-
土壤自古以来就是自然界的万物之源,是植物生长、人类生存的物质基础. 但近年来,随着我国工业的快速发展,土壤重金属污染超标问题已经给人类的生产、生活带来了极大的威胁,使得土壤重金属污染成为了全球性的环境问题[1-2]. 同时,土壤重金属污染具有隐蔽性,是污染物长期积累的结果,等到污染物浓度超过了土壤的自净能力,一系列的土壤生态问题就会显现出来,其中重金属污染尤为突出[3]. 据土壤污染状况调查结果显示,全国土壤总的点位超标率达到了16.1%,中度污染以上的占2.6%,主要以重金属污染为主. 无机污染物(大部分为重金属)的超标点位数占全部超标点位的82.8%,其中Cd、Ni、Pb的点位超标率高达7.0%、4.8%、1.5%[4].
腐殖质(HS)作为一种高分子有机化合物广泛存在于土壤、沉积物、泥炭、风化煤中,是环境中有机质的重要组成部分[5]. HS含有多种官能团,含氧的酸性官能团有羧基、酚羟基等,这些官能团之间以氢键连接,形成表面多孔的分子网络,可以更好地吸附土壤中的重金属离子[6-7]. 通常来说,HS会通过络合、螯合、吸附等反应与多种重金属离子形成稳定性不同的金属-有机配合物,从而影响重金属的迁移转化和生物可利用性[8-9]. 同时HS还会与重金属离子发生氧化还原反应,改变重金属离子的价态,减少重金属离子对人体健康的危害.
然而,HS作为一种有潜力的重金属吸附材料,吸附效果受pH值、溶液离子强度、温度以及重金属离子的种类等多种因素的影响,再加上HS本身的不均一性、空间变异性以及结构的复杂性,使得HS与重金属之间的作用机制极具多变性[10-12],研究HS对重金属迁移转化的影响成为一项重要的课题. 近年来,对HS的来源、性质等问题较多学者做了阐述,但对于HS不同分类及其分离提纯过程等缺乏系统性梳理. 针对HS影响重金属迁移转化和改变重金属活性的研究类文献较多,但还缺乏系统性综述. 因此,本文在前人研究的基础上,对HS的来源、分类提纯、化学特征及其与重金属之间的相互作用关系做了系统性的介绍,为了解HS对土壤中重金属赋存形态的影响以及重金属污染土壤修复提供理论依据.
-
1786和1797年,Achard和Vaquelin分别在实验中用酸、碱对土壤进行处理,得到了深色的无定形沉淀. 1804年,Saussure首次在文章中引入“humus”这一名词来描述土壤中的深色有机物质. 1809年,由于“humus”理论的形成建立了土壤科学. 1822年,Dobereiner提出胶体物质是HS的主要部分,呈弱酸性,并出现了“腐殖酸”这一术语[13-15]. 二十世纪至今,众多科研工作者对HS不断进行更深入的研究,HS的奥秘一步步被揭开.
HS大量存在于陆地、海水、土壤沉积物中,可以作为评价土壤肥力的一项重要指标. 在部分土壤和沉积物中,HS所占比重能达到10%,甚至更高[16]. HS主要是有机物腐殖化的结果,可分为两个过程. 首先,由各种形态和状态的有机物组成的混合物在微生物的作用下先分解为简单的有机化合物. 其次,经过生物、化学、生化过程将简单的有机化合物合成高分子有机物,也就形成了HS. 从化学本质上来说,HS是有机质的主要组成部分,占土壤有机质的60%—90%[17],而且它属于有机胶体的一种,一般为黑色或暗棕色的无定形高分子化合物[18].
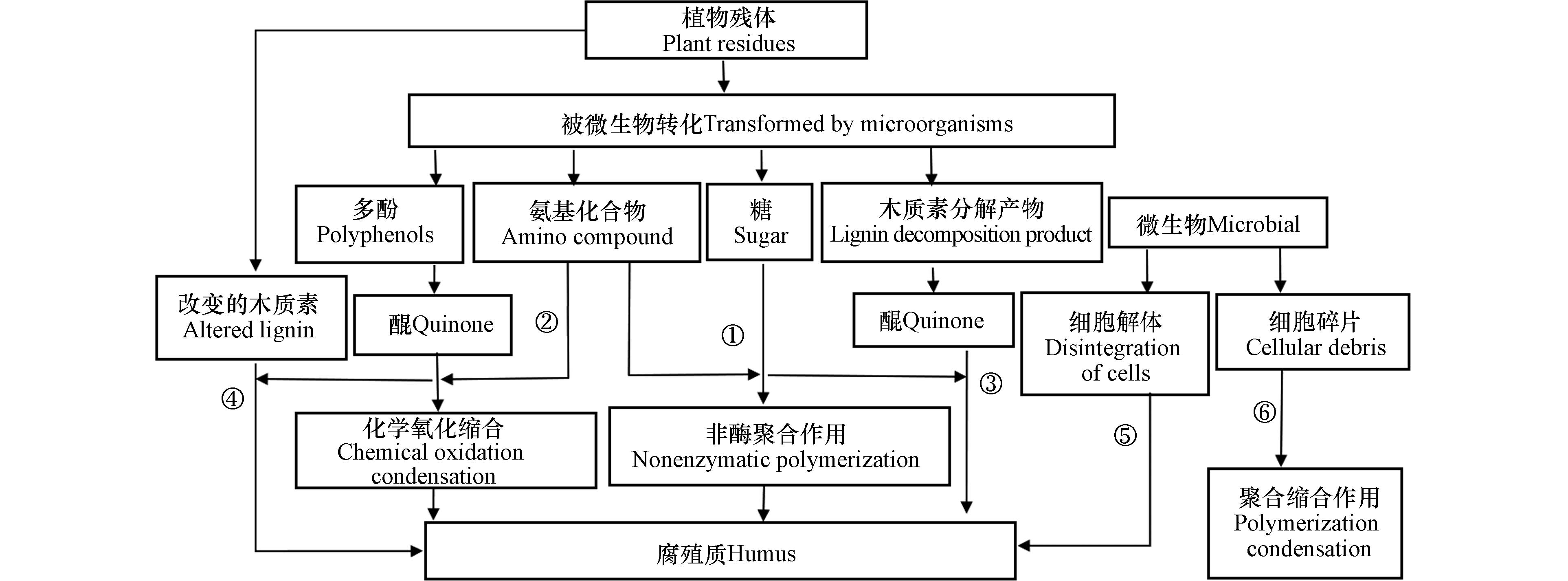
目前,关于HS的形成主要有6种学说(图1). 图1中①—⑥种途径分别为糖-胺缩合学说、多酚学说、木质素起源的多酚学说、木质素学说、微生物合成学说与细胞自溶学说[19]. 糖-胺缩合学说重点强调的是“纯化学反应”,多酚学说和微生物合成学说重点强调的是微生物发挥的作用. 1966年,Kononova提出了多酚学说,认为HS的合成是一个复杂的过程,植物组织的性质并不会影响最后生成的HS的种类[20]. 木质素起源的多酚学说和细胞自溶学说重点强调植物和微生物的共同作用. 其中途径③(木质素起源的多酚学说)和途径②(多酚学说)的形成过程非常相似,主要区别在于途径③中多酚是由木质素转变而来,再进一步形成醌,而途径②中的多酚直接由微生物合成. 木质素学说在1936年由Waksman提出,重点强调的是植物本身的作用. 他认为植物组织(尤其是木质化组织)在土壤中或多或少都会发生一些外表上的变化,这种学说认为HS的性质在很大程度上由植物成分的性质所影响[10, 20]. 此外,HS是多酚和醌的复合体是大家较为公认的说法,木质纤维素通过降解形成多酚,多酚通过进一步氧化形成醌,醌进行自行缩合或者与氨基酸聚合形成富里酸(FA)和胡敏酸(HA),HA经过进一步缩合形成胡敏素(HM)[21-22].
-
HS的分类有很多种,在土壤学上采用最多的方法就是二分法,即将HS分为HA和FA,这两者在一般情况下占HS总量的60%左右[23]. 同时,HS与土壤矿物的结合比较紧密,不能用机械的手段分离. 目前,NaOH和Na4P2O7被认为是提取HS最常用的两种试剂,在大多数土壤中,它们都可以提取出大量的HS[22] . 胡梦淩等[24]在研究不同来源的HS通过淋洗对土壤中Cd、Pb去除效果的实验中,就分别使用1.0 mol·L−1的NaOH、0.1 mol·L−1的NaOH+0.1 mol·L−1的Na4P2O7两种试剂从风化褐煤、污泥、鸡粪等物料中提取HS. 主要操作为将两种提取液与物料按照1:10的固液比混合,然后在转速为180 r·min−1的摇床中振荡0.5 h后取出,静置24 h过滤,即可得到HS淋洗液.
而HS中不同组分的分离,较多采用的方法是根据各组分在不同pH下的溶解度不同,将其分为HM、HA、FA[25]. 但这种方法分离得到的各组分仍含有其他杂质,需要进一步纯化. 国际腐殖质协会(IHSS)[26-27]推荐了一种提纯的方法,这种方法是目前提纯HS各组分最常用的方法之一. 另外,在2006年,窦森结合Pallo法,将粗HM再分为铁结合HM(HMi)、粘粒结合HM(HMc)以及不溶性HM(HMr)[28](图2).
-
对于HS不同组分来说,分子量的大小存在着很大的差异. 比如,FA的分子量在500—5000之间,HA的分子量相对较大,在3000—100000之间[29]. 另外,分子量的不同使腐殖质各组分对重金属的吸附性能以及生物有效性也产生了不同的影响. 低分子量的FA易与重金属形成可溶态络合物,提高重金属的流动性和生物有效性[30],而高分子量的HA与重金属会形成不溶性络合物,减弱土壤对重金属的吸附能力,能够钝化和固定土壤中的重金属[31]. 因此,除了根据溶解度对HS进行分类,还可以利用不同组分分子量的大小进行分类.
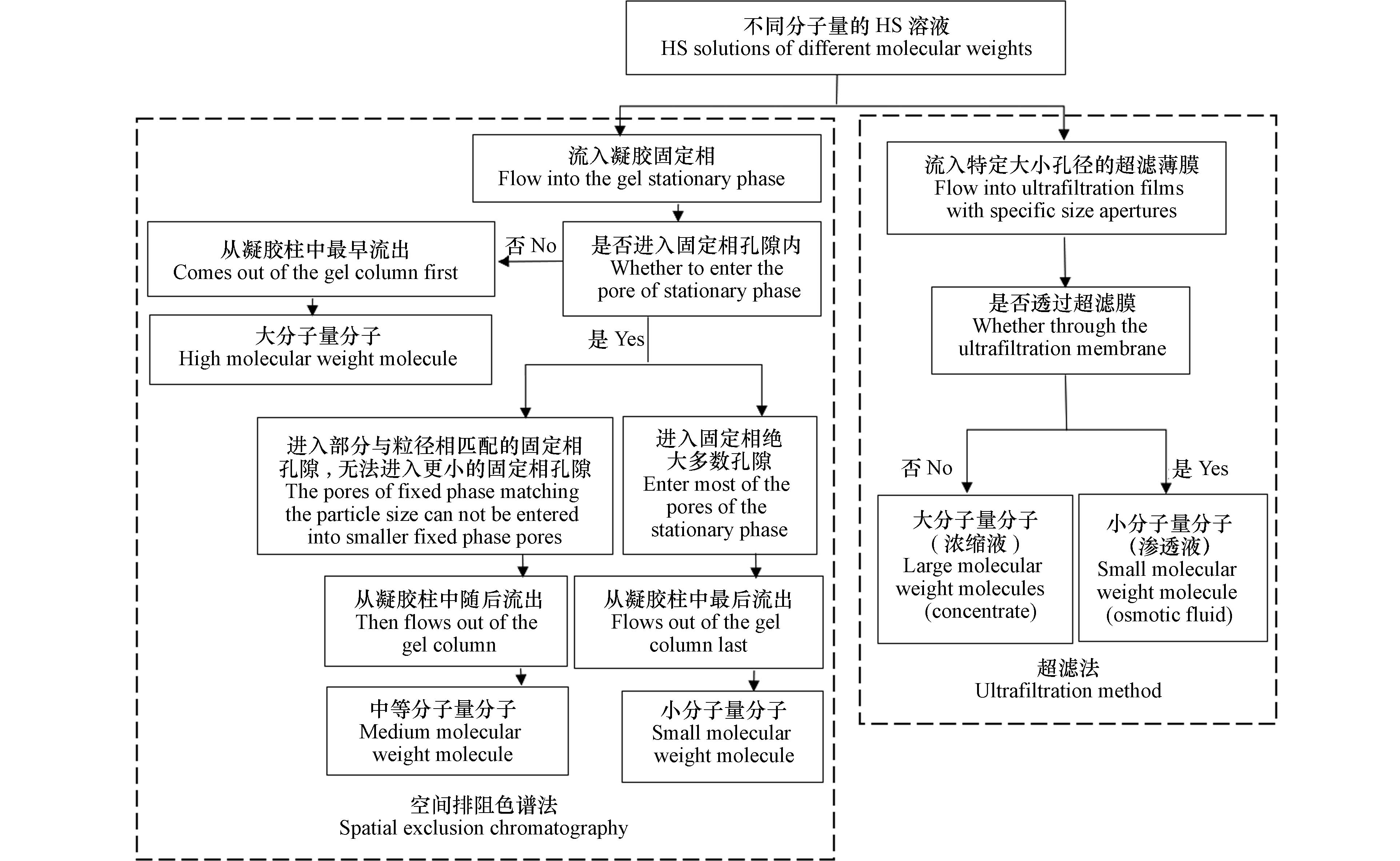
最近几十年来,HS的分类方法有空间排阻色谱、超滤、沉淀、吸附和电泳,其中空间排阻色谱、超滤是根据各组分粒径大小或分子量大小进行分类的. 空间排阻色谱是以化学惰性多孔物质为固定相,根据流动相溶液中分子粒径的不同完成分离,目标溶液会按照分子粒径从大到小的顺序依次排出. 超滤是在较大压力的作用下,以特定大小的孔径筛出不同粒径的分子,从而实现HS中不同分子量大小物质的分离[32](图3).
-
人们已经认识到HS是一种分子结构极其复杂的混合物,可能包括植物碳水化合物、微生物碳水化合物、植物蛋白、微生物蛋白等多种物质,但至今还未有一个具体的结构式[33] . HS大量存在于各类各样的土壤中,是土壤腐殖土的重要组成部分. 由于受气候和排水量的影响,不同土壤中HS的含量大不相同[5]. 同时,对于不同的HS来说其结构特征也存在着很大的差异. 下面,笔者主要从以下几个方面来介绍HS的相关特性.
-
Flaig和Dudas等分别在1982年和1986年发现,HS是疏松多孔的球形结构,形状和海绵相似,具有巨大的比表面积,每克土的表面积可以高达2000 m2[11]. 对于不同的HS,其分子量的大小相差很大,大概介于几百到几十万道尔顿之间. 在2001年,Piccolo[34]提出,HS分子大小主要是由疏水键和氢键的强弱决定,与单体和聚合度有关. 另外,HS分子量的差异与其来源也有很大的关系. 1981年,彭安等[35]发现,从华北运河水体中提取的FA和HA的分子量小于从煤炭和土壤中所得到的FA和HA的分子量,而且该运河中的HA的酸性基含量更多. 1994年,Chin等[36]用高压排阻色谱法测定了从4个天然水样中提取的FA、1种商业HA的分子量,发现这些物质比之前的印象值分子量更小、多分散性更少.
-
HS的组成元素相对稳定,主要由C、H、O、N、S等元素构成,还含有少量的Ca、Mg、Fe、Si及其他微量元素. 对于不同种类的HS来说,其组成元素也不完全相同. 一般来说,国际上认为HS中C的含量为55%—60%,平均为58%,N的含量为3%—6%,平均为5.6%[32]. 对于HS内部组分来说,HM和HA的元素含量基本在同一范围[17],HA和FA的元素含量存在一定的差异.
土壤HS元素含量的变化能间接反映出HS的许多性质,在一定程度上了解土壤退化过程中HS的变化趋势. 比如:C/N比能够反映HS中含氮量的高低,一般国际上认为其比值范围为10∶1—12∶1[11, 32]. O/C比反映的是HS的氧化度,C/H比可以反映HS的缩合度[17]. FA 中C元素含量低于HA,O、S元素含量高于HA,所以导致其缩合度低而氧化度高.
-
土壤HS中含有多种官能团,主要有硫醇基、酚羟基、醇羟基、醌基、甲氧基等,这些官能团对重金属离子具有还原作用,能够通过改变重金属离子的价态来影响HS对重金属的吸附[37-38]. 对于HS不同组分来说,其各种官能团的含量相差也较大. FA的羟基含量显著大于HA的羟基含量,其总酸度也比HA高,而HM中羧基和酚羟基的含量明显低于同一来源的HA,但是无论哪一种来源的HM与同一来源的HA都有着相似的官能团[39-40]. 从HM的不同组分来看,HMc的烷基碳含量较HMi更高,其结构也更为复杂[17].
-
一直以来,HS的化学结构都是土壤学研究的重点,当人们对其化学结构了解的越来越清楚时,对于HS与重金属之间的相互作用机制自然也会越来越明了. 近年来,核磁共振光谱法在HS的研究中得到了广泛的应用,同时结合元素分析、红外光谱、扫描电镜等手段使得对HS化学结构的研究有了较快的进展[41]. 根据当前的研究,对于HS化学结构的看法归纳起来有以下四种:一是认为在HA中,芳香环是中心物质,在芳香环上既有脂肪链与其相连接也有饱和环单元与其相连接;二是认为在HA中,多环芳香核是中心物质,在多环芳香核上有脂肪类化合物与其连接,或者有单个酚类化合物与其连接;三是认为HA是由具有侧链基团和高度缩合芳香核平面骨架构成,其中侧链基团主要是脂肪基、羧基、酰胺基等;四是认为HS完全是非晶形物质[23].
FA含有大量的羧基、碳水化合物以及多糖,苯环数量相对较少,苯环之间可以形成许多网孔,以松散的形式连接[23, 39]. 而HA分子结构比FA的结构更为复杂. HA含有大量的苯环,主要由芳香碳、侧链碳组成,彼此之间连接的较为紧密. 由于芳香碳具有疏水性,侧链碳具有亲水性,使得HA呈现疏松的海绵孔状结构[42]. 另外,与HA相比,HM具有的芳香碳较少、脂肪族碳更多. 在HM中,羧基、碳水化合物和多糖结合在脂肪链上,同时还含有一定量的甲基、醚、酰胺等基团[39, 43].
-
HS对土壤中重金属是一种非常重要的络合剂和吸附剂[44]. 在土壤中,重金属离子会发生吸附、配位、沉淀以及氧化还原等多种反应形式,从而影响重金属离子的迁移转化,其中吸附作用居于首位[45]. HS因其具有较大的比表面积、较高的粘度、较好的分散性能,对重金属离子具有强烈的吸附作用[46]. 而且HS含有羧基、酚羟基、氨基等多种官能团,使得每一个分子都含有大量的络合部位,可以与土壤溶液中的重金属离子结合,形成络合物[9]. 大量的实验已经证实,HS能够吸附Cr、As、Cu、Cd、Pb、Zn、Fe等重金属,影响重金属在土壤中的迁移转化规律,降低重金属的生物有效性[47-49]. 同时,HS与重金属离子的络合机制基本符合“双配体模型”,即在络合反应的过程中,羧基和酚羟基共同起作用. Sannino等[50]在文章中指出,污染物与HS之间会发生共价结合,即每个附加的原子贡献一个相关的电子,形成共价键,使得污染物能够被HS分子更稳定地固定.
大分子的HM和HA可以使重金属钝化,形成不溶性络合物,从而限制动植物对重金属的吸收,降低重金属的毒性. Barnie等[51]研究了不溶性的HS(主要指未溶解的HM、HA)在不同的环境条件下与Cr(Ⅵ)的反应. 研究表明,不溶性HS在吸附、还原Cr(Ⅵ)时,其组分中的酚羟基和羧基起主要作用,其中羧基是络合Cr(Ⅵ)的主要基团. Ko等[52]研究认为,HM可以与As发生络合,生成有机-无机络合物,从而降低As的迁移转化率,使其毒性减弱. 对于不同类型的HS来说,对同一种离子的络合吸附能力也有所不同,又因HS结构复杂、多种多样,所以研究不同HS对于某种重金属离子的吸附规律,寻求最佳吸附条件显得尤为重要. 陈林倩等[27]从不同硒水平的土壤中提取出不同的HS,研究发现,在Pb浓度为3 mg·L−1时,所提取HS的吸附效果最好,且吸附率随着硒水平的提高而增加,呈现正相关的关系.
为了提高HS对土壤重金属的吸附能力,HS改性技术得到了人们的广泛关注. 改性后的HS比表面积增大、羧基等酸性官能团的含量增多,吸附能力明显增强,且作为吸附剂时,不易损失、易再生,可以节约材料、循环利用[53]. HS改性的方法有很多,比如:Zhang等[54]提出将HA制备成磁性纳米级胡敏酸;李慧敏等[3]提出将HS与粘土矿物复合,制成腐殖质-矿物复合体等. 这些方法的目的都是为了增大HS对重金属的吸附量. 何为红[55]通过实验得出,高岭石-胡敏酸复合体、蒙脱石-胡敏酸复合体相较于HA来说,吸附性能大大增强,其中高岭石-胡敏酸复合体对Cu(Ⅱ)有较强的选择性吸附,而蒙脱石-胡敏酸复合体对Cu(Ⅱ)、Cd(Ⅱ)都有很强的吸附能力,且Cu(Ⅱ)对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附几乎没有影响.
在修复土壤有机污染的过程中,解吸反应起着重要的作用,已经吸附的有机污染物能否再次释放以及释放的速率和程度都是由解吸过程控制的[39]. 另外,吸附和解吸是一个可逆的过程,被吸附的重金属离子在pH值变化的条件下可以发生解吸反应. 李光林[11]通过实验发现,pH<6.5时,HA溶液的pH越高,对Cd的吸附量越大,解吸越困难. 随着pH值的降低,HA对Cd的解吸速度增快,解吸总量增大.
-
HS对重金属离子的吸附会受pH值、温度、离子强度、重金属离子的种类等多种因素的影响. pH值会影响HS中羧基和酚羟基等酸性官能团的电离程度. pH=7时,羧基的络合起主要作用;pH>7时,羧基和酚羟基共同起作用[56]. 当pH值升高时,HS对重金属离子的吸附作用会增大,导致其迁移性和有效性显著降低[3]. 朱丽珺等[57]在研究中指出,当pH值为2—4.5时,HS对Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附率急剧上升;pH值为4.5—7时,吸附率达到96%—99%且保持相对稳定. 她[58]还研究了HA对Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附,其pH值的范围有所不同. 当pH值为2.3—6.0时,吸附率随pH值的增加而上升;当pH值大于6.0时,Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附量接近饱和值,曲线呈现S型. 兰亚琼等[59]也指出,当HA浓度、溶液离子强度和Cd(Ⅱ)浓度相同时,pH值越高,HA与Cd(Ⅱ)的络合率就越大. 对于Fe(Ⅲ)和Cu(Ⅱ)来说,pH=5时,80%的Fe(Ⅲ)和52%的Cu(Ⅱ)以强酸性羧基酚羟基形成的络合物的形式存在. 同时有研究表明,pH值降低会导致被固定离子重新活化. Janoš等[60]指出,pH值降低至1时,被固定的Cr会重新以Cr(Ⅲ)的形式进入到溶液中.
另外,在一定的范围内,HS对重金属离子的吸附能力会随着温度的升高而降低,离子浓度的增大而增大. 王强等[61]在研究HA与Fe(Ⅲ)的吸附反应时指出,升高温度,不利于HA对Fe(Ⅲ)的吸附;增大pH值,有利于吸附反应的进行;当离子强度位于0.00—0.10 mol·L−1之间时,增大离子强度,有利于吸附反应的进行,当离子强度从0.10 mol·L−1继续增大到0.15 mol·L−1时,不利于吸附反应的进行. 同时,Li等[62]指出对于不同的金属离子,即使同一种FA,吸附结果也会有较大的差别. 研究表明:吸附容量Cu(Ⅱ)>Pb(Ⅱ)>Cd(Ⅱ). 朱丽珺等[57]也在研究中用 Langmuir吸附等温式推测了HS对 Cu(Ⅱ) 、Pb(Ⅱ) 的饱和吸附量,测得HS对 Pb(Ⅱ) 的饱和吸附量是 Cu(Ⅱ) 的6.4倍.
-
HS因其自身结构的特殊性、复杂性,含有多种官能团,使其可以作为微生物与污染物之间的电子穿梭体或者直接作为微生物厌氧呼吸中的电子受体来参与环境中电子的传递过程[63-66]. 早在1974年,Szilágyi[67]就已经证明了HA能够通过将重金属氧化还原来影响重金属的生物迁移性和毒性. 同时,文章还指出,以HS作为传递电子的中间体与直接将电子传递给Fe(Ⅲ)的化合物相比,速率至少可提高27倍,还原水铁矿的速率也比直接还原至少快7倍以上. 江韬等[68]也在2012年指出HS本身具有还原能力,并与酚羟基、羧基等官能团的含量呈正相关的关系. 另有研究表明,HA的标准氧化还原电位为+528 mV,在一定的环境条件下,由于羧基的作用,使得HA失电子的能力强于得电子的能力,可以与Fe、Cr等金属元素发生氧化还原反应,形成难溶性的复合体,从而限制动植物对重金属元素的吸收[23, 45]. 因此,当HS与具有氧化还原特性的多价态重金属离子相互作用时,除了物理吸附、化学吸附外,还要考虑HS对重金属离子的氧化还原作用[11].
HS具有氧化还原的特性,主要得益于HA中所含有的醌、酚等官能团,尤其是醌基团在电子传递过程中发挥着重要的作用,是HA还原能力的主要来源[69]. 吴云当等[70]在文章中指出,HA处于氧化态时,得电子生成还原态羟醌,然后转移电子与金属离子反应,使金属离子被还原,继而HA又重新变成氧化态,又可以通过电子的转移还原金属离子,如此周而复始,金属离子的迁移转化性被大大地降低. 而且,当金属离子从氧化态转化为还原态时,其溶解性相对来说有所增加,这就解决了部分重金属离子难溶于水的问题,从而加快生物修复的进程. 同时,HS的氧化还原过程具有强pH依赖性. 研究表明,pH=3时,HA可以还原Cr(Ⅵ),降低Cr的价态,但当pH=7时,其还原效率基本上可以忽略不计. 这主要就是由于pH值的改变,影响了HS的溶解度,从而影响了氧化还原能力[66, 69].
-
重金属元素进入土壤后,由于富集作用,会随着动植物进入人体,危害人类健康. 在治理土壤重金属污染的过程中,重金属的生物有效性是很重要的一个评判标准,更能反映作物对重金属吸收利用的程度[71]. 但重金属的生物有效性并不等于重金属的总量,在很大程度上是由重金属的形态所决定的,不同的形态会对环境产生不同的影响[72]. 1979年Tessier等[73]提出五级法,将土壤中重金属的形态分为交换态(包括水溶态)、铁锰氧化物结合态、碳酸盐结合态、有机结合态以及残留态. 在这五种形态中,生物可利用性依次减小,生物毒性也依次降低. 所以,尽可能地将土壤中的重金属从生物易利用态转化为生物难利用态是治理重金属污染的一个方向.
土壤中的HS会与重金属形成配位化合物进而影响重金属在土壤中的赋存形态. 胡梦淩等[74]在文章中指出,HA能够钝化沉积物中的重金属,促进重金属由非稳定态转化为稳定态,从而达到降低重金属生物有效性的目的. 陕红[75]也在文章中指出,通过向土壤中添加秸秆和猪粪,提高了土壤中HA和FA的含量,结果发现交换态镉含量显著降低,碳酸盐结合态及铁锰氧化物结合态镉的含量显著升高,土壤中HA和FA含量的变化是影响Cd生物有效性的主要原因. 另外,HS的不同组分对重金属生物有效性的影响并不相同,大分子的HA比小分子的FA降低生物有效性的效果更为突出[76]. 余贵芬等[77]在研究中指出,HA能够使铁锰氧化态镉的含量有所增加,交换态镉的含量有所下降,抑制植物对镉的吸收,降低镉的生物有效性,而FA恰恰相反,能够增加土壤中镉的活性和生物吸收量. 朱燕等[43]也指出,FA的移动性强,与重金属离子形成的配位化合物一般呈交换态,HA能够使重金属离子形成稳定难溶的形态,降低重金属离子的活性.
众所周知,HS中的HA和HM对重金属有钝化作用,能够改变重金属的赋存形态,减小重金属的危害. 当HS与其他修复材料协同使用时,这种钝化效果被大大提高. Shi等[78]在文章中指出,在重度污染地区,将HM与沸石协同使用,能够更好地原位固定重金属,当两者协同使用时交换态Pb的含量比单施沸石时明显降低. 吴烈善等[1]也在文章中指出,HS+石灰作为复合钝化剂对重金属稳定化的效果比单一石灰处理好的多. 这种复合钝化剂会使土壤中的Cd产生先活化后钝化的效果,被HS先活化的Cd在加入石灰之后,能够更大程度地转化为稳定性较高的有机结合态和残留态,更好地降低Cd的危害.
-
通过分析重金属的赋存形态来研究HS对重金属生物有效性的影响还是具有一定的局限性,采用直接加入HS的方式来研究植物对重金属的吸收情况是更直接有效的研究方法. 这种方法成本低,能有针对性地反映特定植物对特定重金属的吸收效果,但由于植物生长周期的限制,一般所耗时间较长. 在应用的过程中,此方法的关键在于选取对重金属具有一定吸收和耐受能力的植物,比如:玉米、小麦、萝卜等[71, 79-80]. 同时,这种方法还可以用于评估不同种类土壤中重金属的吸收效果. 陕红[75]在研究有机物对土壤镉生物有效性的影响时就提到,分别在潮土、红壤以及黄棕壤中施入猪粪来观察植物各部位镉的浓度,结果发现,酸性土壤(红壤、黄棕壤等)中镉浓度的降低效果明显大于潮土.
另外,在添加HS的过程中,所添加的HS的浓度、种类对植物吸收重金属的数量也有一定的影响. 蔡文昌[81]在探究外源添加HS对重金属赋存形态和玉米生长的影响的实验中指出,来自泥炭土中的溶解性HS(PHS)比来自风化褐煤中的溶解性HS(LHS)对重金属的钝化效果更明显,更能有效地降低重金属的生物有效态活性. 当施加100 mg·kg−1的PHS时,玉米地上部对Cd的吸收量产生了显著的影响;当浓度达到200 mg·kg−1时,玉米地上部和地下部对Cd、Cu、Pb的吸收量都有了较大的影响;当施加200 mg·kg−1的LHS时,玉米地下部对Zn和Pb的吸收量显著降低. 同时,不同的HS添加方式也会影响植物吸收重金属的效果,主要分为叶面喷施和土壤添加两种方式. Bandiera等[82]在含有Cr、Cu、Zn等重金属且有机质含量较低的基质上种植饲料萝卜,分别采用基质混合添加、基质表层添加、叶面喷施的3种不同方式来向基质中添加HA,结果发现向基质中添加低浓度的HA(0.1 g·kg−1)能够促进萝卜的生长而且还增加了植物转移重金属的数量,添加高浓度的HA(1 g·kg−1)不利于萝卜的生长,但在叶面喷施0.1 g·kg−1的HA可以减少高浓度HA(1 g·kg−1)对萝卜的毒害作用. 因此,通过植物对重金属的吸收量能够更加直观地反映出HS对重金属生物有效性的影响.
-
重金属污染问题已经引起了人们的广泛关注,越来越多的人开始致力于重金属污染的修复工作. 起初,人们在研究水体污染时,在水环境中发现了金属-胡敏酸复合物,再加上考虑到重金属的生物有效性,人们开始把目光转向HS. 此外,HS具有来源广泛、方便易得的优点,可以从动物粪便、生活垃圾以及农业废弃物中提取,其组分中含有多种官能团,能够通过络合、吸附、氧化还原等多种方式来降低重金属的活性,减少重金属离子对人类和环境的危害. 然而,HS结构复杂,不同来源、类型的HS以及各种处理环境都会对HS去除重金属离子的过程造成影响,并且在一定的条件下,重金属离子还会发生解吸反应重新释放. 因此本文认为以后的研究可以多关注以下几个方向:
(1)重视对HM的研究. 近年来,人们对HS与重金属之间相互作用的研究大多集中在HA和FA上,对HM的研究较为缺乏. HM大约占HS的40%,对重金属离子也有吸附钝化的能力,且HM本身就具有难溶性的特点,能够与重金属离子形成较为稳定的复合物.
(2)加强HS对重金属复合污染的研究. 目前,对HS与重金属的研究多集中在单一重金属离子上,缺乏对多种重金属离子共存条件下的复合研究. 从实际情况来说,重金属污染多为伴生性或综合性,被污染土壤通常含有多种重金属离子,甚至还有有机无机复合污染,所以增加研究对象的多样性也可能是我们今后的一个研究方向.
(3)研究腐殖质基改性材料和复合材料及其最佳使用条件. HS改性技术能够提高HS对重金属的吸附性能,将改性HS与其他吸附材料协同使用,形成新的复合材料,新材料的吸附效果、最佳pH值、离子浓度等要素的确定也是未来值得关注的一个课题.
(4)关注HS的使用对土壤环境条件的影响. 在利用HS治理重金属污染的过程中,还需要关注HS的各组分对土壤的理化性质以及土壤中动物、微生物的影响. 同时,对于HS与重金属离子反应所生成的中间产物也有待进一步研究.
腐殖质来源、特征及其与土壤中重金属作用机制的研究进展
Research progress on sources, characteristics of humus and mechanism of interaction with heavy metals in soil
-
摘要: 近年来,土壤重金属污染成为全球性的环境问题,给人类的生产、生活带来了极大的危害. 腐殖质(HS)作为土壤有机质的主体部分,含有羧基、酚羟基等众多官能团,能够通过络合、吸附、氧化还原等作用影响重金属离子的活性和迁移转化规律. 为了更好地了解HS和HS与土壤重金属之间的相互作用关系,本文对HS的来源、分类、化学特征做了详细的概述,重点介绍了HS与土壤中重金属之间的相互作用及其影响因素,并分析了HS对重金属活性的影响,最后提出了HS在土壤重金属迁移转化中存在的问题与展望.Abstract: In recent years, soil heavy metal pollution has become a global environmental problem, which has brought great harm to human production and life. As the main part of soil organic matter, humus (HS) contains many functional groups such as carboxyl group and phenolic hydroxyl group, which can affect the activity, migration and transformation of heavy metal ions through complexation, adsorption, redox and other actions. In order to better understand the interaction relationship between HS and heavy metal in soil. In this paper, the source, classification, the chemical characteristics of HS was summarized in detail, mainly introduced the interaction between HS and heavy metals and its influencing factors. What’s more, the effect of humus on heavy metals activity was analyzed.Finally, the problems and prospects of HS in heavy metal migration and transformation are put forward.
-
Key words:
- humus /
- chemical characteristics /
- heavy metals /
- interaction.
-

-
[1] 吴烈善, 曾东梅, 莫小荣, 等. 不同钝化剂对重金属污染土壤稳定化效应的研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(1): 309-313. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.01.041 WU L S, ZENG D M, MO X R, et al. Immobilization impact of different fixatives on heavy metals contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(1): 309-313(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.01.041
[2] AHMAD W, NAJEEB U, ZIA M. Chapter 2 - soil contamination with metals: Sources, types and implications [J]. Soil Remediation and Plants, 2015: 37-61. [3] 李慧敏, 雷静, 王友东. 腐殖质在土壤重金属污染修复中的作用与展望 [J]. 农业研究与应用, 2017(5): 25-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0764.2017.05.006 LI H M, LEI J, WANG Y D. Roles and prospects of humus in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil [J]. Agricultural Research and Application, 2017(5): 25-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0764.2017.05.006
[4] 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[J]. 中国环保产业, 2014(5): 10-11全国土壤污染状况调查公报 [J]. China Environmental Protection Industry, 2014(5): 10-11. [5] NEWCOMB C J. Humic matter in soil and the environment, principles and controversies [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2015, 79(5): 1520. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2015.0004br [6] de MELO B A G, MOTTA F L, SANTANA M H A. Humic acids: Structural properties and multiple functionalities for novel technological developments [J]. Materials Science and Engineering:C, 2016, 62: 967-974. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.12.001 [7] PARK J H, LAMB D, PANEERSELVAM P, et al. Role of organic amendments on enhanced bioremediation of heavy metal(loid) contaminated soils [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 185(2/3): 549-574. [8] 毕冬雪, 邓亚娟, 孟凡德, 等. 腐殖质纳米颗粒对镉污染土壤的修复 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(5): 1295-1302. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201711218 BI D X, DENG Y J, MENG F D, et al. Humic nanoparticles for remediation of Cd-contaminated soils [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2018, 12(5): 1295-1302(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201711218
[9] 杜金彤. 腐殖质与金属离子相互作用的研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2020. DU J T. Study on the interaction between humic substances and metal ions[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2020(in Chinese).
[10] 窦森. 土壤腐殖物质形成转化及其微生物学机理研究进展 [J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2008, 30(4): 538-547. doi: 10.13327/j.jjlau.2008.04.005 DOU S. Review of formation and transformation of soil humic substance and its microbiologic mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2008, 30(4): 538-547(in Chinese). doi: 10.13327/j.jjlau.2008.04.005
[11] 李光林. 腐殖酸与几种重金属离子的相互作用及影响因素研究[D]. 重庆: 西南农业大学, 2002. LI G L. On the reaction of humic acids on some heavy metal ions and the affecting factors[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, , 2002(in Chinese).
[12] WANG K J, XING B S. Chemical extractions affect the structure and phenanthrene sorption of soil humin [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(21): 8333-8340. [13] GHABBOUR E A, DAVIES G. Humic substances : structures, models and functions[M]. Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry, 2001: 387. [14] FRANCIOSO O, SÁNCHEZ-CORTÉS S, TUGNOLI V, et al. Characterization of peat fulvic acid fractions by means of FT-IR, SERS, and 1H, 13C NMR spectroscopy [J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 1998, 52(2): 270-277. doi: 10.1366/0003702981943347 [15] SARIR M S, DURRANI M I. Utilization of natural resources for increase crop production [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Biological Science, 2006, 1(2): 16-18. [16] COATES J D, COLE K A, CHAKRABORTY R, et al. Diversity and ubiquity of bacteria capable of utilizing humic substances as electron donors for anaerobic respiration [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2002, 68(5): 2445-2452. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.5.2445-2452.2002 [17] 窦森, 李凯, 崔俊涛, 等. 土壤腐殖物质形成转化与结构特征研究进展 [J]. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(6): 1148-1158. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2008.06.019 DOU S, LI K, CUI J T, et al. Advancement in the study on formation, transformation and structural characteristics of soil humic substances [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2008, 45(6): 1148-1158(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2008.06.019
[18] HAYES M H B, SWIFT R S. An appreciation of the contribution of Frank Stevenson to the advancement of studies of soil organic matter and humic substances [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2018, 18(4): 1212-1231. doi: 10.1007/s11368-016-1636-6 [19] 郝晓地, 周鹏, 曹亚莉. 污水处理中腐殖质的来源及其演变过程 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(1): 1-11. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201606072 HAO X D, ZHOU P, CAO Y L. Origins and evolution processes of humic substances in wastewater treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(1): 1-11(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201606072
[20] 黄红丽. 堆肥中木质素的生物降解及其与腐殖质形成关系的研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2006. HUANG H L. Lignin biodegradation and its relationship with humus formation in composting[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2006(in Chinese).
[21] YU M D, HE X S, LIU J M, et al. Characterization of isolated fractions of dissolved organic matter derived from municipal solid waste compost [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 635: 275-283. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.140 [22] PARSONS J W. Humus chemistry—genesis, composition, reactions [J]. Soil Science, 1983, 135(2): 129-130. [23] 刘保峰. 土壤腐殖酸及其对重金属化学与生物行为的影响[C]. 中国内蒙古海拉尔: 农业部环境保护科研监测所, 2006: 188-193. LIU B F. Soil humic acid and its effects on chemical and biological behavior of heavy metals[C]. Hailar, Inner Mongolia, China: Environmental Protection Research and Monitoring Institute, Ministry of Agriculture, 2006: 188-193(in Chinese).
[24] 胡梦淩, 曾和平. 不同来源腐殖质淋洗去除土壤中Cd、Pb的研究 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2021, 43(1): 14-19. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2021.01.003 HU M L, ZENG H P. The performance of different sources of humic substances for leaching removal of Cd and Pb from soils [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2021, 43(1): 14-19(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2021.01.003
[25] LI C, GAO S, ZHANG J, et al. Moisture effect on soil humus characteristics in a laboratory incubation experiment [J]. Soil and Water Research, 2016, 11(No.1): 37-43. doi: 10.17221/21/2015-SWR [26] HIRADATE S, YONEZAWA T, TAKESAKO H. Fine fractionation and purification of the fulvic acid fraction using adsorption and precipitation procedures [J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2007, 53(4): 413-419. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0765.2007.00159.x [27] 陈林倩, 武丹, 王征, 等. 富硒土壤腐殖质的组成及其对铅的作用研究 [J]. 环境工程, 2018, 36(6): 163-168. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201806033 CHEN L Q, WU D, WANG Z, et al. Humus composition in selenium-enriched soil and its effects on lead [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2018, 36(6): 163-168(in Chinese). doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201806033
[28] 窦森, 肖彦春, 张晋京. 土壤胡敏素各组分数量及结构特征初步研究 [J]. 土壤学报, 2006, 43(6): 934-940. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2006.06.008 DOU S, XIAO Y C, ZHANG J J. Quantities and structural characteristics of various fractions of soil humin [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2006, 43(6): 934-940(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2006.06.008
[29] ZEHL K, EINAX J. Influence of atmospheric oxygen on heavy metal mobility in sediment and soil (7 pp) [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2005, 5(3): 164-170. doi: 10.1065/jss2005.01.132 [30] BORŮVKA L, DRÁBEK O. Heavy metal distribution between fractions of humic substances in heavily polluted soils [J]. Plant, Soil and Environment, 2011, 50(No.8): 339-345. doi: 10.17221/4041-PSE [31] 陈亭悦. 腐殖酸不同分子量组分对铅生物有效性的调控效应与机制[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2020. CHEN T Y. Effects of humic acids fractions with different molecular weight on speciation of bioavailability of lead[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2020(in Chinese).
[32] 高泽鹏. 腐殖质的分离及其对苯酚光致溴代反应的影响[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2019. GAO Z P. Isolation of humus and its effect on photoinduced bromination of phenol[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2019(in Chinese).
[33] BURDON J. Are the traditional concepts of the structures of humic substances realistic? [J]. Soil Science, 2001, 166(11): 752-769. doi: 10.1097/00010694-200111000-00004 [34] PICCOLO A. The supramolecular structure of humic substances [J]. Soil Science, 2001, 166(11): 810-832. doi: 10.1097/00010694-200111000-00007 [35] 彭安, 王文华. 水体腐殖酸及其络合物: Ⅰ. 蓟运河腐殖酸的提取和表征 [J]. 环境科学学报, 1981, 1(2): 126-139. PENG A, WANG W H. Humic substances and their complex compounds in natural waters Ⅰ. extraction and characterization of humic acid from ji-Yun river [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 1981, 1(2): 126-139(in Chinese).
[36] CHIN Y P, AIKEN G, O'LOUGHLIN E. Molecular weight, polydispersity, and spectroscopic properties of aquatic humic substances [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1994, 28(11): 1853-1858. [37] HUANG S W, CHIANG P N, LIU J C, et al. Chromate reduction on humic acid derived from a peat soil - Exploration of the activated sites on HAs for chromate removal [J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 87(6): 587-594. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.010 [38] JIANG J, KAPPLER A. Kinetics of microbial and chemical reduction of humic substances: Implications for electron shuttling [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(10): 3563-3569. [39] 朱燕. 土壤胡敏素的结构特征及其对多环芳烃(菲)吸附、解吸机理的研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2006. ZHU Y. Structural characteristics of humin from different soils and sorption-desorption behavior of phenanthrene[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2006(in Chinese).
[40] ARSHAD M A, RIPMEESTER J A, SCHNITZER M. Attempts to improve solid state 13C nmr spectra of whole mineral soils [J]. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 1988, 68(3): 593-602. doi: 10.4141/cjss88-057 [41] 刘亚子, 高占启. 腐殖质提取与表征研究进展[J]. 环境科技, 2011, 24(S1): 76-80. LIU Y Z, GAO Z Q. Progress in research on extraction and characterization of humus[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2011, 24(Sup 1): 76-80(in Chinese).
[42] de JONG R, CAMPBELL C A, NICHOLAICHUK W. Water retention equations and their relationship to soil organic matter and particle size distribution for disturbed samples [J]. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 1983, 63(2): 291-302. doi: 10.4141/cjss83-029 [43] 朱燕, 代静玉. 腐殖物质对有机污染物的吸附行为及环境学意义 [J]. 土壤通报, 2006, 37(6): 1224-1230. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2006.06.041 ZHU Y, DAI J Y. Research progress in the structure characterization of humus and its environmental meaning [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2006, 37(6): 1224-1230(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2006.06.041
[44] 陈蕾, 超峰, 王郑, 等. 天然有机质对环境污染物的转化过程的介导作用 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2013, 22(7): 1244-1249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2013.07.026 CHEN L, CHAOFENG, WANG Z, et al. Transformation of environmental pollutants mediated by natural organic matter [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2013, 22(7): 1244-1249(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2013.07.026
[45] 燕爱春. 土壤腐殖物质对重金属的吸附特性及其机理研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2019. YAN A C. Adsorption characteristics and mechanism of heavy metals by soil humus[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2019(in Chinese).
[46] 张艳敏. 胡敏酸对Hg(Ⅱ)的还原作用及其影响因素研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2011. ZHANG Y M. The effects of humic acid on Hg(Ⅱ) abiotic reduction and its influencing factors[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2011(in Chinese).
[47] MAK M S H, LO I M C. Influences of redox transformation, metal complexation and aggregation of fulvic acid and humic acid on Cr(VI) and As(V) removal by zero-valent iron [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 84(2): 234-240. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.04.024 [48] ZHAO K Q, YANG Y, PENG H, et al. Silicon fertilizers, humic acid and their impact on physicochemical properties, availability and distribution of heavy metals in soil and soil aggregates [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 822: 153483. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153483 [49] MAKHINOVA A F, MAKHINOV A N. Role of humus substances in chemical soil pollution during deposit exploitation in Priokhotye and Priamurye [J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 188: 109766. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109766 [50] SANNINO F, SPACCINI R, SAVY D, et al. Remediation of highly contaminated soils from an industrial site by employing a combined treatment with exogeneous humic substances and oxidative biomimetic catalysis [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 261: 55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.06.077 [51] BARNIE S, ZHANG J, WANG H, et al. The influence of pH, co-existing ions, ionic strength, and temperature on the adsorption and reduction of hexavalent chromium by undissolved humic acid [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 212: 209-218. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.08.067 [52] KO I, DAVIS A P, KIM J Y, et al. Effect of contact order on the adsorption of inorganic arsenic species onto hematite in the presence of humic acid [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 141(1): 53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.06.084 [53] 陈荣平, 张银龙, 马爱军, 等. 腐殖酸改性及其对镉的吸附特性 [J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(4): 102-106. CHEN R P, ZHANG Y L, MA A J, et al. Study on the modification of humic acid and its adsorption to cadmium [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2014, 38(4): 102-106(in Chinese).
[54] ZHANG X, ZHANG P Y, WU Z, et al. Adsorption of methylene blue onto humic acid-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2013, 435: 85-90. [55] 何为红. 重金属离子在粘土矿物—胡敏酸复合体上的吸附研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2007. HE W H. Adsorption of heavy metal on clay mineral-humic acid complexes[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2007(in Chinese).
[56] GARCIA-MINA J M. Stability, solubility and maximum metal binding capacity in metal-humic complexes involving humic substances extracted from peat and organic compost [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2006, 37(12): 1960-1972. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2006.07.027 [57] 朱丽珺, 张金池, 宰德欣, 等. 腐殖质对Cu2+和Pb2+的吸附特性 [J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 31(4): 73-76. ZHU L J, ZHANG J C, ZAI D X, et al. Study on the adsorption of heavy metal Cu2+, Pb2+by humus [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2007, 31(4): 73-76(in Chinese).
[58] 朱丽珺, 张金池, 俞元春, 等. 胡敏酸吸附重金属Cu2+Pb2+Cd2+的特征及影响因素 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2008, 27(6): 2240-2245. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2008.06.020 ZHU L J, ZHANG J C, YU Y C, et al. Characteristics and affecting factors of humic acid adsorbing heavy metals Cu2+Pb2+Cd2+ [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2008, 27(6): 2240-2245(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2008.06.020
[59] 兰亚琼. 水环境中镉离子与腐殖酸作用特性的研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2011. LAN Y Q. Study on characterists of heavy metals and humic acid in the water environment[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2011(in Chinese).
[60] JANOŠ P, HŮLA V, BRADNOVÁ P, et al. Reduction and immobilization of hexavalent chromium with coal- and humate-based sorbents [J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 75(6): 732-738. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.01.037 [61] 王强, 魏世强. 胡敏酸吸附解吸Fe3+反应特征研究 [J]. 土壤学报, 2006, 43(3): 414-421. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2006.03.009 WANG Q, WEI S Q. Reaction characteristics of fe3+ adsorption and desorption by humic acid [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2006, 43(3): 414-421(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2006.03.009
[62] LI H, WANG J H, ZHAO B Y, et al. The role of major functional groups: Multi-evidence from the binding experiments of heavy metals on natural fulvic acids extracted from lake sediments [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 162: 514-520. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.038 [63] PHAM A N, ROSE A L, WAITE T D. Kinetics of Cu(II) reduction by natural organic matter [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, 2012, 116(25): 6590-6599. doi: 10.1021/jp300995h [64] LOVLEY D R, COATES J D, BLUNT-HARRIS E L, et al. Humic substances as electron acceptors for microbial respiration [J]. Nature, 1996, 382(6590): 445-448. doi: 10.1038/382445a0 [65] LOVLEY D R, BLUNT-HARRIS E L. Role of humic-bound iron as an electron transfer agent in dissimilatory Fe(III) reduction [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(9): 4252-4254. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.9.4252-4254.1999 [66] 袁英, 何小松, 席北斗, 等. 腐殖质氧化还原和电子转移特性研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(12): 2048-2057. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.12.019 YUAN Y, HE X S, XI B D, et al. Research progress on the redox and electron transfer capacity of humic substances [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(12): 2048-2057(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.12.019
[67] SZILÁGYI M. Valency changes of metal ions in the interaction with humic acids [J]. Fuel, 1974, 53(1): 26-28. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(74)90028-3 [68] 江韬, 魏世强, 李雪梅, 等. 几种胡敏酸还原容量的表征与比较 [J]. 土壤学报, 2012, 49(5): 901-908. doi: 10.11766/trxb201108290323 JIANG T, WEI S Q, LI X M, et al. Characterization of and comparison between reduction capacities of different humic acids [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2012, 49(5): 901-908(in Chinese). doi: 10.11766/trxb201108290323
[69] 栾富波, 谢丽, 李俊, 等. 腐殖酸的氧化还原行为及其研究进展 [J]. 化学通报, 2008, 71(11): 833-837. doi: 10.14159/j.cnki.0441-3776.2008.11.011 LUAN F B, XIE L, LI J, et al. Redox behavior and research progress of humic acid [J]. Chemistry, 2008, 71(11): 833-837(in Chinese). doi: 10.14159/j.cnki.0441-3776.2008.11.011
[70] 吴云当, 李芳柏, 刘同旭. 土壤微生物—腐殖质—矿物间的胞外电子传递机制研究进展 [J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(2): 277-291. WU Y D, LI F B, LIU T X. Mechanism of extracellular electron transfer among microbe–humus–mineral in soil: A review [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(2): 277-291(in Chinese).
[71] 黄迪, 杨燕群, 肖选虎, 等. 土壤重金属生物有效性评价技术进展[J]. 现代化工, 2019, 39(S1): 89-94, 98. HUANG D, YANG Y Q, XIAO X H, et al. Technology for measuring bioavailability of heavy metals in soil[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2019, 39(Sup 1): 89-94, 98(in Chinese).
[72] 杨洁, 瞿攀, 王金生, 等. 土壤中重金属的生物有效性分析方法及其影响因素综述 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2017, 39(2): 217-223. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2017.02.021 YANG J, QU P, WANG J S, et al. Review on analysis methods of bioavailability of heavy metals in soil and its influence factors [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2017, 39(2): 217-223(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2017.02.021
[73] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51(7): 844-851. doi: 10.1021/ac50043a017 [74] 胡梦淩, 曾和平, 董达诚, 等. 腐殖质改良植物修复重金属污染土壤的研究进展 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2020, 36(3): 273-280. doi: 10.19741/j.issn.1673-4831.2019.0165 HU M L, ZENG H P, DONG D C, et al. Humic substances amendments for improving phytoremediation of heavy metal polluted soils: A review [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2020, 36(3): 273-280(in Chinese). doi: 10.19741/j.issn.1673-4831.2019.0165
[75] 陕红. 有机物对土壤镉生物有效性的影响及机理[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2009. SHAN H. Impact and mechanism of organic amendments on cadmium bioavailability in soils[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2009(in Chinese).
[76] WENG L P, TEMMINGHOFF E J, LOFTS S, et al. Complexation with dissolved organic matter and solubility control of heavy metals in a sandy soil [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(22): 4804-4810. [77] 余贵芬, 蒋新, 孙磊, 等. 有机物质对土壤镉有效性的影响研究综述 [J]. 生态学报, 2002, 22(5): 770-776. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.05.021 YU G F, JIANG X, SUN L, et al. A review for effect of organic substances on the availability of cadmium in soils [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2002, 22(5): 770-776(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.05.021
[78] SHI W Y, SHAO H B, LI H, et al. Co-remediation of the lead-polluted garden soil by exogenous natural zeolite and humic acids [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 167(1/2/3): 136-140. [79] 刘玉荣, 党志, 尚爱安. 污染土壤中重金属生物有效性的植物指示法研究 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2003, 25(4): 215-217,242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2003.04.009 LIU Y R, DANG Z, SHANG A A. Study on bioavailability of heavy metals in polluted soil using phytoindicating [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2003, 25(4): 215-217,242(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2003.04.009
[80] 周卫红, 张静静, 邹萌萌, 等. 土壤重金属有效态含量检测与监测现状、问题及展望 [J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(4): 605-615. doi: 10.13930/j.cnki.cjea.160904 ZHOU W H, ZHANG J J, ZOU M M, et al. The detection and monitoring of available heavy metal content in soil: A review [J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(4): 605-615(in Chinese). doi: 10.13930/j.cnki.cjea.160904
[81] 蔡文昌. 腐殖质对污染土壤重金属赋存形态和玉米生长的影响研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2018. CAI W C. Effects of humic substances on heavy metals occurrence mode in contaminated soil and the growth of maize[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2018(in Chinese).
[82] BANDIERA M, MOSCA G, VAMERALI T. Humic acids affect root characteristics of fodder radish (Raphanus sativus L. var. oleiformis Pers. ) in metal-polluted wastes [J]. Desalination, 2009, 246(1/2/3): 78-91. -



 下载:
下载: