-
微塑料是指长度或等容粒径小于等于5 mm的塑料颗粒和碎片,包括粒料、微纤维、颗粒、泡沫或者薄膜等[1]. 其主要组成成分为聚乙烯(PE)、聚丙烯(PP)、聚苯乙烯(PS)、聚氯乙烯(PVC)、聚氨酯(PU)、聚酰胺(PI)、聚酰胺(PA)、聚乳酸(PLA)及聚对苯二甲酸乙二酯(PET)等聚合物[2]. 目前,微塑料污染已在空气、土壤、湖泊、河流和海洋[3 − 4], 甚至是食物[5]和饮用水[6]等各种介质中检出; 另外,微塑料比表面积大,表面疏水性强,易于富集微生物、重金属和有机污染物[7],随着食物链传递和富集, 会对人体健康产生严重危害[8 − 11].
微塑料1972年首次在美国西部沿海被发现,当时研究发现大量0.25—0.5 cm的塑料颗粒[12]; 2004年,英国学者Thompson将其在显微镜下观测到的微小塑料碎片和纤维称为“微塑料(Microplastics)”[1]; Arthur等将微塑料的尺寸上限确定为5 mm[13]. 随着全球塑料产量的快速增长(2019年全球产量超过3.6亿吨[14]),带来的微塑料污染问题也不断增加. 对全球各地的水、沉积物、生物体等造成严重影响. 2022年5月,国务院通过了《新污染物治理行动方案》. 该方案旨在建立健全新污染物治理体系,开展调查监测,评估新污染物环境风险状况对微塑料等重点新污染物制定针对性管控措施,提出“针对微塑料等国内外关注且环境检出率高的其他新污染物,制定管控措施”,我国的微塑料治理防控由此迈入新的阶段. 在微塑料污染的治理工作中,提供可靠的分析技术来检测、识别和量化环境中赋存的微塑料,对促进微塑料环境污染治理和人体风险评估至关重要. 微塑料的检测主要从“形态和物理表征”和“定量和化学表征”两方面展开,前者从颜色、尺寸、形状、丰度等指标评价微塑料在环境介质中的赋存状态;后者从聚合物的组成和含量分析微塑料的物质组成. 物理和化学的综合检测,有利于全面评价微塑料在环境中的赋存、富集与迁移的特征.
在微塑料的物理和化学分析方法中,显微镜(目视)分析是重要的方法,具有简单、快速、成本低廉等优势,能对微塑料的物理性质进行有效分析,结合红外光谱和拉曼光谱等手段,可以对微塑料进行无损的物理化学综合分析;热分析和质谱分析可以进行微塑料聚合物类型的定性和定量分析. 近年来,随着微塑料的研究不断深入,遇到了分辨率难以满足较小(如1 μm以下)微塑料颗粒检测需要、大批量样品检测效率低和应对复杂样品检测难等方面的挑战. 为了克服以上挑战,研究人员从仪器开发、方法创新和对象扩展等角度展开工作,显著提升微塑料检测的空间分辨率和检测效率,并尝试从人体组织微塑料检测等方面直接评价微塑料暴露的人体健康效应. 本文系统综述了微塑料物理化学分析的主要手段,重点介绍应用的主要新方法,以及讨论存在的主要问题,并展望今后的应用前景和发展方向.
-
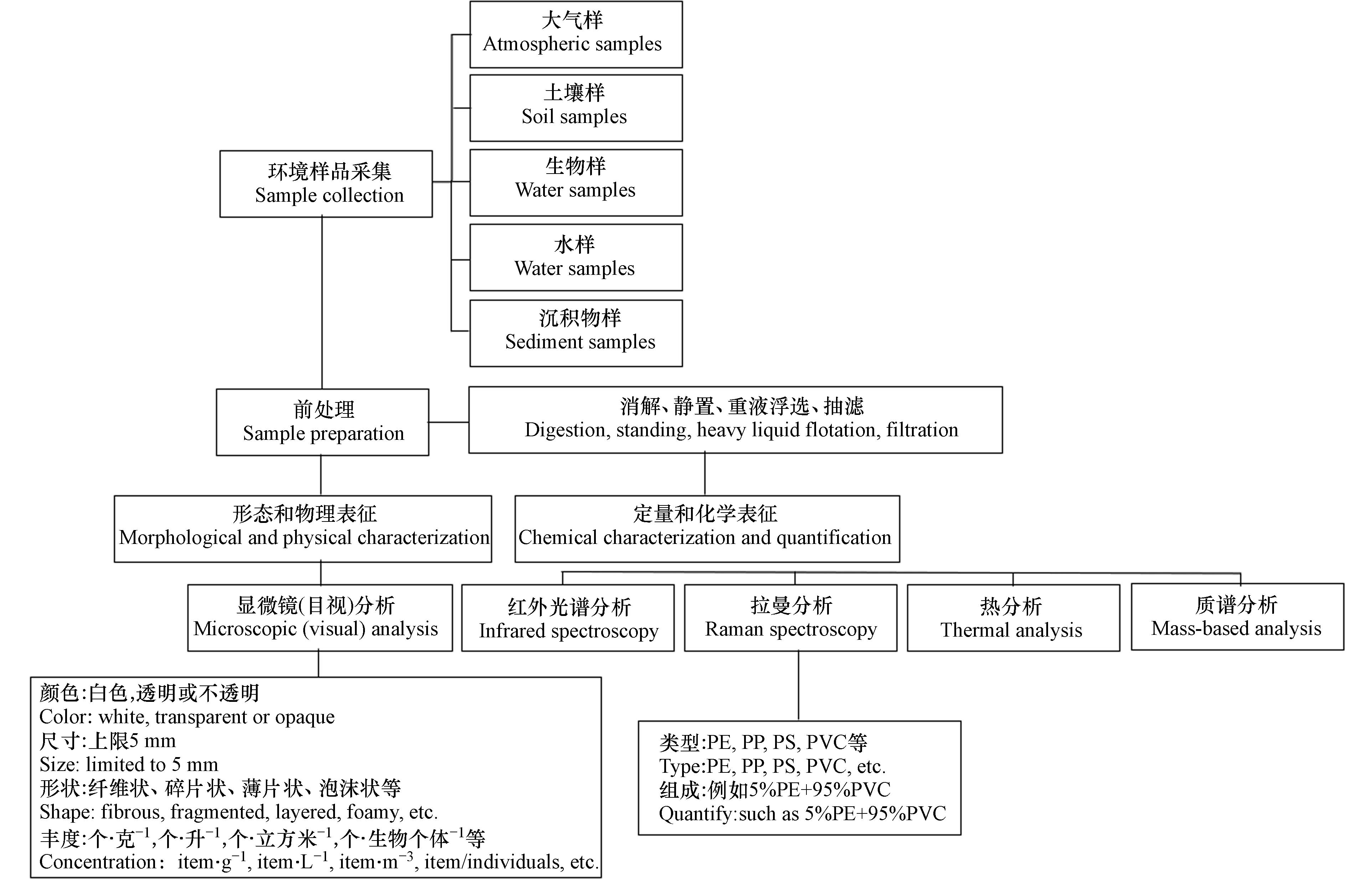
微塑料的检测通过“形态和物理表征”和“定量和化学表征”展开. 微塑料的形态和物理特征通常使用光学显微镜,如体视显微镜来进行评估. 此外,扫描电子显微镜具有高空间分辨率的特征,可以用于小颗粒微塑料的观察. 微塑料的定量和化学特征可以使用光谱、热分析和质谱等手段实现. 微塑料分析流程如图1,样品的分离和消解方法见表1和表2.
微塑料的性质相对稳定,但随着其在环境中遗留的时间变长,会发生磨损[28 − 29]、光化学降解[30]、水解[31]等变化[4],所以即便是同一种组成的微塑料,也会随着时间变化产生不同的形态和化学组成变化,这对微塑料的检测带来了一定的挑战.
-
目视分析法将过滤后滤膜等置于裸眼或显微镜下观察,统计样本中微塑料的丰度、形状、尺寸和颜色等信息. 目视分析法具有操作简单、成本低和无化学危害等优点,是最常用的检测方法(约占所有微塑料检测研究的75%[32]),适合尺寸大于500 μm的微塑料检测. 但是,裸眼和光学显微镜仅能通过外观形貌模糊地识别微塑料,具有以下显著的缺点. 首先无法得到样品的组成信息,这样难免会产生假阳性或假阴性信号,将其他物质错误识别为微塑料. 有研究显示,显微镜(目视)分析有较大误差,特别是鉴别无色透明的微塑料,出错率在20%[33]到70%[34]之间,效率低下[35];其次,检测带有强烈的主观性,对于外观相似的微塑料难以辨别,易造成微塑料颗粒分类错误[36];而且,目视的分辨率低,通常只适用于0.1 mm以上尺寸的微塑料的检测. 检测的微塑料颗粒粒径越小,目检法对颗粒物辨识度越差,辨认准确率越低,误差越大[37]. 虽然目视分析准确度较低不适宜作为独立的鉴别方法,但可以为进一步的仪器化学分析提供基础.
-
扫描电子显微镜(SEM)识别微塑料可以得到超清晰和高倍率(分辨率可至约30 nm)的图像,有助于区分微塑料与其他细小的颗粒样品. 在扫描电镜的基础上增加能量散射X射线光谱分析(SEM-EDS),可对可疑粒子进行元素成分分析,有助于区分以碳为主的微塑料与无机颗粒,用于在低真空模式下测定微塑料颗粒的化学和形态特征[38]. SEM-EDS法也有一定的局限性,如二次电子图像为灰度图像无法表现出样品的颜色;老化的微塑料颗粒表面形状发生明显变化,对分析准确性造成一定的误导[39];不能区分添加剂和吸附物质;样品制备费时费力,需对电镜下的粒子逐个分析,一定时间内可以分析的微塑料数量少,工作效率低[40];以及因SEM使用电子束轰击样品成像,持续的电子束轰击可能在成像过程中对样品产生不可逆的电荷破坏[41].
-
振动光谱基于偶极矩(红外光谱)或极化率(拉曼光谱)的周期性变化来测量分子振动获得特异性的化学信息用于分子类型鉴别[5],样品的化学或结构信息由相应的光谱表征. 红外光谱测定的是样品的透射光谱,当红外光穿过样品,样品分子的基团吸收红外光产生振动,使偶极矩发生变化,得到红外吸收光谱;而拉曼光谱测定的是样品的发射光谱,当单色激光照射到样品上,分子的极化率发生变化,产生拉曼散射. 光谱法利用未知微塑料样品的光谱与从光谱库中获得的已知聚合物的光谱进行比较,进而识别微颗粒的聚合物组成. 微塑料表征多位于中红外(波长4000—400 cm−1,2.5—30 μm)区域[42]. 光谱法主要用于快速无损检测小于100 μm的微塑料[43]. 通过与显微镜结合,红外和拉曼可以对微塑料进行化学成像,实现微塑料的快速、高通量检测、识别和定量,并具有一定的自动化程度[5].
傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)是一种功能强大且常用的微塑料鉴别技术. 使用检测器检测在波数范围(4000—750 cm−1)内的光谱,将检测所得红外光谱图与标准谱图对比确认所分析物质的种类. 因光谱信号依赖于化学键的永久偶极矩的变化,因此FTIR可以灵敏的检测聚合物中的极性官能团,其空间分辨率最低可至5 μm[44]. 具有无需繁杂前处理过程,可以直接识别过滤器上微塑料的优点. 但是对样品要求较高,例如样品中的水分会干扰鉴定,要求观察的样品必须彻底干燥;要求较薄的样品厚度(约150 nm[45]);需要将样品固定在透明的底座上用于红外分析[46]. 而且,因结果受到测量颗粒的外观和多种聚合物产生的复杂光谱的影响,FTIR对不透明或黑色的微塑料分析也较为困难. 由于以上限制,FTIR适合分析干燥透明且粒径大于约20 μm的微塑料颗粒[47]. 基于焦平面阵列的傅里叶变换红外光谱(FPA-FTIR)近年来已成为运用广泛的微塑料分析方法,该技术将傅里叶变换红外光谱与焦平面阵列探测器结合,可在几分钟内获得数千个样品的红外光谱,快速生成化学成像和进行数据分析. 该方法不需要对分析的样品颗粒进行视觉预选,并且不会影响空间分辨率[48],可分析尺寸低至11 μm的微塑料颗粒[49].
拉曼光谱是一种以单色光(激发光)为光源的散射光谱,利用不同样品分子和原子结构的差异所导致的激发光照射到样品上产生不同频率的非弹性散射光,提供样品中分子振动的信息,从而获得各聚合物中的特征拉曼光谱,实现对微塑料的高通量检测. 拉曼光谱取决于化学键极化率周期性变化,由此可以很灵敏检查微塑料中的芳香键、C—H和C=C双键[50,15]. 拉曼光谱与共聚焦光学显微镜的结合以及在可见光范围内应用激光激发能够实现至1 μm甚至更低(最低约300 nm)的空间分辨率[51],适合检测粒径较小的微塑料[52]. 而且,样品厚度和形状也不影响检测,更适合分析不透明和黑色的微塑料颗粒[53]. 此外拉曼光谱对水的干扰不敏感,可用于检测水环境中的微塑料[41]. 同时拉曼光谱覆盖了完整的波长范围,可以检测无定形碳. 自动化的显微拉曼系统还可以对大量样品进行快速分析[54]. 但是,拉曼光谱容易受到环境中有机颗粒(例如藻类、浮游生物和天然碎屑)或无机颗粒(例如沙子和淤泥)发射的荧光光谱的干扰,使信号覆盖微塑料光谱,干扰分析结果[55],因此不能检测含有荧光物质的样品. 针对荧光干扰问题,目前的一些方法如与共聚焦光学显微镜联用,通过选择合适的测量参数(激光波长和功率、光漂白和采集时间,以及物镜放大倍率和共焦模式)可以最大限度地减少或避免强荧光造成的干扰[86]. 另外一个相对FTIR成像的劣势是拉曼成像的测量时间偏长,虽然可以通过改变测量参数来降低测量时间,但这样会降低光谱质量,从而导致可检测微塑料样品的减少[56].
-
热分析技术根据聚合物的降解产物进行鉴定,是一种通过聚合物的热稳定性来测量其物理和化学性质变化的破坏性方法. 样品首先被热降解,生成的产物送到质谱仪进行分析. 将收集到的数据与参考数据进行比较,得到样品的性质、浓度等信息[57]. 热分析方法主要包括差示扫描量热分析(DSC)和热重分析(TGA)、热脱附气相色谱质谱(TDS-GC-MS)及热裂解气相色谱质谱(Py-GC-MS)等.
差示扫描量热法(DSC)是在程序升温的条件下,通过指定的加热速率对样品进行加热,比较样品与参考物之间的能量差随温度变化的分析方法[58],可以对特定聚合物的颗粒质量进行化学定性和定量[59]. 这项技术适用于含有结晶成分的聚合物(如PE、PP、PA和PET),而不能分析不含结晶成分的聚合物(如PS)[41]. DSC具有操作简单、所需样品量少、分析速度快的优点[58],但是由于聚合物的识别和质量定量受到样品颗粒大小的强烈影响,因此在使用DSC测量微塑料时应对样品进行预处理[59]. 热重分析法(TGA)是在一定气体条件(惰性气体或空气)和程序控制温度下,监测样品的质量对时间或温度的依赖关系的热分析方法. 该技术通过监测加热过程中聚合物样品的质量损失和吸热反应进行定量分析. 通常不需要对样品进行前处理,适用于固体复杂样品的分析. 且TGA可分析的样本质量较大,这使得分析的样品更具代表性[60].
热重-差示扫描热联用(TGA-DSC)为多塑料混合物中PE和PP的聚合物类型识别和质量测定提供了一个新方法. 其操作简单、方便,性价比高[58]. 但由于它们的重叠相转变信号,无法鉴定PVC、PA、PES和PET,且由于特征转变温度受聚合物支化程度的改变,鉴定结果易受杂质、添加剂以及颗粒大小的影响[58]. 而且,由于样品粒度对DSC测量的有较大影响,因此在TGA-DSC分析之前,聚合物样品要经过研磨和过滤,以确保最小的颗粒尺寸在200—500 mm的范围内, 较高的预处理要求使得该方法在微塑料分析应用上受到一定的局限性. 热重-质谱(TGA-MS)是一种无需样品预处理的直接定量分析微塑料(例如PET)的方法,通过以一定的升温速率热解样品混合物,记录样品质量损失和参考已知微塑料热解产物的质谱信号强度进而分析未知样品[61].
热脱附气相色谱质谱(TDS-GC-MS)通过将样品置于热重天平上,加热到1000 ℃降解[62],降解产物吸附在固相上后进行热脱附,再升高温度对降解产物进行解吸,用色谱柱分离并进行质谱分析,从而实现微塑料样品的定量检测. TDS-GC-MS方法要求的样品微塑料含量在1%以上,在实际操作中可能需要将样品浓缩. TDS-GC-MS分析中所需样品质量约为Py-GC-MS中所用样品质量的200倍[63],因此TDS-GC-MS适用于质量较高(最高可达100 mg)的样品,能提供良好的定性分析[63 − 64]. 而且,高样品质量保证测量的样品具有代表性的同时,还无需事先耗时地选择聚合物颗粒,适用于测量环境中具有不均匀的复杂基质的样品. 该方法不需要对样品进行特殊的预处理,通过研磨和混合即可使样品均质化,分析时间仅需要2—3 h,是一种可在短时间内分析高样本量的方法[62]. 虽然TDS-GC-MS也提供半定量检测,但必须对结果进行仔细评估,因为根据聚合物类型、吹扫气体流量和使用的样品质量的不同,结果存在很大偏差[64].
将热重分析与固相萃取(TGA-SPE)和热脱附气相色谱质谱(TDS-GC-MS)相结合,称为热萃取-热脱附-气相色谱质谱联用(TGA-SPE-TDS-GC-MS). 该方法同时体现了TGA较热裂解而言检测大尺寸样品的优势,以及GC-MS较DSC而言更高的分辨率. 与Py-GC-MS等相关方法相比,该方法通过分离固相萃取和随后的TDS-GC-MS分析,大大减少了工作量. 由于样品质量易于处理,因此可以对释放的热降解产物进行直接样品比较[64].
热裂解气相色谱质谱(Py-GC-MS)是一种分析聚合物热裂解气体的检测手段,将从样品获得的热解色/质谱与已知聚合物的热解色/质谱进行对比,从而确定聚合物的结构和类型等信息. 分析的流程为: 首先微量高分子样品在惰性气体中被快速加热而生成许多裂解产物导入气相色谱,从所得的色谱图来分析该高分子的化学组成和结构;然后将受热逐步释放出的气体送入质谱检测器,给出所释放气体强度随温度变化的质谱曲线,进而分析所释放气体的物质信息. Py-GC-MS法可用于识别和定量微塑料颗粒的聚合物类型以及相关的有机塑料添加剂[65]. 该方法鉴定不依赖微塑料颗粒的形状、大小或有机或无机污染物的存在,通常不需要对样品进行任何前处理. Py-GC-MS法分析过程所需样本量虽然极少,但在进行复杂的样品分析时,可能会出现样品不具有代表性的问题. 此外,与TDS类似, Py-GC-MS法具有很强的破坏性,无法获得微塑料颗粒的数量、尺寸和形状的信息,而缺失的这些信息对评估微塑料对生物和生态系统的影响却是至关重要的[56].
与TDS-GC-MS相比, Py-GC-MS提供了更高的灵敏度,使其在识别小质量(低至约50 μg)的微塑料时效果更佳[66],主要应用在识别饮用水这种微塑料颗粒可以简单就分离出来的基质中. 但是,面对例如嵌入或附着在其他材料上导致无法分离出来的纳米塑料时,Py-GC-MS的灵敏度可能就无法检测[67]. 此外,目前Py-GC-MS的缺陷还体现在以下方面: 可进样的样品量受到热解器尺寸的限制,每次只能对单个颗粒的进行分析,单个颗粒的预选耗时,效率低下,不适用于常规分析[68];分析样品颗粒的最小尺寸约为50 μm,但小于100 µm尺寸的样品颗粒已很难处理,热脱附管的直径(1.5 mm)也决定了最大尺寸的限制,需要在分析之前对大颗粒进行粉碎[60];由于该方法基体效应强,无法对整个环境样品进行分析,且因其对杂质非常敏感,不适合分析混合有高浓度杂质的样品[54];由于不同的温度行为,分析结果在不同的热解器上的重现性相对较差[64];分析容易受到污染甚至堵塞,特别是在聚合物的热解过程中,产生了高分子量的热解产物,这些热解产物可以在小范围内冷凝转移到细管中,导致使用该方法分析维护成本偏高[62].
虽然微塑料的物化分析有多种方法可供选择,但在实际应用中,单一方法检测微塑料容易受假阳性或假阴性信号的干扰,使检测准确度较低,所以在鉴别过程中需要应用不同的和互补的方法对存疑样品进行综合分析. 可比较各方法的优缺点,根据不同情景对各检测方法进行有机结合(表3).
例如,由于部分物质红外活性和拉曼活性互斥,即有红外活性则无拉曼活性,反之亦然,可以利用拉曼光谱基于光的非弹性散射测量聚合物化学结构对应的能量变化,为红外光谱补充分子振动信息. 一般来说,红外光谱用于鉴定分子的极性官能团,而拉曼光谱用于鉴定主链结构[5],二者可互相补充. 另外,对于微塑料颗粒的鉴定,Py-GC-MS和光谱方法都非常适合表征其化学性质,且二者相结合可以获得非常有价值的互补信息[73]. 体现在红外光谱法具有无损、省时的优点,可用于聚合物类型和无机添加剂的鉴别,而Py-GC-MS虽具破坏性且耗时长(一次约30 min),但可为有机添加剂和非均相/多组分聚合物体系(例如醇酸涂料)提供额外的信息[41]. 并且, Py-GC-MS对聚合物的鉴定结果更为精细,有研究显示Py-GC-MS将μRaman鉴定为PP的两种颗粒分别鉴定为PE和PP共聚物,还发现μRaman鉴定的PA颗粒其实由PE、PP和PA 6组成[74]. 此外,为了对塑料颗粒进行详细的表征,所建立的化学分析方法,如Py-GC-MS、FTIR和μRaman还可以与SEM-EDS联用以增加空间分辨率[75 − 77]. 例如,μRaman和SEM-EDS联用为微米和纳米塑料颗粒的详细化学和形态分析提供了极好的可能性,通过将获得的数据合并在一个软件中,可以在整个滤光片表面导航,并将相同位置的微塑料形态在电子和光学显微镜的空间分辨率下(SEM为1.6 nm, 而光学显微镜仅为1–10 μm)与μRaman光谱的化学识别进行关联[78].
-
尽管目前环境中微塑料的检测已经建立了诸多的分析方法,但是仍存在许多明显的不足. 例如受主观判断和人工熟练度影响、空间分辨率不足、受基底影响大、前处理过程较为繁琐、进样量小、分析成本高等. 近年来,针对以上分析方法的局限,研究人员持续开发出新的方案,在仪器开发、方法创新和对象扩展等方面取得了长足的进展.
-
由于传统的FTIR和拉曼分析受到光衍射的限制,微塑料检测的空间分辨率难以达到纳米级[79]. 近年来,原子力显微镜红外光谱(AFM-IR)[80]、纳米FTIR[81]、表面增强拉曼光谱(SERS)[82]、尖端增强拉曼光谱(TERS)[83]、 空间外差-拉曼光谱(SHRS)[84]、拉曼光镊[85]、和光学光热红外(O-PTIR)[86 − 87]等新技术不断的提升检测分析的精度,使得微塑料分析的空间分辨率不断提高,提升对微塑料形成以及暴露的详细了解.
原子力显微镜红外光谱(AFM-IR)技术使用脉冲可调谐红外激光光源,聚焦在原子力显微镜(AFM)针尖附近的样品上,并调谐到样品的吸收带,吸收的光导致样品局部的光热膨胀,被AFM针尖记录. 由于微悬臂振荡与红外吸收成正比,因此测量AFM悬臂梁振荡幅度作为波长(或波数)的函数,可得到纳米级空间分辨率(约20—50 nm)的局域吸收光谱. Felts等成功地将AFM-IR技术应用于聚合物纳米结构的化学识别和纳米化学成像,以全内反射模式对沉积在红外透明ZnSe棱镜上的PE和PS纳米细线进行了分析,获得了优于100 nm的空间分辨率[88].
纳米FTIR方法基于散射型扫描近场光学显微镜(s-SNOM),可以测量样品表面的宽带红外吸收光谱,空间分辨率低至10—20 nm. 在纳米FTIR实验中,红外光束聚焦在近场探针上,典型的金属涂层针尖和局部天线效应会产生与针尖尺寸相同的纳米尺度焦点. 在针尖扫描表面的过程中,针尖与样品之间的近场相互作用发生周期性变化,然后使用非对称迈克尔逊干涉仪检测由此产生的局部散射强度的变化,散射光的振幅和相位可反映样品的局部红外吸收[89]. 早在2006年,Brehm等就报道了直径为30—70 nm的聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(PMMA)微球的纳米FTIR检测[90].
表面增强拉曼散射(SER)的适用于纳米塑料颗粒拉曼信号弱的问题. 利用当待测物靠近或附着在纳米尺寸的金属(Ag或Au)胶状或粗糙的表面时,其拉曼信号会显著增强这一原理. 通过电磁(局域表面等离子体共振)和化学(电荷转移)增强效应,可实现103—1011倍的样品信号增强效果[91]. Lv等研究表明,使用Ag胶体[92]作为SERS介质,可以显著增强直径为100 nm和500 nm的PS微球的拉曼信号[93].
尖端增强拉曼光谱(TERS)利用AFM(或者扫描隧道显微镜,STM)扫描样品表面的等离激元金属纳米结构,以类似SERS的方式对场进行局域增强. 在TERS实验中,探针尖端位于样品上方,激光激发粒子的局域表面等离子体共振,传导电子的相干振荡. 局域表面等离子体共振极大地增强(高达100—1000倍)纳米颗粒附近的局域电场,信号增加效果最高可达108倍[79]. 目前,TERS系统有不同的配置,包括底部、顶部和侧面光照以及基于抛物面镜的装置,可以实现空间分辨率约为30—50 nm的灵敏化学分析[79,94],对于一些样品(例如碳纳米管)甚至低至1.7 nm(STM联用)[95].
空间外差-拉曼光谱(SHRS)技术融合了空间外差光谱仪(SHS)和拉曼光谱(RS)技术,解决了传统微塑料检测中吞吐量低、信噪比低的问题,提高了对微塑料的识别效率[96]. SHRS系统对微塑料进行拉曼光谱检测,以激光作为激发光源,激光被微塑料样品散射,承载着微塑料样品分子信息的拉曼散射光经过SHRS干涉系统后,在CCD探测器上形成了拉曼光谱. 通过一系列的还原算法,可以得到拉曼光的波数和强度,从而可以对微塑料样品信息进行分析[84].
拉曼光镊直接在水介质中进行微塑料的拉曼分析,因为水是非常弱的拉曼散射体. 这种分析可以通过使用光镊将粒子夹在激光束的焦点中,进而实现μRaman光谱识别[97]. 拉曼光镊技术采用633 nm和785 nm波长激光对分散在水中的塑料颗粒进行研究. 在单颗粒水平上能够明确区分塑料与有机质和矿物沉积物,并评估其的大小和形状. 在此背景下,光镊实现的场流分离和显微拉曼光谱的在线耦合可用于纳米塑料的分析,有研究在流动池中实现了颗粒分离和表征(使用非对称流或离心场流分离结合紫外和多角度光散射)与后续在线显微拉曼光谱化学识别的联用[98].
光学光热红外(O-PTIR)使用连续短波长可见激光探针探测样品中红外吸收区域的光热效应,进而获取分析物的红外光谱[99]. 与FTIR相比,这种探测机制大大提高了微塑料检测的空间分辨率(大约400 nm[100])和灵敏度(约0.4 pg[101]),且不受样品荧光干扰. O-PTIR的这些特性既可以实现单个微塑料颗粒的亚微米分辨率成像,也可以实现组成这些颗粒的化学修饰聚合物的深度成像测定. 有研究成功应用O-PTIR技术识别了婴儿硅胶奶嘴蒸汽清洗后的微塑料分布,结果突出了表面活性硅胶衍生的微塑料颗粒进入人体和环境的途径[87].
-
微塑料分析的各个流程(收集、提取和表征)都很耗时,而且快速量化和识别微塑料的能力受视觉分选或预处理等的影响而效率较低,这些因素导致实施大规模微塑料检测难度较高. 即便如此,目前已有一些研究针对微塑料的大批量样品分析或连续快速分析进行了方法的改良. 例如,结合图像分析技术可以快速识别大量微塑料样品的耦合静态图像分析的半自动显微拉曼光谱[102];高光谱成像技术与图像处理和化学计量学方法结合[103];近红外光谱(NIR)分析与化学计量学结合[104];以及基于量子级联激光的高光谱红外化学成像技术(LDIR)与自动数据分析结合[105]等技术. 这些技术允许在最少的人工机器操作干预下以高效率的方式进行大量的微塑料检测. 此外,一些研究人员试图通过便携仪器对微塑料进行现场检测从而省去复杂的样品采集和提取过程,例如使用便携式可见光近红外光谱仪,直接在现场分析,而不需要费时费力的提取和检测程序,可实现快速评估土壤中微塑料浓度和低密度微塑料颗粒的识别和定量分析[106];有学者通过核磁共振波谱技术(qNMR)排除样品尺寸的干扰直接对溶液中的PE颗粒、PS微珠和PET纤维等微塑料进行定性、定量分析[107];还有基于阻抗谱技术快速识别大通量流水中的微塑料,阻抗谱直接表征单个颗粒在水流中的电学特性,同时可以进行尺寸测量和材料识别[108];还有学者基于高光谱成像快速检测鱼肠道中微塑料,这种新方法直接从肠道内容物的高光谱图像(HIS)中分离、识别和表征微塑料,省去了组织消解的复杂前处理步骤[109];有研究者开发了一种体积法,使用基于阈值的三维分割程序和Z-堆栈共聚焦图像对几乎任何基质(土壤、水、食物等)中的微塑料进行量化,使环境微塑料样品的体积测量成为可能[110]. 总体而言,目前微塑料的自动检测仍存在分析方法仪器要求高、检测手段复杂或者是应用对象有限等缺点,开发广泛适用性的经济便捷的快速大批量微塑料自动检测方法仍是微塑料检测面临的重要问题.
机器辅助也是微塑料检测的重要创新方法,通过机器对可疑数据进行处理,或是代替人工自动判断,可以显著提高数据分析的效率和准确性. 例如,基于FTIR光谱的机器学习算法[111];微塑料全息指纹分形特性[112];微通道微流体技术[113];流式细胞仪[114];支持向量机(SVM)分类器[115];或是对拉曼光谱矩阵进行双主成分分析[116];这些方法可以快速自动识别和可视化微塑料样品. 同时,除机器自动化识别以外,建立模型也可以有效的提升数据分析的效率. 例如,通过基于随机森林(RF)的多变量模型与μFTIR图像识别结合[117],卷积神经网络(CNN)模型与近红外光谱相结合[118],或者是泊松-对数正态分布建模[119]等方式,鉴定和评估样品中微塑料颗粒情况. 总而言之,通过计算机系统的自动识别程序,可以快捷简便的识别样品中的微塑料的类型、分布和组成等情况,大大提升了分析的效率和准确性,是未来进行微塑料检测的有效和可行的分析方法.
此外,针对单个方法易于产生假性结果或受仪器参数影响的弊端,一些学者从多方法结合方面展开工作. 例如,通过多证据结合使用多种分析方法表征微塑料组分,研究者开发出利用聚合物-染料结合化学、密度测试、独特的表面形态特征和荧光染色来识别环境样品中的微纤维的方法[120];结合空气监测仪与拉曼光谱成像用于环境颗粒物样品中可吸入微塑料的检测[121];基于热重分析(TGA)和统计计算相结合的土壤通用模型方法(SUMM),可用于定性和定量测定农业土壤中最常见的微塑料(PE、PS、PVC和PET)[122];用总有机碳(TOC)作为通用综合指标定量测定水体环境中微纳塑料类型和尺寸,该方法具有测量成本低和检出限低的优点[123];将近常光谱成像(FTIR、O-PTIR、共聚焦拉曼)和化学计量学方法结合对玉米粉中痕量微塑料进行原位表征,实现对粉状食品中痕量微塑料的无损可视化检测[124]. 以上使用多方法结合的方式,可以显著的降低单一方法判断不准确、不严谨或是结果易受其他假性因素干扰等问题,是微塑料检测的重要前景方向.
-
随着检测方法空间分辨率、检测方法的便捷性以及检测对象要求的不断提高,微塑料检测不断向着更精密、更快速和更准确的方向发展,目前对纳米微塑料、人体组织微塑料等对象的检测,已经取得了一定的进展.
自然环境中塑料降解是一个持续进行的过程,微米级的微塑料进一步降解到纳米级后称之为纳米塑料. 纳米塑料微小的尺寸会使得它们可以轻易渗透生物屏障进入细胞,导致潜在的细胞毒性和健康风险[125]. 自从首次报道使用Py-GC-MS在北大西洋副热带环流系检测到纳米塑料以来[126],纳米塑料的检测受到了广泛的关注. 早期的纳米塑料检测主要通过连续机械过滤等物理方式进行,可以发现直径约20—50 nm的纳米塑料[47]. 近年来,随着仪器空间分辨率的提升,有研究通过区分激光光斑、像素尺寸或图像分辨率、纳米塑料在激光光斑内尺寸或位置、拉曼信号强度和样品制备等方式,证明了拉曼成像可以成功用于可视化和识别低至100 nm的纳米塑料[127]. 表面增强拉曼光谱(SERS)因其对分子的高度敏感性和易于快速定性被广泛用于纳米微塑料颗粒的检测[125]. 目前,识别复杂环境基质中的纳米塑料仍然是一个挑战,因为纳米塑料的碳基结构导致它们的组成种类繁多,而且与天然有机物相比纳米塑料的环境浓度很低. 虽然如此,Py-GC-MS[128]和热解吸-质子转移反应-质谱仪(TD-PTR-MS)[129]等方法为应对复杂环境基质的纳米塑料检测提供了思路. Py-GC-MS可有效克服环境基质的干扰,为纳米塑料在土壤、灰尘和生物群落等环境基质中的识别和探测提供了新的可能性.TD-PTR-MS具有高灵敏度和高分辨率的特点,允许使用小体积(1 mL)的样品,无需任何预浓缩步骤即可进行实验,已广泛应用于环境中各种复杂有机混合物的分析.
人体组织微塑料检测是判断人体微塑料环境暴露最直接的方式. 虽然人们已经意识到通过食物链传播的人体微塑料暴露,但是目前关于微塑料人体组织内分布特征、人体微塑料迁移途径和富集机制、人体微塑料污染的潜在危害等认识尚不清晰[130 − 132],亟需有效的人体微塑料检测方法以加强微塑料污染的溯源研究、入侵途径和健康效应等方面的研究. 由于在人体对微塑料的摄取中,小于150 μm的颗粒可以通过胃肠道屏障,而小于10 μm的颗粒能穿过细胞膜到达器官. 因此,研究人体生物样品中的微塑料需要研究可靠的技术来分析小至1 μm的颗粒. 目前在检测人体组织微塑料的研究中,已经能够对各种人类生物样本中的微塑料进行表征和研究,研究对象主要集中在人类粪便样本,因为粪便样本提取是一种对人体侵入性较小的微塑料生物监测方法[133]. 人体微塑料的检测通常涉及人体组织消解、微塑料提取和聚合物分析等步骤,从技术层面上,所用的检测方法主要是显微FTIR、显微拉曼和激光红外光谱等. 自2019首次在人体的粪便检测出微塑料[134]以来,研究人员通过FTIR[135]、拉曼光谱[136]、LD-IR[137]、Py-GC–MS[138]等方法,在人体的结肠[135]、肺组织[136,139]、粪便[140 − 141]、唾液[142]、胎盘[137]、血液[138]等中,检测出PC、PA、PU、PI、PP、PS、PVC、PE和PET等多种微塑料聚合物,其中以PET和PU为主要成分. 对微塑料人体分布和暴露来源等方面进行分析,结果表明饮食暴露(如饮用塑料包装的瓶装水)和环境暴露(粉尘暴露和空气吸入)等对人体微塑料的摄入的重要影响. 但是因为目前前期积累的研究基础较差,仍需要有针对性的对现有人体微塑料检测方法进行扩充和进一步发展.
-
环境中微塑料的检测涉及诸多的方法,不同方法所用仪器又有许多区分,为适应新的需要,一些创新的方法亦不断被提出. 总体而言,在物理表征方面,通常使用裸眼、光学或电子显微镜检测形状、颜色、尺寸等信息,而在化学表征方面检测聚合物类型及定量组成等信息,依据应用的原理化学分析可以大致分为,基于光谱的傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)和拉曼光谱;基于热稳定性的差示扫描热分析(DSC)和热重分析(TGA);以及基于质谱的热脱附气相色谱质谱(TDS-GC/MS)和热裂解气相色谱质谱(Py-GC/MS). 在这些方法中,无损的红外光谱和拉曼光谱应用最为广泛,而两者又分别在样品适用性和空间分辨率方面各有优势.DSC和TGA方法检测的样品种类具有局限性,而TDS-GC/MS和Py-GC/MS则可以测试大多数的聚合物种类,但是进样量较小过程繁琐耗时长. 如果能够依据样品实际情况采取不同的方法组合,可以对样品各种信息产生更加全面的了解.
近年来,针对微塑料的检测,从仪器开发、方法创新和对象扩展等方面取得了长足的进展,特别是人体的微塑料检测和纳米塑料的检测等方面,是目前微塑料检测工作的主要热点. 关于环境中微塑料的检测研究展望主要有以下几点:
(1)环境中微塑料样品的采集方法标准化. 微塑料因自身特性,能够在土壤、大气、沉积物和水体等各种环境中迁移富集,所以采集微塑料样品的对象较为广泛,需求的方式也随之各有不同,需要建立统一手段采集样品的标准化程序,提高采样的科学性.
(2)环境中微塑料样品的前处理方法标准化. 主要是针对复杂基质的样品,如何通过有效程序提取分离其中的微塑料颗粒进而开展研究. 许多微塑料的分析方法,如光谱法和质谱分析,都要求将微塑料颗粒分离进行单独的检测,这就要求有高效的前处理手段来对含有各种杂质的复杂样品进行处理.
(3)环境中微塑料样品的复合成分检测. 微塑料易于吸附各种微生物、有机污染物和重金属元素,会随着所附着成分的不同产生差异性的物理化学和毒理效果. 以往研究主要针对微塑料颗粒自身的物理化学性质进行,较少关注到与其有关的有机污染物和重金属元素等. 作为与微塑料息息相关的重要影响因素,在进行微塑料分析时对其附着的有机污染物和重金属元素的同时检测至关重要.
(4)人体微塑料检测和纳米塑料检测. 微塑料在环境中持续分解,纳米塑料是其不可避免的形态. 近年来开发出多种检测纳塑料的新技术新方法,需进一步优化检测技术,使纳米塑料检测技术标准化并能够广泛投入运用. 此外,现有研究已经显示,微塑料对人体有严重的危害作用,目前对人体组织微塑料的检测主要使用常规检测方法,处于起步阶段. 精细准确检测人体中的微塑料对了解其侵入途径、在人体的传播方式和对人体健康响应等至关重要.
环境中微塑料检测方法的研究进展
Research progress on analytical methods for microplastics in the environment
-
摘要: 微塑料是指粒径小于5 mm的塑料碎片或颗粒,能够在大气、土壤和水体中迁移和富集,通过食物链累积,对人体健康产生严重危害. 为了更好地评估环境中微塑料的污染,本文详细综述了微塑料检测方法和技术手段的应用现状,包括显微镜分析、扫描电镜能谱分析、光谱分析、热分析和质谱分析等微塑料常用检测方法并对比了各方法的优缺点. 总结了近年来微塑料检测的新方法和新技术,重点讨论微塑料检测当前面临的技术挑战和未来的研究方向,对建立统一和标准化的微塑料分析方法进行展望, 为系统地和进一步地开展微塑料的污染评价及风险评估提供指导.Abstract: Microplastics are plastic fragments or particles with a size smaller than 5 mm, which can migrate and enrich in the atmosphere, soil and water bodies, and then accumulate through the food chain, posing a serious health risk to humans. For the purpose of assessment of the microplastic pollution in the environment, this paper presents a detailed review of the current application of microplastic detection methods and technological tools, i.e., photomicrography, scanning electron microscopy, spectrometer, thermal and mass spectrometry, and evaluates the advantages and disadvantages of each method. Summarized new methods and techniques for microplastics detection in recent years and discussed current technical challenges and future research directions for microplastics detection. The establishment of unified and microplastics standardized microplastics analytical methods is prospected and the possible guidance for the systematic and further evaluation and risk assessment of microplastic is provided.
-
Key words:
- microplastics /
- analysis methods /
- application prospect.
-

-
表 1 微塑料样品分离方法比较
Table 1. Comparison of microplastic sample separation methods
分离方法
Methods常用试剂
Reagents优点
Advantages缺点
Disadvantages参考文献
References筛分法
Sieving用于样品中微塑料的初步分离,可以在一定程度上简化微塑料的进一步分析检测 不适合分离<1mm的微塑料 [15] 密度分离法
Density separation饱和NaCl溶液
(密度1.2 g∙cm−3)成本低,易操作,对人体无毒 密度较小,对高密度微塑料颗粒的分离效果差 [1] 饱和NaI溶液
(密度1.8 g∙cm−3)对密度较高的微塑料分离效果好 有毒,成本高,污染环境 [16] ZnCl2溶液
(密度1.6 g∙cm−3)对密度较高的微塑料分离效果好 成本高,污染环境 [17] 油提取法
Oil extraction菜籽油、橄榄油、
蓖麻油成本低廉、效率高. 经过酒精洗涤清洗后不会干扰后续的仪器分析 清洗不完全残留的试剂可能导致塑料结构被破坏 [18] 泡沫浮选法
Foam flotation对低密度微塑料颗粒分离效果好 不适于分离高密度微塑料颗粒,且分离效果受微塑料粒度、形状等物理因素的影响 [19] 磁性分离法
Magnetic separation对大尺寸和小尺寸纳米塑料的分离效果较好 微塑料结构可能破坏,铁存在也可能干扰后续分析与表征 [19 − 20] 表 2 微塑料样品有机物消解方法比较
Table 2. Comparison of organic digestion methods for microplastic samples
消解法
Methods常用试剂
Reagents优点
Advantages缺点
Disadvantages参考文献
References酸消解法
Acid digestionHNO3 效率高,有效去除大分子有机杂质 某些类型聚合物如PA、PS和PET消解时被破坏 [21−22] HCl 效率低,使用较少 [19] HNO3-HClO4 可彻底分解有机物,缩短消解时间 耐酸性低的聚合物更容易降解 [23] 碱消解法
Alkali digestionNaOH、KOH 通过裂解蛋白质和脂肪等破坏生物组织,适用于生物样本消解;对微塑料结构的影响相对较弱 破坏特定种类微塑料的结构并使其变色;耗时 [23−24] 氧化法
Oxidative digestionH2O2 适用于于沉积物和土壤 处理富含有机物的样品会产生丰富的泡沫,使微塑料回收率偏低 [25] 芬顿(Fenton)试剂 效率高;有效破坏H2O2难以消解的有机成分和无机化合物 pH超过 5—6,会形成氢氧化铁沉淀,干扰后续分析和化学表征 [26] 酶消解法
Enzymatic digestion蛋白酶K、纤维素酶 不会对微塑料结构产生影响;对环境危害小 成本较高 [27] 工业酶 成本低廉 土壤中有机物的消解效果未知 [19] 表 3 微塑料检测方法比较
Table 3. Comparison of microplastics detection methods
检测方法
Methods原理
Principles尺寸或质量
检出限
Size or
quality LOQ前处理
Preparation获取信息
Information优点
Advantages缺点
Disadvantages适用情景
Application参考文献
References扫描电镜能谱联用
(SEM-EDS)二次电子和背散射电子成像,特征X射线元素分析 20 nm 脱水,
低真空无需
镀膜数量,尺寸,形状(表面特征),基于元素组成的有机无机物判断 空间分辨率高(约nm级),元素点、线、面半定量测定 成本高,耗时 物理形态分析要求较高微塑料分析 [65,69] 傅里叶变换红外光谱
(FTIR)特征红外吸收光谱,干涉图傅里叶变换 10 μm 无需特殊处理(复杂样品需
除杂)数量,聚合物
类型Mirco-FT-IR光谱分析实现样品可视化;能自动采集数据并生成图像;不破坏样品、预处理简单、不受荧光干扰、还可对滤膜进行自动分析 结果受H2O和CO2干扰;需要无尘环境;耗时;不透明/黑色的塑料微粒分析也较为困难 较多数量且微塑料尺寸较大的样品的物理和化学形态的综合分析 [70 − 72] 拉曼光谱 拉曼散射 1 μm 无需特殊处理(复杂样品需
除杂)数量,聚合物
类型采用显微Raman光谱时,无须投加试剂且不破坏样品,满足复杂样品的分析要求 受环境基底影响严重,检测环境样品时常有荧光干扰 尺寸较小不具荧光样品的分析 [69] 热脱附气相色谱质谱(TDS-GC/MS) 有机物萃取挥发,经色谱柱分离,使用质谱
检测无具体要求 涂覆吸附涂层的固相萃取搅拌棒搅拌吸附之后热脱附 微塑料类别,聚合物类型 多种成分定量分析 破坏性分析;实验条件要求高;进样量少 小批量样品精细测量化学组成的分析 [64] 热裂解气相色谱质谱
(Pyr-GC/MS)聚合物热稳定性 0.01—1 μg 采样器配热脱附系统 微塑料类别,聚合物类型 同时鉴定聚合物、表面附加物;无须投加其他溶剂;样品用量小;前处理简单,可直接进样 破坏性分析;实验条件要求高;存在误判风险;允许上机的样品量小 小批量样品精细测量化学组成的分析 [65,72,41] -
[1] THOMPSON R C, OLSEN Y, MITCHELL R P, et al. Lost at sea: where is all the plastic?[J]. Science, 2004, 304(5672): 838-838. [2] 杨婧婧, 徐笠, 陆安祥. 环境中微(纳米)塑料的来源及毒理学研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(3): 383-396. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017071002 YANG J J, XU L, LU A X, et al. Research progress on the sources and toxicology of micro (nano) plastics in environment[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(3): 383-396 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017071002
[3] ROCHA-SANTOS T, DUARTE A C. A critical overview of the analytical approaches to the occurrence, the fate and the behavior of microplastics in the environment[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 65: 47-53. [4] COLE M, LINDEQUE P, HALSBAND C, et al. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(12): 2588-2597. [5] GUO X, LIN H, XU S, et al. Recent advances in spectroscopic techniques for the analysis of microplastics in food[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2022, 70(5): 1410-1422. [6] ZHANG Q, XU E G, LI J, et al. A review of microplastics in table salt, drinking water, and air: direct human exposure[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(7): 3740-3751. [7] SHIM W J, THOMPOSON R C. Microplastics in the Ocean[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2015, 69(3): 265-268. [8] HUERTA LWANGA E, MENDOZA VEGA J, KU QUEJ V, et al. Field evidence for transfer of plastic debris along a terrestrial food chain[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 14071. [9] ZHU D, CHEN Q L, AN X L, et al. Exposure of soil collembolans to microplastics perturbs their gut microbiota and alters their isotopic composition[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2018, 116: 302-310. [10] FARRELL P, NELSON K. Trophic level transfer of microplastic: Mytilus edulis (L. ) to Carcinus maenas (L. )[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 177: 1-3. [11] WATTS A J R, LEWIS C, GOODHEAD R M, et al. Uptake and retention of microplastics by the shore crab carcinus maenas[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(15): 8823-8830. [12] CARPENTER E J, SMITH K L. Plastics on the Sargasso Sea surface[J]. Science, 1972, 175(4027): 1240-1241. [13] ARTHUR C , BAKER J , BAMFORD H. Proceedings of the second research workshop on microplastic debris, November 5−6, 2010[Z]. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS-OR&R-39, 2011. [14] EUROPE P. Plastics–the facts 2020[J]. PlasticEurope, 2020, 1: 1-64. [15] 薛荔栋,张霖琳,于海斌,等. 土壤微塑料监测技术现状及方法标准化建议[J]. 中国环境监测, 2022, 38(5 ): 9-17. XUE L D, ZHANG L L, YU H B, et al. Research status of monitoring technologies for microplastics in soil and suggestions for method standardization[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2022, 38(5): 9-17 (in Chinese).
[16] NUELLE M T, DEKIFF J H, REMY D, et al. A new analytical approach for monitoring microplastics in marine sediments[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014, 184: 161-169. [17] ZOBKOV M B, ESIUKOVA E E. Evaluation of the Munich Plastic Sediment Separator efficiency in extraction of microplastics from natural marine bottom sediments: Munich Plastic Sediment Separator efficiency[J]. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 2017, 15(11): 967-978. [18] CRICHTON E M, NOËL M, GIES E A, et al. A novel, density-independent and FTIR-compatible approach for the rapid extraction of microplastics from aquatic sediments[J]. Analytical Methods, 2017, 9(9): 1419-1428. [19] 陈雅兰,孙可,韩兰芳,等. 土壤中微塑料的分离及检测方法研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 2022, 59(2): 364-380. CHEN Y L, SUN K, HAN L F, et al. Separation, identification, and quantification methods in soil microplastics analysis: A review[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2022, 59(2): 364-380 (in Chinese).
[20] GRBIC J, NGUYEN B, GUO E, et al. Magnetic extraction of microplastics from environmental samples[J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2019, 6(2): 68-72. [21] SCHEURER M, BIGALKE M. Microplastics in Swiss Floodplain Soils[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(6): 3591-3598. [22] GAUQUIE J, DEVRIESE L, ROBBENS J, et al. A qualitative screening and quantitative measurement of organic contaminants on different types of marine plastic debris[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 138: 348-356. [23] QIU Q, TAN Z, WANG J, et al. Extraction, enumeration and identification methods for monitoring microplastics in the environment[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016, 176: 102-109. [24] DEHAUT A, CASSONE A L, FRÈRE L, et al. Microplastics in seafood: Benchmark protocol for their extraction and characterization[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 215: 223-233. [25] ZHAO S, DANLEY M, WARD J E, et al. An approach for extraction, characterization and quantitation of microplastic in natural marine snow using Raman microscopy[J]. Analytical Methods, 2017, 9(9): 1470-1478. [26] HURLEY R R, LUSHER A L, OLSEN M, et al. Validation of a method for extracting microplastics from complex, organic-rich, environmental matrices[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(13): 7409-7417. [27] COURTENE-JONES W, QUINN B, MURPHY F, et al. Optimisation of enzymatic digestion and validation of specimen preservation methods for the analysis of ingested microplastics[J]. Analytical Methods, 2017, 9(9): 1437-1445. [28] ENFRIN M, DUMÉE L F, LEE J. Nano/microplastics in water and wastewater treatment processes – Origin, impact and potential solutions[J]. Water Research, 2019, 161: 621-638. [29] CORCORAN P L, BIESINGER M C, GRIFI M. Plastics and beaches: A degrading relationship[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2009, 58(1): 80-84. [30] BORN M P, BRÜLL C. From model to nature — A review on the transferability of marine (micro-) plastic fragmentation studies[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 811: 151389. [31] ALLEN N S, EDGE M, MOHAMMADIAN M, et al. Hydrolytic degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate): Importance of chain scission versus crystallinity[J]. European Polymer Journal, 1991, 27(12): 1373-1378. [32] HANKE G, GALGANI F, WERNER S, et al. Guidance on monitoring of marine litter in European Seas[Z]. EUR Luxembourg (Luxembourg): Publications Office of the European Union, 2013. [33] ERIKSEN M, MASON S, WILSON S, et al. Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Laurentian Great Lakes[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 77(1-2): 177-182. [34] HIDALGO-RUZ V, GUTOW L, THOMPSON R C, et al. Microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the methods used for identification and quantification[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(6): 3060-3075. [35] 姚浩. 环境中微塑料检测方法的研究进展[J]. 山西化工, 2022 42(2 ): 55-57. YAO H. Research progress on detection methods of micro plastics in environment[J]. Shanxi Chemical Industry, 2022, 42(2): 55-57 (in Chinese).
[36] 顾伟康, 杨国峰, 刘艺, 等. 环境介质中微塑料的处理与检测方法研究进展[J]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文), 2020, 42(1): 135-143. Treatment and detection methods of microplastics from environmental media: A review[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2020, 42(1): 135-143(in Chinese).
[37] 冉泰山,廖洪凯,龙健,等. 微塑料在土壤环境中的分离和检测方法研究进展[J]. 塑料科技, 2022, 50(7 ): 101-104. RAN T S, LIAO H K, LONG J, et al. Research progress on separation and detection methods of microplastics in soil environment[J]. Plastics Science and Technology, 2022, 50(7): 101-104 (in Chinese).
[38] AHMED M B, RAHMAN Md S, ALOM J, et al. Microplastic particles in the aquatic environment: A systematic review[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 775: 145793. [39] 王嘉嘉,王佩瑶,王成浩,等. 土壤中微塑料的检测及其对土壤生态环境的影响[J]. 塑料科技, 2022, 50(10 ): 108-112. WANG J J, WANG P Y, WANG C H, et al. Determination of microplastics in soil and its effects on soil ecosystem[J]. Plastics Science and Technology, 2022, 50(10): 108-112 (in Chinese).
[40] SILVA A B, BASTOS A S, JUSTINO C I L, et al. Microplastics in the environment: Challenges in analytical chemistry - a review[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2018, 1017: 1-19. [41] IVLEVA N P. Chemical analysis of microplastics and nanoplastics: challenges, advanced methods, and perspectives[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(19): 11886-11936. [42] DE FROND H, RUBINOVITZ R, ROCHMAN C M. μATR-FTIR spectral libraries of plastic particles (FLOPP and FLOPP-e) for the analysis of microplastics[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(48): 15878-15885. [43] GAGO J, GALGANI F, MAES T, et al. Microplastics in seawater: recommendations from the marine strategy framework directive implementation process[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2016, 3: 219. [44] ELERT A M, BECKER R, DUEMICHEN E, et al. Comparison of different methods for MP detection: What can we learn from them, and why asking the right question before measurements matters?[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 231: 1256-1264. [45] MALLIKARJUNACHARI G, GHOSH P. Analysis of strength and response of polymer nano thin film interfaces applying nanoindentation and nanoscratch techniques[J]. Polymer, 2016, 90: 53-66. [46] LÖDER M G J, GERDTS G. Methodology used for the detection and identification of microplastics—a critical appraisal[M]//BERGMANN M, GUTOW L, KLAGES M. Marine Anthropogenic Litter. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2015: 201-227[2022-12-20]. [47] HERNANDEZ L M, YOUSEFI N, TUFENKJI N. Are there nanoplastics in your personal care products?[J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2017, 4(7): 280-285. [48] TAGG A S, SAPP M, HARRISON J P, et al. Identification and quantification of microplastics in wastewater using focal plane array-based reflectance micro-FT-IR imaging[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(12): 6032-6040. [49] VIANELLO A, JENSEN R L, LIU L, et al. Simulating human exposure to indoor airborne microplastics using a Breathing Thermal Manikin[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 8670. [50] KÄPPLER A, FISCHER D, OBERBECKMANN S, et al. Analysis of environmental microplastics by vibrational microspectroscopy: FTIR, Raman or both?[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2016, 408(29): 8377-8391. [51] ANGER P M, VON DER ESCH E, BAUMANN T, et al. Raman microspectroscopy as a tool for microplastic particle analysis[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 109: 214-226. [52] RIBEIRO-CLARO P, NOLASCO M M, ARAÚJO C. Characterization of microplastics by Raman spectroscopy[J]. Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 75: 119-151. [53] CABERNARD L, ROSCHER L, LORENZ C, et al. Comparison of Raman and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for the quantification of microplastics in the aquatic environment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(22): 13279-13288. [54] IVLEVA N P, WIESHEU A C, NIESSNER R. Microplastic in aquatic ecosystems[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(7): 1720-1739. [55] LÖDER M G J, IMHOF H K, LADEHOFF M, et al. Enzymatic purification of microplastics in environmental samples[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(24): 14283-14292. [56] MÖLLER J N, LÖDER M G J, LAFORSCH C. Finding microplastics in soils: A review of analytical methods[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(4): 2078-2090. [57] LI J, LIU H, PAUL CHEN J. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection[J]. Water Research, 2018, 137: 362-374. [58] MAJEWSKY M, BITTER H, EICHE E, et al. Determination of microplastic polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) in environmental samples using thermal analysis (TGA-DSC)[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2016, 568: 507-511. [59] RODRÍGUEZ CHIALANZA M, SIERRA I, PÉREZ PARADA A, et al. Identification and quantitation of semi-crystalline microplastics using image analysis and differential scanning calorimetry[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(17): 16767-16775. [60] PEÑALVER R, ARROYO-MANZANARES N, LÓPEZ-GARCÍA I, et al. An overview of microplastics characterization by thermal analysis[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 242: 125170. [61] DAVID J, STEINMETZ Z, KUČERÍK J, et al. Quantitative Analysis of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Microplastics in Soil via Thermogravimetry–Mass Spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(15): 8793-8799. [62] DÜMICHEN E, EISENTRAUT P, BANNICK C G, et al. Fast identification of microplastics in complex environmental samples by a thermal degradation method[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 174: 572-584. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.010 [63] DÜMICHEN E, BARTHEL A K, BRAUN U, et al. Analysis of polyethylene microplastics in environmental samples, using a thermal decomposition method[J]. Water Research, 2015, 85: 451-457. [64] DÜMICHEN E, BRAUN U, SENZ R, et al. Assessment of a new method for the analysis of decomposition gases of polymers by a combining thermogravimetric solid-phase extraction and thermal desorption gas chromatography mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2014, 1354: 117-128. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.05.057 [65] FRIES E, DEKIFF J H, WILLMEYER J, et al. Identification of polymer types and additives in marine microplastic particles using pyrolysis-GC/MS and scanning electron microscopy[J]. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 2013, 15(10): 1949. [66] LI C, GAO Y, HE S, et al. Quantification of nanoplastic uptake in cucumber plants by pyrolysis gas chromatography/mass spectrometry[J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2021, 8(8): 633-638. [67] AKAL N M K, KARAG Z S. Analytical pyrolysis of biomass using gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 61: 11-16. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2014.06.006 [68] ZHOU X , HAO L T, WANG H , et al. Cloud-point extraction combined with thermal degradation for nanoplastic analysis using pyrolysis gas chromatography–mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical chemistry, 2018, 91(3): 1785-1790. [69] VAN CAUWENBERGHE L, VANREUSEL A, MEES J, et al. Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 182: 495-499. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.08.013 [70] BROWNE M A, CRUMP P, NIVEN S J, et al. Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines woldwide: sources and sinks[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(21): 9175-9179. [71] CLAESSENS M, MEESTER S D, LANDUYT L V, et al. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in marine sediments along the Belgian coast[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(10): 2199-2204. [72] DEKIFF J H, REMY D, KLASMEIER J, et al. Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in sediments from Norderney[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014, 186: 248-256. [73] KÄPPLER A, FISCHER M, SCHOLZ-BÖTTCHER B M, et al. Comparison of μ-ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and py-GCMS as identification tools for microplastic particles and fibers isolated from river sediments[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 410(21): 5313-5327. [74] HERMABESSIERE L, HIMBER C, BORICAUD B, et al. Optimization, performance, and application of a pyrolysis-GC/MS method for the identification of microplastics[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 410(25): 6663-6676. [75] TER HALLE A, LADIRAT L, GENDRE X, et al. Understanding the fragmentation pattern of marine plastic debris[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(11): 5668-5675. [76] DONG M, ZHANG Q, XING X, et al. Raman spectra and surface changes of microplastics weathered under natural environments[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 739: 139990. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139990 [77] KARAMI A, GOLIESKARDI A, CHOO C K, et al. Microplastic and mesoplastic contamination in canned sardines and sprats[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 612: 1380-1386. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.005 [78] SARAU G, KLING L, OSSMANN B E, et al. Correlative microscopy and spectroscopy workflow for microplastics[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2020, 74(9): 1155-1160. [79] KUROUSKI D, DAZZI A, ZENOBI R, et al. Infrared and Raman chemical imaging and spectroscopy at the nanoscale[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(11): 3315-3347. [80] DAZZI A, PRATER C B. AFM-IR: technology and applications in nanoscale infrared spectroscopy and chemical imaging[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(7): 5146-5173. [81] MEYNS M, PRIMPKE S, GERDTS G. Library based identification and characterisation of polymers with nano-FTIR and IR-sSNOM imaging[J]. Analytical Methods, 2019, 11(40): 5195-5202. [82] KUROUSKI D, VAN DUYNE R P. In Situ detection and identification of hair dyes using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(5): 2901-2906. [83] LEE H, LEE D Y, KANG M G, et al. Tip-enhanced photoluminescence nano-spectroscopy and nano-imaging[J]. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(10): 3089-3110. [84] XUE Q, WANG N, YANG H, et al. Detection of microplastics based on spatial heterodyne Raman spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2022, 283: 121712. [85] FANG T, SHANG W, LIU C, et al. Nondestructive identification and accurate isolation of single cells through a chip with Raman optical tweezers[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(15): 9932-9939. [86] ZHAO P, ZHAO Y, CUI L, et al. Multiple antibiotics distribution in drinking water and their co-adsorption behaviors by different size fractions of natural particles[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 775: 145846. [87] SU Y, HU X, TANG H, et al. Steam disinfection releases micro (nano) plastics from silicone-rubber baby teats as examined by optical photothermal infrared microspectroscopy[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2022, 17(1): 76-85. doi: 10.1038/s41565-021-00998-x [88] FELTS J R, KJOLLER K, LO M, et al. Nanometer-scale infrared spectroscopy of heterogeneous polymer nanostructures fabricated by tip-based nanofabrication[J]. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(9): 8015-8021. [89] HERMANN R J, GORDON M J. Nanoscale optical microscopy and spectroscopy using near-field probes[J]. Annual Review of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 2018, 9(1): 365-387. [90] BREHM M, TAUBNER T, HILLENBRAND R, et al. Infrared spectroscopic mapping of single nanoparticles and viruses at nanoscale resolution[J]. Nano Letters, 2006, 6(7): 1307-1310. [91] SCHLÜCKER S. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: concepts and chemical applications[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(19): 4756-4795. [92] LEE P C, MEISEL D. Adsorption and surface-enhanced Raman of dyes on silver and gold sols[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1982, 86(17): 3391-3395. [93] LV L, HE L, JIANG S, et al. In situ surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for detecting microplastics and nanoplastics in aquatic environments[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 728: 138449. [94] VERMA P. Tip-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: Technique and Recent Advances[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(9): 6447-6466. [95] CHEN C, HAYAZAWA N, KAWATA S. A 1.7 nm resolution chemical analysis of carbon nanotubes by tip-enhanced Raman imaging in the ambient[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 3312. [96] ISSAKA E, YAKUBU S, SULEMANA H, et al. Current status of the direct detection of microplastics in environments and implications for toxicological effects[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances, 2023, 14: 100449. [97] GILLIBERT R, BALAKRISHNAN G, DESHOULES Q, et al. Raman tweezers for small microplastics and nanoplastics identification in seawater[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(15): 9003-9013. [98] SCHWAFERTS C, SOGNE V, WELZ R, et al. Nanoplastic analysis by online coupling of Raman microscopy and field-flow fractionation enabled by optical tweezers[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(8): 5813-5820. [99] ZHANG D, LI C, ZHANG C, et al. Depth-resolved mid-infrared photothermal imaging of living cells and organisms with submicrometer spatial resolution[J]. Science Advances, 2016, 2(9): e1600521. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1600521 [100] KLEMENTIEVA O, SANDT C, MARTINSSON I, et al. Super‐resolution infrared imaging of polymorphic amyloid aggregates directly in neurons[J]. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(6): 1903004. doi: 10.1002/advs.201903004 [101] LO M, MARCOTT C, KANSIZ M, et al. Sub-micron, non-contact, super-resolution infrared microspectroscopy for microelectronics contamination and failure analyses[C]//2020 IEEE International Symposium on the Physical and Failure Analysis of Integrated Circuits (IPFA). IEEE, 2020: 1-4. [102] FRÈRE L, PAUL-PONT I, MOREAU J, et al. A semi-automated Raman micro-spectroscopy method for morphological and chemical characterizations of microplastic litter[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2016, 113(1-2): 461-468. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.10.051 [103] SHAN J, ZHAO J, LIU L, et al. A novel way to rapidly monitor microplastics in soil by hyperspectral imaging technology and chemometrics[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 238: 121-129. [104] PAUL A, WANDER L, BECKER R, et al. High-throughput NIR spectroscopic (NIRS) detection of microplastics in soil[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(8): 7364-7374. [105] PRIMPKE S, GODEJOHANN M, GERDTS G. Rapid identification and quantification of microplastics in the environment by quantum cascade laser-based hyperspectral infrared chemical imaging[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(24): 15893-15903. [106] CORRADINI F, BARTHOLOMEUS H, HUERTA LWANGA E, et al. Predicting soil microplastic concentration using vis-NIR spectroscopy[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 650: 922-932. [107] PEEZ N, JANISKA M C, IMHOF W. The first application of quantitative 1H NMR spectroscopy as a simple and fast method of identification and quantification of microplastic particles (PE, PET, and PS)[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2019, 411(4): 823-833. [108] COLSON B C, MICHEL A P M. Flow-through quantification of microplastics using impedance spectroscopy[J]. ACS Sensors, 2021, 6(1): 238-244. [109] ZHANG Y, WANG X, SHAN J, et al. Hyperspectral imaging based method for rapid detection of microplastics in the intestinal tracts of fish[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(9): 5151-5158. [110] TARAFDAR A, CHOI S H, KWON J H. Differential staining lowers the false positive detection in a novel volumetric measurement technique of microplastics[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 432: 128755. [111] KEDZIERSKI M, FALCOU-PRÉFOL M, KERROS M E, et al. A machine learning algorithm for high throughput identification of FTIR spectra: Application on microplastics collected in the Mediterranean Sea[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 234: 242-251. [112] BIANCO V, PIRONE D, MEMMOLO P, et al. Identification of microplastics based on the fractal properties of their holographic fingerprint[J]. ACS Photonics, 2021, 8(7): 2148-2157. [113] ZHANG Y, ZHANG M, FAN Y. Assessment of microplastics using microfluidic approach[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2022[2022-12-31]. [114] KAILE N, LINDIVAT M, ELIO J, et al. Preliminary results from detection of microplastics in liquid samples using flow cytometry[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2020, 7: 552688. [115] BACK H de M, VARGAS JUNIOR E C, ALARCON O E, et al. Training and evaluating machine learning algorithms for ocean microplastics classification through vibrational spectroscopy[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 287: 131903. [116] LUO Y, ZHANG X, ZHANG Z, et al. Dual-principal component analysis of the Raman spectrum matrix to automatically identify and visualize microplastics and nanoplastics[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 94(7): 3150-3157. [117] HUFNAGL B, STIBI M, MARTIROSYAN H, et al. Computer-assisted analysis of microplastics in environmental samples based on μFTIR imaging in combination with machine learning[J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2022, 9(1): 90-95. [118] NG W, MINASNY B, MCBRATNEY A. Convolutional neural network for soil microplastic contamination screening using infrared spectroscopy[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 702: 134723. [119] MORGADO V, PALMA C, BETTENCOURT DA SILVA R J N. Bottom-up evaluation of the uncertainty of the quantification of microplastics contamination in sediment samples[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(15): 11080-11090. [120] ZHU X, NGUYEN B, YOU J B, et al. Identification of microfibers in the environment using multiple lines of evidence[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(20): 11877-11887. [121] WRIGHT S L, LEVERMORE J M, KELLY F J. Raman spectral imaging for the detection of inhalable microplastics in ambient particulate matter samples[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(15): 8947-8956. [122] DAVID J, WEISSMANNOVÁ H D, STEINMETZ Z, et al. Introducing a soil universal model method (SUMM) and its application for qualitative and quantitative determination of poly(ethylene), poly(styrene), poly(vinyl chloride) and poly(ethylene terephthalate) microplastics in a model soil[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 225: 810-819. [123] LI P, LAI Y, LI Q, et al. Total organic carbon as a quantitative index of micro- and nano-plastic pollution[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 94(2): 740-747. [124] SHI Y, YI L, DU G, et al. Visual characterization of microplastics in corn flour by near field molecular spectral imaging and data mining[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 862: 160714. [125] XIE L, GONG K, LIU Y, et al. Strategies and challenges of identifying nanoplastics in environment by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2023, 51(1):25-43. [126] TER HALLE A, JEANNEAU L, MARTIGNAC M, et al. Nanoplastic in the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(23): 13689-13697. [127] SOBHANI Z, ZHANG X, GIBSON C, et al. Identification and visualisation of microplastics/nanoplastics by Raman imaging (i): Down to 100 nm[J]. Water Research, 2020, 174: 115658. [128] BLANCHO F, DAVRANCHE M, HADRI H E, et al. Nanoplastics identification in complex environmental matrices: Strategies for Polystyrene and Polypropylene[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(13): 8753-8759. [129] MATERIĆ D, KASPER-GIEBL A, KAU D, et al. Micro- and nanoplastics in alpine snow: A new method for chemical identification and (semi)quantification in the nanogram range[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(4): 2353-2359. [130] COX K D, COVERNTON G A, DAVIES H L, et al. Human consumption of microplastics[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(12): 7068-7074. [131] ABBASI S, TURNER A. Human exposure to microplastics: A study in Iran[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123799. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123799 [132] ZHANG K, SHI H, PENG J, et al. Microplastic pollution in China’s inland water systems: a review of findings, methods, characteristics, effects, and management[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 630: 1641-1653. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.300 [133] KUTRALAM-MUNIASAMY G, SHRUTI V C, PÉREZ-GUEVARA F, et al. Microplastic diagnostics in humans: “The 3Ps” Progress, problems, and prospects[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 856: 159164. [134] SCHWABL P, K PPEL S, K NIGSHOFER P, et al. Detection of various microplastics in human stool: a prospective case series[J]. Annals of Internal Medicine, 2019, 171(7): 453-457. doi: 10.7326/M19-0618 [135] IBRAHIM Y S, TUAN ANUAR S, AZMI A A, et al. Detection of microplastics in human colectomy specimens[J]. JGH Open, 2021, 5(1): 116-121. [136] AMATO-LOURENÇO L F, CARVALHO-OLIVEIRA R, JÚNIOR G R, et al. Presence of airborne microplastics in human lung tissue[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 416: 126124. [137] ZHU L, ZHU J, ZUO R, et al. Identification of microplastics in human placenta using laser direct infrared spectroscopy[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2023, 856: 159060. [138] LESLIE H A, VAN VELZEN M J M, BRANDSMA S H, et al. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood[J]. Environment International, 2022, 163: 107199. [139] JENNER L C, ROTCHELL J M, BENNETT R T, et al. Detection of microplastics in human lung tissue using μFTIR spectroscopy[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 831: 154907. [140] ZHANG N, LI Y B, HE H R, et al. You are what you eat: Microplastics in the feces of young men living in Beijing[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 767: 144345. [141] YAN Z, LIU Y, ZHANG T, et al. Analysis of microplastics in human feces reveals a correlation between fecal microplastics and inflammatory bowel disease status[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(1): 414-421. [142] HUANG S, HUANG X, BI R, et al. Detection and analysis of microplastics in human sputum[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(4): 2476-2486. -



 下载:
下载:

