-
塑料是从石油或天然气中提取的单体聚合而成的高分子化合物[1-2]. 自1907年第一种现代塑料“酚醛塑料”问世以来,塑料便因轻质、耐用、价廉和耐腐蚀等特性广泛应用于生产生活中[3]. 这些特性恰好是塑料对环境造成严重危害的原因之一,塑料消费需求的增加导致了大量的塑料污染. 2004年,英国学者Thompson首次提出“微塑料”的概念,并发现微塑料在海洋水体沉积环境中十分常见[4],后来的研究人员将微塑料定义为粒径小于5 mm的塑料碎片. 根据不同来源微塑料可分为初生微塑料和次生微塑料. 初生微塑料是指工业生产过程中直接排放的微观尺寸的塑料颗粒;次生微塑料是指较大的塑料进入环境中经过分解、破裂形成微型的塑料碎片[5-6]. 微塑料体积小,化学性质稳定,可存在数百上千年,且易吸附多种微生物和化学污染物,被海洋动物摄食后进入食物链,进而影响人体的消化功能[7-9].
近年来微塑料污染受到人们的研究和关注,已有的研究表明在海洋、湖泊、土壤、大气和生物体中均存在微塑料[9-12]. 其中对海洋、湖泊、土壤的研究总结较为深入,检测技术也比较成熟,对大气环境的研究较少. 本文对不同研究中大气环境微塑料的来源、分类、提取方法、检测技术、已有的研究进展进行综述,以期为未来的微塑料研究提供参考.
-
大气环境中微塑料来源广泛. 初级微塑料的主要来源前三位分别是:合成纺织品、合成橡胶轮胎的磨损和城市灰尘,分别占比34.8%、28.3%和24.2%[13]。Dris等[14]提出,室内微塑料污染(例如衣服和家具的塑料碎片)是造成大气微塑料污染的原因之一. 在1997年Roux 等[15]的研究中,从汽车座椅外表面上检测到少量长度不到1 mm的合成纤维. 微塑料在空气中的其它来源还包括建筑物中的材料、垃圾焚烧、垃圾填埋场、工业排放物、颗粒悬浮物、交通释放的颗粒等[16-18]. 此外,对合成材料进行工业上的挤压和切削等加工产生的超细颗粒,也成为大气微塑料的来源之一[19]. 总的来说,无论室内还是室外,合成纺织品被公认为空气中传播微塑料的主要来源,纤维的材料和数量取决于不同季节的衣服时尚发展的变化[15,20-21].
-
微塑料成分组成多种多样,有聚乙烯、聚氯乙烯、聚苯乙烯、聚丙烯、聚碳酸酯、聚苯醚等[21-22]. 颜色也较为丰富,目前发现的颜色有白色、红色、黄色、灰色、绿色、黑色、蓝色、透明等,以白色、黑色和灰色较常见[23-24]. 微塑料形态各异,外形多为圆柱、圆形和圆盘状,种类可分为4种:纤维类、碎片类、薄膜类和发泡类[14,25-26](图1).
-
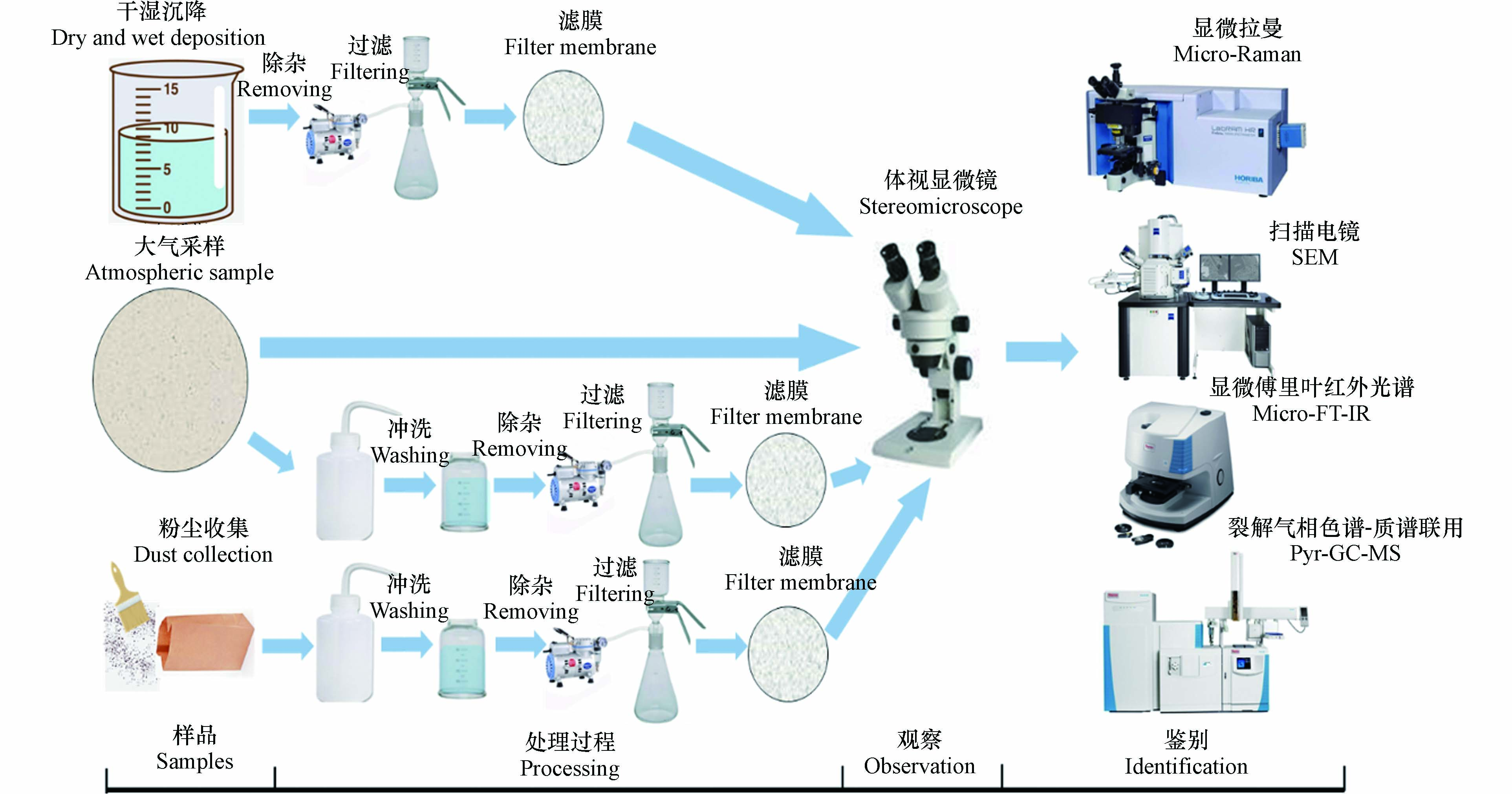
大气环境样品中微塑料的主要采样方法一般有以下3种[27]:干湿沉降法、大气采样法、粉尘收集法.
干湿沉降法是通过收集大气沉降物至容器内,经过一段时间的采集后再对容器中的样品进行处理分析,属于被动采样. Dris等[18]利用漏斗将巴黎大气沉降物收集在一个20 L的玻璃瓶中,每次采样周期7—30 d不等。与干湿沉降法不同,大气采样法则是利用颗粒物采样器将空气中的样品收集至滤膜上,为了避免污染用铝箔纸或其它方法封存好样品[28],直到转移至实验室进行下一步分析,属于主动采样。粉尘收集法顾名思义就是将粉尘收集起来进行微塑料的分析处理,一般对街道或建筑工厂等室外活动场所附近的粉尘进行采集[29]. 不同采样方法优缺点和适用条件见表1.
对于干湿沉降样品,可先利用消解法等提取方法去除干扰物质,接着使用过滤装置将样品过滤至滤膜上. 常见滤膜有:聚醚砜膜、氧化铝膜、镀铝聚碳酸酯膜和银膜等[30]. 将过滤后的滤膜放入玻璃培养皿中,加盖避光,自然风干;或将培养皿置于40 ℃的烘箱中干燥约4 h. 使用各类分析仪器对风干后的滤膜中的微塑料进行观察计数,分析统计微塑料的粒径分布、颜色、形貌特征以及化学成分. 对于粉尘样品,目前还没有标准化的方法来评估粉尘中的微塑料[31]. 一般将装有粉尘的样品用超纯水冲洗于容器中,利用密度分离等方法去除杂质,然后将溶液过滤,重复上述操作. 对于大气采样的滤膜样品,可不做任何前处理,直接进行仪器的分析;也可像粉尘样品处理方法,将膜上样品冲洗于容器中,然后重复上述操作即可(图2).
-
微塑料颗粒类型多样,直径普遍较小,且不易观测,因此从采集的样品中分离识别微塑料组分是提取微塑料的关键[32]. 目前大气中较常见的微塑料提取方法主要有过滤干燥、目检法、密度分离法、消解法等(表2)[5,33-34]. 需要注意的是,实验中所用到的玻璃器皿和设备在使用前都要经过适当的清洗、酸洗和去离子水冲洗。实验前应穿着手套和棉质实验服,避免使用塑料材料和容器[35].
过滤干燥是在分离含有液体的微塑料样品中常使用的方法,一般在干湿沉降法或者使用密度分离法、消解法后为了获取微塑料而使用. 例如,Wright等[36]将收集的湿沉降样品真空过滤到氧化铝膜过滤器上,然后立即将过滤器转移到玻璃培养皿中,并盖上相应的玻璃盖,放在40 ℃的烘箱中干燥4 h后室温下避光保存样品.
目检法是微塑料分析常见的方法,不仅适用于大气中,也适用于其它环境。目检法是直接或在显微镜的协助下用肉眼观察收集到的样品,将微塑料从大量样品中挑取出,并根据其形态、结构和颜色等特点给予分类[37-38].
密度分离法是利用微塑料的密度与其它杂质密度的差异实现轻组分微塑料与杂质的分离. 该方法常见于对海洋或沉积物中的微塑料进行提取,在大气中干湿沉降采集法和粉尘收集法也可使用。密度分离的方法可以有效去除收集的街道灰尘样品里富含的有机物[39-40].
消解法类似密度分离法,其目的是去除干扰微塑料鉴别的有机杂质,适用上述3种采集方法. 消解法又可以细分为两种方法:化学消解和酶消解. 化学消解就是利用酸溶液或碱溶液对样品进行消解. 实验中常用的酸溶液有HNO3、HCl和HClO4混合酸等,常用的碱溶液有KOH、NaOH等[34,41]。Prata等[39]将样品过滤到烧杯中,加入15%的H2O2反应8 d,再过滤一次样品后,加入1.6 g·cm−3的NaI,最后干燥后计数。该方法对纺织纤维的回收率高达94.4%. 酶消解法就是利用酶来降解附着在微塑料上的生物有机质,适用于提取生物组织或生物质含量较高样品中的微塑料. 常用的酶有:脂肪酶、淀粉酶、蛋白酶、壳聚糖酶、纤维素酶等[42].
-
通过上述方法采集的微塑料提取后,对其进行检测分析。常见的分析技术有:体视显微镜(Stereomicroscope)、显微傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(Micro fourier transform infrared spectrometer,micro-FT-IR)、显微拉曼光谱法(Micro-Raman)、扫描电子显微镜-X 射线能谱仪(Scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy,SEM-EDS)、荧光显微镜法(Fluorescence microscope)和裂解气相色谱-质谱联用技术(Pyrolysis gas chromatography-mass spectrometry,pyr-GC-MS)等(表3).
-
在已报道的文献中,大气中微塑料的形状多为圆柱、圆形和圆盘状,种类可分为4种:纤维类、碎片类、薄膜类和发泡类[14,25,26]。微塑料的尺寸一般小于5 mm,不同地区观测到的微塑料尺寸有一定的差异:葡萄牙阿威罗[43]干沉降微塑料平均尺寸室内为250 μm,室外为299 μm;上海市区[26]主动采样微塑料平均尺寸为582.2 μm;爱尔兰郊区[44]湿沉降微塑料平均尺寸为880 μm.
体视显微镜有两个独立的光学路径,方便双眼从不同视角观察样品,以达到给观察者提供更加丰富的三维图像的目的[45]. 其不仅可以用于微塑料颗粒的目视识别和分离,还可以进一步观测获得微塑料颗粒的尺寸、形状和颜色等物理性质[5]. 目视观测后可进一步进行化学分析.
扫描电子显微镜可用于精确检测不同尺寸和形状(如纤维、球体、六边形、不规则多面体)的微塑料颗粒,区别出其它细小样品,得到超清晰和高倍率的图像. 与能谱仪结合时,能够得到微塑料的元素组成(如Na、Mg、Ca、Al、和Si),从而将碳元素为主体的微塑料从无机颗粒中辨别出来[29,45],实现化学组分的分析. 在实际检测时,对样品需进行喷金处理,以增强样品的导电性[46]. 该方法可以揭示塑料聚合物的添加剂或吸附在微塑料表面上的碎片.
荧光显微镜法可以作为对上述方法的一种补充,用荧光染料标记微塑料是实验室跟踪检测微塑料的一种有效工具[47]. 利用高疏水性染料(如尼罗红)对微塑料进行染色,染色后的微塑料在疏水环境中有强烈的荧光,将傅里叶显微镜与荧光过滤器结合即可检测,和目检法起到很好的互补作用[37,48]. 但是,这种方法无法对样品中微塑料的种类组分进行具体分析[29].
-
傅里叶变换红外光谱仪有透射、反射和衰减全反射等3种模式,适用于检测中低粒子数样品(粒子数在150—1000). 透射模式能够提供高质量光谱,但需要红外滤光片. 反射模式是一种理想的检测微塑料的方法,它具有非破坏性、样品制备的最小需求以及对厚而不透明的材料产生红外吸收光谱的能力[45,49]. 衰减全反射FT-IR与反射FT-IR的区别在于折射所产生的误差,在衰减全反射模式下折射误差较小,检测准确度较高[50]. FT-IR法不仅可以获取微塑料的数量信息,鉴别出微塑料的化学成分,而且对样品的回收率没有显著影响[51]. 利用原子力显微镜结合红外光谱仪可以获得高空间分辨率(50100 nm)的红外吸收光谱和吸收图像[52].
拉曼光谱是一种基于光的非弹性散射的振动光谱技术,它以振动光谱的形式提供有关系统分子振动的信息,可以识别样品中的成分. 与傅里叶光谱相比,拉曼光谱具有较高的分辨率(小于1 mm),对非极性官能团的灵敏度更高. 拉曼显微镜是分析小的微塑料不可或缺的工具. 傅立叶红外光谱和拉曼光谱法二者相辅相承[53]. 前者不受样品大小、形状的影响,但易受塑料老化的影响,后者可以获得官能团信息,尤其是非极性官能团,能观察到局部微观形貌,但获得的仅仅是微塑料表面的信息,且易产生荧光干扰[45,54],测量时间也较长,所以它在大气环境的应用还未普及.
裂解气相色谱-质谱联用技术通过对大分子的热裂解产物进行气相色谱-质谱分析来获得大分子的结构信息,是一种具有破坏性的微塑料分析方法. 该技术在严格的实验条件下不断升高样品池温度,使得聚合物在特定温度发生裂解,释放可挥发的小分子化合物,再进入GC-MS 测定质荷比,从而推断聚合物类型. 该方法能够实现复杂基底环境样品的批量分析,虽然对实验条件要求较高,但具有样品用量小、不需要预处理、可同时鉴定聚合物和塑料表面添加剂等优点[37-38,55].
经过上述分析方法的检测,大气中微塑料常见的聚合物类型有:聚乙烯、聚丙烯、聚苯乙烯、聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯和聚酰胺等[17,56].
-
自联合国环境大会第一届会议提出塑料问题以来,基于塑料的污染物颗粒引起了越来越多的全球关注,对海洋微塑料污染的研究不胜枚举. 据报道,每年有480万至1270万吨塑料从陆地进入世界海洋,我国是全球最大的海洋垃圾制造国之一,占192个沿海国家和地区排放总量的近三分之一[57]。Lebreton等[58]经过模拟预测得出,从2015年到2060年,全球塑料废物将增加3倍,达到2.7亿吨,这无疑加速了环境的污染. 随着Dris等[18]首先调查了大气中微塑料的沉积,并发现微塑料可长距离传输至偏远地区,最终进入海洋环境中后,大气中的微塑料研究日益增多. 不同国家和地区相继开展了室内室外的微塑料样品采集,并对其进行检测分析,部分城市地区分析情况见表4.
-
研究估计,7%的海洋微塑料污染是由大气输送造成的[13]. 室外城市环境中空气污染物的分布可能是由城市地形(如建筑物之间的空间)、当地气象和热循环(热岛干扰气流)引起的风向变化造成的[61]. Su等[31]利用多元相关分析和主成分分析发现,城市化和降雨是影响路边微塑料堆积的重要因素. 他们观测到高浓度微塑料的地方一般位于城市土地利用密集型和区域人口较多的地区附近. 微塑料在干燥天气期间积聚在道路和道路边缘,在强降雨中被冲刷转移. Brahney等[60]发现,微塑料沉积速率与长距离或全球迁移指数有关. Evangeliou等[62]对道路交通产生的微塑料颗粒(轮胎磨损颗粒和刹车磨损颗粒)进行大气传输的全球模拟,结果表明轮胎磨损颗粒约43%沉积在陆地上,约57%沉积在海洋中. 每年约28000 t的刹车磨损颗粒沉积在极地地区、山区等冰雪表面. LIU等[63]对上海市常见植物粘附的微塑料进行调查发现,不同地区的植物粘附的微塑料来源相似,大气微塑料在传输过程中暂时在植物叶片上大量储存,然后被风吹散,并可能成为偏远地区微塑料污染的来源. GUO等[64]研究微塑料的吸附性发现,聚苯醚中的含氧官能团会充当氢键受体并与其它分子相互作用,使微塑料更易吸附污染物和微生物. 另外,微塑料进入环境后会发生老化,LIU等[65]利用红外光谱和扫描电镜观测结果表明,老化的微塑料表面有明显的氧化和局部裂纹. 吸附动力学和等温线模型表明,老化微塑料的吸附能力高于原始微塑料,主要机制为静电相互作用和分子间氢键作用. 这些携带吸附物的微塑料颗粒在大气中停留的时间受多种因素影响,较大颗粒物的易于重力沉降,密度较低的通过大气环流输送至偏远地区(图3)(如北极[66]等).
-
微塑料的生态风险和潜在后果已引起越来越多的科学家、公共媒体和非政府组织重视. 在上世纪90年代前后,Grieve等[67]发现合成纤维会对人体健康造成影响,但由于当时并未提出“微塑料”的概念,因此没有引起广泛的关注. Prata等[20,68]发现微塑料除了通过食物链进入人体,还可通过呼吸活动被人吸入. 吸入肺部和鼻子黏液的微塑料可以通过咳嗽、打喷嚏、擤鼻涕等方式排出,或随黏液一起吞咽. Vianello等[69]利用人体模型对室内空气进行采样分析,结果表明,微塑料的浓度为(9.3±5.8)个·m−3,在轻度活动下,人体每小时最高可吸入11.3个微塑料颗粒. Greim等[70]发现,纤维的毒性可通过其与细胞之间的接触来传递. 他们认为这种相互作用可以通过释放细胞内信使和细胞毒性因子导致肺部炎症,然后由于活性氧的不断形成而引起继发性遗传毒性. 长期暴露在高浓度微塑料环境中的人更易患上肺病和慢性支气管炎等病症形成职业病(表5),而对于暴露在低浓度微塑料环境中的研究则较少.
-
微塑料作为一种新型的污染物,在生态系统中无处不在,对其追根溯源难度较大,因此,需要进行更多的调查和研究. 本文综述了大气微塑料的来源、分类、采集方法、提取方法、分析技术、研究进展和对人体的危害,主要结论与展望如下:
(1)大气微塑料污染的采样及分析方法
大气中常见的微塑料采集方法为干湿沉降法,提取方法主要采用滤膜过滤后进行干燥,微塑料样品物理性质分析一般以体视显微镜为主,扫描电镜和荧光显微镜为辅;化学组分的分析使用傅里叶红外光谱仪的居多,拉曼光谱仪则较少。不同的处理方法对不同种类的微塑料类型的回收率也起伏不定,导致相同样品以不同方法分析获得的结果偏差较大. 故应对微塑料的采集、提取、分析、表述方法制定统一的标准.
同时,目前微塑料样品的分析技术大多耗时耗力,成本也较高. 一种方法只能分析少量的参数,而且对样品具有一定的破坏性,样品中微塑料数量有限,因此,开发低样品量、多参数分析方法会具有更广阔的应用前景.
(2)大气微塑料污染的丰度单位
各地范围内均检测出微塑料,目前表征大气微塑料丰度的单位有多种(包括个·m−2·d−1、个·m−3、个·m−2、mg·g−1等),检测出的微塑料种类以纤维类为主. 不同研究及分析方法虽可以高效率收集到微塑料,但是对其浓度结果但并不统一,不同地区的微塑料污染程度无法直接进行比较,因此,需制定统一的丰度单位.
(3)大气微塑料污染的危害及影响
研究大气微塑料污染对人类和环境的危害及影响是一个急切的问题. 在涉及纺织和纤维的相关工业中,虽然已证实高浓度的微塑料被人体吸入后会引起呼吸道疾病和肺病等,但是合成纤维的毒性机制尚未完全解释清晰. 另外,在低浓度环境下,微塑料可诱发的潜在性疾病,需要更多的研究来证明.
(4)大气微塑料的来源和传输过程的研究
纤维类微塑料广泛存在于大气中,其来源多为合成纺织品(如衣物等). 特殊的天气条件(如降雨天气)会有助于微塑料的进一步运输和扩散,通过雨水排放口进入江河湖海. 了解微塑料排放到大气中的来源,将有助于我们能够实施具体的解决方案,以减轻微塑料污染. 目前对微塑料在大气传输过程中发生的变化研究仍较少,大气微塑料沉降物对水体和陆地污染的影响程度需要结合传输轨迹以及气象条件进行深入的研究.
(5)大气微塑料污染的治理
我国在微塑料的防治上还不够全面,对于生活垃圾分类处理的虽有上海、郑州等个别城市开始实行,但大部分城市和居民对塑料垃圾的危害知之甚少,微塑料更是鲜为人知. 对于来自于生活垃圾的塑料垃圾,不合理处置方法在一定程度上会加重微塑料污染. 塑料垃圾在收集之后,大多是采用了集中填埋的方式,并未进行其它特别处理,因此对其降解方法的研究需提上日程. 因此要加强对微塑料污染的宣传力度,建立健全法律制度,让居民了解相关知识,减少使用塑料制品.
大气环境中微塑料污染及其分析技术的研究进展
Progress on microplastics pollution and its analysis methods in the atmosphere
-
摘要: 微塑料污染物(直径小于5 mm的塑料碎片)对生态环境的潜在影响已成为人们关注的热点问题之一. 现有的研究微塑料的文献大多集中在水生环境,尤以海洋环境中的微塑料研究居多. 有关大气环境系统中微塑料污染近几年才受到关注. 本文综述了近年来有关大气微塑料研究的最新进展,概括了大气微塑料的来源及分类. 此外,归纳了目前常用于大气环境中微塑料的采集方法,并进一步列举了不同采集方法可适用的提取、分析方法,指出不同方法的优缺点. 最后,在总结国内外研究进展的基础上,对我国大气环境微塑料研究提出建议:①为使研究结果具有可对比性,大气环境微塑料的丰度单位需统一;②大气微塑料远距离传输的转化和降解过程需要进一步的研究;③微塑料在正常环境下的暴露对人体的危害需要更深入的了解.Abstract: Microplastics (plastic debris with diameter less than 5 mm) have become a hot topic due to their ubiquity in our living environment and potential impact on the ecological environment. Previous literature mainly focused on microplastics in the aquatic environment, especially in the marine environment, only a limited number of papers studied microplastics in the atmosphere. Here, we review the latest research progresses, the source, and the classification of atmospheric microplastics. Moreover, we compare the extraction procedures of different collection methods, summarize the commonly used methods for the analysis of atmospheric microplastics, and evaluate their advantages and disadvantages. Finally, further suggestions are on future microplastic research are proposed: ①The unit of microplastics in the atmosphere should be unified, in order to ensure the comparability of future studies. ②Further studies are required on the transformation and degradation processes of atmospheric microplastics during long-range transport. ③It is necessary to evaluate the potential health threat of microplastic exposure in our living environments.
-
Key words:
- atmospheric environment /
- microplastic /
- extraction methods /
- analysis methods
-

-
表 1 不同采样方法
Table 1. Different methods for collection of microplastics
采样方法
Collection methods适用丰度单位
Suitable unit适用条件
Suitable conditions优点
Advantage缺点
Disadvantage干湿沉降 个·m-2·d-1 被动采样,无需供电,适用于各类环境 自然沉降更客观的反映微塑料丰度 需要较长时间的观测,时间分辨率低 大气采样 个·m-3 主动采样,适用于供电方便地区,偏远无供电地区不适用 可以主动采集悬浮在空中的微塑料 收集到的样品杂质较多,雨天不易收集 粉尘收集 个·m-2,mg·g-1,个·kg-1 室内外各类灰尘聚集区域 可以观测已沉降的微塑料,采样简便 无法对悬浮在大气中的微塑料进行估计,样品杂质也较多 表 2 不同提取方法
Table 2. Different methods for extraction of microplastics
提取方法
Extraction methods适用采集方法
Applicable methods存在问题
Disadvantage目检法 三种方法均可 误判、漏数等原因使准确性受影响 密度分离法 干湿沉降、粉尘收集法 不足以去除全部有机质 消解法 三种方法均可 部分酸性溶液会消解部分类型微塑料 过滤干燥 干湿沉降 过滤及转移过程中会存在部分样品损耗 表 3 不同分析技术汇总
Table 3. Summary of different methods for analysis of microplastics
检测技术
Analysis methods介绍
Introduction优点
Advantage缺点
DisadvantageStereomicroscope[5] 通过形貌观察对样品进行分析 操作简便,检测过程快 对尺寸小于1 mm的微塑料易造成误判 micro-FT-IR[51,53] 通过检测化学键、官能团的振动吸收,
分析样品类型。操作简便,样品无需特殊处理,与Raman技术互补 易受环境影响,检测过程耗时耗力 micro-Raman[51,53] 通过激光激活分子振动,测量分子结构 操作简便,样品无需特殊处理,与FT-IR技术互补 结果受激发光波段选择影响,检测过程耗时耗力 SEM-EDS[29] 通过电子束与样品的相互作用,测量样品表面形态与元素 可精确检测样品表面形貌和成分 前处理过程易损毁样品,时间和人工成本较高 Fluorescence microscope[37,48] 通过染色剂将样品染色以观察,增强识别样品的客观性 与目检法互补,挑拣微塑料样品成功率高 无法对微塑料的种类进行具体分析 Pyr-GC-MS[38,55] 通过高温加热使样品热裂解,经气相色谱分离后,由质谱进行分析鉴定 样品用量小,不需要预处理,可同时鉴定聚合物和塑料表面添加剂 无法分析微塑料的大小、形状和数量,实验条件要求高,对样品的破坏性强 表 4 不同地区的研究情况
Table 4. Studies on microplastics in different areas
采集地点
Site采集年份
Year采集方法
Collection methods提取方法
Extraction methods检测技术
Analysis methods种类
Types丰度范围
Concentration range烟台[25] 2014 干湿沉降 目检、消解 micro-FT-IR 纤维、碎片、薄膜和发泡 1.30×102—6.24×102 个·m−2·d−1 巴黎[18] 2014 干湿沉降 过滤干燥 SEM-EDS 纤维、碎片 2.90×10—2.80×102 个·m-2·d−1 巴黎[14] 2014-2015 干湿沉降 过滤干燥 micro-FT-IR 纤维 2.00—3.55×102 个·m−2·d−1 东莞[24] 2016 干湿沉降 过滤干燥 micro-FT-IR 纤维、碎片、薄膜和发泡 1.75×102—3.13×102 个·m−2·d−1 巴黎[17] 2016 大气采样 目检 micro-FT-IR 纤维 0.3—5.94×10 个·m−3 日本[40] 2017 粉尘收集 密度分离、过滤干燥 micro-FT-IR 纤维、碎片、薄膜 (2.0±1.6)个·m−2 中国39个城市[59] 2017-2018 粉尘收集 目检、密度分离、过滤干燥 micro-FT-IR 纤维 4.6×10-3—2.7×10 mg·g−1 北京[46] 2018 大气采样、干沉降 目检 SEM-EDS 纤维 5.7×103 个·m−3 伦敦[36] 2018 干湿沉降 过滤干燥 micro-FT-IR、Fluorescence microscope 纤维、薄膜 5.10×102—9.25×102 个·m−2·d−1 上海[26] 2018 大气采样 目检 micro-FT-IR 纤维、碎片、薄膜 0—4.18 个·m−3 维多利亚[31] 2018 粉尘收集 目检、消解、过滤干燥 Stereomicroscope、 micro-FT-IR 纤维、碎片 20.6—529.3 个·kg−1 美国11个自然保护区和偏远地区[60] 2017—2019 干沉降和湿沉降 过滤干燥 micro-FT-IR 纤维 132 个·m−2·d−1 阿威罗[43] 2019 大气采样 目检、密度分离、过滤干燥 Stereomicroscope 纤维、碎片 5—6 个·m−3 表 5 近几年微塑料对人体危害的研究
Table 5. Recent studies on the health effects of microplastics on human
-
[1] DERRAIK J G B. The pollution of the marine environment by plastic debris: A Review [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2002, 44(9): 842-852. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00220-5 [2] RIOS L M, MOORE C, JONES P R. Persistent organic pollutants carried by synthetic polymers in the ocean environment [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2007, 54(8): 1230-1237. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.03.022 [3] COLE M, LINDEQUE P, HALSBAND C, et al. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(12): 2588-2597. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.09.025 [4] THOMPSON R C, OLSEN Y, MITCHELL R P, et al. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? [J]. Science, 2004, 304(5672): 838-838. doi: 10.1126/science.1094559 [5] HIDALGO R V, GUTOW L, THOMPSON R C, et al. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Methods Used for Identification and Quantification [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(6): 3060-3075. [6] NAPPER I E. , BAKIR A, ROWLAND S J., et al. Characterisation, quantity and sorptive properties of microplastics extracted from cosmetics [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 99(1/2): 178-185. [7] IVLEVA N P, WIESHEU A C, NIESSNER R. Microplastic in Aquatic Ecosystems [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(7): 1720-1739. doi: 10.1002/anie.201606957 [8] 叶李嘉, 吴南翔. 微塑料的检测及其生态环境影响研究进展 [J]. 环境与职业医学, 2019, 36(12): 1161-1167,1174. YE L J, WU N X. Progress on detection of microplastics and their effects on ecosystem [J]. Journal of Environmental and Occupational Medicine, 2019, 36(12): 1161-1167,1174(in Chinese).
[9] LAW K L, THOMPSON R C. Microplastics in the seas [J]. Science, 2014, 345(6193): 144-145. doi: 10.1126/science.1254065 [10] ZHAO S Y, ZHU L X, LI D J. Microscopic anthropogenic litter in terrestrial birds from Shanghai, China: not only plastics but also natural fibers [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 550: 1110-1115. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.01.112 [11] 周倩, 章海波, 周阳, 等. 滨海潮滩土壤中微塑料的分离及其表面微观特征 [J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(14): 1604-1611. doi: 10.1360/N972015-01098 ZHOU Q, ZHANG H B, ZHOU Y, et al. Separation of microplastics from a coastal soil and their surface microscopic features [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(14): 1604-1611(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N972015-01098
[12] 徐沛. 长江口邻近海域微塑料时空分布特征及生态风险评估初步研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2019. XU P. Spatial and temporal distribution of microplastics and a preliminary study on ecological risk assessment of microplastics in the Changjiang Estuary and East China Sea [D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2019(in Chinese).
[13] JULIEN B, DAMIEN F. Primary microplastics in the oceans[M]. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland, 2017. [14] DRIS R, GASPERI J, SAAD M, et al. Synthetic fibers in atmospheric fallout: A source of microplastics in the environment? [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2016, 104(1/2): 290-293. [15] ROUX C, MARGOT P. The population of textile fibres on car seats [J]. Science & Justice, 1997, 37(1): 25-30. [16] LIEBEZEIT G, LIEBEZEIT E. Origin of Synthetic Particles in Honeys [J]. Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences, 2015, 65(2): 143-147. doi: 10.1515/pjfns-2015-0025 [17] DRIS R, GASPERI J, MIRANDE C, et al. A first overview of textile fibers, including microplastics, in indoor and outdoor environments [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 221: 453-458. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.013 [18] DRIS R, GASPERI J, ROCHER V, et al. Microplastic contamination in an urban area: a case study in Greater Paris [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 12(5): 592-599. doi: 10.1071/EN14167 [19] 张思梦, 查金, 孟伟, 等. 环境中的微塑料及其对人体健康的影响 [J]. 中国塑料, 2019, 33(4): 81-88. ZHANG S M, ZHA J, MENG W, et al. A review of microplastics in environment and their effects on human health [J]. China Plastic, 2019, 33(4): 81-88(in Chinese).
[20] PRATA J C. Airborne microplastics: Consequences to human health? [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 234: 115-126. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.043 [21] GASPERI J, WRIGHT S L, DRIS R, et al. Microplastics in air: Are we breathing it in? [J]. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 2018, 1: 1-5. [22] 田媛, 涂晨, 周倩, 等. 环渤海海岸大气微塑料污染时空分布特征与表面形貌 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(4): 1401-1409. TIAN Y, TU C, ZHOU Q, et al. The temporal and spatial distribution and surface morphplogy of atmospheric microplastics around the Bohai Sea [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(4): 1401-1409(in Chinese).
[23] WANG X H, LI C J, LIU K, et al. Atmospheric microplastic over the South China Sea and East Indian Ocean: abundance, distribution and source [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 389: 121846. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121846 [24] CAI L Q, WANG J D, PENG J P, et al. Characteristic of microplastics in the atmospheric fallout from Dongguan city, China: preliminary research and first evidence [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(32): 24928-24935. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0116-x [25] 周倩, 田崇国, 骆永明. 滨海城市大气环境中发现多种微塑料及其沉降通量差异 [J]. 科学通报, 2017, 62(33): 3902-3909. doi: 10.1360/N972017-00956 ZHOU Q, TIAN C G, LUO Y M. Various forms and deposition fluxes of microplastics identified in the coastal urban atmosphere [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(33): 3902-3909(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N972017-00956
[26] LIU K, WANG X H, FANG T, et al. Source and potential risk assessment of suspended atmospheric microplastics in Shanghai [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 675: 462-471. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.110 [27] ZHANG Q, XU E G B, LI J N, et al. A review of microplastics in table salt, drinking water, and air: Direct human exposure [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(7): 3740-3751. [28] NOIK V J, TUAH P M. A first survey on the abundance of plastics fragments and particles on two sandy beaches in kuching, sarawak, malaysia[C]. Materials Science & Engineering Conference Series, 2015. [29] DEHGHANI S, MOORE F, AKHBARIZADEH R. Microplastic pollution in deposited urban dust, Tehran metropolis, Iran [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(25): 20360-20371. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9674-1 [30] 刘丹童, 宋洋, 李菲菲, 等. 基于显微拉曼面扫的小尺寸微塑料检测方法[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(10): 256-265.LIU D T, SONG Y, LI F F, et al. A detection method of small-sized microplastics based on micro-Raman mapping[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(10): 256-265(in Chinese). [31] SU L, NAN B X, CRAIG N J, et al. Temporal and spatial variations of microplastics in roadside dust from rural and urban Victoria, Australia: Implications for diffuse pollution [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 252: 126567. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126567 [32] BLAESING M, AMELUNG W. Plastics in soil: Analytical methods and possible sources [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 612: 422-435. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.086 [33] ZHAO S Y, ZHU L X, WANG T, et al. Suspended microplastics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary System, China: First observations on occurrence, distribution [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 86(1-2): 562-568. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.06.032 [34] DESFORGES J P W, GALBRAITH M, ROSS P S. Ingestion of microplastics by zooplankton in the Northeast Pacific Ocean [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology, 2015, 69(3): 320-330. [35] BROWNE M A, CRUMP P, Niven Stewart J,et al. Accumulation of microplastic on Shorelines Woldwide: Sources and sinks [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(21): 9175-9179. [36] WRIGHT S L, ULKE J, FONT A, et al. Atmospheric microplastic deposition in an urban environment and an evaluation of transport [J]. Environment International, 2020, 136: 105411. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105411 [37] 汤庆峰, 李琴梅, 魏晓晓, 等. 环境样品中微塑料分析技术研究进展 [J]. 分析测试学报, 2019, 38(8): 1009-1019. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2019.08.019 TANG Q F, LI Q M, WEI X X, et al. Progress on research of analysis techniques for microplastics in environmental samples [J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2019, 38(8): 1009-1019(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2019.08.019
[38] 王昆, 林坤德, 袁东星. 环境样品中微塑料的分析方法研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(1): 27-36.WANG K, LIN K D, YUAN D X. Research progress on the analysis of microplastics in the environment[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(1): 27-36(in Chinese). [39] PRATA J C, CASTRO J L, DA C J P, et al. An easy method for processing and identification of natural and synthetic microfibers and microplastics in indoor and outdoor air [J]. MethodsX, 2020, 7: 1-9. [40] UKIOKA S, TANAKA SI, NABETANI Y, et al. Occurrence and characteristics of microplastics in surface road dust in Kusatsu (Japan), Da Nang (Vietnam), and Kathmandu (Nepal) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 256: 113447. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113447 [41] DEVRIESE L I, VAN D M, MYRA D, et al. Microplastic contamination in brown shrimp (Crangon crangon, Linnaeus 1758) from coastal waters of the Southern North Sea and Channel area [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 98(1-2): 179-187. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.06.051 [42] ZHAO S Y, ZHU L X, LI D J. Microplastic in three urban estuaries, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2015, 206: 597-604. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.08.027 [43] PRATA J C, CASTRO J L, DA C J P, et al. The importance of contamination control in airborne fibers and microplastic sampling: Experiences from indoor and outdoor air sampling in Aveiro, Portugal [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 159: 111522. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111522 [44] ROBLIN B, RYAN M, VREUGDENHIL A J, et al. Ambient atmospheric deposition of anthropogenic microfibers and microplastics on the western periphery of Europe (Ireland) [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2020, 54: 11100-11108. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c04000 [45] 王俊豪, 梁荣宁, 秦伟. 海洋微塑料检测技术研究进展 [J]. 海洋通报, 2019, 38(6): 601-612. WANG J H, LIANG R N, Qin W. Review of analytical methods for detecting microplastics in the ocean [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2019, 38(6): 601-612(in Chinese).
[46] LI Y W, SHAO L Y, WANG W H, et al. Airborne fiber particles: Types, size and concentration observed in Beijing [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 705: 1-9. [47] KARAKOLIS E G, NGUYEN B, YOU J B et al. Fluorescent dyes for visualizing microplastic particles and fibers in laboratory-based studies [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2019, 6(6): 334-340. [48] ANDRADY A. Microplastics in the marine environment [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(8): 1596-1605. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.05.030 [49] OJEDA J J, ROMERO G M E, BANWART S A. Analysis of bacteria on steel surfaces using reflectance micro-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 81(15): 6467-6473. doi: 10.1021/ac900841c [50] HARRISON J P, OJEDA J J, ROMERO G M E. The applicability of reflectance micro-Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy for the detection of synthetic microplastics in marine sediments [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 416: 455-463. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.11.078 [51] HUPPERTSBERG S, KNEPPER T P. Validation of an FT-IR microscopy method for the determination of microplastic particles in surface waters [J]. Methods X, 2020, 7: 100874. [52] LUO H W, XIANG Y Hi, ZHAO Y Y, et al. Nanoscale infrared, thermal and mechanical properties of aged microplastics revealed by an atomic force microscopy coupled with infrared spectroscopy (AFM-IR) technique [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 744: 140944. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140944 [53] LI J Y, LIU H H, CHEN J P. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection [J]. Water Research, 2018, 137: 362-374. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.056 [54] 周倩, 章海波, 李远, 等. 海岸环境中微塑料污染及其生态效应研究进展 [J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(33): 3210-3220. doi: 10.1360/N972015-00714 ZHOU Q, ZHANG H B, LI Y, et al. Progress on microplastics pollution and its ecological effects in the coastal environment [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(33): 3210-3220(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N972015-00714
[55] PRATA J C, COSTA J P D, DUARTE A C, et al. Methods for sampling and detection of microplastics in water and sediment: A critical review [J]. Trac Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 110: 150-159. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2018.10.029 [56] LIU K, WANG X H, WEI N, et al. Accurate quantification and transport estimation of suspended atmospheric microplastics in megacities: Implications for human health [J]. Environment International, 2019, 132: 105127. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105127 [57] JAMBECK J R, GEYER R, WILCOX C, et al. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean [J]. Science, 2015, 347(6223): 768-771. doi: 10.1126/science.1260352 [58] LEBRETON L, ANDRADY A. Future scenarios of global plastic waste generation and disposal [J]. Palgrave Communications, 2019, 5: 6. doi: 10.1057/s41599-018-0212-7 [59] LIU C G, LI J, ZHANG Y L, et al. Widespread distribution of PET and PC microplastics in dust in urban China and their estimated human exposure [J]. Environment International, 2019, 128: 116-124. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.04.024 [60] BRAHNEY J, HALLERUD M, HEIM E, et al. Plastic rain in protected areas of the United States [J]. Science, 2020, 368(6496): 1257-1260. doi: 10.1126/science.aaz5819 [61] FERNANDO H J S, LEE S M, ANDERSON J, et al. Urban fluid Mechanics: Air circulation and contaminant dispersion in cities [J]. Environmental Fluid Mechanics, 2001, 1(1): 107-164. doi: 10.1023/A:1011504001479 [62] EVANGELIOU N, GRYTHE H, KLIMONT Z, et al. Atmospheric transport is a major pathway of microplastics to remote regions [J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1-32. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13993-7 [63] LIU K, WANG X H, SONG Z Y, et al. Terrestrial plants as a potential temporary sink of atmospheric microplastics during transport [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 742: 140523. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140523 [64] GUO X Y, WANG X L, ZHOU X Z, et al. Sorption of four hydrophobic organic compounds by three chemically distinct polymers: Role of chemical and physical composition [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(13): 7252-7259. [65] LIU G Z, ZHU Z L, YANG Y X, et al. Sorption behavior and mechanism of hydrophilic organic chemicals to virgin and aged microplastics in freshwater and seawater [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 246: 26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.100 [66] OBBARD R W, SADRI S, WONG Y Q, et al. Global warming releases microplastic legacy frozen in Arctic Sea ice [J]. Earths Future, 2014, 2(6): 316-320. [67] GRIEVE M C, BIERMANN T. The population of coloured textile fibres on outdoor surfaces [J]. Science & Justice, 1997, 37(4): 231-239. [68] PRATA J C, DA C J P, LOPES I, et al. Environmental exposure to microplastics: An overview on possible human health effects [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 702: 134455. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134455 [69] VIANELLO A, JENSEN R L, LIU L, et al. Simulating human exposure to indoor airborne microplastics using a breathing thermal manikin [J]. Scientific reports, 2019, 9(1): 8670. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45054-w [70] GREIM H P, BORM R, SCHINS K, et al. Toxicity of fibers and particles. Report of the workshop held in Munich, Germany, 26-27 October 2000 [J]. Inhalation Toxicology, 2001, 13(9): 737-754. [71] MASTRANGELO G, FEDELI U, FADDA E, et al. Epidemiologic evidence of cancer risk in textile industry workers: A review and update [J]. Toxicology & Industrial Health, 2002, 18(4): 171-181. [72] HOURS M, FEVOTTE J, LAFONT S, et al. Cancer mortality in a synthetic spinning plant in Besancon, France [J]. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 2007, 64(9): 575-581. doi: 10.1136/oem.2006.028282 [73] DAVISON P, ASCH R G. Plastic ingestion by mesopelagic fishes in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre [J]. Marine Ecology Progress, 2013, 432: 173-180. [74] GALLAGHER L G, LI W J, Ray Roberta M, et al. Occupational exposures and risk of stomach and esophageal cancers: update of a cohort of female textile workers in Shanghai, China [J]. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 2015, 58(3): 267-275. doi: 10.1002/ajim.22412 -




 下载:
下载: