-
近些年来,畜禽养殖业繁荣发展,极大地提高了国民经济总值,确保了我国人口对肉类食品的需求. 抗生素在预防和治疗动物疫病、促进动物生长、保障畜牧业发展方面起到了重大作用,但抗生素违规超量滥用现象相当严重,农业农村部2018年开展了兽用抗菌药使用减量化行动、2020年修订发布了《食品动物中禁止使用的药品及其他化合物清单》[1]. 相关研究发现,抗生素被生命体吸收的能力有限,60%—90%抗生素以原药或代谢物的形式随动物粪便排出体外[2]. 抗生素作为一种“新污染物”,可通过畜禽粪便-有机粪肥-土壤-植物体系接续传递,进入不同的环境介质造成环境污染问题[3-5]. 抗生素具有强持久性、生物活性、生物积累性和缓慢生物降解性等特点,对生态环境和人类健康造成了巨大威胁,同时还严重制约了农业农村和环境生态的可持续发展[6-8]. 在“绿色经济可持续发展”理念的影响下,粪肥资源化是当前粪污处理的主要方式,能有效避免环境污染,同时缓解能源短缺问题[9].
我国畜禽粪肥中抗生素残留种类繁多,常见的抗生素种类有磺胺类、四环素类、喹诺酮类和大环内酯类[10-11]. 畜禽粪便中抗生素分析的前处理方法较为复杂,常用的提取技术有固液振荡提取、超声提取和加压溶剂萃取法等,其中提取溶剂的种类、体积、时间等对提取效果影响显著;常见的净化技术是固相萃取法,能有效地降低背景干扰、提高灵敏度[12-14]. 抗生素残留的主要检测方法有液相色谱法、液相色谱-串联质谱法、酶联免疫法、微生物抑制法等[15-19]. 鉴于当前畜禽粪便中抗生素的污染现状,很多适用于复杂环境基质中的抗生素联合检测方法已经被开发. 戴晓虎等[20]建立了基于固相萃取及高效液相色谱-荧光检测分析污泥中氟喹诺酮类抗生素的方法. 李涛等[19]建立了基于分散固相萃取-超高效液相色谱串联质谱法测定沉积物中大环内酯类抗生素的方法. 柴玉峰等[21]通过液相色谱-串联质谱法建立了猪粪中21种常见抗生素的同步提取检测方法. 从精确度和准确性来讲,液相色谱-串联质谱法是畜禽粪便中抗生素检测的首选方法[22-23]. 近年来,鸡粪中抗生素检测方法报道较少,吴丹等[24]探索了超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法检测鸡粪中16种残留抗生素,但回收率相对偏低(56.4%—94.6%). 刘博等[25]研究了高效液相色谱-荧光检测法同时分析鸡粪中6种氟喹诺酮类抗生素,检出限(0.002—0.022 mg·kg‒1)和定量限(0.0068—0.074 mg·kg‒1)均偏高,目前亟待建立通用且高效的抗生素检测方法. 本研究基于固相萃取-高效液相色谱串联质谱法同时测定鸡粪中27种典型抗生素,该方法具有较高的回收率、较低的检测限和定量限,适合畜禽粪便中多种抗生素的分析,为复杂环境介质中抗生素环境风险监测提供方法支撑.
-
超高效液相色谱-串联质谱联用仪(UPLC-MS/MS,Waters公司),UMV-2型多管漩涡混合器(北京优晟联合科技有限公司),KQ-500E型超声波清洗器(昆山市超声仪器有限公司),H1850型台式高速离心机(湖南湘仪仪器实验开发有限公司),ZLS-2型赫西真空离心浓缩仪(湖南赫西仪器装备有限公司),Master-S30UV型纯水仪(上海和泰仪器有限公司),ME155DU型万分之一电子天平(Mettler Toledo公司).
-
磺胺类抗生素标准品:磺胺吡啶(Sulfapyridine,SPY,99.9%)、磺胺嘧啶(Sulfadiazine,SD,99.9%)、磺胺甲基异恶唑(Sulfamethoxazole,SMZ,99.9%)、磺胺噻唑(Sulfathiazole,STZ,99.9%)、磺胺甲基嘧啶(Sulfamerazine,SMR,99.5%)、磺胺二甲唑(Sulfamoxole,SMOX,98.0%)、磺胺二甲异唑(Sulfisoxazole,SSX,99.9%)、磺胺甲噻二唑(Sulfamethizole,SML, 99.9%)、磺胺二甲嘧啶(Sulfamethazine,SMN, 99.9%)、磺胺间甲氧嘧啶(Sulfamonomethoxine,SMM,98.4%)、磺胺喹恶啉(Sulfaquinoxaline,SQ,99.8%)、磺胺邻二甲氧嘧啶(Sulfadoxine,SFD,98.6%);
喹诺酮类抗生素标准品:诺氟沙星(Norfloxacin,NOR,99.8%)、环丙沙星(Ciprofloxacin,CIP,98.0%)、洛美沙星(Lomefloxacin,LOM,99.8%)、达氟沙星(Danofloxacin,DAN,99.9%)、恩诺沙星(Enrofloxacin,ENR,99.9%)、氧氟沙星(Ofloxacin,OFX,99.9%)、氟罗沙星(Fleroxacin,FLE,99.9%)、双氟沙星(Difloxacin,DIF,99.9%);
四环素类抗生素标准品:甲烯土霉素(Methacycline,MC,98.4%)、多西环素(Doxycycline,DC,92.4%)、土霉素(Oxytetracycline,OTC,93.8%)、金霉素(Chlortetracycline,CTC,81.7%)、四环素(Tetracycline,TC,96.3%);
大环内酯类抗生素标准品:罗红霉素(Roxithromycin,RTM,94.7%)、泰乐菌素(Tylosin,TYL,98.8%). 均购自天津阿尔塔科技有限公司.
试剂材料:色谱纯甲醇、乙腈,购自霍尼韦尔(中国)有限公司;分析纯乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA,≥ 98%),购自上海韶远试剂有限公司;分析纯柠檬酸(≥ 99.5%)、磷酸二氢钠(≥ 99.0%),购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司;甲酸(88%),购自赛默飞世尔科技有限公司;浓硫酸(95.0%—98.0%),购自北京化工厂有限公司;Oasis® HLB固相萃取柱(6 mL/200 mg),购自Waters公司;Filter Unit PTFE滤膜(0.22 μm和0.45 μm),购自北京锐锋同创分析仪器有限公司.
-
标准储备液配置:分别准确称取1.0 mg的磺胺类、喹诺酮类、四环素类和大环内酯类标准品于10 mL容量瓶中,用甲醇定容至10 mL,配置成100 mg·L‒1单标储备液. 分别移取1.0 mL的27种抗生素100 mg·L‒1单标储备液于100 mL容量瓶中,用甲醇定容至100 mL,配置成1.0 mg·L‒1 的混合标准溶液. 单标及混标溶液均放置于−20 ℃保存.
标准溶液配置:以乙腈和0.1%甲酸水混合溶液(V/V,5/95)逐级稀释标准储备液,配置1、2、5、10、20、50、100、200、500 μg·L‒1标准溶液.
-
色谱条件:Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3色谱柱(2.1 mm×50 mm,1.8 μm),柱温40 ℃,流速0.3 mL·min‒1,进样量5 μL,流动相为乙腈(A)和0.1%甲酸水溶液(B),梯度洗脱程序如表1所示.
质谱条件:电喷雾离子源(ESI),正离子模式,毛细管电压 3.0 kV,脱溶剂气(N2)流速700 L·h‒1,锥孔气(N2)流速50 L·h‒1,脱溶剂气温度400 ℃,离子源温度150 ℃,多反应监测(MRM)模式检测,27种抗生素质谱参数如表2所示.
-
鸡粪样品采集于北京顺义区集约化雏鸡养殖场,样品采集后在实验室‒20 ℃冷冻保存. 鸡粪常规理化指标为全氮4.00%、全磷2.84%、全钾2.78%和总有机碳34.3%. 参考吴丹等[24]及廖杰等[26]的分析方法,准确称取1.0 g鸡粪样品于50 mL离心管中,加入10 mL乙腈/ pH 3磷酸-柠檬酸混合液(V/V,5/5,pH = 3)及0.6 g EDTA,涡旋10 min后超声10 min,以10000 r·min‒1高速离心5 min后收集上清液,重复提取3次,合并提取液. 移取上清3 mL过0.45 μm PTFE滤膜,超纯水稀释至40 mL,用5 mol·L−1硫酸溶液调节至pH = 2.5,待净化. HLB固相萃取柱使用前依次用6 mL甲醇、超纯水、pH = 2.5的水溶液活化,将提取液以1 mL·min‒1流速上样,用3 mL甲醇洗脱2次,收集洗脱液用真空离心浓缩仪浓缩干燥,最后用1 mL的乙腈/0.1%甲酸水溶液(V/V,5/95)定容,过0.22 μm PTFE滤膜后待测.
-
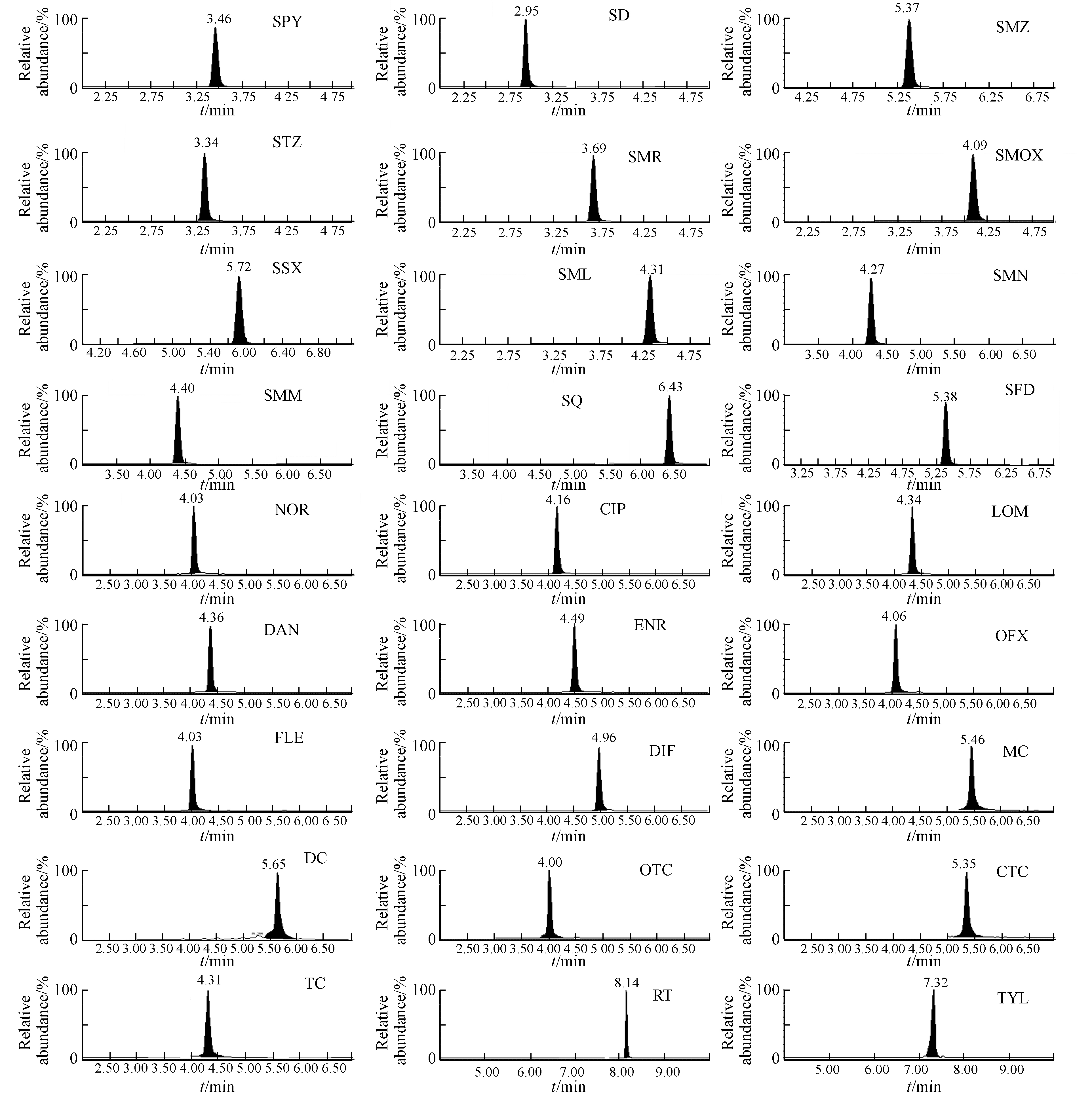
对比甲醇-水、甲醇-0.1%甲酸水溶液、乙腈-水、乙腈-0.1%甲酸水溶液作为流动相进行色谱分析,发现使用乙腈-甲酸水溶液作为流动相时,抗生素的色谱峰较窄,基线噪音较小,响应更高. 已有研究结果证明乙腈作为流动相时,柱效明显提升[19]. 流动相采用梯度洗脱,色谱峰分离度更优. 抗生素的标准溶液通过针泵进入离子源,进行全扫描和子离子扫描,确定定性和定量离子对,优化锥孔电压和碰撞能,27种抗生素的质谱参数见表2,27种抗生素的定量离子色谱图如图1所示.
-
本研究选取了4类抗生素中10种典型抗生素(4种磺胺类抗生素、3种喹诺酮类抗生素、2种四环素类抗生素和1种大环内酯类)抗生素为提取目标物,考察了涡旋、超声、未添加EDTA及涡旋+超声+EDTA等4种不同提取方式对抗生素添加回收率的影响. 如图2所示,使用乙腈/磷酸-柠檬酸混合液作为提取液,在涡旋、超声、未添加EDTA及涡旋+超声+EDTA对应的条件下,鸡粪中10种典型抗生素(100 μg·L‒1)的回收率分别为(6.7 ± 0.8)%—(84.2 ± 3.1)%、(5.7 ± 0.5)%—(71.4 ± 2.6)%、(6.0 ± 0.8)%—(70.7 ± 3.3)%和(70.5 ± 3.1)%—(111.3 ± 9.4)%. 以TC为例,在涡旋和超声条件下,TC的回收率较好分别为(84.2 ± 3.1)%和(71.4 ± 2.6)%,未添加EDTA的条件下,TC的回收率仅为(36.4 ± 1.9)%,添加EDTA且涡旋和超声的条件下,TC的回收率为(96.2 ± 3.5)%. 由此说明,提取液中添加EDTA能有效增加抗生素的回收率,涡旋和超声都有利于抗生素的提取.
-
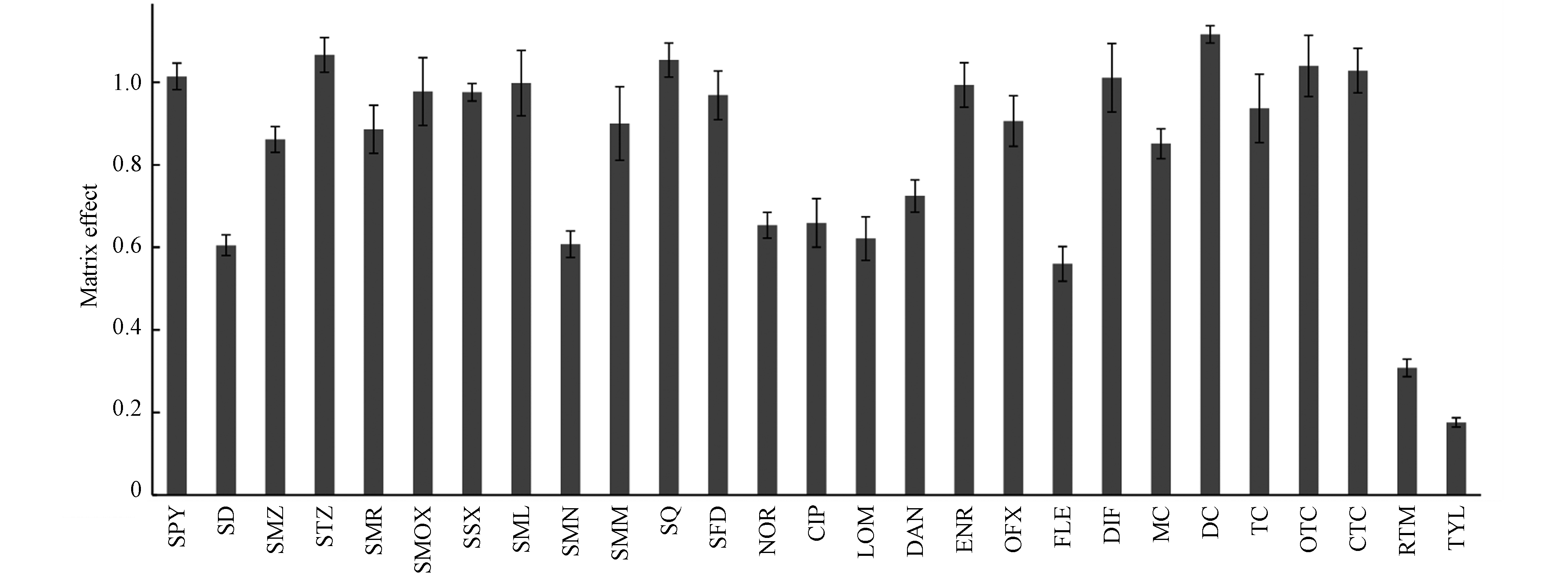
分析纯溶剂和提取液中100 μg·L‒1的抗生素混标的响应值,评估基质效应(matrix effect,ME),ME为样品基质中添加相同含量分析物的响应值/纯溶剂中分析物的响应值,结果如图3所示. ME < 1为基质抑制作用,ME > 1为基质增强作用,0.8 < ME < 1.2为弱基质作用. 其中,9种抗生素SD、SMN、NOR、CIP、LOM、DAN、FLE、RTM和TYL的ME在(0.17 ± 0.01)—(0.72 ± 0.04)之间,为强基质作用;其他18种抗生素的ME在(0.85 ± 0.04)—(1.1 ± 0.02)之间,为弱基质作用. 为满足快速准确的分析要求,本方法采用基质标准曲线进行定量分析.
-
经UPLC-MS/MS检测基质标准溶液后,以抗生素的质量浓度为横坐标,峰面积为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线. 如表3所示,27种抗生素在1—500 μg·L‒1范围内,回归方程的r均大于0.994,线性关系良好. 分别以3倍和10倍信噪比计算方法的检出限和定量限,27种抗生素的检出限为0.1—0.8 μg·kg‒1和0.3—2.7 μg·kg‒1.
-
在空白鸡粪样品中分别做50、100、500 μg·kg‒1 的3个浓度水平的添加回收试验,每个浓度水平做3个重复. 如表4所示,样品中12种磺胺类抗生素平均回收率为66.1%—107.6%,相对标准偏差(RSD)为2.3%—15.0%;样品中8种喹诺酮类抗生素平均回收率为68.2%—105.9%,RSD为3.1%—13.9%;样品中5种四环素类抗生素平均回收率为70.9%—99.8%,RSD为2.4%—13.1%;样品中2种大环内酯类抗生素平均回收率为72.6%—111.3%,RSD为5.4%—12.5%. 综上,样品中鸡粪中27种抗生素的平均回收率在66.1%—111.3%之间,RSD ≤ 15%,能满足鸡粪中抗生素分析方法的要求.
-
采集了4家规模化养鸡场的新鲜鸡粪样品,按照试验方法对样品进行检测分析,每个样品2个平行. 结果表明,4家养殖场的鸡粪中均有不同水平的抗生素检出,共检出16种,如表5所示. 其中,磺胺类抗生素检出3种(STZ、SMOX、SML),喹诺酮类抗生素检出8种(NOR、CIP、LOM、DAN、ENR、OFX、FLE、DIF),四环素类抗生素检出5种(MC、DC、TC、OTC、CTC). 磺胺类、喹诺酮类和四环素类抗生素的检出浓度分别为ND—28.1、ND—120.0和ND—4246.2 μg·kg‒1,部分鸡粪样品中OTC的残余含量达mg·kg‒1级,与沈聪等[27]检测结果一致. 由此推测,养鸡场较为常用的抗生素种类为喹诺酮类和四环素类抗生素. 该结果表明,该方法可用于鸡粪中多种抗生素的同时检测.
-
本文基于固相萃取-超高效液相色谱串联质谱法对复杂鸡粪基质中27种抗生素的同步分析检测方法进行探索与研究. 检测结果表明,12种磺胺类抗生素、8种喹诺酮类抗生素、5种四环素类抗生素和2种大环内酯类抗生素在1—500 μg·L‒1范围内线性关系良好(r > 0.994),检出限和定量限分别为0.1—0.8 μg·kg‒1和0.3—2.7 μg·kg‒1,平均添加回收率在66.1%—111.3%之间,相对标准偏差在2.3%—15.0%之间. 通过分析检测4家规模化养鸡场场的鸡粪样品,共检出16种抗生素,磺胺类、喹诺酮类和四环素类抗生素的检出浓度分别为ND—28.1、ND—120.0和ND—4246.2 μg·kg‒1,其中部分鸡粪样品中OTC的残余含量达mg·kg‒1级,由此推测喹诺酮类和四环素类为鸡场较为常用的抗生素种类. 以上研究表明,该方法精密度高、重现性好、操作较为便捷,能满足鸡粪中多种抗生素的定量分析要求.
固相萃取-超高效液相色谱串联质谱同时测定鸡粪中27种抗生素
Simultaneous determination of 27 antibiotics in chicken manure based on solid phase extraction and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
-
摘要: 基于固相萃取-超高效液相色谱串联质谱建立同时检测鸡粪中27种抗生素(12种磺胺类抗生素、8种喹诺酮类抗生素、5种四环素类抗生素和2种大环内酯类抗生素)的分析方法. 样品中加入乙腈/磷酸-柠檬酸混合液及乙二胺四乙酸,经涡旋和超声提取,HLB固相萃取柱净化,采用高效液相色谱串联质谱测定. 结果表明,27种抗生素在1—500 μg·L‒1范围内线性关系良好,相关系数r均大于0.994,检出限和定量限分别为0.1—0.8 μg·kg‒1和0.3—2.7 μg∙kg‒1. 在50、100、500 μg·kg‒1的3个添加水平条件下,27种抗生素的平均回收率在66.1%—111.3%之间,相对标准偏差在2.3%—15.0%之间. 采集4家养鸡场的鸡粪样品进行验证分析,发现鸡粪样中磺胺类、喹诺酮类和四环素类抗生素的检出浓度分别为未检出ND—28.1、ND—120.0、ND—4246.2 μg·kg‒1. 由此表明,该方法可用于鸡粪中多种抗生素的同时检测.
-
关键词:
- 抗生素 /
- 鸡粪 /
- 固相萃取 /
- 超高效液相色谱串联质谱.
Abstract: Simultaneous determination of 27 antibiotics (i.e., 12 sulfonamides, 8 quinolones, 5 tetracyclines and 2 macrolides) in chicken manure was investigated based on solid phase extraction (SPE) and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). The samples were extracted by acetonitrile/phosphoric acid-citric acid mixture solution and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid with the vortex and ultrasonic method, purified by HLB SPE cartridge, determined by UPLC-MS/MS. The results showed that linear relationship of 27 antibiotics in the range of 1—500 μg·L‒1 was good with the correlation coefficient greater than 0.994. The limit of detection and quantitation of 27 antibiotics in the present method were 0.1—0.8 μg·kg‒1 and 0.3—2.7 μg·kg‒1, respectively. At three spiked levels (i.e., 50, 100, 500 μg·kg‒1), average recoveries of 27 antibiotics in chicken manure were in the range of 66.1%—111.3% with relative standard deviations of 2.3%—15.0%. Chicken manure samples from four chicken farms were collected for verification and analysis. It was found that the concentrations of sulfonamides, quinolones, and tetracyclines were in the range of ND (Not detected)—28.1, ND—120.0 and ND—4246.2 μg·kg‒1, respectively. The results illustrate that the established method can be used for simultaneous detection of multiple antibiotics in chicken manure.-
Key words:
- antibiotics /
- chicken manure /
- SPE /
- UPLC-MS/MS.
-

-
表 1 液相色谱梯度洗脱程序
Table 1. Gradient elution procedure of liquid chromatography
时间/min
TimeA/%
AcetonitrileB/%
0.1% Formic acid water0.00 5.00 95.0 1.00 5.00 95.0 10.00 55.00 45.0 11.00 95.00 5.00 13.00 95.00 5.00 13.01 5.00 95.00 15.00 5.00 95.00 表 2 27种抗生素质谱参数
Table 2. Mass spectrum parameters of 27 antibiotics
序号
Number抗生素
Antibiotics母离子(m/z)
Parent ion子离子
(m/z)
Daughter ion锥孔电压/V
Cone voltage碰撞能/eV
Collision energy1 SPY 249.90 107.97*/155.96 34 24/14 2 SD 251.15 92.10*/156.09 4 26/14 3 SMZ 253.89 107.91*/155.97 30 20/16 4 STZ 255.92 100.88*/107.97 28 16/24 5 SMR 264.97 110.43*/155.95 36 22/14 6 SMOX 267.97 107.97*/112.91 32 22/18 7 SSX 267.97 107.97*/112.91 28 22/14 8 SML 270.86 107.96*/115.90 64 24/18 9 SMN 278.92 107.90*/124.02 36 28/20 10 SMM 280.90 107.97*/125.98 38 24/18 11 SQ 300.91 107.97*/155.95 38 24/14 12 SFD 310.91 107.96*/155.95 36 26/18 13 NOR 320.04 233.00*/276.05 40 22/16 14 CIP 331.99 245.02*/288.06 20 24/16 15 LOM 351.95 265.04*/308.02 42 22/16 16 DAN 357.97 283.03*/314.04 26 24/16 17 ENR 360.04 316.11*/342.05 26 16/20 18 OFX 362.01 204.96*/261.07 40 40/26 19 FLE 369.93 268.99*/326.07 20 26/20 20 DIF 399.99 299.04*/356.06 26 28/20 21 MC 443.01 200.93*/266.98 30 36/24 22 DC 445.20 154.10*/428.20 36 16/26 23 TC 445.30 153.70*/410.20 30 30/20 24 OTC 461.30 426.20*/444.20 35 20/30 25 CTC 478.89 153.98*/443.94 28 38/20 26 RTM 837.20 115.90*/158.02 52 48/38 27 TYL 916.27 100.88*/115.83 60 52/70 注:“*”为定量离子. Note: “*” refer to “the quantitative ion”. 表 3 27种抗生素的线性关系、检出限和定量限
Table 3. Linear relationship, limits of detection (LOD) and limits of quantitation (LOQ) of 27 antibiotics
序号
Number抗生素
Antibiotics回归方程(r)
Linear equation (r)检出限/(μg·kg‒1)
LOD定量限/(μg·kg‒1)
LOQ1 SPY y = 258.5x + 2255(0.9986) 0.2 0.7 2 SD y = 132.7x + 702.8(0.9994) 0.5 1.4 3 SMZ y = 186.3x + 308.2(0.9994) 0.6 2.1 4 STZ y = 266.7x + 1311(0.9992) 0.1 0.3 5 SMR y = 182.7x + 418.4(0.9981) 0.3 1.0 6 SMOX y = 368.9x + 1672(0.9990) 0.3 1.0 7 SSX y = 342.6x + 851.9(0.9997) 0.5 1.5 8 SML y = 85.92x - 49.03(0.9980) 0.3 1.0 9 SMN y = 380.2x + 3330(0.9980) 0.3 1.0 10 SMM y = 0.9222x + 7.680(0.9980) 0.3 1.0 11 SQ y = 249.6x + 227.1(0.9997) 0.2 0.7 12 SFD y = 0.9193x + 7.973(0.9963) 0.1 0.4 13 NOR y = 88.56x + 130.1(0.9980) 0.3 1.0 14 CIP y = 75.69x + 437.5(0.9975) 0.4 1.3 15 LOM y = 151.26x - 104.1(0.9989) 0.5 1.8 16 DAN y = 90.23x - 40.14(0.9966) 0.8 2.7 17 ENR y = 151.1x - 195.8(0.9992) 0.1 0.4 18 OFX y = 176.6x - 317.4(0.9991) 0.1 0.4 19 FLE y = 83.64x - 129.9(0.9971) 0.3 1.0 20 DIF y = 123.4x - 229.6(0.9993) 0.1 0.3 21 MC y = 132.0x + 549.8(0.9981) 0.7 2.1 22 DC y = 51.01x - 434.8(0.9948) 0.2 0.7 23 TC y = 55.56x + 481.7(0.9958) 0.8 2.5 24 OTC y = 38.64x + 83.32(0.9983) 0.5 1.6 25 CTC y = 40.74x + 450.1(0.9943) 0.7 2.3 26 RTM y = 84.52x - 165.6(0.9995) 0.6 1.9 27 TYL y = 159.3x - 147.2(0.9999) 0.4 1.3 表 4 鸡粪中27种抗生素的添加回收率与相对标准偏差
Table 4. Recoveries and relative standard deviation (RSDs) of 27 antibiotics in chicken manure
序号
Number抗生素
Antibiotics回收率(相对标准偏差) /%
Recovery (RSDs)50 μg·kg‒1 100 μg·kg‒1 500 μg·kg‒1 1 SPY 76.0 (15.0) 82.5 (7.5) 75.7 (4.1) 2 SD 82.1 (5.6) 71.6 (4.6) 72.0 (9.3) 3 SMZ 89.4 (2.3) 97.2 (9.2) 102.8 (9.5) 4 STZ 78.6 (8.1) 99.7 (4.4) 97.2 (8.1) 5 SMR 92.5 (3.2) 90.6 (5.7) 74.5 (2.4) 6 SMOX 107.6 (3.2) 101.1 (1.9) 103.6 (4.8) 7 SSX 74.0 (2.6) 77.9 (5.3) 103.8 (3.9) 8 SML 82.1 (3.3) 83.3 (5.3) 98.2 (3.9) 9 SMN 82.1 (5.3) 93.1 (2.8) 102.9 (2.8) 10 SMM 86.3 (2.3) 72.2 (4.7) 92.3 (4.5) 11 SQ 69.6 (2.7) 66.1 (4.5) 77.0 (9.8) 12 SFD 86.8 (5.8) 85.8 (3.4) 103.7 (6.4) 13 NOR 78.4 (12.8) 75.8 (6.6) 86.0 (9.8) 14 CIP 70.9 (8.1) 91.5 (6.7) 83.1 (5.0) 15 LOM 77.3 (11.8) 77.0 (3.3) 71.3 (6.7) 16 DAN 93.9(13.9) 105.9 (11.2) 73.4(9.7) 17 ENR 74.9 (9.8) 77.1 (3.1) 93.5 (5.9) 18 OFX 77.2 (7.3) 68.2 (4.2) 70.1 (6.2) 19 FLE 70.9 (10.2) 85.5 (11.4) 88.7 (3.7) 20 DIF 88.5 (13.3) 70.5 (4.4) 70.0 (6.7) 21 MC 70.9 (10.2) 85.5 (11.4) 88.7 (3.7) 22 DC 78.3 (7.1) 77.4 (13.1) 87.3 (4.4) 23 TC 99.8 (8.6) 81.5 (8.0) 98.1 (8.8) 24 OTC 98.7 (7.3) 96.2 (3.6) 84.4 (3.6) 25 CTC 78.2 (2.4) 84.0 (2.4) 71.5 (6.9) 26 RTM 108.8 (10.8) 111.3 (8.4) 108.1 (6.5) 27 TYL 86.7 (12.5) 72.6 (6.1) 86.2 (5.4) 表 5 4家不同养鸡场鸡粪中的抗生素含量
Table 5. Residues of antibiotics in chicken manure from four different chicken farms
序号
Number抗生素
Antibiotics检出浓度/ (μg·kg‒1)
Detected concentrations1 2 3 4 1 STZ ND* 0.9 ND ND 2 SMOX ND ND 0.5 ND 3 SML ND 28.1 ND ND 4 NOR 117.0 24.7 13.1 70.7 5 CIP 9.3 ND ND ND 6 LOM 2.9 1.2 0.8 ND 7 DAN 43.2 6.5 9.0 19.2 8 ENR 5.7 ND 1.3 12.9 9 OFX 120.0 ND ND ND 10 FLE 8.2 ND 2.2 ND 11 DIF 18.6 ND 21.0 26.1 12 MC 46.6 12.1 9.6 15.8 13 DC 132.5 13.5 ND 126.6 14 TC ND ND 5.7 5.7 15 OTC ND 15.4 99.1 4246.2 16 CTC ND 469.5 ND 1.1 注:“*”为未检出. Note: “*” refer to “not detected”. -
[1] 韦正峥, 向月皎, 郭云, 等. 国内外新污染物环境管理政策分析与建议 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(2): 443-451. WEI Z Z, XIANG Y J, GUO Y, et al. Analysis and suggestions of environmental management policies of new pollutants at home and abroad [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(2): 443-451(in Chinese).
[2] 潘伟, 刘辉, 艾华庭, 等. 畜禽粪便抗生素残留和控制策略的现状研究 [J]. 畜牧业环境, 2020(7): 8-10. PAN W, LIU H, AI H T, et al. Current status research of antibiotic residues and control strategies in livestock manure [J]. Animal Industry and Environment, 2020(7): 8-10(in Chinese).
[3] PAN M, CHU L M. Fate of antibiotics in soil and their uptake by edible crops [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 599/600: 500-512. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.214 [4] PAN M, WONG C K C, CHU L M. Distribution of antibiotics in wastewater-irrigated soils and their accumulation in vegetable crops in the Pearl River Delta, Southern China [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2014, 62(46): 11062-11069. doi: 10.1021/jf503850v [5] 王虹, 蒋卫杰, 余宏军, 等. 禽畜废弃物中的抗生素及其在蔬菜等农作物中的富集 [J]. 中国蔬菜, 2011(12): 10-15. WANG H, JIANG W J, YU H J, et al. Antibiotics in livestock wastes and its enrichment in vegetable crops [J]. China Vegetables, 2011(12): 10-15(in Chinese).
[6] HU Y A, CHENG H F. Health risk from veterinary antimicrobial use in China's food animal production and its reduction [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 219: 993-997. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.099 [7] MUHAMMAD J, KHAN S, SU J Q, et al. Antibiotics in poultry manure and their associated health issues: A systematic review [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2020, 20(1): 486-497. doi: 10.1007/s11368-019-02360-0 [8] ZHOU X, WANG J, LU C, et al. Antibiotics in animal manure and manure-based fertilizers: Occurrence and ecological risk assessment [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 255: 127006. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127006 [9] 罗俊丞, 罗娅君, 陈杨武, 等. 畜禽粪污资源化利用研究进展 [J]. 贵州农业科学, 2020, 48(5): 136-141. LUO J C, LUO Y J, CHEN Y W, et al. Research progress on utilization of livestock manure resources [J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(5): 136-141(in Chinese).
[10] 林辉, 马军伟, 孙万春, 等. 光照对畜禽粪便中抗生素降解和微生物的影响 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(1): 263-272. LIN H, MA J W, SUN W C, et al. Effect of light illumination on antibiotic degradation and microbial community in manure [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(1): 263-272(in Chinese).
[11] 段丽杰, 林丽红. 吉林省畜禽养殖场粪便中抗生素污染特征 [J]. 中国科技信息, 2022(6): 100-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8972.2022.06.032 DUAN L J, LIN L H. Pollution characteristics of antibiotics in feces of livestock and poultry farms in Jilin Province [J]. China Science and Technology Information, 2022(6): 100-102(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8972.2022.06.032
[12] 朱颖杰, 胡红美, 何鹏飞, 等. 环境样品中抗生素检测方法的研究进展 [J]. 环境科学与管理, 2022, 47(3): 127-129,134. ZHU Y J, HU H M, HE P F, et al. Research progress on detection methods for antibiotics in environmental samples [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2022, 47(3): 127-129,134(in Chinese).
[13] 张志超, 程和发. 环境介质中喹诺酮类抗生素的前处理与检测方法研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(1): 1-22. doi: 10.1002/etc.4337 ZHANG Z C, CHENG H F. Recent development in sample pretreatment and detection methods for the determination of quinolones in environmental matrices [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(1): 1-22(in Chinese). doi: 10.1002/etc.4337
[14] 张满成, 黄从建, 王未, 等. 环境样品中抗生素的预处理及检测分析 [J]. 环境保护科学, 2013, 39(2): 84-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2013.02.021 ZHANG M C, HUANG C J, WANG W, et al. Preconcentration and determination of antibiotics in environmental samples [J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2013, 39(2): 84-87(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2013.02.021
[15] 余佩瑶, 陈传胜, 刘寒冰, 等. 固相萃取-高效液相色谱法同时测定鸡粪中四环素类、喹诺酮类和磺胺类抗生素 [J]. 色谱, 2019, 37(5): 518-524. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2018.11006 YU P Y, CHEN C S, LIU H B, et al. Simultaneous determination of tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones, and sulfonamides in chicken manure using solid-phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography [J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2019, 37(5): 518-524(in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2018.11006
[16] 田野. 固相萃取-高效液相色谱串联质谱法同时测定有机肥料中13种抗生素残留 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2017(2): 162-168. TIAN Y. Simultaneous determination of 13 kinds of antibiotics residues in organic fertilizers by SPE-HPLC-MS/MS [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2017(2): 162-168(in Chinese).
[17] 庞昕瑞, 曾鸿鹄, 梁延鹏, 等. 固相萃取-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定地表水中10种磺胺类抗生素残留 [J]. 分析科学学报, 2019, 35(4): 461-466. doi: 10.2116/analsci.18N023 PANG X R, ZENG H H, LIANG Y P, et al. Determination of 10 sulfonamide antibiotics in surface water by solid phase extraction-ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Analytical Science, 2019, 35(4): 461-466(in Chinese). doi: 10.2116/analsci.18N023
[18] 胡钰, 朱青青, 胡立刚, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定土壤中30种抗生素 [J]. 色谱, 2021, 39(8): 878-888. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.02019 HU Y, ZHU Q Q, HU L G, et al. Simultaneous determination of 30 antibiotics in soil by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2021, 39(8): 878-888(in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.02019
[19] 李涛, 王策, 徐兆安, 等. 基于分散固相萃取-超高效液相色谱串联质谱法测定沉积物中大环内酯类抗生素 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(1): 231-240. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020081601 LI T, WANG C, XU Z A, et al. Determination of macrolide antibiotics in the sediment based on dispersed solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(1): 231-240(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020081601
[20] 戴晓虎, 薛勇刚, 刘华杰, 等. 基于固相萃取及高效液相色谱-荧光检测分析的污泥中氟喹诺酮类抗生素研究方法的开发 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(4): 1553-1561. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.04.047 DAI X H, XUE Y G, LIU H J, et al. Development of determination method of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in sludge based on solid phase extraction and HPLC-fluorescence detection analysis [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(4): 1553-1561(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.04.047
[21] 柴玉峰, 钟慧, 陈梅雪, 等. 猪粪中21种常见抗生素的同步提取检测方法研究及应用 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(4): 1252-1260. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020120602 CHAI Y F, ZHONG H, CHEN M X, et al. Research and application of detection method of simultaneous extraction and detection of 21 common antibiotics from pig manure [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(4): 1252-1260(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020120602
[22] 杨青, 田冶, 江志钦, 等. 液质联用技术在抗生素分析中的应用 [J]. 中国药物评价, 2022, 39(2): 113-118. YANG Q, TIAN Y, JIANG Z Q, et al. Application of liquid-mass spectrometry in antibiotic analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Drug Evaluation, 2022, 39(2): 113-118(in Chinese).
[23] 顾艳, 胡文彦, 杨军. 多肽类抗生素的最大残留限量标准分析与检测方法研究进展 [J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2021, 12(24): 9392-9398. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2021.24.spaqzljcjs202124011 GU Y, HU W Y, YANG J. Research progress on maximum residue limit standards and detection methods of polypeptide antibiotics [J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2021, 12(24): 9392-9398(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2021.24.spaqzljcjs202124011
[24] 吴丹, 韩梅琳, 邹德勋, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法检测鸡粪中16种残留抗生素 [J]. 分析化学, 2017, 45(9): 1389-1396. WU D, HAN M L, ZOU D X, et al. Ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of 16 kinds of residual antibiotics in chicken manure [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 45(9): 1389-1396(in Chinese).
[25] 刘博, 薛南冬, 杨兵, 等. 高效液相色谱-荧光检测法同时分析鸡粪中六种氟喹诺酮类抗生素 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(5): 1050-1056. LIU B, XUE N D, YANG B, et al. Simultaneous determination of six fluoroquinolones in chicken manures by high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(5): 1050-1056(in Chinese).
[26] 廖杰, 李青松. 测定13种抗生素的固相萃取-高效液相色谱串联质谱法优化与应用 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(5): 1538-1547. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022021302 LIAO J, LI Q S. Optimization and application of solid phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for determination of 13 antibiotics [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(5): 1538-1547(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022021302
[27] 沈聪, 张俊华, 刘吉利, 等. 宁夏养鸡场粪污和周边土壤中抗生素及抗生素抗性基因分布特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(8): 4166-4178. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202111088 SHEN C, ZHANG J H, LIU J L, et al. Distribution characteristics of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in manure and surrounding soil of poultry farm in Ningxia [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(8): 4166-4178(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202111088
-



 下载:
下载: