-
挥发性有机物(volatile organic compound,VOCs)是熔点低于室温且沸点为50~260 ℃的挥发性有机化合物的总称[1]。大气中的VOCs会危害人群健康[2],影响空气质量并可造成城市光化学烟雾[3]。研发高效低耗的VOCs治理技术是控制VOCs污染的关键。目前,VOCs治理技术主要分为源头控制与末端治理2类[4-6]。其中,催化燃烧法在金属印刷、绝缘材料、油漆、石油化工等行业高浓度VOCs治理中应用广泛[7-9],但存在催化剂价格昂贵、易失活等问题。
臭氧化VOCs治理技术以催化臭氧化技术为代表。EINAGA等[10]将锰氧化物负载至USY沸石上,可催化臭氧化苯环直至矿化。黄金花等[11]制备了MOx/Y催化剂并用于催化臭氧化甲苯气体,该催化剂具有良好的氧化性能和选择性。目前,微气泡臭氧化技术因其具有传质速率快、氧化能力强、臭氧利用率高等优势,在废水治理[12]、地下水修复[13]、污泥减量化[14]等方面已有应用研究。微气泡臭氧化技术能够强化难溶性甲苯气体吸收-氧化过程,可以获得97%以上的去除率和88%以上的氧化矿化率[15],而微气泡臭氧化技术对易溶性VOCs的吸收-氧化去除过程还有待研究。气态乙酸乙酯(ethyl acetate,EA)在臭氧催化氧化中可分解为乙酸、乙烯等中间产物,而后被彻底氧化矿化[16],但溶解吸收后乙酸乙酯的臭氧化降解过程尚需探究。
本研究以纯水作为吸收-氧化反应介质,以易溶性乙酸乙酯气体作为模型VOCs气体,采用微气泡臭氧化术对模拟高浓度乙酸乙酯气体进行处理;同时,比较了普通气泡和微气泡处理过程对乙酸乙酯气体的处理性能,分析了乙酸乙酯气体在实验条件下的吸收-氧化动力学以及吸收后乙酸乙酯氧化矿化反应过程,以期为微气泡臭氧化技术处理高浓度VOC气体处理提供参考。
全文HTML
-
实验装置包括乙酸乙酯气体产生装置、臭氧发生器、微气泡发生器与吸收-氧化反应器(见图1)。通过恒定流量氮气鼓泡法在恒定温度(25 ℃)下制得稳定浓度的模拟乙酸乙酯气体。以高纯氧为气源,采用臭氧发生器(WTS-10G,石家庄冠宇环保科技有限公司)制得臭氧气体。臭氧与乙酸乙酯气体混合进入微气泡发生器(SFMB-F8,北京晟峰恒泰科技有限公司),产生臭氧/乙酸乙酯微气泡,由底部进入吸收-氧化反应器(含有15 L纯水,纯水电阻率为15 MΩ∙cm−1)进行处理。尾气从反应器顶部进行收集检测。作为对照,在吸收-氧化反应器底部设置微孔曝气头,臭氧气体与模拟乙酸乙酯气体混合后通过微孔曝气头产生臭氧/乙酸乙酯普通气泡,进入吸收-氧化反应器处理。
-
1)微气泡强化体系的吸收实验。在恒定25 ℃温度下,稳定通入流量为0.5 L·min−1的氮气对液体乙酸乙酯进行鼓泡曝气,并间隔5 min对气相乙酸乙酯浓度进行检测,待连续3次检测气相乙酸乙酯浓度基本相同后(标准偏差≤5%),即认为获得稳定浓度的模拟乙酸乙酯气体,此时气相乙酸乙酯浓度为(14 700±440) mg·m−3、质量流量为(7.34±0.22) mg∙min−1。模拟乙酸乙酯气体以氮气/乙酸乙酯(N2/EA)普通气泡或微气泡形式进入吸收-氧化反应器,测定尾气乙酸乙酯浓度及质量流量、溶解乙酸乙酯浓度和液相TOC浓度随时间变化,考察微气泡对乙酸乙酯吸收的强化作用。
2)微气泡+臭氧化体系强化氧化实验。将流量为0.15 L∙min−1的臭氧气体,与乙酸乙酯气体混合,乙酸乙酯和臭氧质量流量分别为7.34和4.6 mg∙min−1。臭氧/乙酸乙酯(O3/EA)气体以普通气泡或微气泡的形式进入吸收-氧化反应器,进行微气泡臭氧化和普通气泡臭氧化处理,分别测定不同处理时间尾气乙酸乙酯浓度与臭氧浓度及质量流量的变化情况,同时溶解乙酸乙酯浓度、测定液相TOC浓度和溶解臭氧浓度的变化,考察微气泡+臭氧化对乙酸乙酯的强化氧化作用。进气和尾气中乙酸乙酯对应的TOC量根据测得的乙酸乙酯浓度折合计算。
3)去除效果分析。根据式(1)计算乙酸乙酯去除率,式(2)计算乙酸乙酯氧化矿化率,式(3)计算臭氧利用率,式(4)计算臭氧投加量和乙酸乙酯矿化去除量的比值[15]。
式中:ε为乙酸乙酯去除率;w0为进气乙酸乙酯质量流量,mg∙min−1;wt为t时刻尾气乙酸乙酯质量流量,mg∙min−1;t为处理时间;η为乙酸乙酯氧化矿化率;W0为进气乙酸乙酯对应TOC质量流量,mg∙min−1;Wt为t时刻尾气乙酸乙酯对应TOC质量流量,mg∙min−1;W为t时刻液相TOC累积量,mg;β为臭氧利用率;m0为进气臭氧质量流量,mg∙min−1;mt为t时刻尾气臭氧质量流量,mg∙min−1;R为累积臭氧消耗量与累积乙酸乙酯矿化量之比,mg∙mg−1。
-
进气和尾气乙酸乙酯浓度采用气相色谱仪(GC-7900,上海天美)进行测定,色谱柱为石英毛细管,规格0.25 mm×30 m×0.33 µm,固定相为XE-60。溶解乙酸乙酯浓度采用气相色谱仪(GC-7900,上海天美)进行测定,色谱柱为填充柱,规格2 m×3 mm,固定相为PEG 1500/GDX-101。使用碘量法对气相臭氧浓度进行测定[17]。使用靛蓝法对溶解臭氧浓度进行测定[18]。使用TOC测定仪(TOC-VCPN,日本岛津)进行液相TOC浓度的测定。以5,5-二甲基-1-吡咯啉-N-氧化物(DMPO)作为自旋捕集剂,采用电子自旋共振波谱仪(ESR)(MiniSpcope MS5000, 德国Magnettech)对体系中的自由基进行测定[19],扫描时长60 s,频段为0.046 s,核心磁场区段为336 mT。以环己烷为萃取剂,采用气相色谱-质谱联用仪(GC-MS,Thermo DSQ II,美国)对水介质中有机物进行GC-MS分析,程序升温模式50~250 ℃,进样量1 μL。
1.1. 实验装置
1.2. 实验方法和数据分析
1.3. 检测方法
-
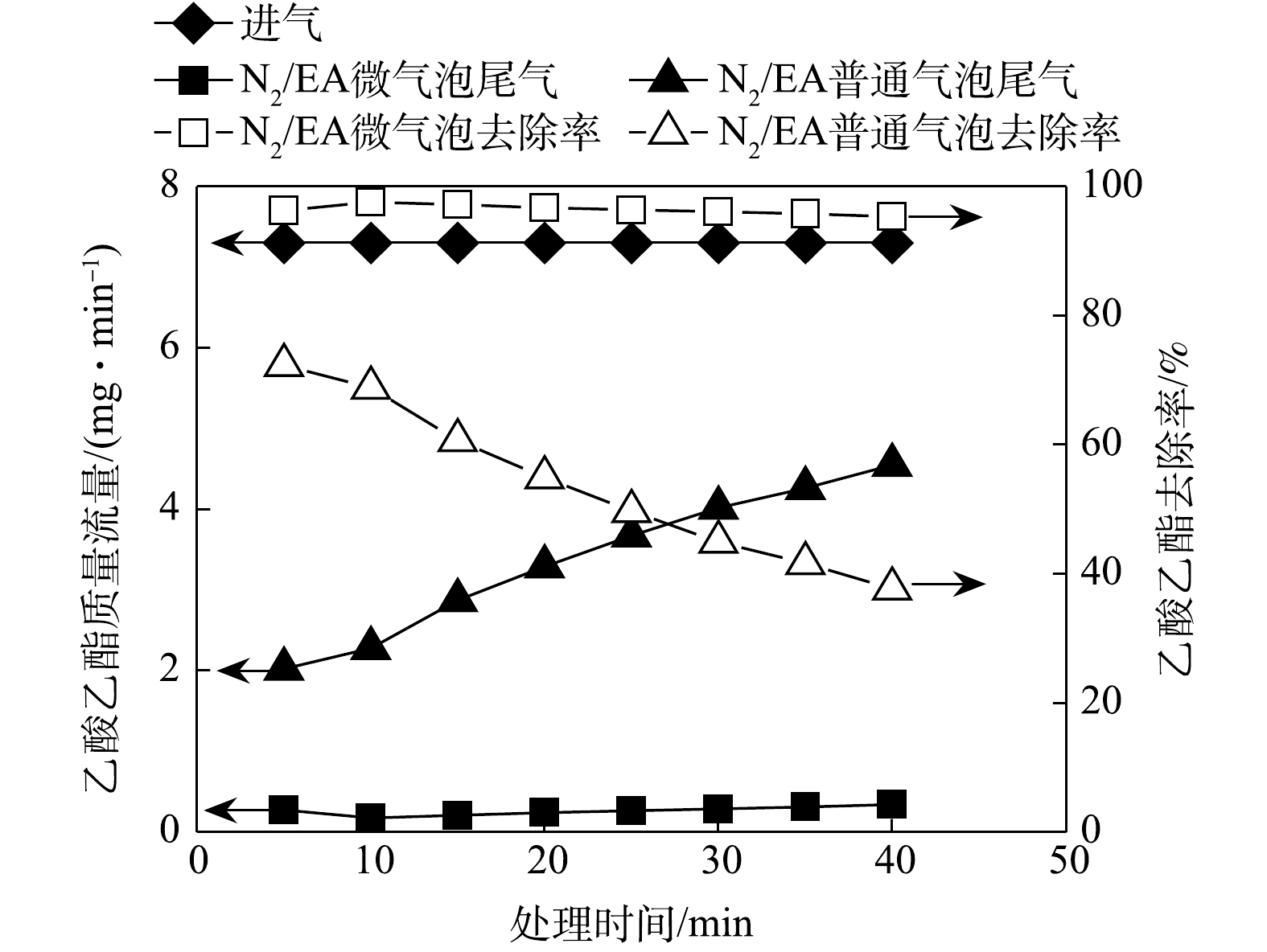
N2/EA微气泡和普通气泡处理过程中,进气和尾气乙酸乙酯质量流量与乙酸乙酯吸收去除率随时间变化如图2所示。由图2可知,进气乙酸乙酯质量流量为7.34 mg∙min−1时,N2/EA微气泡处理40 min内尾气乙酸乙酯平均质量流量值为0.26 mg∙min−1,平均去除率为96.43%。N2/EA普通气泡处理过程中,尾气乙酸乙酯质量流量逐渐升高,处理40 min时达到4.55 mg∙min−1,乙酸乙酯去除率由处理初期的72.4%下降至处理40 min时的37.8%,平均去除率为53.9%。因此,尽管乙酸乙酯气体的水溶性较好,N2/EA微气泡处理使其吸收去除效率又明显得到提升。已有研究结果显示,乙酸乙酯的水溶性较强[15],因此,N2/EA及普通气泡处理对乙酸乙酯气体的吸收效率高于对甲苯的吸收效率。
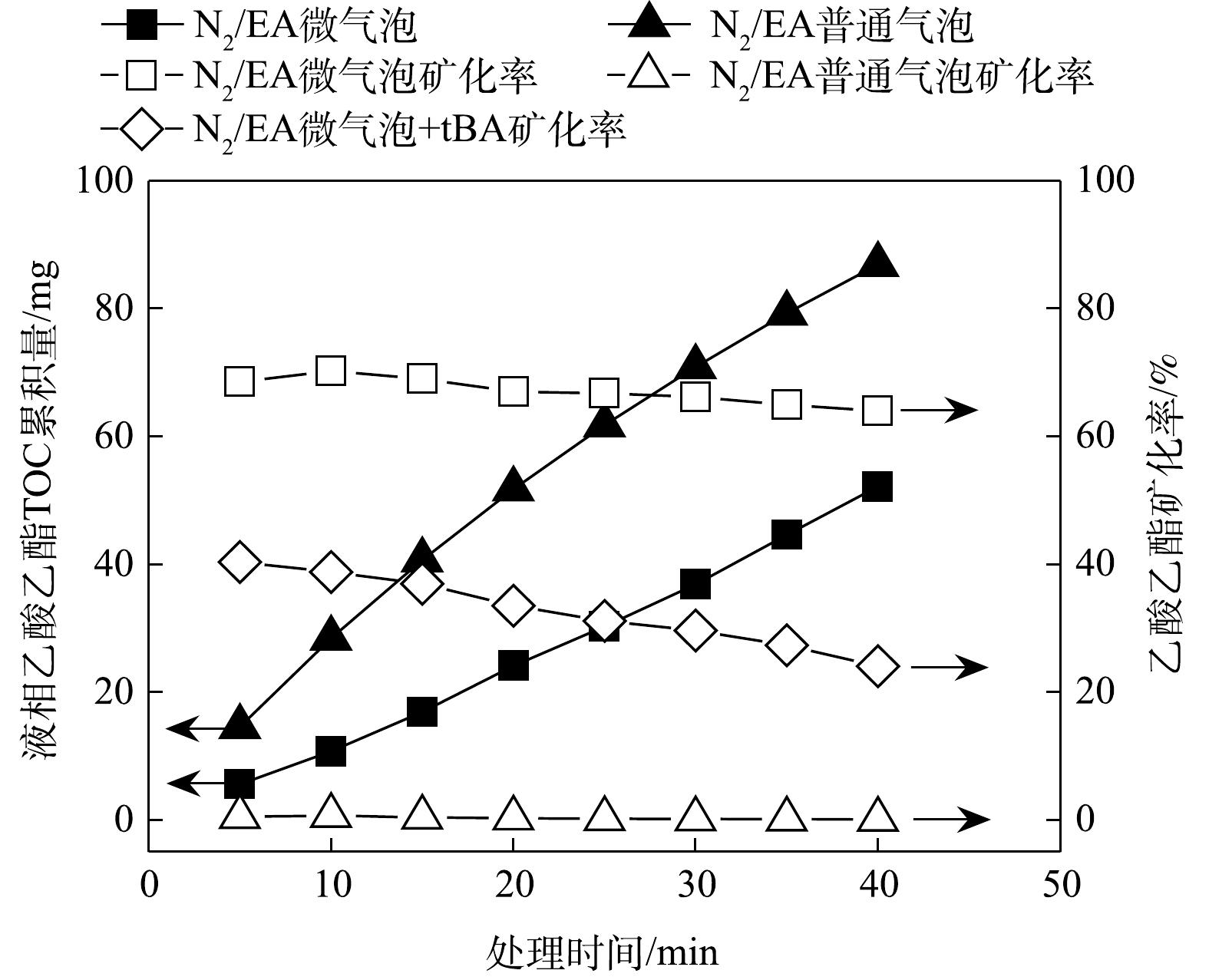
N2/EA微气泡和普通气泡吸收乙酸乙酯气体过程中,液相TOC累积量随时间变化如图3所示。由图3可知,N2/EA普通气泡吸收40 min后液相乙酸乙酯TOC累积量为86.89 mg,进气TOC量和液相累积TOC量及尾气散逸TOC量平衡,表明N2/EA普通气泡处理仅存在吸收过程。而N2/EA微气泡吸收40 min后,液相TOC累积量仅为52.18 mg,故液相累积TOC量与尾气散逸TOC量之和明显小于进气TOC量。这表明N2/EA微气泡处理中,除存在吸收过程外,可能存在吸收后乙酸乙酯的氧化矿化过程。根据式(2)计算N2/EA微气泡处理中乙酸乙酯氧化矿化率随时间变化,结果如图3所示。由图3可知,N2/EA微气泡处理中可保持相对稳定的乙酸乙酯氧化矿化效率,平均氧化矿化率为67.09%。N2/EA微气泡处理体系中不存在强氧化性物质,故乙酸乙酯的氧化矿化可能是由于微气泡收缩破裂产生·OH氧化作用[20-22]。N2/EA微气泡处理中存在·OH捕获剂tBA时,乙酸乙酯去除率未受影响,平均去除率为96.33%;但氧化矿化率明显下降,平均氧化矿化率由67.09%降至32.72%(见图3)。因此,N2/EA微气泡处理中存在的·OH氧化作用,是吸收后乙酸乙酯氧化矿化的主要原因。
-
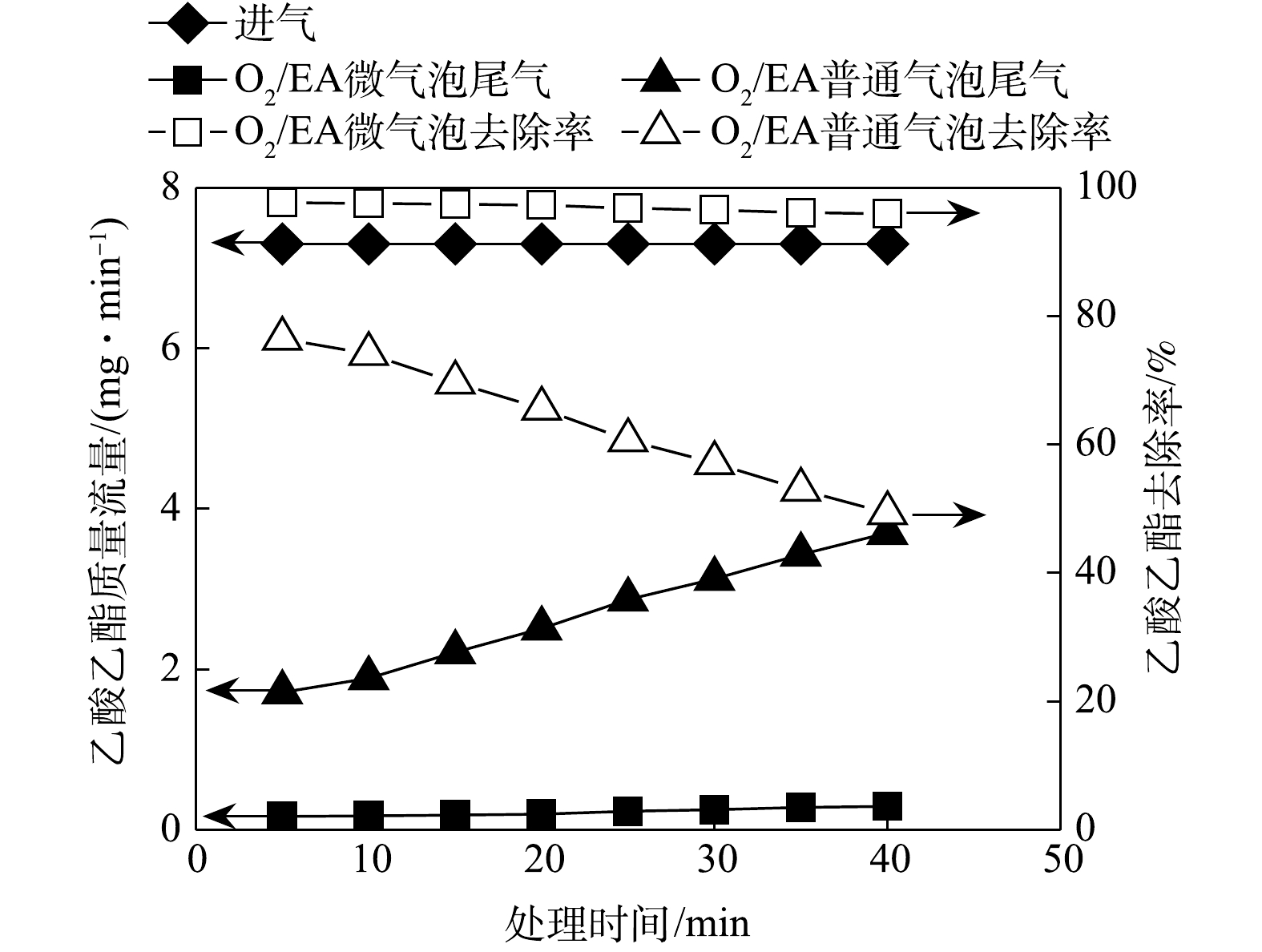
O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡处理乙酸乙酯气体过程中,进气和尾气乙酸乙酯质量流量和去除率随时间变化如图4所示。由图4可知,O3/EA微气泡处理中,尾气乙酸乙酯质量流量平均为0.22 mg∙min−1,乙酸乙酯平均去除率为96.94%。O3/EA普通气泡处理中,尾气乙酸乙酯质量流量逐渐上升,由初始的1.71 mg∙min−1上升至40 min时的3.70 mg∙min−1,乙酸乙酯去除率由76.75%下降至49.86%,平均去除率为63.25%。
O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡处理乙酸乙酯气体过程中,液相TOC累积量随时间变化如图5所示。由图5可知,O3/EA微气泡处理中,液相TOC累积量上升缓慢,40 min时达到6.72 mg,远低于N2/EA微气泡处理中的52.18 mg。O3/EA普通气泡处理中,液相TOC累积量亦逐渐上升,40 min时达到33.42 mg。根据式(2)计算O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡处理中乙酸乙酯氧化矿化率随时间变化,结果如图5所示。O3/EA微气泡中乙酸乙酯平均氧化矿化率达到90.22%,而O3/EA普通气泡中乙酸乙酯平均氧化矿化率仅为47.15%。因此,O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡处理中均存在吸收-氧化过程,但微气泡中乙酸乙酯吸收和氧化矿化效率均明显高于普通气泡。
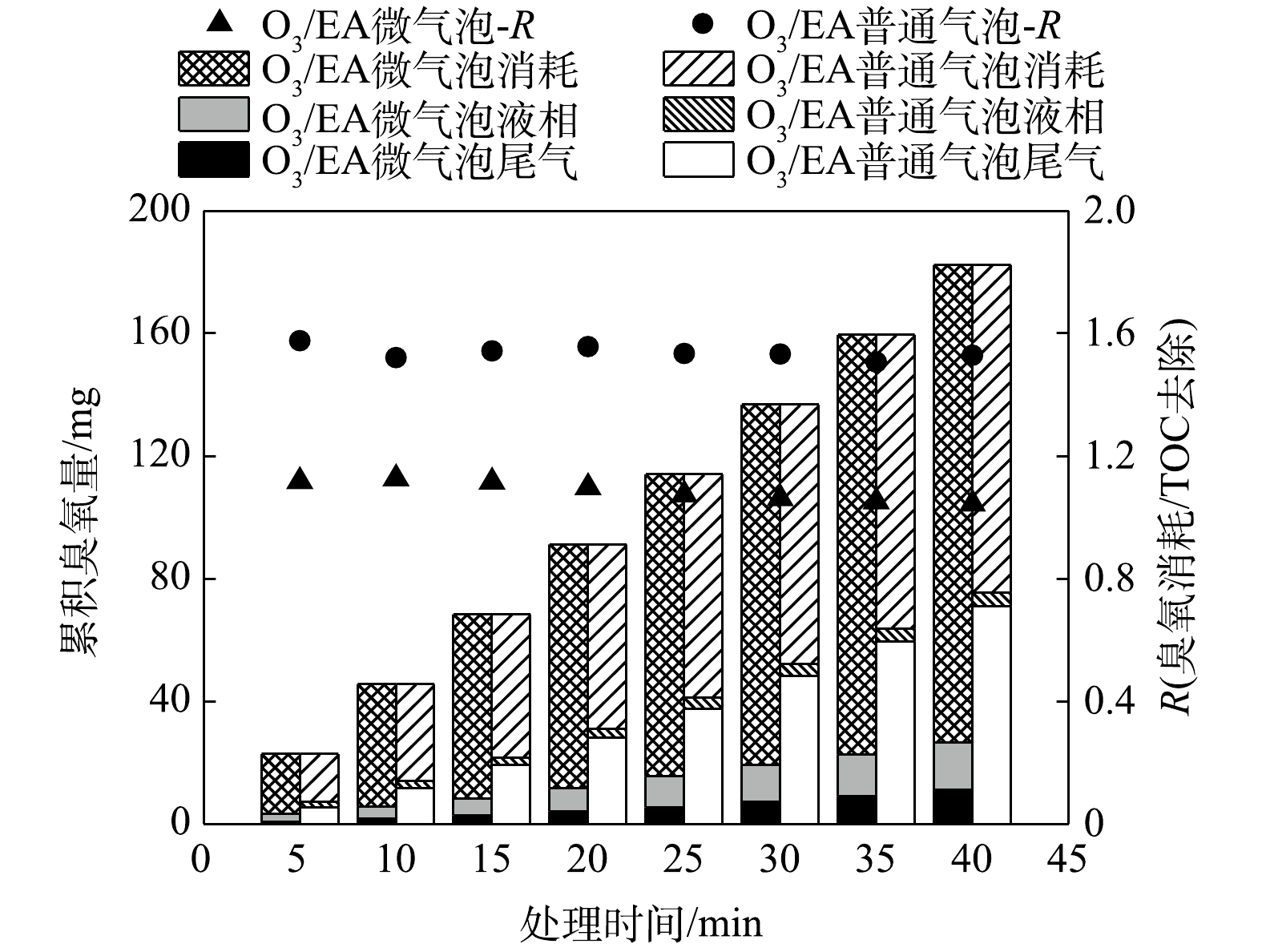
O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡处理中,测定尾气臭氧量、溶解臭氧量,并计算臭氧消耗量及其与TOC去除量的比值R,结果如图6所示。由图6可知,O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡处理中,液相累积臭氧量均相对较低,而微气泡处理中尾气臭氧量远低于普通气泡,因而臭氧消耗利用量显著高于普通气泡,累积臭氧利用率可以达到85.5%,而普通气泡中累积臭氧利用率仅为58.6%。同时,微气泡中R值为1.04 mg∙mg−1,普通气泡中R值为1.53 mg∙mg−1,表明微气泡中氧化矿化等量乙酸乙酯所消耗的臭氧更少,臭氧化反应效率更高。
对O3/EA微气泡处理乙酸乙酯气体过程中的水介质进行GC-MS检测分析,当反应40 min时GC图谱如图7所示。经MS分析,除萃取剂(环己烷)、残留清洗剂(甲醇)等有机杂质外,水介质中有机物基本为保留时间3.74 min的乙酸乙酯。由此可见,O3/EA微气泡处理中乙酸乙酯可被彻底氧化矿化,而几乎无氧化降解中间产物积累。
-
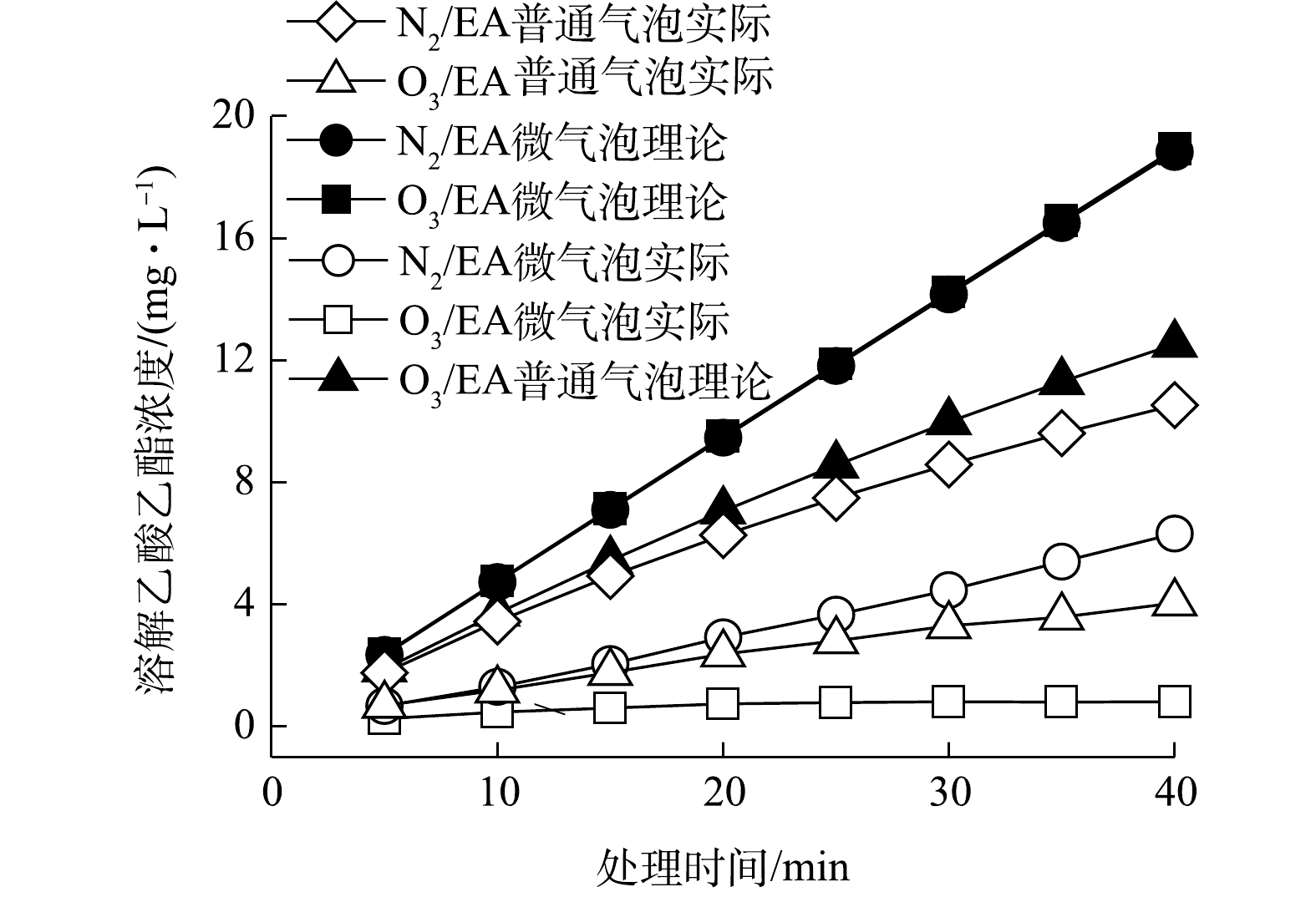
N2/EA微气泡和普通气泡以及O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡处理乙酸乙酯气体中,实际和理论溶解乙酸乙酯浓度如图8所示。其中,N2/EA微气泡、O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡处理中同时存在传质吸收和氧化矿化过程,则其传质理论溶解浓度可根据式(5)计算。
式中:c理论为理论乙酸乙酯溶解浓度,mg∙L−1;V为吸收-反应介质体积,L。
N2/EA普通气泡处理乙酸乙酯气体仅存在传质吸收过程中,则其传质动力学符合式(6)。将边界条件t=0、c=0代入式(6)并积分得式(7),取实验温度下乙酸乙酯饱和溶解溶度为83 000 mg∙L−1,计算ln(cs−c)与t线性关系的斜率,即为KLa,实验条件下求得KLa为3.0×10−6 min−1(R2=0.99)。同时,由于实验中c远小于cs,故式(6)可简化为式(8),即c与t为线性关系,斜率为KLacs。分析c与t的线性关系,得到斜率为0.248 3 mg∙L−1∙min−1(R2=0.99),与KLacs计算值0.249 0 mg∙L−1∙min−1一致。
式中:KLa为乙酸乙酯液相总体积传质系数,min−1;cs为饱和溶解乙酸乙酯质量浓度,mg∙L−1;c为t时刻溶解乙酸乙酯质量浓度,mg∙L−1。
N2/EA微气泡、O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡处理乙酸乙酯气体同时存在传质吸收和氧化矿化过程,根据式(8)计算上述过程传质动力学KLacs值,其分别为0.472 8(R2=1)、0.303 6(R2=0.99)和0.474 8(R2=1) mg∙(L∙min)−1。进一步根据式(9)计算(c理论−c) 与t线性关系的斜率k,求得N2/EA微气泡、O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡中吸收后乙酸乙酯氧化矿化反应速率,分别为0.309 0(R2=1)、0.207 1(R2=0.99)和0.458 4(R2=1) mg∙(L∙min)−1。
通过以上传质和反应速率计算可知,N2/EA微气泡和普通气泡以及O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡处理乙酸乙酯气体中传质吸收和氧化反应动力学在处理时间内均符合表观零级反应。N2/EA普通气泡中传质速率最小,O3/EA普通气泡中由于氧化矿化反应的存在,传质速率得到增强,增强系数为1.22。N2/EA和O3/EA微气泡中传质速率最高,且基本相当,体现了微气泡对传质吸收过程的强化作用。同时,N2/EA微气泡、O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡中,氧化矿化速率与传质速率的比值分别为0.65、0.68和0.97。因此,N2/EA微气泡和O3/EA普通气泡中氧化矿化速率明显低于传质速率,故氧化速率是吸收-氧化过程的限制因素,溶解乙酸乙酯浓度累积明显。O3/EA普通气泡的氧化能力强于N2/EA微气泡,但由于微气泡对传质速率的强化作用,使得N2/EA微气泡的氧化矿化速率高于O3/EA普通气泡。而O3/EA微气泡中传质和氧化能力均得到强化,氧化矿化速率与传质速率基本平衡,吸收-氧化过程效率最高,溶解乙酸乙酯浓度累积缓慢,有利于实现乙酸乙酯气体长期稳定高效处理。
-
N2/EA微气泡、O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡处理体系中,采用电子自旋共振波谱仪(ESR)对DMPO-OH进行检测,结果如图9所示。在图9的每个ESR图谱中均可观察到DMPO-OH信号,这证实了上述处理过程中均可产生·OH。N2/EA微气泡中氮气无活性,仅能通过微气泡自身收缩破裂作用产生·OH(见式(10)),因此,DMPO-OH信号强度最低。由于微气泡产生的·OH有限,故·OH可能会通过活化液相中溶解氧,形成超氧自由基,并发生式(11)所示反应实现较高的乙酸乙酯氧化矿化效率。
O3/EA普通气泡中可通过溶解臭氧自分解产生·OH(反应式(12)~(15))[23-25],DMPO-OH信号强度高于N2/EA微气泡,表明·OH产生效率高于N2/EA微气泡。O3/EA微气泡中可同时通过微气泡收缩破裂和溶解臭氧自分解产生·OH。同时,由于臭氧活性强、臭氧传质效率高,微气泡收缩破裂和溶解臭氧自分解产生·OH的作用可同时被强化[26-27],·OH产生效率大大提高,故DMPO-OH信号强度明显高于N2/EA微气泡和O3/EA普通气泡。
O3/EA微气泡和普通气泡中乙酸乙酯可通过臭氧直接氧化反应和·OH氧化反应实现氧化矿化,其氧化反应过程为反应式(16)。由该反应式可知,在O3/EA微气泡中,由于·OH产生效率高,·OH氧化反应得到增强,可降低臭氧直接氧化反应贡献度,所以去除等量TOC所消耗臭氧量下降,即R值更小,臭氧化反应效率更高。
2.1. 微气泡强化体系对乙酸乙酯气体的吸收作用
2.2. 臭氧微气泡强化乙酸乙酯气体的氧化去除作用
2.3. 乙酸乙酯吸收和氧化反应动力学
2.4. 乙酸乙酯氧化矿化反应过程
-
1)微气泡臭氧化可强化易溶性乙酸乙酯气体吸收-氧化处理效率。N2/EA微气泡处理使其吸收去除效率进一步得到明显提升。同时,由于乙酸乙酯水溶性较强,所以N2/EA及普通气泡处理对乙酸乙酯气体的吸收效率高于对甲苯的吸收效率。
2)液相累积TOC量与尾气散逸TOC量之和明显小于进气TOC量,表明N2/EA微气泡处理中,除存在吸收过程外,可能存在吸收后乙酸乙酯的氧化矿化过程。
3)微气泡臭氧化提高臭氧利用效率,同时强化·OH氧化反应,提高臭氧化反应效率,其累积臭氧利用率达到85.5%,高于普通气泡臭氧化过程的58.6%;臭氧消耗量与乙酸乙酯TOC去除量比值R可低至1.04 mg∙mg−1,明显低于普通气泡臭氧化过程的1.53 mg∙mg−1。上述结果说明微气泡中氧化矿化等量乙酸乙酯所消耗的臭氧更少,臭氧化反应效率更高。
4)微气泡臭氧化处理中,乙酸乙酯传质吸收和氧化矿化反应均符合表观零级动力学方程,氧化矿化速率与传质速率基本平衡,可实现乙酸乙酯气体长期稳定高效处理。




 下载:
下载: