-
重金属污染的形式在自然界之中是繁杂多样的. 大量文献研究了单一重金属元素造成的污染现象,但实际上重金属污染往往是以多种重金属复合的形式出现. 伴生性和综合性[1]是重金属复合污染的显著特征. 在重金属复合污染中,多种金属迁移转化遗存效应的影响要比单一的重金属污染多且复杂.重金属复合污染中元素或化合物之间的交互作用显著影响着重金属污染物的生物效应(吸收、积累和毒性),因此研究重金属复合污染下生物毒性效应,能够对重金属生态环境风险具有更客观的反映.拮抗效应、加和效应与协同效应是不同种类的重金属反应机制、转化机制的一般表现[2-3]. 在拮抗作用中,竞争位点在某种程度上可视为复合污染拮抗作用的直接形成原因.协同作用是指多种污染物共存所产生的毒性效应大于各污染物单独作用的毒性效应之和,即某污染物的毒性被其他污染物所加强[2]. 加和作用是指多种污染物共存时所产生的毒性效应等于各污染物单独作用的毒性效应之和[4]. 重金属复合污染对生物带来的毒性复杂性逐渐为大家所重视,随着研究和分析的技术不断发展与完善,重金属复合污染对生物的影响获得了一定的突破.
-
植物在生长过程中根系会产生高分子化合物(如植物高铁载体、植物络合素、类金属硫蛋白等) 和低分子化合物(如CO2、氨基酸、有机酸等)等主要分泌物. 根际酸化作用、沉淀作用、螯合作用和氧化还原反应受到植物根系分泌物的直接影响,进而影响重金属离子的溶解度和生物可利用性. 多数复合重金属离子被植物吸收后,与根内的蛋白质结合形成稳定的螯合物滞留根内. 当重金属离子达到一定量时,细胞的木质化速度会加快,进而抑制植物根尖细胞的伸长,导致根部变短变粗[5]. 秦月华等[6]研究发现,复合重金属在高浓度条件下可以促进根部对Fe和Ca的摄入. Liu等[7]研究发现,相比于单独暴露,Cd和As联合暴露对小麦的毒性影响更大,Cd和As联合作用对种子萌发频率有相加作用,对幼苗根的伸长有拮抗作用. 王新等[8]对于水稻根中Pb含量的研究表明,其含量较未投加Cd、Cu、Zn、As的处理时降低,Cd、Pb的联合作用使水稻植株的高度和产量均有明显的下降,这几种重金属之间的复合作用,影响了水稻的根系吸收及发育. Guo等[9]研究表明,在Al + Cu双金属混合条件下,与单独Al处理相比,两种耐铝性不同的基因型大麦(Gebeina相对抗性,Shang 70-119相对敏感)的根中,Al、Cd和Cu的浓度均受到Cu的促进,尤其是Shang 70-119. Cai等[10]研究发现,Zn和Cd在地上部和根部都存在很强的拮抗作用. 根系和地上部Cd积累量的减少可以用Zn和Cd之间的竞争以及生物量增加的稀释效应来解释. Zn供应对Cd吸收的拮抗可能是由于Cd从根到地的转运率随Zn活性的增加而增加,而Fe和Mn在地上部随Zn活性的增加而受到强烈的抑制,以及基因型的变化.梁瑞[11]等对低浓度Cd积累突变体T2-1和中籼稻9311两种供试品种研究发现,Cd-Pb-Cu的复合效应抑制水稻根系和地上部Cd吸收,T2-1作用更明显. 此外,随水稻培养天数增加,在Cd及Cd-Pb胁迫下,两种品种的Cd含量在根系增加,而在地上部逐渐降低,说明培养天数增加对根部Cd积累有促进作用. 随培养天数增加,在Cd-Cu及Cd-Pb-Cu胁迫下,水稻地上和地下部Cd积累量均下降,且较单一Cd胁迫含量低,结果表明,低浓度下Cu与Cd具有拮抗作用.
-
重金属复合污染主要是通过对植物光合过程中的电子传递和破坏叶绿素的完整性而影响对植物的光合作用的. 叶绿体是超微结构对重金属联合作用敏感的植物细胞器之一. 复合重金属对叶绿体超微结构的毒害作用也通常是导致植物死亡的一种原因. 叶绿体中含带有高电子密度的少量脂质球[12]. 当叶绿体受到复合重金属胁迫作用时,其结构会发生明显改变. 张嘉桐等[13]研究表明,复合重金属的胁迫对于桑树叶片的光合色素含量、胞间CO2浓度以及蒸腾速率等指标均有影响. 重金属的复合效应对于桑树幼苗的胁迫表现为协同作用. 孟庆俊等[14]通过研究复合重金属对小麦幼苗叶绿素含量的影响发现,Cu与Cd、Cr、Pb、Zn联合作用时,其联合作用类型Cu-Cd表现为协同作用,Cu-Cr为拮抗作用,Cu-Pb趋于相加作用,Cu-Zn表现为拮抗作用. 混合重金属由于作用机理的不同,对于不同作物的同一指标或同一作物的不同指标都可能不同. 铁柏青等[15]通过盆栽试验研究了Cu、Cd、Pb、Zn、As复合污染对灯芯草的联合生理毒性效应及积累和分布情况,研究结果表明,在复合重金属联合作用的条件下,灯芯草中3种酶(POD、CAT、SOD)有着不同的变化趋势,从而抑制了叶绿素的合成.但总体来看,几种酶的协调作用仍能抑制重金属复合污染物对灯芯草造成严重伤害. Shakya等[16]研究了重金属Cu、Zn和Pb对细枝羽藓、散叶羽藓和多叶地钱草的叶绿素含量的影响. Cu的积累相对于Zn、Pb积累,使两种苔藓的叶绿素含量下降不明显,但叶地钱的叶绿素含量显著下降. 混合金属溶液中Cu+Zn+Pb离子共同积累后,两种苔藓叶绿素a/b比值下降较快,Cu+Zn+Pb离子组合时的叶绿素a/b比值高于单独使用Cu、Zn或Pb离子时的浓度. Cu对两种苔藓的叶绿素含量都有较大的破坏作用. 重金属积累造成的叶绿素损失可能是由于叶地钱比苔藓有更多的K+外流所致,表明它们在膜完整性上存在一定的差异. Maria等[17]研究表明,在单一处理和复合处理下,海草带状藻(Zostera Marina)的光合性能下降,但Cu比Cd的影响更大. Cu的总积累量在单一处理和复合处理下均高于Cd,但两者配施时的积累量普遍较低,说明它们之间存在竞争关系.
-
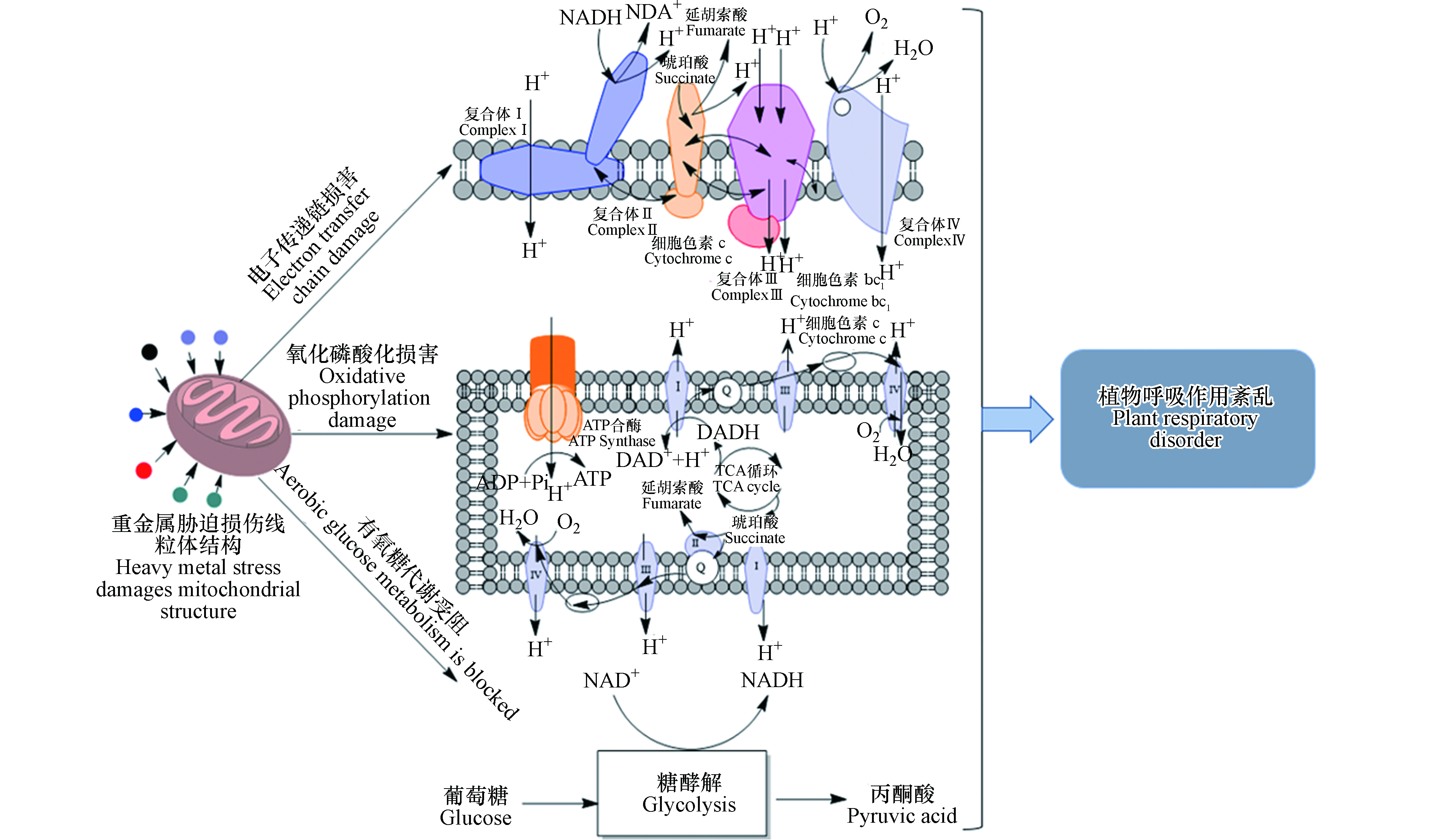
复合重金属对植物呼吸作用的联合毒性主要体现为使正常呼吸作用紊乱,ATP数量减少,而且部分ATP还会在对重金属胁迫的适应过程中被消耗[18]. 植物线粒体内重金属含量过高,会损害正常的电子传递链和氧化磷酸化体系,使糖酵解的正常进行受到阻碍,共同对植物的呼吸作用造成影响[12],详细过程如图1所示. Lösch [19]的研究表明,在重金属离子的影响下,储存大分子中糖的释放减少,将减少线粒体呼吸过程中可利用的底物数量. 刘登义等[20]用Cu和As两种元素处理小麦和黄豆萌发中的种子. 在复合重金属污染条件下,两种种子的新物质生成量、生物能和呼吸强度都有显著的降低,一系列生化和生理过程均被抑制. 谷巍等[21]研究了重金属复合污染与植物呼吸作用的关系. 结果表明,重金属复合污染可对植物的线粒体结构造成破坏并抑制参与呼吸作用的各种酶,从而抑制植物的呼吸作用. 李坤等[22]研究表明,在Cu、Cd、Zn复合污染的影响下,亚心型小球藻和小球藻的呼吸作用受到短暂增强后迅速下降.
-
在细胞水平上,复合重金属对于植物的致毒作用表现为,影响酶、细胞的膜结构和非膜结构、生理生化过程,对植物造成整体的伤害[23]. 果胶质是植物细胞壁的组成成分之一,它能够与多种重金属离子相结合,使得细胞壁能够积累重金属阳离子,在一定程度上阻挡复合重金属离子进入细胞内部[24]. 这些观点在徐勤松等[25]研究的Cd、Zn复合污染对菹草叶片细胞损伤机制的影响结果中被证实,Cd、Zn大量存在于菹草叶片细胞的细胞壁中,这为重金属联合效应导致植物细胞壁松散现象提供了直接依据. 范春辉等[26]探究了金盏菊幼苗根系细胞壁受Pb、Cd复合胁迫的影响. 根据红外和拉曼光谱结果表明,两种重金属金属的复合作用导致其细胞壁收缩形变,表面出现散点颗粒状沉积物.
重金属对植物的毒害机理为,重金属会破坏植物细胞的SOD酶、CAT酶、POD酶等,导致植物细胞器膜过氧化损伤,甚至破坏膜结构[27]. 重金属复合污染会破坏植物细胞膜的透过性,影响细胞的正常生理代谢[28]. 土壤中重金属会胁迫植物根系细胞,使其膜透过性增加[29]. 损伤细胞膜后,会导致结合酶、内酶的失调,还会导致有毒物质的进入和胞内物质外渗致使植株死亡,O2·−、OH·和H2O2等活性氧和自由基也会受到重金属复合污染的胁迫作用[30]. 在植物组织中,活性氧可以由Cu、Pb、Cr和As直接产生,而由Cd间接产生,因为它是一种氧化还原失活的重金属,可以通过酶的失活和刺激脂氧合酶的表达来产生活性氧[31]. 活性氧物种通过从不饱和脂肪酸中去除氢来扭曲脂质双层,并形成脂质自由基和活性醛[32]. 在几种植物中,重金属被认为可以诱导脂质过氧化,降低饱和脂肪酸水平[33],并增加细胞膜的不饱和脂肪酸含量[34]. 重金属会和植物体中的核酸、蛋白质、酶等大分子结合,还可以取代一些植物体中的特殊元素,导致酶和蛋白质的活性降低. Pierre等[35]研究分析了生长在混合金属污染土壤上的杨树中重金属的分布,以及作为叶位和重金属处理的函数的金属微观定位. Zn是土壤和叶片中含量最丰富的污染物,并与Cd一起优先积累在较老的叶片中,而过量的Cu和Pb没有被转移. 其他元素浓度的变化表明,由于金属处理,老化速度加快. 过量的Zn在叶片组织内不规则积累,使叶脉趋于饱和,并且更多地储存在细胞共质体中,而不是质外体. 液泡包括代谢安全和敏感的亚细胞部位,导致大量金属积累和应激反应. ZHOU[36]等研究了宁波东部近海水域中8种最常见重金属的联合毒性及其作用机理. 研究结果表明,重金属混合物使JB6细胞阻滞于S期,诱导ROS生成和细胞凋亡,并且Western blot检测到JB6细胞中C-jun和p65蛋白表达上调,这两个基因在细胞癌变过程中起重要作用.
-
在分子水平上,当植物受到复合重金属胁迫时,细胞核核仁的损伤会影响DNA和染色体的正常合成与复制. An等[37]研究探讨了Cd、Cu复合污染下胡萝卜的遗传变化与表型变化之间的联系. 结果表明,在Cd和Cu复合处理条件下,赤霉素基因的表达下降,进而导致胡萝卜的长度和干重下降.与单一处理相比,混合处理胡萝卜素基因的表达下调幅度更大,从而降低了胡萝卜的抗氧化能力,表现为丙二醛含量的显著增加. Cd和Cu复合施用也使胡萝卜糖基因的表达下降,这可能导致胡萝卜的含糖量显著降低. GUPTA等[38]研究发现,在分子水平上,Hg、Cd、Cu 能改变水生植物叶绿素、蛋白质的含量和造成DNA分子的损伤. 葛才林等[39]研究发现,重金属 Cu 、Cd 和 Hg 的复合作用会导致小麦、水稻叶片内部的基因损伤. 吕朝晖等[40]研究发现,萌发期小麦醇脱氢酶基因表达过程中的RNA和酶活性,在Cd、Pb 的复合胁迫下有着相近的变化趋势. 在植物细胞内,两种重金属能与带负电荷核酸结合,降低RNA和DNA活性,抑制转录的进行.ZHANG等[41]从HgCl2处理的菜豆中分离到一个重金属响应基因PvSR2, 该基因的表达能够受到Hg、Cd、As和Cu等重金属的强烈刺激,产生大量mRNA. Van[42]发现,Cd和As对植物生长的联合作用是相加的或协同的,而联合遗传毒性作用是相加的或拮抗的. 作者认为,由于Cd和As的毒性效应和植物对高水平DNA损伤的反应,导致细胞周期暂时停滞,为DNA修复和自由基清除剂的产生提供了更多的时间. Lanier等[43]研究了Cd、Pd对甘蓝和白三叶联合毒性效应,通过DNA损伤分析显示了复合重金属浓度和时间依赖的相互作用. 短期暴露后,观察到两种重金属的协同效应,10 d后拮抗效应明显,表明两种金属之间存在竞争. Maria等[17]评估了Cu和Cd过量对海草带状藻(Zostera Marina)生理和代谢过程的影响,结果表明过量Cu和Cd的摄入会导致海草带状藻体内金属硫蛋白(MET)基因、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、谷胱甘肽还原酶(GR)和抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX)表达的上调. 两种金属还能诱导DNA甲基转移酶(CMT3和DRM2)表达的上调.
-
重金属能在动物体内不断蓄积并通过食物链进行传递[44],在生物体内不断放大达到致病阈剂量,进而对生物体各个系统造成损伤[45],尤其是生殖系统[46]. 由于生殖系统对于重金属较为敏感,在其他系统尚未呈现病理性损伤时,生殖系统可能就出现了障碍. 生殖系统因重金属复合造成的损伤,会随着生物所处生殖阶段的不同而不同[47],产生的危害包括生物体不育、死胎、子代发育迟缓等[48].
重金属复合污染对雌性动物生殖系统的影响较为复杂.研究表明,当雌性动物体内Pb和Hg的浓度升高时,体内孕激素浓度会随之升高,进而导致机体激素水平紊乱影响机体正常生长发育. Pb和Cd联合作用会抑制雌性动物卵泡发育,造成机体生殖系统的损害. 重金属之间的协同作用对雌性哺乳动物卵泡的发育影响巨大,在高浓度Cd的作用下,Pb对卵泡发育的抑制作用更显著[49]. 小剂量的Cd就可以引起小鼠颗粒细胞凋亡,进而影响小鼠卵巢的正常功能[50],Pb和Cd联合作用还可能造成卵巢发生病理性损伤,甚至会抑制卵巢颗粒细胞和黄体细胞合成类固醇,促进颗粒细胞和黄体细胞凋亡,显著损害雌性哺乳动物的生殖系统. BLOOM等[51]研究发现Hg和Cd联合作用会显著抑制卵巢中卵泡的发育,进而使卵母细胞数量减少,而高浓度Pb也会使处于减数分裂时期的卵母细胞不断减少,损伤生殖系统.对于水生生物来说,重金属离子复合作用会阻碍鱼类胚胎发育、降低鱼卵孵化率、延长鱼卵孵化过程、提高鱼卵发育畸形等. Jezierska等[52]发现鲤鱼暴露在0.2 mg·L−1 Cu溶液和0.2 mg·L−1 Pb溶液,会延长鲤鱼胚胎孵化过程. Witeska等[53]研究表明,圆腹雅罗鱼幼体暴露于Cd、Cu 污染的水体可致使其身体产生畸形以及新孵化幼体的死亡. 黄涛等[54]研究表明,重金属复合污染通过扰乱性激素分泌、增加细胞微核率和DNA损伤程度,对花背蟾蜍雄性性腺造成显著的毒害作用,从而降低精子质量[55],增加生殖细胞畸形率.
-
大量研究表明,通过抑制或增强机体免疫调节反应,重金属可以扰乱机体稳态平衡,最终导致机体免疫功能障碍[56]. 经大气、土壤、水体等途径,重金属可以进入自然环境中被动物摄入,通过干扰机体正常的免疫调节功能来增加机体的易感性[57],进而严重影响动物的免疫能力和健康. Sorvari等[58]通过研究工厂排污对附近同一地区昆虫的影响,发现蚂蚁的免疫应答反应随体内重金属水平的增加而升高,但随着工厂距离越近,蚂蚁的免疫应答反应开始明显下降. 在复合重金属的干扰作用下,蚂蚁体内的免疫系统会被抑制或增强[59],诱导氧化应激干扰免疫细胞功能、导致免疫组织损伤和炎症反应是复合重金属胁迫机体免疫系统的3种方式[60]. 在复合重金属的胁迫作用下,会导致细胞凋亡使免疫细胞在种类、数量上减少和细胞核损伤[61];复合重金属可以干扰胞内信号转导,从而影响基因表达与蛋白质的编码[62];重金属干扰神经-内分泌-免疫调节. 在一项使用Pb、Hg、As和Cd等金属混合物的研究中,Jedhav等[63]观察到雄性大鼠的造血和免疫系统对联合混合物具有毒理学敏感性. 他们得出结论,这可能导致贫血、抑制体液和细胞介导的免疫反应.江红霞等[64]通过研究水体中Cu和Cd污染对草鱼免疫系统的影响,揭示了高浓度、长时间Cu和Cd暴露会使草鱼肾脏出现炎症反应. Morcillo等[65]研究表明甲基汞、As、Cd可降低黑鲈吞噬细胞的免疫功效,而Pb可提高吞噬细胞的免疫功能,Cd和甲基汞都可促使黑鲈白细胞凋亡或坏死. 白晓娟[66]为了探究鸟类免疫系统对长期环境重金属污染暴露的响应,说明环境重金属污染对树麻雀免疫分子水平具有显著的影响. 研究检测了Cu、Pb、Zn和Cd在树麻雀体内的积累水平、分析复合重金属胁迫对鸟类免疫系统的影响. 结果表明,Cu、Pb、Zn和Cd会在树麻雀的免疫器官积累,尤其是导致雏鸟体况显著下降,改变雏鸟和幼鸟腔上囊和脾脏的构造、升高免疫水平、降低血细胞比容,部分雌性成鸟的免疫水平下降.
-
重金属在动物肺部沉积可能会改变动物气道结构并诱发慢性或急性炎症反应. 有研究表明Zn和Cu在生物肺部沉积后会诱导肺部产生特异性反应生成金属硫蛋白,进而引发肺部损伤[67]. 对于鱼类来说,水体中重金属污染物首要攻击的靶器官是鱼鳃,由于鱼鳃对重金属非常敏感,短时间内重金属累积暴露即可影响鱼类呼吸系统行为、破坏鱼类正常呼吸节律[68]. Morcillo等[69]研究表明,在重金属Hg、Cd、As与Pb的复合污染下,可导致鱼体的呼吸强度下降,重金属 Hg可导致鱼体内的白细胞的凋亡与坏死以及增添吞噬细胞的所占百分比. Handy等[70]研究表明在一定浓度Cu的长期胁迫下,可导致鱼类平均游泳速度和淋巴细胞降低,嗜中性粒细胞、酶活性和鱼氧消耗增加,免疫力改变等一系列变化.
-
重金属复合污染的暴露可以诱发神经系统中毒,进而严重威胁着野生哺乳动物的生态平衡.目前研究发现的几种可能机理如下. (1)重金属的联合作用通过改变对金属离子的吸收和转移,使神经系统紊乱. 顾成武[71]在对SD大鼠的研究发现,Pb和Cd协同作用诱导二价金属离子转运蛋白1的合成,损害神经系统[72]. 另一研究发现,大鼠组织受到重金属 Pb、Cu 和 Zn 的共同污染时,Pb大大降低了Cu和Zn在大鼠体内的浓度. Pb已被证明在几种情况下能够诱导金属硫蛋白(metallothioneins,MTs)的合成,Cu和Zn可以结合MTs,Cu和Zn在肾脏和心脏中的积累表明,这两种金属通过配体形成金属复合物,这种复合物会在肾脏和心脏中沉积[73],影响肾脏和心脏的功能[74],造成哺乳动物认知障碍[75]. COBBINA等[76]研究了低剂量Pb、Hg、As和Cd混合物与有毒和必需金属之间的相互作用.结果表明,30d内Pb+Cd暴露使小鼠脑内铅增加479%,Pb+Hg+As+Cd暴露使小鼠脑内Cu增加221%,金属混合物中的相互作用在很大程度上是协同作用. (2)脑源性神经营养因子是一种维持神经系统正常运行的重要蛋白质,复合重金属的胁迫会影响其表达. Rai等[77]通过动物实验发现As、Pb和Cd复合作用可能会对发育中的大鼠星形胶质细胞产生毒性作用,而星形胶质细胞损伤会导致中枢神经系统中的髓磷脂崩解,进而损害神经系统正常生理功能. 在后续的实验中,Rai通过实验证实了髓鞘结构的完整性取决于少突胶质细胞、轴突神经元以及视神经和视网膜轴突之间的结构和功能,但外界重金属复合暴露会破坏机体的动态平衡,进而在中枢神经区域产生髓鞘破裂,损伤机体认知功能. (3)Pb、Cd联合暴露对降低Na+/K+-ATP酶功能具有加和作用,加重对神经系统的损伤[72].
-
在机体组织和器官中,重金属作用的目标通常是细胞表面受体或细胞核和细胞质中的受体[78],大多数重金属离子自由通过细胞膜并直接与细胞内细胞器和生物大分子发生反应,从而干扰细胞内Ca的稳态和转运系统[79]. 此外,大多数重金属会引起活性氧(ROS)的过量生成,并导致细胞器和DNA损坏[80]. 从分子水平上看,与重金属发生相互作用的目标生物分子可能是蛋白质、DNA或离子通道. 重金属与生物体中的这些活性位点相互作用,并诱导生物分子功能或结构功能障碍,最终诱发机体发病[81]. 有研究表明重金属Cd、Pb和As可以改变HepG2和KERTr的细胞活力以及诱导金属硫蛋白(MTs)合成,HepG2和KERTr的细胞活力会随重金属浓度的增加而增加,而Cd、Pb复合污染的HepG2和KERTr细胞可大量诱导MTs合成,从而增加致癌风险[82]. Wu等[83]研究了Pb和Cd联合暴露对蚯蚓(Eisenia fetida)的影响,发现两种金属联合暴露显著抑制了纤维素酶活性. 他们得出结论,Pb和Cd之间的联合毒性效应是复杂的,可能受到两种金属的竞争性吸附及其生物利用度的影响. Vellinger等[84]将普氏革鼠暴露于Cd和As(V)的混合物中,观察到普氏革鼠对暴露的反应是解毒系统的增强,如谷胱甘肽含量、γ谷氨酰-半胱氨酸连接酶活性和金属硫酮浓度的降低. 此外,他们强调,这种反应似乎不仅意味着能量储备利用的变化,还可能意味着能量从运动到排毒的重新分配. Choi等[85]通过细胞体外实验发现重金属复合暴露会抑制细胞增殖并干扰细胞内谷胱甘肽(GSH)和白细胞介素(IL-8)的合成,进而影响细胞免疫反应. Hambach等[86]的研究表明,Pb和Cd的共同暴露增加了Cd和肾脏生物标志物之间的关联. Hg和Cd混合物与红细胞膜的相互作用表明,混合物的横向脂质堆积发生了变化,表现为面积的扩大和膜刚度的增强. 除此之外,自由基被重金属诱导产生后能作用于DNA链使其断裂损坏细胞正常功能[87],产生基因毒性[88]. 重金属通过改变酶分子结构和酶活性对酶造成影响从而对动物造成危害[89],重金属结合酶受体会改变细胞膜的透过性和引发自由基反应[90]. Martínez-Pacheco等[91]将Pb、As和Cd混合物暴露于BALB/C 3T3细胞中. 结果表明,编码蛋白参与细胞过程,包括与金属相关的炎症反应和癌症相关的细胞死亡、生长和增殖,在实验条件下,观察到的mRNA表达变化可能与这种金属混合物产生的miRNA表达谱有关.
-
混合物产生的毒性并非混合物中单一物质的毒性加和[92],因此,我们要借助某些模型来预测混合毒性. 目前常用的混合毒性预测模型有浓度相加模型(Concentration addition model,CA)、独立作用模型(Independent action model,IA)、定量构效关系模型(Quantitative structure-activity relationships model ,QSAR)、动态能量收支模型(Dynamic energy budget model ,DEB)和生物配体模型(Biotic ligand model ,BLM)等. 研究表明,每个模型的适用性可能取决于在评估混合物的综合毒性时所使用的化学品和生物体的组合,评估结果的差异可能取决于物种、暴露时间和浓度等因素.
-
假定各组分之间不存在相互作用,CA模型和IA模型广泛应用于混合物的联合毒性评价[93]. CA模型用于评价具有相同或相似作用机制的化学物质混合物的毒性. [94]. IA模型适用于具有相异作用机制的化学物质的混合毒性评价[95]. CA和IA模型在混合物的组成分别明确符合相似和不同作用的基本思想的情况下,可以表现出很好的预测能力[96]. 近年来,CA和IA模型在定量毒性研究中得到广泛的应用[97-100]. 在特定条件下,CA和IA模型预测的效应浓度值实际上可能是相同的. 一般而言,CA和IA之间的定量关系被认为与混合物组分的数量、混合物组分的浓度比、所考虑的响应水平和单个毒物的RC斜率等4个参数有关[101]. 前3个参数很容易定义,但没有通用的测量方法可以表征整个浓度-反应曲线的斜率. 因此,当满足以下条件时,CA和IA可以产生相等的预测,每个单独混合物组分的浓度-反应关系可以用两参数威布尔模型来描述,曲线严格平行,斜率参数β取值2.3(十进对数) [102].
有研究发现,CA模型所预测的毒性普遍高出IA模型数倍,CA模型的预测有时会高于正常的环境风险. 但从风险评估的角度考虑,CA模型仍是更加安全实用的风险评估模型[103] . 一些研究人员也强调了CA模型对混合物评价的重要性,因为混合物可能具有非特异性相互作用,CA模型通常比IA模型预测更保守的毒性[104]. 特别是不能假定金属在生物体中有独立的作用模式,尽管它们有不同的亲和力和毒性. 例如,Gao等[105]证实CA模型适用于预测Cu+Cd和Cd+Pb混合物对斑马鱼幼虫的毒性. Yoo等[106]采用致死浓度(LCx)和毒性单位(TU)值研究了Cd、As和Pb的联合作用. 研究者以每种金属的LC10值为基础,研究了过氧化氢酶(SOD)和谷胱甘肽酶(GSTs)基因表达和酶活性的调节,进而评估了这些分子标记在评估重金属联合作用及其对抗氧化系统生物反应的影响方面的有效性. 研究发现,CA比IA模型预测的D. celebensis毒性更接近于观察到的致死结果. 说明CA模型可以涵盖元素对转运体的不同亲和性,反映混合条件下的生物利用度.
然而,也有研究支持IA模型在金属混合暴露试验中的应用. 有研究者认为IA模型是CA的替代模型,可以有效地评估具有不同分子靶点但毒性水平等效的组分的混合物毒性[107]. 例如斑马鱼幼虫暴露于Zn+Cd和Cu+Cd混合物中,表明IA模型是更适合预测金属的毒性,其在细胞水平上的目标相似[105]. Nys等[108]还发现,IA模型在预测金属混合物(Ni、Zn和Pb)毒性方面比CA模型对大型水蚤(Daphnia Magna)和两种大麦(D. magna和C. dubia)更准确. Thrupp等[109]研究认为,IA模型是评估成人黑头鲦鱼(Pimephales promelas)中5种合成类固醇药物的更合适的方法. ZHU等[110]测定了重金属对稀有金枪鱼(Gobicypris Rarus)的混合毒性,并发现较高的毒性预测是由IA而不是CA给出的,证明IA模型的预测比CA模型的预测更准确. HUANG等[111]研究也得出相似的结论,认为IA可以预测比CA更高的效果.
-
如果没有成分的作用模式,可以将实验毒性与QSAR模型进行比较,QSAR模型是一种很有前途的技术,可以基于结构相似性分析,识别具有相似毒理作用模式的同类化合物的基线毒性. ZENG等[112]研究测定了5种重金属(Cu、Co、Zn、Fe、Cr)之间的二元复合物对发光菌的抑制作用和毒性评价. 实验结果表明,TU(重金属二元混合物的毒性单位)值在0.15—3.50之间,表现出不同的组合效应(相加效应、协同效应和拮抗效应). 为了预测重金属混合物的毒性,推导了重金属混合物的离子特征参数,并探索了基于离子特征的定量构效关系模型(R2=0.750,Q2=0.649). 定量构效关系模型表明,重金属的混合毒性与电离势((ΔIP)mix)、第一水解常数(lgKOHmix)和生成常数(lgKfmix)的变化有关.
DEB方法以生物体为起点,而不是浓度,因此可以在一个单一的框架内,使用相同的参数来解释致死或亚致死的影响. XIE等[113]研究了Cu和Cd对莱茵衣藻(Chlamydomonas Rehardtii)在单一和复合暴露条件下的毒性效应,比较了不同作用终点作为毒性影响因素的有效性,并建立了预测Cu和Cd对莱茵衣藻亚致死效应的动态能量收支毒理学(DEBtox)模型. 结果表明,对于短期暴露(<24 h),叶绿素荧光参数是较好的毒性效应指标,而对于长期暴露(2—6 d),藻细胞生长较好. 建立的DEBtox模型能较好地预测单一金属对莱茵衣藻的毒性,而组合金属DEBtox模型由于Cu-Cd对莱茵衣藻的拮抗作用,略微高估了Cu-Cd的联合毒性. 研究有助于了解和更好地预测金属亚致死毒性对水生生物的影响. GustavoFonseca等[114]在海洋线虫的研究中,强调影响评估中使用假设驱动设计和概念模型的必要性. 个体和群体水平研究的假设可以从DEB模型中推导出来. 通过微分方程,DEB模型可以推断应激源是否促进了个体生命史上能量分配的变化. 对于群落比值水平的研究,提出并推广了物种丰富度的DEM模型的预测,包括丰富度、均匀度、分类区分度以及组合结构和样本分散的变化. 虽然预测物种丰富度在干扰和富集的中间水平达到峰值,但均匀度随着干扰的增加和富集物/污染物浓度的降低而下降. 基于DEM,富集物和污染物可能通过有利于耐受物种而促进群落结构的变化,而物理干扰可能会由于非选择性死亡而促进样本分散.
BLM模型[115]是为了将金属形态和竞争阳离子的保护效应纳入金属生物有效性和毒性的预测中而发展起来的. BLM的主要假设是,金属毒性是由游离金属离子与生物体-水界面的结合位点反应形成金属-生物配体(BL)络合物所致. 在BLM中,需要金属和竞争阳离子BL络合物的稳定常数来预测重金属的毒性和积累. 先前对BLM的研究,有人提出金属离子占据生物配体可能会导致离子转运受到抑制,从而以降低存活率的形式表现出毒性. 根据这一理论,重金属毒性不受金属种类的影响,而是受金属应激源对生物配体位置的影响. 另一方面,生物配体对Na+、Ca2+等物质的需求与生物种类有关. 根据上述理论,重金属毒性是由于物质转运受到抑制所致. 其他研究人员认为,金属在生物配体上的致命性积累与50%的反应(LA50)有关,取决于任何生物体的敏感酶系统. 酶系统将取决于生物体的种类. 因此,重金属毒性取决于所测试的生物体种类,与重金属种类无关. 先前的研究表明,重金属的积累是造成重金属毒性的限速步骤[116]. 生物体中的重金属含量会比酶等反应物的含量少得多. 因此,研究者认为重金属毒性与两个独立的因素有关,一是依赖于生物体自身的物质运输抑制,二是依赖于暴露时间的积累. 重金属毒性分析可以减少对每种重金属和生物体的毒性试验次数,即利用生物配体与重金属相互作用的时程变化和生物毒性两个因素来预测其毒性. Chen等[117]建立了一个考虑不同阳离子与生物配体结合的几何约束的非线性BLM,为共存阳离子缓解Cd毒性的假想机制提供更可靠的细节. 采用水培方法测定了不同共存阳离子Ca、Mg、K在Cd胁迫下对大豆根系的毒害作用. 用根系伸长(RE)下降50%的Cd活性(Ea)来评价Cd对大豆幼苗的毒害作用,结果表明,提高Ca、Mg、K活性可显著缓解Cd对大豆根系的毒害作用,并且随着Ca、K水平的增加,这种缓解作用明显高于随Mg水平的增加. 因此,从大豆测定获得的真实数据被用来建立Cd根毒性的非线性生物膜模型. 竞争当量和稳定常数两个参数反映了Ca、Mg、K结合在大豆根表面缓解Cd毒害的几何约束和亲和力分布. 与传统的线性BLM相比,非线性BLM能更准确地预测相对RE和Ea. 因此,采用非线性BLM方法将会成功地提高对陆地植物重金属毒性的监测和评价.
-
本文综述了不同功能方面,重金属复合污染对动物及植物生长的致毒机理以及与重金属复合污染相关的毒性预测模型. 尽管近年来,国内外学者扩展研究了重金属复合污染的研究范围与深度,但由于其相互作用机制较为复杂,且复合污染方面的研究仍处于初步阶段,许多方面工作仍有待发展与完善. 因此,为使复合污染研究发展更具重要意义,日后应该着重关注以下相关研究内容. 当前的复合污染主要在两种重金属之间的交互作用的阶段进行研究,3种以上重金属复合污染的研究方法尚未成熟. 因此,需要增加研究对象的数量;由于重金属存在于环境中的浓度、形态、种类的不同,复合形式千变万化,因此相互之间的作用也并不一样,复合的复杂性决定了重金属复合污染研究需要明确特定条件下相互之间作用的差异;外界环境的多介质作用使植物体的种类繁多,而不同的动物因为其生理功能的差异,对复合污染的响应存在个体差异性,重金属复合污染的研究仍不能全面进行特征明确的总结. 目前,重金属复合污染还没有明确的统一方法从环境、功能、基因等角度界定相互之间的作用关系,因此复合污染还需要更完善的发展.
重金属复合污染对生物影响的研究进展
Research progress on the effects of heavy metal compound pollution on organisms
-
摘要: 一直以来,重金属污染都是国内外学者关注的问题. 相比于单一重金属污染,多种重金属并存的复合污染更加普遍. 重金属复合污染具有普遍性、复杂性等特点,它通过加和作用、拮抗作用和协同作用对生态环境产生更多不确定的影响. 本文就重金属复合污染对植物、动物生长的致毒机理做出总结,并归类了重金属复合污染毒性预测模型. 综述了国内外重金属复合污染研究最新进展,从环境科学、环境毒理学、分子生物学等角度出发探讨相关机理,并指出复合污染研究中存在的若干问题和发展方向.Abstract: Heavy metal pollution has always been a concern of scholars at home and abroad. Compared with single heavy metal pollution, multiple heavy metal co-existing compound pollution is more common. Heavy metal combined pollution has the characteristics of universality and complexity, and it has more uncertain effects on the ecological environment through additive, antagonistic and synergistic effects.This article summarizes the toxic mechanism of heavy metal compound pollution to the growth of plants and animals, and classifies the heavy metal compound pollution toxicity prediction model. This review summarizes the latest progress in the study of heavy metal compound pollution at home and abroad, discusses related mechanisms from the perspectives of environmental science, environmental toxicology, and molecular biology, and points out several problems and development directions in the study of compound pollution.
-
Key words:
- heavy metals /
- compound pollution /
- toxic mechanism /
- prediction model
-

-
[1] 周东美, 王慎强, 陈怀满. 土壤中有机污染物-重金属复合污染的交互作用 [J]. 土壤与环境, 2000, 9(2): 143-145. ZHOU D M, WANG S Q, CHEN H M. Interaction of organic pollutants and heavy metal in soil [J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 2000, 9(2): 143-145(in Chinese).
[2] 王恒. 土壤重金属复合污染研究进展 [J]. 科技创新导报, 2016, 13(28): 71-72. WANG H. Research progress of soil heavy metal compound pollution [J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2016, 13(28): 71-72(in Chinese).
[3] 郑振华, 周培疆, 吴振斌. 复合污染研究的新进展 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2001, 12(3): 469-473. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2001.03.037 ZHENG Z H, ZHOU P J, WU Z B. New advances in research of combined pollution [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2001, 12(3): 469-473(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2001.03.037
[4] 窦晶晶. Cd、Cr单一及复合污染对赤子爱胜蚓的毒理研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2015. DOU J J. Individual and combined toxicity of cadmium and chromium on the earthworm Eisenia fetida[D]. Yangling, China: Northwest A & F University, 2015(in Chinese).
[5] JONES D L, DARAH P R, KOCHIAN L V. Critical evaluation of organic acid mediated iron dissolution in the rhizosphere and its potential role in root iron uptake [J]. Plant and Soil, 1996, 180(1): 57-66. doi: 10.1007/BF00015411 [6] 秦月华, 宋锡全. 有机重金属复合污染对香樟吸收营养离子的影响 [J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 28(1): 9-13. QIN Y H, SONG X Q. Effects of organic pollutant and heavy metal complex pollution on nutrient ions absorption of Cinnamomum camphora [J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2010, 28(1): 9-13(in Chinese).
[7] LIU X L, ZHANG S Z, SHAN X Q, et al. Combined toxicity of cadmium and arsenate to wheat seedlings and plant uptake and antioxidative enzyme responses to cadmium and arsenate co-contamination [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2007, 68(2): 305-313. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.11.001 [8] 王新, 梁仁禄, 周启星. Cd-Pb复合污染在土壤-水稻系统中生态效应的研究 [J]. 农村生态环境, 2001, 17(2): 41-44. WANG X, LIANG R L, ZHOU Q X. Ecological effect of Cd Pb combined pollution on soil-rice system [J]. Rural Eco-Environment, 2001, 17(2): 41-44(in Chinese).
[9] GUO T R, ZHANG G P, ZHANG Y H. Physiological changes in barley plants under combined toxicity of aluminum, copper and cadmium [J]. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 2007, 57(2): 182-188. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2007.01.013 [10] CAI Y M, XU W B, WANG M E, et al. Mechanisms and uncertainties of Zn supply on regulating rice Cd uptake [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 253: 959-965. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.077 [11] 梁瑞, 陈慧茹, 刘斌美, 等. 重金属复合污染对水稻镉吸收积累的影响 [J]. 生物学杂志, 2019, 36(03): 42-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2019.03.042 LIANG R, CHEN H R, LIU B M, et al. Effect of heavy metal compound pollution on Cd uptake and accumulation in rice [J]. JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY, 2019, 36(03): 42-46(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2019.03.042
[12] 宇克莉, 孟庆敏, 邹金华. 镉对玉米幼苗生长、叶绿素含量及细胞超微结构的影响 [J]. 华北农学报, 2010, 25(3): 118-123. doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2010.03.026 YU K L, MENG Q M, ZOU J H. Effects of Cd2+ on seedling growth, chlorophyll contents and ultrastructures in maize [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2010, 25(3): 118-123(in Chinese). doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2010.03.026
[13] 张嘉桐, 关颖慧, 司莉青, 等. Pb2+、Cd2+复合胁迫对桑树光合作用的影响 [J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(4): 16-23. ZHANG J T, GUAN Y H, SI L Q, et al. Effects of Pb2+and Cd2+combined stress on photosynthesis of Morus alba [J]. Journal of Beijing for Estry University, 2018, 40(4): 16-23(in Chinese).
[14] 孟庆俊, 袁训珂, 冯启言, 等. 重金属复合污染对小麦幼苗生长的毒性效应 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2008, 36(1): 122-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2008.01.035 MENG Q J, YUAN X K, FENG Q Y, et al. Toxic effects of compound pollution with heavy metals on the growth of wheat seedlings [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2008, 36(1): 122-124(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2008.01.035
[15] 铁柏清, 孙健, 钱湛, 等. 重金属复合污染对灯心草的生态毒性效应及重金属积累特性的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2006, 25(3): 629-636. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2006.03.018 TIE B Q, SUN J, QIAN Z, et al. The eco-toxicological effect of Cu, cd, pb, Zn and as compound pollution on Juncus effuses and its accumulation character of heavy metals [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2006, 25(3): 629-636(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2006.03.018
[16] SHAKYA K, CHETTRI M K, SAWIDIS T. Impact of heavy metals (copper, zinc, and lead) on the chlorophyll content of some mosses [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2008, 54(3): 412-421. doi: 10.1007/s00244-007-9060-y [17] MARIA G, CLAUDIO A S, RODRIGO A C, et al. Cadmium and/or copper excess induce interdependent metal accumulation, DNA methylation, induction of metal chelators and antioxidant defences in the seagrass Zostera marina [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 224: 111-119. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.123 [18] SANTOS R W, SCHMIDT É C, BOUZON Z L. Changes in ultrastructure and cytochemistry of the agarophyte Gracilaria domingensis (Rhodophyta, Gracilariales) treated with cadmium [J]. Protoplasma, 2013, 250(1): 297-305. doi: 10.1007/s00709-012-0412-8 [19] LÖSCH R. Plant mitochondrial respiration under the influence of heavy metals[M]//Heavy Metal Stress in Plants. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2004: 182-200. [20] 刘登义, 王友保. Cu、As对作物种子萌发和幼苗生长影响的研究 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(2): 179-182. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.02.013 LIU D Y, WANG Y B. Effects of Cu and As on germination and seedling growth of crops [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(2): 179-182(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.02.013
[21] 谷巍, 施国新, 韩承辉, 等. 汞、镉污染对轮叶狐尾藻的毒害 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2001, 21(4): 371-375. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2001.04.021 GU W, SHI G X, HAN C H, et al. The toxicity damage effect of Hg2+ and Cd2+ pollution on Myriophyllum verticillatum Linn [J]. China Environmental Science, 2001, 21(4): 371-375(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2001.04.021
[22] 李坤, 李琳, 侯和胜, 等. Cu2+、Cd2+、Zn2+对两种单胞藻的毒害作用 [J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2002, 8(4): 395-398. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-687X.2002.04.013 LI K, LI L, HOU H S, et al. Study on toxicity of heavy metal ions to two species of marine unicellular algae [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2002, 8(4): 395-398(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-687X.2002.04.013
[23] 施国新, 杜开和, 解凯彬, 等. 汞、镉污染对黑藻叶细胞伤害的超微结构研究 [J]. 植物学报, 2000, 42(4): 373-378. SHI G X, DU K H, XIE K B, et al. Ultrastructural study of leaf cells damaged from Hg2+ and Cd2+ pollution in Hydrilla verticillata [J]. Acta Botanica Sinica, 2000, 42(4): 373-378(in Chinese).
[24] POULTER A, COLLIN H A, THURMAN D A, et al. The role of the cell wall in the mechanism of lead and zinc tolerance in Anthoxanthum odoratum L [J]. Plant Science, 1985, 42(1): 61-66. doi: 10.1016/0168-9452(85)90029-9 [25] 徐勤松, 施国新, 杜开和. 重金属镉、锌在菹草叶细胞中的超微定位观察 [J]. 云南植物研究, 2002, 24(2): 241-244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0845.2002.02.012 XU Q S, SHI G X, DU K H. Ultrastructual localization observation of Cd and Zn in leaf cells of Potamogeton crispus [J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 2002, 24(2): 241-244(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0845.2002.02.012
[26] 范春辉, 高雅琳, 杜波. 黄土区金盏菊幼苗根部细胞壁对Pb/Cd复合胁迫响应的FTIR和Raman光谱 [J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(7): 2076-2081. FAN C H, GAO Y L, DU B. Response of FTIR and Raman spectra on cell wall of calendula of ficinalis seedlings roots to the co-contamination stress of lead and cadmium in loess [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2016, 36(7): 2076-2081(in Chinese).
[27] 杨顶田, 施国新, 陈伟民. Cr6+污染对水鳖的超微结构及菱、莼菜、黑藻细胞膜的影响 [J]. 武汉植物学研究, 2001, 19(6): 483-488,537. YANG D T, SHI G X, CHEN W M. The effects of Cr6+'s pollution on the ultrastructure of Hydrocharis dubia and cell membrane of H. verticillata, Brasenia schreberi, Trapa bispinosa [J]. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 2001, 19(6): 483-488,537(in Chinese).
[28] 杨世勇, 王方, 谢建春. 重金属对植物的毒害及植物的耐性机制 [J]. 安徽师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 27(1): 71-74,90. YANG S Y, WANG F, XIE J C. Plant toxicity of heavy metals and the tolerant mechanisms of plants [J]. Journal of Anhui Normal University (Natural Science), 2004, 27(1): 71-74,90(in Chinese).
[29] 李元, 王焕校, 吴玉树. Cd、Fe及其复合污染对烟草叶片几项生理指标的影响 [J]. 生态学报, 1992, 12(2): 147-154. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.1992.02.001 LI Y, WANG H X, WU Y S. Effects of cadmium and iron on the some physiological indicators in leaves of tobacco [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1992, 12(2): 147-154(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.1992.02.001
[30] SHAHID M, POURRUT B, DUMAT C, et al. Heavy-metal-induced reactive oxygen species: phytotoxicity and physicochemical changes in plants [J]. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2014, 232: 1-44. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-06746-9_1 [31] SKÓRZYŃSKA-POLIT E, PAWLIKOWSKA-PAWLĘGA B, SZCZUKA E, et al. The activity and localization of lipoxygenases in Arabidopsis thaliana under cadmium and copper stresses [J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2006, 48(1): 29-39. doi: 10.1007/s10725-005-4745-6 [32] MISHRA S, SRIVASTAVA S, TRIPATHI R D, et al. Lead detoxification by coontail (Ceratophyllum demersum L. ) involves induction of phytochelatins and antioxidant system in response to its accumulation [J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 65(6): 1027-1039. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.03.033 [33] SINGH R, TRIPATHI R D, DWIVEDI S, et al. Lead bioaccumulation potential of an aquatic macrophyte Najas indica are related to antioxidant system [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(9): 3025-3032. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.031 [34] HOSSAIN M A, PIYATIDA P, da SILVA J A T, et al. Molecular mechanism of heavy metal toxicity and tolerance in plants: Central role of glutathione in detoxification of reactive oxygen species and methylglyoxal and in heavy metal chelation [J]. Journal of Botany, 2012, 2012: 1-37. [35] VOLLENWEIDER P, MENARD T, GÜNTHARDT-GOERG M S. Compartmentation of metals in foliage of Populus tremula grown on soils with mixed contamination. I. From the tree crown to leaf cell level [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(1): 324-336. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.07.013 [36] ZHOU Q, GU Y L, YUE X, et al. Combined toxicity and underlying mechanisms of a mixture of eight heavy metals [J]. Molecular Medicine Reports, 2017, 15(2): 859-866. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.6089 [37] AN Q R, HE X L, ZHENG N, et al. Physiological and genetic effects of cadmium and copper mixtures on carrot under greenhouse cultivation [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 206: 111363. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111363 [38] GUPTA M, SARIN N B. Heavy metal induced DNA changes in aquatic macrophytes: Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis and identification of sequence characterized amplified region marker [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21(5): 686-690. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62324-4 [39] 葛才林, 杨小勇, 孙锦荷, 等. 重金属胁迫引起的水稻和小麦幼苗DNA损伤 [J]. 植物生理与分子生物学学报, 2002, 28(6): 419-424. GE C L, YANG X Y, SUN J H, et al. DNA damage caused by heavy metal stress in rice and wheat seedlings [J]. Acta Photophysiologica Sinica, 2002, 28(6): 419-424(in Chinese).
[40] 吕朝晖, 王焕校. 镉铅对小麦醇脱氢酶(ADH)基因表达影响的初步研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 1998, 18(5): 500-503. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.1998.05.010 LV Z H, WANG H X. Effects of cadmium and lead on adh gene experssion [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 1998, 18(5): 500-503(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.1998.05.010
[41] ZHANG Y X, CHAI T Y, DONG J, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of the heavy-metal responsive gene PvSR2 from bean [J]. Plant Science, 2001, 161(4): 783-790. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00470-8 [42] NGUYEN VAN T. Assessment of combined toxic and genotoxic effects of soil metal pollutants: A laboratory and a field experiment using the test plant trifolium repens [D]. University of Milano-Bicocca, 2015. [43] LANIER C, BERNARD F, DUMEZ S, et al. Combined toxic effects and DNA damage to two plant species exposed to binary metal mixtures (Cd/Pb) [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 167: 278-287. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.010 [44] LU C L, SVOBODA K R, LENZ K A, et al. Toxicity interactions between manganese (Mn) and lead (Pb) or cadmium (Cd) in a model organism the nematode C. elegans [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(16): 15378-15389. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1752-5 [45] COOPER N L, BIDWELL J R, KUMAR A. Toxicity of copper, lead, and zinc mixtures to Ceriodaphnia dubia and Daphnia carinata [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2009, 72(5): 1523-1528. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.03.002 [46] VIJVER M G, ELLIOTT E G, PEIJNENBURG W J G M, et al. Response predictions for organisms water-exposed to metal mixtures: A meta-analysis [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2011, 30(6): 1482-1487. doi: 10.1002/etc.499 [47] LUO W, VERWEIJ R A, van GESTEL C A M. Determining the bioavailability and toxicity of lead contamination to earthworms requires using a combination of physicochemical and biological methods [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014, 185: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.10.017 [48] WU X Y, COBBINA S J, MAO G H, et al. A review of toxicity and mechanisms of individual and mixtures of heavy metals in the environment [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(9): 8244-8259. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6333-x [49] EUM K D, WEISSKOPF M G, NIE L H, et al. Cumulative lead exposure and age at menopause in the Nurses' Health Study cohort [J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2014, 122(3): 229-234. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1206399 [50] ADAMS S V, QURAISHI S M, SHAFER M M, et al. Dietary cadmium exposure and risk of breast, endometrial, and ovarian cancer in the Women's Health Initiative [J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2014, 122(6): 594-600. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1307054 [51] BLOOM M S, PARSONS P J, STEUERWALD A J, et al. Toxic trace metals and human oocytes during in vitro fertilization (IVF) [J]. Reproductive Toxicology, 2010, 29(3): 298-305. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2010.01.003 [52] JEZIERSKA B, ŁUGOWSKA K, WITESKA M. The effects of heavy metals on embryonic development of fish (a review) [J]. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 2009, 35(4): 625-640. doi: 10.1007/s10695-008-9284-4 [53] WITESKA M, SARNOWSKI P, ŁUGOWSKA K, et al. The effects of cadmium and copper on embryonic and larval development of ide Leuciscus idus L [J]. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 2014, 40(1): 151-163. doi: 10.1007/s10695-013-9832-4 [54] 黄涛, 求瑞娟, 兰宗宝, 等. 稀土尾矿库渗漏水污染对花背蟾蜍胚后发育的毒性作用 [J]. 南方农业学报, 2019, 50(2): 412-417. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2019.02.28 HUANG T, QIU R J, LAN Z B, et al. The toxic effects of leakage water from rare earth tailings reservoir on the postembryonic development of Strauchbufo raddei [J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2019, 50(2): 412-417(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2019.02.28
[55] 贾秀英, 董爱华, 马小梅. 镉致蟾蜍肝、肾脂质过氧化损伤 [J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2004, 10(1): 92-94. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-687X.2004.01.021 JIA X Y, DONG A H, MA X M. Effect of Cd2+ on lipid peroxidation in liver and kidney of Bufo gargarizans [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2004, 10(1): 92-94(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-687X.2004.01.021
[56] van OOIK T, PAUSIO S, RANTALA M J. Direct effects of heavy metal pollution on the immune function of a geometrid moth, Epirrita autumnata [J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 71(10): 1840-1844. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.02.014 [57] BISER J A, VOGEL L A, BERGER J, et al. Effects of heavy metals on immunocompetence of white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) [J]. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 2004, 40(2): 173-184. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-40.2.173 [58] SORVARI J, RANTALA L M, RANTALA M J, et al. Heavy metal pollution disturbs immune response in wild ant populations [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 145(1): 324-328. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.03.004 [59] CHATELAIN M, GASPARINI J, FRANTZ A. Trace metals, melanin-based pigmentation and their interaction influence immune parameters in feral pigeons (Columba livia) [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2016, 25(3): 521-529. doi: 10.1007/s10646-016-1610-5 [60] BAHADAR H, ABDOLLAHI M, MAQBOOL F, et al. Mechanistic overview of immune modulatory effects of environmental toxicants [J]. Inflammation & Allergy-Drug Targets, 2015, 13(6): 382-386. [61] LUTZ W, WASOWICZ W. Metal-induced modulation of redox cell-signaling in the immune system [J]. Comments on Toxicology, 2003, 9(1): 59-83. doi: 10.1080/08865140302422 [62] DONG J S, LI J J, CUI L Y, et al. Cortisol modulates inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells via the NF-κB and MAPK pathways [J]. BMC Veterinary Research, 2018, 14(1): 30. doi: 10.1186/s12917-018-1360-0 [63] JADHAV S H, SARKAR S N, RAM G C, et al. Immunosuppressive effect of subchronic exposure to a mixture of eight heavy metals, found as groundwater contaminants in different areas of India, through drinking water in male rats [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2007, 53(3): 450-458. doi: 10.1007/s00244-006-0177-1 [64] 江红霞, 凌洁彬, 叶凯甲, 等. 铜和镉对草鱼肾脏中3种白细胞介素基因表达的影响 [J]. 水产科学, 2019, 38(2): 220-225. JIANG H X, LING J B, YE K J, et al. Effects of copper and cadmium on expression of three interleukin genes in kidney of grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus [J]. Fisheries Science, 2019, 38(2): 220-225(in Chinese).
[65] MORCILLO P, CORDERO H, MESEGUER J, et al. In vitro immunotoxicological effects of heavy metals on European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L. ) head-kidney leucocytes [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2015, 47(1): 245-254. [66] 白晓娟. 树麻雀免疫系统对环境重金属污染响应的研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. BAI X J. Study on the response of immune system in tree sparrow to environmental heavy metals pollution[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019(in Chinese).
[67] GERHARDSSON L, ENGLYST V, LUNDSTRÖM N G, et al. Cadmium, copper and zinc in tissues of deceased copper smelter workers [J]. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 2002, 16(4): 261-266. doi: 10.1016/S0946-672X(02)80055-4 [68] SOLGI E, MIRMOHAMMADVALI S. Comparison of the heavy metals, copper, iron, magnesium, nickel, and zinc between muscle and gills of four benthic fish species from shif island (Iran) [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2021, 106(4): 658-664. doi: 10.1007/s00128-021-03155-1 [69] MORCILLO P, CORDERO H, MESEGUER J, et al. Toxicological in vitro effects of heavy metals on gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L. ) head-kidney leucocytes [J]. Toxicology in Vitro, 2015, 30(1): 412-420. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2015.09.021 [70] HANDY R D. Chronic effects of copper exposure versus endocrine toxicity: Two sides of the same toxicological process? [J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A:Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 2003, 135(1): 25-38. [71] 顾成武. 铅镉联合对发育期大鼠中枢神经系统二价金属转运蛋白DMT1基因表达的影响[D]. 汕头: 汕头大学, 2008. GU C W. Combined effect of lead and cadmium on DMT1 expression in central nervous system of budding rat[D]. Shantou, China: Shantou University, 2008(in Chinese).
[72] KARRI V, SCHUHMACHER M, KUMAR V. Heavy metals (Pb, Cd, As and MeHg) as risk factors for cognitive dysfunction: A general review of metal mixture mechanism in brain [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2016, 48: 203-213. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2016.09.016 [73] REGLERO M M, TAGGART M A, CASTELLANOS P, et al. Reduced sperm quality in relation to oxidative stress in red deer from a lead mining area [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(8/9): 2209-2215. [74] ADEMUYIWA O, AGARWAL R, CHANDRA R, et al. Effects of sub-chronic low-level lead exposure on the homeostasis of copper and zinc in rat tissues [J]. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 2010, 24(3): 207-211. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2010.01.002 [75] JANKOVSKÁ I, MIHOLOVÁ D, LANGROVÁ I, et al. Influence of parasitism on the use of small terrestrial rodents in environmental pollution monitoring [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(8/9): 2584-2586. [76] COBBINA S J, CHEN Y, ZHOU Z X, et al. Low concentration toxic metal mixture interactions: Effects on essential and non-essential metals in brain, liver, and kidneys of mice on sub-chronic exposure [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 132: 79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.013 [77] RAI N K, ASHOK A, RAI A, et al. Exposure to As, Cd and Pb-mixture impairs myelin and axon development in rat brain, optic nerve and Retina [J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2013, 273(2): 242-258. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.05.003 [78] BOELSTERLI U A. Mechanistic toxicology: The molecular basis of how chemicals disrupt biological targets[M]. New York:Toxicology,2003 [79] VERMA R, XU X F, JAISWAL M K, et al. In vitro profiling of epigenetic modifications underlying heavy metal toxicity of tungsten-alloy and its components [J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2011, 253(3): 178-187. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2011.04.002 [80] LOU J L, JIN L Z, WU N X, et al. DNA damage and oxidative stress in human B lymphoblastoid cells after combined exposure to hexavalent chromium and nickel compounds [J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2013, 55: 533-540. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.01.053 [81] DORNE J L C M, RAGAS A M J, FRAMPTON G K, et al. Trends in human risk assessment of pharmaceuticals [J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2007, 387(4): 1167-1172. doi: 10.1007/s00216-006-0961-9 [82] XUE S G, SHI L Z, WU C, et al. Cadmium, lead, and arsenic contamination in paddy soils of a mining area and their exposure effects on human HEPG2 and keratinocyte cell-lines [J]. Environmental Research, 2017, 156: 23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2017.03.014 [83] WU B, LIU Z T, XU Y, et al. Combined toxicity of cadmium and lead on the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Annelida, Oligochaeta) [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2012, 81: 122-126. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.05.003 [84] VELLINGER C, GISMONDI E, FELTEN V, et al. Single and combined effects of cadmium and arsenate in Gammarus pulex (Crustacea, Amphipoda): Understanding the links between physiological and behavioural responses [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2013, 140/141: 106-116. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.05.010 [85] CHOI Y, PARK K, KIM I, et al. Combined toxic effect of airborne heavy metals on human lung cell line A549 [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2018, 40(1): 271-282. doi: 10.1007/s10653-016-9901-6 [86] HAMBACH R, LISON D, D’HAESE P C, et al. Co-exposure to lead increases the renal response to low levels of cadmium in metallurgy workers [J]. Toxicology Letters, 2013, 222(2): 233-238. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.06.218 [87] YANG D F, LIU Y L, LIU S, et al. Exposure to heavy metals and its association with DNA oxidative damage in municipal waste incinerator workers in Shenzhen, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 250: 126289. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126289 [88] 张迎梅, 王叶菁, 虞闰六, 等. 重金属Cd2+、Pb2+和Zn2+对泥鳅DNA损伤的研究 [J]. 水生生物学报, 2006, 30(4): 399-403. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3207.2006.04.005 ZHANG Y M, WANG Y J, YU R L, et al. Effects of heavy metals Cd2+, Pb2+ and Zn2+ on DNA damage of loach Misgurnus anguillicandatus [J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2006, 30(4): 399-403(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3207.2006.04.005
[89] SARKAR A. Biomarkers of marine pollution and bioremediation [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2006, 15(4): 331-332. doi: 10.1007/s10646-006-0073-5 [90] VIDALI M. Bioremediation. An overview [J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 2001, 73(7): 1163-1172. doi: 10.1351/pac200173071163 [91] MARTÍNEZ-PACHECO M, HIDALGO-MIRANDA A, ROMERO-CÓRDOBA S, et al. mRNA and miRNA expression patterns associated to pathways linked to metal mixture health effects [J]. Gene, 2014, 533(2): 508-514. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.09.049 [92] 吴晓亭, 王晓昌, 马晓妍. 固定毒性配比法研究重金属与土霉素的联合毒性 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(1): 626-631. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201508115 WU X T, WANG X C, MA X Y. Joint toxicities of binary mixtures between heavy metals and OTC based on predefined TU ratios [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(1): 626-631(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201508115
[93] GE H L, LIU S S, SU B X, et al. Predicting synergistic toxicity of heavy metals and ionic liquids on Photobacterium Q67 [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 268: 77-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.006 [94] BAAS J, van HOUTE B P P, van GESTEL C A M, et al. Modeling the effects of binary mixtures on survival in time [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2007, 26(6): 1320-1327. doi: 10.1897/06-437R.1 [95] LOEWE S, MUISCHNEK H. Effect of combinations: Mathematical basis of problem[J]. Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol,1926 [96] SPURGEON D J, JONES O A H, DORNE J L C M, et al. Systems toxicology approaches for understanding the joint effects of environmental chemical mixtures [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 408(18): 3725-3734. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.02.038 [97] BACKHAUS T, SCHOLZE M, GRIMME L H. The single substance and mixture toxicity of quinolones to the bioluminescent bacterium Vibrio fischeri [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2000, 49(1/2): 49-61. [98] JUNGHANS M, BACKHAUS T, FAUST M, et al. Predictability of combined effects of eight chloroacetanilide herbicides on algal reproduction [J]. Pest Management Science, 2003, 59(10): 1101-1110. doi: 10.1002/ps.735 [99] FAUST M, ALTENBURGER R, BACKHAUS T, et al. Joint algal toxicity of 16 dissimilarly acting chemicals is predictable by the concept of independent action [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2003, 63(1): 43-63. doi: 10.1016/S0166-445X(02)00133-9 [100] WALTER H, CONSOLARO F, GRAMATICA P, et al. Mixture toxicity of priority pollutants at no observed effect concentrations (NOECs) [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2002, 11(5): 299-310. doi: 10.1023/A:1020592802989 [101] DRESCHER K, BOEDEKER W. Assessment of the combined effects of substances: The relationship between concentration addition and independent action [J]. Biometrics, 1995, 51(2): 716. doi: 10.2307/2532957 [102] BACKHAUS T, FAUST M, SCHOLZE M, et al. Joint algal toxicity of phenylurea herbicides is equally predictable by concentration addition and independent action [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2004, 23(2): 258-264. doi: 10.1897/02-497 [103] 陈朗, 姜辉, 贾俊超, 等. 农药混配制剂环境风险评估现状与展望 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2017, 12(4): 15-24. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20170527003 CHEN L, JIANG H, JIA J C, et al. Environmental risk assessment for mixed pesticide products: Current situation and prospects [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2017, 12(4): 15-24(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20170527003
[104] PUCKOWSKI A, STOLTE S, WAGIL M, et al. Mixture toxicity of flubendazole and fenbendazole to Daphnia magna [J]. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 2017, 220(3): 575-582. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2017.01.011 [105] GAO Y F, FENG J F, KANG L L, et al. Concentration addition and independent action model: Which is better in predicting the toxicity for metal mixtures on zebrafish larvae [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 610/611: 442-450. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.058 [106] YOO J W, CHO H, LEE K W, et al. Combined effects of heavy metals (Cd, As, and Pb): Comparative study using conceptual models and the antioxidant responses in the brackish water flea [J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C:Toxicology & Pharmacology, 2021, 239: 108863. [107] BACKHAUS T, FAUST M. Predictive environmental risk assessment of chemical mixtures: A conceptual framework [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(5): 2564-2573. [108] NYS C, VERSIEREN L, CORDERY K I, et al. Systematic evaluation of chronic metal-mixture toxicity to three species and implications for risk assessment [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(8): 4615-4623. [109] THRUPP T J, RUNNALLS T J, SCHOLZE M, et al. The consequences of exposure to mixtures of chemicals: Something from ‘nothing’ and ‘a lot from a little’ when fish are exposed to steroid hormones [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 619/620: 1482-1492. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.081 [110] ZHU B, WU Z F, LI J, et al. Single and joint action toxicity of heavy metals on early developmental stages of Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2011, 74(8): 2193-2202. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.07.033 [111] HUANG W Y, LIU F, LIU S S, et al. Predicting mixture toxicity of seven phenolic compounds with similar and dissimilar action mechanisms to Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. nov. Q67 [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2011, 74(6): 1600-1606. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.01.007 [112] ZENG J J, CHEN F, LI M, et al. The mixture toxicity of heavy metals on Photobacterium phosphoreum and its modeling by ion characteristics-based QSAR [J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(12): e0226541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226541 [113] XIE M D, SUN Y X, FENG J F, et al. Predicting the toxic effects of Cu and Cd on Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a DEBtox model [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2019, 210: 106-116. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.02.018 [114] FONSECA G, GALLUCCI F. The need of hypothesis-driven designs and conceptual models in impact assessment studies: An example from the free-living marine Nematodes [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2016, 71: 79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.06.051 [115] DI TORO D M, ALLEN H E, BERGMAN H L, et al. Biotic ligand model of the acute toxicity of metals. 1. Technical Basis [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2001, 20(10): 2383-2396. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620201034 [116] MARTINS R J E, BOAVENTURA R A R. Uptake and release of zinc by aquatic bryophytes (Fontinalis antipyretica L. ex. Hedw.) [J]. Water Research, 2002, 36(20): 5005-5012. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00233-6 [117] CHEN B C, WANG P J, HO P C, et al. Nonlinear biotic ligand model for assessing alleviation effects of Ca, Mg, and K on Cd toxicity to soybean roots [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2017, 26(7): 942-955. doi: 10.1007/s10646-017-1823-2 -



 下载:
下载:

