Science Reports, 2008, 63(12): 515-582. doi: 10.1016/j.surfrep.2008.10.001 [51] SHI L, WANG T, ZHANG H B, et al. An amine-functionalized iron(Ⅲ) metal-organic framework as efficient visible-light photocatalyst for Cr(Ⅵ) reduction [J]. Advanced Science, 2015, 2(3): 1500006. doi: 10.1002/advs.201500006 [52] HISATOMI T, KUBOTA J, DOMEN K. Recent advances in semiconductors for photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical water splitting [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(22): 7520-7535. doi: 10.1039/C3CS60378D [53] WEI Y C, WU X X, ZHAO Y L, et al. Efficient photocatalysts of TiO2 nanocrystals-supported PtRu alloy nanoparticles for CO2 reduction with H2O: synergistic effect of Pt-Ru [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2018, 236: 445-457. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.05.043 [54] LI C Q,. SUN Z M, SONG A K, et al. Flowing nitrogen atmosphere induced rich oxygen vacancies overspread the surface of TiO2/kaolinite composite for enhanced photocatalytic activity within broad radiation spectrum [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2018, 236: 76-87. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.04.083 [55] MAHMOOD M, YOUSUF M A, BAIG M M, et al. Spinel ferrite magnetic nanostructures at the surface of graphene sheets for visible light photocatalysis applications [J]. Physica B:Condensed Matter, 2018, 550: 317-323. doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2018.08.043 [56] SONU, DUTTA V, SHARMA S, et al. Review on augmentation in photocatalytic activity of CoFe2O4 via heterojunction formation for photocatalysis of organic pollutants in water [J]. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 2019, 23(8): 1119-1136. doi: 10.1016/j.jscs.2019.07.003 [57] ISLAM J B, ISLAM M R, FURUKAWA M, et al. Performance of EDTA modified magnetic ZnFe2O4 during photocatalytic reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) in aqueous solution under UV irradiation [J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A, 2021, 56(1): 44-51. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2020.1835389 [58] IBRAHIM I, KALTZOGLOU A, ATHANASEKOU C, et al. Magnetically separable TiO2/CoFe2O4/Ag nanocomposites for the photocatalytic reduction of hexavalent chromium pollutant under UV and artificial solar light [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 381: 122730. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122730 [59] SURESH R, RAJENDRAN S, KUMAR P S, et al. Recent advancements of spinel ferrite based binary nanocomposite photocatalysts in wastewater treatment [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 274: 129734. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129734 [60] OTHMAN ALI I, MOSTAFA A G. Photocatalytic reduction of chromate oxyanions on MMnFe2O4 (M=Zn, Cd) nanoparticles [J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2015, 33: 189-198. doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2015.01.030 [61] WANG M, ZHANG Y L, DONG C J, et al. Preparation and electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles/carbon nanotubes composites [J]. Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, 2019, 9: 1-7. [62] ZHANG S W, LI J X, ZENG M Y, et al. In situ synthesis of water-soluble magnetic graphitic carbon nitride photocatalyst and its synergistic catalytic performance [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(23): 12735-12743. [63] NIU M, CAO D P, SUI K Y, et al. InP/TiO2 heterojunction for photoelectrochemical water splitting under visible-light [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(20): 11615-11624. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.02.094 [64] VOZNYY O, SUTHERLAND B R, IP A H, et al. Engineering charge transport by heterostructuring solution-processed semiconductors [J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017, 2: 17026. doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2017.26 [65] XU B, DING T, ZHANG Y C, et al. A new efficient visible-light-driven composite photocatalyst comprising ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles and conjugated polymer from the dehydrochlorination of polyvinyl chloride [J]. Materials Letters, 2017, 187: 123-125. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2016.10.094 [66] OJEMAYE M O, OKOH O O, OKOH A I. Performance of NiFe2O4-SiO2-TiO2 magnetic photocatalyst for the effective photocatalytic reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) in aqueous solutions [J]. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2017, 2017: 5264910. [67] CHENG C, CHEN D Y, LI N J, et al. ZnIn2S4 grown on nitrogen-doped hollow carbon spheres: an advanced catalyst for Cr(Ⅵ) reduction [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 391: 122205. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122205 [68] PAN J W, GUAN Z J, YANG J J, et al. Facile fabrication of ZnIn2S4/SnS2 3D heterostructure for efficient visible-light photocatalytic reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) [J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2020, 41(1): 200-208. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63422-4 [69] QIU J H, LI M, XU J, et al. Bismuth sulfide bridged hierarchical Bi2S3/BiOCl@ZnIn2S4 for efficient photocatalytic Cr(Ⅵ) reduction [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 389: 121858. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121858 [70] ZHANG G P, CHEN D Y, LI N J, et al. Preparation of ZnIn2S4 nanosheet-coated CdS nanorod heterostructures for efficient photocatalytic reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2018, 232: 164-174. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.03.017 [71] SHEN X F, ZHENG T, YANG J Y, et al. Removal of Cr(Ⅵ) from acid wastewater by BC/ZnFe2O4 magnetic nanocomposite via the synergy of absorption-photocatalysis [J]. ChemCatChem, 2020, 12(16): 4121-4131. doi: 10.1002/cctc.202000619 [72] THOMAS B, ALEXANDER L K. Enhanced synergetic effect of Cr(Ⅵ) ion removal and anionic dye degradation with superparamagnetic cobalt ferrite meso-macroporous nanospheres [J]. Applied Nanoscience, 2018, 8(1): 125-135. [73] PATNAIK S, DAS K K, MOHANTY A, et al. Enhanced photo catalytic reduction of Cr (Ⅵ) over polymer-sensitized g-C3N4/ZnFe2O4 and its synergism with phenol oxidation under visible light irradiation [J]. Catalysis Today, 2018, 315: 52-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.04.008 [74] EMADIAN S S, GHORBANI M, BAKERI G. Magnetically separable CoFe2O4/ZrO2 nanocomposite for the photocatalytic reduction of hexavalent chromium under visible light irradiation [J]. Synthetic Metals, 2020, 267: 116470. doi: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2020.116470 [75] HE F, LU Z Y, SONG M S, et al. Construction of ion imprinted layer modified ZnFe2O4 for selective Cr(Ⅵ) reduction with simultaneous organic pollutants degradation based on different reaction channels [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 483: 453-462. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.311 [76] SKLIRI E, VAMVASAKIS I, PAPADAS I T, et al. Mesoporous composite networks of linked MnFe2O4 and ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles as efficient photocatalysts for the reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) [J]. Catalysts, 2021, 11(2): 199. doi: 10.3390/catal11020199 [77] BEHERA A, KANDI D, MAJHI S M, et al. Facile synthesis of ZnFe2O4 photocatalysts for decolourization of organic dyes under solar irradiation [J]. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology, 2018, 9: 436-446. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.9.42 [78] OLADOJA N A, ANTHONY E T, OLOLADE I A, et al. Self-propagation combustion method for the synthesis of solar active nano ferrite for Cr(Ⅵ) reduction in aqua system [J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A:Chemistry, 2018, 353: 229-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.11.026 [79] ANTHONY E T, LAWAL I A, BANKOLE M O, et al. Solar active heterojunction of p-CaFe2O4/n-ZnO for photoredox reactions [J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2020, 20: 101060. [80] YANG M Q, ZHANG N, XU Y J. Synthesis of fullerene carbon nanotube and graphene-TiO2 nanocomposite photocatalysts for selective oxidation: a comparative study [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(3): 1156-1164. [81] BEHERA A, MANSINGH S, DAS K K, et al. Synergistic ZnFe2O4-carbon allotropes nanocomposite photocatalyst for norfloxacin degradation and Cr(Ⅵ) reduction [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 544: 96-111. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.02.056 [82] SUN S H, ZENG H, ROBINSON D B, et al. Monodisperse MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Mn) nanoparticles [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(1): 273-279. doi: 10.1021/ja0380852 [83] SUN M, ZHANG G, QIN Y H, et al. Redox conversion of chromium(Ⅵ) and arsenic(Ⅲ) with the intermediates of chromium(Ⅴ) and arsenic(Ⅳ) via AuPd/CNTs electrocatalysis in acid aqueous solution [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(15): 9289-9297. [84] LUO T, WANG S F, HOU X H, et al. Cr-Zn redox battery with NiFe2O4 as catalyst for enhanced degradation of Cr(Ⅵ) pollution [J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(1): 111-116. [85] XUE C, MAO Y P, WANG W L, et al. Current status of applying microwave-associated catalysis for the degradation of organics in aqueous phase a review [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 81: 119-135. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2019.01.019 [86] WEI R, WANG P, ZHANG G S, et al. Microwave-responsive catalysts for wastewater treatment: a review [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 382: 122781. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122781 [87] WANG L X, GUAN Y K, QIU X, et al. Efficient ferrite/Co/porous carbon microwave absorbing material based on ferrite@metal organic framework [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 326: 945-955. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.06.006 [88] QUAN X, ZHANG Y B, CHEN S, et al. Generation of hydroxyl radical in aqueous solution by microwave energy using activated carbon as catalyst and its potential in removal of persistent organic substances [J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2007, 263(1): 216-222. [89] HE J, LIU S, DENG L W, et al. Tunable electromagnetic and enhanced microwave absorption properties in CoFe2O4 decorated Ti3C2 MXene composites [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 504: 144210. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144210 [90] YOSHIKAWA N, XIE G Q, CAO Z P, et al. Microstructure of selectively heated (hot spot) region in Fe3O4 powder compacts by microwave irradiation [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2012, 32(2): 419-424. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.08.028 [91] POLAERT I, BASTIEN S, LEGRAS B, et al. Dielectric and magnetic properties of NiFe2O4 at 2.45 GHz and heating capacity for potential uses under microwaves [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2015, 374: 731-739. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.09.027 [92] TSAY C Y, LIANG S C, LEI C M, et al. A comparative study of the magnetic and microwave properties of Al3+ and In3+ substituted Mg-Mn ferrites [J]. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(4): 4748-4753. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.11.154 [93] GAO J, YANG S G, LI N, et al. Rapid degradation of azo dye direct black BN by magnetic MgFe2O4-SiC under microwave radiation [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 379: 140-149. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.04.041 [94] ZHANG L, LIU X Y, GUO X J, et al. Investigation on the degradation of brilliant green induced oxidation by NiFe2O4 under microwave irradiation [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 173(3): 737-742. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.08.041 [95] PANG Y X, KONG L J, CHEN D Y, et al. Rapid Cr(Ⅵ) reduction in aqueous solution using a novel microwave-based treatment with MoS2-MnFe2O4 composite [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 471: 408-416. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.180 [96] ZHU C Q, LIU F Q, SONG L, et al. Magnetic Fe3O4@polyaniline nanocomposites with a tunable core–shell structure for ultrafast microwave-energy-driven reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) [J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2018, 5(2): 487-496. doi: 10.1039/C7EN01075C [97] HORIKOSHI S, SERPONE N. On the influence of the microwaves thermal and non-thermal effects in titania photoassisted reactions [J]. Catalysis Today, 2014, 224: 225-235. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2013.10.056 [98] LIU X Y, AN S, SHI W, et al. Microwave-induced catalytic oxidation of malachite green under magnetic Cu-ferrites: new insight into the degradation mechanism and pathway [J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2014, 395: 243-250. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2014.08.028 [99] SHEN M L, FU L, TANG J H, et al. Microwave hydrothermal-assisted preparation of novel spinel-NiFe2O4/natural mineral composites as microwave catalysts for degradation of aquatic organic pollutants [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 350: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.02.014 [100] 刘金燕, 刘立华, 薛建荣, 等. 重金属废水吸附处理的研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(9): 2016-2024. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017110105 LIU J Y, LIU L H, XUE J R, et al. Research progress on treatment of heavy metal wastewater by adsorption [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(9): 2016-2024(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017110105
[101] 鲍家泽, 马玉银, 赵伟荣, 等. 基于铬物料资源化利用的制革含铬废水处理技术现状及对策建议 [J]. 广东化工, 2018, 45(11): 187-188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2018.11.085 BAO J Z, MA Y Y, ZHAO W R, et al. Status and countermeasures of chrome wastewater treatment technology based on resource utilization of chromium material [J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2018, 45(11): 187-188(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2018.11.085
[102] 吕斌, 聂军凯, 高党鸽, 等. 控制制革含铬废水污染技术的研究进展 [J]. 中国皮革, 2017, 46(10): 13-20. doi: 10.13536/j.cnki.issn1001-6813.2017-010-003 LV B, NIE J K, GAO D G, et al. Research progress on tannery pollution control of chromium-containing wastewater [J]. China Leather, 2017, 46(10): 13-20(in Chinese). doi: 10.13536/j.cnki.issn1001-6813.2017-010-003
[103] COETZEE J J, BANSAL N, CHIRWA E M N. Chromium in environment, its toxic effect from chromite-mining and ferrochrome industries, and its possible bioremediation [J]. Exposure and Health, 2020, 12(1): 51-62. doi: 10.1007/s12403-018-0284-z -



 下载:
下载: