-
金属有机框架材料(MOFs)材料是一类由无机金属离子或金属簇与含氮、氧刚性有机配体通过自组装形成的多孔材料,具有丰富的结构类型、大比表面积、多金属位点等诸多性能[1].随着研究不断深入,锆基金属有机框架(Zr-MOFs)材料不断涌现. Zr-MOFs材料的晶体结构大都基于金属无机节点[Zr6O4(OH)4]12+簇,每个金属无机节点通过各种配体连接到无机锆簇上. 由于锆离子配位键较强,使得Zr-MOFs材料在水以及酸、碱溶液中均可以保持其结构完整,从而在吸附去除有机污染物方面展现了强大的潜力[2]. Hasan等[3]使用UiO-66及其功能化衍生物UiO-66s(带有‒SO3H或者‒NH2的UiO-66)去除水中双氯芬酸钠,UiO-66和UiO-66s在吸附速率和吸附容量方面都明显优于活性炭,SO3H官能化UiO-66的吸附容量达到了活性炭的13倍; Zhu等[4]研究表明,草甘膦和草铵膦在UiO-67中的理论最大吸附量分别高达537 mg·g−1和360 mg·g−1,远远超过了先前报道过的吸附剂. 与UiO-67相比,Pankajakshan等[5]的研究表明,NU-1000与草甘膦的相互作用更强,分离距离更短,对草甘膦具有更高的吸附能力和更好的重复稳定性.
甲萘威(1-萘基-N-甲基氨基甲酸酯)作为保护谷物、水果、蔬菜和其他作物免受虫害而广泛使用的一种杀虫剂,由于其广谱高效,长期大量大面积的喷施已对环境造成一定程度的污染. 目前,利用MOFs从水溶液中吸附去除甲萘威的研究尚未报道. 本研究从吸附等温线、吸附动力学和热力学等方面分析UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000吸附剂对酸性水中甲萘威的吸附性能,旨在论证利用Zr-MOFs材料去除废水中甲萘威污染的可行性.
-
Ultimate3000型高效液相色谱仪(美国Thermo Fisher公司),D8 Advance型粉末X射线衍射仪(PXRD,德国Bruker公司),Quanta 250热场发射扫描电子显微镜(美国FEI公司),BSD-PM型高性能比表面积及微孔分析仪(贝士德仪器科技(北京)有限公司),BSA224S-CW型电子天平(德国Sartorius公司),Sorvall ST 16R型高速冷冻离心机(美国Thermo Fisher公司).UiO-66和UiO-67根据Katz等[6]的方法制备,NU-1000根据Wang[7]等的方法制备.
-
配制pH 3.0的40 mL初始浓度为5、10、20、40、60、80、100、120、150、180 mg·L−1的甲萘威溶液,分别加入10 mg UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000吸附剂,置于25 °C恒温水浴摇床中180 r·min−1下吸附24 h. 吸附平衡后,以12000 r·min−1的转速离心5 min. 采用高效液相色谱仪(HPLC)测定溶液中甲萘威的平衡浓度. 测试条件:反相C18 HPLC柱,流动相为水/甲醇(45%:55%,V/V),流速为1 mL ·min−1,检测器波长为223 nm,色谱柱温度为25 ℃. 吸附量计算:
${ q=\dfrac{\left({C}_{0}-{C}_{e}\right)}{m}V }$ 。式中,q(mg·g−1)为吸附量,$ {{C}_{0}} $ 和${ {C}_{e}} $ (mg·L−1)分别为甲萘威的初始浓度和平衡浓度. V(L)为溶液的体积,m(g)为吸附剂的质量[3].Langmuir方程
${ \left(\dfrac{Ce}{{q}_{e}}=\dfrac{Ce}{{q}_{m}}+\dfrac{1}{{k}_{L}{q}_{m}}\right)} $ 和Freundlich方程$ {\left(\mathrm{lg}{q}_{e}=\mathrm{lg}{k}_{F}+\dfrac{1}{n}\mathrm{lg}{C}_{e}\right) }$ 用于拟合等温吸附试验数据。式中,$ {{q}_{e} }$ (mg·g−1)是吸附平衡时的吸附量,${ {q}_{m} }$ (mg·g−1)是采用Langmuir方程拟合的吸附剂最大吸附量,${ {k}_{L} }$ (L·mg−1)是Langmuir方程拟合的吸附常数,${ {k}_{F} }$ 和n是Freundlich方程拟合的吸附能力和吸附强度常数. -
配制pH=3.0的40 mL初始浓度为100 mg·L−1的甲萘威溶液,分别加入10 mg吸附剂,将锥形瓶置于20°C水浴恒温振荡器中180 r·min−1下吸附,分别在5、10、20、30、40、50、60、120、180、240、300、360 min不同时刻取样检测溶液中剩余甲萘威的浓度. 准一级动力学方程
${\left( \lg\left({q}_{e}-{q}_{t} \right)={\lg}_{{q}_{e}}-\dfrac{{k}_{1}}{2.303}t \right)}$ 和准二级动力学方程${\left( \dfrac{t}{{q}_{t}}=\dfrac{1}{{k}_{2}{q}_{e}^{2}}+\dfrac{t}{{q}_{e}} \right)}$ 用于拟合吸附动力学数据。式中,${ {q}_{t}} $ (mg·g−1)是在t时吸附剂的吸附量,${ {k}_{1}} $ 、${ {k}_{2} }$ 是准一级和准二级动力学吸附常数. -
配制pH=3.0的40 mL浓度为100 mg·L−1的甲萘威溶液,分别加入10 mg吸附剂,将锥形瓶置于25、30、40、50 ℃水浴恒温振荡器中180 r·min−1,24 h后取样检测溶液中甲萘威的平衡浓度. 热力学参数计算:
$ {{\Delta G}=-RT{lnK} }$ 和$ {{\ln K}=\dfrac{{\Delta S}}{R}-\dfrac{{\Delta H}}{RT} }$ 。式中,T为溶液温度,R是热力学气体常数,K是热力学平衡常数. -
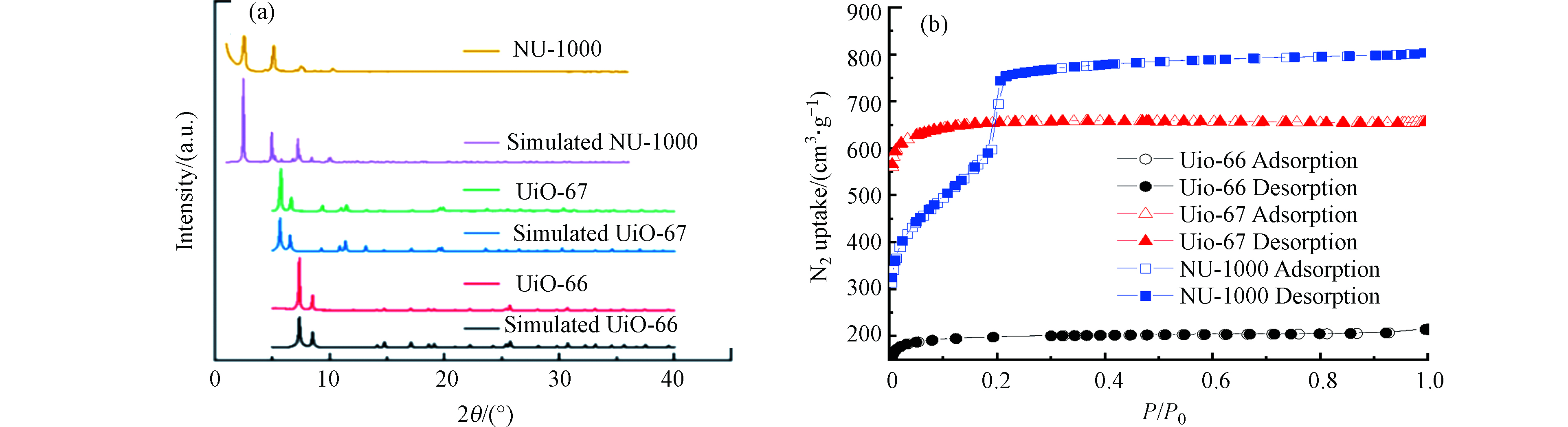
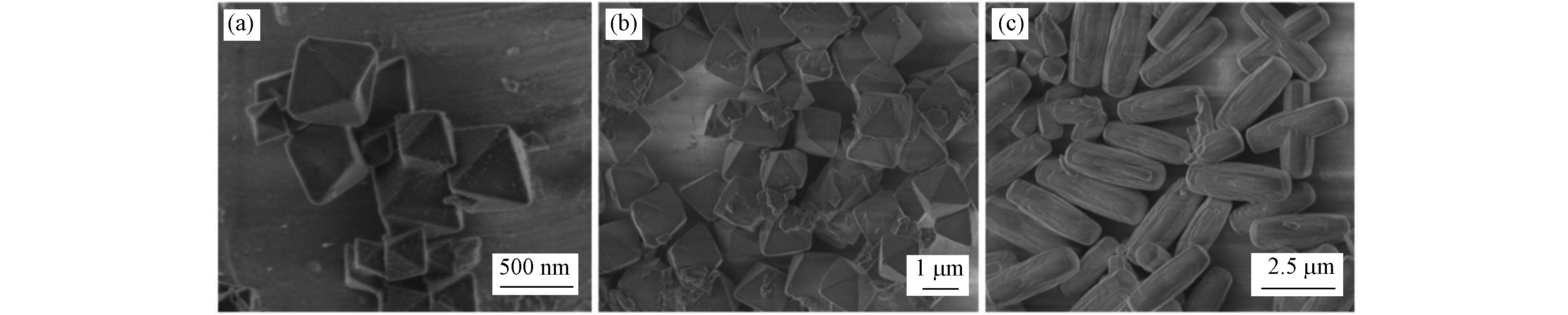
3种Zr-MOFs材料的SEM照片见图1,UiO-66、UiO-67呈规则正八面体结构,晶粒尺寸分别约为500 nm和1.5 μm;NU-1000呈规则棒状晶粒,晶粒尺寸约为2.5 μm,与文献 [5]相符. 利用PXRD对3种Zr-MOFs材料晶体结构进行表征(2(a)),UiO-66分别在2θ=7.4°、8.5°、14.8°、17.1°,UiO-67分别在2θ=5.7°、6.6°、11.5°、13.2°,NU-1000分别在2θ=2.5°、5.1°、7.4°、10.2°出现相应的特征衍射峰,结果与基于晶体数据模拟的结果以及Xia等报道的结果接近[8],表明本研究成功合成了UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000材料. 如图2(b)所示,3种Zr-MOFs材料均为I型等温线,表明具有典型的微孔特征. 此外,由BET模型和密度泛函理论(DFT)方法计算得到UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000的比表面积(1640、2145、2280 m2·g−1)和总孔体积(0.656、1.249、1.578 mL·g−1)与文献报道值接近[6-7].
-
等温吸附试验结果表明,UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000分别在原始浓度为120、150、180 mg·L−1时达到平衡,此时对应的最大吸附量分别为84.50、196.62、282.63 mg·g−1. 由表1可知,Langmuir方程(R2>0.99)拟合的结果要远优于Freundlich方程,说明Langmuir方程较为符合3种Zr-MOFs材料对甲萘威的吸附过程. 此外,由Langmuir方程计算得到的UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000吸附甲萘威的最大吸附量
$ {q}_{m} $ 分别为115.05、221.45、310.97 mg·g−1. -
吸附动力学试验结果表明,UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000对甲萘威的吸附在20 min时均基本达到平衡,吸附效率较高. 由表2可知,准二级动力学方程线性拟合的相关系数(R2=0.999)要优于准一级动力学方程,表明准二级动力学方程能更好的描述3种Zr-MOFs材料对甲萘威的吸附过程,且化学吸附起主要作用. 此外,由准二级动力学方程得到的UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000吸附甲萘威的
$ {q}_{e} $ 值分别为90.58、178.78、239.08 mg·g−1,与试验得到的吸附数据(89.90、178.34、238.44 mg·g−1)相近. -
吸附热力学试验结果表明,UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000对甲萘威的吸附能力均随着温度的升高而增加,升温有利于反应的进行和吸附能力的提升,说明是吸热反应,相关热力学参数见表3. 其中,
$ {\Delta G} $ <0且随着温度的升高而减小,这表明吸附过程是自发的。∆S>0,表明反应过程中固/液界面混乱度上升。 -
UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000对甲萘威的吸附在溶液pH 3.0的条件下能取得较好的吸附效果,因此Zr-MOFs材料可用作吸附剂处理偏酸性的甲萘威废水. UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000对甲萘威的吸附过程符合Langmuir等温吸附方程,属于单分子层吸附,理论最大吸附量分别为115.05、221.45、310.97 mg·g−1. UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000对甲萘威的吸附效率较高,20 min内基本达到吸附平衡,吸附过程符合准二级动力学方程,化学吸附起主要作用. UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000对甲萘威的吸附是自发进行的吸热反应,升温有利于吸附,反应过程中固/液界面混乱度上升.
锆基金属有机框架材料对酸性水中甲萘威的吸附
Generated Zirconium Based Metal Organic Framework Materials for Carbaryl adsorption in Acidic Aqueous Solutions
-
摘要: 对比分析了UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000等3种锆基金属有机框架(Zr-MOFs)材料在pH 3.0水溶液中对甲萘威的吸附特性. 批量吸附试验结果表明,UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000对甲萘威均表现出高效的吸附性能,20 min内基本达到吸附平衡;等温吸附试验结果表明,吸附过程与Langmuir等温吸附方程拟合程度较高(R2>0.99),理论最大吸附量分别为115.05、221.45、310.97 mg·g-1;吸附动力学试验结果表明,吸附过程符合准二级动力学方程(R2=0.999),且化学吸附起主要作用;热力学参数计算结果表明,吸附过程是自发进行的吸热反应,升温有利于吸附.
-
关键词:
- 锆基金属有机框架材料 /
- 甲萘威 /
- 吸附 /
- 水
Abstract: The adsorption characteristics of zirconium based metal organic framework materials (UiO-66, UiO-67 and NU-1000) on carbaryl in pH 3.0 aqueous solution were compared and analyzed. Adsorption experiments showed that the three adsorbents exhibited efficiently adsorption performance for carbaryl, and reached basically the adsorption equilibrium within 20 min. The adsorption isotherm experiments showed that the adsorption process fitted well with Langmuir equation (R2>0.99), and the theoretical maximum adsorption capacity were 115.05, 221.45 and 310.97 mg·g-1, respectively. The adsorption kinetics experiments showed that the adsorption process conformed to the quasi-second-order kinetic equation (R2=0.999), and chemical adsorption played a major role. Calculation of thermodynamic parameters$ \Delta G $ ,$ \Delta H $ and$ \Delta S $ showed that the adsorption process was a spontaneous endothermic reaction, and heating was beneficial to adsorption.-
Key words:
- zirconium based metal organic framework materials /
- carbaryl /
- adsorption /
- water
-

-
表 1 UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000对甲萘威的等温吸附方程拟合参数
Table 1. Fitting parameters of adsorption isotherms of carbaryl on UiO-66, UiO-67 and NU-1000
吸附剂类型 Langmuir方程 Freundlich方程 qm/(mg·g−1) kL/(L·mg−1) R2 kF 1/n R2 UiO-66 115.05 0.030 0.997 5.42 0.64 0.977 UiO-67 221.45 0.075 0.998 21.70 0.53 0.959 NU-1000 310.97 0.094 0.994 39.12 0.46 0.961 表 2 UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000对甲萘威的吸附动力学拟合参数
Table 2. Fitting parameters of the adsorption kinetic of carbaryl on UiO-66, UiO-67 and NU-1000
吸附剂
类型准一级 准二级 试验结果 qe/(mg·g−1) k1/min−1 R2 qe/(mg·g−1) k2(mg·g−1·min−1) R2 qe/(mg·g−1) UiO-66 81.79 0.196 0.975 90.58 0.0023 0.999 89.90 UiO-67 171.83 0.2733 0.933 178.78 0.0026 0.999 178.34 NU-1000 232.34 0.2374 0.937 239.08 0.0023 0.999 238.44 表 3 UiO-66、UiO-67和NU-1000对甲萘威的吸附热力学参数
Table 3. Adsorption thermodynamic parameters of carbaryl on UiO-66, UiO-67 and NU-1000
吸附剂类型 T/k ∆G/(kJ·mol−1) ∆S/(J·mol−1·K−1) ∆H(kJ·mol−1) R2 UiO-66 298 −0.70 52.75 15.55 0.975 303 −0.54 313 −0.97 323 −1.44 UiO-67 298 −2.75 56.81 14.14 0.992 303 −3.10 313 −3.70 323 −4.17 NU-1000 298 −4.35 45.73 9.24 0.985 303 −4.67 313 −5.06 323 −5.52 -
[1] ROJAS S, HORCAJADA P. Metal-organic frameworks for the removal of emerging organic contaminants in water [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(16): 8378-8415. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00797 [2] AHMAD K, NAZIR M A, QURESHI A K, et al. Engineering of Zirconium based metal-organic frameworks (Zr-MOFs) as efficient adsorbents [J]. Materials Science and Engineering:B, 2020, 262: 114766. doi: 10.1016/j.mseb.2020.114766 [3] HASAN Z, KHAN N A, JHUNG S H. Adsorptive removal of diclofenac sodium from water with Zr-based metal-organic frameworks [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 284: 1406-1413. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.087 [4] ZHU X Y, LI B, YANG J, et al. Effective adsorption and enhanced removal of organophosphorus pesticides from aqueous solution by Zr-based MOFs of UiO-67 [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(1): 223-231. [5] PANKAJAKSHAN A, SINHA M, OJHA A A, et al. Water-stable nanoscale zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks for the effective removal of glyphosate from aqueous media [J]. ACS Omega, 2018, 3(7): 7832-7839. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b00921 [6] KATZ M J, BROWN Z J, COLÓN Y J, et al. A facile synthesis of UiO-66, UiO-67 and their derivatives [J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(82): 9449-9451. doi: 10.1039/c3cc46105j [7] WANG T C, VERMEULEN N A, KIM I S, et al. Scalable synthesis and post-modification of a mesoporous metal-organic framework called NU-1000 [J]. Nature Protocols, 2016, 11(1): 149-162. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.001 [8] XIA X X, CAO M, LIU Z L, et al. Elucidation of adsorption cooling characteristics of Zr-MOFs: Effects of structure property and working fluids [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 204: 48-58. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2019.04.006 -






 下载:
下载: