-
硫元素参与构成的官能团包括硫醚、亚砜、砜、磺酰胺、氨基磺酸等,多数具备丰富的化学和生物学意义,在医药和农药设计开发中被广泛应用. 医药中硫的使用频率排名第五,25%的小分子医药存在含硫官能团[1],青霉素、头孢等抗生素也均含有硫元素. 同时,含硫农药在保证农作物的产量和质量方面也至关重要,英国《农药手册》中记载的
1630 多种除草剂、杀虫剂等农药中,超过30%至少含有一个硫原子[2]. 数千种含硫有机物及其转化衍生物极易通过水循环广泛存在于水生系统中,成为痕量水平微污染物(ng·L−1—μg·L−1级),并长期影响人体健康和生态系统安全,形成极大潜在风险. 目前已有研究证明世界各地的地表水与地下水中普遍检测到含硫有机微污染物(sulfur-containing organic micropollutants,SOM)及其代谢衍生物[3 − 4],且大多数代谢衍生物的毒性及检出浓度近似甚至高于其母体物质[5],如砜和亚砜等代谢衍生产物[6]. 因此,水环境中含硫有机微污染物的有效削减及风险防控具有重要意义及现实紧迫性.本文总结归纳了水环境中SOM种类及理化性质,全面综述了SOM在水环境中的风险及污染分布情况,并深入分析了典型SOM去除技术及机理,以期为SOM环境风险的防范及控制提供指导.
-
SOM往往分为两大类——含硫农药和含硫医药,其理化性质主要由官能团的性质决定. 在医药中根据效价官能团的类别,可分为磺胺类、砜与亚砜类、硫醚噻唑类、青霉素头孢类等,这些含硫医药通过自身的碳—硫、氧—硫和氮—硫键的特殊性质和作用机制表现出较大的活性[7]. 硫醚噻唑是各种已批准的医药的基本基团,硫醚在体内可迅速代谢为砜和亚砜来激活化合物,噻唑通常与酶结合产生反应,常见噻唑类医药如法莫替丁[8]. 砜是最常用的医药支架,引入亚砜基团可获得良好的药物代谢动力学特性,提高溶解度及化学稳定性. 磺胺类医药是发展中国家广泛采用的抗菌医药,应用于细菌、真菌、寄生虫感染,可以提高代谢稳定性,降低毒性,并改善跨膜扩散[9].
含硫农药主要包括磺酰脲类、含硫杂环类、砜与亚砜类、磺胺磺酰胺类、含硫有机磷类等,引入含硫基团可以增强农药的选择性,降低对哺乳动物毒性[10],还可通过影响结合位点活性等参数显著改变生物活性,如硫与目标受体或酶结合,可使生物活性分子运输到目标位点来促进代谢活性[11]. 磺酰脲类除草剂是世界上主流的除草剂品种,效率高且选择性强,在环境中易分解,对哺乳动物较安全[12]. 许多现代杀虫剂如噻虫嗪、噻虫胺也都含有硫原子,其在环境降解过程中提供反应位点,包括直接光解和光催化氧化等[13]. 本文结合当前污染物生态毒性风险评估的研究[14 − 15],根据不同的含硫基团对污染物进行分类归纳,总结出环境风险较高的常见典型12种含硫医药及10种含硫农药,并汇总其理化性质如表1所示.
-
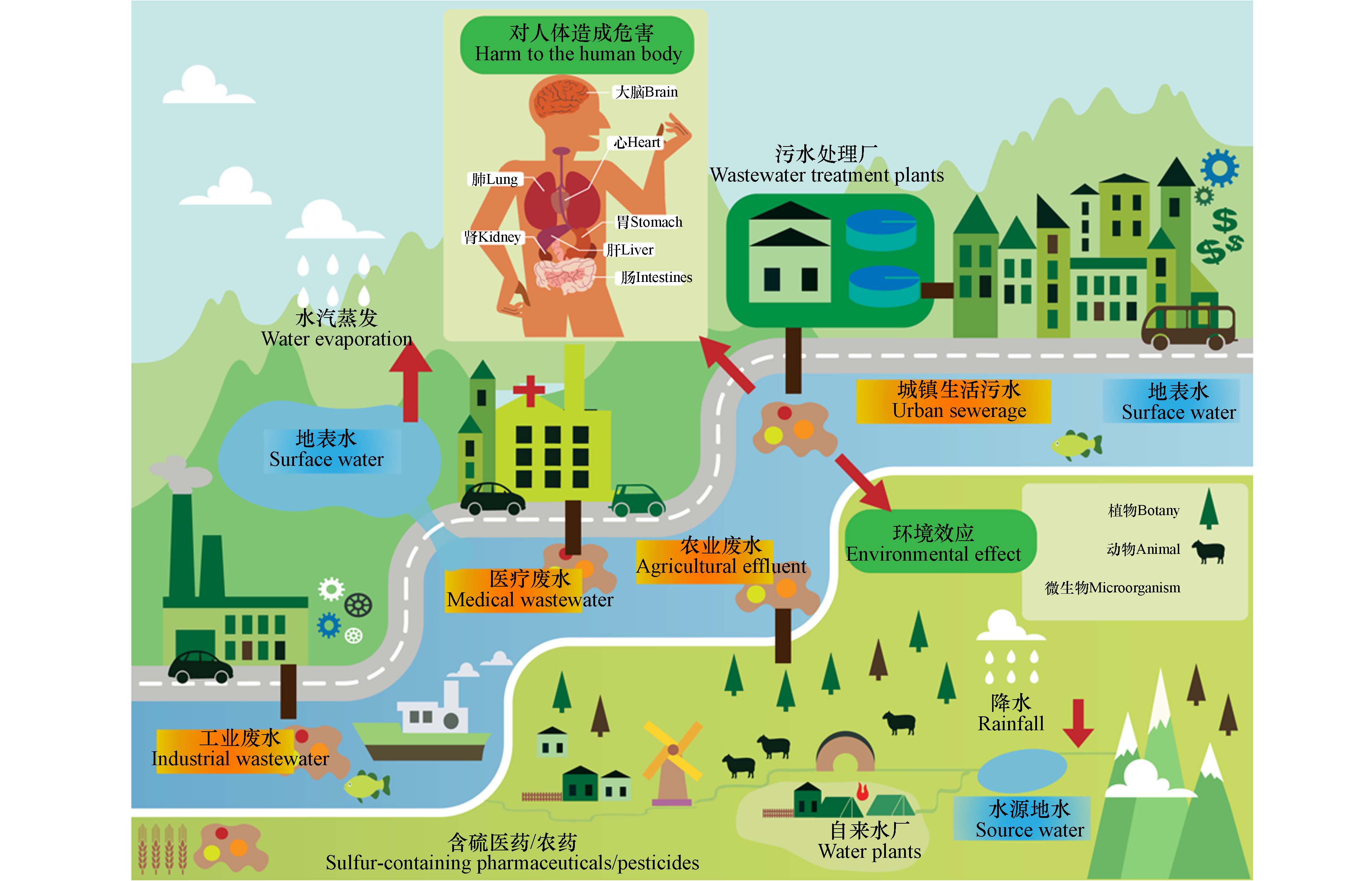
水环境中的SOM往往通过城镇生活污水、医疗废水、制药工业废水、农业废水以及含过量兽药的畜禽养殖废水排放进入湖泊、河流和海洋中(图1). 人类和养殖业禽畜的含硫医药使用量大,且被人体或动物摄入的青霉素头孢类及磺胺类医药并不能完全被吸收利用,部分未被利用的物质随着尿液和粪便排泄至污水系统,而以活性污泥法为主体的城镇污水处理厂并不能完全去除城镇生活污水中的含硫医药如奥美拉唑等,因此尾水中残留的含硫医药被排放至受纳水体,同时医疗和制药工业废水排放也会使得生产中的部分含硫医药进入水环境[16]. 此外,人类为了提高农产品产量,长期向农作物中施用噻虫嗪、氟虫腈等高残留、较难降解的含硫农药,然而通常只有少量能够附着或施用于农作物上,其余绝大部分残留在土壤和飘浮在大气中,然后通过降雨径流进入地表水,使得下游水环境中存在农药残余[17]. 总之,含硫医药由于在人和动物体内的代谢较低,可能会以原始形式存在于水生环境中或通过自然光降解及微生物作用转化为其他代谢衍生物;而含硫农药结构稳定且半衰期较长,其能通过污水排放和径流等多种方式迁移,且易通过食物链的传递产生生物放大效应.
与污水中的常规污染物相比,SOM在环境中的实际赋存浓度不高,但含硫医药和农药在日常生活中使用十分频繁,将长期存在于水环境中,还会与其他污染物结合产生复杂的复合毒性效应,形成的环境风险较大. 目前已有毒理学研究表明SOM普遍存在较强的生物毒性,能够抑制微生物生长、影响植物生长发育、影响动物人类健康. 例如磺胺嘧啶会抑制微生物活性并降低土壤还原细菌对Fe3+的还原能力;大部分含硫除草剂可以抑制叶绿体和酶活性;噻虫嗪等含硫农药对蜜蜂等传粉动物的高毒性,影响飞行能力破坏神经系统[18]. 相关研究也证实了低浓度磺胺类医药对斑马鱼胚胎具有毒性作用[19],也有一些水生物种(如藻类、浮游生物、水生植物以及鱼类)对水生环境中存在的阿莫西林等抗生素极度敏感[20-21].
因此,为保障水质安全,部分发达国家已将一些SOM纳入控制名单且设定浓度限值,如澳大利亚在《澳大利亚水回用标准(2008)》中首次对污水厂二级出水设置了含硫药物排放阈值,其中就包括磺胺甲恶唑不得超过35 μg·L−1[22];欧盟第93/67/EEC号指令根据含硫污染物的环境风险程度将磺胺类医药归类为有害化合物,并被《环境分类药品(2009)》归类为剧毒化合物[23]. 而我国也对部分危害性较高的含硫农药采取了限制排放措施,如《杂环类农药工业水污染物排放标准(GB
21523 — 2008)》规定了原药生产企业的氟虫腈排放不得超过0.01 mg·L−1. 此外近年来我国已陆续出台多个关于含硫医药的源头控制政策,如2017年农业部发布《全国遏制动物源细菌耐药行动计划》,明确推进磺胺类兽用抗菌药物减量化使用;2018年农业农村部组织制定了《兽用抗菌药使用减量化行动试点工作方案》,确定了各地磺胺类兽用抗菌药使用减量化行动试点养殖场数量. -
为进一步探究水环境中SOM的污染现状,本研究对已报道的研究文献数据进行提取,汇总得出我国地表水中典型SOM的检出率及检出浓度(图2),结果表明典型的12种含硫医药和10种含硫农药在我国自然水体中均存在高频检出情况.
含硫医药中磺胺甲恶唑、磺胺嘧啶、磺胺二甲嘧啶、磺胺噻唑、西咪替丁、阿莫西林、头孢噻肟以及含硫农药中噻虫嗪、噻虫胺、特丁净、三唑磷在部分地区地表水中检出率可达100%;而乙硫磷普遍检出率较低,可能与近年我国对此类农药的严格管控存在一定关系. 各个SOM检出率变化较大,由此可见中国各地污染情况参差不齐,需要对各区域水体进行全面检测筛查分析后才能因地制宜对当地环境风险最大的SOM展开针对性治理.
我国地表水中SOM的浓度水平均在ng·L−1级别,含硫医药浓度范围为0—300 ng·L−1,含硫农药浓度范围为0—150 ng·L−1. 含硫医药的检出浓度分布较分散,如磺胺嘧啶检出浓度最高为287 ng·L−1,而其最小检出浓度仅有0.004 ng·L−1,这再次证明含硫医药性质并不稳定,受采样时间、空间位置及环境因素影响较大,故检出浓度差别较大. 具体而言,磺胺嘧啶、磺胺二甲嘧啶、磺胺甲恶唑等磺胺类医药最高检出浓度较高(均超过250 ng·L−1);阿莫西林、头孢噻肟等青霉素头孢类含硫抗生素平均检出浓度较高(约为15 ng·L−1);而奥美拉唑和法莫替丁等常用胃药检出浓度较低. 此外,由于含硫农药化学性质较稳定,相应的检出浓度分布也较均匀,氟虫腈、特丁净等砜与亚砜类农药浓度水平最高(60—100 ng·L−1),甲磺隆、苄嘧磺隆等磺酰脲类农药(12—50 ng·L−1)以及噻虫胺、噻虫嗪等日常使用较多的含硫杂环类农药浓度(9—26 ng·L−1)也普遍较高. 目前已有研究指出地表水中的含硫医药背景值浓度随地区存在差异,如欧洲河流中的含硫医药通常在100 ng·L−1以下,而美国则高一个数量级,这可能是受到不同国家地区的生活、用药习惯和降雨量的影响[24];噻虫嗪、氟虫腈等含硫农药在世界范围内检出率普遍较高,在欧美国家检出浓度约10 ng·L−1,并有研究表明其在中国和欧洲潜在风险值均较高[25 − 26],因此亟需开发SOM控制技术.
-
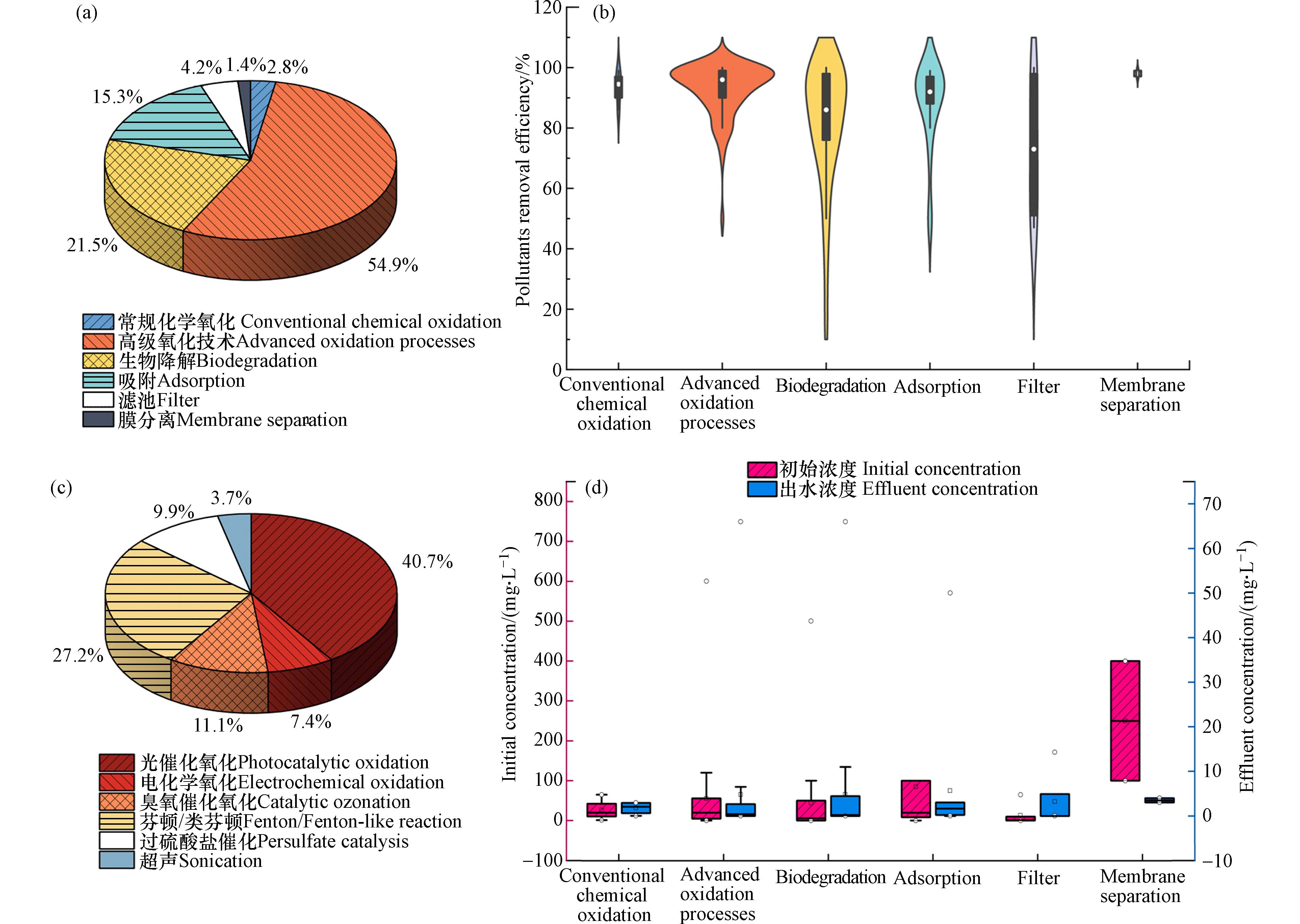
本研究采用文献计量学方法分析SOM的去除技术及效果,即在Web of Science Core Collection数据库中以“含硫有机微污染物”、“水”“去除”为主题进行检索,共获得时间跨度为1980—2022年的
6382 篇文章. 检索结果表明从首次报道SOM至今,相关研究文章数量呈指数增长,2021年文章数量甚至高达1027 篇,且在此期间共有112个国家或组织发表过相关文章,中国以2639 篇的发文数量遥遥领先,其次是美国,共发表708篇文章. 从关键词热图中也可以看出水环境中SOM的相关研究越来越得到重视,尤其是含硫医药研究需求非常迫切,具体而言“磺胺甲恶唑”、“阿莫西林”、“高级氧化”、“生物降解”、“吸附”、“动力学”、“机理分析”均是当前研究的热点话题(图3).进一步分析检索结果中与SOM去除技术高度相关的144篇研究论文,可将主流技术分为6个类别(图4),相关报道频率由高至低依次为高级氧化技术(54.9%)> 生物降解(21.5%)> 吸附(15.3%)>滤池(4.2%)>常规化学氧化(2.8%)> 膜分离(1.4%),大多数观察值分布在高级氧化技术、生物降解和吸附法中,说明这3类技术在现实中应用较多,SOM去除技术仍以高级氧化技术为主,生物降解及吸附法也占有一定比重. 6类主流技术基本上都可达到80%的污染物去除率,而高级氧化技术的稳定性明显高于生物降解及吸附法. 不同技术的去除率存在显著差异,处理技术的污染物去除效果分别为膜分离(98.0%)> 常规化学氧化(93.5%)> 高级氧化技术(92.8%)> 吸附(87.9%)> 生物降解(81.5%)> 滤池(73.7%),其中生物降解技术对SOM的去除率总体上较低,很大程度上是由于SOM自身对微生物存在较大毒性,但值得肯定的是生物技术可以极大地促进中间代谢产物的降解[27]. 由于高级氧化技术占比大且种类多,故根据活化方法将其分为光催化氧化、芬顿/类芬顿体系、臭氧催化氧化、过硫酸盐催化、电化学氧化和超声处理,其中光催化氧化技术占比最大,达到40.7%,其次是芬顿体系占比27.2%,使用超声活化的研究最低,为3.7%. 当前SOM去除技术研究中涉及的污染物初始浓度差异大,因此相应去除技术的适用浓度差别也较大,各类技术的适用浓度从高到低分别是膜分离(250.0 mg·L−1)> 吸附(84.8 mg·L−1)> 高级氧化技术(55.2 mg·L−1)> 生物降解(44.2 mg·L−1)> 常规化学氧化(26.5 mg·L−1)> 生物过滤(12.9 mg·L−1),而最终出水浓度基本上均低于5 mg·L−1. 由此可见膜分离在高浓度SOM的去除中具有显著优势,而滤池、常规化学氧化倾向于处理低浓度SOM废水. 从整体来看,研究中SOM的平均浓度仍然很高,这意味着大部分技术开发方面的研究都是采用污染物初始浓度较高的实验条件,并没有切实考虑污染物在自然水体中的实际浓度.
对于每种典型SOM,其去除效果也存在显著差异(图5),通常含硫农药(平均去除率78.5%)比含硫医药(92.1%)更难被去除,这也证明含硫农药的化学性质往往更加稳定. 污染物所含官能团与结构不同也是造成去除效果不同的主要原因,磺胺类医药与青霉素头孢相比更易被去除,而以奥美拉唑(78.0%)为代表的含有砜与亚砜基团的污染物则难以去除. 含硫农药中含硫有机磷类的三唑磷平均去除率最高,为96.8%,而磺酰脲类农药苄嘧磺隆平均去除率仅有72.0%,最低的是唑嘧磺草胺,为50.0%,这可能与该污染物相关研究匮乏有关.
-
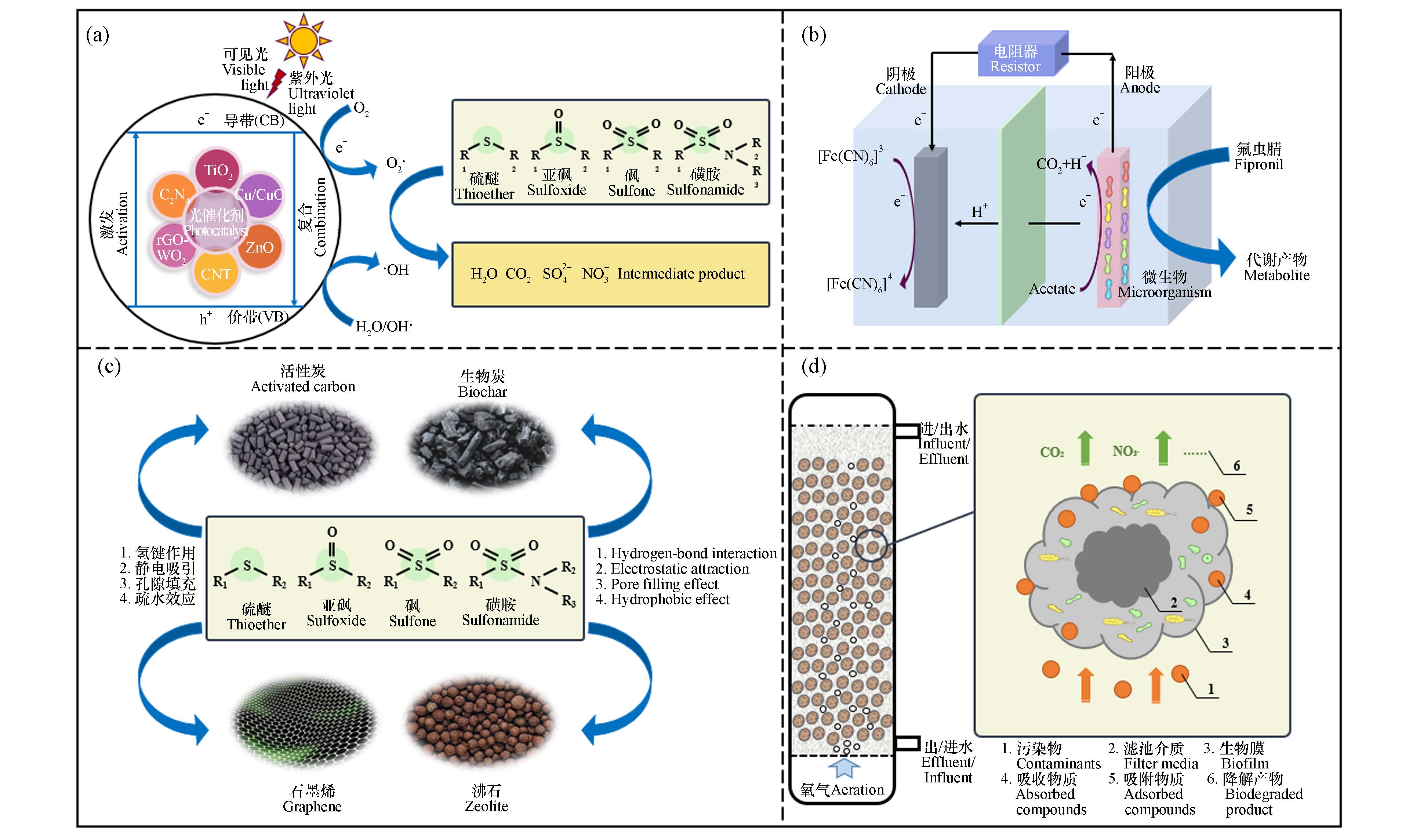
本节深入探究6类SOM主流处理技术的特点及潜在机理. 高级氧化技术是去除SOM的重要手段,其特点是反应速率快、二次污染小,即在活化剂存在条件下使用氧化剂作为前体生成自由基(如·OH),因其对有机污染物具有极强的氧化作用而达到去除难降解污染物的目的. 以研究占比最多的光催化氧化技术为例,往往采用二氧化钛[28]、氧化锌[29]、氧化铜[30]、氧化钨[31]、氮化碳[32]、碳纳米管[33]、石墨烯[34]等半导体作为光催化剂,其基本原理是基于光从半导体带的价带(VB)激发电子(e–)到其导带(CB)[35]的能力,从而在VB中产生相等数量的正电荷空穴(h),随后被e–和h还原和氧化,产生了极高的氧化还原势将SOM降解为CO2和H2O等物质,使用光催化降解污染物的过程如图6a所示.
生物降解是目前污水处理厂应用较广泛的技术,对SOM的去除至关重要,具有运行成本低、反应条件温和等优点. 当前的研究主要是探究膜生物反应器法(MBR)[36]、微生物燃料电池(MFC)[37]、厌氧消化[38]等工艺的去除效果,也有部分研究具体针对特异性去除SOM的生物酶[39]、降解菌种[40]、细菌群落[41]进行筛选驯化. 从MBR中分离出的Microbacterium sp.的BR1菌株能够利用SOM作为唯一碳源,完全降解磺胺甲恶唑,该机制普遍认为是由基因Sad A和Sad B引起的异羟基化导致污染物的磺胺基团降解,主要代谢产物为3-氨基-5-甲基异恶唑[42],降解磺胺类污染物的细菌种群主要为变形菌门和拟杆菌门,而芽孢杆菌属和金细菌属是主要属[43]. Zhang等指出降解的MFC系统功能微生物包括电细菌(Sphaerochaeta和Pseudomonas)和有机化合物降解菌(Azospirillum,Azoarcus和Chryseobacterium),其中电细菌负责通过乙酸盐的代谢提供电子和发电,以提高氟虫腈降解相关细菌的共代谢反应效率,并证实假单胞菌是MFC阳极生物膜中占主导地位的关键菌种[37],如图6b.
吸附法主要原理是污染物结构中的含O、N、S官能团通过氢键作用、静电吸引、孔隙填充、疏水效应、
$ \mathrm{\pi }-\mathrm{\pi } $ 作用等被吸附到吸附剂表面以便SOM从水体中分离(图6c),其效果主要取决于吸附剂表面性质、表面积及孔隙率[44]. 活性炭[45]、生物炭[46]、石墨烯[47]、改性沸石[48]、纳米颗粒[49]等多孔材料均被证实是SOM的高效吸附剂,也有研究表明聚多巴胺/锆(Ⅳ)碘酸盐等复合凝胶材料130 min内也可去除99.12%的氨苄西林,其吸附过程具有吸热性质且由孔隙扩散主导,符合Langmuir等温线和伪二阶动力学模型[50].滤池工艺是通过滤料、微生物/植物之间的联合作用去除污染物,主要涉及过滤、吸附、吸收和微生物降解等过程(图6d),目前常用的滤池工艺包括曝气生物滤池、人工湿地等,该工艺污染物去除效率受多种因素影响,主要包括水深、水力负荷率、水力停留时间、生物物种及温度、pH、光照等环境条件. Wu等[51]利用地下流人工湿地去除98%的三唑磷,并表明三唑磷的高效去除与底物的高脲酶活性有关,这归因于厚壁菌门中杆菌科的相对丰度较高;Kai等[52]应用含有泥炭层的活性土壤过滤器去除雨水中的特丁净,证明生物降解是该过滤系统关键环节,而过滤材料的吸附是成功去除污染物的先决条件.
根据SOM化学结构的特性不同,还可以采用不同的常规化学氧化方法进行接触反应从而降解污染物,但是往往受pH、温度及杂质离子的影响较大,且易产生有毒副产物,如苄嘧磺隆的氯化遵循二阶动力学,随着pH增大,反应副产物三氯甲烷增加[53]. 纳滤、反渗透等膜分离技术也可高效去除SOM,并被广泛应用到废水深度处理及回用工程中,大多数纳滤膜由羧基或磺酸等表面官能团的解离带电,通过离子和膜表面之间的静电相互作用选择性地传递或排斥进水中的离子,且滤膜孔径及性质可以通过表面涂层、表面嫁接等修饰途径来调节,如Hajar Azad等人用CeO2纳米颗粒合成了一种交联聚(乙烯基丁基)-聚丙烯腈吸附膜可以去除99.84%的头孢噻肟[54].
此外具有不同含硫官能团的SOM降解路径也存在区别,磺胺类一般对酸水解敏感,在碱性条件下比较稳定,芳香磺胺在254 nm光照条件下会降解生成游离胺;磺酰脲类化合物在酸性条件下易水解,产生磺胺、二氧化碳和游离胺;硫醚通过酸催化水解产生相应的硫醇,也易被氧化成亚砜和砜,经过强紫外光的照射易产生重排异构体. 总之在SOM去除技术中,普通吸附的性能通常不可靠,且饱和吸附剂的再生成本高、技术复杂,而高级氧化技术可以有效地降解含硫化合物,但往往受到实际水体成分干扰产生毒性更强的副产物,其副产物经过生物降解则可极大程度降低毒性.
-
水体中广泛存在的含硫有机微污染物主要来源是生产生活中大量使用的难降解含硫医药及农药,其生物毒性易造成较大的环境风险. 当前我国SOM的污染情况较为严重,含硫医药检出浓度可达300 ng·L−1,含硫农药也达到150 ng·L−1,远高于欧美发达国家. 为此,本文采用文献计量学方法总结归纳了高级氧化技术、生物降解、吸附、滤池、常规化学氧化、膜分离等6类主流SOM去除技术及机理,其中高级氧化技术去除效果最佳,生物降解法应用较为广泛.
目前SOM相关研究方兴未艾,笔者认为未来应在以下五个方面开展相关工作:
(1)优化污染物高精确度检测手段:优化基于高分辨率质谱的SOM靶向/非靶向筛查和准定量技术,提高检测技术的精确度及检测效率,提高SOM快速检测能力.
(2)完善复合污染物风险评估方法:SOM的种类逐年增加,应考虑多种微污染物的联合效应,加快建立SOM复合污染物的综合性环境风险指标,为制定SOM环境基准值提供科学证据.
(3)开发高选择性的污染控制技术:针对含有硫醚、亚砜、砜、磺酰胺、磺胺等效价官能团的SOM开发高效低耗的去除技术,实现水环境中SOM的精准管控.
(4)建立效价官能团-环境效应数据库:探究官能团结构对环境效应的影响,建立数据库预测SOM转化路径及环境响应机制,为新型含硫药物的低风险开发及后续产物污染控制提供理论指导.
(5)加强区域水循环体系协同治理:全面普查城市水循环系统(地表水、污水厂、自来水厂)SOM赋存特征及迁移归趋,推动多介质SOM高效削减及风险防控,实现区域再生水安全再利用.
水环境中含硫有机微污染物:污染现状、去除技术及机理分析
Sulfur-containing organic micropollutants in water environment: Pollution status, removal techniques and mechanism analysis
-
摘要: 含硫有机微污染物在国内外自然水体中高频检出,其主要包含生产生活中广泛应用的含硫医药和农药,具有难降解性及生物毒性,已形成较高环境风险. 本文系统总结了含硫有机微污染物的种类及典型污染物理化性质,全面综述了其在水环境中的来源、环境风险及污染现状,采用文献计量学方法重点分析了含硫有机微污染物的去除技术及机理,并从优化污染物高精确度检测手段、完善复合污染物风险评估方法、开发高选择性的污染控制技术、建立效价官能团-环境效应数据库、加强区域水循环体系协同治理5个方面展望了未来研究的热点趋势,以期为水环境中含硫有机微污染物的有效削减及风险防控提供参考.Abstract: Sulfur-containing organic micropollutants are frequently detected in natural water at home and abroad, mainly including sulfur-containing pharmaceuticals and pesticides widely used in production and life, which are difficult to degrade and biotoxic, and pose a high environmental risk. In this paper, the types and physicochemical properties of sulfur-containing organic micropollutants are systematically summarized, and their sources, environmental risks and pollution status in water environment are comprehensively reviewed. The removal technology and mechanism of sulfur-containing organic micropollutants are emphatically analyzed by bibliometric methods. And the hot trends of future research are prospected from five aspects: optimizing the high precision detection method of pollutants, improving the risk assessment method of complex pollutants, developing the highly selective pollution control technology, establishing the database of characteristic functional groups - environmental effects, and strengthening the cooperative governance of regional water cycle system, in order to provide reference for the effective reduction and risk control of sulfur-containing organic micropollutants in water environment.
-

-
图 2 地表水中含硫有机微污染物污染现状(a)含硫医药的检出率;(b)含硫农药的检出率;(c)含硫医药浓度分布;(d)含硫农药浓度分布
Figure 2. Pollution status of sulfur-containing organic micropollutants in surface water: (a) detection rate of sulfur-containing pharmaceuticals; (b) detection rate of sulfur-containing pesticides; (c) concentration distribution of sulfur-containing pharmaceuticals; (d) concentration distribution of sulfur-containing pesticides
表 1 典型含硫有机微污染物的种类及理化性质
Table 1. Types and physicochemical properties of typical sulfur-containing organic micropollutants
种类
Type含硫有机
微污染物
SOMCAS编号
CAS
number分子式
Molecular
formula相对分子
质量/
(g·mol−1)
Molecular
weight含硫官能团类别
Category of
sulfur-containing
functional
groups用途
Application分子结构
Molecular structure医药 磺胺甲恶唑 723-46-6 C10H11N3O3S 253 磺胺类 抗菌抗感染 
医药 磺胺嘧啶 68-35-9 C10H10N4O2S 250 磺胺类 抗菌抗感染 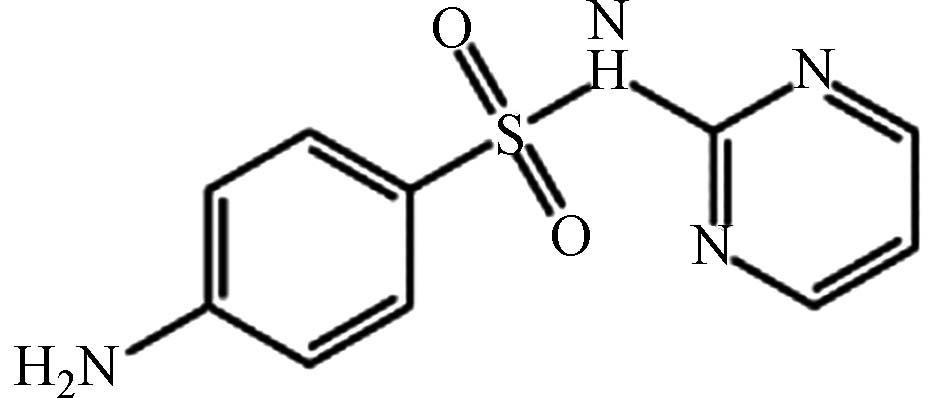
医药 磺胺二甲
嘧啶57-68-1 C12H14N4O2S 278 磺胺类 抗菌抗感染 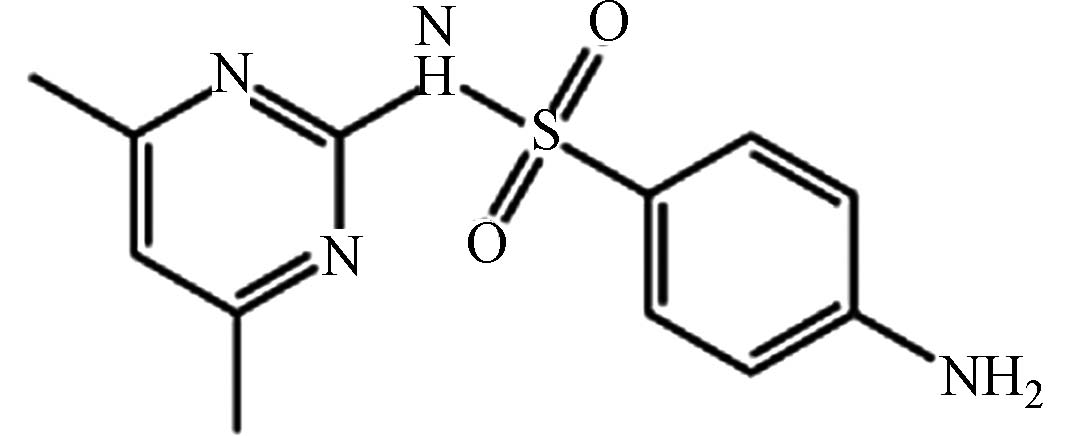
医药 磺胺噻唑 72-14-0 C9H9N3O2S2 255 磺胺类 抗菌抗感染 
医药 奥美拉唑 73590 -58-6C17H19N3O3S 345 砜与亚砜类 抑制胃酸分泌 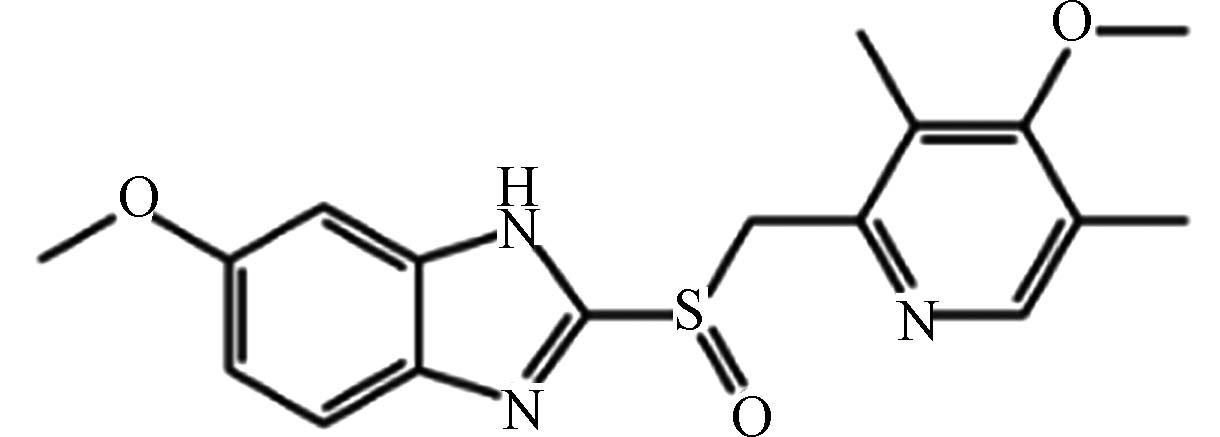
医药 替硝唑 19387 -91-8C8H13N3O4S 247 砜与亚砜类 抗菌抗感染 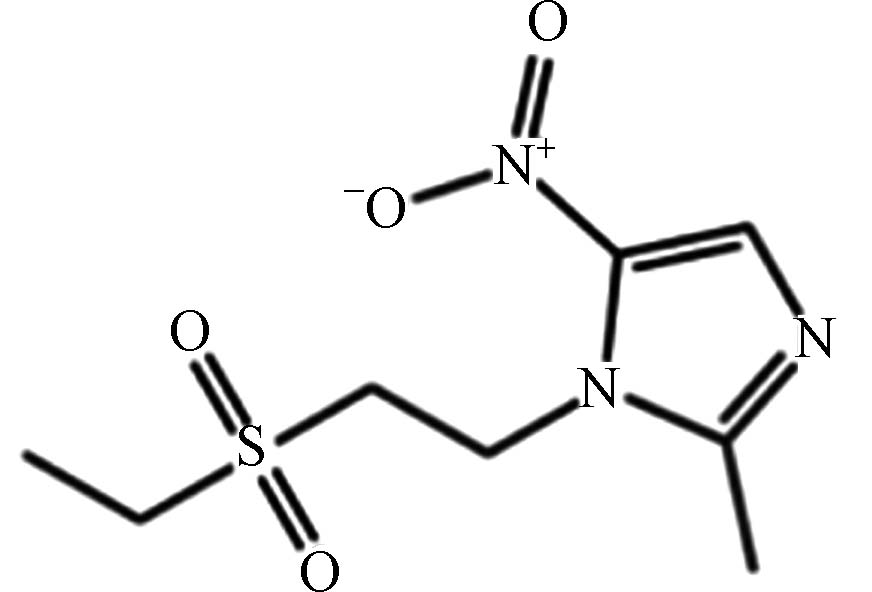
医药 西咪替丁 51481 -61-9C10H16N6S 252 硫醚噻唑类 抑制胃酸分泌 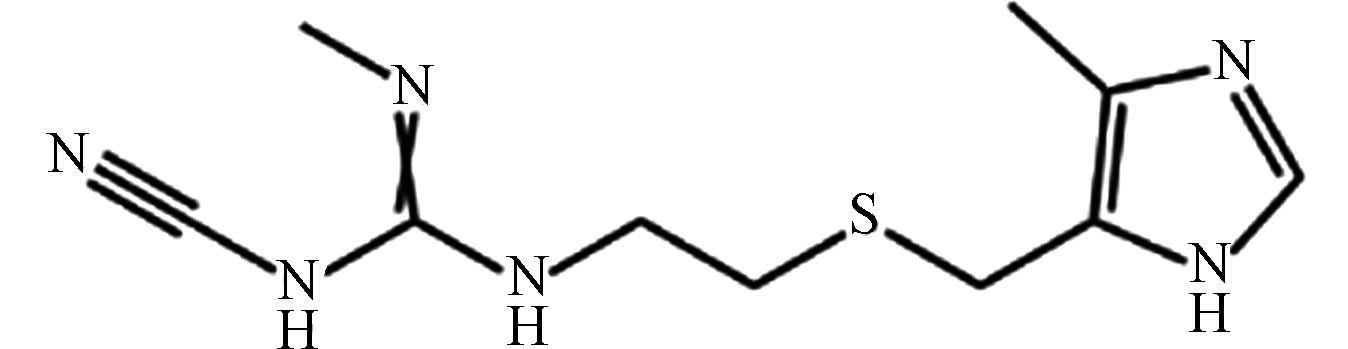
医药 法莫替丁 76824 -35-6C8H15N7O2S3 337 硫醚噻唑类 抑制胃酸分泌 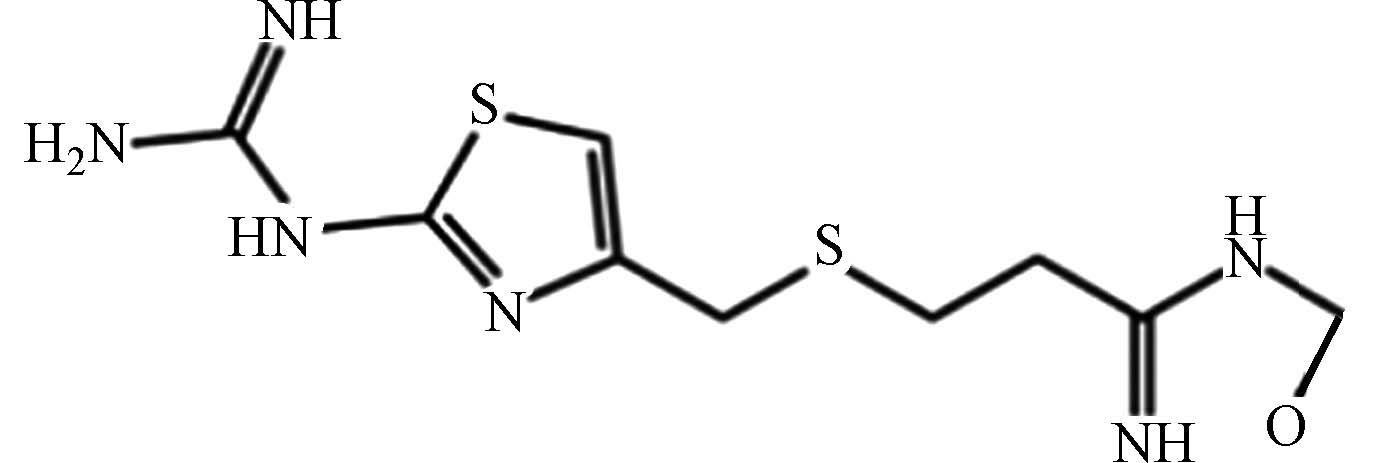
医药 阿莫西林 26787 -78-0C16H19N3O5S 365 青霉素头孢类 抗菌抗感染 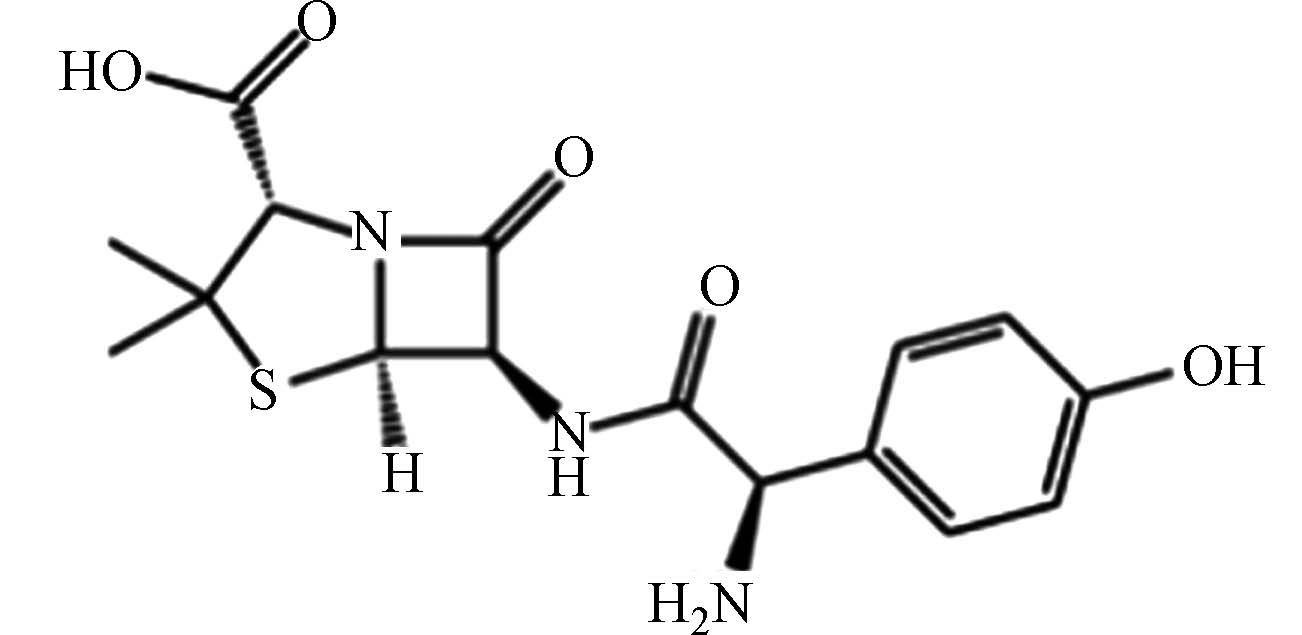
医药 氨苄西林 69-53-4 C16H19N3O4S 349 青霉素头孢类 抗菌抗感染 
医药 头孢噻肟 63527 -52-6C16H17N5O7S2 455 青霉素头孢类 抗菌抗感染 
医药 头孢氨苄 15686 -71-2C16H17N3O4S 347 青霉素头孢类 抗菌抗感染 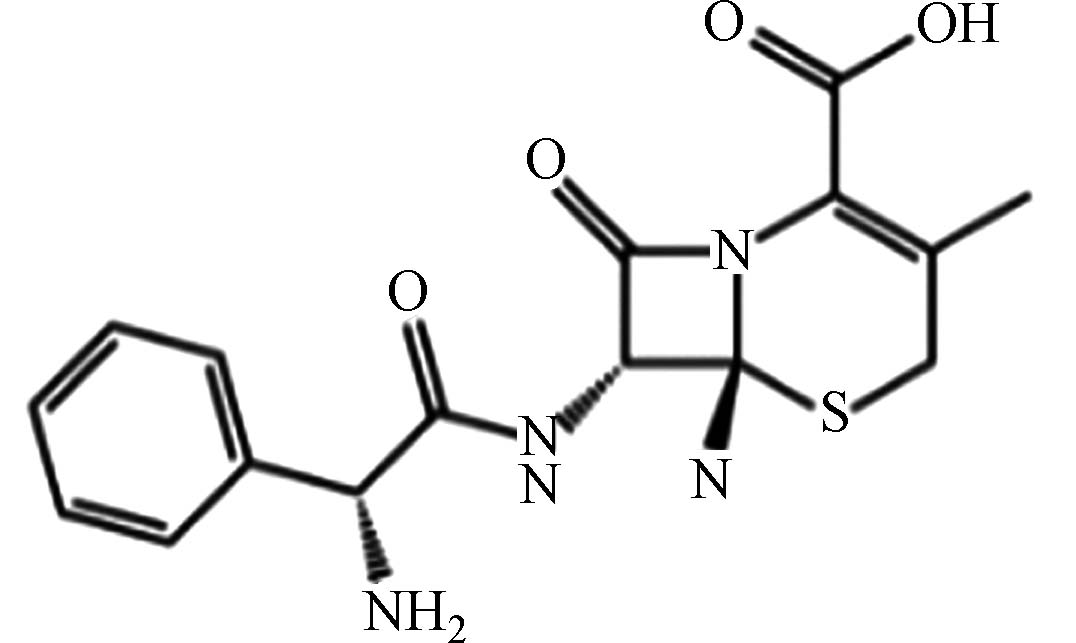
农药 苄嘧磺隆 83055 -99-6C16H18N4O7S 410 磺酰脲类 稻麦田除草剂 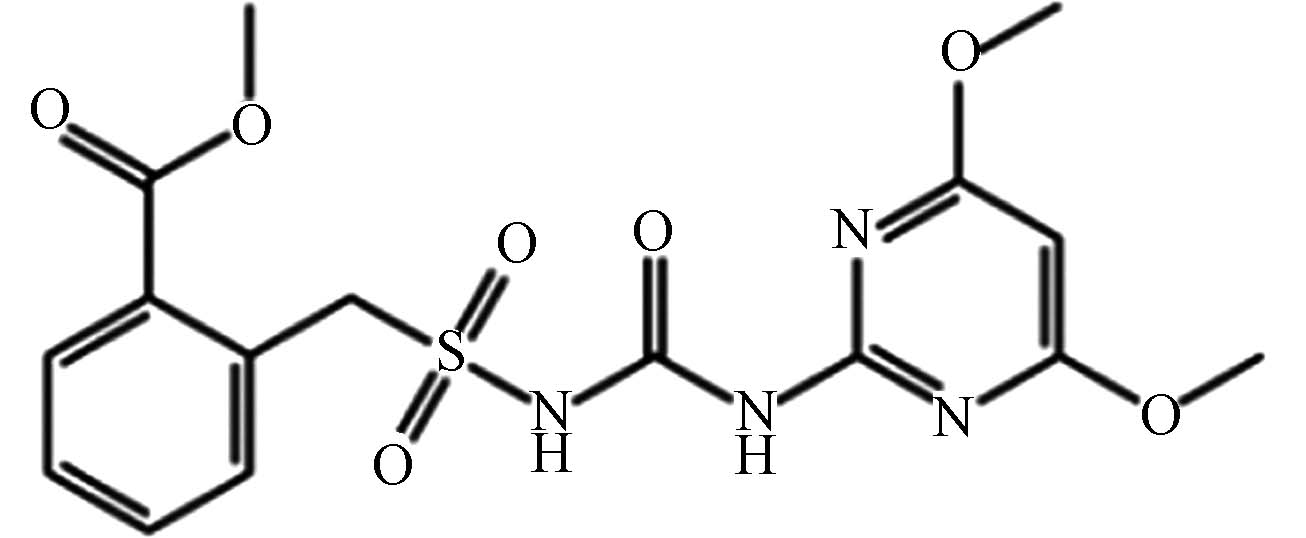
农药 甲磺隆 74223 -64-6C14H15N5O6S 381 磺酰脲类 稻麦田除草剂 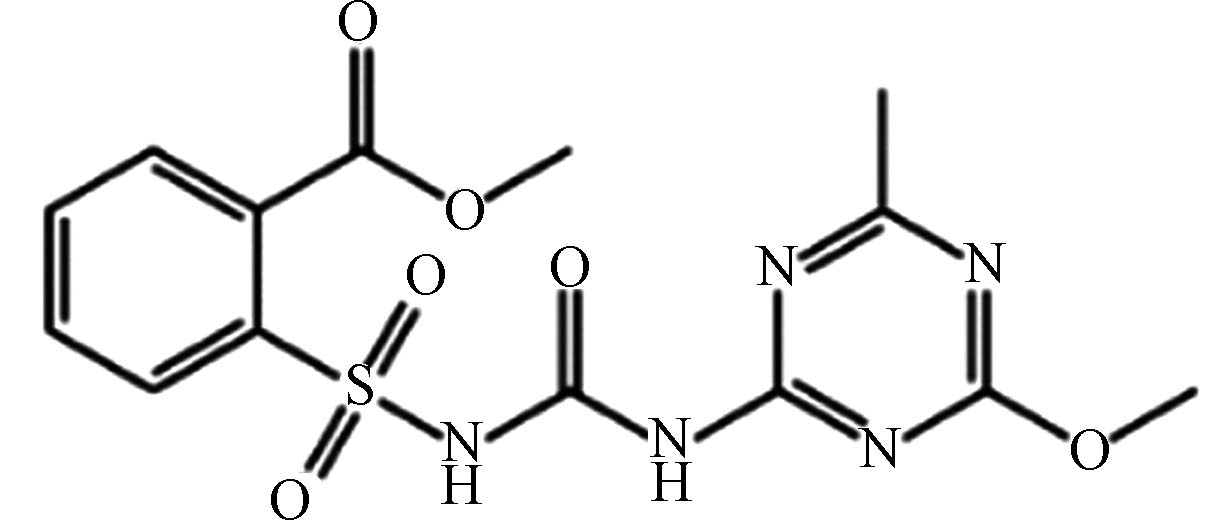
农药 噻虫嗪 153719 -23-4C8H10ClN5O3S 292 含硫杂环类 新烟碱杀虫剂 
农药 噻虫胺 210880 -92-5C6H8ClN5O2S 250 含硫杂环类 新烟碱杀虫剂 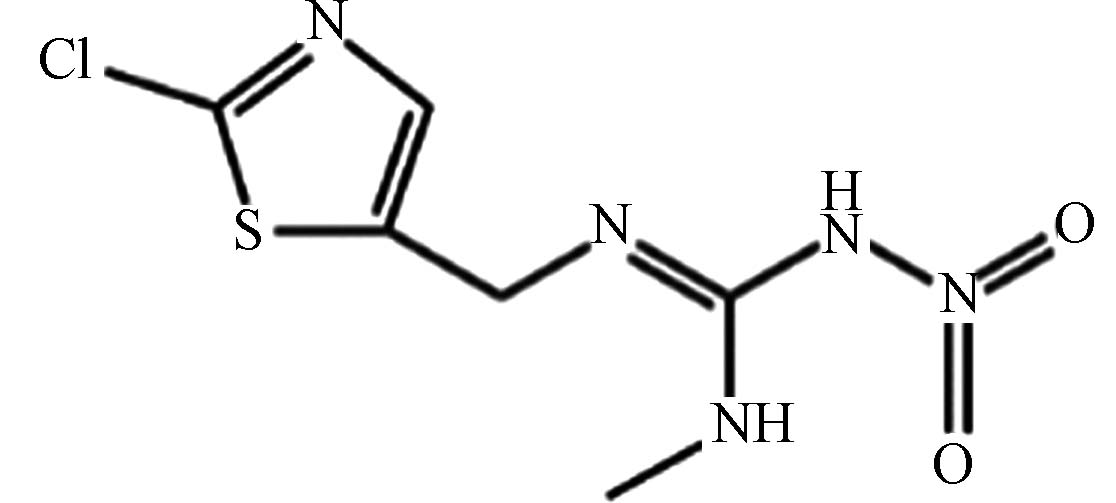
农药 氟虫腈 120068 -37-3C12H4Cl2F6N4OS 437 砜与亚砜类 广谱性杀虫剂 
农药 特丁净 886-50-0 C10H19N5S 241 砜与亚砜类 旱田除草剂 
农药 唑嘧磺草胺 98967 -40-9C12H9F2N5O2S 325 磺胺磺酰胺类 旱田除草剂 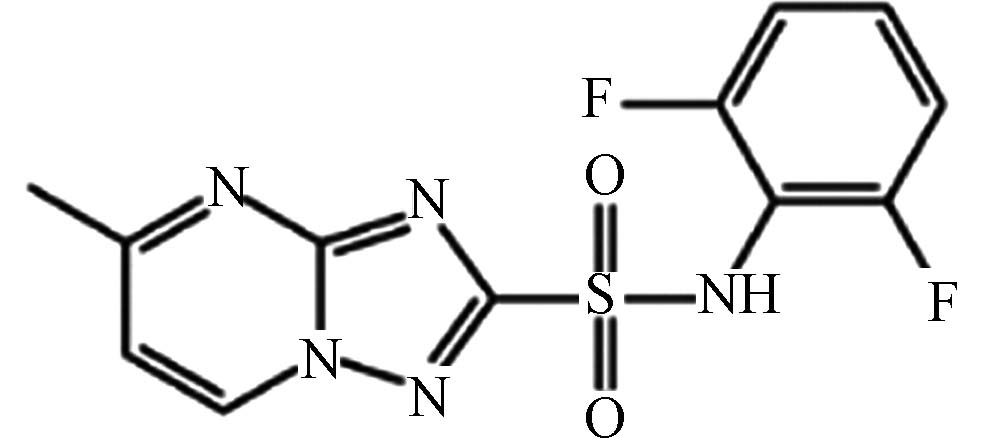
农药 氟磺胺草醚 72178 -02-0C15H10ClF3N2O6S 439 磺胺磺酰胺类 豆田除草剂 
农药 三唑磷 24017 -47-8C12H16N3O3PS 313 含硫有机磷类 广谱性杀虫剂 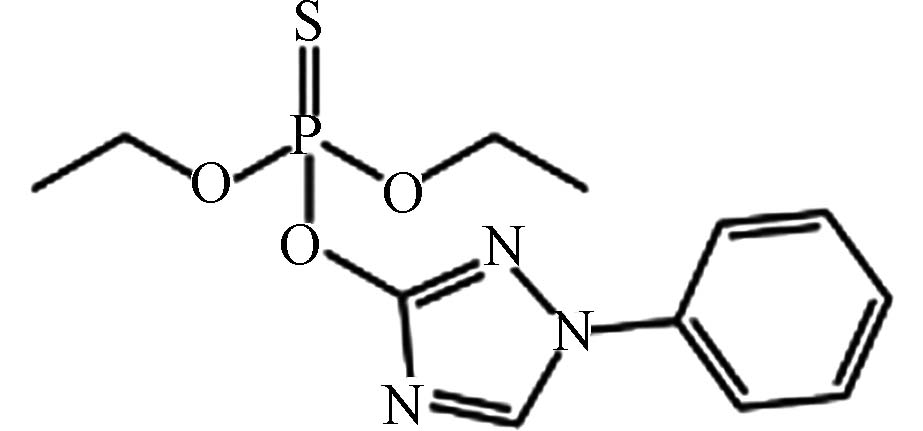
农药 乙硫磷 563-12-2 C9H22O4P2S4 384 含硫有机磷类 广谱性杀虫剂 
-
[1] SMITH B R, EASTMAN C M, NJARDARSON J T. Beyond C, H, O, and N!Analysis of the elemental composition of U. S. FDA approved drug architectures[J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2014, 57(23): 9764-9773. doi: 10.1021/jm501105n [2] TOMLIN C D S, TOMLIN C D S. The pesticide manual[M]. British Crop Protection Council, 2000: 1-1250. [3] SHIMIZU A, TAKADA H, KOIKE T, et al. Ubiquitous occurrence of sulfonamides in tropical Asian waters[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 452/453: 108-115. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.027 [4] 代倩子, 徐枫, 虞霖, 等. 太湖区域13种磺酰脲类除草剂污染特征[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(9): 1-6. DAI Q Z, XU F, YU L, et al. Pollution characteristics of 13 sulfonylurea herbicides in Taihu Lake area[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44(9): 1-6 (in Chinese).
[5] LIU Q Q, FU Z Q, WANG Z Y, et al. Rapid and selective oxidation of refractory sulfur-containing micropollutants in water using Fe-TAML/H2O2[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2022, 315: 121535. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121535 [6] 刘清泉, 陈景文, 蔡喜运. Fe-TAML催化降解水体中含硫污染物的研究[C]. 第十三届全国水处理化学大会暨海峡两岸水处理化学研讨会, 南京, 2016: 16. LIU Q Q, CHEN J W, CAI X Y. Study on catalytic degradation of sulfur-containing pollutants in water by Fe-TAML[C]. The 13th National Conference on Water Treatment Chemistry and Workshop on Water Treatment Chemistry in the Straits, Nanjing, 2016: 16(in Chinese).
[7] SENTER P D. Potent antibody drug conjugates for cancer therapy[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2009, 13(3): 235-244. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.03.023 [8] MUSTAFA M, WINUM J Y. The importance of sulfur-containing motifs in drug design and discovery[J]. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery, 2022, 17(5): 501-512. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2022.2044783 [9] FENG M H, TANG B Q, LIANG S H, et al. Sulfur containing scaffolds in drugs: Synthesis and application in medicinal chemistry[J]. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 2016, 16(11): 1200-1216. doi: 10.2174/1568026615666150915111741 [10] DEVENDAR P, YANG G F. Sulfur-containing agrochemicals[J]. Topics in Current Chemistry, 2017, 375(6): 82. doi: 10.1007/s41061-017-0169-9 [11] CASIDA J E, FUKUNAGA K. Pesticides: Metabolism, degradation, and mode of action[J]. Science, 1968, 160(3826): 445-450. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3826.445 [12] BIZET V, HENDRIKS C M M, BOLM C. Sulfur imidations: Access to sulfimides and sulfoximines[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(11): 3378-3390. doi: 10.1039/C5CS00208G [13] YIN F D, GROSJEAN D, SEINFELD J H. Analysis of atmospheric photooxidation mechanisms for organosulfur compounds[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 1986, 91(D13): 14417-14438. doi: 10.1029/JD091iD13p14417 [14] ZHONG M M, WANG T L, ZHAO W X, et al. Emerging organic contaminants in Chinese surface water: Identification of priority pollutants[J]. Engineering, 2022, 11: 111-125. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2020.12.023 [15] YANG Y, ZHANG X R, JIANG J Y, et al. Which micropollutants in water environments deserve more attention globally?[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(1): 13-29. [16] 张焕军, 王席席, 李轶. 水体中抗生素污染现状及其对氮转化过程的影响研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(4): 1168-1181. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021102405 ZHANG H J, WANG X X, LI Y. Progress in current pollution status of antibiotics and their influences on the nitrogen transformation in water[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(4): 1168-1181 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021102405
[17] 贺艳, 邓月华. 水环境中新烟碱类农药去除技术研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(7): 1963-1976. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019082102 HE Y, DENG Y H. A review on the removal technologies of neonicotinoid pesticides from aquatic environment[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(7): 1963-1976 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019082102
[18] GREGORC A, SILVA-ZACARIN E C M, CARVALHO S M, et al. Effects of Nosema ceranae and thiametoxam in Apis mellifera: A comparative study in Africanized and Carniolan honey bees[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 147: 328-336. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.030 [19] LIN H, NIU J F, XU J L, et al. Electrochemical mineralization of sulfamethoxazole by Ti/SnO2-Sb/Ce-PbO2 anode: Kinetics, reaction pathways, and energy cost evolution[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 97: 167-174. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2013.03.019 [20] KRAEMER S A, RAMACHANDRAN A, PERRON G G. Antibiotic pollution in the environment: From microbial ecology to public policy[J]. Microorganisms, 2019, 7(6): 180. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7060180 [21] KOVALAKOVA P, CIZMAS L, McDONALD T J, et al. Occurrence and toxicity of antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 251: 126351. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126351 [22] 文湘华, 申博. 新兴污染物水环境保护标准及其实用型去除技术[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(3): 847-857. WEN X H, SHEN B. Standards of water environmental protection and practical removal technologies of emerging contaminants[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(3): 847-857 (in Chinese).
[23] BARAN W, ADAMEK E, ZIEMIAŃSKA J, et al. Effects of the presence of sulfonamides in the environment and their influence on human health[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 196: 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.082 [24] SINGH R, SINGH A P, KUMAR S, et al. Antibiotic resistance in major rivers in the world: A systematic review on occurrence, emergence, and management strategies[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 234: 1484-1505. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.243 [25] FANG W D, PENG Y, MUIR D, et al. A critical review of synthetic chemicals in surface waters of the US, the EU and China[J]. Environment International, 2019, 131: 104994. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.104994 [26] TANG F H M, LENZEN M, McBRATNEY A, et al. Risk of pesticide pollution at the global scale[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2021, 14(4): 206-210. doi: 10.1038/s41561-021-00712-5 [27] MUKHOPADHYAY D, KHAN N, KAMAL N, et al. Degradation of β-lactam antibiotic ampicillin using sustainable microbial peroxide producing cell system[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 361: 127605. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127605 [28] RAFQAH S, WONG-WAH-CHUNG P, AAMILI A, et al. Degradation of metsulfuron methyl by heterogeneous photocatalysis on TiO2 in aqueous suspensions: Kinetic and analytical studies[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2005, 237(1/2): 50-59. [29] FENOLL J, HELLÍN P, FLORES P, et al. Fipronil decomposition in aqueous semiconductor suspensions using UV light and solar energy[J]. Journal of the Taiwa Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2014, 45(3): 981-988. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2013.09.015 [30] PAKZAD K, ALINEZHAD H, NASROLLAHZADEH M. Euphorbia polygonifolia extract assisted biosynthesis of Fe3O4@CuO nanoparticles: Applications in the removal of metronidazole, ciprofloxacin and cephalexin antibiotics from aqueous solutions under UV irradiation[J]. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2020, 34(11): e5910. doi: 10.1002/aoc.5910 [31] ZHU W Y, SUN F Q, GOEI R, et al. Facile fabrication of RGO-WO3 composites for effective visible light photocatalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2017, 207: 93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.02.012 [32] GAO B R, WANG J, DOU M M, et al. Novel nitrogen-rich g-C3N4 with adjustable energy band by introducing triazole ring for cefotaxime removal[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 241: 116576. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116576 [33] deLa FLOR M P, CAMARILLO R, MARTÍNEZ F, et al. Synthesis and characterization of bimetallic TiO2/CNT/Pd-Cu for efficient remediation of endocrine disruptors under solar light[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2022, 10(2): 107245. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2022.107245 [34] CAI Z J, HU X T, LI Z A, et al. Hypercrosslinking porous polymer layers on TiO2-graphene photocatalyst: Enhanced adsorption of water pollutants for efficient degradation[J]. Water Research, 2022, 227: 119341. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.119341 [35] LI S, CHEN H, WANG X, et al. Catalytic degradation of clothianidin with graphene/TiO2 using a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma system[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(23): 29599-29611. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09303-0 [36] TRINH T, van den AKKER B, STUETZ R M, et al. Removal of trace organic chemical contaminants by a membrane bioreactor[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2012, 66(9): 1856-1863. doi: 10.2166/wst.2012.374 [37] ZHANG Q H, ZHANG L, LI Z H, et al. Enhancement of fipronil degradation with eliminating its toxicity in a microbial fuel cell and the catabolic versatility of anodic biofilm[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 290: 121723. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121723 [38] ZHU F P, DUAN J L, YUAN X Z, et al. Hydrolysis, adsorption, and biodegradation of bensulfuron methyl under methanogenic conditions[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 199: 138-146. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.149 [39] CHEN X C, ZHOU Q Z, LIU F M, et al. Removal of nine pesticide residues from water and soil by biosorption coupled with degradation on biosorbent immobilized laccase[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 233: 49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.144 [40] BOUFERCHA O, MONFORTE A R, BOUDEMAGH A, et al. Biodegradation and metabolic pathway of the neonicotinoid insecticide thiamethoxam by Labrys portucalensis F11[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(22): 14326. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214326 [41] ANWAR S, WAHLA A Q, ALI T, et al. Biodegradation and subsequent toxicity reduction of Co-contaminants tribenuron methyl and metsulfuron methyl by a bacterial consortium B2R[J]. ACS Omega, 2022, 7(23): 19816-19827. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01583 [42] WANG J L, WANG S Z. Microbial degradation of sulfamethoxazole in the environment[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(8): 3573-3582. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-8845-4 [43] 万家秀, 何碧红, 张永合, 等. 水环境中磺胺类抗生素的生物降解[J]. 广州化工, 2022, 50(22): 153-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2022.22.046 WAN J X, HE B H, ZHANG Y H, et al. Biodegradation of sulfa antibiotics in aquatic environment[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2022, 50(22): 153-156(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2022.22.046
[44] ARYEE A A, HAN R P, QU L B. Occurrence, detection and removal of amoxicillin in wastewater: A review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 368: 133140. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133140 [45] KLARICH K L, PFLUG N C, DeWALD E M, et al. Occurrence of neonicotinoid insecticides in finished drinking water and fate during drinking water treatment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2017, 4(5): 168-173. [46] FERNANDES J O, BERNARDINO C A R, MAHLER C F, et al. Biochar generated from agro-industry sugarcane residue by low temperature pyrolysis utilized as an adsorption agent for the removal of thiamethoxam pesticide in wastewater[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2021, 232(2): 67. [47] CHEN H, GAO B, LI H. Removal of sulfamethoxazole and ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions by graphene oxide[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 282: 201-207. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.03.063 [48] MEHTA T, RATHI A, VERMA A, et al. Elimination of Fipronil insecticide by adsorption technique from aqueous solution by Cu-13X zeolite composite: Isotherms, kinetic and thermodynamic studies[J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 102(17): 4969-4985. doi: 10.1080/03067319.2020.1790545 [49] RANI M, SHANKER U. Removal of chlorpyrifos, thiamethoxam, and tebuconazole from water using green synthesized metal hexacyanoferrate nanoparticles[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(11): 10878-10893. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1346-2 [50] RAHMAN N, VARSHNEY P. Assessment of ampicillin removal efficiency from aqueous solution by polydopamine/zirconium(Ⅳ) iodate: Optimization by response surface methodology[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(34): 20322-20337. doi: 10.1039/D0RA02061C [51] WU J, FENG Y Q, DAI Y R, et al. Biological mechanisms associated with triazophos (TAP) removal by horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands (HSFCW)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 553: 13-19. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.067 [52] BESTER K, BANZHAF S, BURKHARDT M, et al. Activated soil filters for removal of biocides from contaminated Run-off and waste-waters[J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 85(8): 1233-1240. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.017 [53] HU C Y, CHENG M, LIN Y L. Chlorination of bensulfuron-methyl: Kinetics, reaction factors and disinfection by-product formation[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2015, 53: 46-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2015.02.029 [54] AZAD H, MOHSENNIA M, CHENG C, et al. Cross-linked poly(vinyl butyral)/amine-functionalized polyacrylonitrile adsorptive membrane nano-composited with CeO2 nanoparticles for simultaneous aqueous removal of heavy metals and cefotaxime[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 435: 134849. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.134849 -



 下载:
下载: