-
大规模工业化以来,全球水污染事件频发. 以我国为例,随着工业化发展,中国经历了急剧的环境恶化,造成了大范围的水体污染和生态破坏. 例如在我国太湖流域的部分地区,被发现水体、沉积物等重金属浓度过高,在鱼类和牡蛎各器官中发现铅、铜、镉和铬等重金属高度富集[1];地表水中常常有消毒副产物的检出[2];湖泊不同环境介质中抗生素普遍存在;在全球范围内,水和沉积物中抗生素的暴露水平相对较高[3]. 目前传统的水体污染治理修复的方法主要有离子交换法、膜处理法、混凝-絮凝法、植物修复法、光催化法等[4-7],然而上述方法尚且存在一定的缺陷:膜处理法由于是通过压力驱动,往往需要很高的能量,使得处理成本大幅提高;且在膜直接过滤过程中,废水中的有机物、无机物、悬浮物等成分是潜在的污染物,会造成严重的膜污染,导致膜的使用寿命缩短[8-9];对于植物修复来说,虽然其成本低且绿色环保,但其也面临着严重耗时又耗空间的问题[10-11];光催化法同样面临着对于可见光的利用率低以及光催化剂用于大规模安装后的快速分离和回收困难的问题[12-13].
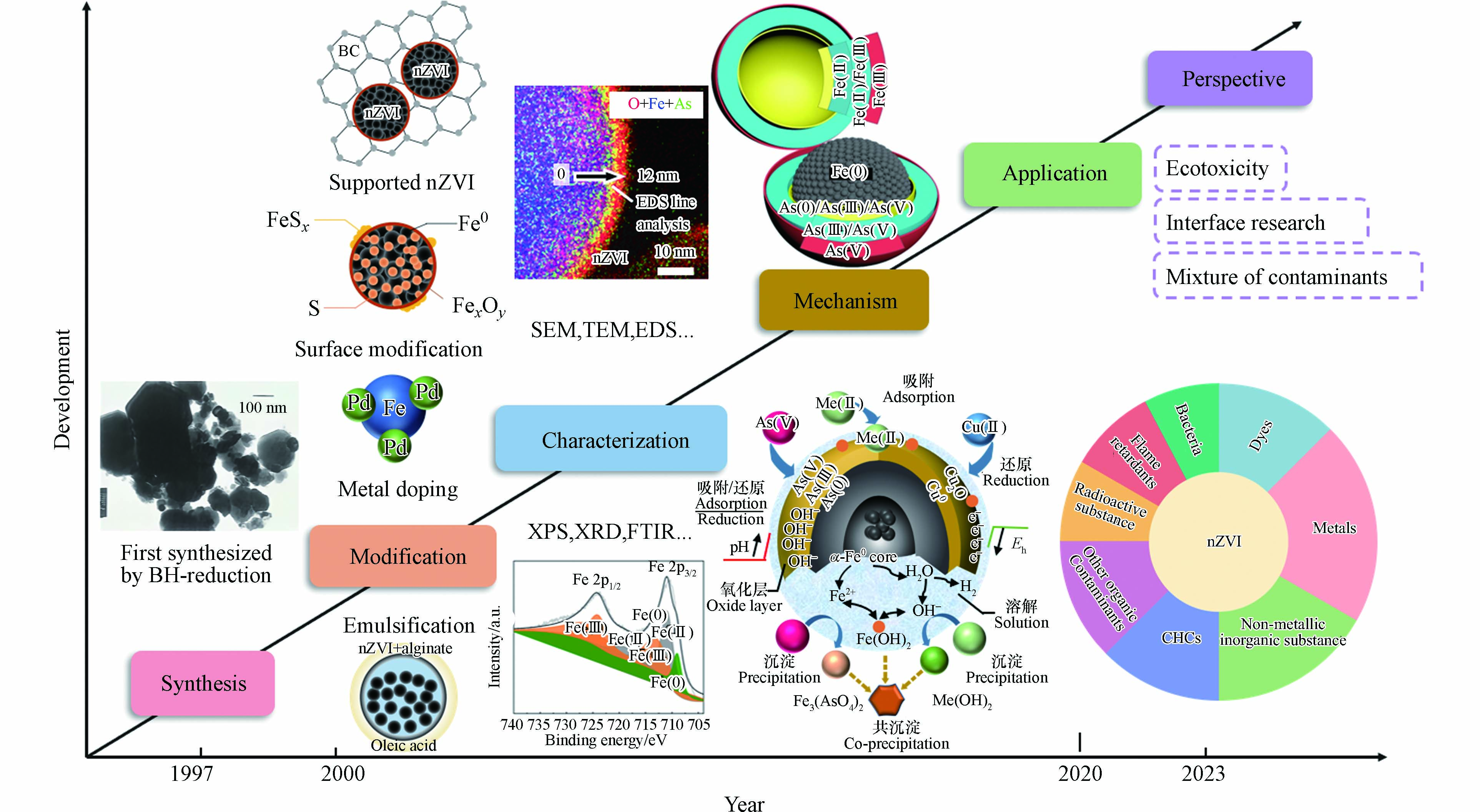
而纳米零价铁材料能一定程度上弥补上述缺陷,其为一种直径大小介于1—100 nm之间的“零价”铁颗粒,其结构为“壳核结构”,即由铁氧化物壳层和零价铁内核构成[14-15],因为其具有良好的还原性能[16-17](其标准氧化还原电位约为−0.45 V)、吸附性能[18-19]、优良的比表面积[20-21]、产量丰富、易于获取和制备以及成本低廉等优势而在水处理中有良好的应用前景[22-24],能够广泛地去除水体中的污染物[25]. 已有的研究表明,纳米零价铁可以有效地去除水体中的重金属、卤代物、硝基芳烃、染料化合物等污染物[26-30]. 铁是地壳中含量最丰富的金属元素之一[31],制备纳米零价铁的原料来源广泛,同时,铁元素是地球化学循环的重要元素之一[32],因此纳米零价铁是绿色环境纳米材料,能最大限度地减少环境的二次污染[33-34]. 1997年,在Environmental Science & Technology上报道了纳米零价铁用于地下水中卤代有机物还原脱卤以来,有关nZVI用于环境治理的研究蓬勃展开. 1997年距今的25年间,科技的进步推动了纳米零价铁这一领域的发展,研究者借助不断更新的技术对纳米零价铁的制备、改性、机理以及环境应用做出了深入的探究, 图1为近25年来在纳米零价铁的研究历程[35-41],从纳米零价铁的制备(球磨法、化学还原法等)、纳米零价铁的改性(负载改性、硫化改性、双金属改性等)、通过高分辨透射电镜(transmission electronic microscope, TEM)、X-射线光电子能谱(X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy,XPS)、能量损失谱(energy electron lose spectra,EELS)、基于同步辐射光的X-射线吸收精细结构谱(X-ray adsorption fine structure,XAFS)等光谱学技术微观观察纳米零价铁表面性质、推测纳米零价铁去除污染物的机理,再到纳米零价铁的实际应用,纳米零价铁环境化学已经发展成为一个引人注目的学科.
文献计量学是一种分析某一科研领域发展的科学方法,知识图谱是文献计量学的一种表示方法,知识图谱是通过图的形式表达事物之间内在联系的知识库[42]. CiteSpace是目前应用较为广泛的绘制知识图谱的可视化软件,通过CiteSpace可视化分析,可以体现出某一研究领域的研究现状、合作网络、研究热点等[43-44]. 该文通过CiteSpace软件分析了25年来发表在Web of Science核心合集上的期刊文章,分析总结了25年来纳米零价铁在水体污染修复治理方面的研究进展以及未来可能的热点研究方向.
-
笔者以Web of Science核心合集数据库为检索数据库,检索式为:TS=(nZVI OR nano zero valent iron OR nanoscale zero valent iron) AND TS=(water),文献类型为“Article”,检索时间范围为1997-01-01到2022-12-31,数据采集时间为2023年3月4日. 下载格式为“全记录与引用的参考文献”,文件格式为“纯文本”.
-
采用CiteSpace6.1.R6进行可视化分析,首先对收集到的2479篇文献进行去重操作,去除可能存在的资讯和无作者的文献,去重后结果仍为2479条文献. 分别统计国家、机构、作者对该领域的贡献,每个期刊的发文量的多少,并依据不同时期发文量的多少将整个研究时段分为3个时期,针对每个时期进行聚类和关键词突现分析,探讨各个时期的研究热点. 最后,对文献进行共被引分析,选取被引最高的文献以及每个阶段他引最高的综述文献进行深入分析,探寻对过去25年来纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域有重要影响的文章. 可视化分析的参数设置为:(1)时间跨度为1997—2022,时间切片(time slicing)为1年;(2)选择的节点类型(node types)分别为作者(author)、机构(institution)、国家(country)、关键词(keyword)和被引文献(reference);(3)连线强度(link strength)选择cosine算法;(4)算法标准(selection criteria)选择g index算法,k值设置为10或25,其他参数不变;(5)裁剪方式(pruning)选择Minimun Spanning Tree、Pruning sliced networks、Pruning the merged network;(6)聚类方法选择log-likelihood Ratio Test method(LLR)算法自动从施引文献的关键词中提取共现频次最高的关键词作为聚类标签.
-
从时间尺度上对纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域的文章进行分析,统计年发文量的多少和发文的主要期刊. 根据年发文量的多少可以判断出该领域的研究变化趋势,帮助学者掌握该领域的整体发展情况. 笔者人为地依据年发文量的情况将25年来纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域的发展历程分为3个阶段:即初步探索期(1997—2004年),年发文量均未超过3篇;缓慢发展期(2005—2013年),年发文量缓慢增加,从2005年的12篇增加到2013年的78篇;迅速增长期(2014—2022年),年发文量快速增长,均超过100篇,从2014年的125篇增加到2021年时最多的331篇,详见图2.
-
在初步探索期,累计发文共10篇,占总发文量的0.4%,年发文量均未超过3篇,说明纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理这一领域刚刚开始起步,受到的关注不多. 在这一时期发文的主要期刊是Environmental Science Technology和Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects. 其中,1997年由Wang Chuan-bao和Zhang Wei-xian发表在Environmental Science Technology上的“Synthesizing Nanoscale Iron Particles for Rapid and Complete Dechlorination of TCE and PCBs”是纳米零价铁环境应用领域的开篇之作[40],该文章首次提出纳米零价铁可以用作三氯乙烯的完全脱氯,进而提出纳米零价铁可以用于处理地下水污染,不足之处是该文章没有详细讨论金属表面脱氯的机理和步骤,这一定程度上也是受制于表征手段的单一. 2001年由Danielw.Elliott和Zhang Wei-xian发表在Environmental Science Technology上的“Field Assessment of Nanoscale Bimetallic Particles for Groundwater Treatment”是纳米零价铁用于现场实验的首篇文章[45],在现场实验中,将纳米双金属(Fe/Pd)颗粒重力注入到被三氯乙烯和其他氯化脂肪烃污染的地下水中,尽管纳米颗粒用量很低,但在4周的监测期内,三氯乙烯的还原效率高达96%,现场实验的数据与实验室研究的结果一致,表明纳米零价铁颗粒有快速还原脱氯的效果,不足之处是该文章所选污染场地污染物较为简单,体系并不复杂,且没有设法增加纳米零价铁的可迁移性、未探究纳米零价铁用作现场实验后可能对现场环境条件带来的影响.
-
在缓慢发展期,累计发文量359篇,占总发文量的14.5%,年发文量均在10—78篇,说明这一时期该领域的研究受到的关注有一定增加. 在这一时期发文的期刊也逐渐增多,主要有Environmental Science Technology、Journal of Hazardous Materials、Water Research、Chemical Engineering Journal、Chemosphere等. 其中,2006年由Li Xiao-qin和Zhang Wei-xian发表在Langmuir上的“Iron nanoparticles: the core-shell structure and unique properties for Ni(Ⅱ) sequestration”是纳米零价铁第一次应用于重金属去除的理论及应用的文章[46],该文章提出了纳米零价铁的壳核结构,并且指出了纳米零价铁对重金属的吸附和还原的双重作用. 根据Web of Science核心数据库的引文分析结果可知,在这一阶段,被引最高的文章是2011年Hardiljeet K. Boparai等发表在Journal of Hazardous Materials上的“Kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ion removal by adsorption onto nano zerovalent iron particles”[47],该文章研究了纳米零价铁颗粒吸附去除镉离子的动力学和热力学,在该研究中,使用纳米零价铁颗粒研究了Cd2+浓度在25—450 mg·L−1范围内的去除效果. 探究了温度对纳米零价铁颗粒吸附镉动力学和平衡的影响. 与吸热反应一致,温度的升高导致镉吸附率的增加. 伪二阶动力学模型很好地拟合了吸附动力学,吸附活化能为54.8 kJ·mol−1,说明吸附过程为化学吸附. 在297 K条件下,纳米零价铁对Cd2+的最大吸附量为769.2 mg·g−1,不足之处是该文章只探讨了纳米零价铁的镉的吸附动力学,研究对象较为单一,应当对比纳米零价铁对多种重金属离子的吸附动力学,从而得到纳米零价铁对不同的重金属离子的去除机理.
-
在迅速增长期,在2015—2016年和2019—2020年的年增长均高达57篇. 这一时期累计发文量2110篇,占总发文量的85.1%,年发文量均在100篇以上,其中2021年发文量更是高达331篇,说明这一时期该领域的关注度很高,掀起了研究热潮. 在这一时期发文量较大的期刊主要有Chemical Engineering Journal、Chemosphere、Journal of Hazardous Materials、Science of The Total Environment等,同时也不乏顶级期刊上关于纳米零价铁的报道,如2018年Ling Lan等发表在Advanced Materials上的“Enrichment of Precious Metals from Wastewater with Core–Shell Nanoparticles of Iron”[48]提出用于水处理后的纳米零价铁颗粒中含有的贵金属远远高于传统的金属矿石,对其的回收具有很高的成本效益;2021年Liu Yangzhi等发表在Nature Nanotechnology上的“A new strategy using nanoscale zero-valent iron to simultaneously promote remediation and safe crop production in contaminated soil”[49]阐明了纳米零价铁衍生的根铁斑块形成在水稻安全生产中的具体作用,并确定了纳米零价铁处理和水稻栽培在纳米零价铁促进的根际五氯苯酚微生物降解中的协同作用,这项工作为纳米材料在土壤修复中的应用开辟了新的策略;2022年Wei Kai等发表在Advanced Functional Materials上的“Strained Zero-Valent Iron for Highly Efficient Heavy Metal Removal”[50]提出了通过间隙硼掺杂对零价铁施加拉伸应变,使晶格中的铁相互作用不稳定,从而释放出铁储层中的电子,提高零价铁对重金属的去除能力. 根据Web of Science核心数据库的引文分析结果可知,在这一阶段,被引最高的文章是Dong Haoran发表在Journal of Hazardous Materials上的“Stabilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI)with modified biochar for Cr(Ⅵ) removal from aqueous solution”[51]. 该文章提出用生物炭(biochar, BC)、酸改性生物炭(HCl-BC)、碱改性生物炭(KOH-BC)、氧化生物炭(H2O2-BC)合成生物炭负载的纳米零价铁,并比较了它们对六价铬的去除效果,结果说明,HCl处理的生物炭负载到纳米零价铁上可以增强对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除. 纳米零价铁与HCl-BC的质量比对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除效果有重要的影响. HCl-BC占比较少时不能阻止纳米零价铁颗粒在HCl-BC表面的聚集,而HCl-BC占比过多会阻塞纳米零价铁的活性位点,影响去除效果. 同时研究了酸改性生物炭负载的纳米零价铁去除六价铬的机理,即六价铬还原形成的三价铬更多的会迁移到HCl-BC表面,因此在纳米零价铁表面的活性点位就能够继续还原六价铬,不足之处是该文章只得出了酸改性生物炭的负载有利于纳米零价铁对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除,对其他重金属污染物或者有机污染物的去除是增强还是减弱需要进一步对比分析.
-
根据Web of Science核心数据库的统计结果以及CiteSpace的分析,笔者列出了在纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理这一领域发文排名前十的国家/地区、作者和机构,具体信息见表1. 由表1可见发文超过百篇的国家/地区有Peoples Republic of China(中国)、USA(美国)、Iran(伊朗)、India(印度)和South Korea(韩国)在CiteSpace得出的共现图谱中,可以用中介中心性(between centrality, BC)表示某个节点的重要性,BC大于0.1的节点外圈为紫色,表明该节点在共现图谱中占据重要地位. 由图3(a)可知,Peoples Republic of China、England、Czech Republic、Germany、Canada等国家的节点外圈为紫圈(BC分别为0.21、1.13、0.28、0.43、0.29),说明这些国家在纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理这一领域的发文较多且具有一定权威性,同时与其它国家有着密切的合作关系.
发文最多的作者是Zhang Wei-xian、Eljamal Osama、Chen Zuliang等,结合图3(b)可知,同济大学Zhang Wei-xian(张伟贤)团队的几位学者(Zhang Wei-xian、Liu Airong、Ling Lan、Wang Wei等),日本九州大学Eljamal Osama团队的几位学者(Eljamal Osama、Sugihara Yuji、Maamoun Ibrahim、Matsunaga Nobuhiro、Ahmed M E Khalil等),发文都较多. 但是总体上看,作者之间的合作网络还是不够密切,研究总体较为零碎,未来应当加强作者之间的交流合作,促进领域的长远发展.
发文量最多的几个机构是Chinese Academy of Science(中国科学院)、Tongji University(同济大学)、 Zhejiang University(浙江大学)、Hunan University(湖南大学)、Harbin lnstitute of Technology(哈尔滨工业大学)等,其中Chinese Academy of Science和Tongji University显著多于其它机构,结合图3(c)可知,Chinese Academy of Science和Tongji University的节点外圈为紫圈(BC分别为0.36和0.21),其它机构的发文主要以这两个机构为中心展开,说明Tongji University和Chinese Academy of Science与其它机构合作十分密切,这两个机构的发文具有一定的重要性和权威性.
-
对初步探索期、缓慢发展期和迅速增长期这3个时期的关键词进行关键词聚类分析和突现分析,探讨各个时期纳米零价铁基材料的研究热点,以把握该领域的发展脉络和研究趋势,方便走在研究的前线. 通过使用CiteSpace的共现频次(cooccurrence frequency, CF)和中介中心性的值的大小来评价该领域的研究热点. 同时使用CiteSpace的突现分析,了解关键词的兴起与衰落情况,关键词突现强表示该关键词在较短的时间内出现的频次高.
-
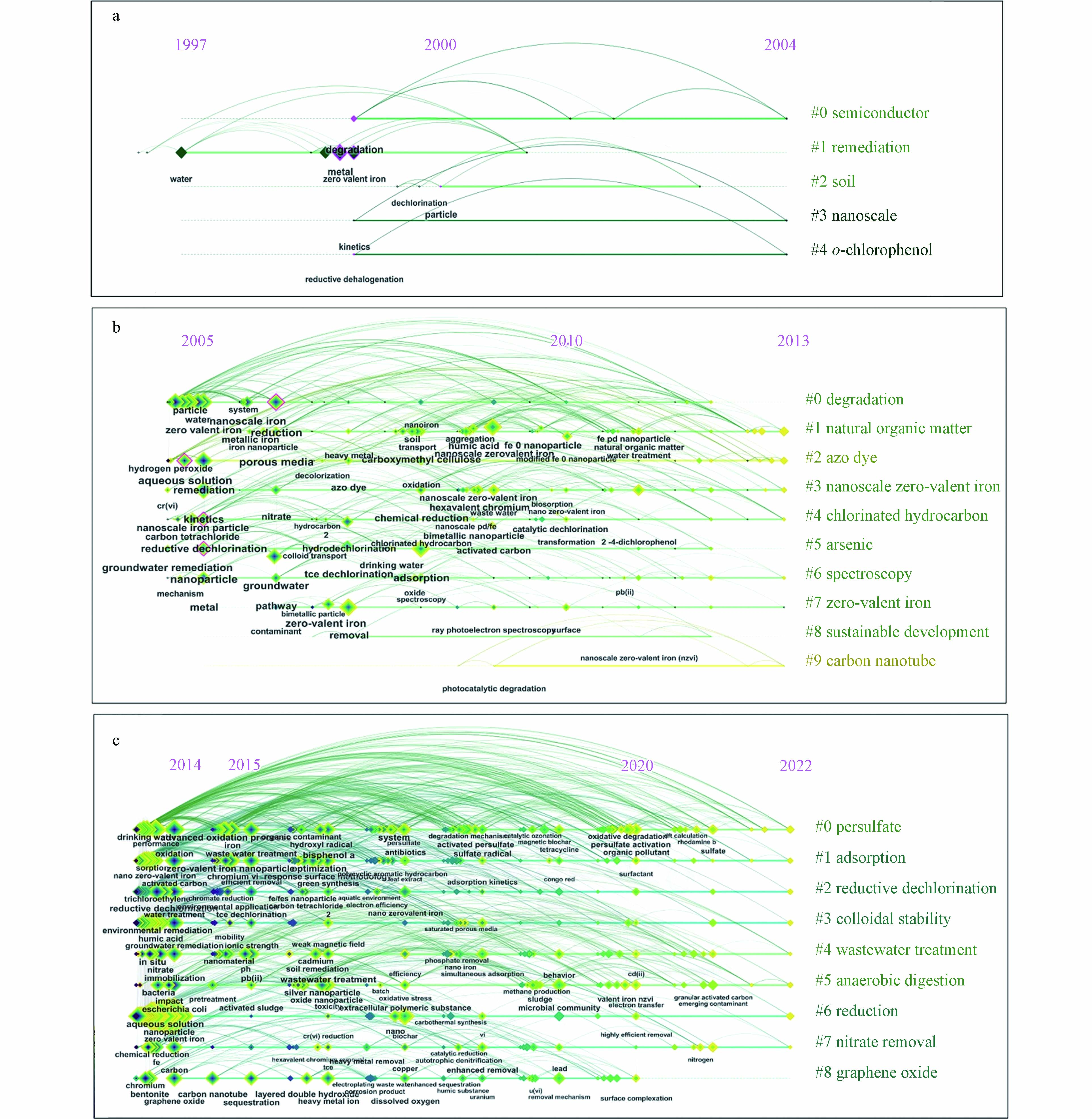
图4(a)为初步探索期的纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域的时间线图谱,该图一共显示了#0 semiconductor (半导体)、#1 remediation (修复)、#2 soil (土壤)、#3 nanoscale (纳米级)、#4 o-chlorophenol (邻氯苯酚)等5个聚类. 1999年出现的节点zero valent iron (零价铁,CF值为7,BC值为0.15)是整个时间线图中节点最大的,代表该节点是初步探索阶段出现频次最多的关键词,中介中心性最高的是节点degradation (降解,CF值为4,BC值为0.56),表明初步探索期纳米零价铁的研究重点主要集中在纳米零价铁的制备合成以及对水体中含氯有机物和金属元素等的去除. 此外有较高共现频次和中介中心性的关键词还有:water (水,CF值为6,BC值为0.09)、metal (金属,CF值为5,BC值为0.33)、reductive dehalogenation (还原脱卤,CF值为3,BC值为0.15)、rapid dechlorination (快速脱氯,CF值为3,BC值为0.15)、particle (粒子,CF值为3,BC值为0.17)、kinetics (动力学,CF值为2,BC值为0.10). 由以上关键词可以看出,在初步探索阶段的研究方向主要为利用纳米零价铁颗粒通过还原作用、脱氯作用等方式去除水溶液中的卤代物以及金属元素等. 由于在初步探索期纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域整体的研究较少,所以没有出现频次极具变化的关键词,所以CiteSpace并未检测出关键词的突现.
-
图4(b)为缓慢发展期的纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域的时间线图谱,该图一共显示了#0 degradation (降解)、#1 natural organic matter (天然有机物)、#2 azo dye (偶氮染料)、#3 nanoscale zero-valent iron (纳米零价铁)、#4 chlorinated hydrocarbon (氯化烃)、#5 arsenic (砷)、#6 spectroscopy (光谱学)、#7 zero-valent iron (零价铁)、#8 sustainable development (可持续发展)、#9 carbon nanotube (碳纳米管)10个聚类. 其中2005年出现的关键词zero valent iron (零价铁,CF值为156,BC值为0.03)是该阶段整个时间线图中节点最大的,代表该节点是缓慢发展阶段出现频次最多的关键词,中介中心性最高的是节点reduction (还原,CF值为78,BC值为0.13),表明缓慢发展期纳米零价铁的研究重点主要集中在研究纳米零价铁对环境中污染物的还原作用. 此外有较高共现频次和中介中心性的关键词还有:water (水,CF值为132,BC值为0.02)、nanoparticle (纳米颗粒,CF值为102,BC值为0.11)、particle (颗粒,CF值为97,BC值为0.01)、dechlorination (脱氯作用,CF值为95,BC值为0.05)、kinetics (动力学,CF值为92,BC值为0.07)、remediation (修复,CF值为87,BC值为0.09)、groundwater (地下水,CF值为80,BC值为0.07)、removal (去除,CF值为74,BC值为0.07)、degradation (降解,CF值为43,BC值为0.05)、adsorption (吸附,CF值为60,BC值为0.08)、aqueous solution (水溶液,CF值为43,BC值为0.13)、reductive dechlorination (还原脱氯,CF值为24,BC值为0.10). 由以上关键词可以看出,在缓慢发展期关于纳米零价铁的研究主题逐渐变得丰富和多元化,且关键词的共现频次有了明显的提升,纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域受到的关注有明显的增加,表明在这一阶段研究者开始考虑到纳米零价铁对于实际水体的修复作用,并且关注纳米零价铁去除污染物的内在机理.
对缓慢发展阶段进行了关键词突现分析,共得到了9个关键词突现,结果见表2. 由表2可知,在缓慢发展阶段,一共有9个关键词突现,分别是:nanoscale iron particle (纳米铁颗粒)、chlorinated methane (氯代甲烷)、carbon tetrachloride (四氯化碳)、granular iron (粒状铁)、kinetics (动力学)、contaminant (污染物)、nanoscale iron (纳米铁)、tce dechlorination (三氯乙烯脱氯)、nanoiron (纳米铁). 其中,突现强度最大的是nanoscale iron particle (纳米铁颗粒),这表明研究者在这段时间对纳米零价铁颗粒有大量的关注,是这段时间的研究热点. granular iron (粒状铁)、contaminant (污染物)等关键词的突现时间较长,这也表明在这一时期,由纳米零价铁基材料衍生的相关铁颗粒用于水污染处理以及纳米零价铁用于水体中多种的污染物的去除研究越来越广泛.
-
图4(c)为迅速增长期的纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域的时间线图谱,该图一共显示了#0 persulfate (过硫酸盐)、#1 adsorption (吸附)、#2 reductive dechlorination (还原脱氯)、#3 colloidal stability (胶体稳定性)、#4 wastewater treatment (废水处理)、#5 anaerobic digestion (厌氧消化)、#6 reduction (还原)、#7 nitrate removal (去除硝酸盐)、#8 graphene oxide (氧化石墨烯)等9个聚类. 在迅速增长阶段共出现了12个关键词的共现频次大于300次,分别为:zero valent iron (零价铁,CF值为810)、nanoparticle (纳米颗粒,CF值为697)、aqueous solution (水溶液,CF值为617)、water (水,CF值为588)、waste water (废水,CF值为581)、removal (去除,CF值为576)、adsorption (吸附,CF值为507)、degradation (降解,CF值为410)、reduction (降解,CF值为378)、zerovalent iron (纳米零价铁,CF值为337)、nZVI (纳米零价铁,CF值为331)、remediation (修复,CF值为327). 此外还出现了21个共现频次大于100次的关键词,由于在这一阶段的关键词众多,这也导致没有关键词的中介中心性较大,这表明在迅速增长期,关于纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域的研究内容十分广泛,研究主题更加丰富,研究量更多,研究者的关注点已经从初步发展时期纳米零价铁去除卤代物已经扩展到纳米零价铁用于去除水环境中的多种重金属、化学染料等污染物,同时深入研究了纳米零价铁在环境中作用的机理,此外,在纳米零价铁与其他工艺的联合作用上做出了大量的研究,例如纳米零价铁的硫化、高级氧化、与生物处理的结合、表面修饰提高在地下水修复中的迁移性与稳定性等,这些关键词表明该领域受到关注的广度和深度都有了空前的发展.
对迅速增长阶段进行了关键词突现分析,共得到了25个关键词突现,结果见表3. 由表3可以看出,在该阶段一共检测出25个突现关键词,与前两个阶段相比,关键词突现有了很大幅度的提升,表明这一时期,对纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域的研究越来越深入,关注点越来越广泛. 在这25个突现关键词中,突现强度最高的几个是:particle(颗粒)、spectroscopy(光谱学)、performance(性能)、porous media(多孔介质)、dechlorination(脱氯作用)、nitrate reduction(硝酸盐还原)、sedimentation(沉积)等,这些关键词的高突现强度表明在迅速增长期研究者通过光谱学手段对纳米零价铁去除水体污染物的机理等进行了更深入的研究,研究了纳米零价铁颗粒的微观壳核结构,各种多孔负载材料对纳米零价铁去除水体污染物效果的改善情况,纳米零价铁在实际含水的污染土壤中的迁移与沉积情况等. 突现持续时间较长的关键词有spectroscopy(光谱学)、TCE dechlorination(三氯乙烯脱氯)、microbial community(微生物群落)、removal mechanism(去除机理),说明研究者早已不局限于纳米零价铁的单一作用,而是纳米零价铁与多种污染物以及多种影响因素存在的条件下的复杂联合作用,以及对纳米零价铁去除污染物的机理展开了长时间深入探讨,此外,还通过一些生物指标研究了纳米零价铁用于水处理之后的效果和生物毒性等,如通过发光细菌毒性实验以及细菌丰度评估纳米零价铁处理后的地表水毒性[52].
-
根据《期刊引用报告》(JCR)2022年发布的2021的期刊影响因子,筛选出了检索出的文献中影响因子大于10的所有期刊,通过分析这些期刊最近5年(2018—2022年)发表的文章的关键词突现情况,预测未来可能的研究热点. 近5年的纳米零价铁基材料用于水体修复治理领域的关键词汇总如表4所示,共得到9个突现关键词. 近5年,受到关注较多的关键词有:green synthesis (绿色合成)、sulfate radical (硫酸根)、system (系统)、reactivity (反应性)、nano iron (纳米铁)、enhanced sequestration(增强封存)、metal ion(金属离子)、ferrous ion (亚铁离子)、sulfidation (硫化作用)等. 这些关键词受到的关注说明近年来纳米零价铁的研究重点主要集中在纳米零价铁的绿色合成方法探究、硫化纳米零价铁的合成以及与硫酸根自由基等基团的相互作用、纳米零价铁在复杂系统中的反应性、实际水体中原本存在的金属离子等对纳米零价铁应用的影响、纳米零价铁对放射性元素如铀的封存作用等. 对于纳米零价铁的传统化学合成方法,由于其通常使用的是昂贵且有毒的试剂(即NaBH4)制备,这对纳米零价铁的实际应用带来了困难,而绿色合成方法通常采用植物提取物中的生物活性物质将铁或亚铁离子还原为零价铁[53],Vesna Kecic等使用橡树叶提取物绿色合成的纳米零价铁对品红染料废水具有良好的去除效果,去除率在反应60 min可达到84.06%[54],绿色合成法是一种环境友好且低成本的纳米零价铁的合成方法,在未来关于纳米零价铁的高效绿色合成可能是研究热点之一. 对于纳米零价铁在复杂系统中的应用效果的研究,Zhang Nuanqin等人研究了复合材料纳米零价铁-二氧化铈在去除四环素过程中的相互作用,结果表明纳米零价铁和二氧化铈的复合材料能够显著促进Fenton体系中羟基自由基的生成,这主要是因为二氧化铈不仅提高了催化剂的吸附性能,而且由于表面丰富的氧空位,加速了电子转移,促进了过氧化氢的分解从而加快了四环素的降解[55],Zhang Dejin等研究了在上流式厌氧污泥床中添加生物炭稳定的硫化改性的纳米零价铁(S-nZVI@BC),对硝基苯厌氧生物降解的增强作用及其对微生物群落结构的影响. 结果表明,与其他厌氧体系相比,S-nZVI@BC耦合体系可以显著促进硝基苯的还原和苯胺的形成,提高了细胞外聚合物质的含量,促进了挥发性脂肪酸的转化,提高了甲烷产量[56]. 在未来研究更加复杂多元的体系中纳米零价铁与其他材料或者多种污染物之间的相互作用关系可能仍然是研究热点之一. 纳米零价铁对铀的封装也是研究热点之一,Ling Lang等人的研究表明纳米零价铁对铀有良好且快速的分离和封装能力,在核燃料捕获和减少核废物方面有潜在的应用价值[57]. 上述研究热点可能在未来的一段时间内仍然会受到较多的关注,也可能互相交叉融合,发展出新的研究热点,因此值得研究者们的广泛关注.
-
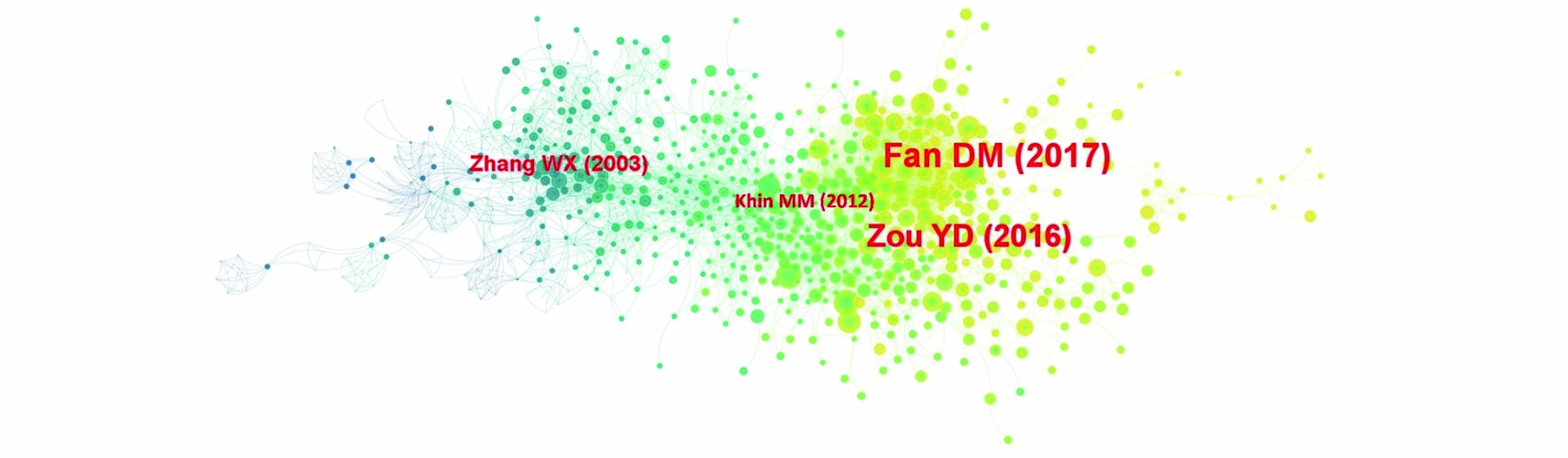
通过CiteSpace的文献共被引分析,可以清楚地了解在该领域高被引文献,可以让研究者更好地了解所在领域的发展情况,探寻学科发展规律,从而推动现有的研究工作的深入发展. 对检索到的1997到2022年间纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域的影响因子大于10的文章进行共被引分析,得到的结果见图5,并筛选出3个阶段中每个阶段他引频次最高的综述文献进行分析.
图中最大的节点是:Fan DM(2017)代表整个时期共被引频次最高的文献,另外3篇文献为3个阶段中他引频次最高的文献,详细信息见表5所示.
2003年Zhang Weixian发表在Journal of Nanoparticle Research上的“Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: An overview”是初步探索期他引频次最高的文献[58]. 该文章综述了纳米零价铁在初步发展阶段的研究进展,评估了不同前驱体合成纳米零价铁的方法、纳米零价铁在较长时间内对土壤和水中污染物的反应性以及纳米零价铁颗粒注入含水层和地下的原位反应现场实验,为纳米零价铁未来的长远发展奠定了基础.
2012年Khin Mya Mya等发表在Energy & Environmental Science的“A review on nanomaterials for environmental remediation”是缓慢发展期他引频次最高的文献 [59]. 该文章综述了纳米材料在环境修复中的应用,对铁基纳米材料指出了应当研究铁基纳米材料的表面改性,以优化工艺,提高可重复使用性和延长用寿命是降低环境修复成本的重要途径,纳米零价铁材料的功能特性需要进一步研究,为了充分挖掘其真正的潜力,需要进行重要的基础和机理研究,为纳米零价铁领域的研究指出了发展方向.
2016年Zou Yidong等发表在Environmental Science Technology的“Environmental Remediation and Application of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron and Its Composites for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions:A Review” 是迅速增长期他引频次最高的文献[60]. 该文章综述了纳米零价铁及其复合材料去除重金属及应用于环境修复的效果,提出了纳米零价铁常用的改性方法,如负载、硫化、乳化以及双金属改性等,对基于纳米零价铁的材料探究了其去除重金属的相互作用机制,讨论了不同环境条件,如pH值、温度、共存离子等对纳米零价铁材料的影响,以及利用密度泛函理论计算(Discrete Fourier Transformation, DFT)和X射线吸收精细结构谱技术(Extended X-ray absorption fine structure, EXAFS)探究纳米零价铁去除重金属离子的潜在问题,指出了纳米零价铁基材料的可能改进和未来在环境修复中应用的潜在领域.
2017年Fan Dimin等发表在Environmental Science Technology上的“Sulfidation of Iron-Based Materials: A Review of Processes and Implications for Water Treatment and Remediation”是整个时期共被引频次最高的文献[61]. 该文章综述了硫化对铁基材料在水处理和修复过程中的影响,提出了硫化处理可以大大提高还原剂去除污染物的效率. 这可能是由于硫化作用抑制了铁基材料的腐蚀,硫化作用也能有利于污染物去除的途径,例如通过还原消除而不是氢解来脱氯,以及硫化物作为纳米零价铁的隔离层,可以抵抗氧化,在含氧条件下,硫化作用可以增强污染物的多相催化氧化. 硫化作用对铁基材料去除污染物的效应可能大大提高其在水处理和污染地下水修复中的实际效用,这为纳米零价铁的发展方向提供了新的思路.
上述文章可以为需要了解纳米零价铁用于水体污染修复治理领域的研究者提供了很好的了解途径,通过阅读上述文献,可以快速了解纳米零价铁的发展脉络.
-
(1)利用citeSpace对WoS核心合集上25年来(1997—2022年)关于纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域的相关文献进行了文献计量学可视化分析,探索了该领域的发展脉络;主要从事该领域工作的国家、机构和作者之间的合作关系;对该领域发展有着重要贡献的经典文献;各个时期的研究热点以及未来可能的研究前沿等.
(2)发展脉络:25年来纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域经历了初步探索期、缓慢发展期和迅速增长期3个时期,发文量分别占总发文量的0.4%、14.5%和85.1%,从初步探索期的10篇到缓慢发展期的359篇再到迅速增长期的2110篇这一文章增长的跨度也说明了对于该领域的研究越来越火热,同时介绍了每个发展阶段重要的研究成果,有利于读者掌握这一领域的发展脉络.
(3)合作网络:在纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域国家间的合作十分密切,尤其是在中国、英格兰、捷克共和国等国家之间有着广泛的合作关系;Tongji University(同济大学)和Chinese Academic of Science(中国科学院)是在该领域合作较多的权威性机构,很多研究机构通过与这两个机构合作展开研究;而作者之间的合作相对较为松散,研究总体较为零碎,只有少数作者团体有稳定的合作对象. 在未来,各个国家、机构以及作者之间应当进一步加强相互之间的合作关系,加强彼此之间的联系,避免单打独斗的现象,以便更好的推动该领域的研究发展.
(4)研究热点与前沿:在纳米零价铁发展的这25年来,纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域的研究热点也是不断地在发展变化的. 从初步发展期的关注重点集中在纳米零价铁的合成及其“还原作用”和“脱氯作用”等演变到缓慢发展期时受到广泛关注纳米零价铁对于实际水体的修复作用等,再演变到迅速增长期的纳米零价铁的“硫化”、“高级氧化”和“与生物处理的结合”等. 近5年的关键词突现分析结果表明,未来纳米零价铁的可能研究热点在于纳米零价铁的绿色合成方法的优化以及在复杂多元的体系中纳米零价铁与其他材料或者多种污染物之间的相互作用关系的探究.
(5)经典文献:通过被引文献分析找到了被引频次最高的文献,以及3个阶段中每个阶段他引频次最高的综述文献,这4篇文献主要详细综述了纳米零价铁的制备过程、改性方法、对多种类型的环境污染物的去除效果以及如何利用DFT和EXAFS等技术对纳米零价铁的机理进行探究等,对于想要较为系统地了解纳米零价铁基材料的研究者具有很大的帮助.
-
(1)纳米零价铁作为应用最广泛的环境纳米材料之一,为实现在地下水、土壤修复及废水处理领域的实际应用,其低成本宏量制备技术的开发,是未来的研究热点之一.
(2)纳米零价铁由于本身具有高活性,在与污染物的反应过程中,其本身的结构、性质也发生演变,从而对污染物的去除效能产生影响,研究纳米零价铁的动态结构性能演变与污染物去除效能的关系,评价环境归宿及其对于环境安全性的潜在影响,也是需要关注的问题之一.
(3)分析仪器的进步,使得原子尺度研究纳米零价铁与污染物之间分子水平的反应机理的成为可能,结合DFT理论计算,探索去除污染物反应的最本质的机理,也成为目前的热点之一.
(4)纳米零价铁技术具有良好的还原型和吸附性能,但是其本身仍然具有一定的局限性,与其他技术,如微生物技术联合进行复杂介质中污染物的去除,具有重要的研究前景.
基于文献计量学的纳米零价铁水污染控制研究热点分析
Research hotspot analysis of nano zero-valent iron for water pollution treatment based on bibliometrics
-
摘要: 近几十年来,随着工业生产的不断发展,水体污染事件频发. 纳米零价铁(nano zero-valent iron,nZVI)作为水体污染治理修复研究的热点材料之一而受到广泛关注. 该综述基于CiteSpace 6.1.R6可视化软件,对Web of science核心合集数据库25年(1997—2022年)有关纳米零价铁在水体污染修复治理方面的文献进行检索,得到满足检索条件的2479篇文献并进行了可视化分析. 结果表明:(1)25年来,纳米零价铁在水体污染修复治理方面的发展经历了初步探索期、缓慢发展期、迅速增长期的3个时期,发文量分别占总发文量的0.4%、14.5%和85.1%. (2)国家和机构之间的联系和合作较为密切,而作者之间的合作较为松散. (3)3个时期的研究热点各不相同,研究的主题不断拓宽,未来可能的研究热点是纳米零价铁的绿色低成本合成方法探究、纳米零价铁去除污染物原子尺度机理研究以及与微生物技术等联合处理复杂介质中的污染物等.Abstract: In recent decades, with the continuous development of industrial production, water pollution incidents have occurred frequently. Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) has received much attention as one of the hot materials for water pollution control. Based on the CiteSpace 6.1.R6 visualization software, this review covers Web of science core collection database for 25 years (1997—2022) for nZVI in water remediation. The results show that: (1) In the past 25 years, the development of nZVI in water pollution treatment has gone through three periods: the initial exploration period, the slow development period and the rapid growth period, with the number of publications accounting for 0.4%, 14.5% and 85.1% of the total number of publications, respectively; (2) The connection and cooperation among countries and institutions are closer, while the cooperation among authors is looser; (3) The research hotspots of the three periods are different, and the research topics are constantly broadened. The potential research hotspots in the future are the exploration of green and low cost synthesis methods of nZVI, the study of atomic scale mechanism of nZVI to remove pollutants, and the joint treatment of pollutants in complex media with microbial technology.
-
Key words:
- bibliometrics /
- nanoscale zero-valent iron /
- CiteSpace /
- water pollution.
-

-
表 1 近25年纳米零价铁用于水体污染治理领域发文前十的国家/地区、作者、机构
Table 1. The top ten countries/regions, authors and institutions in the field of water pollution control using nanoscale zero-valent iron in the past 25 years
排名
Ranking国家/地区
Countries or regions作者
Author机构
Institution1 Peoples Republic of China(1333) Zhang Wei-xian(40) Chinese Academy of Science(175) 2 USA(337) Eljamal Osama(25) Tongji University(122) 3 Iran(182) Chen Zuliang(22) Zhejiang University (63) 4 India(134) Dong Haoran(21) Hunan University (47) 5 South Korea(119) Xu Jiang(19) Harbin lnstitute of Technology (39) 6 Taiwan(93) Zeng Guangming(18) Islamic Azad University (34) 7 Australia(88) Wang Wei(18) Carnegie Mellon University (34) 8 Czech Republic(64) Cernik Miroslav(17) Tsinghua University (33) 9 Canada(62) Lowry Gregory V(16) Shandong University (32) 10 Italy(52) Mukheriee Amitava(14) South China University Technology(32) 注:括号内数据为发文篇数. Note: The data in brackets are the number of articles published. 表 2 缓慢发展期的纳米零价铁用于水体污染治理领域的关键词突现
Table 2. Burstness of keywords in the field of application of nanoscale zero-valent iron to water pollution control in the slow development period
关键词
Keywords突现强度
Strength开始年份
Starting year结束年份
End year2005—2013年 nanoscale iron particle 3.17 2005 2007 ▲▲▲■■■■■■ chlorinated methane 3.44 2005 2006 ▲▲■■■■■■■ carbon tetrachloride 3.01 2005 2007 ▲▲▲■■■■■■ granular iron 2.73 2005 2008 ▲▲▲▲■■■■■ kinetics 2.81 2006 2007 ■▲▲■■■■■■ contaminant 2.63 2006 2009 ●▲▲▲▲■■■■ nanoscale iron 2.39 2006 2008 ●▲▲▲■■■■■ tce dechlorination 3.91 2008 2010 ●●■▲▲▲■■■ nanoiron 2.76 2008 2010 ●●●▲▲▲■■■ 注:表中三角形代表关键词的突现,正方形代表关键词未突现,圆形代表关键词未出现.
Note: In the table, triangles represent the burstness of keywords, rectangles represent the non-burstness of keywords, and ellipses represent the absence of keywords.表 3 迅速增长期的纳米零价铁用于水体污染治理领域的关键词突现
Table 3. Burstness of keywords in the field of application of nanoscale zero-valent iron to water pollution control in the rapid growth period
关键词
Keywords突现强度
Strength开始年份
Starting year结束年份
End year2014—2022年
From 2014 to 2022关键词
Keywords突现强度
Strength开始年份
Starting year结束年份
End year2014—2022年
From 2014 to 2022particle 8.63 2014 2016 ▲▲▲■■■■■■ nanoscale zero valent iron 4.91 2015 2016 ■▲▲■■■■■■ spectroscopy 6.51 2014 2017 ▲▲▲▲■■■■■ transport 4.31 2015 2016 ■▲▲■■■■■■ porous media 5.91 2014 2016 ▲▲▲■■■■■■ chromate reduction 4.01 2015 2017 ●▲▲▲■■■■■ dechlorination 5.79 2014 2016 ▲▲▲■■■■■■ environmental application 3.9 2015 2017 ●▲▲▲■■■■■ nitrate reduction 5.23 2014 2015 ▲▲■■■■■■■ nitrate removal 3.95 2017 2018 ■■■▲▲■■■■ sedimentation 5.1 2014 2016 ▲▲▲■■■■■■ microbial community 4.14 2019 2022 ●●●●●▲▲▲▲ modified Fe0 nanoparticle 4.77 2014 2016 ▲▲▲■■■■■■ magnetic biochar 4.06 2019 2020 ●●●●●▲▲■■ granular iron 4.72 2014 2017 ▲▲▲▲■■■■■ removal mechanism 3.89 2019 2022 ●●●●●▲▲▲▲ polybrominated diphenyl ether 4.61 2014 2015 ▲▲■■■■■■■ performance 6.52 2020 2022 ■■■■■■▲▲▲ metallic iron 4.6 2014 2017 ▲▲▲▲■■■■■ biochar 4.19 2020 2022 ●●●■■■▲▲▲ Fe 4.16 2014 2015 ▲▲■■■■■■■ activation 3.9 2020 2022 ■■■■■■▲▲▲ hydrogen peroxide 3.97 2014 2016 ▲▲▲■■■■■■ sulfidation 3.9 2020 2022 ■■■■■■▲▲▲ TCE dechlorination 5.21 2015 2018 ●▲▲▲▲■■■■ 表 4 近5年纳米零价铁用于水体污染治理领域的关键词突现
Table 4. Burstness of keywords in the field of application of nanoscale zero-valent iron to water pollution control in recent five years
关键词
Keywords突现强度
Strength开始年份
Starting year结束年份
End year2018—2022年
From 2018 to 2022green synthesis 2.1 2018 2019 ▲▲■■■ sulfate radical 1.76 2018 2019 ▲▲■■■ system 1.75 2018 2019 ▲▲■■■ reactivity 1.45 2018 2019 ▲▲■■■ nano iron 1.41 2018 2019 ▲▲■■■ enhanced sequestration 1.4 2018 2019 ▲▲■■■ metal ion 1.4 2018 2019 ▲▲■■■ ferrous ion 1.84 2019 2020 ●▲▲■■ sulfidation 1.45 2020 2022 ●●▲▲▲ 表 5 纳米零价铁基材料用于水体污染修复治理领域的高被引/他引文献
Table 5. High cited literature in the field of application of nanoscale zero-valent iron to water pollution control
作者
Author文献号
DOI时间
Time被引/他
引频次CF期刊
Periodical标题
TitleZHANG W X[58] 10.1023/A:1025520116015 2003 1517 Journal of Nanoparticle Research Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: An overview KHIN M M ,等[59] 10.1039/c2ee21818f 2012 887 Energy & Environmental Science A review on nanomaterials for environmental remediation ZOU Y D,等[60] 10.1021/acs.est.6b01897 2016 878 Environmental Science & Technology Environmental Remediation and Application of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron and Its Composites for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions:A Review FAN D M,等[61] 10.1021/acs.est.7b04177 2017 239 Environmental Science & Technology Sulfidation of Iron-Based Materials: A Review of Processes and Implications for Water Treatment and Remediation -
[1] RAJESHKUMAR S, LIU Y, ZHANG X Y, et al. Studies on seasonal pollution of heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and oyster from the Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake in China [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 191: 626-638. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.078 [2] 赵玉丽, 李杏放. 饮用水消毒副产物: 化学特征与毒性 [J]. 环境化学, 2011, 30(1): 20-33. ZHAO Y L, LI X. Drinking water disinfection byproducts: Chemical characterization and toxicity [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 30(1): 20-33(in Chinese).
[3] LIU X H, LU S Y, GUO W, et al. Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: A review of lakes, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 627: 1195-1208. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.271 [4] PHOON B L, ONG C C, MOHAMED SAHEED M S, et al. Conventional and emerging technologies for removal of antibiotics from wastewater [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 400: 122961. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122961 [5] CHEN G Y, YU Y, LIANG L, et al. Remediation of antibiotic wastewater by coupled photocatalytic and persulfate oxidation system: A critical review [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 408: 124461. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124461 [6] ZAMORA-LEDEZMA C, NEGRETE-BOLAGAY D, FIGUEROA F, et al. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods [J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021, 22(1957): 101504. [7] 高宝玉. 水和废水处理用复合高分子絮凝剂的研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2011, 30(1): 337-345. GAO B Y. Progress in the research of composite polymeric flocculants for water and wastewater treatment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 30(1): 337-345(in Chinese).
[8] HUBE S, ESKAFI M, HRAFNKELSDÓTTIR K F, et al. Direct membrane filtration for wastewater treatment and resource recovery: A review [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 710: 136375. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136375 [9] OBOTEY EZUGBE E, RATHILAL S. Membrane technologies in wastewater treatment: A review [J]. Membranes, 2020, 10(5): 89. doi: 10.3390/membranes10050089 [10] MUTHUSARAVANAN S, SIVARAJASEKAR N, VIVEK J S, et al. Phytoremediation of heavy metals: Mechanisms, methods and enhancements [J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2018, 16(4): 1339-1359. doi: 10.1007/s10311-018-0762-3 [11] WEI Z H, van LE Q, PENG W X, et al. A review on phytoremediation of contaminants in air, water and soil [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123658. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123658 [12] AL-MAMUN M R, KADER S, ISLAM M S, et al. Photocatalytic activity improvement and application of UV-TiO2 photocatalysis in textile wastewater treatment: A review [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2019, 7(5): 103248. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2019.103248 [13] 任学昌, 马学琴, 任晓亮, 等. TiO2/PANI/Fe3O4的低温水热法制备及其光催化活性与磁回收性能 [J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(11): 2149-2155. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.11.019 REN X C, MA X Q, REN X L, et al. Preparation of TiO2/PANI/Fe3O4 by low temperature hydrothermal method and its photocatalytic activity and magnetic recovery characteristic [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(11): 2149-2155(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.11.019
[14] 黄潇月, 王伟, 凌岚, 等. 纳米零价铁与重金属的反应: “核-壳”结构在重金属去除中的作用 [J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(6): 529-537. doi: 10.6023/A17020051 HUANG X Y, WANG W, LING L, et al. Heavy metal-nZVI reactions: The core-shell structure and applications for heavy metal treatment [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2017, 75(6): 529-537(in Chinese). doi: 10.6023/A17020051
[15] LIU A R, LIU J, HAN J H, et al. Evolution of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in water: Microscopic and spectroscopic evidence on the formation of nano- and micro-structured iron oxides [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 322: 129-135. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.12.070 [16] 刘静, 刘爱荣, 张伟贤. 纳米零价铁及其在环境介质中氧化后性质演变研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(4): 576-583. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.04.009 LIU J, LIU A R, ZHANG W X. Review on transformation of oxidized nanoscale zero valent iron in environment media [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(4): 576-583(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.04.009
[17] 刘爱荣, 李季, 王伟, 等. 纳米零价铁处理含重金属工业废水研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(4): 1278-1291. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021082203 LIU A R, LI J, WANG W, et al. Advance of heavy metal-loading industrial wastewater treatment with nanoscale zero-valent iron [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(4): 1278-1291(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021082203
[18] YAO Y H, HUANG S M, ZHOU W, et al. Highly dispersed core-shell iron nanoparticles decorating onto graphene nanosheets for superior Zn(Ⅱ) wastewater treatment [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(1): 806-815. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3631-5 [19] LI Z T, WANG L, MENG J, et al. Zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: New findings on simultaneous adsorption of Cd(Ⅱ), Pb(Ⅱ), and As(Ⅲ) in aqueous solution and soil [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 344: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.09.036 [20] JIANG Q, ZHANG Y, JIANG S M, et al. Graphene-like carbon sheet-supported nZVI for efficient atrazine oxidation degradation by persulfate activation [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 403: 126309. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126309 [21] ZHAO X, LIU W, CAI Z Q, et al. An overview of preparation and applications of stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles for soil and groundwater remediation [J]. Water Research, 2016, 100: 245-266. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.019 [22] LU H J, WANG J K, FERGUSON S, et al. Mechanism, synthesis and modification of nano zerovalent iron in water treatment [J]. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(19): 9962-9975. doi: 10.1039/C6NR00740F [23] MUKHERJEE R, KUMAR R, SINHA A, et al. A review on synthesis, characterization, and applications of nano zero valent iron (nZVI) for environmental remediation [J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2016, 46(5): 443-466. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2015.1103832 [24] WANG P, FU F G, LIU T Y. A review of the new multifunctional nano zero-valent iron composites for wastewater treatment: Emergence, preparation, optimization and mechanism [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 285: 131435. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131435 [25] LIU A R, FU J H, LIU J, et al. Copper nanostructure genesis via galvanic replacement and kirkendall growth from nanoscale zero-valent iron [J]. ACS ES& T Water, 2022, 2(8): 1353-1359. [26] TESH S J, SCOTT T B. Nano-composites for water remediation: A review [J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(35): 6056-6068. doi: 10.1002/adma.201401376 [27] HE F, LI Z J, SHI S S, et al. Dechlorination of excess trichloroethene by bimetallic and sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(15): 8627-8637. [28] LIU X, CAO Z, YUAN Z L, et al. Insight into the kinetics and mechanism of removal of aqueous chlorinated nitroaromatic antibiotic chloramphenicol by nanoscale zero-valent iron [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 334: 508-518. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.060 [29] LIU J, LIU A R, LI J, et al. Probing the performance and mechanisms of Congo red wastewater decolorization with nanoscale zero-valent iron in the continuing flow reactor [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 346: 131201. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131201 [30] KAO L C, HA Y, CHANG W J, et al. Trace key mechanistic features of the arsenite sequestration reaction with nanoscale zerovalent iron [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(40): 16538-16548. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c06159 [31] HAUSMANN J N, BELTRÁN-SUITO R, MEBS S, et al. Evolving highly active oxidic iron(III) phase from corrosion of intermetallic iron silicide to master efficient electrocatalytic water oxidation and selective oxygenation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural [J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(27): 2008823. doi: 10.1002/adma.202008823 [32] 张礼知, 张伟贤. 铁环境化学: 环境和地球化学的研究热点 [J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(6): 519-520. ZHANG, L Z, ZHANG, W X. Environmental chemistry of iron-a frontier in environmental chemistry and geochemistry [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2017, 75(6): 519-520(in Chinese).
[33] CHENG Y J, DONG H R, LU Y, et al. Toxicity of sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron to Escherichia coli in aqueous solutions [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 220: 523-530. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.159 [34] 权衡, 牛琳, 时迪, 等. 负载纳米零价铁的铁碳材料制备及其降解抗生素性能研究 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(12): 2732-2747. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2022.07.17 QUAN H, NIU L, SHI D, et al. Preparation of iron-carbon materials loaded with nano zero-valent iron and their performance of degrading antibiotics [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(12): 2732-2747(in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2022.07.17
[35] YANG S M, LIU A R, LIU J, et al. Advance of sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron: Synthesis, properties and environmental application [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(11): 1536. doi: 10.6023/A22080345 [36] YAN J C, HAN L, GAO W G, et al. Biochar supported nanoscale zerovalent iron composite used as persulfate activator for removing trichloroethylene [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 175: 269-274. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.103 [37] LIU A R, WANG W, LIU J, et al. Nanoencapsulation of arsenate with nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI): A 3D perspective [J]. Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(24): 1641-1648. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2018.12.002 [38] ZHOU Y Y, TANG L, YANG G D, et al. Phosphorus-doped ordered mesoporous carbons embedded with Pd/Fe bimetal nanoparticles for the dechlorination of 2, 4-dichlorophenol [J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016, 6(6): 1930-1939. [39] HUANG Q, GU T H, LIU A R, et al. Probing pollutant reactions at the iron surface: A case study on selenite reactions with nanoscale zero-valent iron [J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2021, 8(9): 2650-2659. doi: 10.1039/D1EN00458A [40] WANG C B, ZHANG W X. Synthesizing nanoscale iron particles for rapid and complete dechlorination of TCE and PCBs [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1997, 31: 2154-2156. [41] CHANG J, WOO H, KO M S, et al. Targeted removal of trichlorophenol in water by oleic acid-coated nanoscale palladium/zero-valent iron alginate beads [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 293: 30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.021 [42] CHEN C M. CiteSpace Ⅱ: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature [J]. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 2006, 57(3): 359-377. doi: 10.1002/asi.20317 [43] 陈悦, 陈超美, 刘则渊, 等. CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能 [J]. 科学学研究, 2015, 33(2): 242-253. doi: 10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.2015.02.009 CHEN Y, CHEN C M, LIU Z Y, et al. The methodology function of CiteSpace mapping knowledge domains [J]. Studies in Science of Science, 2015, 33(2): 242-253(in Chinese). doi: 10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.2015.02.009
[44] CHEN C M, HU Z G, LIU S B, et al. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: A scientometric analysis in CiteSpace [J]. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 2012, 12(5): 593-608. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2012.674507 [45] ELLIOTT D W, ZHANG W X. Field assessment of nanoscale bimetallic particles for groundwater treatment [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2001, 35(24): 4922-4926. [46] LI X Q, ZHANG W X. Iron nanoparticles: The core-shell structure and unique properties for Ni(Ⅱ) sequestration [J]. Langmuir:the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids, 2006, 22(10): 4638-4642. doi: 10.1021/la060057k [47] BOPARAI H K, JOSEPH M, O’CARROLL D M. Kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ion removal by adsorption onto nano zerovalent iron particles [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(1): 458-465. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.029 [48] LING L, HUANG X Y, ZHANG W X. Enrichment of precious metals from wastewater with core–shell nanoparticles of iron [J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(17): 1705703. doi: 10.1002/adma.201705703 [49] LIU Y Z, WU T, WHITE J C, et al. A new strategy using nanoscale zero-valent iron to simultaneously promote remediation and safe crop production in contaminated soil [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2021, 16(2): 197-205. doi: 10.1038/s41565-020-00803-1 [50] WEI K, LI H, GU H Y, et al. Strained zero-valent iron for highly efficient heavy metal removal [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(26): 2200498. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202200498 [51] DONG H R, DENG J M, XIE Y K, et al. Stabilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar for Cr(Ⅵ) removal from aqueous solution [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 332: 79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.03.002 [52] NGUYEN N H A, ŠPÁNEK R, KASALICKÃ V, et al. Different effects of nano-scale and micro-scale zero-valent iron particles on planktonic microorganisms from natural reservoir water [J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2018, 5(5): 1117-1129. doi: 10.1039/C7EN01120B [53] NASIRI J, MOTAMEDI E, NAGHAVI M R, et al. Removal of crystal violet from water using β-cyclodextrin functionalized biogenic zero-valent iron nanoadsorbents synthesized via aqueous root extracts of Ferula persica [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 367: 325-338. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.079 [54] KECIĆ V, KERKEZ Đ, PRICA M, et al. Optimization of azo printing dye removal with oak leaves-nZVI/H2O2 system using statistically designed experiment [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 202: 65-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.117 [55] ZHANG N Q, CHEN J Y, FANG Z Q, et al. Ceria accelerated nanoscale zerovalent iron assisted heterogenous Fenton oxidation of tetracycline [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 369: 588-599. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.112 [56] ZHANG D J, SHEN J Y, SHI H F, et al. Substantially enhanced anaerobic reduction of nitrobenzene by biochar stabilized sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron: Process and mechanisms [J]. Environment International, 2019, 131: 105020. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105020 [57] LING L, ZHANG W X. Enrichment and encapsulation of uranium with iron nanoparticle [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(8): 2788-2791. doi: 10.1021/ja510488r [58] ZHANG W X. Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: An overview [J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2003, 5(3): 323-332. [59] KHIN M M, NAIR A S, BABU V J, et al. A review on nanomaterials for environmental remediation [J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(8): 8075-8109. [60] ZOU Y D, WANG X X, KHAN A, et al. Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: A review [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(14): 7290-7304. [61] FAN D M, LAN Y, TRATNYEK P G, et al. Sulfidation of iron-based materials: A review of processes and implications for water treatment and remediation [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(22): 13070-13085. -



 下载:
下载: