-
近年来,随着工业的快速发展,土壤重金属污染问题日益加剧,目前常用的土壤修复技术主要包括物理修复、钝化修复、生物修复以及复合修复[1-3]。重金属钝化修复技术是指向污染土壤添加钝化材料,通过降低土壤中重金属有效含量或改变其赋存形态,阻止重金属迁移的土壤修复技术,通常用于修复中轻度污染土壤[4]。目前钝化材料多采用黏土矿物,如坡缕石、膨润土、海泡石、沸石等[5-9]。
坡缕石是一种富含镁铝型黏土矿物,在我国物量丰富、价格低廉且具极强吸附性,多用于重金属污染土壤修复[10-12]。但因矿物自身含大量杂质,为提高其使用效率,通常需对坡缕石原矿进行改性处理。改性坡缕石方法不一,主要分为物理方法和化学方法。常见的物理改性坡缕石方法主要有高温、超声波、微波改性等,而化学改性主要以酸碱改性与有机改性为主[13]。目前较多使用酸作改性处理,坡缕石经酸改性后内部结构及孔道杂质部分溶解,小孔数目及比表面积有所增加,吸附及离子交换性能提升[13-14],
陈雪芳等[15]研究发现坡缕石经酸改性后可去除自身部分杂质,有效比表面积提高。但目前为止,不同酸改性坡缕石吸附重金属能力存在差异,其优劣性尚未探明,需据使用目的,选择酸改性条件[16]。田振华等[13]研究表明,酸改性处理可溶解坡缕石内部的多面体结构,提高吸附性能,但过度酸改性会破坏坡缕石自身结构。
本文选用不同酸改性条件下的坡缕石对Ni-Cr污染土壤的钝化效果进行研究,以期根据污染土壤中重金属钝化及植物富集情况,筛选出修复Ni-Cr污染土壤的最佳钝化材料,为后续重金属污染土壤的治理及坡缕石应用提供理论依据和数据支撑。
-
供试土壤由人工模拟污染土壤与实际污染土壤两部分组成。人工模拟Ni-Cr复合污染土壤按国家《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》(GB 15618—2018)标准,以未受污染的农田表层土壤进行配制(400 mg·kg−1-Ni和600 mg·kg−1-Cr),然后维持70%的土壤含水率,于室温((25 ± 2 )℃)稳定3周后自然风干、过筛(2 mm)备用;实际Ni-Cr复合污染土壤取自甘肃省白银市某一冶炼厂附近东大沟区域(N36°59′96″, E104°22′76″),pH值为7.28,土壤电导率EC值为1457 μS·cm−1,污染土壤中重金属总量经HF-HClO4-HNO3法消解后利用火焰原子分光光度吸收仪测定,测得实际污染土壤中重金属Ni总量为261.54 mg·kg−1、Cr总量为327.71 mg·kg−1。
钝化材料以坡缕石原矿为原始材料、由甘肃瀚兴环保科技有限公司提供,采自甘肃省临泽县板桥镇。将事先准备的坡缕石原料(200目)在固液比1∶10、搅拌速度为500 r·min−1的条件下[14],以不同质量分数(2.5%、5%、7.5%、10%、12.5%、15%)的H2SO4溶液,分别酸改性处理12、24、36、48、72、96 h,静置沉淀待烘干后过筛(200目)制得36种酸改性坡缕石钝化材料(表1)。
玉米种子(Zea mays L.)为金穗3号,购自白银金穗种业有限公司。
-
在不同塑料盆中装入1.5 kg人工模拟重金属污染土壤,分别添加12 g已制备的酸改性坡缕石,以未做酸改性坡缕石原矿为对照(CK),充分搅拌混匀,保持70%的田间持水量,每种处理重复3次,于室温自然通风条件下培养钝化,钝化30 d后,利用醋酸提取法测定土样中重金属酸溶态含量。
在初次完成钝化实验的土壤表层(1—2 cm),于室温播种10粒种子,保持土壤湿润。待出苗后进行间苗保留至3株,继续生长30 d左右,取出玉米幼苗洗净、烘干至恒重后,研磨过筛测定玉米幼苗体内重金属含量。结合土壤中重金属钝化及玉米幼苗中重金属富集情况,筛选出最佳酸改性坡缕石材料。
-
将完成筛选的最佳酸改性坡缕石,分别按2、4、8、16、24 g·kg−1添加到实际重金属污染土壤中,以未添加酸改性坡缕石土壤为对照(CK),按上述1.2中方法继续钝化30 d,待钝化实验完成后,测定土壤中重金属生物有效态含量及各化学形态组分。
-
将收集后的土样,去除杂质、自然风干并研磨过筛(2 mm)后,密封保存,用于土壤样品中各项指标的测定。土壤有效态Ni和Cr含量采用DTPA提取法测定;采用BCR连续提取法测定土壤中重金属化学形态 [17]。
将完成盆栽实验的玉米幼苗整株取出,经去离子水冲洗干净后用滤纸吸掉植株上多余的水分、鼓风烘干(70 ℃)至恒重后,剪碎研磨过筛,置于密封袋保存,用于玉米幼苗中各指标的测定。植物总Ni和总Cr含量经HNO3-HClO4消解后利用火焰原子分光光度吸收仪测定。
-
土壤钝化实验通常以钝化剂的钝化容量来衡量该钝化剂对土壤中重金属的钝化能力[11],以重金属酸溶态含量表示钝化完成后的可溶出浓度[18]。其中酸改性坡缕石对重金属的钝化容量按式(1)计算:
式中,Cap:钝化容量(mg·g−1);Ci:土壤钝化前金属元素的酸溶态含量(mg·L−1);Ce:土壤钝化后金属元素的酸溶态含量(mg·L−1);V:提取液的体积(L);W:酸改性坡缕石用量(g)。
通常用重金属的可迁移因子评价土壤中重金属的迁移率或生物利用度[19]。重金属可迁移因子按式(2)计算:
式中,C1:酸溶态F1的含量;C2:可还原态F2的含量;C3:可氧化态F3的含量;C4:残渣态F4的含量;MF:可迁移部分(F1+F2)占形态总量的百分比。
重金属修复效率(RRm)按式(3)计算[17]:
采用Statistic 7.0 软件对试验数据进行统计分析后,利用Origin 2019b软件作图,其中采用Duncan多重比较检验法分析各指标间的差异显著性。
-
通常用钝化剂对重金属的钝化容量Cap值来评判该钝化剂对重金属的钝化能力,且二者之间显著正相关[11,20]。不同酸改性条件均可显著影响坡缕石对土壤中重金属Ni、Cr的钝化容量,增加酸改性时间及H2SO4质量分数,坡缕石对Ni、Cr的钝化容量均呈现先增加后降低趋势(表2)。当酸处理72 h时,坡缕石对土壤重金属Ni、Cr的钝化容量均达最高,但二者使用H2SO4质量分数条件有异。坡缕石对重金属Ni的钝化容量在H2SO4质量分数为10%时最高(6.16 mg·g−1),相比对照提高了4.96倍;而坡缕石对重金属Cr的钝化容量在H2SO4质量分数为12.5%条件下最高(3.22 mg·g−1),相比对照可提高6.57倍(表2)。因此,针对重金属Ni-Cr污染土壤钝化的坡缕石材料,最佳酸改性条件为:酸处理72 h,H2SO4质量分数为10%与12.5%。这与张媛等[14]研究会宁坡缕石酸改性结果相似。这可能是因为酸改性处理会溶解坡缕石内部结构,增强其吸附性能,但过度酸改性则会破坏坡缕石自身结构,使其吸附性能降低。因此,控制好坡缕石的酸改性条件至关重要。
-
廖启林等[18, 21]研究表明,坡缕石因比表面积大、吸附性能强,可将土壤中可溶性重金属元素吸附在其表面或固定于矿物层间结构中,进而滞缓土壤中重金属向植物的迁移。在本研究中,坡缕石在不同酸改性时间、H2SO4质量分数及二者交互作用下均对玉米幼苗富集Ni、Cr含量影响显著(表3)。随着酸改性时间及H2SO4质量分数的增加,玉米幼苗富集Ni、Cr含量均先升高后降低(表4)。坡缕石经质量分数为10%的H2SO4溶液改性72 h后,可使玉米幼苗富集Ni含量降至最低(60.12 mg·kg−1),相比对照,可降低79.77%;在相同酸改性时间下,当H2SO4质量分数为12.5%时,玉米幼苗富集Cr含量降至最低(93.17 mg·kg−1),相比对照,可降低61.13%。这可能是因为,坡缕石经酸改性后其吸附性能增强,阻碍土壤中重金属元素迁移,使玉米幼苗富集Ni和Cr含量降低。这与叶鸣等 [22]用酸对坡缕石进行改性处理后结果一致。本研究根据以上实验结果,筛选出2种最佳酸改性坡缕石钝化材料S45(酸改性条件:H2SO4质量分数10%、酸改性时间72 h)、S55(酸改性条件:H2SO4质量分数12.5%、酸改性时间72 h),可为后续工程应用提供参考。
-
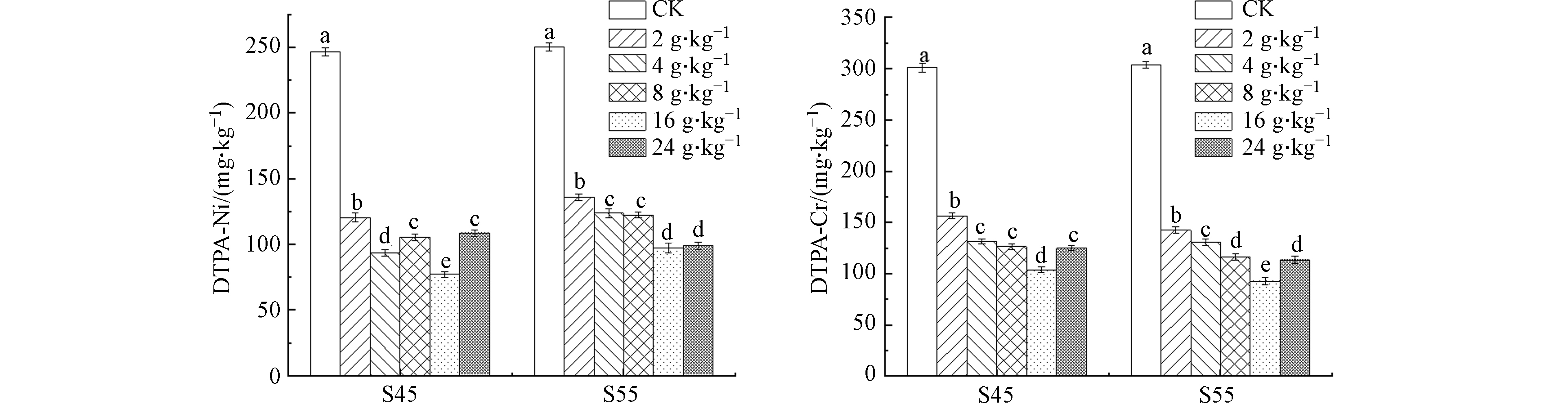
通常用土壤中重金属总量判定重金属污染对生物及环境的影响程度,但重金属生物有效态是土壤中易被生物吸收利用的重金属部分,可反映土壤中重金属的危害程度。因此,降低土壤中重金属有效态含量对于修复重金属污染土壤至关重要[23]。通常选用DTPA提取法作为检验土壤重金属生物有效性的关键方法[24]。酸改性坡缕石对重金属污染土壤的钝化效果不仅与钝化剂种类有关,也与钝化剂的添加量紧密相关。在本研究中,不同添加量的酸改性坡缕石S45、S55均可降低土壤中有效态Ni含量,在添加量为16 g·kg−1时,降低最显著,较对照分别降低68.76%与61.19%(图1)。相同条件下,添加16 g·kg−1酸改性坡缕石S45、S55可使土壤中有效态Cr含量降低最多,较对照分别降低65.50%与69.53%(图1)。目前使用坡缕石修复重金属污染土壤,一方面是通过改善土壤理化环境,使重金属得到固定[25];另一方面是坡缕石具有较大的比表面积和吸附性能,可将土壤中的可溶性重金属元素吸附于其表面或进入层间结构[21,26]。这与本研究结果一致。
-
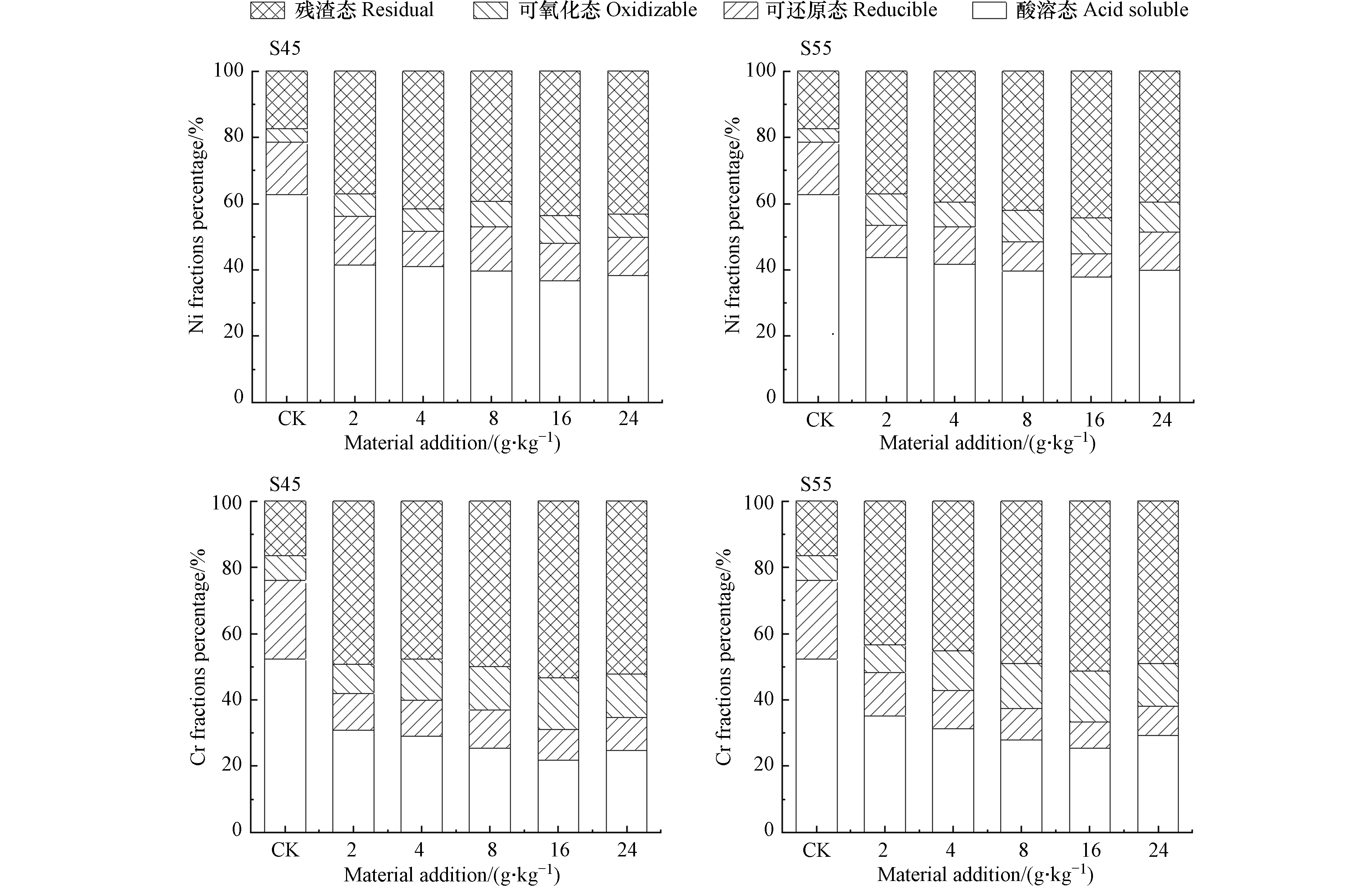
通过BCR连续提取法将重金属形态分为酸溶态、可还原态、可氧化态和残渣态。相比酸溶态和可还原态,可氧化态与残渣态稳定性较强,不易发生迁移被生物利用,环境风险较低,通常被合称为重金属稳定形态组分[27]。在对照土壤中,重金属Ni与Cr主要以酸溶态存在,分别占62.76%和52.42%;添加不同酸改性坡缕石可显著影响Ni-Cr污染土壤中重金属元素形态转化,促使土壤中重金属由活性较高的酸溶态转化为活性较低的可氧化态与残渣态,使土壤中重金属稳定形态组分增加。其中,重金属Ni稳定形态组分分别增加22.38%—30.52%与25.15%—33.6%,重金属Cr稳定形态组分分别增加34.16%—45.15%与27.84%—42.9%(图2);添加16 g·kg−1酸改性坡缕石时,重金属Ni、Cr稳定形态组分增加最多,其中以残渣态增加为主(图2)。这与张静静[28]和袁兴超等[1]研究结果一致。这可能是因为钝化剂与土壤中重金属发生了沉淀、络合和吸附等反应,将重金属从高活性形态转化为低活性形态,进而实现土壤中重金属稳定化 [1, 29]。
-
通常根据钝化剂对完成钝化后土壤中重金属的迁移及修复程度,评估该钝化材料的应用价值。在本研究中,添加酸改性坡缕石S45、S55,重金属Ni、Cr的可迁移性因子值分别介于44.95%—55.30%与31.03%—48.34%之间,修复效率介于37.12%—43.51%与43.47%—53.30%之间。其中,添加16 g·kg−1酸改性坡缕石时,重金属Ni、Cr的可迁移性因子与修复效率变化最显著;可迁移性因子最高可分别降低15.82%与31.15%,修复效率分别提高19.23%与17.94%(表5)。这与罗宁临等[27]和谭科艳等[9]研究结果相似。这可能是因为坡缕石自身吸附属性,可降低重金属可迁移组分,使植物对可利用态重金属吸收受阻,缓解了重金属对生物的毒害作用[25]。
-
(1) 酸改性坡缕石对Ni-Cr复合污染土壤钝化效果良好,坡缕石最佳酸改性条件为:H2SO4质量分数为10%与12.5%,酸改性时间为72 h 。
(2) 酸改性坡缕石可提高对重金属Ni与Cr的钝化容量,促使污染土壤中重金属形态由酸溶态转化为可氧化态与残渣态,降低土壤DTPA-Ni和DTPA-Cr含量,减缓植物中重金属富集情况。
(3) 添加酸改性坡缕石,重金属Ni和Cr的可迁移性因子整体降低,修复效率升高,添加量为16 g·kg−1时钝化效果最佳。
酸改性坡缕石对Ni和Cr污染土壤的钝化效果
Stabilization of Ni and Cr in contaminated soil by acid-modified palygorskite
-
摘要: 通过钝化实验与盆栽实验研究酸改性坡缕石对土壤中重金属Ni和Cr的钝化效果及植物富集的影响,结合可迁移性因子、钝化容量和修复效率对钝化效果进行评价。结果表明,10%和12.5%浓度硫酸处理72 h后的坡缕石对土壤中Ni和Cr的钝化效果显著高于原矿和其它酸改性处理,与对照相比,钝化容量分别提高了4.96倍与6.57倍。种植在这两种酸改性坡缕石钝化土壤中的植物内Ni和Cr的富集量显著低于其它钝化处理,富集量降低了79.77%与61.13%。随着酸改性坡缕石添加量的增加,重金属Ni与Cr由酸溶态转化为稳定性较强的可氧化态与残渣态,可迁移性因子整体降低,钝化容量和修复效率提高。酸改性坡缕石添加量为16 g·kg−1时,修复效率和钝化效果显著高于其它处理。 酸改性可显著提高坡缕石对土壤重金属的钝化修复效能,并且,酸改性坡缕石具有规模化应用在土壤重金属污染原位修复工程中的潜力。Abstract: The incubation and pot experiments were conducted to explore the influences of acid-modified palygorskite on stabilization efficiency and accumulation of Cr and Ni in contaminated soil, the stabilization efficiency was evaluated by mobolity fator (MF), stabilization capacity (Cap) and remediation ratio (RR). The results suggested that the stabilization efficiency of palygorskite modified by 10% and 12.5% H2SO4 72 h time of duration were significantly higher than raw mineral and other acid-modified palygorskite for Cr and Ni in soil, and the Cap was increased by 4.96 and 6.57 times, the accumulation content of Ni and Cr in corn planted in soils treated by these two acid-modified palygorskite reduced 79.77% and 61.13%, respectively. More acid-soluble Cr and Ni transformed into more inactive oxidizable and residual speciation with addition of acid-modified palygorskite, and MF decreased, Cap and RR increased. The Cap and RR were significantly higher than other treatments in 16 g·kg−1 additive amount of acid-modified palygorskite. The acid-modified treatment can evidently improve the stabilization function of palygorskite, and the acid-modified palygorskite has the potential for large scale in-situ remediation of soils polluted by heavy metals.
-
Key words:
- palygorskite /
- Ni /
- Cr /
- stabilization /
- accumulation
-

-
表 1 酸改性坡缕石钝化材料
Table 1. The stabilizer of palygorskite acid-modification
时间/h
TimeH2SO4质量分数 Mass fractions 2.5% 5% 7.5% 10% 12.5% 15% 12 S11 S21 S31 S41 S51 S61 24 S12 S22 S32 S42 S52 S62 36 S13 S23 S33 S43 S53 S63 48 S14 S24 S34 S44 S54 S64 72 S15 S25 S35 S45 S55 S65 96 S16 S26 S36 S46 S56 S66 表 2 不同酸改性坡缕石钝化剂对重金属Ni和Cr的钝化容量(mg·g−1)
Table 2. Stabilization capacity of different acid-modified palygorskite for heavy metals Ni and Cr (mg·g−1)
重金属
Heavy metalH2SO4质量分数/%
H2SO4 mass fractions酸处理时间 F 12 h 24 h 36 h 48 h 72 h 96 h Ni CK 1.21Cc 1.24Cb 1.26Da 1.24Eb 1.27Ca 1.26Da 1.87** 2.5 4.10Ac 3.97Bc 3.96Cc 4.34Db 4.61Ba 4.42Bb 1.99** 5 3.99Ab 3.57Bc 4.36Cb 4.64Da 4.75Ba 4.57Ca 6.86** 7.5 4.45Ab 3.74Bc 4.63Cb 4.81Ca 4.21Cb 3.92Bc 9.16** 10 3.92Bd 4.49Bc 4.73Cb 4.49Dc 6.16Aa 3.99Cd 2.57** 12.5 4.23Ad 4.61Bc 6.00Aa 5.89Aa 4.65Bc 5.64Ab 10.32** 15 4.84Ac 5.07Ab 5.61Ba 5.25Bb 5.82Aa 5.54Aa 2.64** F 46.08*** 25.14*** 52.32*** 77.41*** 32.93*** 75.42*** Cr CK 0.56Ea 0.54Eb 0.52Dc 0.51Ec 0.49Ec 0.50Dc 1.41** 2.5 0.79Cb 0.65Db 0.71Bb 1.13Ca 1.35Da 1.16Ca 12.94** 5 0.85Cc 0.67Dd 0.97Bb 1.11Ca 1.40Da 1.10Ca 56.22** 7.5 0.64De 0.92Cd 0.65Ce 1.24Bc 1.83Cc 3.09Aa 33.46** 10 2.96Aa 2.72Ac 2.97Aa 3.00Aa 2.85Bb 2.77Bc 29.57** 12.5 2.07Be 2.37Bd 2.57Ac 2.66Ab 3.22Aa 2.58Bc 2.13*** 15 2.52Ac 2.61Ac 2.85Ab 2.93Ab 2.86Bb 3.03Aa 1.45* F 101.68*** 38.45*** 73.66*** 53.14*** 28.17*** 30.92*** 注:大写字母表示不同酸改性H2SO4质量分数之间的差异性,小写字母表示不同酸改性时间之间的差异性;***表示极显著差异P<0.001,**表示较显著差异0.001<P<0.01,*表示显著差异0.01<P<0.05,以下同. Notes: Capital letters indicate the difference between different acid modified H2SO4 mass fractions, lowercase letters indicate the difference between different acid modification times. *** extremely significant difference P<0.001, ** more significant difference 0.001<P<0.01, * significant difference 0.01<P<0.05. The same below. 表 3 H2SO4质量分数和酸改性时间对玉米幼苗富集Ni和Cr含量影响的方差分析
Table 3. Variance analysis of the influence of H2SO4 fraction and pickling time on the accumulation content of Ni and Cr in corn
重金属
Heavy metal因素
Factor自由度
Degree of freedomF Ni 酸改性时间 6 40.594** H2SO4质量分数 6 24.776** 酸改性时间×H2SO4质量分数 36 4.984*** Cr 酸改性时间 6 18.649** H2SO4质量分数 6 12.677** 酸改性时间×H2SO4质量分数 36 3.135*** 表 4 不同酸改性坡缕石钝化处理下玉米幼苗富集Ni和Cr含量(mg·kg−1)
Table 4. The accumulation content of Ni and Cr in corn relative to different acid-modified palygorskite (mg·kg−1)
重金属
Heavy metalH2SO4质量分数/%
H2SO4 mass fractions12 h 24 h 36 h 48 h 72 h 96 h F Ni CK 261.27Aa 231.14Ab 229.31Ac 233.81Ab 229.22Ac 231.41Ab 3.22** 2.5 116.88 Ba 114.62Bb 113.51 Bb 110.87Be 102.61Bb 107.45Bd 65.21*** 5 111.36 Ba 107.22Bb 110.31 Ba 105.42 Bb 86.87Cc 99.26Cc 1403.37** 7.5 95.16 Ca 88.33 Cb 84.27 Cb 81.32 Cb 73.79 Dc 77.68 Dc 129.62** 10 83.21 Da 79.48 Db 76.81 Db 69.45 Dc 60.12Ed 64.78 Ec 217.40** 12.5 87.16 Da 81.43 Db 79.31 Dc 73.61 Dc 65.24Ec 67.33 Ed 329.91*** 15 98.43 Ea 93.26 Cb 72.55 Dc 70.43 Dc 68.47 Ed 71.40 Dc 11.91*** F 129.60*** 59.65*** 38.92*** 751.94*** 332.14*** 429.71*** Cr CK 246.18Aa 242.31Ab 239.18Ac 242.33Ab 239.72Ac 241.37Ab 7.63** 2.5 158.37 Bb 157.41 Ba 152.31 Bb 151.55 Bb 152.27 Ba 143.18 Bc 75.35** 5 148.34 Ca 145.22 Ca 141.61 Cb 147.25 Ca 137.74 Cc 139.16 Bb 602.94*** 7.5 136.45 Da 134.26 Da 126.64 Db 128.26 Db 115.87 Ec 124.13 Cb 356.26*** 10 129.60 Ea 126.42 Ea 122.27 Db 121.56 Db 102.41 Fd 111.16 Dc 79.60*** 12.5 125.25 Ea 121.22 Ea 114.32 Eb 108.34 Ec 93.17 Fd 106.42 Ec 276.35*** 15 141.22 Ca 120.31 Eb 120.11 Db 115.42 Ec 107.26 Ed 109.46 Ed 127.26*** F 192.02*** 132.91*** 236.04*** 245.36*** 601.85*** 886.70*** 表 5 酸改性坡缕石对土壤Ni和Cr迁移因子和修复效率的影响
Table 5. Effects of acid-modified palygorskite on migration factor and recovery on Ni and Cr
重金属
Heavy metal酸改性坡缕石
Acid-modified
palygorskite钝化指标
Stabilization indicator材料添加量 Material addition F 2 g·kg−1 4 g·kg−1 8 g·kg−1 16 g·kg−1 24 g·kg−1
Ni
S45MF 53.40±0.11a 52.91±0.06a 48.59±0.02c 44.95±0.03d 51.35±0.05b 6.85*** RRm 37.12±0.19d 39.46±0.14c 42.10±0.20b 44.26±0.11a 39.39±0.17c 21.08***
S55MF 56.17±0.04a 51.69±0.12b 53.04±0.14b 48.02±0.03c 49.78±0.07c 10.28*** RRm 37.12±0.12d 41.57±0.16b 39.29±0.21c 43.51±0.17a 43.08±0.15a 27.32***
Cr
S45MF 42.02±0.06a 39.95±0.04b 36.97±0.11c 31.03±0.03d 34.73±0.07c 7.95** RRm 49.18±0.13b 47.76±0.23c 49.97±0.18b 53.30±0.14a 52.27±0.22a 19.95**
S55MF 48.34±0.05a 42.95±0.13b 37.37±0.08c 33.28±0.06d 38.13±0.15c 11.17*** RRm 43.47±0.18d 45.27±0.09c 48.91±0.16b 51.27±0.11a 49.00±0.27b 41.12*** 注:同列不同小写字母表示各处理间存在差异性;***表示极显著差异P<0.001,**表示较显著差异0.001<P<0.01,*表示显著差异0.01<P<0.05. Notes: Significant differences among treatments are indicated by different lowercase letters. *** extremely significant difference P<0.001, ** more significant difference 0.001<P<0.01, * significant difference 0.01<P<0.05. -
[1] 袁兴超, 李博, 朱仁凤, 等. 不同钝化剂对铅锌矿区周边农田镉铅污染钝化修复研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(4): 807-817. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0672 YUAN X C, LI B, ZHU R F, et al. Immobilization of Cd and Pb using different amendments of cultivated soils around lead-zinc mines [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(4): 807-817(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0672
[2] CUI H B, FAN Y C, XU L, et al. Sustainability of in situ remediation of Cu- and Cd-contaminated soils with one-time application of amendments in Guixi, China [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2016, 16: 1498-1508. doi: 10.1007/s11368-015-1317-x [3] JIANG G J, LIU Y H, FU Q L, et al. Immobilization of Soil Exogenous Lead Using Raw and Activated Phosphate Rocks [J]. Environmental Progress and Sustainable Energy, 2014, 33: 81-86. doi: 10.1002/ep.11754 [4] 张迪, 吴晓霞, 丁爱芳, 等. 生物炭和熟石灰对土壤镉铅生物有效性和微生物活性的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(11): 2526-2534. ZHANG D, WU X X, DING A F, et al. Effects of hydrated lime and biocharon available Cd and Pb and microbial activity in a contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(11): 2526-2534(in Chinese).
[5] 曹心德, 魏晓欣, 代革联, 等. 土壤重金属复合污染及其化学钝化修复技术研究进展 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2011, 5(7): 1441-1453. CAO X D, WEI X X, DAI G L, et al. Combined pollution of multiple heavy metals and their chemical immobilization in contaminated soils: A review [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2011, 5(7): 1441-1453(in Chinese).
[6] SHIN W, KIM Y K. Stabilization of heavy metal contaminated marine sediments with red mud and apatite composite [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments. 2016, 16: 726-735. [7] LI L F, AI S Y, WANG Y H, et al. In situ field-scale remediation of low cd-contaminated paddy soil using soil amendments [J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2016, 227: 342. doi: 10.1007/s11270-016-3041-6 [8] ALEKSANDRA B. Influence of Zeolites, humic acids, and selenates (Ⅵ) on lead and cadmium immobilization and selected soil properties [J]. Polish journal of environmental studies, 2012, 21: 813-820. [9] 谭科艳, 刘晓端, 刘久臣, 等. 凹凸棒石石用于修复铜锌镉重金属污染土壤的研究 [J]. 岩矿测试, 2011, 30(4): 451-456. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.04.012 TAN K Y, LIU X D, LIU J C, et al. Remediation experiments of attapulgite clay to heavy metal contaminated Soil [J]. Rock and mineral analysis, 2011, 30(4): 451-456(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.04.012
[10] 殷飞, 王海娟, 李燕燕, 等. 不同钝化剂对重金属复合污染土壤的修复效应研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(3): 438-448. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.03.005 YIN F, WANG H J, LI Y Y, et al. Remediation of multiple heavy metal polluted soil using different immobilizing agents [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(3): 438-448(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.03.005
[11] 吴烈善, 曾东梅, 莫小荣, 等. 不同钝化剂对重金属污染土壤稳定化效应的研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(1): 309-313. WU L S, ZENG D M, MO X R, et al. Immobilization Impact of Different Fixatives on Heavy Metals Contaminated Soil [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(1): 309-313(in Chinese).
[12] 徐奕, 李剑睿, 黄青青, 等. 坡缕石钝化与喷施叶面硅肥联合对水稻吸收累积镉效应影响研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(9): 1633-1641. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016-0838 XU Y, LI J R, HUANG Q Q, et al. Effect of palygorskite immobilization combined with foliar silicon fertilizer application on Cd accumulation in rice [J]. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences, 2016, 35(9): 1633-1641(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016-0838
[13] 田振华, 薛胜平. 凹凸棒石改性及其修复重金属污染土壤的研究 [J]. 应用化工, 2019, 48(4): 883-887. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2019.04.036 TIAN Z H, XUE S P. Attapulgite modification and its research of repairing the soil of heavy metal contaminated [J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2019, 48(4): 883-887(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2019.04.036
[14] 张媛, 尹建军, 王文波, 等. 酸活化对甘肃会宁凹凸棒石微观结构及亚甲基蓝吸附性能的影响 [J]. 非金属矿, 2014, 37(2): 58-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2014.02.018 ZHANG Y, YIN J J, WANG W B, et al. Effects of acid activation on the microstructure and adsorption capacity for methylene blue of attapulgite clay from huining of Gansu [J]. Non-Metallic Mines, 2014, 37(2): 58-62(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2014.02.018
[15] 陈雪芳, 熊莲, 王璨, 等. 酸改性对低品位凹凸棒石的白度和组成结构的影响 [J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2017, 36(12): 4198-4204. CHEN X F, XIONG L, WANG C, et al. Effect of acid modification on whiteness and composition structure of low grade palygorskite [J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2017, 36(12): 4198-4204(in Chinese).
[16] 高华. 凹凸棒土的改性与应用研究[D]. 合肥 : 安徽大学, 2010. GAO H. Study on modification and application of attapulgite[D]. Hefei : Anhui University, 2010 (in Chinese).
[17] NEMATI K, ABU BAKAR N K, ABAS M R, et al. Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 192(1): 402-410. [18] 陶玲, 杨欣, 颜子皓, 等. 酸活化坡缕石制备重金属钝化材料的研究 [J]. 非金属矿, 2018, 41(1): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2018.01.004 TAO L, YANG X, YAN Z H, et al. Study on the function of passivant for heavy metals with palygorskite modified by acid [J]. Non-Metallic Mines, 2018, 41(1): 11-14(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2018.01.004
[19] WAN M W, KAN C C, ROGEL B D, et al. Adsorption of copper(Ⅱ) and lead (Ⅱ)ions from aqueous solution on chitosan-coated sand [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2010, 80: 891-899. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.12.048 [20] 缪德仁. 重金属复合污染土壤原位化学稳定化试验研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2010. MIAO D R. Chemical immobilization bench-scale studies on in-situ remediation of multi-heavy metals contaminated soils[D]. Beijing : China University of Geosciences, 2010 (in Chinese).
[21] 廖启林, 刘聪, 朱伯万, 等. 凹凸棒石调控Cd污染土壤的作用及其效果 [J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(5): 1693-1704. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.05.023 LIAO Q L, LIU C, ZHU B W, et al. The role and effect of applying attapulgite to controlling Cd-contaminated soil [J]. Geology of China, 2014, 41(5): 1693-1704(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.05.023
[22] 叶鸣, 李丽, 张先斌, 等. 盐酸改性凹凸棒石条件对去除Cd2+效果的影响 [J]. 工业用水与废水, 2013, 44(6): 49-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2013.06.014 YE M, LI L, ZHANG X B, et al. Influencing factors of Cd2+ removal by HCl modified attapulgite [J]. Industrlal Water and Wastewater, 2013, 44(6): 49-52(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2013.06.014
[23] EWA S G, JOLANTA K, ANNA K. Effect of peat on the accumulation and translocation of heavy metals by maize grown in contaminated soils [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(6): 4706-4714. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3706-x [24] FUENTES A, LLORENS M, SAEZ J, et al. Ecotoxicity, phytotoxicity and ex-tractability of heavy metals from different stabilised sewage sludges [J]. Environment Pollution, 2006, 143(2): 355-360. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.11.035 [25] 曾秀君, 程坤, 黄学平, 等. 石灰、腐植酸单施及复配对污染土壤铅镉生物有效性的影响 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2020, 36(1): 121-128. ZENG X J, CHENG K, HUANG X P, et al. Effect of single and multiple application of lime and humic acid on the bioavailability of lead and cadmium in contaminated soil [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2020, 36(1): 121-128(in Chinese).
[26] 赵廷伟, 李洪达, 周薇, 等. 施用凹凸棒石对Cd污染农田土壤养分的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(10): 2313-2318. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0783 ZHAO T W, LI H D, ZHOU W, et al. Effects of attapulgite application on soil nutrients in Cd-contaminated farmland [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(10): 2313-2318(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0783
[27] 罗宁临, 李忠武, 黄梅, 等. 壳聚糖(改性)-沸石对农田土壤重金属镉钝化技术研究 [J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 47(4): 132-140. LUO N L, LI Z W, HUANG M, et al. Immobilizing cadmium in paddy soil by using modified chitosan-zeolite [J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences), 2020, 47(4): 132-140(in Chinese).
[28] 张静静, 赵永芹, 王菲菲, 等. 膨润土、褐煤及其混合添加对铅污染土壤钝化修复效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(2) : 395-402. ZHANG J J, ZHAO Y Q, WANG F F, et al. Immobilization and remediation of Pb contaminated soil treated with bentonite, lignite and their mixed addition [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(2) : 395-402 (in Chinese).
[29] ZHU Y G, CHEN S B, YANG J C. Effects of soil amendments on lead up-take by two vegetable crops from a lead-contaminated soil from Anhui, China[J]. Environment International, 2004, 30(3) : 351-356. -



 下载:
下载: