-
水是物质循环和能量流动的重要组成部分,也是生态环境和人类社会发展必不可少的自然资源. 氟作为一种与人体健康密切相关的必需微量元素,广泛地存在于自然水体中. 中国是典型的大面积高氟地区,也是世界上地方性氟中毒危害最严重的国家之一[1]. 在2022年中国环境公报中,城市集中式饮用水水源(地级市、县级)和农村集中式饮用水水源存在9.50%、15.6%、32.30%监测点不达标,数据显示氟化物是主要超标物质[2]. 其中,区域气象气候条件[3]、地形地质条件[4]、水动力条件、水化学性质[5]、工业生产所排放的“三废”,是引起水体中氟含量升高的主要原因. 人体所需的氟主要来自饮用水,国家生活饮用水标准规定饮用水中氟含量不得超过 1.0 mg·L−1,世界卫生组织规定饮用水中氟含量在 0.5—1.0 mg·L−1,水中过量的氟会严重威胁人类身体健康. 研究发现,长期暴露于高氟废水条件下的儿童智力水平会显著降低[6]. 长期饮用高氟水,不仅会出现氟斑牙、氟牙症、氟骨症疾病,还会引起过敏、神经系统疾病等,最终甚至会导致癌症等致命疾病. 因此,对水体氟污染区域进行有效治理和修复显得尤为重要.
目前,常见的水体除氟方法有吸附法[7]、沉淀法[8]、离子交换法[7]、膜分离法[9]、电化学法[10 − 11]、冷冻法[12]以及植物方法[13]等. 与其他方法相比较,吸附法具有操作简单、适用性广泛、高效率低成本、运行稳定等优点,同时,吸附材料可重复再生、来源广泛. 然而,吸附容量有限、处理水量小以及易受其他因素影响等问题限制了吸附法在实际中的应用. 因此,探索开发新型吸附材料及制备工艺成为亟需突破的难题.
基于此,本文在归纳常用除氟吸附材料的基础上,探讨了各种环境因素对氟吸附过程的影响作用,概括了天然吸附材料、金属基吸附材料、生物质吸附材料、其他废弃物吸附材料以及新型吸附材料除氟的吸附机理,并展望了今后吸附材料的发展方向.
-
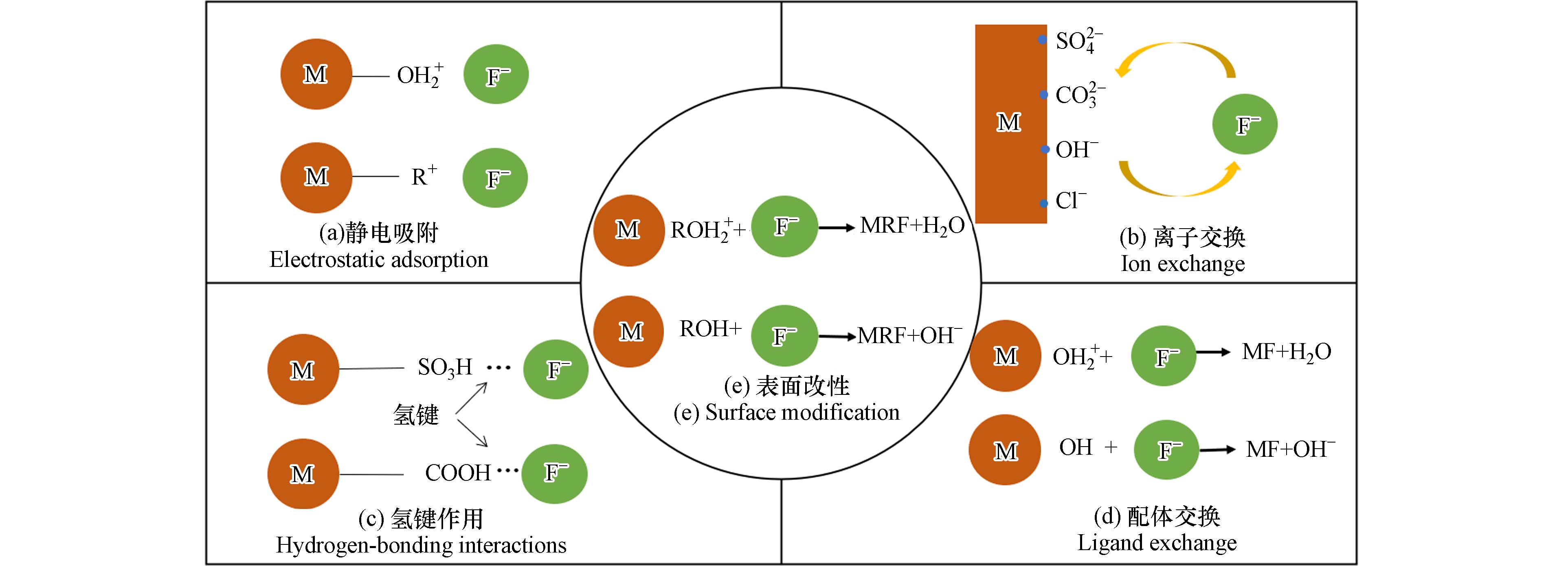
吸附法是利用具有高比表面积的吸附材料吸附水中氟离子,降低水体中氟含量[1]. 值得注意的是,不同类型的吸附材料,在水体中除氟吸附机制也有所不同. 总体而言,吸附除氟的机制主要有:静电吸附、离子交换、氢键作用、配体交换以及吸附材料表面化学修饰[14],如图1 所示.
基于特点和功能作用,去除机制可以分为非特异性作用和特异性作用. 静电吸附和离子交换属于非特异性作用(图1a、图1b),而特异性作用包括氢键和配体交换作用(图1c、图1d). 静电吸附是由于正负电荷的吸引相互靠近而引起的,如阳离子与阴离子氟之间的静电引力[15]. 然而,离子交换则是弱物理非特异性作用,是指吸附材料表面离子与氟离子交换,使溶液中游离的氟离子固定到吸附材料表面,同时释放出表面离子或基团,比如硫酸根离子、碳酸根离子、碳酸氢根离子、氯离子、羟基基团、羧基基团等. 氢键作用则是利用带正电荷的氢原子与另一水分子中含有孤电子对、带有部分负电荷的离子产生的相互吸引作用,如煤基吸附剂表面的氢键作用[16]. 在溶液中,具备配体交换作用的吸附材料与阴离子之间通过形成强共价化学键,实现水体中氟的有效去除. 值得注意的是,具备该除氟性能的吸附材料,对阴离子有很高的选择性. 再者,吸附材料表面的化学改性 (图1e) 主要是利用改性剂对吸附材料表面进行化学改性(酸浸处理或者金属阳离子负载),使其表面带正电荷,进而吸附携带负电荷的氟离子. 然而,通常吸附除氟材料去除水体氟离子的过程,不仅仅是单一机制发挥作用,更多的是离子、基团甚至于环境因素等引起的多种机理作用的结果.
-
大部分环境条件 (如,pH、共存离子、反应温度、吸附材料投加量以及污染物的初始浓度等) 都会直接或间接影响吸附材料对废水中氟的去除效率,其中最主要的参数主要是 pH、共存离子以及反应温度.
如图2a 所示,pH 决定了结合态和游离态的氟的存在比例. 具体而言,在 pH=3 左右,氟离子与氢氟酸所占比例相当;在 pH<3 时,主要以氢氟酸的形式存在;在 pH > 3时,存在形式主要为氟离子. 然而,吸附材料主要去除含氟废水中以游离态形式存在的氟离子. 由此可见,pH 通过直接影响结合态和游离态的氟的存在比例,从而间接影响吸附材料的除氟效率. 另外,吸附材料表面的电荷性质也由溶液 pH 决定. 当 pH 低于零电荷点时,吸附材料表面发生质子化的作用使其表面带正电荷,从而通过静电吸附作用和离子/配体交换作用去除水体氟离子,当溶液 pH 高于零电荷点时,发生去质子化过程使得吸附材料表面带负电荷,与氟离子发生静电排斥(图2b). 值得注意的是,在强酸条件下,溶液中以结合态形式存在的氢氟酸和 pH 低于零电荷点发生的质子化效应会共同影响除氟效率. 其中,当质子化效应较强时,表现为吸附材料对氟的强吸附去除能力. 反之,则对氟的吸附能力下降. 除此之外,碱性条件下,氢氧根离子与氟离子的竞争吸附作用,会对氟离子的去除有抑制作用.
共存离子 (HCO3−、CO32−、HPO42−、PO43−、SO42−、NO3− 及金属阳离子) 的存在会明显影响吸附材料除氟能力. 吸附材料对竞争离子的不同选择性,主要取决于离子大小、电荷、极化率、电负性差异等[18],直接影响吸附材料的吸附性能. 电荷半径比值(CO32− > SO42− > PO43− > Cl−)越高,相互作用越强[19],更能抑制水中氟离子的吸附. 水合离子半径(SO42− > PO43− > Cl− > NO3−)大小对氟去除率也产生一定影响. 更大的水合离子半径,能通过长程静电力促进吸附材料外层络合物的形成,降低吸附材料对氟的去除效率[20]. 同时,依据实验数据发现,多电荷的阴离子(CO32−、HPO42−、PO43−、SO42−)更容易与吸附材料相互吸引,竞争吸附材料表面活性位点,从而降低了氟化物的去除率[21]. 此外,弱酸根离子(HCO3−、CO32−、HPO42−和 PO43−)发生水解作用使体系中氢氧根离子增多,间接产生的氢氧根离子与氟离子产生竞争吸附作用,降低了氟的去除效果. 然而,随着 Ca2+和 Mg2+金属阳离子的增加,除氟效果提高,这可能是由于形成了不溶性 CaF2 和 MgF2 所致[22].
随着温度的升高,粒子运动更加剧烈,分子间发生碰撞和成键的可能性增大,导致在一定时间内吸附强度增加. 在高温条件下吸附材料孔隙结构中的大多数物质被除去,减小吸附材料表面电阻,增强了其交换和吸附能力[23],使得吸附速率性能提高. 然而,随着温度的升高,污染物质在吸附材料活动趋势增大,导致吸附材料表面吸附容量降低. 由此可见,吸附材料的热力学吸附特性对其在不同温度下的吸附性能有很大的影响.
-
以沸石、高岭土、蒙脱石、海泡石为代表的天然吸附材料具有高选择性,高除氟效率和低成本的特点. 由于其发达的孔道结构,使得在水体氟化物处理方面得到了广泛的应用. 天然吸附材料主要通过静电吸附、离子交换去除水体中氟化物,而改性的天然材料则趋向于配体交换机制去除氟.
沸石具有巨大的比表面积和优异的化学稳定性,但较低的吸附容量(0.012 mg·g−1)限制了其在处理水体氟污染的实际应用[24]. 目前,最常见的方法是通过改性方法提升沸石的吸附容量. 同时,通过选择合适的水处理参数来进一步改善吸附性能. 天然沸石经氯化钙改性后,除氟效果显著提高,在初始氟化物浓度为100.0 mg·L−1时的最大氟化物吸附容量达到了1.77 mg·g−1[25]. 沸石中引入金属基氢氧化铝物质后,反应过程中形成的铝-氟化学键以及羟基离子的交换作用,能够实现对氟的有效去除(去除率> 92.00%,最大吸附量为 18.12 mg·g-1)[26]. 但是,由于HCO3−和CO32−对氟离子吸附表现出强烈的竞争效应,降低了氟化物的去除效率. 相比较于化学改性(盐改性、常用金属负载),利用镧锆稀土金属作为负载材料,吸附能力提升更加显著. 锆改性沸石饱和除氟容量达 19.84 mg·g−1,饱和吸附率为93.40%,除氟性能远优于沸石原矿(56.40%)和酸改性沸石(84.40%)[27]. 由于羟基的配体交换作用,镧改性沸石对氟的最大吸附容量更是高达 141.50 mg·g−1[28]. 值得注意的是,负载生物高分子材料壳聚糖的沸石,在 pH=5 时,对氟离子也达到了 104.00 mg·g−1的最大吸附容量[29].
值得注意的是,经过表面改性后沸石表面结构和性质发生改变,在反应体系中满足最佳pH小于pHpzc的规律,零电荷点提高. 使得在更宽的pH条件下,沸石吸附性能和去除效率提高. 然而,沸石类吸附材料还受到竞争离子浓度变化的影响. 虽然在低浓度下,去除效率几乎不受共存离子的影响,但在高浓度下,竞争效应则很强烈,其中HCO3−、CO32−、SO42−离子的影响最为明显,如表1所示. 因此,在寻找高效吸附除氟材料的基础上,也要对其改性方法以及环境影响参数进行深入研究.
黏土矿物因其吸附能力强、比表面积大,不同的黏土矿物具有不同的吸附性能,如表2所示. 天然黏土矿物的吸附容量低于1.00 mg·g−1,对其进行物理和化学改性后,吸附容量显著增加. 特别是在热处理后,海泡石的吸附容量高达169.95 mg·g-1[36]. 高岭土经机化激活后,其比表面积从15.11 m2·g−1增加至32.43 m2·g-1[18],加入聚羟基铁后,其对重金属的去除效率可达90.30%[38]. 对于黏土矿物来说,HCO3−似乎在活性位点与氟离子有竞争作用,竞争离子浓度的增加,氟离子去除效率明显降低. 此外,在某些情况下,黏土类吸附材料还表现出了可再生的特点. 经一次解吸后,蒙脱石以具有58.00%的氟去除率[39]. 采用稀土元素、铝元素等对其进行处理后,其再生效率在80.00%以上,而质量损失在10.00%以下[40],具有一定的可重复利用性.
-
金属基吸附材料具有比表面积大、孔道结构发达、表面活性强等特点,在物质的迁移转化中起着重要作用,被广泛用于水体中污染物的去除. 金属基吸附材料主要通过静电吸附、离子/配体交换等方式去除水体氟化物.
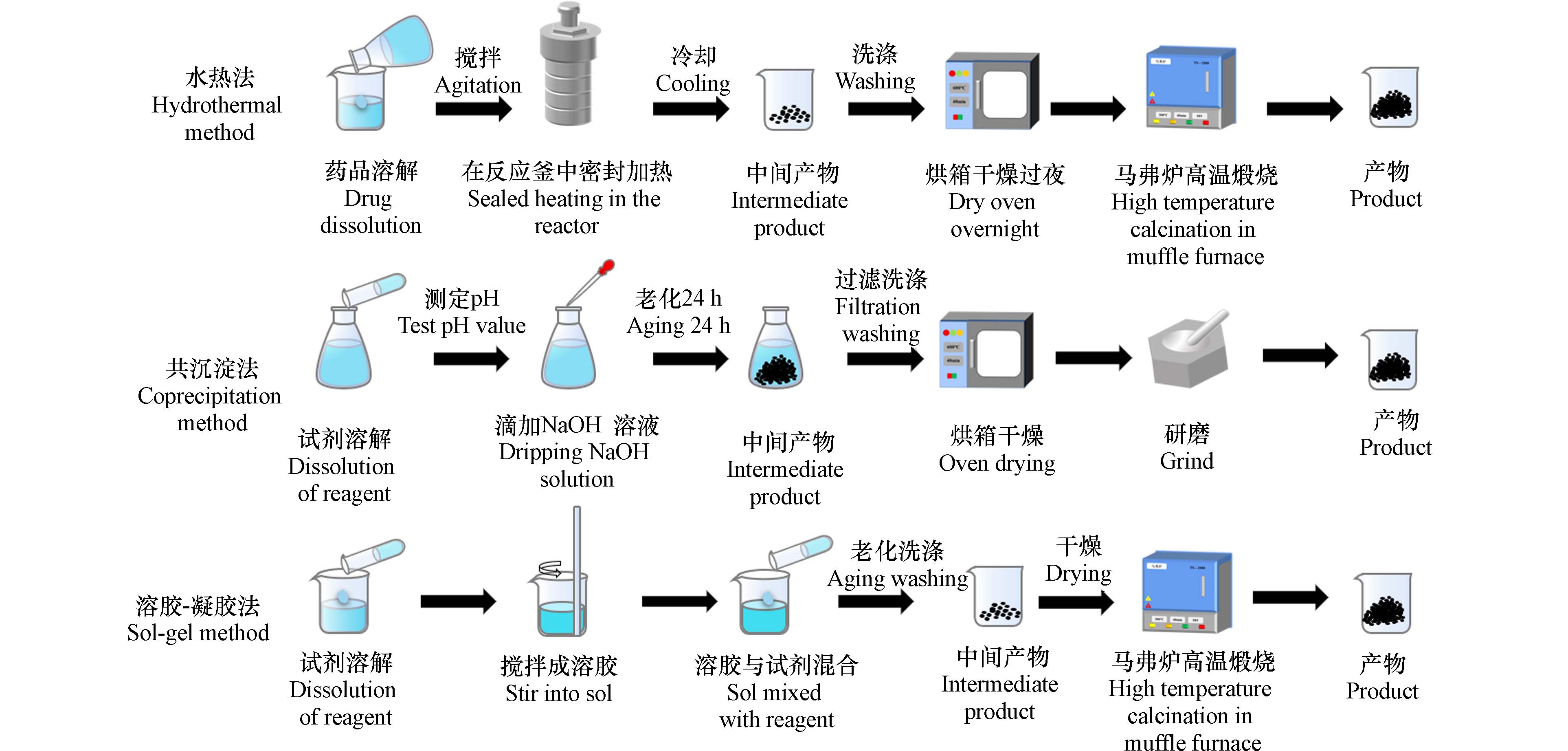
活性氧化铝吸附交换法是一种处理含氟废水最成熟的方法[41]. 该材料具有较高的分散度,丰富的孔结构. 因此,改性物质可分散并黏附于孔道结构中增大吸附材料比表面积,提高吸附容量和效率. 引入锰氧化物和氢氧化物,在较短的时间内,活性氧化铝最大的氟去除率从38.00%提高到67.00%[42]. 此外,羟基磷灰石作为分散相进入孔隙当中,吸附容量更是提高到了未改性活性氧化铝的5倍(14.40 mg·g−1)[43]. 而不同的合成方法也显著影响吸附性能. 采用溶胶-凝胶法制备的氧化铝对氟化物的去除率为活性氧化铝的1.35倍,60 min内的除氟率可达90.00%以上[44]. 合成的大孔活性氧化铝具有较高的孔隙率和比表面积,其吸附容量随着比表面积和孔隙率的增大而增大(最大吸附容量119.20 mg·g−1)[45]. 如图3所示活性氧化铝合成流程,与其他方法相比,水热法在吸附性能上提升并不明显,而共沉淀法、溶胶-凝胶法等在吸附性能上的提升则相对较大,这可能与其在高温煅烧后得到了更大的比表面积有关[46]. 如表3所示,不同的修饰合成方式使得吸附材料受不同环境因素的限制. 在酸性条件下,活性氧化铝具有良好的吸附除氟效果;而在竞争离子浓度升高后氟去除效率明显受到弱酸根离子竞争效应的影响.
自然界中普遍存在着赤铁矿、磁铁矿、针铁矿和水铁矿等铁氧化物[55]. 以氧化铁涂层材料为载体,对氟化物的去除作用也是十分明显的,在低pH条件下,去除氟化物的效率可以达到90.00%[56]. 但是,铁氧化物的吸附容量较低,只有10.00 mg·g−1左右. 然而,经过乙醇处理后的氧化铁,拥有更高的比表面积和吸附速率,在2 min内达到吸附平衡容量的80.00%,最大吸附量可达60.80 mg·g−1,且在CO32−为100 mg·L−1时,该吸附剂仍能获得较高的氟化物去除效率[57].
稀土金属与氟有良好的亲和力,在水体净化方面表现出优异的吸附性能. 在30 min内,氧化镧可去除90.00%的氟化物,经过10次再生后,依然具有良好地吸附除氟能力[58]. 锆水合氧化物对氟离子的吸附具有很高的选择性,在 pH值为3时,其饱和吸附量更是达到 124.00 mg·g−1[59-60]. 但碍于成本因素,稀土元素一般都是用在负载方面. 将稀土离子与吸附材料结合,可显著提高吸附材料的吸附效果. 包覆镧活化氧化铝,在120 min可达到93.00%的去除率[61]、用氧化锆/沸石分子筛对氟的最大去除率可达95.48%[62]. 而以掺镧的交联凝胶为吸附材料,在50 mL不同浓度的水溶液中加入0.20 g吸附材料,其对氟离子的去除效果可达到98.80%的高去除率[63].
多金属比单一金属具有更高的氟去除率,单一的铁修饰分子筛的最大去除效率达到80.23%[64],而铁锆修饰分子筛在80 min后仍保持91.60%的高去除率[65]. 在中性条件下,180 min内,负载有氧化镁的活性氧化铝可以除去95.00%以上的氟化物[66]. 然而,镧镁双金属负载在吸附时间120 min内,对高氟水去除率就可以达到97.70%[52]. 与负载单一金属相比,氟去除率提高了2.00%—5.00%. 采用多元复合金属材料对水体氟进行吸附,可以弥补单种金属材料对水体氟修饰的不足,从而实现对水体氟的高效去除.
-
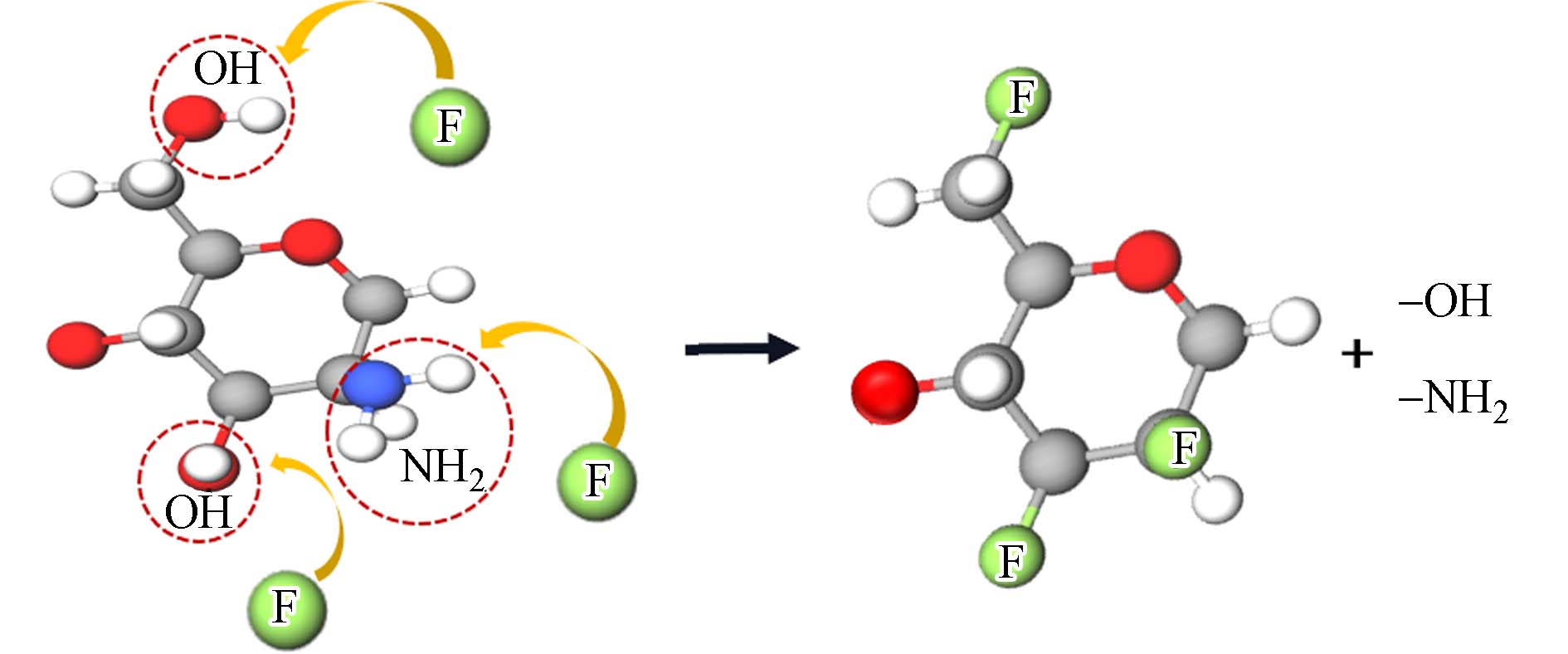
生物性吸附材料因其价格低廉,无二次污染,且可回收利用广泛应用于水体氟污染治理当中,是一种良好的除氟吸附材料. 作为一种典型的吸附材料,壳聚糖通过其表面的氨基和羟基与氟发生交换作用,去除水体中的氟[29],如图4所示. 然而,未改性的壳聚糖吸附容量较低,需要对其进行表面修饰以提高其吸附量. 采用戊二醛、铈与壳聚糖进行交联与络合,合成了高吸附能力的改性壳聚糖吸附材料,其饱和吸附能力达到153.00 mg·g−1,是天然壳聚糖的11.6倍[67]. CO3 2−是影响改性壳聚糖吸附氟离子的重要阴离子,如表4所示. 但即使在含有复合阴离子的环境中,负载铈元素的壳聚糖对氟的吸附能力依然高达12.30 mg·g−1[76]. 然而,将稀土元素镧负载到壳聚糖基体上,吸收速率明显加快,20 min即可达到峰值,但其容易受到竞争离子(Cl−、SO42−、NO3−、HCO3−和CO32−)的影响. 特别是在HCO3−和CO3 2−的存在下,基本都没有去除氟化物,这可能是由于pH的变化以及阴离子的竞争效应[77].
以动植物为原料制成的生物炭具有多孔性、高比表面积等特性,是一种极具应用前景的吸附材料. 在生物炭类吸附材料,在酸性条件下表现出良好的除氟效果. 由于氟化物在吸附位点上的扩散增强以及对吸附材料活性较低位点的利用,使得蛋壳提取物在pH=3时,对氟的去除效率更达到了99.00%. 在实际应用中,尽管竞争离子存在,但其除氟率仍然保持在80.00%以上[78]. 如表4所示,吸附剂的吸附性能明显受到反应体系中pH值和竞争离子的影响. 在低pH条件下,涂有氢氧化铝的废蘑菇堆生物炭可以利用静电吸附和配体交换作用来去除氟离子,最大吸附量为36.50 mg·g−1,浓度降低到1 mg·L−1以下,符合饮用水水质标准[69]. 虽然水葫芦叶和象草叶经过碱性蒸汽处理,但其依然在酸性条件下,能够去除85.00%氟化物[68],却在反应过程中受到竞争离子的影响,使得吸附效果的降低.
-
工业废弃物通过物理、化学作用,逐步向环境中释放出有毒有害物质,严重危害人类的身体健康. 必须对其进行合理处置,实现其资源化利用,以期减少对人体危害. 赤泥是制铝工业提取氧化铝时排出的工业固体废物,赤泥中铁、铝及钠后的残渣仍含适量的活性物质[79],以该残渣为吸附剂,实验条件下对氟的去除率可达95.00%以上[80],但其吸附容量仅为1.21 mg·g−1. 如表4所示,其中经过煅烧活化后的赤泥, 20 min内迅速地达到反应平衡,饱和吸收容量更是高达91.28 mg·g−1,远高于未处理的吸附容量. 同时,处理后出水氟浓度为0.69 mg·L−1,低于国家饮用水标准1 mg·L−1[71]. 矿渣经过镧和铝在表面负载修饰后,会形成大量的杆状复合金属氧化物,其无定型结构为氟离子去除提供了良好的条件,通过静电吸附作用和离子/配体交换作用,增加氟的去除[81]. 虽然,赤泥和矿渣具有良好的除氟效果,但存在固液难以分离的缺陷. 而钢渣对氟离子有较强的吸附作用,且液固分离非常快,对氟离子的去除率在4 s内达到80.98%,2 min时达到最大去除率(99.58%),但会随着共存离子浓度的增大,SO42−、HCO3−不同程度地抑制氟的吸附[74],使得吸附容量减少. 工业废弃物尽管具有很好的除氟性能,降低了氟化物对水体的危害,但由于其自身含有剧毒、有污染的金属,在水处理的过程中会导致新的污染现象的发生.
-
由于纳米吸附材料不仅仅具有高比表面积、高表面活性等优点,还具有催化电位和高活性等独特的特性,使其成为比传统材料更好的吸附材料[82]. 在污水处理领域具有广阔的应用前景,纳米材料主要通过静电吸附作用、配体或者离子交换作用去除水体中的氟. 然而,纳米吸附材料因其组成、形貌、结构的差异具有不同的除氟效果. 如介孔结构的氧化钙空心球,拥有发达的孔结构,比表面积更大,且其表面羟基与氟离子发生交换作用,其最大吸附量达到181.96 mg·g−1[83] (图5 a),同样地,氢氧碳酸铈纳米球其表面羟基、碳酸根等可以与氟离子发生交换反应,但在低初始浓度的氟离子溶液中具有极高的去除效率(图5 b)[84]. 同时,纳米球的薄层介孔结构进一步强化了材料的传递能力,提高了吸附反应速率和吸附容量[85]. 多孔片状的纳米材料也表现出了良好氟化物的吸附能力,表面吸附位点增多,在pH=2—11的范围内,通过羟基和表面碳酸盐与氟离子的交换作用,有效地去除水中的氟化物,最大吸附量超过185.50 mg·g−1[86],见图5 c. 然而,同一物质形态的差异也会影响其对氟离子的吸附性能. 例如,纳米棒、八面体和纳米立方体形貌的CeO2对氟离子的最大吸附量分别为71.50、28.30、7.00 mg·g−1[87].
磁性纳米材料由于其独特的磁性特性,可以通过磁场有效地分离氟化物离子,从而更容易实现其固液分离及吸附材料的回收利用. 磁性纳米体系的表面具有活性,可以通过表面修饰实现对其物理化学性质的调控. 经过改性纳米级Fe3O4分散性更好,随着吸附材料用量的添加和反应时间的延长,除氟效率相应地提高,虽然CO32−对除氟效果影响稍大,但对其去除率仍在70.00%以上,在适宜的条件下,更是达到84.80%[88]. 介孔结构的Fe3O4纳米粒子,在初始浓度为200.0 mg·L−1时,最大吸附能力达到70.64 mg·g−1. 即使有竞争阴离子存在,它仍然可以实现80.00%的高去除率,这当中,羟基基团的交换机制起了至关重要的作用[89].
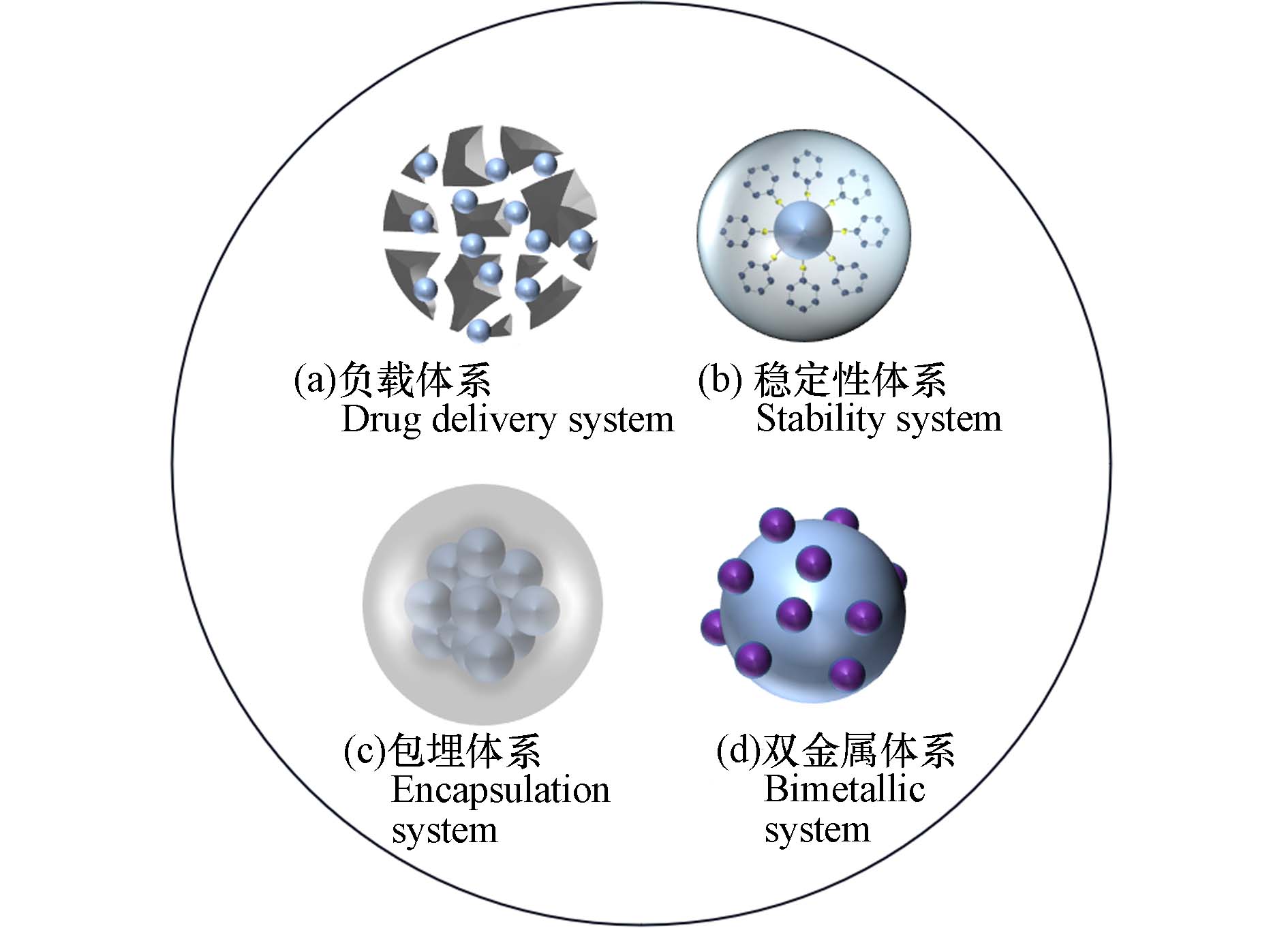
在实际应用中,纳米体系会产生易于团聚,易于氧化、难以分离等问题,进而影响到水处理效率. 因此,逐步发展出了复合改性体系. 以纳米铁为例,共有四大复合改性体系,即:负载、改性稳定性、包埋以及双金属体系. 如图6a所示,负载在其他材料(活性炭)表面和孔隙之中,改善易于材料团聚的缺陷,提高分散性. 而改性稳定化体系则趋向于表面改性,多利用淀粉、壳聚糖、羧甲基纤维素等有机物,对其进行功能化修饰,以增强其水溶性、分散性,增加空间位阻,促进电子转移,从而高效地除去水中的氟离子(图6 b). 包埋体系不仅具有更高的氟吸附性能,还具有更好的固-液分离特性(图6 c). 双金属体系能够通过使用不同的金属元素的特性相互协作来移除水中的氟化物,吸附容量显著提高(图6 d).
-
新型纳米吸附材料主要有碳基纳米材料(石墨烯、碳纳米管等)[82]、纳米复合金属氧化物材料(钙、铝、铁、镧、铈等)以及其他类纳米吸附材料(金属有机框架). 纳米复合金属氧化物相比较于其他纳米材料,发展应用较早. 而碳基纳米材料和金属有机框架在20世纪末21世纪初才开始被逐渐认识研究,随着对纳米材料的研究不断深入,两者应用前景逐渐展现.
其中,碳基纳米材料被认为是去除污染物的最佳吸附剂. 然而,碳纳米管用于除氟的潜力很少被研究. 同时,实验发现碳纳米管的除氟吸附容量(2.83 mg·g−1)[91]和去除率(71.00%)[92]明显小于石墨烯. 相对来说,石墨烯是碳纳米管良好的替代品. 石墨烯是人类已知的最薄材料,具有单层碳原子网结构,电子在其中也能高速运动,是一种性能优良的氟离子吸附材料. 与碳纳米管相比,由于石墨烯吸附剂具有两个可用于污染物吸附的接触面[82],因此大大提高了反应效率,是水处理的理想材料. 研究发现,在稀土锆及生物材料壳聚糖的修饰下,该体系对水中重金属离子的去除率从84.80%提升到97.17%[93],而氧化石墨烯和氧化铝复合体系的去除率更是达到99.50%[54]. 然而,石墨烯复合材料在循环利用过程中,因其分子链断裂,材料分散,影响了对氟化物的去除效果,不具有重复利用性. 值得注意的是,另外一类具有较高脱附再生速率的纳米材料—金属有机框架却表现出较高的脱附再生吸附性能.
金属有机框架作为一类新型的金属离子或金属簇和有机配体组成的有机-无机杂化材料,具有孔道结构多样,孔道尺寸可调,配位点不饱和,功能可设计等诸多优势[94]. 与其他吸附材料比较,可回收性高,可循环吸附并固定氟离子,在较大的酸碱度变化区间,能有效地去除水体中的氟化物,以离子交换机制为主来去除水体氟化物[95]. 由于改性方法和材料的差异,在环境因子的调控下,会产生不同的吸附能力和去除率. 前期研究发现 pH值和阴离子种类等因素会对体系中氟去除产生影响,其中SO42−、 NO3−、Cl−等离子对吸附材料除氟性能影响较小,但PO43−、HCO3−、CO32−等离子由于水解作用,与氟离子产生竞争效应,从而使吸附材料的氟去除率受到很大的影响. 但从氟化物去除率以及自然水体中竞争离子的浓度来看,这种影响几乎不考虑. 其中,MIL-96 (Al)对pH响应性大,在强酸条件下,去除效率几乎可达100%且解吸再生去除率在60.00%以上[96],而MOF-801 对 pH在2—10之间亦有良好的去除效率[95]. 然而,UiO-66 (Zr)则表现出不同的趋势,在pH=3—6范围内随着pH的增大而增大,pH=5—7 范围内的吸附效果最好;但是在 pH升至8—11时,去除效果明显降低;在 pH为11时,去除率下降至42.00%[97]. 这可能是由于在不同的pH下,吸附材料表面的电荷发生改变,使得去除率降低. 此外,经解吸和再生处理后,金属有机框架的除氟率依然达到了70.00%. 而Zr-MOFs在6次脱附后,其对氟的去除率依然在85%以上,且可循环利用[98],如表5所示.
相比传统的除氟材料,新型纳米除氟吸附材料具有高吸附容量、高且稳定的吸附效率及耐久性的优势. 能够在更宽的 pH 范围内依然保持着良好的氟去除效率,在自然水体中几乎不受竞争离子的影响,在不同的水质条件下保持高效地除氟性能. 同时,新型纳米除氟材料具有良好的循环再生吸附性能,能够反复利用于水体氟污染当中,从而降低了材料成本. 值得注意的是,新型除氟吸附材料不容易在水污染处理过程中产生二次污染,具有绿色环保性. 此外,由于其低成本且易于制备,可以在大规模应用中实现经济与环境双重效益. 基于此,新型纳米除氟材料成为一类极具应用前景的除氟吸附材料.
-
吸附法具有除氟效果好、操作简便等优点,被广泛用于饮用水、工业含氟废水的处理. 然而,不同类别的吸附除氟材料却存在着许多问题. 对天然吸附材料和生物质吸附材料来说,存在着选择性差、吸附容量小、反应速率慢及易受其他因素干扰的问题. 同时,生物质吸附材料的来源和制备工艺也是需要考虑的另一个问题. 金属基吸附材料在吸附过程中,反应活性逐渐减弱,去除效率降低. 且金属离子本身在水处理过程也可能产生一类有毒有害的污染物质,危害人体和环境健康. 此外,作为资源化利用的工业废弃物材料,虽然具有廉价易得的优点,但本身含有的有毒有害物质,导致新一类环境污染现象的发生. 值得注意的是,吸附除氟材料大多都具有再生难度大、成本高的缺陷,其次材料本身存在的稳定性和耐久性问题,使其能否在复杂多变的水体环境中实现对含氟物质的高效稳定去除,还需进一步深入研究.
因此,探索吸附除氟材料的制备改性材料、方法和工艺,充分发挥材料优势和协同作用,拓宽吸附除氟材料的应用范围;寻找研发更加环保、经济、高效、稳定、持久的新型吸附除氟材料,实现对水中氟化物的高效处理与修复,以便更好地满足实际需求是今后水体除氟吸附材料的研究发展方向. 同时,也要加深对于水体氟化物去除的机制及影响因素的研究,从而更好地完善完备制备工艺、方法以及吸附材料的改性. 能根据水体污染和水情状况,综合运用各种去除氟化物的技术,如沉淀法、电化学法等,最终达到对水体中氟化物进行高效去除和控制,降低水体中氟化物的污染风险. 此外,在秉持高效率、高稳定性、低成本目标的同时,也要注重资源与环境的保护,采用符合经济效益的方法,促进人与环境的可持续发展.
不同功能性除氟吸附材料在饮用水及含氟废水中的研究进展
Research progress of different functional defluorination adsorbent materials in drinking water and fluorinated wastewater
-
摘要: 水体氟污染会引起氟斑牙和骨骼畸形等疾病,已经严重危害到了人类健康. 利用不同功能性吸附材料吸附除氟已经成为处理含氟水当中的关键技术. 为减轻水体氟污染所诱发的环境问题,有效降低水体氟污染的环境健康风险,本文归纳了不同功能性吸附材料(天然吸附材料、金属基吸附材料、生物质吸附材料、工业废弃物吸附材料以及纳米吸附材料等)在水体氟污染处理中的吸附机理和效果. 同时,探讨了不同环境因素对功能性吸附材料在水体除氟过程中的关键影响,并展望了除氟吸附材料未来的发展趋势,以期为今后的水体氟污染治理提供一定的理论指导和依据.Abstract: Water fluorine pollution can cause dental fluorosis, bone deformity and other diseases, which have seriously harmed human health. The removal of fluorine using different functional adsorption materials has become a key technology in water fluorine pollution. To effectively reduce the environmental problems and the environmental health risk caused by water fluoride pollution, the adsorption mechanisms and effects of different functional adsorption materials (e.g., natural adsorption materials, metal-based adsorption materials, biomass adsorption materials, waste adsorption materials and nano-adsorption materials) in water fluoride pollution treatment are summarized. Furthermore, the primary impacts of diverse environmental factors on water fluoride removal by functional adsorption materials are deeply discussed, and the future development trend of fluoride removal materials is looked into, thereby providing the certain theoretical guidance and basis for the treatment of water fluoride pollution.
-
水是物质循环和能量流动的重要组成部分,也是生态环境和人类社会发展必不可少的自然资源. 氟作为一种与人体健康密切相关的必需微量元素,广泛地存在于自然水体中. 中国是典型的大面积高氟地区,也是世界上地方性氟中毒危害最严重的国家之一[1]. 在2022年中国环境公报中,城市集中式饮用水水源(地级市、县级)和农村集中式饮用水水源存在9.50%、15.6%、32.30%监测点不达标,数据显示氟化物是主要超标物质[2]. 其中,区域气象气候条件[3]、地形地质条件[4]、水动力条件、水化学性质[5]、工业生产所排放的“三废”,是引起水体中氟含量升高的主要原因. 人体所需的氟主要来自饮用水,国家生活饮用水标准规定饮用水中氟含量不得超过 1.0 mg·L−1,世界卫生组织规定饮用水中氟含量在 0.5—1.0 mg·L−1,水中过量的氟会严重威胁人类身体健康. 研究发现,长期暴露于高氟废水条件下的儿童智力水平会显著降低[6]. 长期饮用高氟水,不仅会出现氟斑牙、氟牙症、氟骨症疾病,还会引起过敏、神经系统疾病等,最终甚至会导致癌症等致命疾病. 因此,对水体氟污染区域进行有效治理和修复显得尤为重要.
目前,常见的水体除氟方法有吸附法[7]、沉淀法[8]、离子交换法[7]、膜分离法[9]、电化学法[10 − 11]、冷冻法[12]以及植物方法[13]等. 与其他方法相比较,吸附法具有操作简单、适用性广泛、高效率低成本、运行稳定等优点,同时,吸附材料可重复再生、来源广泛. 然而,吸附容量有限、处理水量小以及易受其他因素影响等问题限制了吸附法在实际中的应用. 因此,探索开发新型吸附材料及制备工艺成为亟需突破的难题.
基于此,本文在归纳常用除氟吸附材料的基础上,探讨了各种环境因素对氟吸附过程的影响作用,概括了天然吸附材料、金属基吸附材料、生物质吸附材料、其他废弃物吸附材料以及新型吸附材料除氟的吸附机理,并展望了今后吸附材料的发展方向.
1. 吸附除氟机制及影响因素(The mechanism and influencing factors of the adsorptive removal of fluorine)
1.1 去除机制
吸附法是利用具有高比表面积的吸附材料吸附水中氟离子,降低水体中氟含量[1]. 值得注意的是,不同类型的吸附材料,在水体中除氟吸附机制也有所不同. 总体而言,吸附除氟的机制主要有:静电吸附、离子交换、氢键作用、配体交换以及吸附材料表面化学修饰[14],如图1 所示.
基于特点和功能作用,去除机制可以分为非特异性作用和特异性作用. 静电吸附和离子交换属于非特异性作用(图1a、图1b),而特异性作用包括氢键和配体交换作用(图1c、图1d). 静电吸附是由于正负电荷的吸引相互靠近而引起的,如阳离子与阴离子氟之间的静电引力[15]. 然而,离子交换则是弱物理非特异性作用,是指吸附材料表面离子与氟离子交换,使溶液中游离的氟离子固定到吸附材料表面,同时释放出表面离子或基团,比如硫酸根离子、碳酸根离子、碳酸氢根离子、氯离子、羟基基团、羧基基团等. 氢键作用则是利用带正电荷的氢原子与另一水分子中含有孤电子对、带有部分负电荷的离子产生的相互吸引作用,如煤基吸附剂表面的氢键作用[16]. 在溶液中,具备配体交换作用的吸附材料与阴离子之间通过形成强共价化学键,实现水体中氟的有效去除. 值得注意的是,具备该除氟性能的吸附材料,对阴离子有很高的选择性. 再者,吸附材料表面的化学改性 (图1e) 主要是利用改性剂对吸附材料表面进行化学改性(酸浸处理或者金属阳离子负载),使其表面带正电荷,进而吸附携带负电荷的氟离子. 然而,通常吸附除氟材料去除水体氟离子的过程,不仅仅是单一机制发挥作用,更多的是离子、基团甚至于环境因素等引起的多种机理作用的结果.
1.2 环境影响因素
大部分环境条件 (如,pH、共存离子、反应温度、吸附材料投加量以及污染物的初始浓度等) 都会直接或间接影响吸附材料对废水中氟的去除效率,其中最主要的参数主要是 pH、共存离子以及反应温度.
如图2a 所示,pH 决定了结合态和游离态的氟的存在比例. 具体而言,在 pH=3 左右,氟离子与氢氟酸所占比例相当;在 pH<3 时,主要以氢氟酸的形式存在;在 pH > 3时,存在形式主要为氟离子. 然而,吸附材料主要去除含氟废水中以游离态形式存在的氟离子. 由此可见,pH 通过直接影响结合态和游离态的氟的存在比例,从而间接影响吸附材料的除氟效率. 另外,吸附材料表面的电荷性质也由溶液 pH 决定. 当 pH 低于零电荷点时,吸附材料表面发生质子化的作用使其表面带正电荷,从而通过静电吸附作用和离子/配体交换作用去除水体氟离子,当溶液 pH 高于零电荷点时,发生去质子化过程使得吸附材料表面带负电荷,与氟离子发生静电排斥(图2b). 值得注意的是,在强酸条件下,溶液中以结合态形式存在的氢氟酸和 pH 低于零电荷点发生的质子化效应会共同影响除氟效率. 其中,当质子化效应较强时,表现为吸附材料对氟的强吸附去除能力. 反之,则对氟的吸附能力下降. 除此之外,碱性条件下,氢氧根离子与氟离子的竞争吸附作用,会对氟离子的去除有抑制作用.
共存离子 (HCO3−、CO32−、HPO42−、PO43−、SO42−、NO3− 及金属阳离子) 的存在会明显影响吸附材料除氟能力. 吸附材料对竞争离子的不同选择性,主要取决于离子大小、电荷、极化率、电负性差异等[18],直接影响吸附材料的吸附性能. 电荷半径比值(CO32− > SO42− > PO43− > Cl−)越高,相互作用越强[19],更能抑制水中氟离子的吸附. 水合离子半径(SO42− > PO43− > Cl− > NO3−)大小对氟去除率也产生一定影响. 更大的水合离子半径,能通过长程静电力促进吸附材料外层络合物的形成,降低吸附材料对氟的去除效率[20]. 同时,依据实验数据发现,多电荷的阴离子(CO32−、HPO42−、PO43−、SO42−)更容易与吸附材料相互吸引,竞争吸附材料表面活性位点,从而降低了氟化物的去除率[21]. 此外,弱酸根离子(HCO3−、CO32−、HPO42−和 PO43−)发生水解作用使体系中氢氧根离子增多,间接产生的氢氧根离子与氟离子产生竞争吸附作用,降低了氟的去除效果. 然而,随着 Ca2+和 Mg2+金属阳离子的增加,除氟效果提高,这可能是由于形成了不溶性 CaF2 和 MgF2 所致[22].
随着温度的升高,粒子运动更加剧烈,分子间发生碰撞和成键的可能性增大,导致在一定时间内吸附强度增加. 在高温条件下吸附材料孔隙结构中的大多数物质被除去,减小吸附材料表面电阻,增强了其交换和吸附能力[23],使得吸附速率性能提高. 然而,随着温度的升高,污染物质在吸附材料活动趋势增大,导致吸附材料表面吸附容量降低. 由此可见,吸附材料的热力学吸附特性对其在不同温度下的吸附性能有很大的影响.
2. 吸附除氟材料(Adsorptive materials for flouride removal)
2.1 天然吸附材料
以沸石、高岭土、蒙脱石、海泡石为代表的天然吸附材料具有高选择性,高除氟效率和低成本的特点. 由于其发达的孔道结构,使得在水体氟化物处理方面得到了广泛的应用. 天然吸附材料主要通过静电吸附、离子交换去除水体中氟化物,而改性的天然材料则趋向于配体交换机制去除氟.
沸石具有巨大的比表面积和优异的化学稳定性,但较低的吸附容量(0.012 mg·g−1)限制了其在处理水体氟污染的实际应用[24]. 目前,最常见的方法是通过改性方法提升沸石的吸附容量. 同时,通过选择合适的水处理参数来进一步改善吸附性能. 天然沸石经氯化钙改性后,除氟效果显著提高,在初始氟化物浓度为100.0 mg·L−1时的最大氟化物吸附容量达到了1.77 mg·g−1[25]. 沸石中引入金属基氢氧化铝物质后,反应过程中形成的铝-氟化学键以及羟基离子的交换作用,能够实现对氟的有效去除(去除率> 92.00%,最大吸附量为 18.12 mg·g-1)[26]. 但是,由于HCO3−和CO32−对氟离子吸附表现出强烈的竞争效应,降低了氟化物的去除效率. 相比较于化学改性(盐改性、常用金属负载),利用镧锆稀土金属作为负载材料,吸附能力提升更加显著. 锆改性沸石饱和除氟容量达 19.84 mg·g−1,饱和吸附率为93.40%,除氟性能远优于沸石原矿(56.40%)和酸改性沸石(84.40%)[27]. 由于羟基的配体交换作用,镧改性沸石对氟的最大吸附容量更是高达 141.50 mg·g−1[28]. 值得注意的是,负载生物高分子材料壳聚糖的沸石,在 pH=5 时,对氟离子也达到了 104.00 mg·g−1的最大吸附容量[29].
值得注意的是,经过表面改性后沸石表面结构和性质发生改变,在反应体系中满足最佳pH小于pHpzc的规律,零电荷点提高. 使得在更宽的pH条件下,沸石吸附性能和去除效率提高. 然而,沸石类吸附材料还受到竞争离子浓度变化的影响. 虽然在低浓度下,去除效率几乎不受共存离子的影响,但在高浓度下,竞争效应则很强烈,其中HCO3−、CO32−、SO42−离子的影响最为明显,如表1所示. 因此,在寻找高效吸附除氟材料的基础上,也要对其改性方法以及环境影响参数进行深入研究.
表 1 沸石吸附性能比较Table 1. Comparison of the zeolite adsorption properties材料Material pH 温度/℃Temperature 竞争离子影响大小Competitive ion effect size 平衡时间Equilibrium time 最大吸附容量/(mg·g−1)Qmax 氯化钙改性沸石[25] 6 25±1 CO32− > SO42− > Cl− 360 min 1.77 氢氧化铝改性辉沸石[30] 5—8 23±2 HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− 180 min 12.12 铁改性辉沸石[31] 6.94 25 — 120 min 2.31 锰改性沸石[32] 9 25 SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 240 min 2.17 镧改性沸石[28] 6.3 25 HCO3− > SO42−≈Cl−≈NO3− — 141.50 镧铁改性沸石[33] 5—7 25 HCO3− > CO32− > SO42− — 2.64 黏土矿物因其吸附能力强、比表面积大,不同的黏土矿物具有不同的吸附性能,如表2所示. 天然黏土矿物的吸附容量低于1.00 mg·g−1,对其进行物理和化学改性后,吸附容量显著增加. 特别是在热处理后,海泡石的吸附容量高达169.95 mg·g-1[36]. 高岭土经机化激活后,其比表面积从15.11 m2·g−1增加至32.43 m2·g-1[18],加入聚羟基铁后,其对重金属的去除效率可达90.30%[38]. 对于黏土矿物来说,HCO3−似乎在活性位点与氟离子有竞争作用,竞争离子浓度的增加,氟离子去除效率明显降低. 此外,在某些情况下,黏土类吸附材料还表现出了可再生的特点. 经一次解吸后,蒙脱石以具有58.00%的氟去除率[39]. 采用稀土元素、铝元素等对其进行处理后,其再生效率在80.00%以上,而质量损失在10.00%以下[40],具有一定的可重复利用性.
表 2 黏土矿物吸附性能对比Table 2. Comparison of the adsorption properties of clay minerals材料Material 改性前吸附容量/(mg·g−1)q 改性处理Modified treatment pH 温度/℃Temperature 竞争离子影响大小Competitive ion effect size 平衡时间/minEquilibrium time 最大吸附容量/(mg·g−1)Qmax 高岭土[18] 0.11 球磨 3 50 HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 30 0.78 膨润土[34] 0.62 金属改性 3—10 25±2 HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 720 2.26 蒙脱石[35] 0.26 纳米材料 3 — — 60 11.15 海泡石[36] 0.94 热处理 3 25 HPO42− > HCO3− > SO42−> NO3− — 169.95 火山岩[37] 8.44 盐改性、热处理 4—11 55 HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 240 13.77 2.2 金属基吸附材料
金属基吸附材料具有比表面积大、孔道结构发达、表面活性强等特点,在物质的迁移转化中起着重要作用,被广泛用于水体中污染物的去除. 金属基吸附材料主要通过静电吸附、离子/配体交换等方式去除水体氟化物.
活性氧化铝吸附交换法是一种处理含氟废水最成熟的方法[41]. 该材料具有较高的分散度,丰富的孔结构. 因此,改性物质可分散并黏附于孔道结构中增大吸附材料比表面积,提高吸附容量和效率. 引入锰氧化物和氢氧化物,在较短的时间内,活性氧化铝最大的氟去除率从38.00%提高到67.00%[42]. 此外,羟基磷灰石作为分散相进入孔隙当中,吸附容量更是提高到了未改性活性氧化铝的5倍(14.40 mg·g−1)[43]. 而不同的合成方法也显著影响吸附性能. 采用溶胶-凝胶法制备的氧化铝对氟化物的去除率为活性氧化铝的1.35倍,60 min内的除氟率可达90.00%以上[44]. 合成的大孔活性氧化铝具有较高的孔隙率和比表面积,其吸附容量随着比表面积和孔隙率的增大而增大(最大吸附容量119.20 mg·g−1)[45]. 如图3所示活性氧化铝合成流程,与其他方法相比,水热法在吸附性能上提升并不明显,而共沉淀法、溶胶-凝胶法等在吸附性能上的提升则相对较大,这可能与其在高温煅烧后得到了更大的比表面积有关[46]. 如表3所示,不同的修饰合成方式使得吸附材料受不同环境因素的限制. 在酸性条件下,活性氧化铝具有良好的吸附除氟效果;而在竞争离子浓度升高后氟去除效率明显受到弱酸根离子竞争效应的影响.
表 3 活性氧化铝吸附性能对比Table 3. Comparison of activated alumina材料Material 合成方法Synthetic method pH 温度/℃Temperature 竞争离子影响大小Competitive ion effect size 平衡时间/minEquilibrium time 最大吸附容量/(mg·g−1)Qmax 介孔氧化铝[47] 水热法 3 25 — 180 8.25 镧铝改性氧化铝[48] 水热法 5—10 30 — 720 94.64 钙铝镧复合材料[49] 水热法 6.8 — PO43− >HCO3− > SO42− > NO3− > Cl− 180 29.30 大孔活性氧化铝[45] 溶胶-凝胶法 5 25 — 240 119.20 铁镁锆氢氧化物[50] 共沉淀法 3 25 SO42− > HΡO42− > Cl−≈HCO3−≈CO32− 60 88.55 锆铝镧金属复合材料[51] 共沉淀法 3 25 PO43− > SO42− > NO3− 400 90.48 镧镁改性活性氧化铝[52] — 7 25 CO32− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 120 8.56 硫酸氯化铝改性活性氧化铝[53] — 6—7 25 CO32− > HΡO42− > HCO3− > H2PO4− > SO42− > Cl−≈NO3− 120 6.46 氧化石墨烯氧化铝复合材料[54] 水热法 6 25 PO43− > HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 90 11.52 自然界中普遍存在着赤铁矿、磁铁矿、针铁矿和水铁矿等铁氧化物[55]. 以氧化铁涂层材料为载体,对氟化物的去除作用也是十分明显的,在低pH条件下,去除氟化物的效率可以达到90.00%[56]. 但是,铁氧化物的吸附容量较低,只有10.00 mg·g−1左右. 然而,经过乙醇处理后的氧化铁,拥有更高的比表面积和吸附速率,在2 min内达到吸附平衡容量的80.00%,最大吸附量可达60.80 mg·g−1,且在CO32−为100 mg·L−1时,该吸附剂仍能获得较高的氟化物去除效率[57].
稀土金属与氟有良好的亲和力,在水体净化方面表现出优异的吸附性能. 在30 min内,氧化镧可去除90.00%的氟化物,经过10次再生后,依然具有良好地吸附除氟能力[58]. 锆水合氧化物对氟离子的吸附具有很高的选择性,在 pH值为3时,其饱和吸附量更是达到 124.00 mg·g−1[59-60]. 但碍于成本因素,稀土元素一般都是用在负载方面. 将稀土离子与吸附材料结合,可显著提高吸附材料的吸附效果. 包覆镧活化氧化铝,在120 min可达到93.00%的去除率[61]、用氧化锆/沸石分子筛对氟的最大去除率可达95.48%[62]. 而以掺镧的交联凝胶为吸附材料,在50 mL不同浓度的水溶液中加入0.20 g吸附材料,其对氟离子的去除效果可达到98.80%的高去除率[63].
多金属比单一金属具有更高的氟去除率,单一的铁修饰分子筛的最大去除效率达到80.23%[64],而铁锆修饰分子筛在80 min后仍保持91.60%的高去除率[65]. 在中性条件下,180 min内,负载有氧化镁的活性氧化铝可以除去95.00%以上的氟化物[66]. 然而,镧镁双金属负载在吸附时间120 min内,对高氟水去除率就可以达到97.70%[52]. 与负载单一金属相比,氟去除率提高了2.00%—5.00%. 采用多元复合金属材料对水体氟进行吸附,可以弥补单种金属材料对水体氟修饰的不足,从而实现对水体氟的高效去除.
2.3 生物性吸附材料
生物性吸附材料因其价格低廉,无二次污染,且可回收利用广泛应用于水体氟污染治理当中,是一种良好的除氟吸附材料. 作为一种典型的吸附材料,壳聚糖通过其表面的氨基和羟基与氟发生交换作用,去除水体中的氟[29],如图4所示. 然而,未改性的壳聚糖吸附容量较低,需要对其进行表面修饰以提高其吸附量. 采用戊二醛、铈与壳聚糖进行交联与络合,合成了高吸附能力的改性壳聚糖吸附材料,其饱和吸附能力达到153.00 mg·g−1,是天然壳聚糖的11.6倍[67]. CO3 2−是影响改性壳聚糖吸附氟离子的重要阴离子,如表4所示. 但即使在含有复合阴离子的环境中,负载铈元素的壳聚糖对氟的吸附能力依然高达12.30 mg·g−1[76]. 然而,将稀土元素镧负载到壳聚糖基体上,吸收速率明显加快,20 min即可达到峰值,但其容易受到竞争离子(Cl−、SO42−、NO3−、HCO3−和CO32−)的影响. 特别是在HCO3−和CO3 2−的存在下,基本都没有去除氟化物,这可能是由于pH的变化以及阴离子的竞争效应[77].
表 4 生物质及工业废弃物吸附材料吸附性能对比Table 4. Comparison of the adsorption performance of biomass and industrial waste adsorption materials材料Material pH 温度/℃Temperature 竞争离子影响大小Competitive ion effect size 平衡时间/minEquilibrium time 最大吸附容量/(mg·g−1)Qmax 壳聚糖[67] 3 20 CO32− > NO3−≈ SO42− > Cl− 230 153.00 水葫芦叶柄[68] 4 30 HCO3− > SO42− > CO32−≈PO43−≈NO3− 210 5.00 象草叶[68] 4 30 HCO3− > SO42− > CO32− > NO3− > PO43− 210 7.00 废蘑菇堆生物炭[69] 6—8 25±2 SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 180 36.47 锆碳化花生壳[70] 3 25 HCO3− > SO42−≈Cl− 180 1.26 赤泥[71] 7—8 25 — 20 91.28 煤渣[72] 2 30 — 300 15.46 石灰污泥废物[73] 6.75 27 — 30 0.94 钢渣[74] 3 25 SO42− > Cl− > HCO3− 10 1.23 废泥浆[75] 5 20±1 PO43− > SO42− > NO3− 60 27.20 以动植物为原料制成的生物炭具有多孔性、高比表面积等特性,是一种极具应用前景的吸附材料. 在生物炭类吸附材料,在酸性条件下表现出良好的除氟效果. 由于氟化物在吸附位点上的扩散增强以及对吸附材料活性较低位点的利用,使得蛋壳提取物在pH=3时,对氟的去除效率更达到了99.00%. 在实际应用中,尽管竞争离子存在,但其除氟率仍然保持在80.00%以上[78]. 如表4所示,吸附剂的吸附性能明显受到反应体系中pH值和竞争离子的影响. 在低pH条件下,涂有氢氧化铝的废蘑菇堆生物炭可以利用静电吸附和配体交换作用来去除氟离子,最大吸附量为36.50 mg·g−1,浓度降低到1 mg·L−1以下,符合饮用水水质标准[69]. 虽然水葫芦叶和象草叶经过碱性蒸汽处理,但其依然在酸性条件下,能够去除85.00%氟化物[68],却在反应过程中受到竞争离子的影响,使得吸附效果的降低.
2.4 工业废弃物吸附材料
工业废弃物通过物理、化学作用,逐步向环境中释放出有毒有害物质,严重危害人类的身体健康. 必须对其进行合理处置,实现其资源化利用,以期减少对人体危害. 赤泥是制铝工业提取氧化铝时排出的工业固体废物,赤泥中铁、铝及钠后的残渣仍含适量的活性物质[79],以该残渣为吸附剂,实验条件下对氟的去除率可达95.00%以上[80],但其吸附容量仅为1.21 mg·g−1. 如表4所示,其中经过煅烧活化后的赤泥, 20 min内迅速地达到反应平衡,饱和吸收容量更是高达91.28 mg·g−1,远高于未处理的吸附容量. 同时,处理后出水氟浓度为0.69 mg·L−1,低于国家饮用水标准1 mg·L−1[71]. 矿渣经过镧和铝在表面负载修饰后,会形成大量的杆状复合金属氧化物,其无定型结构为氟离子去除提供了良好的条件,通过静电吸附作用和离子/配体交换作用,增加氟的去除[81]. 虽然,赤泥和矿渣具有良好的除氟效果,但存在固液难以分离的缺陷. 而钢渣对氟离子有较强的吸附作用,且液固分离非常快,对氟离子的去除率在4 s内达到80.98%,2 min时达到最大去除率(99.58%),但会随着共存离子浓度的增大,SO42−、HCO3−不同程度地抑制氟的吸附[74],使得吸附容量减少. 工业废弃物尽管具有很好的除氟性能,降低了氟化物对水体的危害,但由于其自身含有剧毒、有污染的金属,在水处理的过程中会导致新的污染现象的发生.
3. 纳米吸附除氟材料(Nano-adsorption of fluoride removal materials)
3.1 常见纳米吸附材料
由于纳米吸附材料不仅仅具有高比表面积、高表面活性等优点,还具有催化电位和高活性等独特的特性,使其成为比传统材料更好的吸附材料[82]. 在污水处理领域具有广阔的应用前景,纳米材料主要通过静电吸附作用、配体或者离子交换作用去除水体中的氟. 然而,纳米吸附材料因其组成、形貌、结构的差异具有不同的除氟效果. 如介孔结构的氧化钙空心球,拥有发达的孔结构,比表面积更大,且其表面羟基与氟离子发生交换作用,其最大吸附量达到181.96 mg·g−1[83] (图5 a),同样地,氢氧碳酸铈纳米球其表面羟基、碳酸根等可以与氟离子发生交换反应,但在低初始浓度的氟离子溶液中具有极高的去除效率(图5 b)[84]. 同时,纳米球的薄层介孔结构进一步强化了材料的传递能力,提高了吸附反应速率和吸附容量[85]. 多孔片状的纳米材料也表现出了良好氟化物的吸附能力,表面吸附位点增多,在pH=2—11的范围内,通过羟基和表面碳酸盐与氟离子的交换作用,有效地去除水中的氟化物,最大吸附量超过185.50 mg·g−1[86],见图5 c. 然而,同一物质形态的差异也会影响其对氟离子的吸附性能. 例如,纳米棒、八面体和纳米立方体形貌的CeO2对氟离子的最大吸附量分别为71.50、28.30、7.00 mg·g−1[87].
磁性纳米材料由于其独特的磁性特性,可以通过磁场有效地分离氟化物离子,从而更容易实现其固液分离及吸附材料的回收利用. 磁性纳米体系的表面具有活性,可以通过表面修饰实现对其物理化学性质的调控. 经过改性纳米级Fe3O4分散性更好,随着吸附材料用量的添加和反应时间的延长,除氟效率相应地提高,虽然CO32−对除氟效果影响稍大,但对其去除率仍在70.00%以上,在适宜的条件下,更是达到84.80%[88]. 介孔结构的Fe3O4纳米粒子,在初始浓度为200.0 mg·L−1时,最大吸附能力达到70.64 mg·g−1. 即使有竞争阴离子存在,它仍然可以实现80.00%的高去除率,这当中,羟基基团的交换机制起了至关重要的作用[89].
在实际应用中,纳米体系会产生易于团聚,易于氧化、难以分离等问题,进而影响到水处理效率. 因此,逐步发展出了复合改性体系. 以纳米铁为例,共有四大复合改性体系,即:负载、改性稳定性、包埋以及双金属体系. 如图6a所示,负载在其他材料(活性炭)表面和孔隙之中,改善易于材料团聚的缺陷,提高分散性. 而改性稳定化体系则趋向于表面改性,多利用淀粉、壳聚糖、羧甲基纤维素等有机物,对其进行功能化修饰,以增强其水溶性、分散性,增加空间位阻,促进电子转移,从而高效地除去水中的氟离子(图6 b). 包埋体系不仅具有更高的氟吸附性能,还具有更好的固-液分离特性(图6 c). 双金属体系能够通过使用不同的金属元素的特性相互协作来移除水中的氟化物,吸附容量显著提高(图6 d).
3.2 新型纳米吸附材料
新型纳米吸附材料主要有碳基纳米材料(石墨烯、碳纳米管等)[82]、纳米复合金属氧化物材料(钙、铝、铁、镧、铈等)以及其他类纳米吸附材料(金属有机框架). 纳米复合金属氧化物相比较于其他纳米材料,发展应用较早. 而碳基纳米材料和金属有机框架在20世纪末21世纪初才开始被逐渐认识研究,随着对纳米材料的研究不断深入,两者应用前景逐渐展现.
其中,碳基纳米材料被认为是去除污染物的最佳吸附剂. 然而,碳纳米管用于除氟的潜力很少被研究. 同时,实验发现碳纳米管的除氟吸附容量(2.83 mg·g−1)[91]和去除率(71.00%)[92]明显小于石墨烯. 相对来说,石墨烯是碳纳米管良好的替代品. 石墨烯是人类已知的最薄材料,具有单层碳原子网结构,电子在其中也能高速运动,是一种性能优良的氟离子吸附材料. 与碳纳米管相比,由于石墨烯吸附剂具有两个可用于污染物吸附的接触面[82],因此大大提高了反应效率,是水处理的理想材料. 研究发现,在稀土锆及生物材料壳聚糖的修饰下,该体系对水中重金属离子的去除率从84.80%提升到97.17%[93],而氧化石墨烯和氧化铝复合体系的去除率更是达到99.50%[54]. 然而,石墨烯复合材料在循环利用过程中,因其分子链断裂,材料分散,影响了对氟化物的去除效果,不具有重复利用性. 值得注意的是,另外一类具有较高脱附再生速率的纳米材料—金属有机框架却表现出较高的脱附再生吸附性能.
金属有机框架作为一类新型的金属离子或金属簇和有机配体组成的有机-无机杂化材料,具有孔道结构多样,孔道尺寸可调,配位点不饱和,功能可设计等诸多优势[94]. 与其他吸附材料比较,可回收性高,可循环吸附并固定氟离子,在较大的酸碱度变化区间,能有效地去除水体中的氟化物,以离子交换机制为主来去除水体氟化物[95]. 由于改性方法和材料的差异,在环境因子的调控下,会产生不同的吸附能力和去除率. 前期研究发现 pH值和阴离子种类等因素会对体系中氟去除产生影响,其中SO42−、 NO3−、Cl−等离子对吸附材料除氟性能影响较小,但PO43−、HCO3−、CO32−等离子由于水解作用,与氟离子产生竞争效应,从而使吸附材料的氟去除率受到很大的影响. 但从氟化物去除率以及自然水体中竞争离子的浓度来看,这种影响几乎不考虑. 其中,MIL-96 (Al)对pH响应性大,在强酸条件下,去除效率几乎可达100%且解吸再生去除率在60.00%以上[96],而MOF-801 对 pH在2—10之间亦有良好的去除效率[95]. 然而,UiO-66 (Zr)则表现出不同的趋势,在pH=3—6范围内随着pH的增大而增大,pH=5—7 范围内的吸附效果最好;但是在 pH升至8—11时,去除效果明显降低;在 pH为11时,去除率下降至42.00%[97]. 这可能是由于在不同的pH下,吸附材料表面的电荷发生改变,使得去除率降低. 此外,经解吸和再生处理后,金属有机框架的除氟率依然达到了70.00%. 而Zr-MOFs在6次脱附后,其对氟的去除率依然在85%以上,且可循环利用[98],如表5所示.
表 5 纳米除氟吸附材料吸附性能对比Table 5. Comparison of adsorption properties of new nano-fluoride adsorption materials材料Material pH 温度/℃Temperature 竞争离子影响大小Competitive ion effect size 平衡时间/minEquilibrium time 最大吸附容量/(mg·g−1)Qmax 介孔氧化钙[83] 6.5 25 CO32− > SO42− > Cl− 90 181.96 氢氧碳酸铈纳米球[84] 7±0.2 25 CO32− > HCO3− > Cl− > SO42− ≈ PO43− ≈ NO3− 240 48.15 多孔氧化镁纳米片[86] 7 25 PO43− > CO32− > HCO3− > SO42−≈Cl− ≈NO3− 60 185.50 石墨烯[99] 7 25 — 60 35.59 改性石墨烯[93] 3—11 25 — 45 29.06 氧化石墨烯复合材料[54] 6 25 PO43− > HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 90 11.83 MOF-801[95] 2—10 30 PO43− > HCO3− > SO42−≈Cl− ≈ NO3− 120 40.26 MIL-96(Al)[96] 3—11 25 CO32− > SO42−≈Cl−≈NO3− 90 42.19 Zr-MOFs[97] 3—9 25 SO42− > PO43−≈CO32−≈HCO3−≈ Cl− ≈NO3− 20 103.95 UiO-66(Zr)[98] 5—7 25 PO43− > HCO3− >CO32− > SO42− ≈ Cl− ≈ NO3− 240 295.00 Al-FuMOF[100] 2—9 20 SO42− > CO32− > HCO3− > Cl− > PO43− > NO3− 1440 600.00 相比传统的除氟材料,新型纳米除氟吸附材料具有高吸附容量、高且稳定的吸附效率及耐久性的优势. 能够在更宽的 pH 范围内依然保持着良好的氟去除效率,在自然水体中几乎不受竞争离子的影响,在不同的水质条件下保持高效地除氟性能. 同时,新型纳米除氟材料具有良好的循环再生吸附性能,能够反复利用于水体氟污染当中,从而降低了材料成本. 值得注意的是,新型除氟吸附材料不容易在水污染处理过程中产生二次污染,具有绿色环保性. 此外,由于其低成本且易于制备,可以在大规模应用中实现经济与环境双重效益. 基于此,新型纳米除氟材料成为一类极具应用前景的除氟吸附材料.
4. 总结与展望(Summary and outlook)
吸附法具有除氟效果好、操作简便等优点,被广泛用于饮用水、工业含氟废水的处理. 然而,不同类别的吸附除氟材料却存在着许多问题. 对天然吸附材料和生物质吸附材料来说,存在着选择性差、吸附容量小、反应速率慢及易受其他因素干扰的问题. 同时,生物质吸附材料的来源和制备工艺也是需要考虑的另一个问题. 金属基吸附材料在吸附过程中,反应活性逐渐减弱,去除效率降低. 且金属离子本身在水处理过程也可能产生一类有毒有害的污染物质,危害人体和环境健康. 此外,作为资源化利用的工业废弃物材料,虽然具有廉价易得的优点,但本身含有的有毒有害物质,导致新一类环境污染现象的发生. 值得注意的是,吸附除氟材料大多都具有再生难度大、成本高的缺陷,其次材料本身存在的稳定性和耐久性问题,使其能否在复杂多变的水体环境中实现对含氟物质的高效稳定去除,还需进一步深入研究.
因此,探索吸附除氟材料的制备改性材料、方法和工艺,充分发挥材料优势和协同作用,拓宽吸附除氟材料的应用范围;寻找研发更加环保、经济、高效、稳定、持久的新型吸附除氟材料,实现对水中氟化物的高效处理与修复,以便更好地满足实际需求是今后水体除氟吸附材料的研究发展方向. 同时,也要加深对于水体氟化物去除的机制及影响因素的研究,从而更好地完善完备制备工艺、方法以及吸附材料的改性. 能根据水体污染和水情状况,综合运用各种去除氟化物的技术,如沉淀法、电化学法等,最终达到对水体中氟化物进行高效去除和控制,降低水体中氟化物的污染风险. 此外,在秉持高效率、高稳定性、低成本目标的同时,也要注重资源与环境的保护,采用符合经济效益的方法,促进人与环境的可持续发展.
-
表 1 沸石吸附性能比较
Table 1. Comparison of the zeolite adsorption properties
材料Material pH 温度/℃Temperature 竞争离子影响大小Competitive ion effect size 平衡时间Equilibrium time 最大吸附容量/(mg·g−1)Qmax 氯化钙改性沸石[25] 6 25±1 CO32− > SO42− > Cl− 360 min 1.77 氢氧化铝改性辉沸石[30] 5—8 23±2 HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− 180 min 12.12 铁改性辉沸石[31] 6.94 25 — 120 min 2.31 锰改性沸石[32] 9 25 SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 240 min 2.17 镧改性沸石[28] 6.3 25 HCO3− > SO42−≈Cl−≈NO3− — 141.50 镧铁改性沸石[33] 5—7 25 HCO3− > CO32− > SO42− — 2.64 表 2 黏土矿物吸附性能对比
Table 2. Comparison of the adsorption properties of clay minerals
材料Material 改性前吸附容量/(mg·g−1)q 改性处理Modified treatment pH 温度/℃Temperature 竞争离子影响大小Competitive ion effect size 平衡时间/minEquilibrium time 最大吸附容量/(mg·g−1)Qmax 高岭土[18] 0.11 球磨 3 50 HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 30 0.78 膨润土[34] 0.62 金属改性 3—10 25±2 HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 720 2.26 蒙脱石[35] 0.26 纳米材料 3 — — 60 11.15 海泡石[36] 0.94 热处理 3 25 HPO42− > HCO3− > SO42−> NO3− — 169.95 火山岩[37] 8.44 盐改性、热处理 4—11 55 HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 240 13.77 表 3 活性氧化铝吸附性能对比
Table 3. Comparison of activated alumina
材料Material 合成方法Synthetic method pH 温度/℃Temperature 竞争离子影响大小Competitive ion effect size 平衡时间/minEquilibrium time 最大吸附容量/(mg·g−1)Qmax 介孔氧化铝[47] 水热法 3 25 — 180 8.25 镧铝改性氧化铝[48] 水热法 5—10 30 — 720 94.64 钙铝镧复合材料[49] 水热法 6.8 — PO43− >HCO3− > SO42− > NO3− > Cl− 180 29.30 大孔活性氧化铝[45] 溶胶-凝胶法 5 25 — 240 119.20 铁镁锆氢氧化物[50] 共沉淀法 3 25 SO42− > HΡO42− > Cl−≈HCO3−≈CO32− 60 88.55 锆铝镧金属复合材料[51] 共沉淀法 3 25 PO43− > SO42− > NO3− 400 90.48 镧镁改性活性氧化铝[52] — 7 25 CO32− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 120 8.56 硫酸氯化铝改性活性氧化铝[53] — 6—7 25 CO32− > HΡO42− > HCO3− > H2PO4− > SO42− > Cl−≈NO3− 120 6.46 氧化石墨烯氧化铝复合材料[54] 水热法 6 25 PO43− > HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 90 11.52 表 4 生物质及工业废弃物吸附材料吸附性能对比
Table 4. Comparison of the adsorption performance of biomass and industrial waste adsorption materials
材料Material pH 温度/℃Temperature 竞争离子影响大小Competitive ion effect size 平衡时间/minEquilibrium time 最大吸附容量/(mg·g−1)Qmax 壳聚糖[67] 3 20 CO32− > NO3−≈ SO42− > Cl− 230 153.00 水葫芦叶柄[68] 4 30 HCO3− > SO42− > CO32−≈PO43−≈NO3− 210 5.00 象草叶[68] 4 30 HCO3− > SO42− > CO32− > NO3− > PO43− 210 7.00 废蘑菇堆生物炭[69] 6—8 25±2 SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 180 36.47 锆碳化花生壳[70] 3 25 HCO3− > SO42−≈Cl− 180 1.26 赤泥[71] 7—8 25 — 20 91.28 煤渣[72] 2 30 — 300 15.46 石灰污泥废物[73] 6.75 27 — 30 0.94 钢渣[74] 3 25 SO42− > Cl− > HCO3− 10 1.23 废泥浆[75] 5 20±1 PO43− > SO42− > NO3− 60 27.20 表 5 纳米除氟吸附材料吸附性能对比
Table 5. Comparison of adsorption properties of new nano-fluoride adsorption materials
材料Material pH 温度/℃Temperature 竞争离子影响大小Competitive ion effect size 平衡时间/minEquilibrium time 最大吸附容量/(mg·g−1)Qmax 介孔氧化钙[83] 6.5 25 CO32− > SO42− > Cl− 90 181.96 氢氧碳酸铈纳米球[84] 7±0.2 25 CO32− > HCO3− > Cl− > SO42− ≈ PO43− ≈ NO3− 240 48.15 多孔氧化镁纳米片[86] 7 25 PO43− > CO32− > HCO3− > SO42−≈Cl− ≈NO3− 60 185.50 石墨烯[99] 7 25 — 60 35.59 改性石墨烯[93] 3—11 25 — 45 29.06 氧化石墨烯复合材料[54] 6 25 PO43− > HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− 90 11.83 MOF-801[95] 2—10 30 PO43− > HCO3− > SO42−≈Cl− ≈ NO3− 120 40.26 MIL-96(Al)[96] 3—11 25 CO32− > SO42−≈Cl−≈NO3− 90 42.19 Zr-MOFs[97] 3—9 25 SO42− > PO43−≈CO32−≈HCO3−≈ Cl− ≈NO3− 20 103.95 UiO-66(Zr)[98] 5—7 25 PO43− > HCO3− >CO32− > SO42− ≈ Cl− ≈ NO3− 240 295.00 Al-FuMOF[100] 2—9 20 SO42− > CO32− > HCO3− > Cl− > PO43− > NO3− 1440 600.00 -
[1] 郑丹阳, 耿存珍. 水体除氟方法的最新研究进展[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2014, 39(11): 31-34. ZHENG D Y, GENG C Z. Research progress for removing fluorine from water[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2014, 39(11): 31-34 (in Chinese).
[2] 2022 年中国生态环境状况公报(摘录)[J]. 环境保护, 2023, 51(Z2): 64-81. China ecological environment status bulletin 2022 (Excerpt)[J]. Environmental Protection, 2023, 51(Z2): 64-81(in Chinese).
[3] 张启贤, 张成, 徐瑶, 等. 高氟水处理技术发展现状[J]. 绿色科技, 2021, 23(12): 46-49. ZHANG Q X, ZHANG C, XU Y, et al. Treatment status of high fluorine water[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2021, 23(12): 46-49 (in Chinese).
[4] GAO Z J, SHI M J, ZHANG H Y, et al. Formation and in situ treatment of high fluoride concentrations in shallow groundwater of a semi-arid region: Jiaolai basin, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(21): 8075. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17218075 [5] DAS S K, DAS R K. Investigation on fluoride concentration in ground water by hydrochemical pathway[J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 101(15): 2551-2567. doi: 10.1080/03067319.2019.1694672 [6] DUAN Q, JIAO J, CHEN X, et al. Association between water fluoride and the level of children’s intelligence: A dose-response metaanalysis[J]. Public Health, 2018, 154: 87-97. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2017.08.013 [7] TOMAR V, PRASAD S, KUMAR D. Adsorptive removal of fluoride from water samples using Zr-Mn composite material[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2013, 111: 116-124. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2013.04.007 [8] DAVARKHAH R, ZEINAB P, HOSSEIN M A, et al. Co-application of coagulation and electrochemical processes to remove fluoride from water[J]. FLUORIDE, 2020, 53(3): 483-490. [9] 杨彬, 樊贵盛, 梁镇海. 膜法水处理技术与传统方法的比较[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2004, 35(2): 155-159,163. YANG B, FAN G S, LIANG Z H. The comparison of membrane technology and conventional methods for water treatment[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2004, 35(2): 155-159,163 (in Chinese).
[10] ARAHMAN N, MULYATI S, LUBIS M R, et al. The removal of fluoride from water based on applied current and membrane types in electrodialyis[J]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 2016, 191: 97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluchem.2016.10.002 [11] ARAR O, YAVUZ E, YUKSEL U, et al. Separation of low concentration of fluoride from water by electrodialysis (ED) in the presence of chloride and sulfate ions[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2009, 44(7): 1562-1573. doi: 10.1080/01496390902775943 [12] SADAT H S, HOSSEIN M A. Removal of fluoride from drinking water by freezing technology[J]. Fluoride, 2019, 52(3): 231-247. [13] KARMAKAR S, MUKHERJEE J, MUKHERJEE S. Biosorption of fluoride by water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes) from contaminated water[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2018, 15(4): 801-810. doi: 10.1007/s13762-017-1439-3 [14] LOGANATHAN P, VIGNESWARAN S, KANDASAMY J, et al. Defluoridation of drinking water using adsorption processes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 248/249: 1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.12.043 [15] LIU X W, WANG Y X, CUI X Y, et al. Fluoride removal from wastewater by natural and modified gibbsite[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2021, 66(1): 658-668. [16] SIVASAMY A, SINGH K P, MOHAN D, et al. Studies on defluoridation of water by coal-based sorbents[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2001, 76(7): 717-722. [17] CORRAL-CAPULIN N G, VILCHIS-NESTOR A R, GUTIÉRREZ-SEGURA E, et al. Comparison of the removal behavior of fluoride by Fe3+ modified geomaterials from water[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2019, 173: 19-28. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2019.03.003 [18] MEENAKSHI S, SUNDARAM C S, SUKUMAR R. Enhanced fluoride sorption by mechanochemically activated kaolinites[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 153(1/2): 164-172. [19] 段平洲, 贾晓波, 后希康, 等. 磁性铝基 MOF 的表征和对水体中氟化物吸附性能研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(5): 1139-1147. DUAN P Z, JIA X B, HOU X K, et al. Characterization and adsorption properties of magnetic Al-MOF composite for fluoride[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 34(5): 1139-1147 (in Chinese).
[20] CHAKRABORTY A, NASKAR M K. Study on the synthesis and structural properties of zeolite A-MgO composite for defluoridation of water[J]. Transactions of the Indian Ceramic Society, 2021, 80(3): 199-207. doi: 10.1080/0371750X.2021.1978864 [21] 张静, 陈男, 冯传平. 铁负载壳聚糖颗粒吸附除氟研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2015, 41(7): 31-36. ZHANG J, CHEN N, FENG C P. Adsorption of fluoride by iron-impregnated chitosan(Fe-CTS)granule[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2015, 41(7): 31-36 (in Chinese).
[22] CHEN N, ZHANG Z Y, FENG C P, et al. Fluoride removal from water by granular ceramic adsorption[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 348(2): 579-584. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2010.04.048 [23] LU W J, ZHANG C H, SU P D, et al. Research progress of modified natural zeolites for removal of typical anions in water[J]. Environmental Science:Water Research & Technology, 2022, 8(10): 2170-2189. [24] 陈连军, 陈劲松. 载镧天然沸石对水体中 F-的去除性能研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2022, 45(4): 38-46. CHEN L J, CHEN J S. Study on the removal performance of lanthanum-loaded natural zeolite for F- in water[J]. Environmental Science& Technology, 2022, 45(4): 38-46 (in Chinese).
[25] ZHANG Z J, TAN Y, ZHONG M F. Defluorination of wastewater by calcium chloride modified natural zeolite[J]. Desalination, 2011, 276(1/2/3): 246-252. [26] CHEN J B, YANG R J, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Removal of fluoride from water using aluminum hydroxide-loaded zeolite synthesized from coal flyash[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 421: 126817. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126817 [27] 陈文, 陈东, 刘林艳. 锆改性沸石的动态除氟研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2012, 35(4): 64-67. CHEN W, CHEN D, LIU L Y. Dynamic fluoride removal of zirconium modified natural zeolite[J]. Non-Metallic Mines, 2012, 35(4): 64-67 (in Chinese).
[28] YANG R J, CHEN J B, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Performance and mechanism of lanthanum-modified zeolite as a highly efficient adsorbent for fluoride removal from water[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 307: 136063. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136063 [29] DÍAZ-FLORES P E, ARCIBAR-OROZCO J A, FLORES-ROJAS A I, et al. Synthesis of a chitosan-zeolite composite modified with La(III): Characterization and its application in the removal of fluoride from aqueous systems[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2021, 232(6): 1-14. [30] DESSALEGNE M, ZEWGE F, DIAZ I. Aluminum hydroxide supported on zeolites for fluoride removal from drinking water[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2017, 92(3): 605-613. [31] SUN Y B, FANG Q H, DONG J P, et al. Removal of fluoride from drinking water by natural stilbite zeolite modified with Fe(III)[J]. Desalination, 2011, 277(1/2/3): 121-127. [32] YANG B, SUN G R, QUAN B X, et al. An experimental study of fluoride removal from wastewater by Mn-Ti modified zeolite[J]. Water, 2021, 13(23): 3343. doi: 10.3390/w13233343 [33] JIA C M, FAN Y J, JIANG R L, et al. Preparation of La(III), Fe(III) modified zeolite molecular sieves for the removal of fluorine from water[J]. Water, 2022, 14(19): 2946. doi: 10.3390/w14192946 [34] THAKRE D, RAYALU S, KAWADE R, et al. Magnesium incorporated bentonite clay for defluoridation of drinking water[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 180(1/2/3): 122-130. [35] NAGHIZADEH A, GHOLAMI K. Bentonite and montmorillonite nanoparticles effectiveness in removal of fluoride from water solutions[J]. Journal of Water and Health, 2017, 15(4): 555-565. doi: 10.2166/wh.2017.052 [36] LEE J I, HONG S H, LEE C G, et al. Experimental and model study for fluoride removal by thermally activated sepiolite[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 241: 125094. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125094 [37] 宋倩. 火山岩基多孔陶粒吸附去除地下水中氟的特性和机理研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2018. SONG Q. Performance and mechanism of fluoride adsorption from aqueous solution by granular ceramic adsorbent based on native volcanic rocks[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2018 (in Chinese).
[38] MUSCHIN T, ZULCHIN H, JIA M L. Adsorption behavior of polyhydroxy-iron-modified coal-bearing Kaolin for fluoride removal[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2021, 6(13): 3075-3083. doi: 10.1002/slct.202100226 [39] TOR A. Removal of fluoride from an aqueous solution by using montmorillonite[J]. Desalination, 2006, 201(1/2/3): 267-276. [40] ZHANG S Y, LYU Y, SU X S, et al. Removal of fluoride ion from groundwater by adsorption on lanthanum and aluminum loaded clay adsorbent[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(5): 401. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-5205-x [41] 王晨晨, 段颖, 徐微, 等. 活性氧化铝改性除氟性能研究[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2014, 41(2): 248-252. WANG C C, DUAN Y, XU W, et al. Performance of modified activated alumina for fluoride removal[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2014, 41(2): 248-252 (in Chinese).
[42] GAO Y J, YOU K, FU J X, et al. Manganese modified activated alumina through impregnation for enhanced adsorption capacity of fluoride ions[J]. Water, 2022, 14(17): 2673. doi: 10.3390/w14172673 [43] TOMAR G, THAREJA A, SARKAR S. Enhanced fluoride removal by hydroxyapatite-modified activated alumina[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2015, 12(9): 2809-2818. doi: 10.1007/s13762-014-0653-5 [44] RAFIQUE A, ALI AWAN M, WASTI A, et al. Removal of fluoride from drinking water using modified immobilized activated alumina[J]. Journal of Chemistry, 2013, 2013: 1-7. [45] YU C L, LIU L, WANG X D, et al. Fluoride removal performance of highly porous activated alumina[J]. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2023, 106(2): 471-479. doi: 10.1007/s10971-022-05722-2 [46] COLLEDGE G T, OUTRAM J G, MILLAR G J. Improved remediation of fluoride contaminated water using titania-alumina sorbents[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2022, 49: 103091. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.103091 [47] XU N C, LIU Z, DONG Y P, et al. Controllable synthesis of mesoporous alumina with large surface area for high and fast fluoride removal[J]. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(14): 15253-15260. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.06.164 [48] JIANG G M, JIN L F, PAN Q L, et al. Structural modification of aluminum oxides for removing fluoride in water: Crystal forms and metal ion doping[J]. Environmental Technology, 2022, 43(21): 3248-3261. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2021.1921044 [49] XIANG W, ZHANG G K, ZHANG Y L, et al. Synthesis and characterization of cotton-like Ca-Al-La composite as an adsorbent for fluoride removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 250: 423-430. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.118 [50] ZHANG Y Z, HUANG K. Defluoridation behavior of layered Fe-Mg-Zr hydroxides and its continuous purification of groundwater[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2019, 578. [51] ZHOU J, ZHU W K, YU J, et al. Highly selective and efficient removal of fluoride from ground water by layered Al-Zr-La Tri-metal hydroxide[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 435: 920-927. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.108 [52] 张小磊, 李尚明, 李红艳, 等. 负载镧镁改性活性氧化铝的除氟性能[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(8): 4189-4195. ZHANG X L, LI S M, LI H Y, et al. Adsorption fluoride removal by La-Mg-loaded modified activated alumina[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(8): 4189-4195 (in Chinese).
[53] 王晨晨, 段颖, 徐微, 等. 硫酸与氯化铝复合改性活性氧化铝吸附除氟研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2014, 40(8): 29-32,37. WANG C C, DUAN Y, XU W, et al. Study of defluorination by composite modified activated alumina adsorption[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2014, 40(8): 29-32,37 (in Chinese).
[54] XU N C, LI S X, LI W, et al. Removal of fluoride by graphene oxide/alumina nanocomposite: Adsorbent preparation, characterization, adsorption performance and mechanisms[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2020, 5(6): 1818-1828. doi: 10.1002/slct.201904867 [55] 杨小洪, 魏世勇, 李永峰. 几种铁氧化物吸附氟的能力及影响因素的研究[J]. 湖北民族学院学报(自然科学版), 2009, 27(3): 248-253. YANG X H, WEI S Y, LI Y F. Fluoride adsorption capacity and influence factors of several iron oxides[J]. Journal of Hubei University for Nationalities (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 27(3): 248-253 (in Chinese).
[56] 高乃云, 徐迪民, 范瑾初, 等. 氧化铁涂层砂改性滤料除氟性能研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2000, 16(1): 1-4. GAO N Y, XU D M, FAN J C, et al. A study on the performance of modified filter media using iron oxide coated sand for fluoride removal[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2000, 16(1): 1-4 (in Chinese).
[57] ZHANG C, LI Y Z, WANG T J, et al. Synthesis and properties of a high-capacity iron oxide adsorbent for fluoride removal from drinking water[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 425: 272-281. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.06.159 [58] NAGENDRA RAO C R, KARTHIKEYAN J. Removal of fluoride from water by adsorption onto lanthanum oxide[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2012, 223(3): 1101-1114. [59] 周春琼, 邓先和, 刘海敏, 等. 吸附法处理含氟水溶液的研究与应用[J]. 水处理技术, 2006, 32(1): 1-5. ZHOU C Q, DENG X H, LIU H M, et al. Treatment of aqueous solution containing fluoride by absorption process[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2006, 32(1): 1-5 (in Chinese).
[60] DOU X M, MOHAN D, PITTMAN C U, et al. Remediating fluoride from water using hydrous zirconium oxide[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 198/199: 236-245. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.084 [61] 郑利祥, 高杰, 杨建超. 载镧活性氧化铝制备及含氟废水除氟因素研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(9): 87-92. ZHENG L X, GAO J, YANG J C. Study on preparation of La-loaded active alumina and factors affecting fluoride removal for fluorinecontaining wastewater[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46(9): 87-92 (in Chinese).
[62] 郜玉楠, 茹雅芳, 王静, 等. 微米氧化锆/沸石分子筛处理高氟地下水的研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2020, 36(3): 49-53. GAO Y N, RU Y F, WANG J, et al. Treatment of high fluoride groundwater by micron zirconia/zeolite molecular sieve[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2020, 36(3): 49-53 (in Chinese).
[63] ZHOU Y M, YU C X, SHAN Y. Adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution on La3+-impregnated cross-linked gelatin[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2004, 36(2): 89-94. doi: 10.1016/S1383-5866(03)00167-9 [64] BILICI BASKAN M, BIYIKLI A R. The adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solutions by Fe, Mn, and Fe/Mn modified natural clinoptilolite and optimization using response surface methodology[J]. Water Environment Research:a Research Publication of the Water Environment Federation, 2021, 93(4): 620-635. doi: 10.1002/wer.1464 [65] YANG B, JIA C M, SUN G R, et al. Enhancing the adsorption function of F- by iron and zirconium doped zeolite: Characterization and parameter optimization[J]. Environmental Engineering Research, 2023, 28(2): 220010. [66] MALIYEKKAL S M, SHUKLA S, PHILIP L, et al. Enhanced fluoride removal from drinking water by magnesia-amended activated alumina granules[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 140(1/2/3): 183-192. [67] ZHU T Y, ZHU T H, GAO J, et al. Enhanced adsorption of fluoride by cerium immobilized cross-linked chitosan composite[J]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 2017, 194: 80-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluchem.2017.01.002 [68] MANNA S, ROY D, SAHA P, et al. Defluoridation of aqueous solution using alkali-steam treated water hyacinth and elephant grass[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2015, 50: 215-222. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2014.12.003 [69] CHEN G J, PENG C Y, FANG J Y, et al. Biosorption of fluoride from drinking water using spent mushroom compost biochar coated with aluminum hydroxide[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2016, 57(26): 12385-12395. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2015.1049959 [70] ALAGUMUTHU G, RAJAN M. Kinetic and equilibrium studies on fluoride removal by zirconium (IV): Impregnated groundnut shell carbon[J]. Hemijska Industrija, 2010, 64(4): 295-304. doi: 10.2298/HEMIND100307017A [71] 魏宁, 栾兆坤, 王军, 等. 铝改性赤泥吸附剂的制备及其除氟效能的研究[J]. 无机化学学报, 2009, 25(5): 849-854. WEI N, LUAN Z K, WANG J, et al. Preparation of modified red mud with aluminum and its adsorption characteristics on fluoride removal[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2009, 25(5): 849-854 (in Chinese).
[72] 李彦儒. 超声波辅助铁改性煤渣的制备及除氟性能研究[D]. 临汾: 山西师范大学, 2013. LI Y R. Preparation of ultrasonic assisting ferric chloride modified cinder and fluoride in performance research[D]. Linfen: Shanxi Normal University, 2013 (in Chinese).
[73] MOHAN R, BORA A J, DUTTA R K. Fluoride removal from water by lime-sludge waste[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2018, 112: 19-33. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2018.21918 [74] 朱殿梅, 邵波霖, 钟可意, 等. 镧改性钢渣对水中氟离子的吸附性能[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(4): 1167-1176. ZHU D M, SHAO B L, ZHONG K Y, et al. Adsorption performance of lanthanum-modified steel slag towards fluoride ion in water[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2023, 17(4): 1167-1176 (in Chinese).
[75] KEMER B, OZDES D, GUNDOGDU A, et al. Removal of fluoride ions from aqueous solution by waste mud[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 168(2/3): 888-894. [76] 张伟彬. 改性壳聚糖微球处理含氟废水的研究[J]. 电镀与环保, 2020, 40(2): 74-76. ZHANG W B. Study on treatment of fluorine-containing wastewater by modified chitosan microspheres[J]. Electroplating & Pollution Control, 2020, 40(2): 74-76 (in Chinese).
[77] KAMBLE S P, JAGTAP S, LABHSETWAR N K, et al. Defluoridation of drinking water using chitin, chitosan and lanthanum-modified chitosan[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2007, 129(1/2/3): 173-180. [78] WORKENEH K, ZEREFFA E A, SEGNE T A, et al. Eggshell-derived nanohydroxyapatite adsorbent for defluoridation of drinking water from bofo of Ethiopia[J]. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2019, 2019: 1-12. [79] 路坊海, 王芝成, 彭南丹, 等. 提铝钠铁后赤泥残渣的除氟性能[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2019(1): 73-76. LU F H, WANG Z C, PENG N D, et al. Defluorination performance of red mud residue after recovery of Al, Na and Fe[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2019(1): 73-76 (in Chinese).
[80] 郑雁, 郑红, 赵磊, 等. 赤泥除氟效果及吸附特性研究[J]. 有色矿冶, 2008, 24(5): 38-41. ZHENG Y, ZHENG H, ZHAO L, et al. Study on the adsorption effect and characteristics of fluorine by red mud[J]. Non-Ferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 2008, 24(5): 38-41 (in Chinese).
[81] ZHANG S Y, LU Y, LIN X Y, et al. Removal of fluoride from groundwater by adsorption onto La(III)- Al(III) loaded scoria adsorbent[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 303: 1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.01.169 [82] SANTHOSH C, VELMURUGAN V, JACOB G, et al. Role of nanomaterials in water treatment applications: A review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 306: 1116-1137. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.053 [83] 李杰. 新型纳米材料的制备及其除氟性能研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2019. LI J. Preparation of novel nano materials for fluoride adsorption from water[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2019 (in Chinese).
[84] 张开胜. 纳米吸附材料的设计、制备及对水中氟离子去除机理研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2016. ZHANG K S. Design and preparation of nano- adsorbents and adsorption mechanism for fluoride in water[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2016 (in Chinese).
[85] TEE G T, GOK X Y, YONG W F. Adsorption of pollutants in wastewater via biosorbents, nanoparticles and magnetic biosorbents: A review[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 212: 113248. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113248 [86] JIN Z, JIA Y, ZHANG K S, et al. Effective removal of fluoride by porous MgO nanoplates and its adsorption mechanism[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 675: 292-300. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.118 [87] KANG D J, YU X L, GE M F. Morphology-dependent properties and adsorption performance of CeO2 for fluoride removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 330: 36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.140 [88] 吴承慧, 陈长安, 高旭波, 等. 改性纳米级 Fe3O4对地下水中氟的吸附性能研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(6): 82-88. WU C H, CHEN C A, GAO X B, et al. Adsorption of fluoride from groundwater by modified nanoscale Fe3O4[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 42(6): 82-88 (in Chinese).
[89] ZHANG K S, ZHU B S, YANG W, et al. Fluoride removal performance and mechanism of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2021, 233: 281-291. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2021.27541 [90] WANG P, FU F G, LIU T Y. A review of the new multifunctional nano zero-valent iron composites for wastewater treatment: Emergence, preparation, optimization and mechanism[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 285: 131435. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131435 [91] DEHGHANI M H, HAGHIGHAT G A, YETILMEZSOY K, et al. Adsorptive removal of fluoride from aqueous solution using single-and multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2016, 216: 401-410. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2016.01.057 [92] ARAGA R, KALI S, SHARMA C S. Coconut-shell-derived carbon/carbon nanotube composite for fluoride adsorption from aqueous solution[J]. CLEAN-Soil, Air, Water, 2019, 47(5): 1800286. doi: 10.1002/clen.201800286 [93] ZHANG J, CHEN N, SU P Y, et al. Fluoride removal from aqueous solution by Zirconium-Chitosan/Graphene Oxide Membrane[J]. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 2017, 114: 127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2017.03.008 [94] 鲁浩, 杨强, 孔赟. 金属有机框架材料对水体中有机污染物的吸附去除及氧化降解研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(4): 170-182. LU H, YANG Q, KONG Y. Advances research in adsorption removal and oxidation degradation of organic pollutants from aquatic environments by MOFs materials[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(4): 170-182 (in Chinese).
[95] ZHU X H, YANG C X, YAN X P. Metal-organic framework-801 for efficient removal of fluoride from water[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2018, 259: 163-170. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.10.001 [96] WANG X G, ZHU H, SUN T S, et al. Synthesis and study of an efficient metal-organic framework adsorbent (MIL-96(Al)) for fluoride removal from water[J]. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2019, 2019: 1-13. [97] HE J Y, CAI X G, CHEN K, et al. Performance of a novelly-defined zirconium metal-organic frameworks adsorption membrane in fluoride removal[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 484: 162-172. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.08.074 [98] 谢东华. 铁、锆、铝基金属有机框架材料的制备及其对水体污染物的去除和检测研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2019. XIE D H. Fabrication of iron, zirconium, and aluminum based metal organic frameworks for removal and detection of water pollutants[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2019 (in Chinese).
[99] LI Y H, ZHANG P, DU Q J, et al. Adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution by graphene[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2011, 363(1): 348-354. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2011.07.032 [100] KARMAKAR S, DECHNIK J, JANIAK C, et al. Aluminium fumarate metal-organic framework: A super adsorbent for fluoride from water[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 303: 10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.030 -






 下载:
下载: