-
在社会经济快速发展以及城市化进程不断加快的背景下,污染场地已经成为全球范围内都要面临的一个全新环境问题[1]. 由于一些人类活动导致的场地重金属污染,会对土壤环境造成严重污染,破坏生态环境,同时也会通过暴露及食物链对人类健康造成一定影响. 目前国内外对污染场地的重金属监测、风险评估和来源识别研究主要集中在矿区[2 − 5]、冶炼厂[6 − 9]、工业区[10 − 14]等. 随着军事场地土壤重金属污染方面研究的增加[15],军事场地的土壤重金属污染问题也受到了国内外学者的广泛关注,主要以靶场、训练场等为主,如Christou等[16]发现,某靶场土壤中的Pb浓度范围为791 mg·kg−1至7265 mg·kg−1,比对照背景样本高几十甚至几百倍;Johnsen等[17]在挪威某射击场土壤中发现,Pb和Cu含量高达3700 mg·kg−1和1654 mg·kg−1;王亮等[18]对西藏某军事训练场土壤重金属污染的研究发现,As和Cu的污染源于靶场人为炮弹射击;王诗雨等[19]对吉林某试验场重金属分布特征、潜在生态风险和来源进行了分析,判断Zn、Pb和Cd主要与试验活动相关的污染源有关;刘玉通等[20 − 22]对几种军事场地的重金属的监测发现,留在土壤里的弹药残余物等都能不断地释放出重金属,造成重金属污染在土壤里长期存在;李烨玲、Bai等[23 − 24]也分别对中国5个靶场重金属污染水平进行了探究. 而我国对弹药销毁场重金属污染的报道较少. 报废弹药销毁处置是部队及兵工厂的经常性工作,其处置方式主要有分解拆卸、倒空、焚烧以及炸毁等[25],弹药各零部件中重金属成分种类繁多,长期销毁作业会导致场地受到严重的重金属污染[26 − 27].
本研究对中国山西某弹药销毁场土壤进行了重金属污染监测分析,分析场地重金属的污染程度和潜在风险,并解析了重金属的来源,为后续对特征重金属污染物的针对性治理修复提供科学依据.
-
根据《建设用地土壤污染状况调查技术导则》(HJ 25.1-2019)中的要求,并结合地形特征和工艺环节等因素,选择了可能污染较重的地块进行采样点位的布设. 在可能存在重度污染的销毁中心(研究区南面)采集了32个土壤样品,编号依次为S1—S32,采样点分布如图1所示,研究区北面为弹壳堆放区,也可能受到重金属物污染,在其附近采集了土壤样品7个,编号依次为S33—S39,研究区中部为工房建筑,其余区域已做路面硬化处理,不具备样品采集条件. 所有样品采样深度均为0—20 cm,采用手持GPS进行采样点定位,另外在远离研究区的农田处采集了背景样品3个,用于对照分析. 每个采样点采用五点取样法,去除杂物后采集1.0 kg,混匀后带回实验室. 土壤样品经过自然风干后,挑出石块、植物根系,用玛瑙研磨之后,过2 mm尼龙筛,放入密封袋后待测.
土壤pH测定采用水土比2.5:1(V/M)浸提后,用pH计测定;有机质(OM)采用重铬酸钾外加热法测定;采用乙酸铵浸提法测定阳离子交换量(CEC). 使用激光粒度仪(Analysette 22,Fritsch)对土壤粒径进行分析,粒径测量范围为0.01—2000 μm,样品均进行3次检测. 样品通过酸溶法消解后,使用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)测定了Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Cd、Sb和Pb这8种重金属的含量,其检出限分别为2、1、0.6、1、0.4、0.09、0.08、2 mg·kg−1. 每批试样设2个空白样,2个平行双样,空白样结果远小于检出限,平行样结果的相对偏差低于10%. 以标准物质GBW07405/GSS-5为质量控制标准,回收率为85%—110%.
-
单因子指数法用以表征土壤中重金属的环境污染程度[28]. 其计算公式如下:
式中,Pi指重金属i的单因子污染指数;Ci指测定的土壤中重金属含量,mg·kg−1;Si指相关标准中重金属的安全限值,取《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》(GB15618-2018)中重金属的筛选值,mg·kg−1. 由于该标准缺乏Sb的安全限制,本文选用35 mg·kg−1[29]为安全限值.
-
内梅罗综合污染指数法是一种综合考虑土壤中各重金属污染物平均污染程度,突出最严重重金属污染物平均污染程度的方法,能综合反映某一污染物的污染水平[30],计算公式如下:
式中,PN指内梅罗综合污染指数;Pmax和Pave分别指各重金属单因子指数的最大值和平均值.
-
地累积指数综合考虑了天然成岩造成的背景值的变化和人类活动等污染因素的影响[31]. 计算公式如下:
式中,Igeo为重金属的地累积系数,无量纲;Cn指某重金属的含量,Bn指土壤中该重金属的背景值,mg·kg−1;k为成岩效应,一般取1.5,无量纲.
上述3种污染指数法评价重金属污染的程度见表1.
-
潜在生态风险指数是Hakason[32]提出的一种计算土壤重金属潜在风险的有效定量方法. 该方法充分考虑了重金属的含量及其毒性,它已被广泛应用于土壤重金属污染的评估[33]. 其计算公式如下:
式中,Ei指单项重金属的潜在生态危害指数,无量纲;RI为潜在生态风险指数;Cr指重金属实测值,Cn指重金属参比值,mg·kg−1;
$ {T}_{r} $ 为重金属的毒性系数,无量纲,As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Pb、Ni、Zn、Sb的毒性响应系数分别为10、30、2、5、5、5、1和7[34-35]. 土壤重金属污染评价标准见表2. -
采用绝对主成分得分-多元线性回归模型(APCS-MLR受体模型)[36]定量解析污染源贡献率. 重金属元素的标准化公式如下:
式中,Zij指标准化值;Cij指重金属含量,mg·kg−1;
$ \bar{C}_{i} $ 为重金属的平均含量,mg·kg−1;σi为重金属的标准差,mg·kg−1.每种元素引进1个0浓度人为样本,其计算公式如下:
APCSp计算公式如下:
将重金属含量和APCSp做多元线性回归,并将回归方程运用于各重金属的拟合,通过拟合分析,检验APCS-MLR模型的精确度. 计算公式如下:
式中,Cim指重金属元素i的拟合值,mg·kg−1;b0i为对重金属i的回归常数项,mg·kg−1;bpi为源p与重金属元素i之间的回归系数,mg·kg−1;APCSp是旋转之后因子p的得分数[36].
计算污染源贡献时会出现负值,因此采用绝对值来计算污染源贡献. 解析出各源贡献率计算公式如下:
其他源贡献率的公式如下:
式中,PCjm是污染源的贡献率.
-
通过Excel软件对数据进行统计分析,采用SPSS Statistics 25软件对数据进行相关性分析、主成分分析,采样点分布图和数据分析图分别使用ArcGIS 10.7和Origin 2022软件绘制.
-
研究区土壤pH的范围为7.38—9.81,均值为8.5,呈碱性,与吉林某销毁场研究一致[26],而背景点的pH均值为7.90,研究区pH的升高可能是焚烧造成的,燃烧后土壤pH会随着有机酸变性、有机质氧化、阳离子释放和碱性灰分进入土壤剖面等机制而升高[37]. 有机质含量为0.59%—4.38%,天然有机质会在销毁区频繁的高温灼烧和物理扰动下分解,留在土壤中的有机质可能来源于有机炸药[27]. 销毁区土壤为砂质土壤,土壤质地在高温下可能发生改变,当燃烧期间土壤表面温度超过250 °C,细粘土颗粒聚集形成沙子,高温也可能导致最上层土层的颗粒增加[37]. 背景点阳离子交换量均值为25.29 mg·kg−1,研究区阳离子交换量范围为5.20—40.29 mg·kg−1,均值为16.78 mg·kg−1,阳离子交换量的降低可能与土壤质地有关,连续的燃烧活动会因含沙量的增加而降低土壤CEC[37].
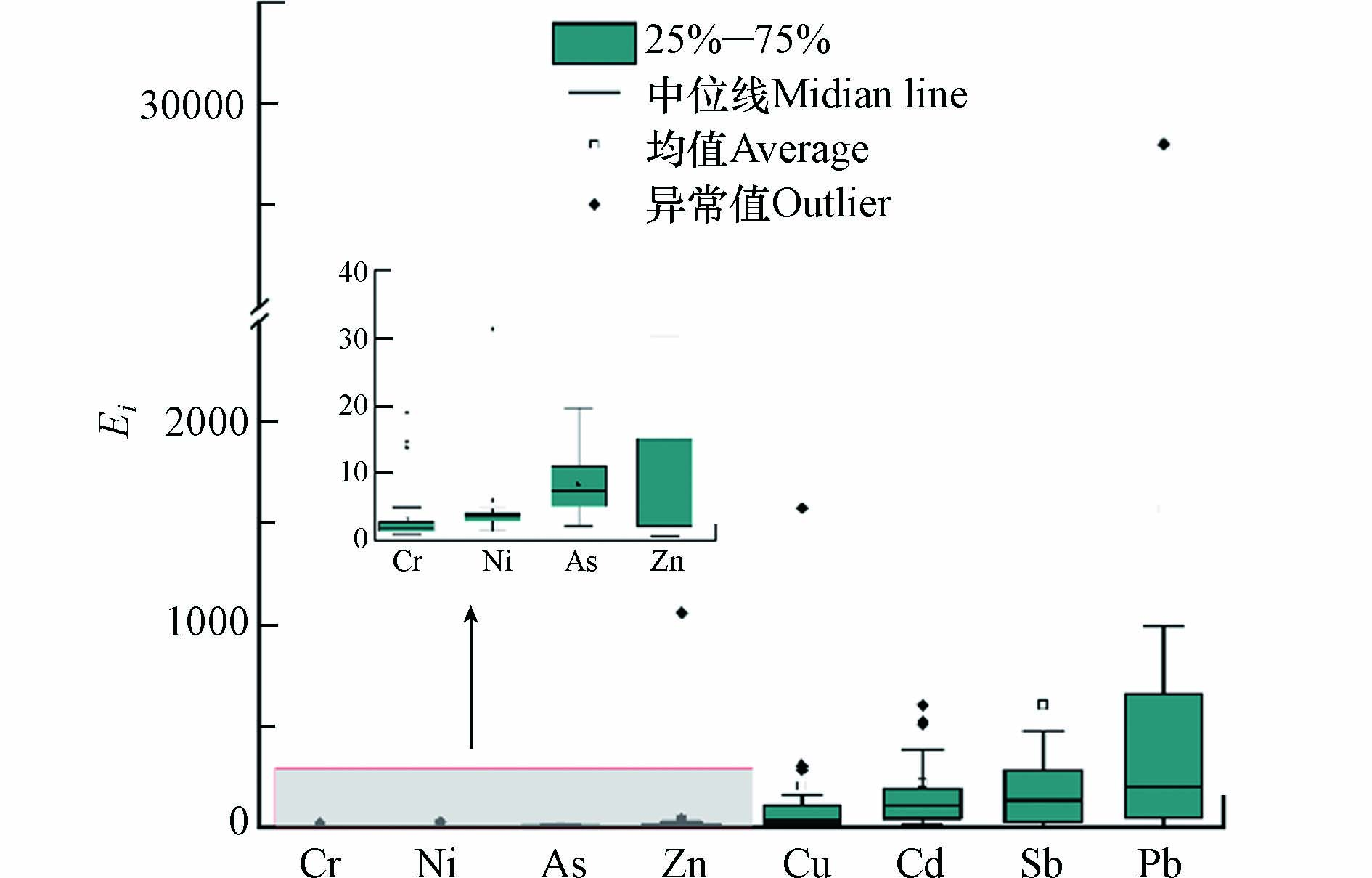
对土壤样品中重金属元素含量的测定结果如表3所示. 弹壳堆放区表层土壤8项重金属元素Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Cd、Sb、Pb的平均含量分别为45.57、23.43、325.54、265.43、9.53、0.42、304.17、13174.29 mg·kg−1,其余区域表层土壤8项重金属元素Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Cd、Sb、Pb的平均含量分别为102.09、26.75、1137.18、3007.13、7.71、0.95、70.65、2894.97 mg·kg−1,前者As、Sb、Pb的平均含量高于后者. 重金属超标率大小顺序为重金属超标率大小顺序为:Zn(79.5%)>Pb(71.8%)>Cu(48.7%)>Sb(35.9%)>Cd(25.6%)>Cr(7.7%)>Ni(2.6%)>As(0),各元素的平均含量显著高于背景区及山西省背景值,且重金属Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Cd、Sb、Pb含量的平均值是相应筛选值的0.37、0.14、9.92、8.38、0.32、1.42、3.22、27.88倍,说明销毁活动导致研究区土壤中重金属含量明显上升.
Pb是大多数样本中的主要重金属污染物,其次是Zn和Cu. Cd的浓度相对较低,平均浓度约为1 mg·kg−1或更低,可能是由于它的浓度水平普遍较低. Pb、Cu、Zn浓度的最大值比其他重金属高2—4个数量级,其他重金属的浓度偏低,孟欢等[27]在某弹药销毁场的研究中也发现销毁作业使土壤中Pb、Cu、Zn含量升高. 变异系数(CV)代表土壤中重金属分布的均匀程度,CV越大,表明受人类活动干扰越大[19]. 一般认为,CV<0.10为弱变异,0.1<CV<1为中等程度变异,CV>1为强变异[18]. 研究区土壤重金属元素的变异系数大小顺序为Zn>Cu>Cd>Pb>Sb>Ni>Cr>1>As>0.1,除As为中等变异外,其余重金属均表现出强变异,表明受到外界因素影响较大. Pb、Cu、Zn这3种浓度较高的重金属具有较大的异质性,其最低浓度范围和最高浓度范围相差3个数量级. 另外,Sb和Cr元素部分被测样品的浓度较高,导致整体平均水平显著升高. Ni和Cd个别样品浓度较大,导致了其高变异系数,反映了销毁场地内表层土壤中重金属的不均匀分布.
-
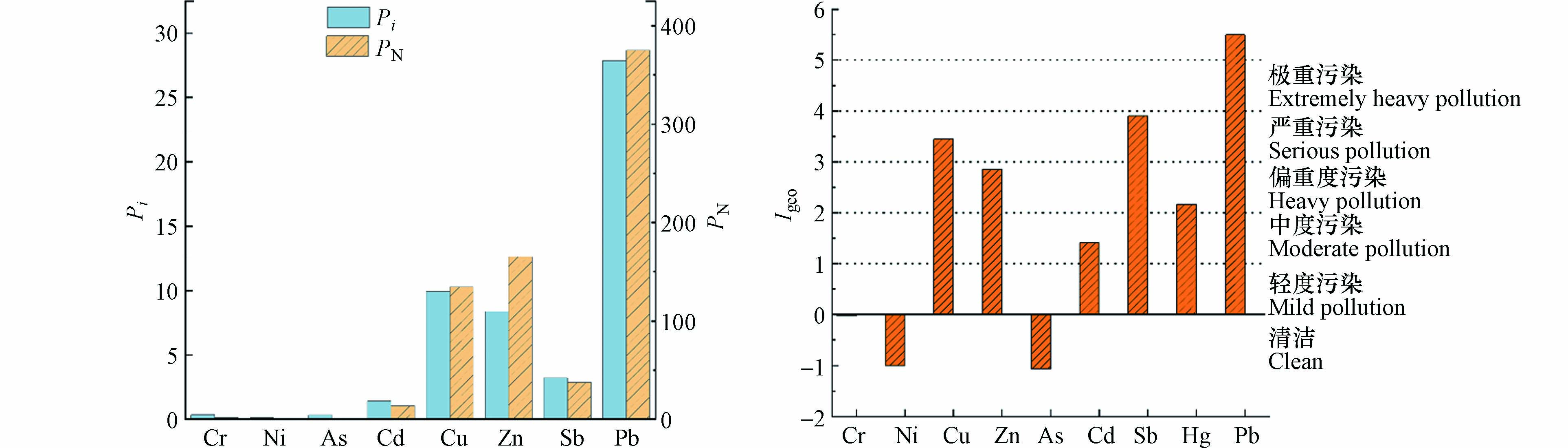
如图2,土壤重金属单项污染指数大小依次为Pb>Cu>Zn>Sb>Cd>Cr>As>Ni,其中Pb、Cu、Zn为重度污染水平,Sb为中度污染水平,Cd、Cr、As、Ni无污染;综合污染指数大小依次为Pb>Zn>Cu>Sb>Cd>Cr>Ni>As,其中Pb、Zn、Cu、Sb、Cd为重度污染水平,Cr为轻微污染水平,Ni为预警,As为清洁;可以看出尽管单项污染指数表明Zn、Sb、Cd仅为中度、轻度或轻微污染水平,但是在考虑整个区域综合污染指数的情况下,Zn、Sb、Cd达到了重度污染水平. 地累积指数均值结果大小依次为Pb>Sb>Cu>Zn>Cd>Cr>As>Ni,其中Pb为严重污染,Sb为偏重度污染,Cu、Zn为重度污染,Cd为偏重度污染,Cr、As、Ni为清洁. 综合几种重金属污染评价结果,Pb、Zn、Cu、Sb、Cd的污染较重,Cr、As、Ni的污染较轻.
-
研究区各重金属潜在生态风险Ei大小依次为Pb>Sb>Cu>Cd>Zn>As>Ni>Cr(图3),Cr、Ni、As、Zn重金属污染风险指数Ei<40,均表现为轻微生态危害风险级别;其余重金属中除Cd为强生态风险级别外,均表现为极强生态风险级别,这与重金属的污染指数评价结果基本一致. Zn的轻微生态风险级别可能与其较低的毒性系数有关,而Cd的强生态风险级别可能是因为Cd具有较高的毒性系数[39]. 值得注意的是,Pb的污染风险指数为1569.53,是极强生态风险等级上限的9.8倍,土壤中Pb的升高可被视为最重要的健康危害[24]. 重金属潜在生态风险RI为2653.35,是极强风险等级上限的4.42倍. 综合考虑重金属含量、污染指数和潜在生态风险,重金属的污染尤为严重,对周边生态环境安全和人类健康存在巨大的隐患. 因弹药销毁而产生的重金属不仅会对周边居民健康产生不良影响,还会对研究区销毁工作人员的健康构成威胁[40],应特别重视重金属对健康的危害,并适时制定应对策略,采取切实有效的保护措施,例如,考虑弹药销毁场地的选址,开展销毁工艺优化等工作.
-
不同重金属之间的pearson相关性分析见表4,元素Cr-Ni-Zn和Ni-Cd-Zn两两之间呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),说明这几种重金属可能具有相同或相似的来源[41]. Sb-Pb之间存在极显著正相关(P<0.01),表明这两种重金属的来源可能相同[19]. Cr-Cd-Sb-Pb两两之间呈显著正相关(P<0.05),Cu、Zn之间呈显著正相关(P<0.05),说明Cu、Sb、Pb的来源可能与Cr-Ni-Zn-Cd来源一致. As和Ni之间存在正相关(P<0.05),表明As和Ni来源可能相同[42].
-
为了进一步明确重金属污染的来源,本文根据相关性分析的结果对以上重金属元素的主成分进行分析,结果见表5. 由相关研究可知,当抽样适合性检验KMO值大于0.6,且Bartlett的球形度检验P<0.001,适合做因子分析[36]. 在这项研究中,8种重金属被测试,其中KMO值为0.654,P值为0.000,并且通过相关性分析结果说明,各重金属之间具备良好的相关性,适用于进行因子分析. 土壤重金属因子分析结果见表5,经过Kaiser旋转(表6),因子采用特征值为1以上,结果共3项,因子累积解释整体为82.47%. 据此推测出研究区内存在三大土壤重金属污染源[36].
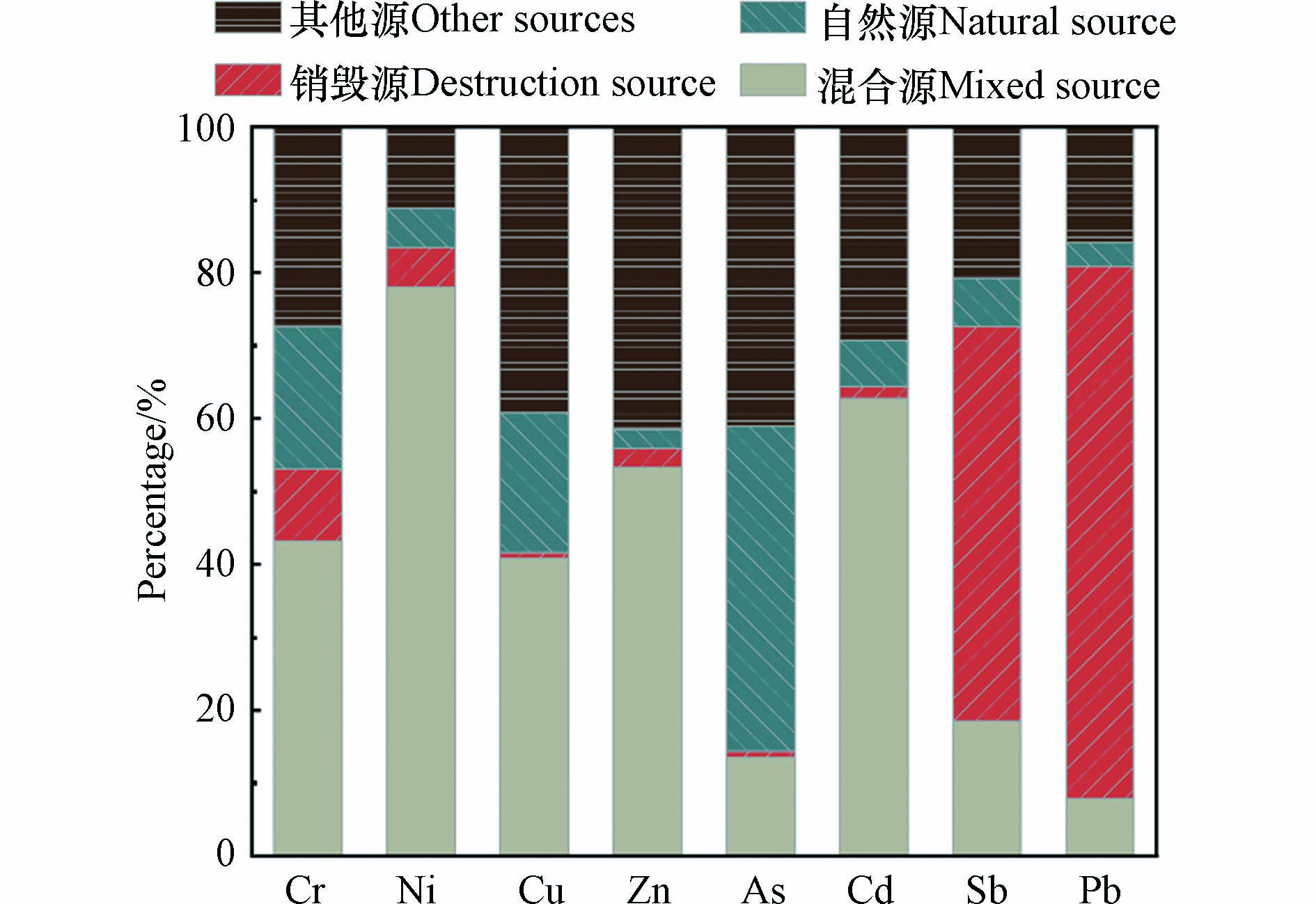
由因子分析结果可知,因子1解释了整体的42.39%,在Zn、Ni、Cd、Cr和Cu上有较大载荷,且载荷依次减小. 在每个因子上具有较大载荷的元素,载荷系数都大于0.6. 由相关性可知,重金属Zn、Ni、Cd、Cr和Cu两两之间呈极显著相关性,有研究表明,铜锌合金用来增加弹壳的硬度[43],钢芯弹药的燃烧会产生大量Cu和Zn[44]. 而在迫击炮、大炮、火箭、瞄准设备和炮弹外壳中也使用了Cu,弹壳和子弹头夹套中高含量的Cu会导致土壤受到严重的Cu污染[43]. 军事装备的涂料中含有Cd[45],Ni、Cr会在弹药的制造中以合金的形式加入[43],这5种重金属变异系数较大,易受弹药拆解、销毁等生产作业中产生的废气、废渣等人为因素的影响,有研究表明,Cu、Zn、Cd、Cr、Ni等是军事场地常见的重金属污染物[15],且这些重金属的累积地点位于焚烧区的主导风向上,会通过大气沉降、地表径流、固废堆弃等方式在土壤中形成富集. 另外,有研究指出肥料、杀虫剂等农产品中Cd、Zn、Cu等重金属含量较高[36,46],机械设备加工、交通运输等也会产生Cd和Cu等重金属[47],重金属会通过这些途径进入土壤. 以上表明因子1是人为活动(包括焚烧、农业、工业及交通运输等)综合影响. 因子2解释了整体的26.61%,在Pb和Sb上有极高正荷载(0.99和0.98),Pb和Sb呈极显著相关(P<0.01). 考虑到Pb和Sb累积处附近区域实际销毁大量枪弹底火,而底火中含有Pb和Sb的化合物[48],通常Pb和Sb会以相对较高的浓度作为共同污染物存在,故因子2可视为销毁活动人为因素. 因子3解释了整体的13.47%,在As上有较大载荷,研究区As的污染程度和CV较小,受销毁和其他活动影响较小,可以归结为土壤母质及风化累积的结果[49],因此因子3为自然源.
-
由APCS-MLR受体模型,得出8种重金属的决定系数R2. R2的结果为0.41—0.98,其中,元素Ni、Zn、Cd、Sb、Pb的R2均大于0.90,拟合度较好. 由此可得,各重金属元素进行APCS-MLR受体模型分析的结果具备良好的精确度.
-
由PCA和APCS-MLR受体模型分析得到3个主要污染源. 如图4,研究区重金属Ni、Cd、Zn、Cr和Cu的来源主要为焚烧、农业、工业及交通运输混合源,其贡献率分别为78.04%、62.84%和53.25%、43.21%、40.86%;Pb和Sb的主要来源是焚烧销毁源,其贡献率分别为72.94%、53.99%,另外还有7.93%和18.55%来自混合源,因为Pb为典型的工业源重金属[50],汽车轮胎的磨损以及汽车尾气中也会产生Pb[51],在交通运输方面Pb常被作为机动车污染源的指示性元素[46],且Pb是弹头核心的主要组成成分,Sb是起爆药的主要成分[48],与几种混合源相一致;对于As,自然源对其贡献率最大,为44.63%,其次是40.99%的其他源,有13.47%来自混合源,据研究表明,As可作合金添加剂生产铅制弹丸,是铅合金霰弹枪弹药的成分[43],采矿和其他很多工业活动都会释放大量As[36],工业燃煤产生的As最终会以大气沉降的方式进入土壤. 研究区重金属的来源是许多因素共同作用的结果,所以自然源对Cr贡献占比也较高,达到19.49%,而其他源对Zn、Cu、Cd和Cr的贡献也较大,占比分别为41.60%、39.24%、29.36%和27.50%,特别是Cu元素,其他源与混合源的占比几乎相同,这也可能是导致Cu变异性特别高的原因[36].
-
(1)土壤理化性质受到了销毁活动的影响,销毁活动也导致了土壤中重金属含量明显上升,其中重金属Pb、Cu、Zn超标率较高,污染较严重.
(2)污染指数评价结果表明,Pb、Zn、Cu、Sb、Cd的污染较重,Cr、As、Ni的污染较轻.
(3)研究区重金属Cr、Ni、As、Zn为轻微生态危害风险级别,Cd为强生态风险级,Pb、Zn、Cu、Sb为极强生态风险级别,其中Pb的污染风险指数为1569.53,是极强生态风险等级上限的9.8倍. 重金属潜在生态风险RI为2653.35,是极强风险等级上限的4.42倍.
(4)应特别重视重金属对健康的危害,并适时制定应对策略,采取切实有效的保护措施,例如,考虑弹药销毁场地的选址,开展销毁工艺优化等工作.
(5)根据相关性和PCA-APCS-MLR分析,Pb、Cu、Zn、Sb、Cd、Cr、Ni主要来源于混合源,Pb和Sb的主要来源是焚烧销毁源,As主要来源为自然源.
基于APCS-MLR受体模型的弹药销毁场土壤重金属源解析
Analysis of heavy metal sources in soil of ammunition destruction site based on APCS-MLR receptor model
-
摘要: 为了掌握弹药销毁场重金属污染状况与来源,以山西某典型弹药销毁场为例,对该销毁场39个表层土壤重金属(Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Cd、Sb、Pb)的污染状况、分布特征与污染来源进行评价与分析. 结果表明,弹壳堆放区表层土壤重金属Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Cd、Sb、Pb的平均含量分别为45.57、23.43、325.54、265.43、9.53、0.42、304.17、13174.29 mg·kg−1,其余区域表层土壤重金属Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Cd、Sb、Pb的平均含量分别为102.09、26.75、1137.18、3007.13、7.71、0.95、70.65、2894.97 mg·kg−1,均高于山西省背景值. 污染指数评价结果表明,Pb、Zn、Cu、Sb和Cd的累积程度较高. 研究区土壤重金属生态危害指数为2653.35,达到极高生态风险水平. 绝对主成分得分-多元线性回归模型(APCS-MLR)表明,Ni、Cd、Zn、Cr和Cu的来源主要为混合源,贡献率为72.94%,Pb和Sb的主要来源是销毁源,贡献率为53.99%,自然源对As贡献率最大,为44.63%.
-
关键词:
- 弹药销毁场 /
- 重金属 /
- 污染特征 /
- 潜在生态风险 /
- APCS-MLR受体模型
Abstract: In order to grasp the pollution status and sources of heavy metals in ammunition destruction sites, the pollution status, distribution characteristics and pollution sources of 39 surface soil heavy metals (Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd, Sb, Pb) in this destruction site were evaluated and analyzed, taking a typical ammunition destruction site in Shanxi as an example. The results showed that the average contents of the surface soil heavy metals Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd, Sb and Pb in the shell dumping area were 45.57, 23.43, 325.54, 265.43, 9.53, 0.42, 304.17, 13174.29 mg·kg−1, respectively, while the average contents of the surface soil heavy metals Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd, Sb and Pb in the rest of the area were 45.57, 23.43, 325.54, 265.43, 9.53, 0.42, 304.17, 13174.29 mg·kg−1, respectively, As, Cd, Sb and Pb were 102.09, 26.75, 1137.18, 3007.13, 7.71, 0.95, 70.65 , 2894.97 mg·kg−1 respectively, which were all higher than the background values in Shanxi Province. The results of the pollution index evaluation showed that the accumulation of Pb, Zn, Cu, Sb and Cd was high. The ecological hazard index for soil heavy metals in the study area was 2653.35, reaching a very high ecological risk level. The absolute principal component score-multiple linear regression model (APCS-MLR) showed that the sources of Ni, Cd, Zn, Cr and Cu were mainly mixed sources with a contribution of 72.94%, the main sources of Pb and Sb were destruction sources with a contribution of 53.99%, and natural sources contributed the most to As with a contribution of 44.63%. -

-
表 1 土壤重金属污染程度划分表
Table 1. Classification table of soil heavy metal pollution levels
地累积指数
Ground accumulation index单因子污染指数
Single pollution index内梅罗综合污染指数
Nemerow comprehensive pollution indexIgeo 污染程度 Pi 污染程度 PN 污染程度 Igeo≤0 清洁 Pi≤1 无 PN≤0.7 清洁 0<Igeo≤1 轻度污染 1<Pi≤2 轻微 0.7<PN≤1.0 预警 1<Igeo≤2 偏中度污染 2<Pi≤3 轻度 1.0<PN≤2.0 轻微污染 2<Igeo≤3 中度污染 3<Pi≤5 中度 2.0<PN≤3.0 中度污染 3<Igeo≤4 偏重度污染 Pi>5 重度 PN>3.0 重度污染 4<Igeo≤5 严重污染 Igeo>5 极重污染 表 2 土壤重金属潜在生态风险划分表
Table 2. Classification table of potential ecological risks of heavy metals in soil
单个重金属潜在生态风险指数
Potential ecological risk index of individual heavy metals潜在生态风险指数
Potential ecological risk index风险等级
Risk levelEi≤40 RI≤150 轻微 40<Ei≤60 150<RI≤300 中等 60<Ei≤160 300≤RI<600 强 160≤Ei 600≤RI 极强 表 3 土壤重金属污染描述性统计
Table 3. Descriptive statistics of soil heavy metal pollution
场地 统计量 Cr Ni Cu Zn As Cd Sb Pb 研究区 含量范围/
(mg·kg−1)28.00—
550.009.00—
197.0037.40—
1.90×10438.00—
7.00×1042.10—
18.700.05—
11.600.66—
1850.0020.00—
9.00×104平均值/
(mg·kg−1)91.95 26.15 991.50 2515.03 8.04 0.85 112.56 4739.97 标准差 111.60 28.27 3162.46 10981.82 3.98 1.83 314.75 15158.4 CV 1.21 1.08 3.19 4.37 0.5 2.14 2.8 3.2 山西背景值/
(mg·kg−1)57.9[38] 31.4[38] 24.4[38] 66.2[38] 9.5[38] 0.12[38] 1.3[38] 15.1[38] 超标率/% 7.7 2.6 48.7 79.5 0 25.6 35.9 71.8 筛选值/(mg·kg−1) 250 190 100 300 25 0.6 35 170 表 4 销毁场土壤重金属相关性
Table 4. Correlation of soil heavy metals in destruction site
Cr Ni Cu Zn As Cd Sb Pb Cr 1 0.506** 0.167 0.466** 0.03 0.387* 0.348* 0.317* Ni 1 0.352* 0.981** 0.345* 0.927** 0.298 0.199 Cu 1 0.338* 0.054 0.312 0.118 0.091 Zn 1 0.305 0.962** 0.266 0.162 As 1 0.312 0.13 0.081 Cd 1 0.214 0.111 Sb 1 0.991** Pb 1 表 5 土壤重金属元素主成分分析
Table 5. Principal component analysis of heavy metal elements in soil
成分
composition初始特征值
Initial eigenvalue旋转载荷平方和
Sum of the squares of rotating loads总计 方差百分比 累积% 总计 方差百分比 累积% 1 3.721 46.509 46.509 3.391 42.387 46.509 2 1.801 22.510 69.019 2.129 26.613 69.001 3 1.076 13.455 82.474 1.078 13.473 82.474 4 0.785 9.812 92.286 5 0.540 6.756 99.042 6 0.063 0.782 99.825 7 0.011 0.135 99.960 8 0.003 0.040 100.000 表 6 土壤重金属Kaiser旋转后的因子分析结果
Table 6. Factor analysis results of heavy metal in soil after Kaiser rotation
1 2 3 Cr 0.498 0.392 −0.232 Ni 0.968 0.149 0.043 Cu 0.439 0.041 −0.619 Zn 0.973 0.107 0.03 As 0.365 0.054 0.796 Cd 0.953 0.047 0.064 Sb 0.152 0.977 0.036 Pb 0.049 0.990 0.013 -
[1] YAN K, WANG H Z, LAN Z, et al. Heavy metal pollution in the soil of contaminated sites in China: Research status and pollution assessment over the past two decades[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 373: 133780. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133780 [2] ZHONG X, CHEN Z W, LI Y Y, et al. Factors influencing heavy metal availability and risk assessment of soils at typical metal mines in Eastern China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 400: 123289. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123289 [3] LEE P K, KANG M J, YU S, et al. Assessment of trace metal pollution in roof dusts and soils near a large Zn smelter[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 713: 136536. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136536 [4] OBIRI-NYARKO F, DUAH A A, KARIKARI A Y, et al. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils at the Kpone landfill site, Ghana: Implication for ecological and health risk assessment[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 282: 131007. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131007 [5] 李强, 曹莹, 何连生, 等. 典型冶炼行业场地土壤重金属空间分布特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(12): 5930-5937. LI Q, CAO Y, HE L S, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and source analysis of soil heavy metals at typical smelting industry sites[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(12): 5930-5937 (in Chinese).
[6] RAN H Z, DENG X G, GUO Z H, et al. Pollution characteristics and environmental availability of toxic elements in soil from an abandoned arsenic-containing mine[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 303: 135189. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135189 [7] YIN Y, WANG X J, HU Y A, et al. Soil bacterial community structure in the habitats with different levels of heavy metal pollution at an abandoned polymetallic mine[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 442: 130063. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130063 [8] 顾会, 赵涛, 高月, 等. 贵州省典型铅锌矿区土壤重金属污染特征及来源解析[J]. 地球与环境, 2022, 50(4): 506-515. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2022.50.003 GU H, ZHAO T, GAO Y, et al. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in soils of a typical lead-zinc mining area in Guizhou Province[J]. Earth and Environment, 2022, 50(4): 506-515 (in Chinese). doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2022.50.003
[9] 李强, 何连生, 王耀锋, 等. 中国冶炼行业场地土壤污染特征及分布情况[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(3): 586-595. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.03.017 LI Q, HE L S, WANG Y F, et al. The characteristics and distribution of soil pollution in smelting industry sites in China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(3): 586-595 (in Chinese). doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.03.017
[10] XU L, DAI H P, SKUZA L, et al. Integrated survey on the heavy metal distribution, sources and risk assessment of soil in a commonly developed industrial area[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022, 236: 113462. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113462 [11] KHAN J, SINGH R, UPRETI P, et al. Geo-statistical assessment of soil quality and identification of Heavy metal contamination using Integrated GIS and Multivariate statistical analysis in Industrial region of Western India[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2022, 28: 102646. [12] 张义, 周心劝, 曾晓敏, 等. 长江经济带工业区土壤重金属污染特征与评价[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(4): 2062-2070. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202106237 ZHANG Y, ZHOU X Q, ZENG X M, et al. Characteristics and assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils of industrial regions in the Yangtze River economic belt[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(4): 2062-2070 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202106237
[13] 毛盼, 王明娅, 孙昂, 等. 某典型废弃硫酸场地土壤重金属污染特征与评价[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(2): 511-525. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021071304 MAO P, WANG M Y, SUN A, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and assessment in soil of a typical abandoned sulfuric acid site[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(2): 511-525 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021071304
[14] 张施阳. 钢铁厂遗留场地土壤重金属和多环芳烃的污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2022, 44(10): 1336-1342. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2022.10.012 ZHANG S Y. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils of remaining site left by a steel plant[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2022, 44(10): 1336-1342 (in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2022.10.012
[15] SKALNY A V, ASCHNER M, BOBROVNITSKY I P, et al. Environmental and health hazards of military metal pollution[J]. Environmental Research, 2021, 201: 111568. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111568 [16] CHRISTOU A, HADJISTERKOTIS E, DALIAS P, et al. Lead contamination of soils, sediments, and vegetation in a shooting range and adjacent terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems: A holistic approach for evaluating potential risks[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 292: 133424. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133424 [17] JOHNSEN I V, AANEBY J. Soil intake in ruminants grazing on heavy-metal contaminated shooting ranges[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 687: 41-49. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.086 [18] 王亮, 李宏伟, 李昂泽, 等. 军事训练场炮弹靶场土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价: 以西藏某训练场为例[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(8): 2646-2654. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022012705 WANG L, LI H W, LI A Z, et al. Study on characteristics and ecological risks of heavy metal pollution in soil of projectile range in military training ground—a case of a training ground in Tibet[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(8): 2646-2654 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022012705
[19] 王诗雨, 李淳, 赵洪伟, 等. 某试验场土壤重金属分布特征及其污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(3): 1657-1667. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202201279 WANG S Y, LI C, ZHAO H W, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of heavy metals in soils of a testing range[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(3): 1657-1667 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202201279
[20] 刘玉通, 方振东, 杨琴, 等. 某轻武器射击场土壤重金属总量及赋存形态分析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2013, 13(5): 103-107. LIU Y T, FANG Z D, YANG Q, et al. Analysis of the total concentration and the existing speciation of heavy metals in small arms shooting range soils[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2013, 13(5): 103-107 (in Chinese).
[21] 刘玉通, 方振东, 杨琴, 等. 某军事区域土壤重金属污染状况及其评价[J]. 后勤工程学院学报, 2010, 26(1): 62-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7843.2010.01.014 LIU Y T, FANG Z D, YANG Q, et al. State and evaluation of heavy metal pollution of soil from a military area[J]. Journal of Logistical Engineering University, 2010, 26(1): 62-65 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7843.2010.01.014
[22] 刘玉通, 方振东, 杨琴, 等. 基于GIS的某训练场土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(5): 1725-1730. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2012.05.051 LIU Y T, FANG Z D, YANG Q, et al. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in soils from a training ground based on GIS[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(5): 1725-1730 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2012.05.051
[23] 李烨玲. 靶场土壤中铅的环境行为及生物有效性研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2018. LI Y L. The environmental fate and bioavailability of lead in shooting range soils[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2018 (in Chinese).
[24] BAI J A, ZHAO X F. Ecological and human health risks of heavy metals in shooting range soils: A meta assessment from China[J]. Toxics, 2020, 8(2): 32. doi: 10.3390/toxics8020032 [25] 张怀智, 刘鹏, 曹宏安, 等. 报废弹药烧毁作业环境废气污染治理研究[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2011, 37(12): 32-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2011.12.013 ZHANG H Z, LIU P, CAO H A, et al. Study on the treatment of waste gas environmental pollution in abandoned ammunition burining[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2011, 37(12): 32-34 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2011.12.013
[26] ZHANG H J, ZHU Y B, WANG S Y, et al. Contamination characteristics of energetic compounds in soils of two different types of military demolition range in China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 295: 118654. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118654 [27] 孟欢, 朱勇兵, 王晴, 等. 吉林某弹药销毁场土壤炸药污染调查及其赋存状态研究[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2022, 12(3): 31-39. MENG H, ZHU Y B, WANG Q, et al. Investigation on soil explosive pollution and occurrence status of a certain ammunition destruction site in Jilin Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 12(3): 31-39 (in Chinese).
[28] 刘春跃, 王辉, 白明月, 等. 沈阳市老城区表层土壤重金属分布特征及风险评价[J]. 环境工程, 2020, 38(1): 167-171. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202001027 LIU C Y, WANG H, BAI M Y, et al. Risk assessment and characteristics of heavy metals in surface soil of old town of Shenyang[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2020, 38(1): 167-171 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202001027
[29] 熊佳, 韩志伟, 吴攀, 等. 独山锑冶炼厂周边土壤锑砷空间分布特征、污染评价及健康风险评估[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(2): 655-664. XIONG J, HAN Z W, WU P, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics, contamination evaluation and health risk assessment of arsenic and antimony in soil around an antimony smelter of Dushan County[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(2): 655-664 (in Chinese).
[30] 崔罗肖, 胡启智, 李蒙, 等. 清远电子垃圾拆解区土壤重金属污染空间分布特征及风险评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2022, 41(10): 2200-2211. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2022-0630 CUI L X, HU Q Z, LI M, et al. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soils of Qingyuan e-waste dismantling area, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2022, 41(10): 2200-2211 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2022-0630
[31] 马杰, 刘萍, 刘今朝, 等. 重庆市煤矸山周边农用地土壤重金属污染评价和定量溯源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(12): 5698-5709. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202202123 MA J, LIU P, LIU J Z, et al. Pollution evaluation and quantitative traceability analysis of heavy metals in farmland soils around the gangue heap of a coal mine in Chongqing[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(12): 5698-5709 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202202123
[32] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [33] 施建飞, 靳正忠, 周智彬, 等. 额尔齐斯河流域典型尾矿库区周边土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1015-1023. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.05.017 SHI J F, JIN Z Z, ZHOU Z B, et al. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in the soil around A typical tailing reservoir in Irtysh River Basin[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(5): 1015-1023 (in Chinese). doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.05.017
[34] 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 等. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(2): 112-115. XU Z Q, NI S J, TUO X G, et al. Calculation of heavy metals' toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 31(2): 112-115 (in Chinese).
[35] WANG N N, WANG A H, KONG L H, et al. Calculation and application of Sb toxicity coefficient for potential ecological risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 610/611: 167-174. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.268 [36] 张旺, 高珍冉, 邰粤鹰, 等. 基于APCS-MLR受体模型的贵州喀斯特矿区水田土壤重金属源解析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(3): 212-219. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.03.025 ZHANG W, GAO Z R, TAI Y Y, et al. Source analysis of the heavy metals in paddy field soils in Karst mining areas of Guizhou using APCS-MLR receptor model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(3): 212-219 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.03.025
[37] FACHIN P A, COSTA Y T, THOMAZ E L. Evolution of the soil chemical properties in slash-and-burn agriculture along several years of fallow[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 764: 142823. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142823 [38] 史崇文, 赵玲芝, 郭新波, 等. 山西土壤元素背景值及其特征[J]. 华北地质矿产杂志, 1994(2): 188-196. SHI C W, ZHAO L Z, GUO X B, et al. Background values of soil elementsin Shanxi and their distribution feature[J]. Journal of Geology & Min Resources North China, 1994, 9 ( 2) : 188-196. (in Chinese)
[39] 王敏, 董佳琦, 白龙龙, 等. 浙江省香榧主产区土壤重金属空间异质性及其生态风险[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(12): 5949-5957. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202104238 WANG M, DONG J Q, BAI L L, et al. Spatial variation and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of main Torreya grandis plantation region in Zhejiang Province[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(12): 5949-5957 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202104238
[40] 张慧君, 朱勇兵, 赵三平, 等. 炸药的多相界面环境行为与归趋研究进展[J]. 含能材料, 2019, 27(7): 569-586. doi: 10.11943/CJEM2019047 ZHANG H J, ZHU Y B, ZHAO S P, et al. A review on environmental behavior and fate of explosives in multiphase interfaces[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2019, 27(7): 569-586 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11943/CJEM2019047
[41] 郑宇娜, 刘鹏, 刘金河, 等. 台州市典型电子垃圾拆解场地周边农田土壤重金属污染特征和来源解析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2022, 41(7): 1442-1451. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2021-1395 ZHENG Y N, LIU P, LIU J H, et al. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in farmland soils around the e-waste dismantling sites in Taizhou City, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2022, 41(7): 1442-1451 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2021-1395
[42] 张一修, 王济, 张浩. 贵阳市区地表灰尘重金属污染分析与评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(1): 169-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.01.030 ZHANG Y X, WANG J, ZHANG H. Pollution analysis and evaluation of heavy metals in urban dust in Guiyang[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2011, 20(1): 169-174 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.01.030
[43] BARKER A J, CLAUSEN J L, DOUGLAS T A, et al. Environmental impact of metals resulting from military training activities: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 265: 129110. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129110 [44] MARIUSSEN E, FJELLSBØ L, FRØMYR T R, et al. Toxic effects of gunshot fumes from different ammunitions for small arms on lung cells exposed at the air liquid interface[J]. Toxicology in Vitro, 2021, 72: 105095. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2021.105095 [45] BORDELEAU G, MARTEL R, AMPLEMAN G, et al. Environmental impacts of training activities at an air weapons range[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2008, 37(2): 308-317. doi: 10.2134/jeq2007.0197 [46] 陈丹丹, 谭璐, 聂紫萌, 等. 湖南典型金属冶炼与采选行业企业周边土壤重金属污染评价及源解析[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(9): 2667-2679. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021010901 CHEN D D, TAN L, NIE Z M, et al. Evaluation and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in the soil around typical metal smelting and mining enterprises in Hunan Province[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(9): 2667-2679 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021010901
[47] 黄波涛. 典型危废处置利用企业周边土壤重金属分布特征、来源及风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(2): 435-445. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022062403 HUANG B T. Distribution characteristics, sources analysis and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils surrounding typical hazardous waste disposal and utilization plants[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(2): 435-445 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022062403
[48] 姜昱聪, 贾晓洋, 夏天翔, 等. 起爆药污染场地土壤中锑的环境风险评估[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(2): 485-493. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2019.06.03 JIANG Y C, JIA X Y, XIA T X, et al. Environmental risk assessment of antimony in contaminated soil by primary explosives[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(2): 485-493 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2019.06.03
[49] 李朋飞, 刘超, 陶春军, 等. 再生铅工业园周边土壤重金属分布特征及来源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(4): 663-671. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.04.03 LI P F, LIU C, TAO C J, et al. Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in soils around recycled lead industrial park[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(4): 663-671 (in Chinese). doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.04.03
[50] 江雅琪, 桂和荣, 陈晨, 等. 宿州市城市景区水域底泥重金属含量特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(8): 2410-2418. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020111302 JIANG Y Q, GUI H R, CHEN C, et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment in urban scenic area[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(8): 2410-2418 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020111302
[51] 杨新明, 钟雅琪, 李国锋, 等. 典型工业城市大气降尘中重金属分布特征及其来源解析: 以济南市为例[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41((1): ): 94-103. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020090803 YANG X M, ZHONG Y Q, LI G F, et al. Distribution characteristic and source apportionment of heavy metals in atmospheric dust in a typical industrial city—a case study of Jinan[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41((1): ): 94-103 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020090803
-



 下载:
下载: