-
有机气溶胶在灰霾天气中扮演着主要角色,其在污染重灾区的 PM2.5 中质量占比可高达约60%左右[1-2],不仅能够通过长距离传输对区域和全球气候变化产生重要影响[3],还对人体健康存在一定危害. 空气中大部分污染源都可能释放或形成有机气溶胶,主要涵盖污染源如生物质或化石燃料燃烧等过程释放到环境中的一次有机气溶胶(POA)和由气体前体物(主要是挥发性有机物)经过大气氧化等过程而形成的二次有机气溶胶(SOA)[4]. 有机气溶胶因不同来源,其理化性质存在一定差异,对空气质量和人体健康的危害水平也有所不同[5]. 只有弄清楚主要污染源的排放特征及相对贡献,才能制定有针对性的污染控制措施. Simoneit等[6]最先在有机气溶胶分析中提出有机示踪物的应用,而后因有机示踪物良好的源指向性,在有机气溶胶源解析过程中应用广泛,且在污染物传输和大气寿命预测中发挥着重要作用[7-8]. 然而近年来基于有机示踪物的源解析方法存在一些质疑,Rutter等[9]在应用示踪物产率法研究美国大气中不同来源的气体前体物对SOA贡献时指出,烟雾箱实验确定的有机示踪物是在有限的实验条件下生成的中间氧化产物,如果与实际大气中所经历的光化学过程不同,将导致实际大气中部分 SOA 的来源无法解析[10]. 冯加良等[11]基于元素碳(EC)法、水溶性有机碳(WSOC)法、示踪法和正矩阵分解(PMF)模型对上海市 SOA 的季节贡献进行评估时发现,示踪法与 WSOC 法解析的 SOA 贡献存在较大偏差,上海 PM2.5 中的部分 SOA 不能用基于示踪物的方法来解释.
一般来说,作为大气气溶胶的有机示踪物,需要具备以下条件:(1)该物质本身不存在于大气中,且不能由大气反应生成;(2)具有特异性,是所解析污染源的特征组分;(3)不易发生各种反应,释放含量保持较高稳定性. 表1中列举了常见的大气气溶胶有机示踪物,一些研究表明,将这些有机示踪物暴露于·OH、O3等大气氧化剂存在的环境中,会在液(固)、气两相中发生非均相氧化反应,影响其大气寿命,这就会给有机气溶胶源解析的准确性带来一定挑战. Weitkamp等[12]探究了机动车化石燃料燃烧产生的 POA 中藿烷等有机示踪物的·OH自由基非均相氧化,其动力学分析结果表明藿烷的非均相氧化会导致传统的化学质量平衡(CMB)模型低估汽车尾气对有机气溶胶的相对贡献,如果车辆排放物的大气寿命为4 d,那么传统的 CMB 模型将低估车辆排放物总浓度的50%. Lai等[13]的研究发现,·OH自由基对顺松油酸(天然源α-蒎烯SOA的二次示踪物)的非均相氧化是明显的,从而推测在外场观测中得到的顺松油酸浓度很可能低估了α-蒎烯对于 SOA 的相对贡献. 由此可见,如果有机示踪物能够发生非均相氧化反应,则会不同程度地影响有机气溶胶源解析和 相对贡献估算的准确性[14] ,因此有机示踪物化学稳定性的评估对于大气污染防控至关重要.
-
生物质燃烧产生的有机污染物是POA和SOA的重要来源[15]. 在燃烧过程中,木质素等热解会转化为大量左旋葡聚糖[7, 16]等单糖物质,甾族化合物通常转化为β-谷甾醇[14],秸秆等会产生萜类化合物[14]. 由于在其他有机气溶胶来源中未检测到这些物质,故这些有机物可以作为生物质燃烧源的有机示踪物.
-
长期以来,左旋葡聚糖被认为具有相对的化学稳定性、来源特异性和较高的浓度含量[17],是生物质燃烧的重要有机示踪物之一,然而也有一些学者对其在大气中的稳定性提出了质疑. Sang等[18]采用稳定碳同位素比率法测量气溶胶样品中的左旋葡聚糖,发现左旋葡聚糖会被气相中的·OH自由基所氧化. Hennigan等[19]在流动管反应器中的研究表明左旋葡聚糖的衰变程度与总的·OH自由基暴露量有关,当其暴露在典型的夏季条件(·OH自由基浓度为106 molecules·cm−3)下时,左旋葡聚糖的大气寿命约为0.7—2.2 d. Slade等[20]也利用流动管反应器,在较高的·OH自由基浓度范围内,测定了左旋葡聚糖的反应吸收系数. 当·OH自由基浓度从2.6×107—3×109 molecules·cm−3升高到4.1×1010—6.7×1010 molecules·cm−3时,吸收系数从0.05—1下降为0.008—0.034,表明该反应吸收系数随·OH自由基浓度升高而降低,该研究指出这种关系可以用Langmuir–Hinshelwood模型来描述:在与左旋葡聚糖发生碰撞时,·OH自由基首先吸附到表面,然后发生反应,当·OH自由基浓度较高时,表面活性位点耗尽,导致·OH自由基的吸收系数下降. Hoffmann等[21]以动力学实验模拟左旋葡聚糖的氧化过程及其大气寿命,研究发现,在高相对湿度(RH=90%)条件下,左旋葡聚糖在典型大气·OH自由基浓度(106—107 molecules·cm−3)下的大气寿命约为0.5—3.5 d. 目前国内对于左旋葡聚糖的非均相氧化研究的报道较少,柏静等[22]在实验室模拟了·OH自由基浓度为2×106 molecules·cm−3时与左旋葡聚糖的反应,在298 K时,二者的反应速率常数为(3.09 ± 0.18)×10−13 cm3·molecules−1·s−1,随着温度的升高反应速率常数将会增大,在实验条件下对应着约26 d的大气寿命. Lai等[23]使用流动反应器在·OH自由基浓度为(7×106 — 5×107) molecules·cm−3条件下研究了·OH自由基与左旋葡聚糖的非均相氧化,测得纯左旋葡聚糖的反应速率常数为(9.17±1.16)×10−12 cm3molecules−1·s−1,与之相比,涂覆在(NH4)2SO4或NaCl的左旋葡聚糖速率常数分别增加到(9.53 ± 0.39)×10−12 cm3·molecules−1·s−1和(10.3 ± 0.45)×10−12 cm3·molecules−1·s−1,而涂敷在煤烟上的速率常数则减少到(4.04 ± 0.29)×10−12 cm3·molecules−1·cm−1,研究分析其可能的原因是:涂敷在无机盐上的左旋葡聚糖具有更高的分散度而促进反应的进行;而煤烟具有较大的比表面积,左旋葡聚糖易进入烟尘的内部通道,从而阻碍其与·OH自由基之间的表面接触,且煤烟也可能对·OH自由基有反应性,导致分散在煤烟上的左旋葡聚糖反应性较低. 在不同的条件下测得左旋葡聚糖的大气寿命约为1.2—3.9 d. 王宁[24]的研究表明,NO3自由基和SO4−·自由基也可以对左旋葡聚糖上的H进行抽提从而引发非均相氧化反应.
Li等[25]的研究表明,如果不考虑左旋葡聚糖在大气中的降解,左旋葡聚糖将主要通过湿沉降和较小程度的干沉降来平衡其全球浓度,这种平衡将导致左旋葡聚糖的平均寿命为7.3 d. 而以上研究表明,左旋葡聚糖能够被大气中·OH、NO3、SO4−等自由基所氧化,在典型的大气·OH自由基浓度范围(106—107 molecules·cm−3)内,其大气寿命约为0.5 — 4 d左右,小于其不考虑降解时的平均寿命. 这意味着过去利用左旋葡聚糖进行源解析时,实地测量的左旋葡聚糖浓度可能被低估,从而导致生物质燃烧源的气溶胶的贡献被低估.
-
脱氢枞酸(DHAA)经常应用于软木类生物质燃烧源的有机示踪物[26-27],其特征性可与硬木类生物质燃烧源相区分[28]. Knopf 等[29]测定了DHAA等有机物与O3、NO2、N2O5和 NO3的反应吸收系数. 在O2存在的情况下,其反应吸收系数分别在(1—8)×10−5、10−6—5×10−5、(4—6)×10−5和(1—26)×10−3范围内. 在典型污染条件下,左旋葡聚糖与DHAA在O3、NO2、N2O5和 NO3氧化下的大气寿命约为1 — 112 min. Bai等[30]研究了O3和·OH自由基对DHAA的非均相氧化,在298 K和标准大气压下,DHAA+·OH和DHAA+O3的速率常数分别为
$ \text{0.89×}{\text{10}}^{{-11}}{\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ 和$ \text{2.29×}{\text{10}}^{{-20}}\;{\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{\text{-1}} $ ,研究指出·OH自由基对DHAA的氧化效果比O3更加显著. Lai等[31]也模拟了DHAA与·OH自由基在不同环境条件下的非均相氧化,在室温和40%相对湿度下,纯 DHAA 与·OH自由基的有效速率常数为(5.72 ± 0.87)×10−12$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{\text{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{\text{-1}} $ ,并考察了种子气溶胶存在对 DHAA 降解动力学的影响,在相同温度、湿度环境中,与纯 DHAA 相比,在 (NH4)2SO4 混合效应下的 DHAA有效速率常数降低到(4.58 ± 0.95)×10−12$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{\text{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{\text{-1}} $ ,其分析可能的原因为:一些DHAA被 (NH4)2SO4 所包裹,形成了内部混合的 (NH4)2SO4和DHAA,混合样品表面的 (NH4)2SO4可能会略微抑制·OH自由基在DHAA表面上的扩散,从而抑制反应的进行. 在不同的环境条件下,DHAA 的平均大气寿命约为2.3 — 4.4 d.以上研究表明混合状态对DHAA等有机示踪物的降解动力学和寿命有显著影响,而实际大气环境所形成的有机示踪物通常都以混合状态存在,故有机示踪物纯物质的降解动力学应为真实对流层降解动力学的上限,但需要指出的是,以上研究所测得的气溶胶有机示踪物的最长寿命仍短于气溶胶在对流层的停留时间(数十天),因此在利用有机示踪物进行气溶胶源解析时, 可能会使得有机示踪物的实际作用被低估.
-
甲氧基苯酚类有机化合物被广泛作为木材烟雾排放源的有机示踪物. Liu等[32]使用流动管反应器研究了·OH自由基对甲氧基苯酚的非均相氧化. 在室温,RH为40%时,3种甲氧基苯酚:香草醛(VA)、松柏醛(CA)和丁香醛(SA)的反应速率常数分别为(4.72 ± 0.51)×10−12
$ {\text{}\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ 、(10.59 ± 0.50)×10−12$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ 和(12.25 ± 0.60)×10−12$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ . 研究结果表明,高温对这些反应起到了促进作用,而高相对湿度具有一定的抑制作用. 根据测定的速率常数,这3种甲氧基苯酚在不同条件下的大气寿命约为0.54 — 2.18 d. 丁香醇(2, 6-二甲氧基苯酚)也是大气中木材烟雾排放的潜在有机示踪物,为了研究丁香醇在大气中的反应性,Lauraguais等[33]在(294 ± 2 )K的烟雾箱中测定了其与·OH自由基反应的速率常数为(9.66 ± 1.11)×10−11$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ ,所对应丁香醇的大气寿命约为1.8 h. Liu等[34]使用流动管反应器在不同的羟基浓度、温度和相对湿度下研究了·OH自由基对木材燃烧排放的潜在有机示踪物松柏醇(一种甲氧基苯酚)的降解动力学. 研究表明·OH自由基能有效降解松柏醇,平均反应速率常数为(11.6 ± 0.5)×10−12$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{\text{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{\text{-1}} $ . 此外,在40%相对湿度下,温度升高有利于松柏醇的降解,而相对湿度的增加对松柏醇的降解有负面影响,根据在不同条件下获得的速率常数,松柏醇的大气寿命在(13.5 ± 0.4)—(22.9 ± 1.4)h范围内. 2-甲氧基苯酚(愈创木酚)也是大气中木材烟雾排放的潜在有机示踪物,为了研究这类化合物在大气中的反应性,Coeur-Tourneur 等[35]采用气相色谱和相对速率法,在(294 ± 2)K和1个大气压下条件下测定其与·OH自由基的反应速率系数为(7.53 ± 0.41)× 10−11$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{\text{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{\text{-1}} $ .国内外研究表明,NO3自由基也能引起甲氧基苯酚类有机示踪物的非均相氧化反应. Zhang等[36]研究了丁香醇和4-乙基愈创木酚与NO3自由基的非均相氧化反应,在298 K条件下,丁香醇和4-乙基愈创木酚与NO3自由基的反应速率系数为(1.6 ± 0.4)×10−13
$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ 和(1.1 ± 0.2)×10−12$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{\text{-1}} $ ,其大气寿命分别为3.5 h和0.5 h. Lauraguais 等[37]利用8000 L常压烟雾箱中,在(294 ± 2)K条件下,研究了5种甲氧基苯酚与NO3自由基的非均相氧化反应. 利用相对动力学测定其相对速率常数(以$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ 为单位)结果为:愈创木酚:(2.69 ± 0.57)×10−11、3-甲氧基苯酚:(1.15 ± 0.21)×10−11、 4-甲氧基苯酚:(13.75 ± 7.97)×10−11、2-甲氧基-4-甲基苯酚:(8.41 ± 5.58)×10−11、丁香醇:(15.84 ± 8.10)×10−11. Yang等[38] 采用相对速率法研究了NO3自由基与几种甲氧基苯酚(愈创木酚、甲酚和丁香醇)的非均相氧化反应. 测定愈创木酚、甲酚和丁香醇与NO3自由基在298 K和1个大气压下的反应速率常数分别为3.2×10−12、2.4 × 10−13、4.0×10−13$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ . 在典型的对流层 NO3 浓度(${\text{5×10}}^{\text{8}}\; {\text{molecules}}\cdot{\rm{cm}}^{{-3}}$ )下,愈创木酚、甲酚和丁香醇对NO3自由基的大气寿命分别为0.2 h、2.3 h、1.4 h.一些学者还讨论了O3与甲氧基苯酚类有机示踪物之间的非均相氧化. Net等[39]在无光和模拟太阳光照射下对涂有香草醛、丁香醛、针叶醇等的O3非均相氧化进行了研究,实验结果表明,这些甲氧基苯酚类有机示踪物在O3氧化下均会发生一定程度的降解,且香草醛和丁香醛在模拟阳光下的浓度损失比无光下的浓度损失更大. Net等[40]还在O3浓度为1.59×1014
$ {\text{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{\text{-3}} $ 条件下监测了吸附在二氧化硅颗粒上的松柏醛的非均相氧化,并模拟不同光照条件下的反应,在无光条件下速率常数为(7.2 ± 0.9)×10−19$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{\text{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{\text{-1}} $ ,在模拟光照条件下为(7.6 ± 1.7)×10−19$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{\text{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{\text{-1}} $ ,实验结论分析紫外-可见光(λ>300 nm)不会影响O3对松柏醛的降解,但会诱导松柏醛发生缓慢光解. O’Neill等[41]使用漫反射红外光谱法监测吸附在NaCl和α-Al2O3基质上甲氧基苯酚的非均相氧化. 在且O3浓度为1.06×1012$ {\text{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{\text{-3}} $ 环境中,NaCl吸附的甲氧基苯酚对O3的平均吸收系数为(2.3 ± 0.8)×10−7,大气寿命约为1.2 d. α-Al2O3吸附的甲氧基苯酚对O3的平均吸收系数为(9.7 ± 7.3)×10−8,对应于2.8 d的大气寿命.Lauraguais 等[42]在(295 ± 2) K条件下,使用相对动力学方法和原位傅里叶变换红外光谱进行化学分析,首次确定了氯原子与一系列甲氧基苯酚类化合物非均相氧化反应的速率系数,其相对速率常数(以
$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{\text{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{\text{-1}} $ 为单位)分别为: 愈创木酚(2.97 ± 0.66)×10−10、3-甲氧基苯酚(2.99 ± 0.62)×10−10、4-甲氧基苯酚(2.86 ± 0.58)×10−10、2-甲氧基-4-甲基苯酚(3.35 ± 0.68)×10−10、2,3-二甲氧基苯酚(4.73 ± 1.06)×10−10、丁香醇(2.71 ± 0.61)×10−10.以上研究表明甲氧基苯酚类气溶胶的有机示踪物与大气中·OH自由基、NO3自由基、O3等氧化剂都能够发生不同程度的非均相氧化反应,温度、湿度、光照条件等因素都会对反应产生一定影响. 总的来说,温度升高能够促进有机示踪物的降解,而相对湿度的增加对降解有负面作用,在太阳光照条件下比无光条件下的降解作用更为显著. 因此在以后的研究中,应注意需要将环境温度、湿度等具有季节性特征的因素以及白天、夜晚的时间因素影响一并考虑到源解析准确性校正的研究中.
-
油酸、棕榈烯酸和胆甾醇[43-45]常用作餐饮源的有机示踪物,估算肉类等烹饪过程中产生的有机污染物对POA的贡献. 然而目前已有研究表明这些餐饮排放源的一次有机示踪物能够与O3、NO3自由基等氧化剂发生非均相氧化反应.
Docherty等[46]采用在线和离线质谱联用技术,在烟雾箱内研究了油酸气溶胶与NO3自由基的非均相氧化,同时暴露在NO2、N2O5和O2环境中时,其氧化的主要产物为羧酸. Hearn 等[47]采用气溶胶化学电离质谱仪(Aerosol CIMS)和流动管反应器研究了O3与油酸的非均相氧化反应,O3与油酸的反应被确定发生在气溶胶表面,其吸收系数为(8.8 ± 0.5)×10−4,并且研究发现该反应的中间产物还可以与气溶胶中的水、醇和醛等反应,进一步影响其在大气中的寿命. Hearn 等[48]在另一篇文章中同样利用气溶胶化学电离质谱技术,在流动管反应器中研究O3与油酸的反应,测得油酸的反应吸收系数为(7.5 ± 1.2)×10−4. He等[49]采用流动管反应器与微型傅里叶红外光谱仪相结合的方式,研究了O3引发的油酸非均相氧化反应,测得 O3对油酸的摄取系数为(1.45 ± 0.11)×10−3,且研究发现油酸与O3反应的速率常数和摄取系数与相对湿度的变化无明显关系. Morris 等[50]采用新型气溶胶质谱技术研究了亚微米油酸气溶胶与O3的反应动力学,通过建模获得反应的吸收系数为(1.6 ± 0.2)×10−3. Gallimore等[51]使用电喷雾萃取电离质谱监测油酸气溶胶与O3之间非均相反应的动力学,所得到的吸收系数为(5 ± 2)× 10−4. Smith等[52]利用单颗粒质谱技术和流动管反应器,测量油酸气溶胶对O3的吸收系数. 实验结果发现,反应吸收系数取决于颗粒的大小,半径为680 nm至2.45 μm的颗粒,吸收系数范围为(7.3 ± 1.5)×10−3 —(0.99 ± 0.09)×10−3,研究结果分析,随着粒径的增加吸收系数降低是由于反应受到颗粒内油酸扩散的限制. 该研究还进一步估算了不受油酸扩散限制颗粒的吸收系数约为(5.8 — 9.8)×10−3.
一些研究表明大气中复杂环境因素,可能对油酸的非均相氧化具有一定抑制作用. Robinson等[53]测得在大气环境(O3浓度为1.99×1012
$ {\text{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{\text{-3}} $ 左右)中油酸的O3氧化寿命约为1—10 d,而Morris等[50]所测得暴露在2.64×1012$ {\text{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{\text{-3}} $ O3浓度下的纯油酸气溶胶的大气寿命仅为几分钟. Hung等[54]利用衰减全反射红外光谱(ATIR)在O3浓度为2.64×1012$ {\text{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{\text{-3}} $ 条件下,同样测得纯油酸气溶胶的寿命约为2 min,研究指出如此短的纯油酸气溶胶颗粒的寿命与Katrib 等[55]在环境中测量的混合油酸气溶胶的大气寿命为数天到数周的结果不一致,其分析可能是气溶胶的物理相态和组成等其他因素在此过程中发挥着很大作用. Ziemann [56]使用热脱附粒子束质谱仪研究了O3与纯油酸气溶胶和混合油酸气溶胶的反应. 研究发现纯油酸气溶胶的反应速率更快,大气寿命仅为几分钟,而在液相/固相颗粒基质中的反应速率常数可能要慢几个数量级. Kara等[57]在烟雾箱中将胆甾醇、油酸和棕榈烯酸等有机示踪物暴露于O3环境下,在12种不同的混合物中测量了胆甾醇、油酸和棕榈酸的速率常数,其氧化速率常数都强烈依赖于气溶胶成分,有效速率常数随混合物成分的变化较大,相差一个数量级.Weitkamp 等[12]在典型的夏季条件(O3浓度为1.06×1012
$ {\text{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{\text{-3}} $ )下,棕榈烯酸、油酸和胆甾醇所对应的大气化学寿命分别为0.1—0.7 d、0.1—1.0 d和0.4—0.9 d. Dreyfus等[58]在烟雾袋中,研究了胆甾醇(平均直径为100 nm和200 nm)在伪一级条件下与O3反应,测定的反应吸收系数为(2.8 ± 0.4)×10−6,且在研究的粒径范围内,吸收系数与粒径无关. 该研究指出对于排放到大气中的胆甾醇来说,其大气寿命约为几天,故胆甾醇可以作为有机气溶胶的局部来源示踪物,而不适用于确定肉类烹饪操作区域来源的示踪物.以上在O3浓度为1012
$ {\text{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{{-3}} $ 范围内的研究所得餐饮源气溶胶的有机示踪物的大气寿命在几分钟到几天不等,可能是由于反应条件及气溶胶的组成成分导致的较大差异,故在后续的研究中应进一步探究餐饮源排放的有机气溶胶的共存组分以及其对棕榈烯酸、油酸和胆甾醇等有机示踪物非均相氧化的影响. -
燃油汽车等都以化石燃料燃烧作为能源,其燃烧会排放烷烃、多环芳烃等有机物[59]. 藿烷类[60]化合物是化石燃料燃烧的主要有机示踪物;甾烷类化合物[60]主要存在于机油中,故可应用于机油燃烧的一次有机示踪物.
Lambe等[14]在烟雾箱内模拟大气环境条件,研究了柴油机排放的机油和主要有机气溶胶中有机示踪物(C25-C32n-烷烃、霍烷和甾烷)的氧化动力学. 当·OH自由基浓度为
$ {\text{10}}^{\text{6}}\;{\text{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{{-3}} $ 时,机油(不添加柴油)中有机示踪物的反应速率常数范围为(8.4—16)×10−12$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ ,对应的大气氧化寿命约为1 d;在添加了柴油的 POA中有机示踪物反应速率常数范围为(3.6—6.2)×10−11$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ ,其氧化速度比纯机油快2—4倍. Weitkamp等[12]为了研究大气中有机示踪物的化学稳定性,将雾化机油暴露在烟雾箱内的夏季典型·OH自由基水平((4 ± 1) × 106$ {\text{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{{-3}} $ )下,测定了霍烷、甾烷被 ·OH自由基非均相氧化的速率常数分别为:(0.05—3.40)×10−11$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{\text{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{\text{-1}} $ 和(0.04—1.30)×10−11$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ ,大气寿命约为几天. 且该研究发现相对湿度对有效速率常数有显著影响,当相对湿度为75%时,藿烷和甾烷的氧化速度比相对湿度为10%时慢约4倍.上述研究表明曾被认为不易发生降解的霍烷等有机示踪物也能够与·OH自由基等发生反应,鉴于近年来对于机动车排放的广泛关注,须考虑到化石燃料燃烧源气溶胶有机示踪物的氧化效应所产生的潜在偏差,才能够更好地制定控制策略.
以上研究结果表明,大气氧化剂对气溶胶的一次有机示踪物非均相氧化作用显著,如果在源解析中不考虑非均相氧化对这些有机示踪物浓度的影响,源解析过程中各污染源对POA的相对贡献很可能会被低估.
-
相对于一次有机示踪物的非均相氧化研究,二次有机示踪物的非均相氧化报道较少,仍处于起步阶段. 近几年学者获得的一次有机示踪物的非均相氧化研究成果,为系统地考察二次有机示踪物的非均相氧化提供了重要借鉴.
Lai等[13]利用流动管反应器探究了·OH自由基对顺松油酸(天然源α-蒎烯SOA的示踪物)的非均相氧化过程. 在室温、40%RH条件下,顺松油酸与·OH自由基反应的有效速率常数为(5.1—7.24)×10−12
$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ ,所对应的大气寿命约为2.1—3.3 d. 研究发现不同的相对湿度环境不会引起反应速率常数的明显改变,而升高温度能够加速反应的进程.Claeys等[61]在南美洲的热带雨林气溶胶样品中发现了大量含有非对映异构体2-甲基四醇的异戊二烯-C5-骨架. 他们提出,这些化合物可以被视为大气中异戊二烯衍生天然源 SOA 的特定有机示踪物. Chen等[62]研究了2-甲基四醇硫酸盐(由异戊二烯衍生的环氧树脂酸所形成的气溶胶的二次有机示踪物)的非均相氧化反应,在相对湿度为 61%±1%,·OH自由基浓度为
${\text{1.5}\text{×}{10}^{6}\;\text{molecules}\cdot \text{cm}}^{{-3}}$ 时,该反应的有效速率常数为(4.9 ± 0.6)×10−13$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ ,对应 2-甲基四醇硫酸盐的大气寿命约为(16 ± 2)d. Hu 等[63]也采用氧化流反应器(OFR)研究了 2-甲基四醇硫酸盐的·OH自由基非均相氧化过程,其反应速率常数为(4.0 ± 2.0)×10−13$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ ,大气寿命约为14 d. 2-甲基四氢呋喃也被广泛用作异戊二烯衍生的SOA的有机示踪物,虽然通常认为它们相对不活跃,但有研究证明纯赤藓糖醇颗粒(2-甲基四氢呋喃的类似物)可被 ·OH自由基以显著速率非均匀氧化. Xu 等[64]研究了在相对湿度高达85%的流动管反应器中,纯赤藓糖醇气溶胶和含有赤藓糖醇和硫酸铵的气溶胶在不同无机-有机质量比(IOR)下的非均相 ·OH自由基氧化,结果表明,随着赤藓糖醇用量的减少或硫酸铵用量的增加,反应速率降低. 当IOR由0.0增大到5.0时,反应速率常数从(5.39 ± 0.12)×10−13$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{\text{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{\text{-1}} $ 降低至(1.56 ± 0.04)×10−13$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{\text{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{\text{-1}} $ . Kessler等[65]也使用赤藓糖醇作为2-甲基四醇的替代物,考察了·OH自由基对纯赤藓糖醇气溶胶的非均相氧化,RH为30%时,反应速率常数为(2.54 ± 0.22)×10−13$ {\text{cm}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{molecules}}^{\text{-1}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{\text{-1}} $ ,大气寿命约为(13.8 ± 1.4)d.本课题组前期也进行了一些二次有机示踪物非均相氧化反应的研究工作. 黄亚娟[66]利用原位红外法,在O3浓度为(4.23 ± 0.26)×1012
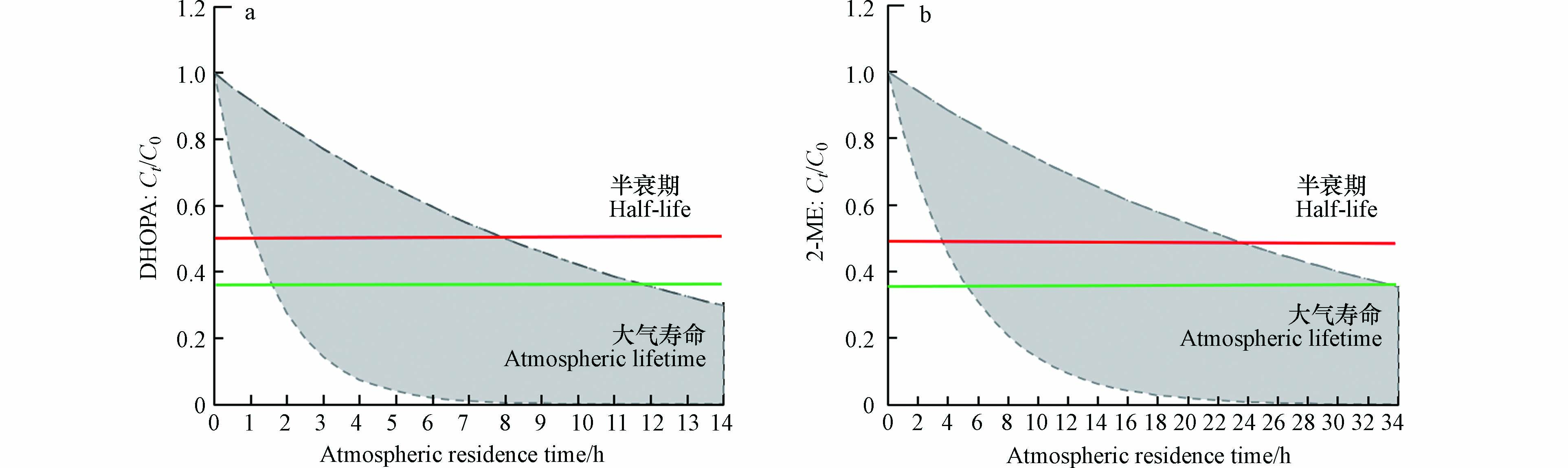
$ {\text{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{{-3}} $ 的大气烟雾箱中,分别模拟了天然源异戊二烯和人为源甲苯两种气体前体物生成的SOA的有机示踪物2-甲基赤藓糖醇(2-ME)和2, 3-二羟基-4-氧代戊酸(DHOPA)的非均相氧化反应,结合深圳市夏季大气条件(日均O3浓度4.49×1012$ {\text{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{{-3}} $ ),两种有机示踪物的大气寿命分别为11.0—56.3 d、8.1—37.3 d. 研究指出如果2-ME和DHOPA的能够在大气环境中存在5 d左右,源解析所得异戊二烯和甲苯气体前体物对SOA的贡献最多可低估高达50%. 该研究还以2-ME的替代物赤藓糖醇(analogue of 2-methyl erythritol,AME)纯气溶胶的非均相氧化作为参照,探究SOA中的共存组分对反应的影响,实验发现异戊二烯SOA中的2-ME氧化速度是AME纯物质气溶胶的1/3,大气平均寿命多出约30 d;甲苯SOA中DHOPA的大气寿命也比纯DHOPA气溶胶长16.2 d左右,故分析SOA中的共存组分可能对非均相氧化过程产生一定的抑制作用. 黄亚娟[67]在大气烟雾箱中以AME和DHOPA纯物质气溶胶为模型物质,探究了影响二次有机示踪物O3非均相氧化过程的因素. 实验结果表明,较高的O3浓度能够正向影响反应的进程;将两种有机示踪物以不同比例混合时,O3对混合组分中占比较高的物质氧化速率更快. 王润华等[68]在大气烟雾箱中,对异戊二烯、甲苯两种气体前体物及其混合物制备的SOA中的有机示踪物进行了非均相氧化实验,采用相对速率法确定了有机示踪物与O3反应的有效速率常数,并探究了种子气溶胶种类和初始VOC0/NOx对示踪物非均相氧化的影响. 实验结果表明,种子气溶胶的存在能够促进SOA中2-ME和DHOPA的非均相氧化,且酸性较强的种子气溶胶更能加快氧化反应;而速率常数随VOC0/NOx比值的增加而降低. 王润华等[69]还采用了原位傅里叶红外光谱法研究了O3对AME和DHOPA纯物质气溶胶的非均相氧化. 在25 ℃,相对湿度为30%条件下,有机示踪物暴露于5.29×1014$ {\text{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{{-3}} $ O3浓度下,其反应吸收系数分别为(1.3 ± 0.8)×10−8和(4.5 ± 2.7)× 10−8 ,虽然能够发生氧化反应,但其氧化过程非常缓慢,所以其推断在以O3为主要氧化剂的大气条件下,AME和DHOPA可以认为是稳定的. 基于假设大气O3浓度为1.99×1012$ {\text{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{{-3}} $ 和实验测得的2-ME和DHOPA示踪物的臭氧非均相氧化有效速率常数的极值,确定了二次有机气溶胶中DHOPA和2-ME示踪物在大气中可能经历的浓度衰减范围,如图1所示. 根据其衰减模拟过程,30 d后,大约55%—95%的DHOPA和40%—90%的2-ME示踪物会被氧化,这使得利用示踪物产率法估算异戊二烯和甲苯对二次源贡献的结果偏低.本课题组还利用两种不同的反应体系,研究了2-ME和DHOPA与·OH的非均相氧化反应. 胡倩[70]利用大气烟雾箱,将异戊二烯SOA的有机示踪物2-ME暴露于接近大气·OH自由基浓度(106—107
$ {\rm{molecules\cdot cm}}^{\rm{-3}} $ )长达4—6 h,用以模拟异戊二烯SOA有机示踪物的·OH非均相氧化反应. 研究结果表明,2-ME与·OH反应速率常数为3.64 ×10−11 — 4.15×10−11$ {\rm{cm}}^{\rm{3}}\cdot{\rm{molecules}}^{\rm{-1}}\cdot{\rm{s}}^{\rm{-1}} $ ,所对应的大气寿命为0.37 — 1.98 h. 王润华[71]利用流动管反应器模拟了甲苯SOA的有机示踪物DHOPA暴露于浓度较高的·OH自由基环境中(1013$ {\rm{molecules}}\cdot {\rm{cm}}^{\rm{-3}} $ )的非均相氧化反应. 实验结果表明,DHOPA 与·OH非均相氧化反应的有效速率常数为2.40×10−18—1.80×10−17$ {\rm{cm}}^{\rm{3}}\cdot{\rm{molecules}}^{\rm{-1}}\cdot{\rm{s}}^{\rm{-1}} $ ,所对应的大气寿命为1.07—1.85 h. DHOPA在高浓度·OH自由基环境中(1013$ {\rm{molecules\cdot cm}}^{\rm{-3}} $ )的衰减模拟过程如图2所示,大约3 h就会有30% — 90%的DHOPA被氧化;2-ME在大气·OH自由基环境中(1.5×106$ {\rm{molecules\cdot cm}}^{\rm{-3}} $ )的衰减模拟过程如图2所示,大约在12 h会有30%—90%的2-ME被氧化. 相比较而言,两种二次有机示踪物的·OH自由基氧化速率常数远大于O3,其大气有效寿命也具有显著性差异,由此可见,相比于O3,·OH自由基对这两种有机示踪物的氧化能力更强. 后续将研究高浓度·OH自由基环境中2-ME和大气·OH自由基环境中DHOPA的衰减过程,以完善两种示踪物在大气中的非均相氧化过程模拟.综上,大气气溶胶的一次和二次有机示踪物都能够与某些大气氧化剂发生不同程度的非均相氧化反应,温度、湿度、氧化剂浓度、共存组分和种子气溶胶种类等因素会对反应速率常数及相对大气寿命产生一定影响. 在非均相氧化反应的作用下,这些有机示踪物对应几分钟到几天的大气寿命,而有机气溶胶在对流层的停留时间为数十天,这说明在以往的研究中进行源解析时所测得的示踪物浓度可能被低估,从而低估有机气溶胶对于污染的相对贡献. 尽管基于有机示踪物方法溯源的准确性受到质疑,但不可否认的是有机示踪物具有很好的源特异性,依然能够在今后的源解析工作发挥重要作用. 因此未来应持续更新这些有机示踪物在大气中的氧化效应,且应用有机示踪物对大气气溶胶进行源解析时,须考虑非均相氧化反应的影响,才能够更为精准地得到源解析结果,从而制定精准有效的污染防控措施.
-
近年来,关于大气中有机气溶胶的来源及其性质的研究已经取得了很多进展,而有机示踪物的非均相氧化反应正逐渐成为一个新的问题焦点. 本文综述了大气中有机示踪物非均相氧化反应的国内外研究现状,并讨论了其在源解析中的不确定性. 为了更加精准地识别特定污染源的相对贡献,科学地制定有效的控制策略,今后更深层次的研究将成为主要发展方向:
(1)现阶段关于二次有机示踪物的大气氧化研究较少,在未来的研究中需要对更多的有机示踪物进行更全面的非均相氧化研究,以建立系统的科学评价体系.
(2)由于实际大气环境的复杂性,有机示踪物非均相氧化的实验室研究是校正源解析估算结果的重要基础性工作,有机示踪物与不同大气氧化剂反应的氧化机理、氧化反应的相关影响因素等工作都有待进一步研究和讨论.
(3)基于流动管反应器、大气烟雾箱等实验室模拟研究与实际大气环境仍存在一定差距,未来有机示踪物非均相氧化的外场观测实验将成为一项具有挑战性的工作.
(4)如果未来能够确定某时刻气溶胶已在大气中所经历的停留时间,结合有机示踪物的衰减曲线,即能较好地对源解析的偏差进行校正,这将成为今后该领域的一个重要研究方向.
大气气溶胶有机示踪物的非均相氧化研究进展
Research progress on heterogeneous oxidation of organic tracers of atmospheric aerosols
-
摘要: 为确定大气中有机气溶胶的来源与贡献,制定有效的污染防控措施,有机示踪物广泛应用于识别和评价某一特定污染源对空气质量的危害效应. 然而有研究表明大气气溶胶的有机示踪物与大气氧化剂(·OH、O3、NO3 等)发生的非均相氧化反应将导致其在源解析时产生不确定性. 本文综述了现阶段关于大气气溶胶有机示踪物的非均相氧化研究进展,主要包括用于解析生物质燃烧、餐饮排放等来源气溶胶的一次有机示踪物和用于解析天然源或人为源气体前体物生成的气溶胶的二次有机示踪物. 国内外学者在不同地点采用不同方法的研究均表明一直以来广泛应用于大气气溶胶源解析的有机示踪物存在不稳定性,其大气寿命也因示踪物种类和大气环境的不同而有所差异. 旨在为未来修正示踪物解析准确性和相关污染防控措施的改进提供一定的参考价值.Abstract: In order to determine the source and contribution of organic aerosols in the atmosphere and take effective pollution prevention and control measures, organic tracers are widely used to identify and evaluate harmful effects of a specific pollution source on air quality. However, studies have found that the heterogeneous oxidation reactions of organic tracers of atmospheric aerosols with atmospheric oxidants (·OH, O3, NO3, etc.) could lead to uncertainties in the source apportionment. This paper reviews the current research progress on the heterogeneous oxidation of organic tracers of atmospheric aerosols, mainly including primary organic tracers used to analyze aerosols from biomass combustion and cooking emissions etc., as well as secondary organic tracers for the analysis of natural or anthropogenic aerosols from gas phase precursors. The studies by domestic and foreign scholars using different methods in different locations have shown that the organic tracers that have been widely used in the source analysis of atmospheric organic aerosols were unstable, and their atmospheric lifetimes also changed with the types of organic tracers and the atmospheric environment. This paper aims to provide valuable references for accuracy correction of the tracer-based analysis in future studies and improvement of related pollution prevention and control measures.
-

-
表 1 不同来源的有机气溶胶成分及其主要有机示踪物
Table 1. Organic aerosols components from different sources and their main organic tracers
一次有机
气溶胶(POA)有机气溶胶来源
Organic aerosols source主要有机物
Main organic matter气溶胶的一次有机示踪物
Primary organic tracers of aerosols生物质燃烧 脂肪酸、单糖、酚类、多环芳烃等 左旋葡聚糖、甘露聚糖、半乳聚糖、β-谷甾醇、
萜类化合物、脱氢松香酸等餐饮排放 脂肪酸、多环芳烃、二元羧酸等 胆甾醇、油酸、棕榈烯酸等 化石燃料燃烧 烷烃、多环芳烃、脂肪酸、酚类等 17α(H)、21β(H) 藿烷类化合物、甾烷类化合物 二次有机
气溶胶(SOA)气体前体物来源
Source of gas precursors主要气体前体物
Main gas precursors气溶胶的二次有机示踪物
Secondary organic tracers of aerosols天然源(植物等排放) 异戊二烯 2-甲基四丁醇、2-甲基甘油酸、2-甲基赤藓糖醇
(2-ME)及其类似物赤藓糖醇(AME)人为源(机动车尾气、工业排放等) 苯、甲苯、烯烃等 2, 3-二羟基-4,氧代戊酸(DHOPA) -
[1] SAXENA P, HILDEMANN L M. Water-soluble organics in atmospheric particles: A critical review of the literature and application of thermodynamics to identify candidate compounds [J]. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 1996, 24(1): 57-109. doi: 10.1007/BF00053823 [2] PUTAUD J P, RAES F, van DINGENEN R, et al. A European aerosol phenomenology—2: Chemical characteristics of particulate matter at kerbside, urban, rural and background sites in Europe [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2004, 38(16): 2579-2595. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.01.041 [3] 谢绍东, 于淼, 姜明. 有机气溶胶的来源与形成研究现状 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2006, 26(12): 1933-1939. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2006.12.001 XIE S D, YU M, JIANG M. Research progress in source and formation of organic aerosol [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2006, 26(12): 1933-1939(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2006.12.001
[4] FU P Q, KAWAMURA K, CHEN J, et al. Secondary production of organic aerosols from biogenic VOCs over Mt. Fuji, Japan [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(15): 8491-8497. [5] 何凌燕, 胡敏, 黄晓锋, 张远航. 北京大气气溶胶PM2.5中的有机示踪化合物 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2005, 25(1): 23-29. HE L Y, HU M, HUANG X F, et al. Determination of organic molecular tracers in PM2.5 in the atmosphere of Beijing [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2005, 25(1): 23-29(in Chinese).
[6] SIMONEIT B R T. Organic matter of the troposphere—III. Characterization and sources of petroleum and pyrogenic residues in aerosols over the western United States [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 1984, 18(1): 51-67. doi: 10.1016/0004-6981(84)90228-2 [7] FRASER M P, LAKSHMANAN K. Using levoglucosan as a molecular marker for the long-range transport of biomass combustion aerosols [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2000, 34(21): 4560-4564. [8] SIMONEIT B R T, ELIAS V O, KOBAYASHI M, et al. Sugars: Dominant water-soluble organic compounds in soils and characterization as tracers in atmospheric particulate matter [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(22): 5939-5949. [9] RUTTER A P, SNYDER D C, STONE E A, et al. Preliminary assessment of the anthropogenic and biogenic contributions to secondary organic aerosols at two industrial cities in the upper Midwest [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 84: 307-313. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.11.014 [10] STONE E A, ZHOU J B, SNYDER D C, et al. A comparison of summertime secondary organic aerosol source contributions at contrasting urban locations [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(10): 3448-3454. [11] FENG J L, LI M, ZHANG P, et al. Investigation of the sources and seasonal variations of secondary organic aerosols in PM2.5 in Shanghai with organic tracers [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 79: 614-622. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.07.022 [12] WEITKAMP E A, LAMBE A T, DONAHUE N M, et al. Laboratory measurements of the heterogeneous oxidation of condensed-phase organic molecular makers for motor vehicle exhaust [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(21): 7950-7956. [13] LAI C Y, LIU Y C, MA J Z, et al. Heterogeneous kinetics of cis-pinonic acid with hydroxyl radical under different environmental conditions [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2015, 119(25): 6583-6593. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.5b01321 [14] LAMBE A T, MIRACOLO M A, HENNIGAN C J, et al. Effective rate constants and uptake coefficients for the reactions of organic molecular markers (n-alkanes, hopanes, and steranes) in motor oil and diesel primary organic aerosols with hydroxyl radicals [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(23): 8794-8800. [15] SANG X, GENSCH I, KAMMER B, et al. Chemical stability of levoglucosan: An isotopic perspective [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(10): 5419-5424. doi: 10.1002/2016GL069179 [16] SIMONEIT B R T. Biomass burning—a review of organic tracers for smoke from incomplete combustion [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2002, 17(3): 129-162. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00061-0 [17] 王鑫彤, 鞠法帅, 韩德文, 等. 大气颗粒物中生物质燃烧示踪化合物的研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(10): 1885-1894. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.10.2015040704 WANG X T, JU F S, HAN D W, et al. Research progress on the organic tracers of biomass burning in atmospheric aerosols [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(10): 1885-1894(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.10.2015040704
[18] SANG X F, GENSCH I, LAUMER W, et al. Stable carbon isotope ratio analysis of anhydrosugars in biomass burning aerosol particles from source samples [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(6): 3312-3318. [19] HENNIGAN C J, SULLIVAN A P, COLLETT J L J, et al. Levoglucosan stability in biomass burning particles exposed to hydroxyl radicals [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010, 37(9): L09806. [20] SLADE J H, KNOPF D A. Heterogeneous OH oxidation of biomass burning organic aerosol surrogate compounds: Assessment of volatilisation products and the role of OH concentration on the reactive uptake kinetics [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(16): 5898-5915. doi: 10.1039/c3cp44695f [21] HOFFMANN D, TILGNER A, IINUMA Y, et al. Atmospheric stability of levoglucosan: A detailed laboratory and modeling study [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(2): 694-699. [22] 柏静. 典型生物质燃烧标识物及生物质排放的VOCs在大气中的降解机理及动力学研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2013. BAI J. Degradation mechanism and kinetics study of typical biomass combustion molecular marker and biomass emissions of VOCs in the atmosphere[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2013(in Chinese).
[23] LAI C Y, LIU Y C, MA J Z, et al. Degradation kinetics of levoglucosan initiated by hydroxyl radical under different environmental conditions [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 91: 32-39. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.03.054 [24] 王宁. 大气中典型VOCs降解过程均相反应机理和异相成核机理的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2017. WANG N. The mechanism of homogeneous reaction and heterogeneous nucleation in VOCs degradation process in the atmosphere[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2017(in Chinese).
[25] LI Y M, FU T M, YU J Z, et al. Impacts of chemical degradation on the global budget of atmospheric levoglucosan and its use As a biomass burning tracer [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(8): 5525-5536. [26] SIMONEIT B R T, ROGGE W F, MAZUREK M A, et al. Lignin pyrolysis products, lignans, and resin acids as specific tracers of plant classes in emissions from biomass combustion [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1993, 27(12): 2533-2541. [27] STANDLEY L J, SIMONEIT B R T. Resin diterpenoids as tracers for biomass combustion aerosols [J]. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 1994, 18(1): 1-15. doi: 10.1007/BF00694371 [28] SCHMIDL C, MARR I L, CASEIRO A, et al. Chemical characterisation of fine particle emissions from wood stove combustion of common woods growing in mid-European Alpine regions [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42(1): 126-141. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.09.028 [29] KNOPF D A, FORRESTER S M, SLADE J H. Heterogeneous oxidation kinetics of organic biomass burning aerosol surrogates by O3, NO2, N2O5, and NO3 [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2011, 13(47): 21050-21062. doi: 10.1039/c1cp22478f [30] BAI J, SUN X M, ZHANG C X, et al. The atmospheric degradation reaction of dehydroabietic acid (DHAA) initiated by OH radicals and O3 [J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 92(8): 933-940. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.03.004 [31] LAI C Y, LIU Y C, MA J Z, et al. Laboratory study on OH-initiated degradation kinetics of dehydroabietic acid [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015, 17(16): 10953-10962. doi: 10.1039/C5CP00268K [32] LIU C G, ZENG C H. Heterogeneous kinetics of methoxyphenols in the OH-initiated reactions under different experimental conditions [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 209: 560-567. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.131 [33] LAURAGUAIS A, COEUR-TOURNEUR C, CASSEZ A, et al. Rate constant and secondary organic aerosol yields for the gas-phase reaction of hydroxyl radicals with syringol (2, 6-dimethoxyphenol) [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2012, 55: 43-48. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.02.027 [34] LIU C G, HE Y C, CHEN X E. Kinetic study on the heterogeneous degradation of coniferyl alcohol by OH radicals [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 241: 125088. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125088 [35] COEUR-TOURNEUR C, CASSEZ A, WENGER J C. Rate coefficients for the gas-phase reaction of hydroxyl radicals with 2-methoxyphenol (guaiacol) and related compounds [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2010, 114(43): 11645-11650. doi: 10.1021/jp1071023 [36] ZHANG H X, YANG B, WANG Y F, et al. Gas-phase reactions of methoxyphenols with NO3 radicals: Kinetics, products, and mechanisms [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, 2016, 120(8): 1213-1221. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.5b10406 [37] LAURAGUAIS A, EL ZEIN A, COEUR C, et al. Kinetic study of the gas-phase reactions of nitrate radicals with methoxyphenol compounds: Experimental and theoretical approaches [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2016, 120(17): 2691-2699. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.6b02729 [38] YANG B, ZHANG H X, WANG Y F, et al. Experimental and theoretical studies on gas-phase reactions of NO3 radicals with three methoxyphenols: Guaiacol, creosol, and syringol [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 125: 243-251. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.11.028 [39] NET S, ALVAREZ E G, GLIGOROVSKI S, et al. Heterogeneous reactions of ozone with methoxyphenols, in presence and absence of light [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2011, 45(18): 3007-3014. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.03.026 [40] NET S, GOMEZ ALVAREZ E, BALZER N, et al. Photolysis and heterogeneous reaction of coniferyl aldehyde adsorbed on silica particles with ozone [J]. Chemphyschem, 2010, 11(18): 4019-4027. doi: 10.1002/cphc.201000446 [41] O'NEILL E M, KAWAM A Z, van RY D A, et al. Ozonolysis of surface-adsorbed methoxyphenols: Kinetics of aromatic ring cleavage vs. alkene side-chain oxidation [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2014, 14(1): 47-60. doi: 10.5194/acp-14-47-2014 [42] LAURAGUAIS A, BEJAN I, BARNES I, et al. Rate coefficients for the gas-phase reaction of chlorine atoms with a series of methoxylated aromatic compounds [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2014, 118(10): 1777-1784. doi: 10.1021/jp4114877 [43] SCHAUER J J, ROGGE W F, HILDEMANN L M, et al. Source apportionment of airborne particulate matter using organic compounds as tracers [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 1996, 30(22): 3837-3855. doi: 10.1016/1352-2310(96)00085-4 [44] SCHAUER J J, CASS G R. Source apportionment of wintertime gas-phase and particle-phase air pollutants using organic compounds as tracers [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2000, 34(9): 1821-1832. [45] ROGGE W F, HILDEMANN L M, MAZUREK M A, et al. Sources of fine organic aerosol. 1. Charbroilers and meat cooking operations [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1991, 25(6): 1112-1125. [46] DOCHERTY K S, ZIEMANN P J. Reaction of oleic acid particles with NO3 radicals: Products, mechanism, and implications for radical-initiated organic aerosol oxidation [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, 2006, 110(10): 3567-3577. doi: 10.1021/jp0582383 [47] HEARN J D, LOVETT A J, SMITH G D. Ozonolysis of oleic acid particles: Evidence for a surface reaction and secondary reactions involving Criegee intermediates [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2005, 7(3): 501-511. doi: 10.1039/b414472d [48] HEARN J D, SMITH G D. Kinetics and product studies for ozonolysis reactions of organic particles using aerosol CIMS [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2004, 108(45): 10019-10029. doi: 10.1021/jp0404145 [49] HE X, LENG C B, PANG S F, et al. Kinetics study of heterogeneous reactions of ozone with unsaturated fatty acid single droplets using micro-FTIR spectroscopy [J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(6): 3204-3213. doi: 10.1039/C6RA25255A [50] MORRIS J W, DAVIDOVITS P, JAYNE J T, et al. Kinetics of submicron oleic acid aerosols with ozone: A novel aerosol mass spectrometric technique [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2002, 29(9): 71-1. [51] GALLIMORE P J, GRIFFITHS P T, POPE F D, et al. Comprehensive modeling study of ozonolysis of oleic acid aerosol based on real-time, online measurements of aerosol composition [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2017, 122(8): 4364-4377. doi: 10.1002/2016JD026221 [52] SMITH G D, WOODS E, DEFOREST C L, et al. Reactive uptake of ozone by oleic acid aerosol particles: Application of single-particle mass spectrometry to heterogeneous reaction kinetics [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2002, 106(35): 8085-8095. doi: 10.1021/jp020527t [53] ROBINSON A L, DONAHUE N M, ROGGE W F. Photochemical oxidation and changes in molecular composition of organic aerosol in the regional context [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2006, 111(D3): D03302. [54] HUNG H M, ARIYA P. Oxidation of oleic acid and oleic acid/sodium chloride(aq) mixture droplets with ozone: Changes of hygroscopicity and role of secondary reactions [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, 2007, 111(4): 620-632. doi: 10.1021/jp0654563 [55] KATRIB Y, BISKOS G, BUSECK P R, et al. Ozonolysis of mixed oleic-acid/stearic-acid particles: Reaction kinetics and chemical morphology [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, 2005, 109(48): 10910-10919. doi: 10.1021/jp054714d [56] ZIEMANN P J. Aerosol products, mechanisms, and kinetics of heterogeneous reactions of ozone with oleic acid in pure and mixed particles [J]. Faraday Discussions, 2005, 130(0): 469-490. [57] HUFF HARTZ K E, WEITKAMP E A, SAGE A M, et al. Laboratory measurements of the oxidation kinetics of organic aerosol mixtures using a relative rate constants approach [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2007, 112(D4): D04204. [58] DREYFUS M A, TOLOCKA M P, DODDS S M, et al. Cholesterol ozonolysis: Kinetics, mechanism, and oligomer products [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, 2005, 109(28): 6242-6248. doi: 10.1021/jp050606f [59] 赵红帅, 常淼, 赵起越, 等. 有机气溶胶中甾醇类化合物的研究进展 [J]. 分析试验室, 2016, 35(1): 121-124. doi: 10.13595/j.cnki.issn1000-0720.2016.0028 ZHAO H S, CHANG M, ZHAO Q Y, et al. Research progress of sterols compounds in organic aerosol [J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2016, 35(1): 121-124(in Chinese). doi: 10.13595/j.cnki.issn1000-0720.2016.0028
[60] 袁杨森, 刘大锰, 车瑞俊, 等. 北京夏季大气颗粒物中有机污染源的生物标志物示踪 [J]. 中国科学院研究生院学报, 2007, 24(5): 601-611. YUAN Y S, LIU D M, CHE R J, et al. Source tracing of biomarkers in the organic pollutants from atmospheric particulates in Beijing City during summer [J]. Journal of the Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2007, 24(5): 601-611(in Chinese).
[61] CLAEYS M, GRAHAM B, VAS G, et al. Formation of secondary organic aerosols through photooxidation of isoprene [J]. Science, 2004, 303(5661): 1173-1176. doi: 10.1126/science.1092805 [62] CHEN Y Z, ZHANG Y, LAMBE A T, et al. Heterogeneous hydroxyl radical oxidation of isoprene epoxydiol-derived methyltetrol sulfates: Plausible formation mechanisms of previously unexplained organosulfates in ambient fine aerosols [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2020, 7(7): 460-468. [63] HU W W, PALM B, DAY D, et al. Volatility and lifetime against OH heterogeneous reaction of ambient isoprene-epoxydiols-derived secondary organic aerosol (IEPOX-SOA) [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2016, 16(18): 11563-11580. doi: 10.5194/acp-16-11563-2016 [64] XU R S, LAM H K, WILSON K R, et al. Effect of inorganic-to-organic mass ratio on the heterogeneous OH reaction rates of erythritol: Implications for atmospheric chemical stability of 2-methyltetrols [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 20(6): 3879-3893. doi: 10.5194/acp-20-3879-2020 [65] KESSLER S H, SMITH J D, CHE D L, et al. Chemical sinks of organic aerosol: Kinetics and products of the heterogeneous oxidation of erythritol and levoglucosan [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(18): 7005-7010. [66] 黄亚娟. PM2.5中二次有机示踪物的臭氧非均相氧化研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018. HUANG Y J. Heterogeneous oxidation of secondary organic tracers in PM2.5 by ozone[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018(in Chinese).
[67] 黄亚娟, 曹罡, 朱荣淑, 等. 异戊二烯和甲苯二次有机示踪物的臭氧非均相氧化 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(3): 1163-1171. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201803064 HUANG Y J, CAO G, ZHU R S, et al. Heterogeneous oxidation of secondary organic tracers of isoprene and toluene by ozone [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(3): 1163-1171(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201803064
[68] WANG R H, HUANG Y J, CAO G. Heterogeneous oxidation of isoprene SOA and toluene SOA tracers by ozone [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 249: 126258. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126258 [69] WANG R, HUANG Y, HU Q, et al. In-situ FTIR study of heterogeneous oxidation of SOA tracers by ozone [J]. Frontiers in Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 2: 732219. doi: 10.3389/fenvc.2021.732219 [70] 胡倩. 异戊二烯SOA示踪物的非均相氧化研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021. HU Q. Heterogeneous oxidation of isoprene SOA tracers[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021(in Chinese).
[71] 王润华. 甲苯SOA示踪物的羟基自由基非均相氧化研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021. WANG R H. Heterogeneous oxidation of toluene SOA tracers by hydroxyl radical[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021(in Chinese).
-




 下载:
下载: