-
土壤重金属具有不能降解、自净能力差、隐蔽性强和毒性大等特点,给人类生存和生态安全带来极大风险,从而备受社会关注[1]. 根据国家(原)环保部门的调查和统计显示[2],我国每年有1.2×107 t粮食受到重金属污染,土壤环境质量总体不容乐观. 土壤作为农业生产的主要载体和生态环境的重要组成部分,探明其重金属污染特征、污染来源和基于源成分谱的生态风险状况是当下土壤重金属污染防治工作的迫切需求[3].
近年来,土壤重金属含量特征、来源情况和生态风险状况受到国内外学者广泛关注. Keshavarzi等[4]对北爱尔兰工业、农业和城市地区土壤中重金属的含量特征、污染累积和生态风险水平进行分析,结果表明Mn含量最高,Cd含量最低,As、Cd和Pb有很高的生态风险;Wang等[5]对中国西南部喀斯特地区土壤中重金属的含量和来源进行分析,结果表明土壤中的重金属污染主要与自然来源有关,而人类活动的影响也不容忽视. 然而当前研究一方面较多集中于表层土壤,但表层土壤厚度相对固定,可能涵盖了多年的混合重金属积累信息. 因此,仅对表层的研究不足以解释重金属在不同土壤层中的积累及其垂直污染特征[6],也很难解释在不同管理措施(如耕作、施肥)、淋溶、母质和积累影响下的垂直分布特征[7-8];另一方面,现有研究大多集中在典型地区非农业因素影响下的农田土壤污染,如化工厂、采矿和冶炼区[9-10],但我国大部分地区目前的农业活动相对独立,主要受农业因素本身影响[11];施肥、管理、耕作、灌溉等其他农业活动已被证实在一定程度上影响了不同土壤层中重金属的富集和转化能力[7-8]. 因此,对农业活动本身造成的重金属污染的探索是不可忽视的,尤其是在农田土壤剖面研究中,重金属的垂直分布和污染特征具有重要的现实意义,可以提供有关污染历史的重要信息.
四川省富顺县地处四川盆地南部,沱江下游,农业生产以粮食作物为主,农业劳动力以中老年为主,“单打独斗”的现象较为明显,是典型的传统小农经济[12]. 近年来为满足现代化发展的需求,开始建设以水稻、高粱、玉米为主的优质粮油高产示范区,重点发展优质“中稻+再生稻”、优质“高粱+再生高粱”等特色优势产业[13]. 该区域属于大面积的峨眉山玄武岩和碳酸盐岩分布区,是典型的金属元素地球化学高背景区[14],土壤中金属元素富集程度较高,易在生物体内富集影响人类健康和区域生态系统平衡[15],但目前针对该区域土壤重金属污染状况的专门研究尚未见报道.
本文以四川省富顺县典型丘陵区农田剖面土壤(0—70 cm)为研究对象,将正定矩阵因子分解模型(PMF)与污染累积和生态风险评价指数相结合,对区域内农田土壤重金属(Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn)的垂直分布特征、污染现状和主要污染源及其污染贡献量进行探究,以期加强对川南丘陵典型农作区对土壤剖面重金属污染特征影响的认识,并为土壤重金属污染治理提供科学依据.
-
研究区域位于四川省自贡市富顺县某典型农作区内(105°07′ N, 29°11′ E),属亚热带季风湿润气候,地貌以中丘为主,土壤类型主要为水稻土和紫色土,土地利用类型以水田和旱地为主,种植制度主要为中稻—冬水稻、玉米/高粱—油菜/小麦轮作,玉米/高粱—红苕套作、菜—菜轮作制度. 区域内耕地集中连片分布,周围没有大型居民区、工矿区,道路主要为机耕道.
-
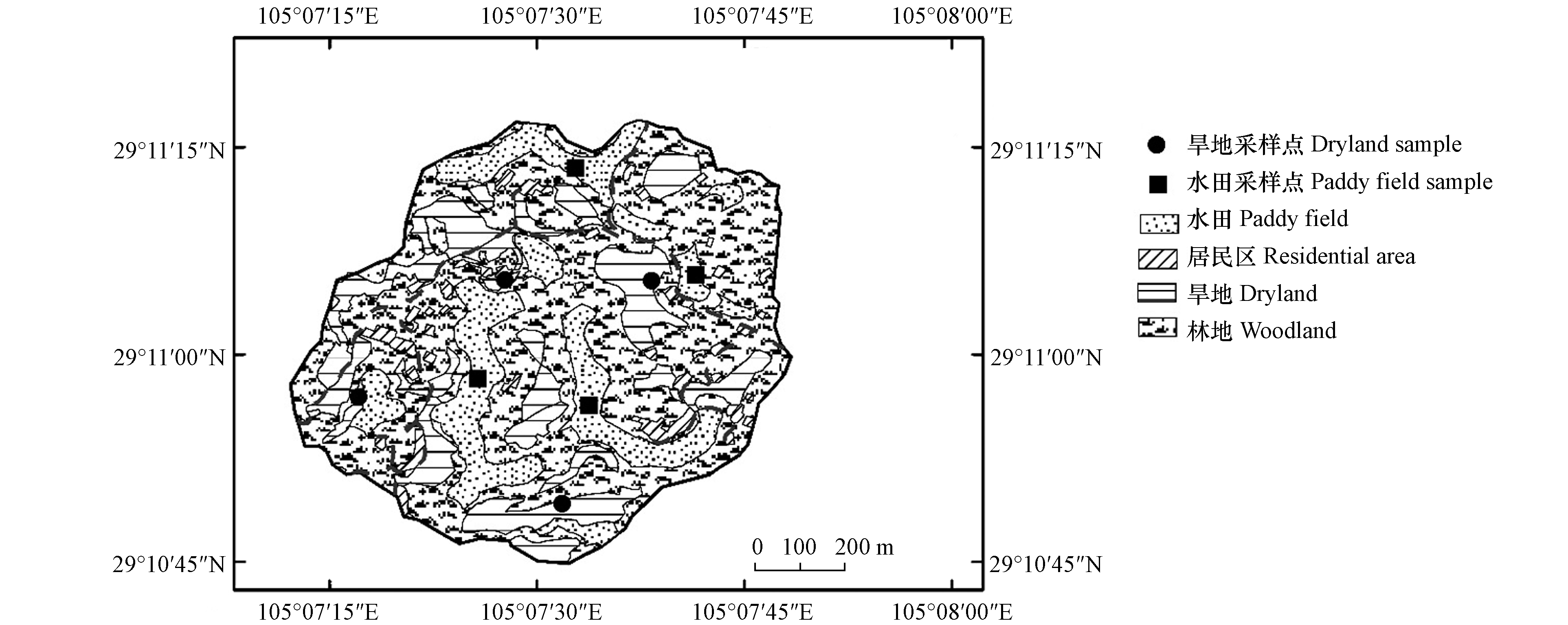
根据研究区农业用地类型分布和地形条件,采用随机网格法进行布点,于2020年5月采集水田、旱地各4个剖面土壤(图1). 采样深度70 cm,每10 cm为1个土层,每层样品采集量约为1 kg,置于干净塑料袋中、注明标号,运回实验室,置于室内自然晾干. 剔除杂物、捣碎,过20目尼龙筛,再取0.5 kg进一步研磨,过100目尼龙筛,分别装入聚乙烯塑料袋中密封,置于干燥处保存备用. 采用 HNO3—HF—HClO4对制备的土样进行消煮后,再采用火焰原子吸收分光光度法测定Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn全量,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP—MS,7900,Agilent Technologies,USA)测定Cd 全量. 在检测过程中所用的所有试剂均为优级纯,每批样品进行2次平行试验,采用国家标准土壤参比物质(GSS—3)进行质量控制,各元素的回收率均在95 %±5 %. 土壤样品的pH值用电位法测定(水土比为2.5∶1).
-
正定矩阵因子分解模型(positive matrix factorization model, PMF)最早由PAATERO和TAPPER于1994年提出[16],是美国环境保护局[17]推荐的一种源解析工具,可以定量识别重金属污染源的受体模型,该模型利用数据分析,使源成分谱与源贡献率的物理意义更加真实可靠[18-19]. 其基本公式如下:
式中,
Xij 表示第j 个元素在第i 个样品中的浓度,是样品的含量矩阵;Gik 表示第i 个样品中源k 的贡献,是源贡献矩阵;Fkj 表示第j 个元素在源k 中的浓度,是源成分谱矩阵;Eij 表示为残差矩阵,即浓度矩阵Eij 在PMF模型中不能解释样品的部分.在PMF模型中,矩阵
X 的分解基于受限定加权最小二乘法进行迭代计算,该模型最主要目标是最优化目标函数Q ,使其达到最小化,目标函数Q 的计算公式为式中:
Uij 表示第j 个元素在第i 个样品中的不确定度.当
C≤MDL 时:当
C>MDL 时:式中,
Uij 为不确定度,Urel 为相对不确定度,取10%;C 为实测元素浓度;MDL 为方法检出限.由于区域内水田和旱地相邻且位于同一地理位置,因而认为两种土地利用类型下土壤受到污染源的相同,但影响程度不同. 基于此,本文将水田和旱地的数据视为一个数据集,然后使用所有数据运行PMF模型. 为了了解水田、旱地的特定源贡献概况,使用以下程序计算每种土地利用方式中每个源(即因子)的贡献.
首先,源于
k 的样品i 中重金属元素j 的浓度(Cjik )通过以下方程式计算:式中:
Cti 为样品i 中元素的总浓度;Ski 为源k 对样品 i 中所有元素浓度的贡献;Mkj 为源k 对元素j 的总贡献.然后,来自于源
k 的所有水田样品中所有元素的总浓度(Ckt ) 通过以下方程式计算:式中:
m 为元素的数量,本研究中为6;n 为样品数量,水田为28.然后,水田中所有确定来源的所有元素的总浓度
(Ct) 通过以下方程式计算:式中:
n 为已识别源的数量.各来源(F)的贡献计算如下:
旱地中各种来源的贡献采用同样方式进行计算.
-
Müller提出的地累积指数法(Geoaccumulation Index,
Igeo )将土壤样品中的金属浓度与其背景浓度进行比较,最初用于沉积物污染评估[20]. 自20世纪60年代末以来,该指数已被广泛应用于评估土壤污染中重金属的污染水平,与其他污染评估方法的差异在于地累积指数法考虑了自然成岩作用引起背景值变动的因素. 本文将结合PMF模型得到的源成分谱进行地累积指数法分析:式中:
Cjik 来自公式 (5),用于代替重金属元素的含量计算基于源成分谱的地累积指数;K 为成岩作用可能对背景值的影响,取1.5;Bi 为重金属i 在土壤中的背景值 (mg·kg−1),本文以四川省土壤背景值为参考值[21].Igeo 的分级标准为:Igeo <0,清洁;0≤Igeo <1.0,轻度污染积累;1.0≤Igeo <2.0,中度污染积累;2.0≤Igeo <3.0,中强污染积累;3.0≤Igeo <4.0,强污染积累;4.0≤Igeo <5.0,高强污染积累;Igeo ≤5.0,极强污染积累. -
内梅罗综合风险指数(Nemerow Integrated Risk Index, NIRI)可以对区域内土壤重金属生态风险水平进行评价,该指数综合了潜在生态危害指数(Potential Ecological Risk Index, PERI)[22]和内梅罗综合污染指数(Nemerow Integrated Pollution Index, NIPI)的优点,考虑了环境污染物对生物群的毒性及每种重金属的毒性反应因子,可以更准确的评估多种元素对环境的影响[23]. 本文将其结合PMF模型得到的源成分谱以便对生态风险的来源进行进一步分析.
式中:
Eir 为单一金属潜在生态风险因子;Cjik 来自公式 (5),用于代替重金属元素的含量计算基于源成分谱的内梅罗综合风险指数;Cir 为土壤背景参考值,本文以四川省土壤背景值为参考值[21].Tir 为不同金属生物毒性响应因子,其中 T(Hg) = 40,T(Cd) = 30,T(As) = 10,T(Pb) =T(Cu) =5,T( Ni) =T(Cr) =2,T(Zn) =1.NIRI 为内梅罗指数,(Eir)max 是土壤中重金属单项污染指数的最大值;(Eir)ave 是土壤重金属单项污染指数的平均值.Eir 的分级标准为:Eir ≤40,轻微生态风险;40<Eir ≤80,中等生态风险;80<Eir ≤160,强生态风险;160<Eir ≤320,很强生态风险;Eir >320,极强生态风险.NIRI 的分级标准为:NIRI ≤40,轻微生态风险;40<NIRI ≤80,中等生态风险;80<NIRI ≤160,强生态风险;160<NIRI ≤320,很强生态风险;NIRI >320,极强生态风险. -
土壤重金属和不同土地利用类型、不同深度的相关指标使用 SPSS 24.0 进行比较分析;数据处理汇总和图表制作利用 Microsoft Excel 2016,Origin 2021实现,来源分析基于EPA PMF5.0软件实现.
-
研究区内农田剖面土壤中的重金属含量结果表明(图2),Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb和Zn在水田土壤剖面中的含量分别为0.19—0.62、47.94—51.15、19.90—21.02、25.61—29.67、18.75—22.15、59.24—71.13 mg·kg−1,旱地土壤剖面中的含量分别为0.15—0.62、47.53—58.39、18.91—22.04、25.26—32.13、17.45—21.75、59.78—77.58 mg·kg−1. 研究区属大面积的峨眉山玄武岩和碳酸盐岩分布区,是典型的金属元素地球化学高背景区[14],相较于同样地球化学元素高背景的火山岩风化农田区,本区域土壤中的Cu、Ni和Zn含量明显低于其土壤中相应重金属含量(其平均值分别为33.97、39.84、91.72 mg·kg−1),Pb含量与之较为接近,但本区域土壤中Cd含量远高于火山岩风化区土壤中其含量(0.09 mg·kg−1)[24]. 相较于受人为活动影响剧烈的长江经济带农田区,本区域Cr、Cu、Pb和Zn含量明显低于长江经济带农田土壤中其含量(其平均值分别为73.58、37.09、40.90、99.12 mg·kg−1),Ni含量与之较为接近,但本区域土壤中Cd含量仍明显高于长江经济带农田土壤中其含量(0.45 mg·kg−1)[25]. 相较于非地球化学元素高背景区和同样较少受人为活动影响的崇明岛和松嫩平原农田土壤,本研究区土壤中的Cd、Cr、Cu和Pb的4种重金属含量明显高于崇明岛农田土壤中其含量(其平均值分别为0.18、40.1、27.8、17.8 mg·kg−1)[26],6种重金属除Ni外均明显高于松嫩平原区农田土壤其重金属含量(Cd、Cr、Cu、Pb和Zn平均含量分别为0.11、11.7、8.89、16.9、42.4 mg·kg−1)[27].
水田和旱地两种土地利用方式下Cd和Pb的垂直分布都表现出明显的表聚性,最大含量都在0—10 cm土层,Cd均为0.62 mg·kg−1,Pb分别为21.75—22.15 mg·kg−1,且Cd在水田和旱地中均超过了背景值,表明研究区域土壤Cd和Pb垂直分布受到一定程度的外来源干扰,且已有研究表明表层土壤中的Cd、Pb受人为活动影响较明显[28]. 旱地中的Cu和Zn都随土层加深呈先降低后升高的趋势,最大含量都在60—70 cm土层,分别为22.04 mg·kg−1和77.58 mg·kg−1,最小含量在20—50 cm土层,分别为19.25 mg·kg−1和 62.11 mg·kg−1,说明旱地的人为管理措施导致了Cu、Zn在表层土壤的积累,而底层土壤其含量偏高更多的是受母质影响[29];但水田土壤剖面中Cu(19.90—21.02 mg·kg−1)的垂直变化不明晰,这可能是因为Cu相较于其它元素是水溶性较高的金属元素,会随水田中的淋溶作用往深层土壤迁移[30-32],从而导致其纵向分布没有明显表聚性,呈现表剖较为均匀的状态;水田中的Zn虽然有明显表聚趋势,最大含量在0—10 cm土层(71.13 mg·kg−1),最小含量在60—70 cm土层(62.41 mg·kg−1),但相较于旱地,其表层含量较低、中间层较高,也表现了一定程度的向下迁移趋势. 在0—50 cm的土层,Cr(47.94—54.41 mg·kg−1)和Ni(25.61—28.42 mg·kg−1)含量的垂直分布波动不大,但在>50 cm的土层,其含量随土层加深有明显增大的趋势,说明因研究区域土地利用方式单一,农业措施也不易带来Cr、Ni元素[23-34],没有相关的污染历史,主要受母质影响. 根据6种重金属元素的剖面分布特征,将土层划分为表土层(0—20 cm)、心土层(20—50 cm)和底土层(>50 cm)进行后续研究.
-
本研究基于软件EPA PMF5.0的模型实现,输入文件包括研究区域6种重金属的浓度数据和不确定度数据,因子数分别设为3、4、5,系统设置100次,以获得最佳解决方案. 最后,通过比较不同因子数下的Q值和Qrob/Qexp,发现因子数为3时Q值最小且稳定,残差范围在−3—3[35],6种重金属元素的观测值和预测值之间的变异系数(
r2 )在0.317(Pb)— 0.999(Cd)之间,表明PMF模型有良好的拟合效果,分配得到的因子能够很好的解释原数据集包含的信息. PMF模型分析结果表明该区域土壤重金属有3个主要来源(图3),3个主要来源对每个重金属元素的贡献率如图3所示.从不同源对土壤重金属的贡献来看(图3a),因子1中,Cu的贡献率最高,达到61.5%,而Zn、Pb、Cr、Ni和Cd的贡献率依次为46.9%、45.8%、35.1%、26.8和23.7%. 在中国西南地区的地质背景研究中[36-38],Cu、Zn的含量通常偏高,因此这两种元素多被认为来源于母质. 但也有研究表明Cu、Zn和Pb这3种重金属与污水灌溉[39]、污泥应用以及肥料和杀虫剂[34]等农业来源有关. 研究区重金属的垂直分布中,Cu和Zn的含量随土层加深先降低后升高,这也证实了Cu和Zn的含量同时受到了表土层的外来输入和底土层的母质影响,Pb明显的表聚现象也说明了人为管理措施对其的影响. 因此,因子1可视为混合源,即自然和人为输入共同作用的结果. 因子2对Ni的贡献率最高,达45.8%,其次是Cr,达40.4%. 以往较多研究认为Ni作为汽车尾气颗粒物会经由大气沉降进入农田土壤[40-41],因此,Ni通常被认为来源于交通输入,但研究区长期以传统农业为主,仅有少量生产道路分布,无大型机动车聚集往来,因此Ni没有交通输入带来的污染历史. 结合其垂直分布来看,如果是大气沉降输入会有明显表聚性,但Ni在表土层与剖面其它土层差异不大,表明研究区Ni元素主要来源于母质[42],也的确有大量研究表明Ni和Cr可能来源于母质[43-45]. 因此,因子2可视为自然源. 因子3中,Cd的贡献率最高,达到70.9%. 现有研究的农田土壤中重金属Cd多来源于不恰当地施用化肥农药造成的土壤Cd污染 [46-47],使用地膜覆盖地表也会导致Cd在土壤中残留[48]. 研究区作为典型传统农作区,其常用的磷肥或农药中一般都含有Cd元素,Cd也是所研究的6种重金属中唯一超过背景值的元素,且其垂直分布也呈现出显著表聚趋势,显示了Cd确实受到农业措施的影响. 因此,因子3可视为农业源.
从各源对土壤剖面各层的贡献分析来看(图3b),表土层为农业源(50.6%—55.1%)> 混合源(23.6%—28.1%)> 自然源(21.3%),表明表土层更多地受到农业管理活动的影响;在心土层和底土层中则为混合源(43.9%—58.7%)的贡献率最高,但在底土层中农业源在水田中的贡献率高于旱地,这可能是因为水田的耕作层次更深,而研究区心土层通透性较好,重金属元素更容易被淋溶迁移到更深的层次[49-50].
-
以四川省土壤重金属背景值为参照[21],采用PMF模型运行后得出的源成分谱数据计算地累积指数去评价区域内6 种重金属的污染累积水平(图4). 基于重金属含量分析的结果表明(图4a),其
Igeo 平均值的顺序为: Cd>Ni>Zn>Cu≈Pb≈Cr,仅在Cd上体现出轻度到中强污染累积(0.39—2.37),其余都属于“清洁(Igeo <0)”. 且Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn和Ni在不同土层的地累积指数差异不明显,仅Cd呈明显的表土层 > 心土层 > 底土层的趋势. 基于源成分谱的分析结果表明(图4b),各源对Cd地累积指数的贡献为农业源 > 混合源 > 自然源;对Cu、Pb、Zn地累积指数的贡献则为混合源 > 自然源 > 农业源;对Cr和Ni地累积指数的贡献为自然源 > 混合源 > 农业源. 水田与旱地在不同来源不同重金属的地累积指数表现总体上趋于一致,仅底土层中农业源的贡献在旱地会显著低于水田. -
采用PMF模型运行后得出的源成分谱数据计算多元素综合潜在生态风险指数去评价区域内6 种重金属的生态风险水平. 从基于重金属含量分析的结果表明(图5a),水田表土层的NIRI (144.9) 属强风险;旱地则属很强风险(166.6),旱地在表层的生态风险水平明显大于水田. 而在心土层和底土层则相反,虽然NIRI都属中等风险(42.4—79.4),但明显水田的值更大,说明水田在心土层和底土层的生态风险值得重视. 进一步分析发现,各种金属的
Eir 表现在各土层中皆为Cd>Pb≈Cu>Ni>Cr>Zn,说明生态风险在总体上具有一致性. 且无论是水田还是旱地其在土壤剖面各层的主要污染因子基本都是Cd,生态风险处于中等到很强(58.9—232.1)的范围. 现有研究表明,被Cd污染的耕地中种植农作物会使其产量和质量大打折扣[51],且农产品中富集的Cd元素还会威胁人们的身体健康[52-53],因此需要关注对Cd污染土壤的防治及修复. 基于源成分谱的分析结果表明(图5b),除旱地的底土层中是混合源 > 农业源 >自然源,其余土壤剖面各层都是农业源 > 混合源 > 自然源,且农业源的贡献尤为显著. 这与地累积指数的结果较为一致,结合上述分析这可能是由施肥和农药等农业生产活动导致了重金属的累积[54]. 因此应加强对农业源的防治,选用绿色化肥农药,控制施用量. -
(1)研究区土壤剖面中,6种土壤重金属含量的变化规律不相同,仅Cd超过背景值. 分布特征上水旱较为一致,但水田剖面表现更为均匀,旱地表聚性更加显著.
(2)PMF解析出研究区6种重金属的主要来源为农业源、混合源和自然源. 其中农业源的贡献率随土层加深而降低,在表土层中的贡献尤为突出(水田50.6%;旱地55.1%),混合源的贡献率随土层加深而升高,在底土层中的贡献尤为突出(水田55.5%;旱地58.7%),自然源的贡献率受土层影响不大、较为均匀,为21.3%—33.3%.
(3)基于源成分谱的污染累积与生态风险评价表明,研究区土壤Cd元素存在较强的污染累积和生态风险,且以农业源的风险最大,混合源风险最小;其余五种重金属元素无污染累积风险,但存在轻微生态风险. 生态风险中以农业源贡献最大,平均达65.3%,其次为混合源 (29.1%),自然源贡献率平均仅为5.6%. 水田由于受迁移淋溶作用影响更大,其污染累积和生态风险的程度会比旱地的层次更深.
(4)建议研究区域内控制传统农业耕作中化肥农药施用量,重点关注该区域土壤重金属Cd污染问题,采用联合修复技术,并加强农业源的防治.
地球化学元素高背景农作区土壤剖面重金属来源解析及污染评价
Source identification and pollution assessment of heavy metals in soil profile of agricultural area with high background of geochemical elements
-
摘要: 为探明典型地球化学元素高背景农作区土壤剖面重金属的含量及污染风险,以四川省富顺县典型农作区田和旱地为研究对象,明晰其土壤中重金属元素(Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn)的垂直分布特征,并利用正定矩阵因子分析法(PMF)探究其重金属污染来源,基于PMF得到的源成分谱,利用地累积指数法和内梅罗综合风险指数法分析区域内每种源对重金属累积及污染风险的贡献. 结果表明,Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb和Zn在水田土壤剖面中的含量分别为0.19—0.62、47.94—51.15、19.90—21.02、25.61—29.67、18.75—22.15、59.24—71.13 mg·kg−1,旱地土壤剖面中的含量分别为0.15—0.62、47.53—58.39、18.91—22.04、25.26—32.13、17.45—21.75、59.78—77.58 mg·kg−1. 6种重金属中仅Cd元素含量的平均值高于四川省背景值. 水田和旱地土壤的Cd和Pb具有明显的表聚性,而Cr、Cu、Ni、Zn则随土层加深整体呈先降低后增加的趋势. PMF模型结果表明农业源的贡献率随土层加深而降低,在表土层中的贡献尤为突出(水田,50.6%;旱地,55.1%),混合源的贡献率随土层加深而升高,在底土层中的贡献尤为突出(水田55.5%;旱地58.7%),自然源的贡献率受土层影响不大、较为均匀,为21.3—33.3%. 基于源成分谱的污染累积与生态风险评价表明,研究区土壤Cd元素存在较强的污染累积和生态风险,且以农业源的风险最大,混合源风险最小;其余5种重金属元素无污染累积风险,但存在轻微生态风险. 3种源中以农业源对生态风险的贡献最大,平均达65.3%,其次为混合源(29.1%),自然源贡献率平均仅为5.6%. 研究结果表明,应重点关注该区域土壤重金属Cd污染问题,且需加强对农业源的防治.
-
关键词:
- 土壤剖面 /
- 重金属 /
- 垂直分布 /
- 正定矩阵因子分解PMF /
- 污染评价.
Abstract: In order to investigate the content and pollution risk of heavy metals (HMs) in the soil profile of typical agricultural areas with high background of geochemical elements, the vertical distribution characteristics of HMs (Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) in soils of paddy field and dryland that collected from a typical agricultural area in Fushun County, Sichuan Province were studied; the sources of HM pollution were explored by using positive matrix factorization (PMF); and the contribution of each source to the pollution assessment in the region was analyzed by using Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo ) and Nemerow Integrated Risk Index (NIRI). The results showed that the contents of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in the soil profile of paddy field were 0.19—0.62, 47.94—51.15, 19.90—21.02, 25.61—29.67, 18.75—22.15, and 59.24—71.13 mg·kg−1, respectively. The contents of the above six HMs in dryland soil profile were 0.15—0.62, 47.53—58.39, 18.91—22.04, 25.26—32.13, 17.45—21.75, and 59.78—77.58 mg·kg−1, respectively. Among the six HMs, only the average content of Cd was higher than the background value in Sichuan Province. Meanwhile, Cd and Pb had obvious surface aggregation in paddy field and dryland soil, whereas Cr, Cu, Ni and Zn decreased first and then increased with the deepening of soil layer. The results of PMF model showed that the contribution rate of agricultural source was the highest in the topsoil layer (paddy field, 50.6%; dryland, 55.1%), and decreased with the deepening of soil layer. The contribution rate of mix source also increased with the deepening of soil layer, but the largest contribution was in subsoil (paddy field, 55.5%; dryland, 58.7%). In addition, the contribution rate of lithogenic source was not changed with soil layer, the values were ranging from 21.3% to 33.3%. The pollution accumulation and ecological risk assessment based on source component spectrum showed that there were moderately polluted accumulation and considerable ecological risk of Cd in the study area. Furthermore, the risk of the agricultural source was the highest, and the risk of mixed source was the least. The other five heavy metals have no cumulative pollution risk, but have slight ecological risk. Among the three sources, agricultural source contributed the most to the ecological risk, with an average contributed rate was 65.3%, followed by mixed source (29.1%), and natural sources contributed only 5.6%. In conclusion, it needs to pay more attention to the problem of soil Cd pollution in this region, and the prevention and control of agricultural sources should be strengthened. -
镉(Cadmium)是自然环境中普遍存在且毒性极强的重金属元素,几乎所有土壤、地表水和植物体内均含有镉元素,镉化学活性强且易于转化,故其一直是国内外土壤重金属污染研究的重点和热点[1]. 镉是贵州省主要环境污染元素之一[2]. 土壤中镉成因复杂、空间差异明显,贵州地表土壤和沉积物中镉的地球化学背景值为0.31×10−6,贵州地表介质具有镉高背景分布特征[3]. 贵州遵义地区是贵州省农业生产的重要基地,遵义地区工业结构主要以资源型和内源型为主,在生产过程中物耗、能耗都较高,污染较严重[4].
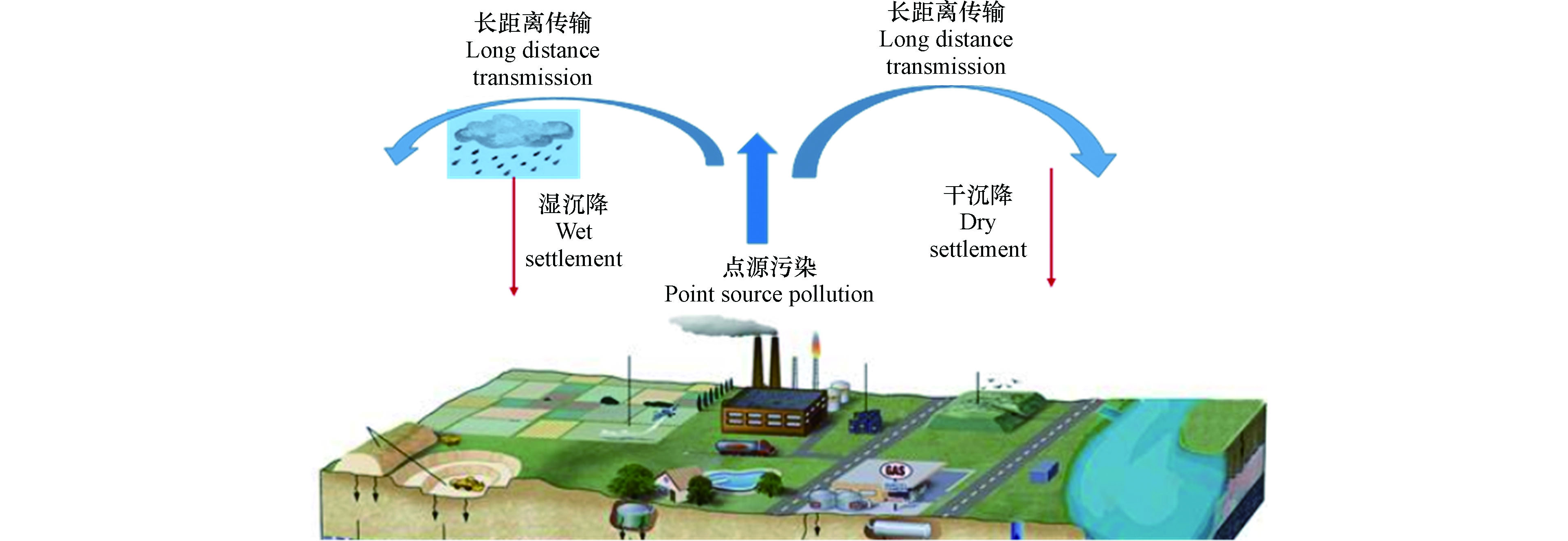
大气沉降是地表生态环境中金属元素的主要来源之一[5],是农耕区土壤重金属元素的重要输入途径之一[6-7],也是严重影响农田生态系统循环的重要因子. 工业废气、车辆尾气、化石燃料燃烧等产生大量含镉的有害气体和粉尘,经过降水和自身重力的沉降而进入土壤[8],从而对土壤镉的分布造成影响. 大气沉降一直是环境科学领域众多学者重点关注的研究对象之一[9-13].
大气沉降样品的采集分为主动采样和被动采样. 主动采样技术能够准确获得大气体积,但需要电力设施和现场维护,并不利于在偏远的极地或高山环境中使用;被动采样技术具有不需要电源和操作简单的优势,可以在上述恶劣环境中进行采集[14],因此采用苔藓为监测物质的苔袋法来研究重金属大气干湿沉降、污染物来源、迁移及时空分布等得到了广泛应用[15-17]. 该方法具有以下优点:(1)暴露时间易控制;(2)可以反映出污染物沉积的相对速率;(3)背景浓度明确,不受根系吸收干扰;(4)简便经济、选点灵活,适用于全年监测等[18-23]. 大气沉降镉一般停留在表层土壤[24],其原因和机理有待揭示.
本文利用苔袋法采集遵义地区大气沉降、采集遵义地区表层土壤及剖面土壤,分析其表层土壤镉含量及剖面土壤镉分布特征、化学形态和镉吸附热力学,对揭示遵义地区表层农业土壤镉污染状况以及镉大气沉降通量对表层土壤的影响具有一定的意义.
1. 材料和方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 研究区域概况
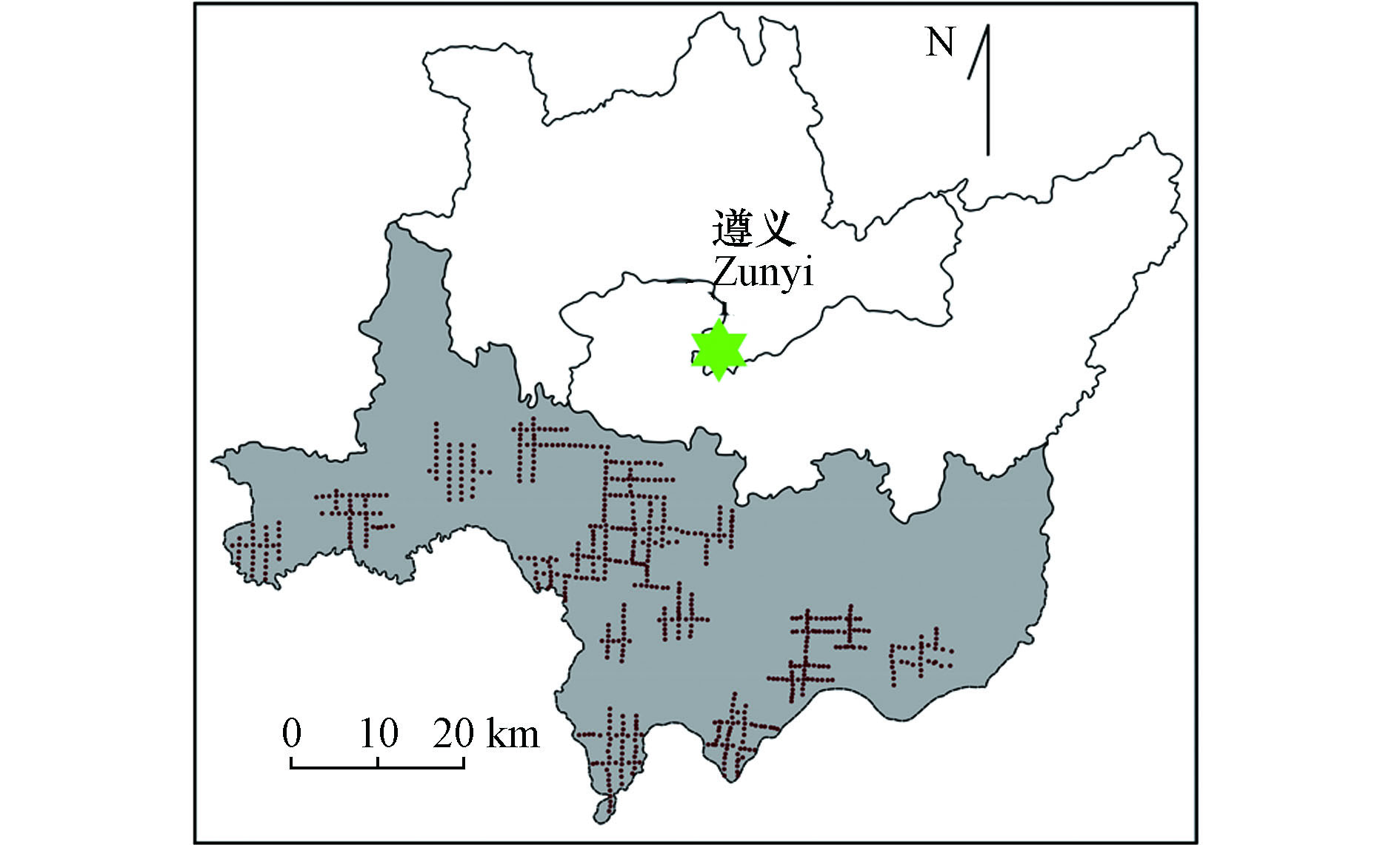
研究区域贵州遵义地区位于云贵高原向湖南丘陵和四川盆地过渡的斜坡地带,地形起伏大,地貌类型复杂,地处:东经106°17′22″—107°25′25″,北纬27°13′15″—28°04′09″. 总面积4092.66 km2,土壤类型以黄壤土、水稻土、紫色土为主. 遵义属亚热带季风气候,平均有霜期为9.5 d,无霜期长,雨量充沛,年平均降雨1035 mm. 遵义地区是全国无公害农产品示范基地.
1.2 采样布点
根据土壤中镉分布的空间变异性和城郊土壤空间差异明显的特点,采用非均匀布点方法,共采集表层土壤样本889个、剖面土壤样本20个;根据当地农业区域规划和气象条件选取8个大气沉降采样点,采集大气沉降样本64个. 表层土壤样品采样点分布见图1.
土壤采样点选在土壤类型特征明显且地形相对平坦、稳定、植被良好的地点. 坡脚、洼地等不设采样点,城镇、住宅、道路附近等人为干扰大且失去土壤代表性的地方不设采样点,水土流失严重或表土被破坏处不设采样点,多种土类、多种母质母岩交错分布、面积较小的边缘地区不设采样点.
选取大气沉降采样点时着重考虑如下原则:避开点、线源的局部污染,如烟囱和交通要道等;避免受地面扬尘污染以及一些不可控的人为污染影响;采样点周围无(树枝、树叶等)遮挡.
1.3 采样方法
1.3.1 表层土壤采集
表层土壤采用梅花型采样,在100 亩土壤内随机确定1个10 m×10 m正方形作为取样点,土壤样品从正方形的4个顶点和中心共5处各采集1 kg表土(0—20 cm),均匀混合后用四分法选取1 kg作为该点样品,同时用GPS测定正方形中心的地理坐标并编号记录.
1.3.2 剖面土壤采集
夏增禄等[25]的研究表明,在污染土壤中,重金属进入土壤后,由于土壤对它们的固定,多集中分布在耕作层,不易向下迁移,向下迁移深度大约在20—60 cm. 因此选择采样深度分别为0—15 cm、15—25 cm、25—40 cm、40—60 cm. 剖面的规格为长1.5 m,宽0.8 m,深1.2 m. 挖掘土壤剖面要使观察面向阳,采样次序自下而上,尽量用竹片或竹刀去除与金属采样器接触的部分土壤,再用其取样,采样完成后将底土和表土按原层回填到采样坑中.
1.3.3 土壤样品处理
采集后的土壤样品置于清洁的风干室内自然风干,将风干后的土样放在清洁塑料板上用木棍辗压,除去2 mm以上杂物,使样品全部过20目分样筛. 将过筛后的土样经玛瑙研钵研细后过100目尼龙网筛,充分混合均匀备用.
1.3.4 苔袋法(Moss Bag Method)采集大气沉降
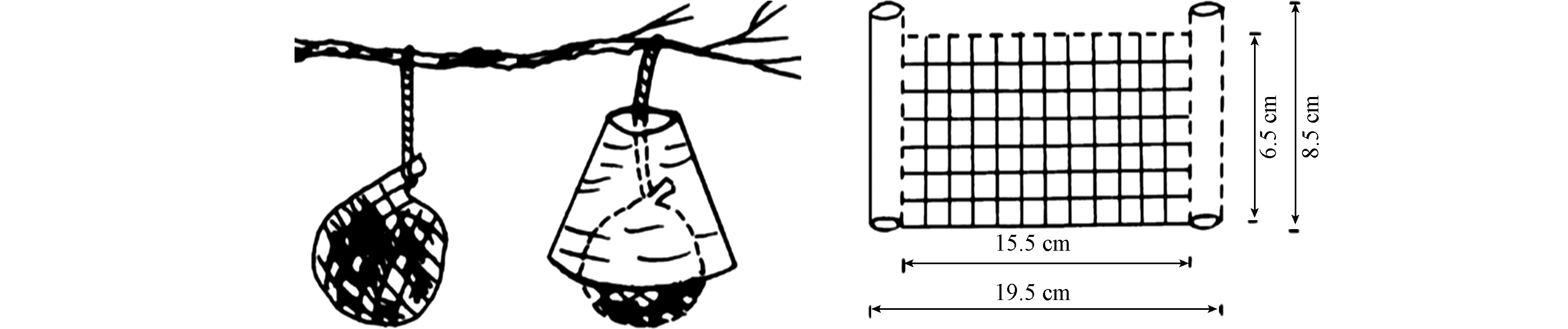
本研究选用采自贵州省贵阳市乌当区盘龙山的大灰藓(Hypnum plumaefoeme )作为监测材料. 采集长度>6 cm的植株,除去死去的茎叶与杂物,用自来水清洗表面泥土与浮尘颗粒,用l%的硝酸浸泡24 h,再用去离子水清洗3次,每次0.5 h,置于清洁处自然风干. 用尼龙袋(网眼2.0 mm×2.0 mm)做成规格为15.5 cm×6.5 cm的口袋,称取(3.0±0.2) g干苔藓装进袋内封口,即可提供100 cm2的苔袋表面积[26]. 制作苔袋时应戴乳胶手套避免污染,装好的苔袋置于密封袋内备用.
将Moss Bags悬挂在各监测点离地面3—3.5 m的位置,每个监测点悬挂n组(n>5),以便于对离群数据进行分析,每组中一个完全暴露于空气中,另一个用塑料罩覆盖如图2所示,分别用于采集总沉降和干沉降,每3个月取下的Moss Bags所损失的重量不大于5%. 将采集的苔袋加以标签保存在干净的密封袋内备用.
1.4 分析方法
1.4.1 仪器与试剂
电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP MS):Agilent 7800;石墨炉原子吸收光谱仪:Vario 6;火焰原子吸收光谱仪:ICE 3300;微波消解仪:Milestone ETHOS UP;水浴恒温振荡器:WHY-2A;低速离心机:TD5Z. 去离子水;盐酸、高氯酸、氢氟酸、硝酸、双氧水:优级纯;乙酸、乙酸钠:分析纯.
1.4.2 土壤样品分析方法
土壤样品按照中华人民共和国国家标准GB/T 17141—1997《土壤质量铅、镉的测定石墨炉原子吸收分光光度法》测定,称取土壤样品(0.1000±0.0005)g于50.00 mL聚四氟乙烯坩埚中,用去离子水润湿后加人5.00 mL盐酸于电热板上低温加热,当蒸发至约2—3 mL时,取下稍冷,然后加人5.00 mL硝酸、4.00 mL氢氟酸、2.00 mL高氯酸,加热至冒浓厚高氯酸白烟时,加盖,待坩埚上的黑色有机物消失后,开盖驱赶白烟并蒸至内容物呈粘稠状,消解溶液定容至25.00 mL,用石墨炉原子吸收光谱仪检测,分析过程加入国家标准土壤样品(GSS-2、GSS-5)进行分析质量控制.
1.4.3 苔藓样品分析方法
称取采集的苔藓(0.3000±0.0005) g,加入5.00 mL硝酸和2.00 mL双氧水,用微波消解仪消解3 h,同时设空白样. 将完全消解的样品定容至25.00 mL,用ICP-MS上机检测.
1.4.4 表层土壤镉化学形态分析方法
称取土壤样品10.00 g,采用Tessier法进行表层土壤镉元素形态的提取,具体见表1,提取后溶液用ICP-MS上机检测.
表 1 Tessier法步骤Table 1. Tessier method steps步骤Step 实验提取试剂 Experimental extraction reagent 实验条件 Experimental conditions 土/液Soil/Liquid 1 1 mol·L−1MgCl2(pH=7.0) 25 ℃下振荡1 h 1∶8 2 1 mol·L−1NaAc(HAc调pH=5.0) 25 ℃下振荡5 h 1∶8 3 0.04 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl的25% HAc溶液 96 ℃水浴浸提6 h 1∶20 4 0.01 mol·L−1 HNO3、30% H2O2 3.2 mol·L−1 NH4Ac、20% HNO3溶液 85 ℃水浴浸提2 h 85 ℃水浴浸提2 h 25 ℃下振荡30 min 1∶8 1∶11 1∶20 1.4.5 吸附热力学
称取(2.000±0.0002)g土样置于50.00 mL的离心管中,分别加入0.00、0.50、1.00、5.00、10.00、20.00 mg·L−1浓度的Cd溶液10.00 mL,分别在15、25、35 ℃恒温振荡后在4000 r·min−1转速下离心5 min,然后将上清液过0.45 μm滤膜,用火焰原子吸收光谱仪检测.
1.5 数据分析
1.5.1 地统计学分析和数据统计
采用Excel、SPSS、Arc GIS数据处理软件对所测的数据进行统计分析. 变异函数计算公式如下:
r(h)=12N(h)N(h)∑i=1[z(xi)−z(xi+h)]2 式中,h为两个样本点之间的空间距离,N(h)为以h为间距的所有观测点的样本对数,Z(xi)、Z(xi+h)为样本点在空间位xi、xi+h处的样本值.
1.5.2 沉降通量的计算
大气沉降通量表示的是,单位面积单位时间沉降的重金属量,其计算公式为 :
Fd=M×S−1×D−1 式中,Fd为沉降通量(µg·m−2·d−1);M为Moss Bags 富集重金属元素量(µg);S为元素沉降面积(m2);D为采样天数(d).
1.5.3 吸附热力学计算
本实验采用吉布斯自由能方程来分析温度对平衡吸附系数的影响(根据Freundlich方程拟合参数来计算),吉布斯自由能变化值(∆G0)可用于评估吸附反应是否自发进行:
ΔG0=−RTlnKF ΔG0=ΔH0−TΔS0 式中,∆G0为标准吉布斯自由能(kJ·mol−1);KF为Freundlich常数;T—绝对温度(K);∆H0为吸附标准焓变(kJ·mol−1);∆S0为标准熵变(kJ·(mol·K)−1).
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 表层土壤镉含量分布特征
遵义地区表层土壤中镉含量坐标分布和空间差异分布见图3. 土壤所有样点镉含量原始数据描述性统计结果列于表2,结果表明用平均值加减3倍标准差替换异常值后,镉含量分布在峰度与偏度上显著下降,平均值和中位数更为接近,标准差和变异系数也明显减小. 表层土壤镉含量最大值为2.565 mg·kg−1,最小值为0.099 mg·kg−1. 经过变异函数的分析,得到变异函数模型和变异参数如表3所示,块金值与基台值之比称为基底效应,可以表明样本变量的空间相关性程度,若比值<25%,说明系统具有强烈的空间相关性[27]. 在研究区内,土壤镉元素的块金值与基台值之比在16.54%,表明遵义地区表层土壤镉具有强烈的空间相关性,在空间分布上受土壤内在属性、地形及大气沉降的影响较大. 主变程为0.0488,总体来说遵义地区表层土壤镉呈非均匀分布.
表 2 遵义地区表层土壤镉含量的描述统计Table 2. Descriptive statistics of cadmium content in surface soil in Zunyi area元素Element 样品数 Number of samples 平均值 Average value 标准差 Standard deviation 中位数 Median 范围 Range 变异系数Coefficient of variation 峰度Kurtosis 偏度Skewness Cd 889 0.357 0.24 0.344 0.099—2.565 0.67 13.66 3.15 异常值检验后结果统计 Result statistics after outlier test 元素Element 样品数Number of samples 平均值Average value 标准差Standard deviation 中位数Median 范围 Range 变异系数Coefficient of variation 峰度Kurtosis 偏度Skewness Cd 889 0.356 0.217 0.344 0.099—2.07 0.61 8.66 2.62 2.2 大气沉降通量结果分析
2.2.1 大气总沉降通量结果分析
遵义地区大气总沉降通量统计结果见表4,各采样点大气沉降通量差异明显,变异系数在0.68—1.15之间,变异系数均较大,镉大气沉降通量最小值为0.32 µg·m−2·d−1,最大值为14.9 µg·m−2·d−1,平均值5.50 µg·m−2·d−1. 镉大气沉降通量分布不均匀,局部地区可能受到点源污染,受人为源影响在大气中迁移扩散.
表 3 变异函数模型及变异参数Table 3. Variation function model and variation parameters元素Element 变异函数模型 Variogram model 块金值 Nugget value 基台值 Abutment value 主变程 Main variable range 块金值/基台值/% Nugget value/abutment value Cd Spherical 0.0274 0.1658 0.0488 16.54 表 4 遵义地区大气总沉降通量统计结果 (µg·m−2·d−1)Table 4. Statistical results of total atmospheric deposition flux in Zunyi area (µg·m−2·d−1)采样点Sampling site 1—3月 January —March 4—6月 April —June 7—9月 July —September 10—12月October —December 最大值Max 最小值Minimum 标准差Standard deviation 变异系数Coefficient of variation S1 10.5 5.7 1.2 12.8 12.8 1.2 5.16 0.68 S2 11.9 5.7 1.2 14.9 14.9 1.2 6.15 0.73 S3 8.7 4.3 0.91 12.8 12.8 0.91 5.18 0.78 S4 5.3 3.3 0.63 7.5 7.5 0.63 2.92 0.70 S5 3.3 0.9 0.32 5.8 5.8 0.32 2.50 0.97 S6 8.9 1.9 0.42 6.7 8.9 0.42 3.98 0.89 S7 10.3 1.1 0.64 8.2 10.3 0.64 4.92 0.97 S8 13.1 1.5 0.26 5.3 13.1 0.26 5.79 1.15 遵义地区与其他地区镉大气沉降通量对比见表5,与其他地区相比遵义地区镉大气沉降通量偏高,这与遵义曾是贵州地区历史土法炼锌工业区有关,遵义地区大气受到了一定的污染;但与矿区周边相比要低很多,说明遵义地区大气镉污染比采矿周边大气污染要小,但是也不容忽视.
表 5 遵义地区与其他地区镉大气沉降通量(µg·m−2·d−1)Table 5. Cadmium atmospheric deposition flux in Zunyi area and other areas (µg·m−2·d−1)2.2.2 大气干湿沉降分布特征
遵义地区镉元素大气干、湿沉降通量统计见表6,各季度大气干、湿沉降通量差异明显,干沉降变异系数在0.83—1.25之间,湿沉降变异系数在0.51—1.04之间,变异系数均较大,镉的大气沉降通量季节差异较为明显,整体上冬半年高于夏半年,干沉降在春东两季所占比重要高于夏秋两季,这与镉元素主要来自冶炼、燃煤、石油和垃圾焚烧等产生的废气[35]有关,随着冬半年燃煤量的增加镉大气沉降通量也有所增加. 湿沉降所占比重在夏秋两季偏高,降雨量增加随雨水迁移到土壤的湿沉降也随之 增加.
2.2.3 大气沉降中镉的来源分析
大气中镉的来源如图4所示. 大气镉的污染主要来自于铅锌矿开采、有色金属冶炼、燃煤、电镀、电池、油漆生产等. 在前期研究报道过在贵州土法炼锌地区,镉在大气典型的排放源10 km范围内用藓袋法可监测到3.32—47.2 mg·m−2·mon−1[36],陈强等2020年报道广东大宝山矿区镉大气沉降通量平均值为1.97 g·hm−2·a−1[37],一煤矿工厂区镉的大气沉降通量为12.0 g·hm−2·a−1,超过我国平均水平(4 g·hm−2·a−1)约3倍[38]. 大气是镉赋存和传输的重要媒介,进入大气的镉随风向、重力、降水等进行大范围扩散,造成大气中镉向土壤沉降,最终导致表层土壤镉含量较高. 许多工业发达国家,大气沉降对土壤系统中重金属累积贡献率在各种外源输入因子中排在首位[37]. 由此可知镉大气沉降会对土壤镉污染造成一定程度的影响,因此监测镉大气沉降通量是非常有意义的.
表 6 遵义地区镉大气沉降通量(µg·m−2·d−1)Table 6. The atmospheric dry deposition flux of cadmium in Zunyi area (µg·m−2·d−1)采样点Sampling site 1—3月January to March 4—6月April to June 7—9月 July to September 10—12月October to December 最大值Max 最小值Minimum 标准差Standard deviation 变异系数Coefficient of variation 干沉降 S1 6.3 2.10 0.42 8.5 8.5 0.42 3.72 0.86 S2 7.6 2.50 0.51 9.2 9.2 0.51 4.12 0.83 S3 5.2 1.90 0.31 8.1 8.1 0.31 3.47 0.90 S4 3.1 1.20 0.25 5.2 5.2 0.25 2.19 0.90 S5 2.1 0.21 0.12 2.3 2.3 0.12 1.18 1.00 S6 5.7 0.72 0.15 4.2 5.7 0.15 2.69 1.00 S7 6.2 0.43 0.28 4.6 6.2 0.28 2.99 1.04 S8 9.1 0.52 0.11 3.5 9.1 0.11 4.15 1.25 湿沉降 S1 4.2 3.60 0.78 4.3 4.3 0.78 1.65 0.51 S2 4.3 3.20 0.69 5.7 5.7 0.69 2.12 0.61 S3 3.5 2.40 0.60 4.7 4.7 0.60 1.74 0.62 S4 2.2 2.10 0.38 2.3 2.3 0.38 0.91 0.52 S5 1.2 0.69 0.20 3.5 3.5 0.20 1.46 1.04 S6 3.2 1.20 0.27 2.5 3.2 0.27 1.31 0.74 S7 4.1 0.67 0.36 3.6 4.1 0.36 1.94 0.89 S8 4.0 1.00 0.15 1.8 4.0 0.15 1.65 0.96 2.3 不同深度土壤剖面镉含量分布特征
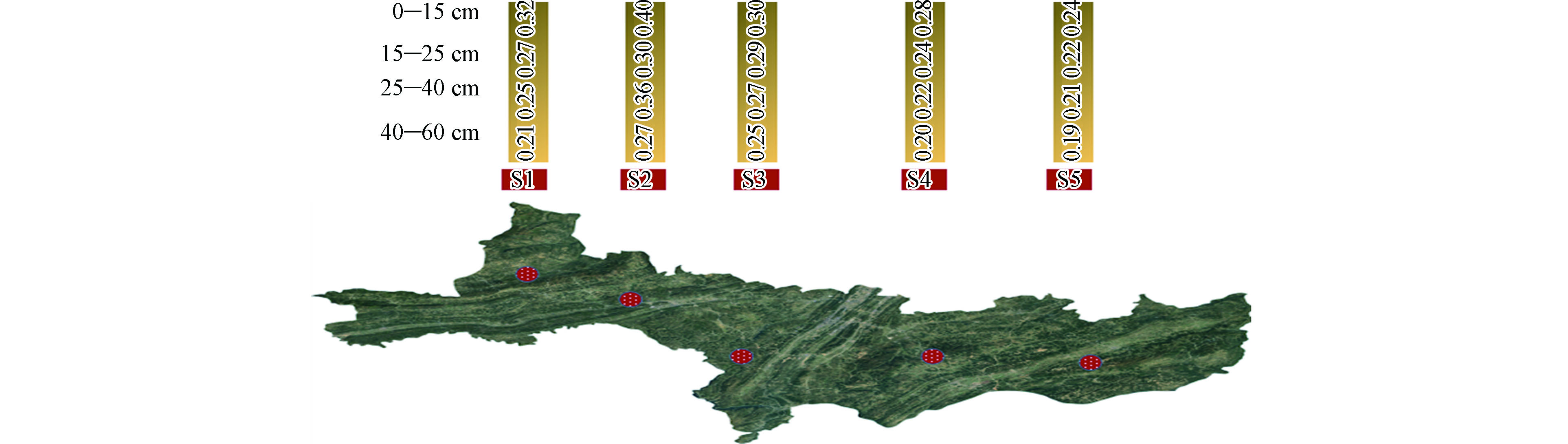
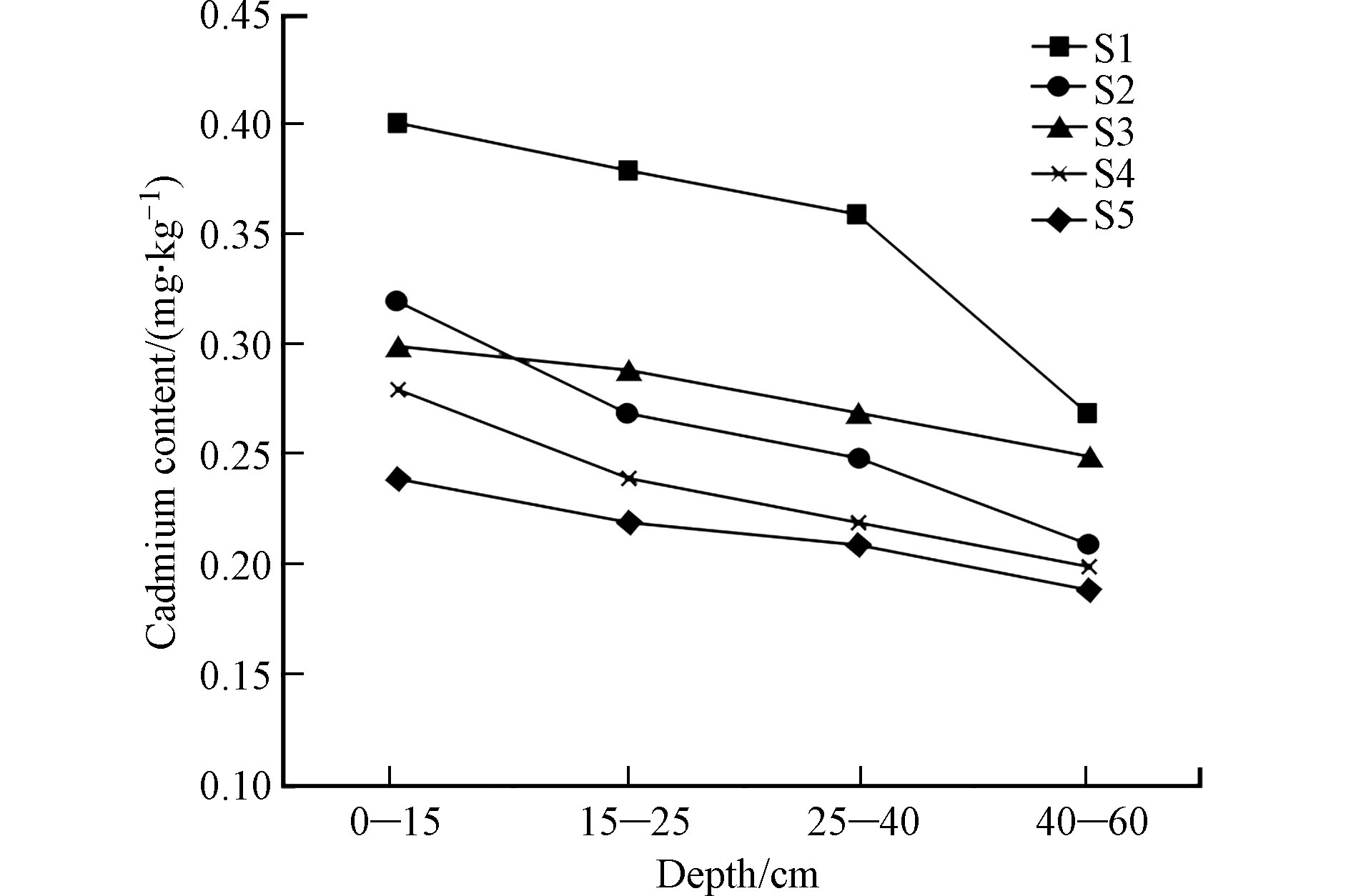
不同深度的剖面土壤镉含量随深度变化示意见图5,含量与深度关系见图6,由图可知剖面样镉元素最大值为0.40 mg·kg−1,最小值为0.19 mg·kg−1,平均值为0.268 mg·kg−1. 镉元素在各个土壤剖面的含量呈从高到低逐渐降低趋势,表层土壤镉元素含量大于深层土壤镉元素含量. 镉元素在40—60 cm处镉元素含量变化不大,以此推断垂向剖面更深层土壤中镉元素含量将趋于稳定. 土壤深度越深受人类活动影响越小,深层土壤能近似地反映原生环境元素分布、赋存状态,而浅层土壤与生态环境联系密切,受人为干扰最严重. 镉大部分富集在土壤表层,给农业生产带来了极大的风险.
2.4 大气沉降影响下表层土壤镉化学形态分布特征
土壤中的镉按照Tessier法提取顺序可划分为5种形态:可交换态(EXC)(包括水溶态)、碳酸盐结合态(CA)(包括专性结态)、铁猛氧化物结合态(Fe-Mn)、有机物-硫化物结合态(OM)(简称有机结合态)、残留态(RES)(即硅酸盐态).
对遵义地区剖面土壤0—15 cm层土壤进行镉形态提取及测定,镉各形态含量占比见图7,遵义地区0—15 cm层土壤镉形态以EXC和Fe-Mn为主,EXC占到土壤镉总形态的18%—40%,可交换态的镉毒性最强,能较好地反映出人为因素所造成的污染,这些土壤化学活动性较高,当其作为农用土壤使用时,Cd的可交换态部分会随着环境的改变被植物吸收从而进入食物链并在人体内累积[1],这将对人体健康构成威胁.
2.5 表层土壤对镉的吸附行为
Freundlich模型能较好地拟合镉在土壤中的等温吸附数据[39],根据吉布斯自由能方程和Freundlich方程拟合参数,计算得到相关热力学参数见表7. 当0<|∆G0|<20 kJ·mol−1时吸附类型为物理吸附[40],本实验|∆G0|<20 kJ·mol−1因此土壤对镉的吸附过程属于物理吸附,主要作用力为范德华力. 在不同实验温度下,|∆G0|大小顺序基本为:308 K>298 K>288 K,吸附作用随温度的升高而减小,这说明低温或者是常温更有利于Cd在土壤表面的吸附.
表 7 镉在土壤上的吸附热力学参数Table 7. Adsorptionthermodynamic parameters of Cd in soils ofnineareas土壤编号 Soil number KF ∆G0/(kJ·mol−1) ∆H0/ (kJ·mol−1) ∆S0/ (kJ·(mol·K)−1) 288 K 298 K 308 K 288 K 298 K 308 K 1号 63.665 96.472 1326.173 −9.946 −11.321 −18.412 199.991 0.709 2号 34.857 46.602 29.689 −8.503 −9.518 −8.683 −34.404 −0.0835 3号 37.932 53.543 74.542 −8.706 −9.862 −11.041 25.249 0.118 4号 1.866 51.439 46.541 −1.494 −9.763 −9.778 −9.295 0.00157 5号 11.013 17.828 17.997 −5.744 −7.137 −7.401 0.721 0.0264 2.6 镉大气沉降与表层0—15 cm土壤分析
大气是镉赋存和传输的重要媒介,在前期研究报道过在土法炼锌地区,镉元素在大气典型的排放源10 km范围内用藓袋法可监测到3.32—47.2 mg·m−2·mon−1[36],造成大气中向土壤可沉降的镉总量增加,最终导致附近土壤表层镉含量较高,土法炼锌区域土壤受镉污染的其中一条重要途径是大气中镉的干湿沉降. 干湿沉降与土壤相关性分析表明,大庆市干湿沉降中Cd、Zn含量与土壤中Cd、Zn含量呈现出极强相关性[32]. 大气沉降中的镉迁移到土壤中具有较强的吸附力,吸附率在85%—95%,一般停留在表层0—15 cm的土壤中,15 cm以下含量显著减少[24]. 大气中镉沉降与土壤中对镉负载有一定关系.
2.6.1 大气沉降影响表层土壤镉的生物有效性
大气颗粒物中镉具有极强的的水溶性,其水溶性在10%—40%之间,苔袋法为阳离子交换过程为捕获空气中的细颗粒提供了非常大的表面积,可以捕获空气中的微粒[26,41-42]. 因此苔袋法监测的是大气颗粒物中细颗粒物镉大气沉降通量,镉水溶性在粒径0.44—0.77 μm的细颗粒中达到最大值[43],因此水溶性的镉在随大气沉降迁移至土壤表面时由于具有较强的化学活动性而被表层土壤吸附,在土壤表层迁移扩散. 大气颗粒物水溶性重金属具有较高的毒性,随大气沉降进入土壤后会增加土壤镉可交换态含量.
2.6.2 大气沉降中的镉吸附在土壤表层不易向下扩散机理分析
吸附热力学实验表明镉的|∆G0|<20 kJ·mol−1,属于物理吸附,范德华力占主导作用,且低温(或者是常温下)更有利于镉在土壤表面的吸附. 大气沉降中镉迁移到土壤中时有强烈的吸附作用. 这一吸附作用可以看作土壤与溶液界面的吸附,从吸附速度看,溶液中吸附速度一般比气体慢,表现出扩散速度比较慢,因此很容易停留在土壤表面而不易向下深度扩散.
土壤作为胶体表面往往结合H2O后在土壤晶格点上会形成羟基和氢键,它们都属于弱键在常温下容易与镉结合并在土壤表面吸附、负载. 镉元素在土壤中的固定,主要由于黏土矿物和腐殖酸的吸附,一般土壤胶体越多或胶体上的负电荷越多,对镉的吸附能力越强.
3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)遵义地区表层土壤中镉含量最大值2.656 mg·kg−1,最小值0.099 mg·kg−1,土壤各镉元素的块金值与基台值之比在16.54%具有强烈的空间相关性,主变程为0.0488,说明均一性较弱呈非均匀分布;土壤剖面镉含量垂直分布规律为表层土壤含量高,深度在0—60 cm内随着土壤深度增加而逐渐降低.
(2)采用苔袋法(Moss bag)监测遵义地区镉元素大气沉降通量平均值为5.5 µg·m−2·d−1高于全国平均水平(1.1 µg·m−2·d−1),镉的大气沉降通量冬半年高于夏半年;大气沉降镉元素进入土壤后虽然会发生不同程度的流失和转移但大部分富集在土壤耕作层,长期来看大气输入土壤的镉元素给农业生产带来的风险,应引起足够的重视.
(3)大气中镉沉降与土壤中对镉负载有一定关系,通过热力学计算得出表层土壤对镉的吸附属于物理吸附,大气沉降中的镉迁移到土壤中具有较强的吸附力,这一吸附力可以看作土壤和溶液的固液吸附扩散速度慢,因此镉元素大气沉降会影响表层土壤镉元素含量分布.
-
-
[1] 韩春梅, 王林山, 巩宗强, 等. 土壤中重金属形态分析及其环境学意义 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2005, 24(12): 1499-1502. HAN C M, WANG L S, GONG Z Q, et al. Chemical forms of soil heavy metals and their environmental significance [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2005, 24(12): 1499-1502(in Chinese).
[2] 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[R]. 北京: 中华人民共和国国土资源部, 2014. State Environmental Protection Administration of China, State Environmental Land and Resources Administration of China. Bulletin of national soil pollution survey[R]. Beijing: State Environmental Land and Resources Administration of China, 2014 (in Chinese).
[3] 余垚, 朱丽娜, 郭天亮, 等. 我国含磷肥料中镉和砷土壤累积风险分析 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(7): 1326-1331. YU Y, ZHU L N, GUO T L, et al. Risk assessment of cadmium and arsenic in phosphate fertilizer [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(7): 1326-1331(in Chinese).
[4] KESHAVARZI A, KUMAR V, ERTUNÇ G, et al. Ecological risk assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals contamination: an appraisal based on the Tellus soil survey [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2021, 43(5): 2121-2142. doi: 10.1007/s10653-020-00787-w [5] WANG Y T, GUO G H, ZHANG D G, et al. An integrated method for source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils and model uncertainty analysis [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 276: 116666. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116666 [6] 阿吉古丽·马木提, 麦麦提吐尔逊·艾则孜, 艾尼瓦尔·买买提. 新疆焉耆县耕地土壤重金属垂直分布特征与污染风险 [J]. 水土保持研究, 2018, 25(2): 367-373. AJIGULI M, MAIMAITITUERXUN A, AINIWAER M. Vertical distribution characteristics and risk assessment of soil heavy metal contamination of farmlands in Yanqi County, Xinjiang [J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 25(2): 367-373(in Chinese).
[7] 张炜华, 于瑞莲, 杨玉杰, 等. 厦门某旱地土壤垂直剖面中重金属迁移规律及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(8): 3764-3773. ZHANG W H, YU R L, YANG Y J, et al. Migration and source analysis of heavy metals in vertical soil profiles of the drylands of Xiamen City [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(8): 3764-3773(in Chinese).
[8] 韩张雄, 万的军, 胡建平, 等. 土壤中重金属元素的迁移转化规律及其影响因素 [J]. 矿产综合利用, 2017(6): 5-9. HAN Z X, WAN D J, HU J P, et al. Migration and transformation of heavy metals in soil and its influencing factors [J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(6): 5-9(in Chinese).
[9] 杨学兰, 马云飞. 基于PMF模型的济南市郊土壤重金属来源解析 [J]. 河北环境工程学院学报, 2020, 30(6): 44-47,72. YANG X L, MA Y F. Analysis of heavy metals sources in the soil of suburb area in Jinan based on PMF model [J]. Journal of Hebei University of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 30(6): 44-47,72(in Chinese).
[10] 孟敏, 杨林生, 韦炳干, 等. 我国设施农田土壤重金属污染评价与空间分布特征 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2018, 34(11): 1019-1026. MENG M, YANG L S, WEI B G, et al. Contamination assessment and spatial distribution of heavy metals in greenhouse soils in China [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2018, 34(11): 1019-1026(in Chinese).
[11] 李亚娜. 我国农田土壤重金属污染现状分析 [J]. 节能, 2019, 38(7): 118-119. LI Y N. Brief probe into heavy metal pollution of agricultural soils in China [J]. Energy Conservation, 2019, 38(7): 118-119(in Chinese).
[12] 陈小林, 李良均. 富顺县高粱+大豆产业发展模式分析 [J]. 大豆科技, 2020(4): 34-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3547.2020.04.009 CHEN X L, LI L J. Analysis on the development mode of Sorghum + soybean industry in Fushun County [J]. Soybean Science & Technology, 2020(4): 34-36(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3547.2020.04.009
[13] 郑里. 农业现代化的县域发展途径 以四川省富顺县为例 [J]. 当代县域经济, 2017(4): 46-47. ZHENG L. The way of county development of agricultural modernization: a case study of Fushun County, Sichuan Province [J]. Contemporary County Economy, 2017(4): 46-47(in Chinese).
[14] 成杭新, 彭敏, 赵传冬, 等. 表生地球化学动力学与中国西南土壤中化学元素分布模式的驱动机制 [J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(6): 159-191. CHENG H X, PENG M, ZHAO C D, et al. Epigenetic geochemical dynamics and driving mechanisms of distribution patterns of chemical elements in soil, Southwest China [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(6): 159-191(in Chinese).
[15] 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 等. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(2): 112-115. XU Z Q, NI S J, TUO X G, et al. Calculation of heavy metals' toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 31(2): 112-115(in Chinese).
[16] PAATERO P, TAPPER U. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values [J]. Environmetrics, 1994, 5(2): 111-126. doi: 10.1002/env.3170050203 [17] NORRIS G, DUVALL R, BROWN S, et al. 2014. EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide. U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Washington, DC 20460. EPA/600/R-14/108[R]. [18] CHAI L, WANG Y H, WANG X, et al. Pollution characteristics, spatial distributions, and source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil in Lanzhou, China [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 125: 107507. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107507 [19] 朱晓丽, 薛博倩, 李雪, 等. 基于PMF模型的宝鸡铅锌尾矿库周边农田土壤重金属源解析 [J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 51(1): 43-53. ZHU X L, XUE B Q, LI X, et al. Sources apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soil around lead-zinc tailings reservoir based on PMF model [J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 51(1): 43-53(in Chinese).
[20] MÜLLER G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River [J]. Geology Journal, 1969, 2: 108-118. [21] 傅绍清, 苏方康, 宋怡, 等. 成都平原菜园土壤及主要蔬菜作物重金属背景值的研究 [J]. 西南农业学报, 1992, 5(1): 34-40. FU S Q, SU F K, SONG Y, et al. Background values of heavy metals in garden soil and vegetables in Chengdu plain [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 1992, 5(1): 34-40(in Chinese).
[22] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [23] MEN C, LIU R M, XU L B, et al. Source-specific ecological risk analysis and critical source identification of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 388: 121763. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121763 [24] 左文萍, 黎清华, 张彦鹏, 等. 火山岩风化区农田重金属污染及健康风险评价——以海口江东新区为例[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 1-15. ZUO W P, LI Q H, ZHANG Y P, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and health risk in farmland in the volcanic weathering area — a case study in Jiangdong new district of Haikou[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 1-15(in Chinese).
[25] 刘孝严, 樊亚男, 刘鹏, 等. 基于文献计量分析的长江经济带农田土壤重金属污染特征[J]. 环境科学,2022, 43(11): 5169-5179. LIU X Y, FAN Y N, LIU P, et al. Characteristics of heavy metals pollution in farmland soil of the Yangtze River economic belt based on bibliometric analysis[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 1-16(in Chinese).
[26] 徐志豪, 吴健, 唐浩, 等. 崇明岛农田土壤重金属分布特征及生态风险[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2022,41(11):2488-2496. XU Z H, WU J, TANG H, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metals in soil of arable land on Chongming Island[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2022,41(11):2488-2496(in Chinese).
[27] 崔艳红, 孙鹏, 曹冬梅, 等. 松嫩平原产油区农田土壤重金属含量及污染风险评价 [J]. 土壤通报, 2022, 53(5): 1-12. CUI Y H, SUN P, CAO D M, et al. Analysis of heavy metal contents and pollution risk assessment in farmland soil in oil producing areas on Songnen Plain [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2022, 53(5): 1-12(in Chinese).
[28] 何腾兵, 黄会前, 付天岭, 等. 施用10年猪粪肥的黄壤剖面重金属分布及风险评价 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2018, 18(2): 789-794. HE T B, HUANG H Q, FU T L, et al. Analysis of the heavy metal risk content rate through the vertical profile of the yellow soil a decade late due to the swine manure application [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2018, 18(2): 789-794(in Chinese).
[29] 李融. 闽西中堡银多金属矿区周边农田土壤剖面重金属分布及其评价 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(31): 237-241. LI R. Distribution and evaluation of heavy metals in soil profiles in agricultural fields around Zhongbao silver polymetallic mining in Western Fujian [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(31): 237-241(in Chinese).
[30] 史锐, 岳荣, 张红. 有色金属采选冶基地周边土壤中重金属纵向分层研究 [J]. 土壤通报, 2016, 47(1): 186-191. SHI R, YUE R, ZHANG H. Research on vertical distribution of heavy metal in soil around non-ferrous metal industry area [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(1): 186-191(in Chinese).
[31] 杨军, 郑袁明, 陈同斌, 等. 中水灌溉下重金属在土壤中的垂直迁移及其对地下水的污染风险 [J]. 地理研究, 2006, 25(3): 449-456. YANG J, ZHENG Y M, CHEN T B, et al. Leaching of heavy metals in soil column under irrigation reclaimed water: A simulation experiment [J]. Geographical Research, 2006, 25(3): 449-456(in Chinese).
[32] 郑顺安. 我国典型农田土壤中重金属的转化与迁移特征研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2010. ZHENG S A. Studies on the transformation and transport of heavy metals in typical Chinese agricultural soils[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2010(in Chinese).
[33] ZHANG M, WANG X P, LIU C, et al. Identification of the heavy metal pollution sources in the rhizosphere soil of farmland irrigated by the Yellow River using PMF analysis combined with multiple analysis methods—using Zhongwei City, Ningxia, as an example [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(14): 16203-16214. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-07986-z [34] WU J, LI J, TENG Y G, et al. A partition computing-based positive matrix factorization (PC-PMF) approach for the source apportionment of agricultural soil heavy metal contents and associated health risks [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 388: 121766. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121766 [35] CHAI L, WANG Y H, WANG X, et al. Quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil and associated model uncertainty [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 215: 112150. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112150 [36] 贺灵, 吴超, 曾道明, 等. 中国西南典型地质背景区土壤重金属分布及生态风险特征 [J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(3): 384-396. HE L, WU C, ZENG D M, et al. Distribution of heavy metals and ecological risk of soils in the typical geological background region of southwest China [J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(3): 384-396(in Chinese).
[37] 姜寒冰, 姜常义, 钱壮志, 等. 云南峨眉山高钛和低钛玄武岩的岩石成因 [J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(5): 1117-1134. JIANG H B, JIANG C Y, QIAN Z Z, et al. Petrogenesis of high-Ti and low-Ti basalts in Emeishan, Yunnan, China [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(5): 1117-1134(in Chinese).
[38] 胡瑞忠, 陶琰, 钟宏, 等. 地幔柱成矿系统: 以峨眉山地幔柱为例 [J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(1): 42-54. HU R Z, TAO Y, ZHONG H, et al. Mineralization systems of a mantle plume: A case study from the Emeishan igneous Province, southwest China [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(1): 42-54(in Chinese).
[39] LIU Y B, MA Z H, LIU G N, et al. Accumulation risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in different types of farmland in a typical farming area of Northern China [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2021, 43(12): 5177-5194. doi: 10.1007/s10653-021-01002-0 [40] 柴磊, 王新, 马良, 等. 基于PMF模型的兰州耕地土壤重金属来源解析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(9): 3919-3929. CHAI L, WANG X, MA L, et al. Sources appointment of heavy metals in cultivated soils of Lanzhou based on PMF models [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(9): 3919-3929(in Chinese).
[41] PARDYJAK E R, SPECKART S O, YIN F, et al. Near source deposition of vehicle generated fugitive dust on vegetation and buildings: Model development and theory [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42(26): 6442-6452. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.04.024 [42] WU Q M, HU W Y, WANG H F, et al. Spatial distribution, ecological risk and sources of heavy metals in soils from a typical economic development area, Southeastern China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 780: 146557. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146557 [43] 宋波, 张云霞, 庞瑞, 等. 广西西江流域农田土壤重金属含量特征及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(9): 4317-4326. SONG B, ZHANG Y X, PANG R, et al. Analysis of characteristics and sources of heavy metals in farmland soils in the Xijiang River draining of Guangxi [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(9): 4317-4326(in Chinese).
[44] NANOS N, RODRÍGUEZ MARTÍN J A. Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in soils: Spatial variability in the Duero River Basin (Spain) [J]. Geoderma, 2012, 189-190: 554-562. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.06.006 [45] 张爱国, 魏兴萍. 西南典型岩溶槽谷土壤重金属污染与来源解析 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(12): 166-176. ZHANG A G, WEI X P. Pollution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils of typical Karst troughs in southwestern China [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(12): 166-176(in Chinese).
[46] 张云芸. 基于海量文献的中国农田土壤重金属镉的时空分布及风险评价[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2019. ZHANG Y Y. Temporal and spatial distribution and risk assessment of cadmium in farmland soils in China based on bibliometrics[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University, 2019(in Chinese).
[47] NING C C, GAO P D, WANG B Q, et al. Impacts of chemical fertilizer reduction and organic amendments supplementation on soil nutrient, enzyme activity and heavy metal content [J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2017, 16(8): 1819-1831. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61476-4 [48] 曾庆庆, 付天岭, 邹洪琴, 等. 贵州省某县辣椒种植区土壤重金属空间分布特征及来源解析 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(1): 102-113. ZENG Q Q, FU T L, ZOU H Q, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in soil in a pepper growing area of County in Guizhou Province, China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(1): 102-113(in Chinese).
[49] RAJMOHAN N, PRATHAPAR S A, JAYAPRAKASH M, et al. Vertical distribution of heavy metals in soil profile in a seasonally waterlogging agriculture field in Eastern Ganges Basin [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2014, 186(9): 5411-5427. doi: 10.1007/s10661-014-3790-x [50] 马晓慧, 郝春明, 王梦露, 等. 峰峰煤矿塌陷区典型农田土壤剖面重金素元素化学风化规律 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(3): 1202-1210. MA X H, HAO C M, WANG M L, et al. Chemical weathering law of heavy metal element in typical farmland soil profile in subsidence area of Fengfeng coal mine [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(3): 1202-1210(in Chinese).
[51] 黄卫, 庄荣浩, 刘辉, 等. 农田土壤镉污染现状与治理方法研究进展 [J]. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报, 2022, 45(1): 49-56. doi: 10.7612/j.issn.1000-2537.2022.1.hnsfdx-zr202201006 HUANG W, ZHUANG R H, LIU H, et al. Recent advances of the current situation and remediation methods of cadmium contamination in paddy soil [J]. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University, 2022, 45(1): 49-56(in Chinese). doi: 10.7612/j.issn.1000-2537.2022.1.hnsfdx-zr202201006
[52] RUBY M V, LOWNEY Y W. Selective soil particle adherence to hands: Implications for understanding oral exposure to soil contaminants [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(23): 12759-12771. [53] WANG K, MA J Y, LI M Y, et al. Mechanisms of Cd and Cu induced toxicity in human gastric epithelial cells: Oxidative stress, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 756: 143951. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143951 [54] 陈瑜佳, 屈星辰, 张斌, 等. 香河县农田土壤重金属污染生态与健康风险评价[J] . 环境科学, 2022, 43(12): 5728-5741. CHEN Y J, QU X C, ZHANG B, et al. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil of Xianghe County[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(12): 5728-5741(in Chinese).
-







 下载:
下载: