-
重金属废水具有重金属毒性大、稳定性强、难以降解等特性,吸附法是治理重金属废水经济高效的方法之一[1],制备比表面积高、吸附位点丰富、成本低的吸附材料一直是研究的热点,例如活性炭、矿物材料、纳米材料等均为常用的吸附剂[2-5]。这些吸附材料去除水中重金属的作用机制一直是研究难点和热点。 通常利用各种光谱技术,如X射线衍射(XRD)、红外光谱(FTIR)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)等进行研究[6-7],而基于各机制对重金属总吸附量贡献的研究十分缺乏,仅集中在生物炭吸附重金属方面[8-11]。例如,Wang等[8]较早地研究了Pb(Ⅱ)在花生壳和中药渣生物炭上的吸附机制的贡献,发现Pb(Ⅱ)与矿物组分的共沉淀作用是最主要贡献,占82.6%—85.6%;Su等[12]发现,水滑石/生物炭复合材料吸附水中Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)的主要贡献机制为沉淀作用,分别占76.26%和45.0%。张雪[13]研究发现,镁铝水滑石吸附水中Pb(Ⅱ)和Cd(Ⅱ)的主要贡献机制为络合作用,经聚乙二醇插层改性后,降低了络合作用的吸附量,显著提升了沉淀作用的贡献。
二维层状纳米材料因具有比表面积高、电子转移速度快、制备和剥离容易等优势而备受关注[14],水滑石和二硫化钼是其中的典型代表。水滑石,又被称为双金属氢氧化物(LDHs),由无数的带正电的主体层板和层间阴离子组成,具有独特的层状结构和化学组成的可调控性,已被广泛应用于吸附分离领域[15-19]。例如,毛方琪等[18]总结了水滑石在重金属污染土壤/水修复方面的研究进展,论述了材料结构与重金属去除效率之间的内在联系,阐述了水滑石在重金属污染修复领域具有良好的应用潜力以及面临的水滑石绿色化制备、回收再生利用、降低成本等方面的挑战。Shan等[20]采用共沉淀法制备了MgAl-CO3-LDH和磁性Fe3O4/MgAl-CO3-LDH,明确了其吸附水中Cd(Ⅱ)的沉淀、表面络合和表面吸附作用机制。二硫化钼(MoS2)属于一种典型的过渡金属硫化合物,已被应用于重金属吸附领域[21]。 例如,MoS2纳米片对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附量达740 mg·g−1,且具有选择性[22];在pH = 6时,对Ag(I)的吸附量高达4000 mg·g−1[23]. 但由S–Mo–S组成得的“三明治”状结构,使得MoS2易堆积而导致活性位点密度减少[24],因此制备复合材料是有效解决方法之一。例如,将MoS2纳米片分散到交联纤维素气凝胶中而得到的纳米复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)具有优异的吸附能力、快速的吸附动力学和很好的选择性,适用于复杂水体中Pb(Ⅱ)的净化[25]。
已有学者成功制备二硫化钼与水滑石的复合材料,并应用于光催化[26-28]、电催化析氧[29]、填料[30]和阻燃剂[31]等方面,但未见应用于去除水中重金属的研究。因此,为了进一步提升二维层状纳米材料吸附性能,并研究对重金属的作用机制及其贡献,本文制备并表征了二硫化钼-水滑石(MoS2-LDH)复合材料,选择Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cd(Ⅱ)作为典型重金属,研究了MoS2-LDH的吸附性能,重点进行了吸附机制研究,以期为高效去除重金属的二维层状纳米复合材料的设计合成提供理论支撑,并丰富界面吸附理论。
-
首先,采用共沉淀法制备MgAl-LDH。称取32.0 g硝酸镁和23.3 g硝酸铝,溶于100 mL蒸馏水中,记为溶液A。称取16.9 g氢氧化钠和13.32 g碳酸钠,用100 mL蒸馏水溶解,记为溶液B。在四颈烧瓶中倒入蒸馏水,逐滴加入溶液A和溶液B,在60 oC下连续搅拌12 h(转速150 r·min−1),始终保持pH值在10左右。反应后静置结晶6 h,将沉淀物离心、洗涤、80 oC下干燥,得到MgAl-LDH。
其次,采用水热法制备MoS2-LDH。将1.24 g钼酸铵和1.07 g硫脲溶于60 mL蒸馏水中,加入0.5 g的MgAl-LDH,磁力搅拌30 min让其混合均匀,转入高压反应釜,在200 oC反应12 h。最后,将得到的黑色固体沉淀用无水乙醇和去离子水洗涤后,置于80 oC烘箱中干燥12 h,得到MoS2-LDH. MoS2作为对照,采用上述方法合成,未加MgAl-LDH。
-
对吸附剂进行了扫描电镜(SEM,S4800,日本日立公司)、Zeta电位(ZS90,英国马尔文公司)、X射线衍射(XRD,D8,德国布鲁克公司)、红外光谱(FTIR,Vertex 70,德国布鲁克公司)和X光电子能谱(XPS,ESCALAB 250XI,美国赛默飞世尔公司)等分析。
-
采用批次平衡实验方法研究MoS2-LDH吸附水中Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)的性能。将0.05 g的MoS2-LDH和20 mL重金属溶液置于离心管中,在25 oC恒温振荡箱(速率为200 r·min−1)中进行反应,然后用离心机在8500 r·min−1的速度下分离得到上清液,采用原子吸收光谱仪(AA7000,日本岛津公司)测定重金属离子浓度,通过加入和吸附反应后测定的重金属浓度之间的差值计算吸附量和去除率。根据预实验结果,确定Cd(Ⅱ)初始浓度为100 mg·L−1、Cu(Ⅱ)和Pb(Ⅱ)为200 mg·L−1。对于pH影响实验,为防止重金属的沉淀,调节重金属初始溶液pH值为2—8(Pb(Ⅱ) < 6、Cu(Ⅱ) < 7、Cd(Ⅱ) < 8.5),然后进行吸附实验,反应时间为120 min(Pb(Ⅱ)、Cd(Ⅱ))和240 min(Cu(Ⅱ))。对于动力学实验,未调节重金属溶液的pH值(200 mg·L−1 Cu(Ⅱ)、100 mg·L−1 Cd(Ⅱ)和200 mg·L−1 Pb(Ⅱ)的初始pH分别为5.10、5.85、5.73),反应时间为0—360 min。吸附等温线的实验条件为:未调节重金属溶液的pH,反应时间分别为120 min(Pb(Ⅱ)、Cd(Ⅱ))和240 min(Cu(Ⅱ))。
-
收集吸附Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cd(Ⅱ)的MoS2-LDH材料,去离子水清洗一次,干燥后采用XRD、FTIR、Zeta电位测定仪和XPS对进行表征,研究MoS2-LDH与重金属的作用机制。然后采用顺序提取法对上述机制的贡献进行分析,具体步骤如下:
(1)物理吸附:在0.1 g吸附重金属后的MoS2-LDH中加入20 mL蒸馏水,振荡24 h,测定上清液中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cd(Ⅱ)的浓度,根据式(1)计算物理吸附的吸附量,简写为Qphy。
式中,c0、ce分别对应重金属的初始浓度及平衡溶液中的浓度(mg·L−1);V为解吸溶液(蒸馏水、乙酸钠、NaNO3)的体积(L);m为吸附剂的重量(g)。
(2)沉淀作用:完成步骤(1)后,加入20 mL 乙酸钠溶液(1 mol·L−1),振荡5 h,测定上清液重金属浓度,根据式(1)计算沉淀作用吸附量(Qpre)。
(3)静电吸引作用:完成步骤(2)后,加入20 mL NaNO3溶液(0.01 mol·L−1),反应24 h后测定重金属浓度,根据式(1)计算静电吸引作用吸附量(Qele)。
(4)同晶置换作用:测定吸附过程前后溶液中Mg(Ⅱ)浓度,根据其差值计算同晶置换的吸附量(Qsub)。
(5)络合反应:络合反应的吸附量(Qcom)通过总吸附量减去上述吸附作用的吸附量而得到。
最后,计算上述吸附机制的吸附量与总吸附量的比值,得到各吸附机制的贡献率。
-
分别采用拟一级动力学方程(式(2))、拟二级动力学方程(式(3))、Langmuir模型(式(4))和Freundlich模型(式(5))对吸附动力学和等温线数据进行计算,具体公式如下:
式中,qt和qe分别为t时刻(min)和平衡状态下MoS2-LDH对Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附量(mg·g−1);k1(min−1)和k2(mg·min−1·g−1)分别为拟一级和拟二级动力学方程的速率常数;ce为金属离子吸附平衡后的剩余浓度(mg·L−1);qm为Langmuir模型计算的理论吸附量;b是Langmuir等温线模型常数(L·mg−1);k和n为Freundlich等温线模型常数。
-
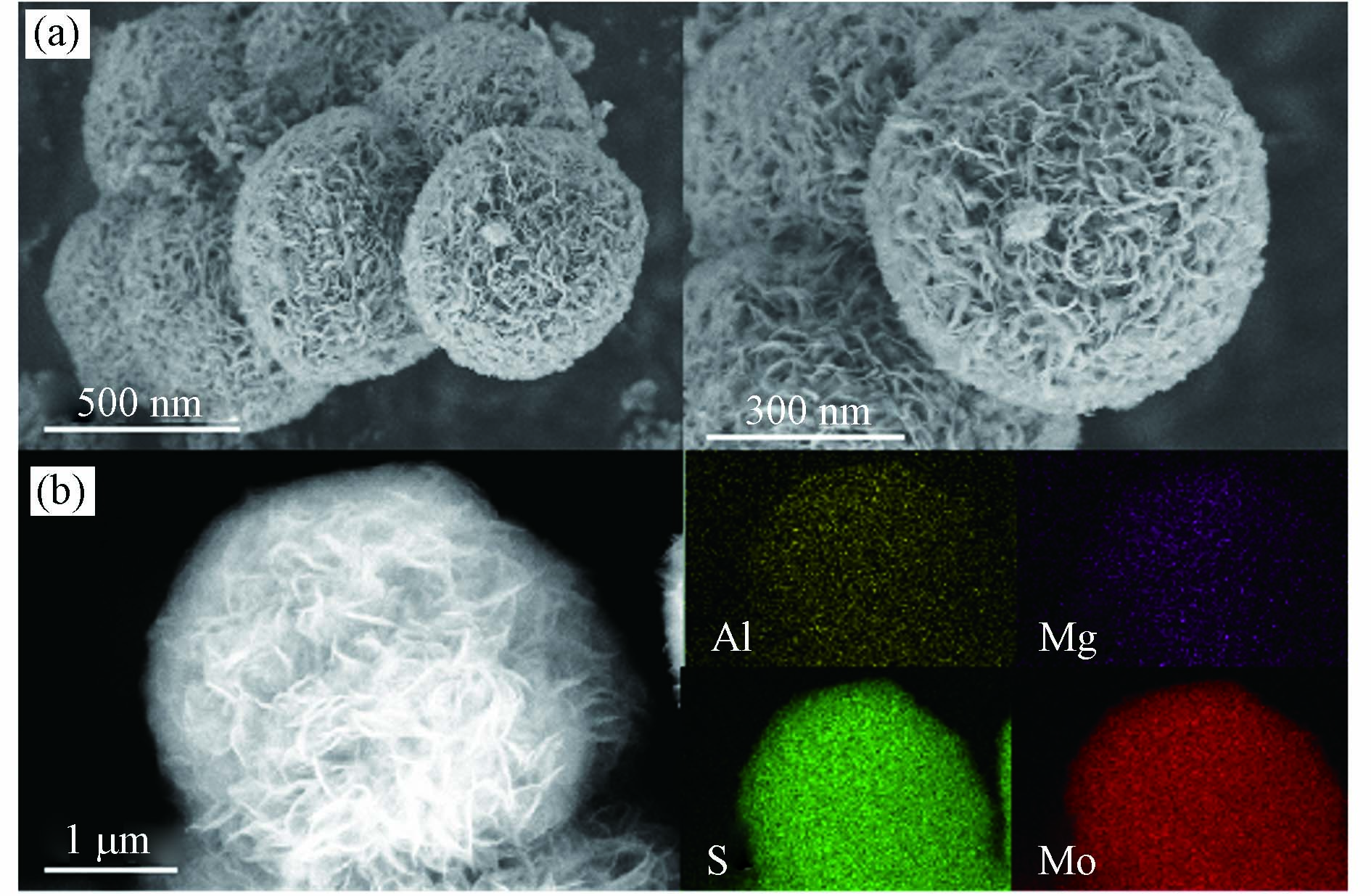
从图1可知,本实验制备的MoS2-LDH复合材料呈现出典型的花瓣状形貌特征,大量的纳米片堆积成球状,含有元素Mg、Al、Mo、S,并且均匀的分散在材料表面。
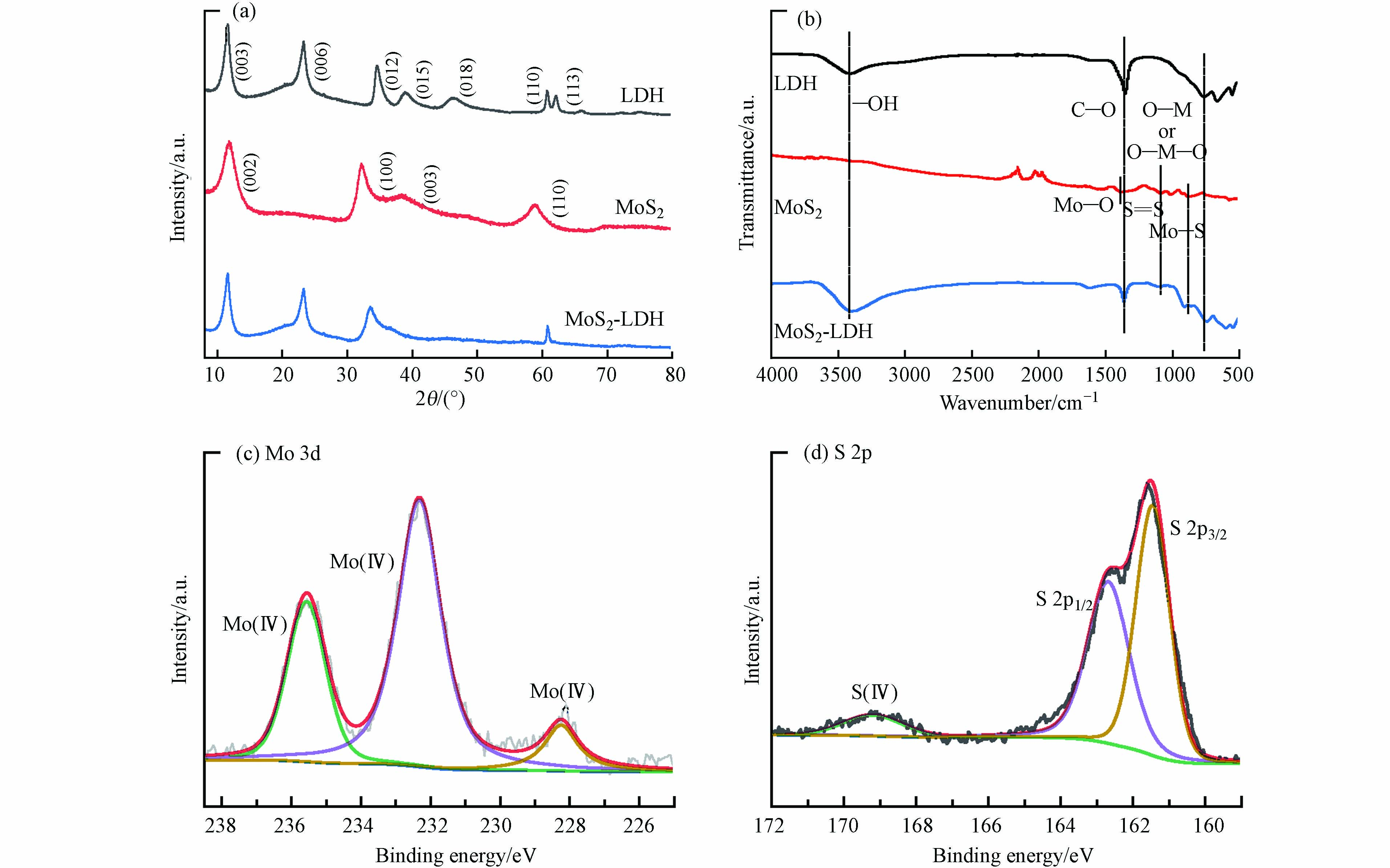
图2a为LDH、MoS2和MgAl-LDH的XRD图谱。MgAl-LDH中出现了7个尖锐的衍射峰,分别对应于(003)、(006)、(012)、(015)、(018)、(110)和(113)晶面[20]。
对于MoS2,在2θ = 14.53°、32.68°、39.54°和58.33°的衍射峰分别对应其基面(002)、(100)、(103)和(110)[32]。而在复合材料MoS2-LDH的光谱中观察到4个衍射峰,其中2θ = 11.53°、23.40°和60.97°的峰属于MgAl-LDH的(003)、(006)和(110)特征衍射峰,2θ = 33.29°的峰为MoS2的(100)晶面,说明MoS2-LDH材料成功制备且晶型较好。
如图2b,MgAl-LDH在3450 cm−1处的吸收带对应于层间水分子和表面的–OH拉伸振动,760 cm−1处的吸收峰对应于金属–氧的振动,1346 cm−1处存在C–O的振动伸缩[12]。MoS2中的吸收峰分别对应Mo–O、S=S和Mo–S[32]。在MoS2-LDH中均可以观察到相同的特征峰。进一步对MoS2-LDH进行了XPS表征,对于Mo 3d,在235.8 eV的为Mo(Ⅵ),232.2 eV和228.7 eV处的为Mo(Ⅳ)(图2c);S 1s图谱在169.2、162.7、161.4 eV处的3个峰分别对应着S(Ⅳ)、S 2p1/2以及S 2p3/2(图2d),这与文献报道的一致[12,32].
-
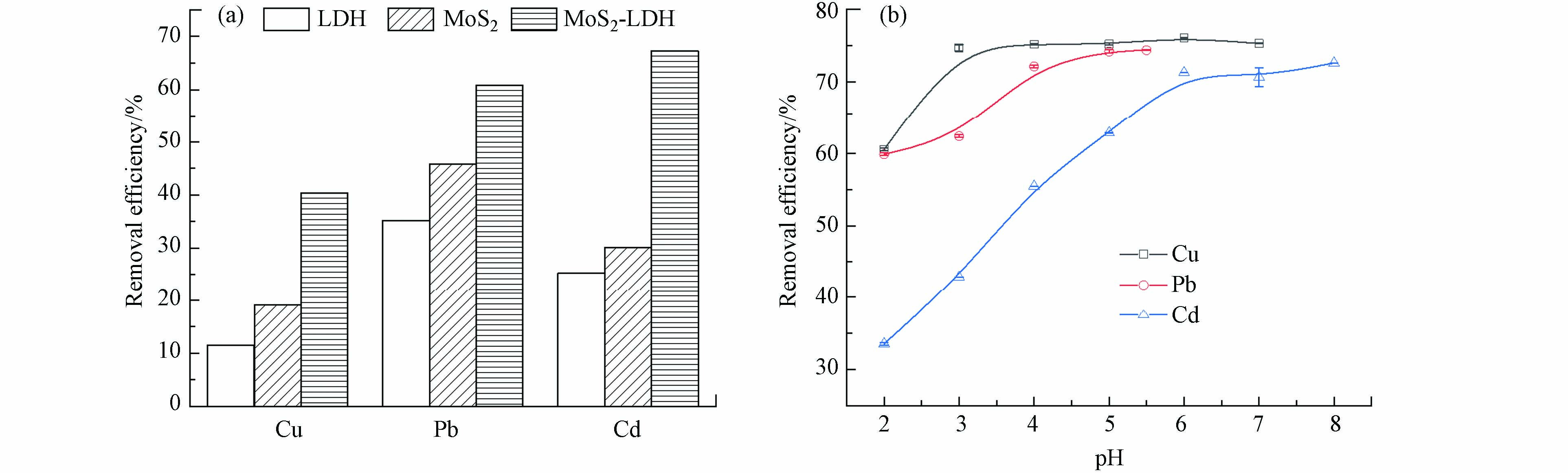
选择Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cd(Ⅱ)作为典型重金属,以MoS2-LDH为吸附剂进行了预实验。由图3a可知,复合材料MoS2-LDH相对于MgAl-LDH、MoS2对3种重金属的吸附量有明显的提升。
溶液pH对MoS2-LDH吸附3种重金属的影响结果如图3b所示,MoS2-LDH对Cu(Ⅱ)和Pb(Ⅱ)的去除率在pH为4.0左右时达到平衡,对Cd(Ⅱ)在pH约6.0时达到平衡。当重金属溶液为原始pH值,即Cu(Ⅱ)为5.10,Cd(Ⅱ)为5.85,Pb(Ⅱ)为5.73时,去除率能够达到最大。因此在随后的实验中,选择原始pH值的重金属溶液进行实验。
-
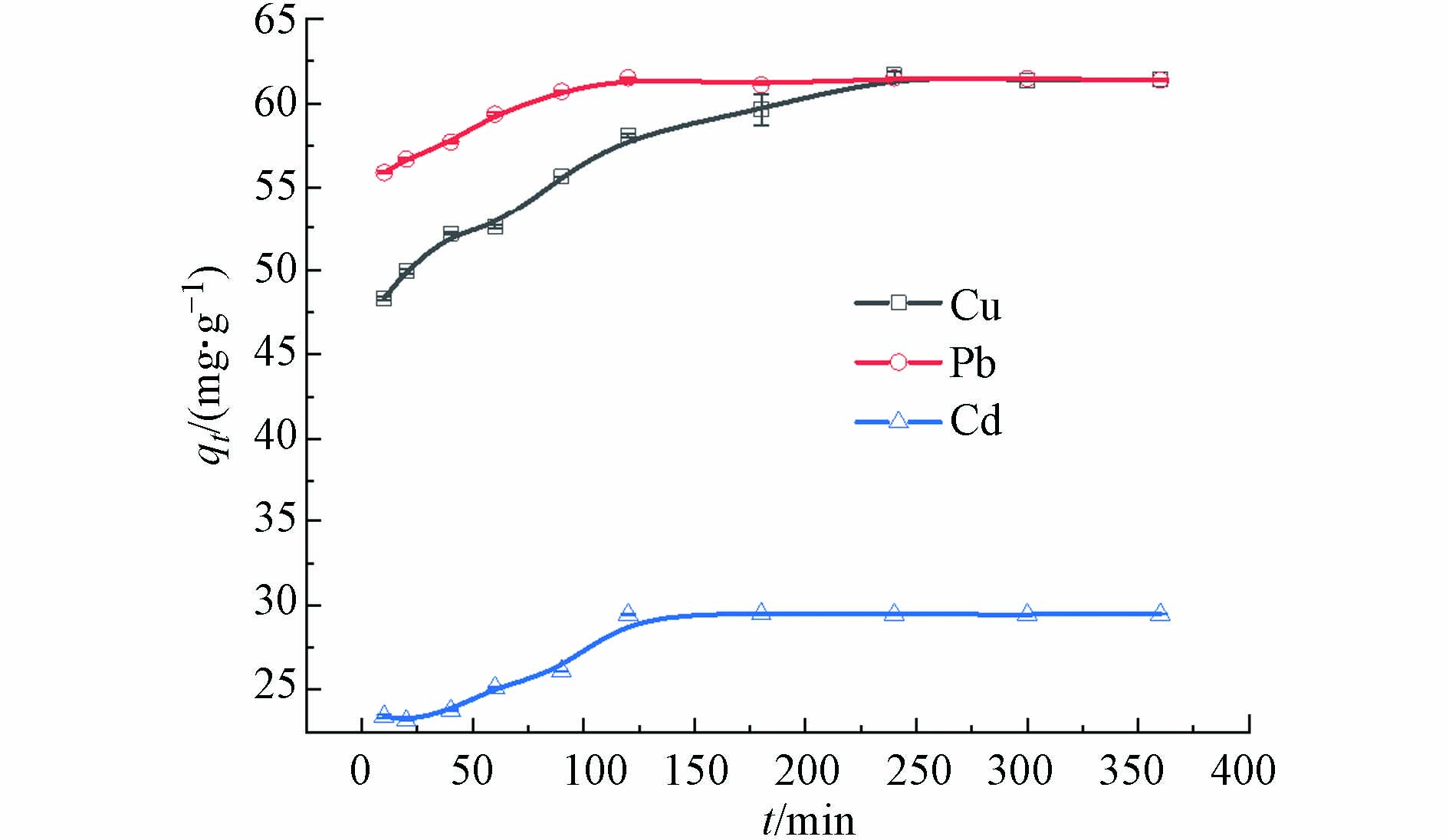
如图4所示,MoS2-LDH对重金属的去除率先明显增加,然后趋于稳定。MoS2-LDH对Pb(Ⅱ)和Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附平衡时间为120 min,对于Cu(Ⅱ)为240 min。
采用拟一级和拟二级动力学方程对上述动力学数据进行分析,表1为拟合得到的相关参数,拟二级动力学模型拟合的相关系数(R2 > 0.99)大于拟一级动力学方程的,说明拟二级动力学更匹配MoS2-LDH吸附Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)的过程,以化学吸附为主导作用[33]。
-
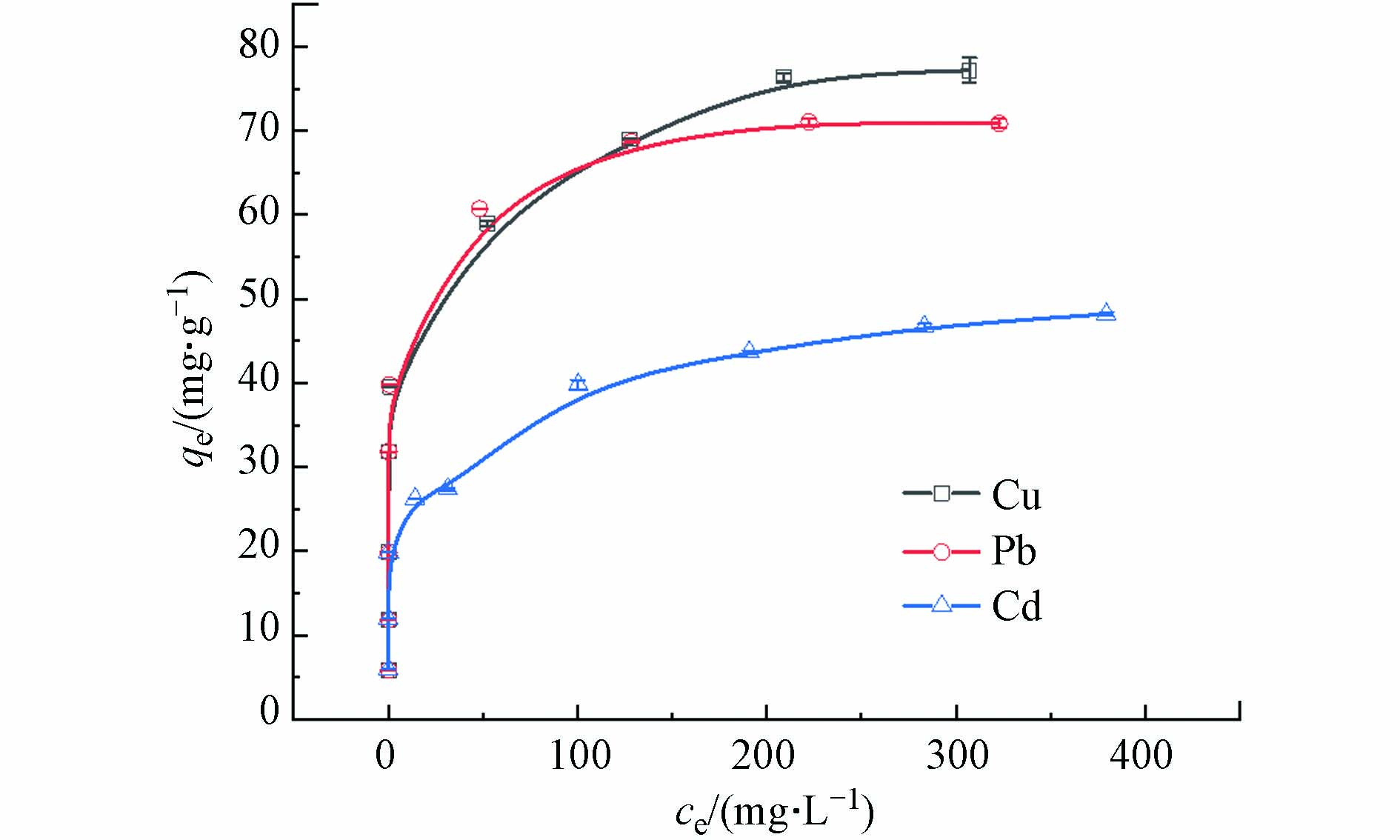
图5是MoS2-LDH吸附3种重金属的等温线,通过Langmuir和Freundlich吸附模型分析了实验数据,结果列于表2。通过对比两种模型的R2,发现MoS2-LDH的吸附数据符合Langmuir模型(R2 > 0.99)。 此外,MoS2-LDH对Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)的最大吸附量(qm)分别为48.31、71.33、77.16 mg·g−1。表3列举了不同水滑石、MoS2吸附剂对重金属的吸附量,经比较发现MoS2-LDH的吸附量大于很多其他吸附剂.
-
为了探究MoS2-LDH吸附Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)的机制,对吸附后的MoS2-LDH进行了XRD、XPS、FTIR和Zeta电位表征。
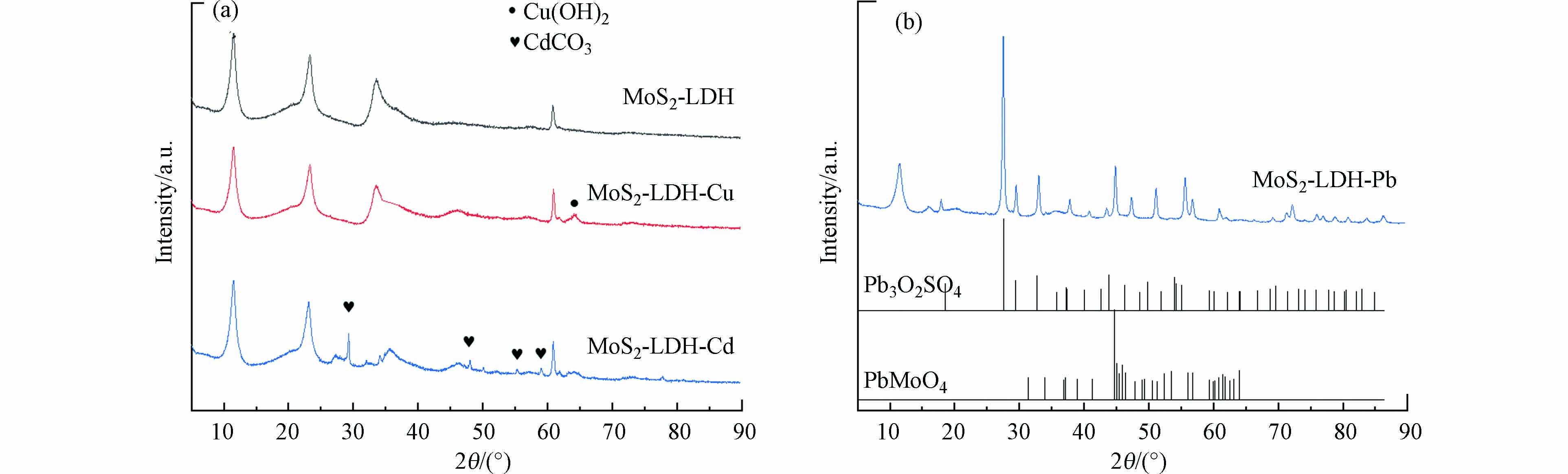
如图6所示,吸附Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)后的MoS2-LDH仍保留了MoS2和MgAl-LDH的特征峰,说明MoS2-LDH的晶体结构在吸附重金属过程中保持稳定。吸附Cd(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)后,MoS2-LDH的XRD谱图中出现了对应于Cu(OH)2以及CdCO3的新特征峰,说明生产了重金属沉淀,这与之前MgAl-CO3-LDH及磁性Fe3O4/MgAl-CO3-LDH吸附Cd(Ⅱ)后的研究结果一致[20]。吸附Pb(Ⅱ)后,新出现的衍射峰主要对应于不溶性化合物Pb3O2SO4和PbMoO4,这与MoS2@高岭土和MoS2-N-H吸附Pb(Ⅱ)后的XRD图谱一致[40-41]。另外,由于MoS2的特殊结构,使–OH易攻击S–Mo–S键产生SO42−[42],与Pb(Ⅱ)反应生成不溶性化合物。因此,沉淀作用是MoS2-LDH吸附Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)的机制之一。
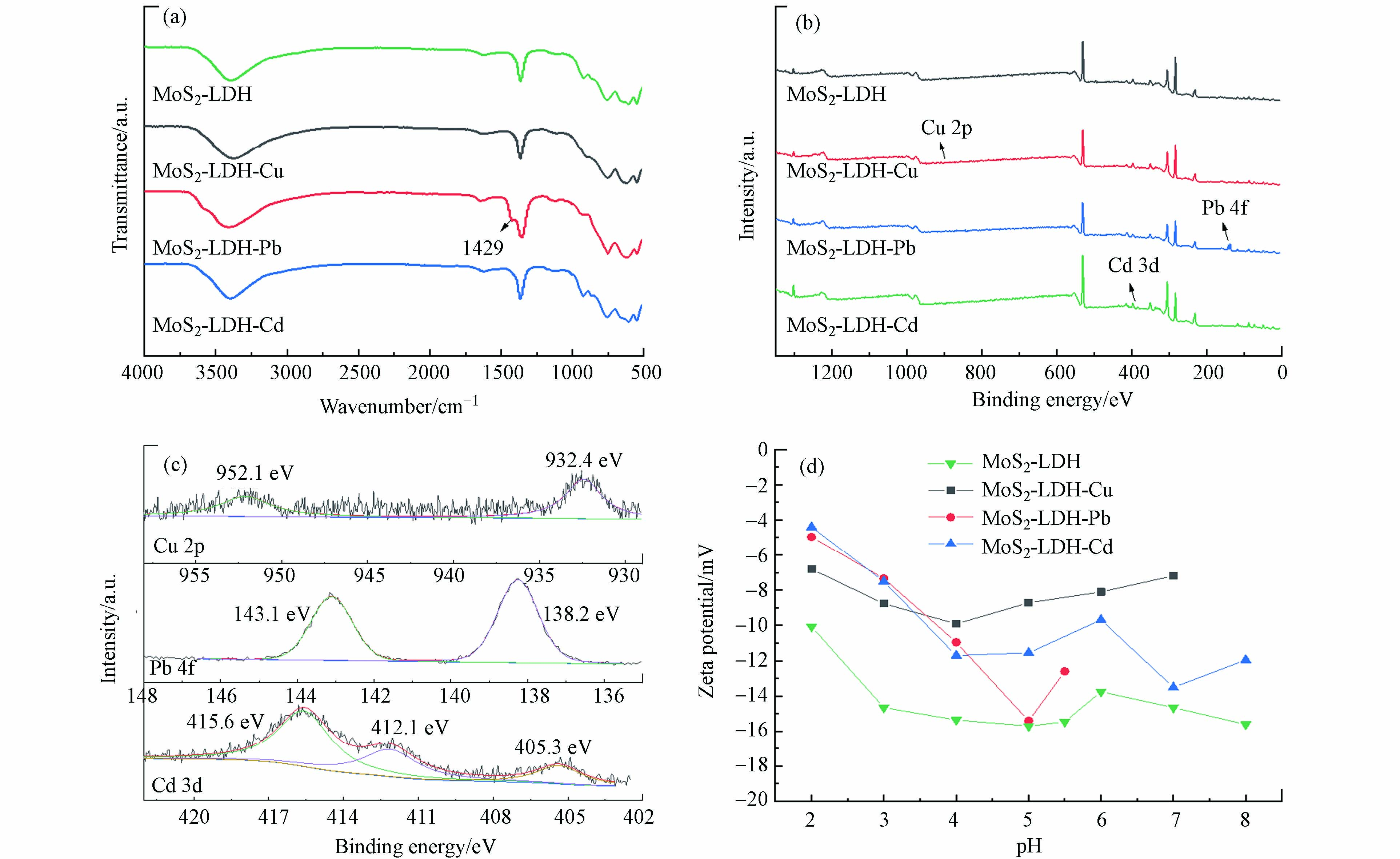
如图7a所示,吸附重金属后的MoS2-LDH的FTIR图谱没有发生明显变化仅在吸附Pb(Ⅱ)后于1429 cm−1处出现了一个新的吸收峰,这是由于C—O键的弯曲振动发生位移,说明C—O参与了Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附过程[43]。
在MoS2-LDH吸附重金属后的XPS总谱图(图7b)中可以观察到材料本身各元素的存在,表明吸附后MoS2-LDH的结构没有明显改变,与XRD的分析一致。还检测出了Cu 2p、Pb 4f 和Cd 3d的能谱峰,如图7c所示,Cu 2p在952.1eV和932.4 eV处出现的峰对应于Cu(OH)2或CuO,说明与羟基(—OH或—O—)发生了络合反应,形成了—O—Cu或—OH—Cu[12,44];MoS2-LDH吸附Pb(Ⅱ)后在138.2eV和143.1 eV处出现两个峰,分别代表Pb 4f7/2和Pb 4f5/2[12];在Cd 3d的谱图中含有Cd 3d5/2(405.3 eV)和Cd 3d3/2(412.1、415.6 eV)的3个峰,对应于CdCO3和Cd(OH)2,说明存在Cd–O键[45-46]。通过分析MoS2-LDH的C 1s和O 1s的分峰,吸附重金属后峰的位置未发生明显变化,但峰面积产生了变化(表4),进一步说明吸附过程中重金属和MoS2-LDH的官能团发生了络合反应。
如图7d,在pH = 2—8的范围,MoS2-LDH的Zeta电位均为负值,说明材料表面含有大量的负电荷,吸附重金属后MoS2-LDH的电位有所升高,这表明重金属离子与MoS2-LDH发生了静电吸引作用。另外,计算了MoS2-LDH吸附Cu(Ⅱ)、Cd(Ⅱ)和Pb(Ⅱ)后的Mg/Al物质的量比,由2.31分别降低到1.17、1.43和1.72,证明了同晶置换作用的发生。
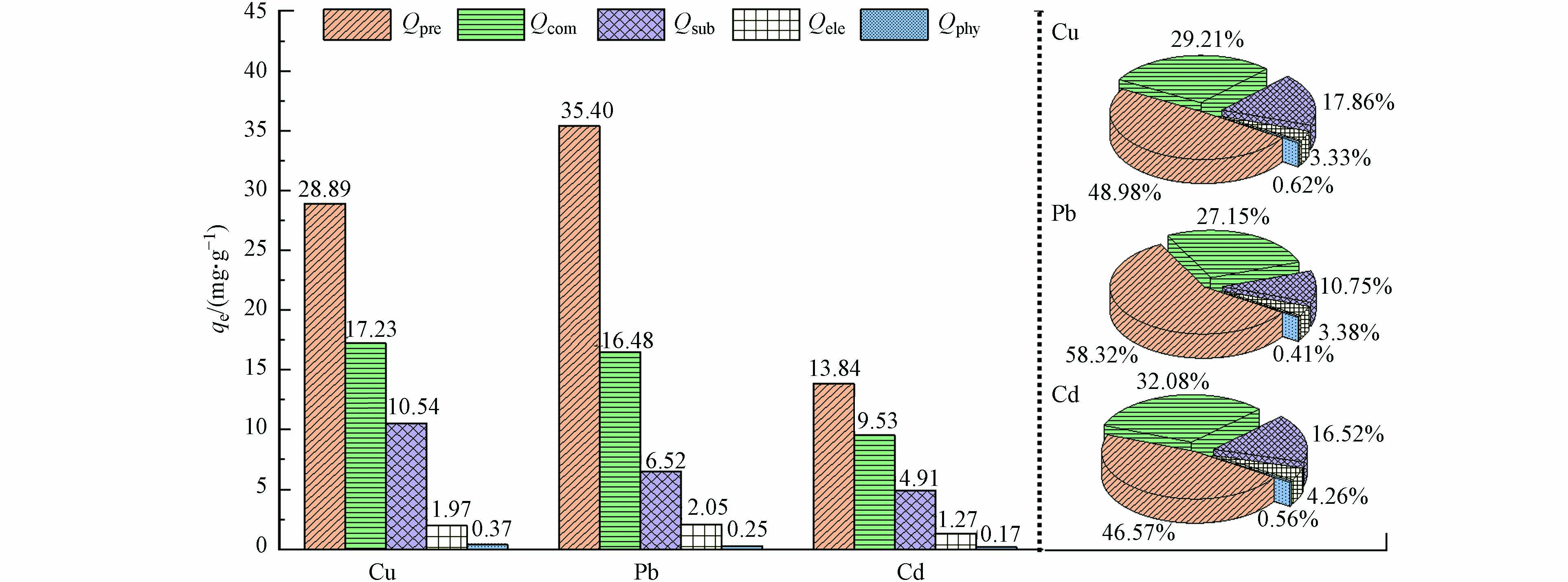
综上讨论,MoS2-LDH吸附Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)的作用机制包括沉淀反应、络合作用、静电吸引和同晶置换。为了进一步量化各作用机制的贡献,采用顺序提取法进行了分析,结果如图8所示。
MoS2-LDH吸附Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cd(Ⅱ)的机制贡献中,以沉淀作用为主导,贡献率分别为48.98%、58.32%和46.57%,即MoS2-LDH吸附重金属后在表面形成了沉淀,这与XRD和XPS分析的结论一致。其次为络合作用,贡献率分别为29.21%(Cu(Ⅱ))、27.15%(Pb(Ⅱ))和32.08%(Cd(Ⅱ))。
对比MoS2-LDH吸附重金属前后的溶液Mg(Ⅱ)的浓度,得到了同晶置换机制的贡献量,对Cu(Ⅱ)(17.86%)和Cd(Ⅱ)(16.52%)贡献率高于Pb(Ⅱ)(10.75%),这是因为Cu(Ⅱ)和Cd(Ⅱ)的水合离子半径大小与Mg(Ⅱ)的更相近,更易发生同晶置换。MoS2-LDH的表面的负电荷有利于静电吸引作用的发生,但静电吸引机制的贡献量仅为3.33%–4.26%,另外物理作用的贡献率较小(0.41%–0.62%),可忽略不计。
-
(1)采用水热法制备了MoS2-LDH复合材料,进行了SEM、XRD、FTIR、XPS和Zeta电位表征,结果表明MoS2-LDH成球状,具有MoS2和LDH的特征X光衍射峰。
(2)将MoS2-LDH用于去除水中Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ),对实验数据进行了动力学和等温线模型拟合,吸附实验数据符合拟二级动力学方程和Langmuir模型。MoS2-LDH对Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)的最大吸附量分别为48.31、71.33、77.16 mg·g−1。
(3)通过分析MoS2-LDH吸附Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)前后的XRD、FTIR、Zeta电位和XPS可知,MoS2-LDH与重金属的作用机制包括沉淀、官能团络合、静电吸引和同晶置换作用。
(4)对各吸附机制的量化结果表明,沉淀作用、络合反应和同晶置换为MoS2-LDH吸附Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cd(Ⅱ)的主要机制,贡献率分别为46.57%—58.32%、27.15%—32.08%和10.75%—17.86%,能够为高效去除重金属的二维复合材料的设计合成提供理论支撑。
二硫化钼-水滑石复合材料对水中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附机制
Adsorption mechanisms of MoS2-LDH composite for aqueous Cu(Ⅱ), Pb(Ⅱ) and Cd(Ⅱ)
-
摘要: 二维层状纳米材料可以有效去除水中的重金属,而吸附机制一直是研究难点和热点。为进一步提升材料性能,明确吸附反应机制,以典型的水滑石和二硫化钼为原料,采用共沉淀法制备镁铝水滑石,然后利用水热法负载二硫化钼,制备了复合材料(MoS2-LDH)。结果表明,MoS2-LDH对水中Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附作用机制包括沉淀、络合、同晶置换和静电吸引作用,其中沉淀作用为主导,贡献率占46.57%—58.32%,其次为络合作用(27.15%—32.08%)和同晶置换作用(10.75%—17.86%),静电吸引的贡献最小(3.33%—4.26%);吸附过程与拟二级动力学方程和Langmuir模型相符,最大吸附量达到48.31、71.33、77.16 mg·g−1。对高效去除重金属的吸附机制的详细研究,可为二维复合材料的设计合成提供理论支撑。Abstract: Two-dimensional layered nanomaterials can remove heavy metals from aqueous solutions by adsorption and the interaction mechanism is the active research focus and difficult issue. In order to increase the adsorption capability and clarify the interaction mechanism, the magnesium-aluminum layered double hydroxide (MgAl-LDH) was prepared using the co-precipitation method, and MoS2 was loaded using the hydrothermal method to obtain the composite of MoS2-LDH. The results indicated that the adsorption mechanisms of MoS2-LDH for aqueous Cd(Ⅱ), Cu(Ⅱ) and Pb(Ⅱ) involved the precipitation, complexation, isomorphic substitution and electrostatic attraction. The precipitation was the key mechanism and the contribution percentages were 46.57%—58.32%. The surface complexation (27.15%—32.08%) and isomorphic substitution (10.75%—17.86%) were followed by, and the contribution of electrostatic attraction was only 3.33%—4.26%. The adsorption process was in accordance with the pseudo-second-order kinetic equation and Langmuir isotherm model, respectively. The maximum adsorption capacities of MoS2-LDH for Cd(Ⅱ), Pb(Ⅱ) and Cu(Ⅱ) reached 48.31, 71.33 and 77.16 mg·g−1, respectively. In conclusion, the detailed adsorption mechanisms can provide theoretical support for the design and synthesis of two-dimensional composite to efficiently remove aqueous heavy metals.
-
Key words:
- heavy metal wastewater /
- adsorption mechanism /
- precipitation /
- complexation.
-

-
表 1 MoS2-LDH吸附Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)的动力学模型参数
Table 1. Kinetic parameters of Cd(Ⅱ), Pb(Ⅱ) and Cu(Ⅱ) adsorption by MoS2-LDH
拟一级动力学模型
Pseudo-first order kinetic mode拟二级动力学模型
Pseudo-second order kinetics modeqe/ (mg·g−1) k1/min−1 R2 qe/ (mg·g−1) k2/ (mg·min−1·g−1) R2 Cu(Ⅱ) 13.91 0.008 0.854 62.77 0.002 0.999 Pb(Ⅱ) 3.455 0.005 0.545 61.77 0.009 0.999 Cd(Ⅱ) 6.061 0.005 0.782 30.22 0.004 0.999 表 2 MoS2-LDH吸附Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)的等温线模型参数
Table 2. Isothermal parameters of Cd(Ⅱ), Pb(Ⅱ) and Cu(Ⅱ) adsorption by MoS2-LDH
Langmuir Freundlich qm/ (mg·g−1) b/ (L·mg−1) R2 kf 1/n R2 Cu(Ⅱ) 77.16 0.214 0.999 1.785 0.753 0.704 Pb(Ⅱ) 71.33 0.363 0.999 1.585 0.848 0.837 Cd(Ⅱ) 48.31 0.100 0.999 1.689 0.748 0.637 表 3 不同水滑石、MoS2材料对Cd(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)吸附量的比较
Table 3. Comparison of adsorption capacity of LDH and MoS2-based adsorbents for Cd(Ⅱ), Pb(Ⅱ) and Cu(Ⅱ)
表 4 MoS2-LDH吸附重金属前后的XPS图谱的高反褶积
Table 4. High deconvolution of XPS spectra of MoS2-LDH before and after heavy metal adsorption
C—C/% C—O/% —OH/% 反应前 69.0 23.4 7.6 Cu(II) 84.2 11.3 4.5 Pb(II) 79.5 15.2 5.3 Cd(II) 84.9 10.5 4.6 -
[1] 刘金燕, 刘立华, 薛建荣, 等. 重金属废水吸附处理的研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(9): 2016-2024. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017110105 LIU J Y, LIU L H, XUE J R, et al. Research progress on treatment of heavy metal wastewater by adsorption [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(9): 2016-2024(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017110105
[2] SHABTAI I A, LYNCH L M, MISHAEL Y G. Designing clay-polymer nanocomposite sorbents for water treatment: A review and meta-analysis of the past decade [J]. Water Research, 2021, 188: 116571. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116571 [3] XIAO X, CHEN B L, CHEN Z M, et al. Insight into multiple and multilevel structures of biochars and their potential environmental applications: A critical review [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(9): 5027-5047. [4] 曾辉平, 翟龙雪, 李冬, 等. 基于铁泥的磁性水处理材料制备及应用进展 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(1): 26-36. ZENG H P, ZHAI L X, LI D, et al. Preparation and application of magnetic water treatment materials based on iron sludge [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(1): 26-36(in Chinese).
[5] 苏欣悦, 丁欣欣, 闫良国. Fe3O4磁性纳米材料的制备及水处理应用进展 [J]. 中国粉体技术, 2020, 26(6): 1-10. SU X Y, DING X X, YAN L G. Research progress of preparation of Fe3O4 magnetic nanomaterials and applications in wastewater treatment [J]. China Powder Science and Technology, 2020, 26(6): 1-10(in Chinese).
[6] ZAERA F. Probing liquid/solid interfaces at the molecular level [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2012, 112(5): 2920-2986. doi: 10.1021/cr2002068 [7] 李伟, 罗磊, 张淑贞. 应用先进光谱技术研究无机离子的环境界面化学 [J]. 化学进展, 2011, 23(12): 2576-2587. LI W, LUO L, ZHANG S Z. Towards A molecular scale understanding of the chemistry of inorganic ions at environmental interfaces: Application of spectroscopic techniques [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2011, 23(12): 2576-2587(in Chinese).
[8] WANG Z Y, LIU G C, ZHENG H, et al. Investigating the mechanisms of biochar's removal of lead from solution [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 177: 308-317. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.077 [9] GAO L Y, DENG J H, HUANG G F, et al. Relative distribution of Cd2+ adsorption mechanisms on biochars derived from rice straw and sewage sludge [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 272: 114-122. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.138 [10] XIAO J, HU R, CHEN G C. Micro-nano-engineered nitrogenous bone biochar developed with a ball-milling technique for high-efficiency removal of aquatic Cd(II), Cu(II) and Pb(II) [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 387: 121980. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121980 [11] TIAN Y, LI J B, WHITCOMBE T W, et al. Application of oily sludge-derived char for lead and cadmium removal from aqueous solution [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 384: 123386. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123386 [12] SU X Y, CHEN Y, LI Y F, et al. Enhanced adsorption of aqueous Pb(Ⅱ) and Cu(Ⅱ) by biochar loaded with layered double hydroxide: Crucial role of mineral precipitation [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 357: 119083. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2022.119083 [13] 张雪. 插层镁铝水滑石对水中重金属的吸附性能与机理研究[D]. 济南: 济南大学, 2021. ZHANG X. Study on adsorption performance and mechanisms of intercalated MgAl-layered double hydroxide for heavy metals from water[D]. Jinan: University of Jinan, 2021(in Chinese).
[14] ZHOU J Y, LIN Z Y, REN H Y, et al. Layered intercalation materials [J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(25): 2004557. doi: 10.1002/adma.202004557 [15] LAIPAN M W, YU J F, ZHU R L, et al. Functionalized layered double hydroxides for innovative applications [J]. Materials Horizons, 2020, 7(3): 715-745. doi: 10.1039/C9MH01494B [16] 吕维扬, 孙继安, 姚玉元, 等. 层状双金属氢氧化物的控制合成及其在水处理中的应用 [J]. 化学进展, 2020, 32(12): 2049-2063. LV W Y, SUN J A, YAO Y Y, et al. Morphology control of layered double hydroxide and its application in water remediation [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2020, 32(12): 2049-2063(in Chinese).
[17] 张爽, 丁欣欣, 闫良国. 改性水滑石类材料的制备及其吸附性能研究进展 [J]. 中国粉体技术, 2021, 27(1): 1-10. ZHANG S, DING X X, YAN L G. Research progress on preparation and adsorption properties of modified layered double hydroxides [J]. China Powder Science and Technology, 2021, 27(1): 1-10(in Chinese).
[18] 毛方琪, 郝培培, 孔祥贵, 等. 双金属复合氢氧化物在重金属污染土壤/水修复方面的研究进展 [J]. 中国科学:化学, 2021, 51(5): 493-508. doi: 10.1360/SSC-2020-0123 MAO F Q, HAO P P, KONG X G, et al. Layered double hydroxides as amendment for remediation of heavy metal ions in water and soil [J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2021, 51(5): 493-508(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/SSC-2020-0123
[19] XIE Y Y, YUAN X Z, WU Z B, et al. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Mg/Fe layered double hydroxide with Fe3O4-carbon spheres on the removal of Pb(II) and Cu(II) [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 536: 440-455. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.10.066 [20] SHAN R R, YAN L G, YANG K, et al. Adsorption of Cd(II) by Mg-Al-CO3- and magnetic Fe3O4/Mg-Al-CO3-layered double hydroxides: Kinetic, isothermal, thermodynamic and mechanistic studies [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 299: 42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.06.003 [21] LIU C, WANG Q M, JIA F F, et al. Adsorption of heavy metals on molybdenum disulfide in water: A critical review [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 292: 111390. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111390 [22] WANG Z Y, TU Q S, SIM A, et al. Superselective removal of lead from water by two-dimensional MoS2 nanosheets and layer-stacked membranes [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(19): 12602-12611. [23] WANG Z Y, SIM A, URBAN J J, et al. Removal and recovery of heavy metal ions by two-dimensional MoS2 nanosheets: Performance and mechanisms [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(17): 9741-9748. [24] LEE Y H, ZHANG X Q, ZHANG W J, et al. Synthesis of large-area MoS2 atomic layers with chemical vapor deposition [J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(17): 2320-2325. doi: 10.1002/adma.201104798 [25] QIU S J, WANG X, ZHANG Q R, et al. Development of MoS2/cellulose aerogels nanocomposite with superior application capability for selective lead(II) capture [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 284: 120275. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120275 [26] YANG F, CAO Z F, WANG J, et al. In situ self-assembly of molybdenum disulfide/Mg-Al layered double hydroxide composite for enhanced photocatalytic activity [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 817: 153308. [27] CHEN S, YANG F, CAO Z F, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of molybdenum disulfide by compositing ZnAl-LDH [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2019, 586: 124140. [28] 李红艳. 基于生物模板的LDHs/钼系微纳复合光催化剂的制备及其性能研究[D]. 济南: 济南大学, 2017. LI H Y. Preparation of LDHs/molybdenum-based micro/nano composite photocatalyst based on biological template and its properties[D]. Jinan : University of Jinan, 2017(in Chinese).
[29] WEI Y H, LI G S, WANG J H, et al. Self-assembled nanohybrid from opposite charged sheets: Alternate stacking of CoAl-LDH and MoS2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Structural Chemistry, 2018, 37(7): 1093-1101. [30] LI X Y, GUO M, Bandyopadhyay P, et al. Two-dimensional materials modified layered double hydroxides: A series of fillers for improving gas barrier and permselectivity of poly (vinyl alcohol) [J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2020, 207: 108568. [31] ZHOU K Q, GAO R, QIAN X D. Self-assembly of exfoliated molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets and layered double hydroxide (LDH): Towards reducing fire hazards of epoxy [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 338: 343-355. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.05.046 [32] SU X Y, GUO Y X, YAN L G, et al. MoS2 nanosheets vertically aligned on biochar as a robust peroxymonosulfate activator for removal of tetracycline [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 282: 120118. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120118 [33] HO Y S, MCKAY G. A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 1998, 76(4): 332-340. doi: 10.1205/095758298529696 [34] ZHANG X, YAN L G, LI J, et al. Adsorption of heavy metals by l-cysteine intercalated layered double hydroxide: Kinetic, isothermal and mechanistic studies [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 562: 149-158. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.12.028 [35] GONZÁLEZ M A, PAVLOVIC I, BARRIGA C. Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) sorption on different layered double hydroxides. A kinetic and thermodynamic study and competing factors [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 269: 221-228. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.094 [36] ZHU S D, ASIM KHAN M, WANG F Y, et al. Rapid removal of toxic metals Cu2+ and Pb2+ by amino trimethylene phosphonic acid intercalated layered double hydroxide: A combined experimental and DFT study [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 392: 123711. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123711 [37] AGHAGOLI M J, BEYKI M H, SHEMIRANI F. Facile synthesis of Fe3O4/MoS2 nanohybrid for solid phase extraction of Ag(I) and Pb(II): Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies [J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 97(14/15): 1328-1351. [38] LIU C, ZENG S L, YANG B Q, et al. Simultaneous removal of Hg2+, Pb2+ and Cd2+ from aqueous solutions on multifunctional MoS2 [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 296: 111987. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111987 [39] LUO J M, FU K X, SUN M, et al. Phase-mediated heavy metal adsorption from aqueous solutions using two-dimensional layered MoS2 [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(42): 38789-38797. [40] YUAN W Q, KUANG J Z, YU M M, et al. Facile preparation of MoS2@Kaolin composite by one-step hydrothermal method for efficient removal of Pb(II) [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 405: 124261. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124261 [41] KUMAR N, FOSSO-KANKEU E, RAY S S. Achieving controllable MoS2 nanostructures with increased interlayer spacing for efficient removal of Pb(II) from aquatic systems [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(21): 19141-19155. [42] ZHANG L, HE X, ZHOU Q X, et al. Fabrication of 1T-MoS2 nanosheets and the high-efficiency removal of toxic metals in aquatic systems: Performance and mechanisms [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 386: 123996. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123996 [43] DENG Y Y, HUANG S, LAIRD D A, et al. Adsorption behaviour and mechanisms of cadmium and nickel on rice straw biochars in single- and binary-metal systems [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 218: 308-318. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.081 [44] KOSTENKO L S, TOMASHCHUK I I, KOVALCHUK T V, et al. Bentonites with grafted aminogroups: Synthesis, protolytic properties and assessing Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) adsorption capacity [J]. Applied Clay Science, 2019, 172: 49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2019.02.009 [45] WU J W, WANG T, ZHANG Y S, et al. The distribution of Pb(II)/Cd(II) adsorption mechanisms on biochars from aqueous solution: Considering the increased oxygen functional groups by HCl treatment [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 291: 121859. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121859 [46] ZHANG C, SHAN B Q, TANG W Z, et al. Comparison of cadmium and lead sorption by Phyllostachys pubescens biochar produced under a low-oxygen pyrolysis atmosphere [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 238: 352-360. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.04.051 -



 下载:
下载: