-
土壤是社会可持续发展的物质基础,其质量直接关系到人民群众的身体健康。为保证农业发展,农药以及含有抗生素残留畜禽粪便的大量使用,带来了严重的土壤污染问题。据统计我国抗生素使用量占全球一半,每年抗生素的使用量高达12000 t,其中大环内酯类使用量占20%[1-3],长期将含有是此类抗生素的有机肥投入到农田,会增加被作物吸收的风险最终给人类带来潜在风险[4]。苯醚甲环唑(difenoconazole,DZ)是一种内吸性三唑类杀菌剂,通过破坏细胞膜结构和功能达到杀灭真菌的目的,其具有低毒、高效、广谱等优点,在我国广泛使用[5],且在研究区的使用频率均较高,是当地的高风险农药。目前有研究表明20 mg·kg-1大环内酯类抗生素处理可显著抑制土壤细菌繁殖[6],不同地区土壤中DZ的降解率存在差异[7-8],主要原因是由不同地区土壤有机质含量、含水率以及酸碱度不同导致[9]。
不同用地类型因种植作物不同和农药、有机肥料的施用种类及施用量也存在较大差异,导致农药和抗生素的检测浓度存在差异性。翟程凯等发现有机氯农药在水田中的残留浓度要高于菜地和果园[10],赵方凯等发现农田、园地、林地的检出限及检出含量存在较大差异[11],张涛等通过对江西梅江流域土壤中11种抗生素采样测试发现,抗生素总浓度在耕地中含量最高,而草地中含量最少[12]。然而,目前对土壤抗生素和农药的污染特征的研究较为单一,并且在复合污染下进行让环境质量评价的相关研究仍相对较少。
针对日益严重的土壤污染问题及当前研究背景,本文以我国华北某农产品基地为研究区,通过对研究区内果园、菜地土壤取样并进行系统分析,揭示区内土壤中共存的杀菌剂和大环内酯类抗生素污染现状,以及其空间分布特征,并采用生态风险指数法对区内土壤质量进行简单评估。研究结果可供今后农业健康发展及土壤修复侧重提供参考,警示人们注重经济快速发展的同时也要注重土壤健康。
-
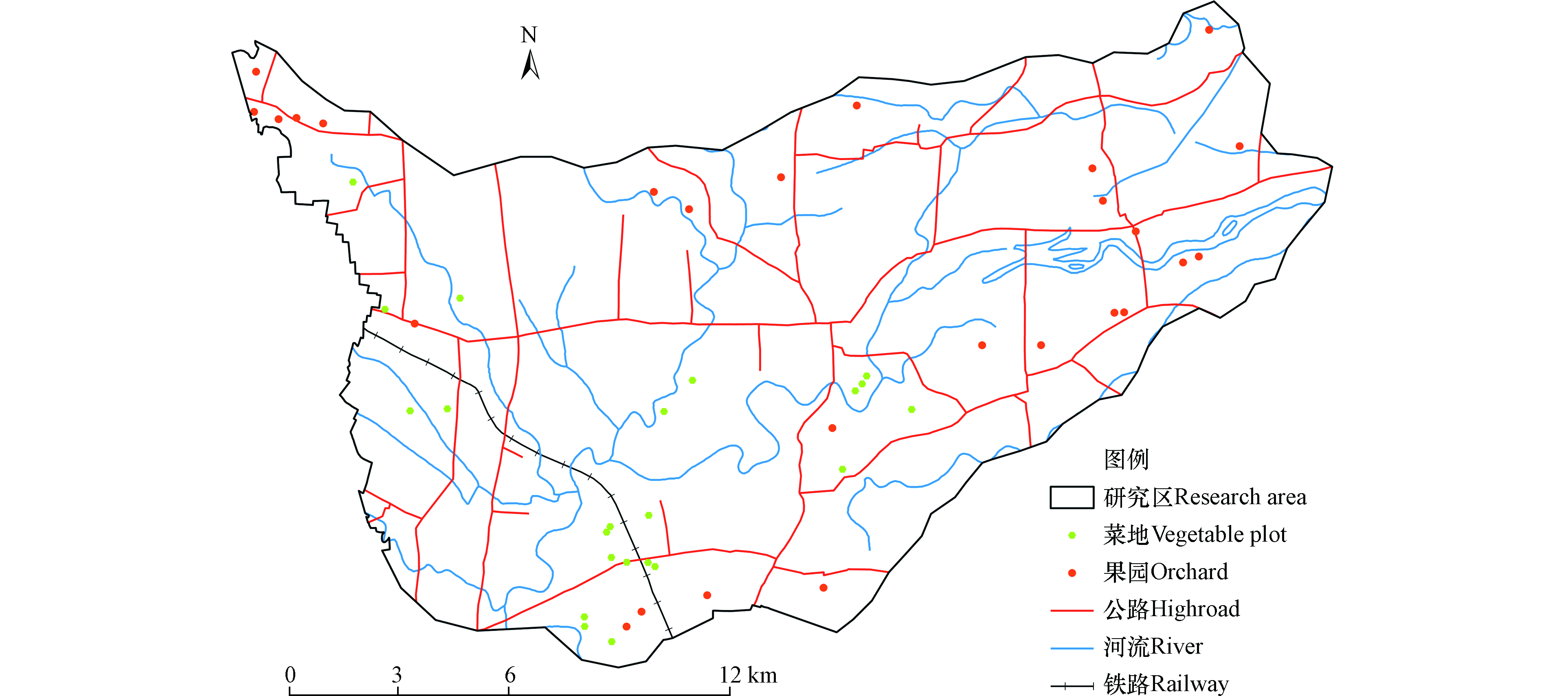
研究区隶属我国华北地区,地势东北高,西南低,属温带大陆性季风气候,年平均降水量为629.4 mm,土壤类型主要有褐土、潮土。研究区主要以农业与养殖业为主,区内养殖场产生的大量禽畜粪便往往不经处理便施入果园、菜地,其中以鸡粪、牛粪、羊粪等为主。经走访调查发现,当地仍广泛使用农药防治病虫害,且DZ使用频率较高。为了追求产量与效益,农药与含有抗生素残留的有机肥在长期高频使用下,导致土壤受农药与抗生素残留污染的威胁。为了解华北农业区土壤DZ及抗生素残留污染情况,对区内不同耕种类型土壤采样,共采集土壤样品49个,其中果园样点27个,菜地样点22个。分析农药与抗生素残留对土壤环境的影响,并对可能带来的环境影响做出评价。
-
通过卫星数据以及现场踏勘调查,综合考虑研究区地形条件、土地利用类型、乡镇分布、地形分布等情况,利用ArcGIS软件在区内共布设49个采样点(图1)。根据地块大小采用棋盘法或蛇形法进行采样,土壤采样深度为0—20 cm,每个样点采集3—5个样品进行混合,最终取样1 kg,样品混合后用密封袋密封并标号,样品放置低温保温箱中保存并及时送至实验室。
-
实验室测试指标包括土壤中的重金属Cu、As、Cd、Cr、Hg、Pb、土壤pH,以及土壤中红霉素(erythromycin,ERY)、罗红霉素(roxithromycin,ROX)、苯醚甲环唑(difenoconazole,DZ)。采用离子计法测定土壤的pH值,Cr、Cu、Cd、Pb、Hg、As参考《土壤和沉积物无机元素的测定波长色散X射线荧光光谱法》(HJ 780-2015)、《土壤质量铅、镉的测定石墨炉原子吸收分光光度法》(GB/T 17141-1997)、《土壤和沉积物汞、砷、硒、铋、锑的测定 微波消解/原子荧光法》(HJ 680-2013)的方法测定。利用HPLC-MS/MS对土壤中红霉素及罗红霉素进行定量测定,并增添加标回收率实验,样品前处理具体参照文献[13-14],采用Agilent 6890N(配置ECD检测器)对土壤苯醚甲环唑进行测定,具体操作及预处理参考文献[15]。虽环境样品复杂多样,分析过程步骤较多,但方法的准确度符合样品分析要求,最终ERY与ROX的实际回收率在87%—111%范围内,标准偏差低于7%。DZ的回收率为79%,回收率标准偏差在1%—16%范围内,所有测试均设3次重复处理。
分析主要采用软件为Origin 8.0、Canoco 4.5、SPSS 24,绘图由ArcGIS 10.3完成。
-
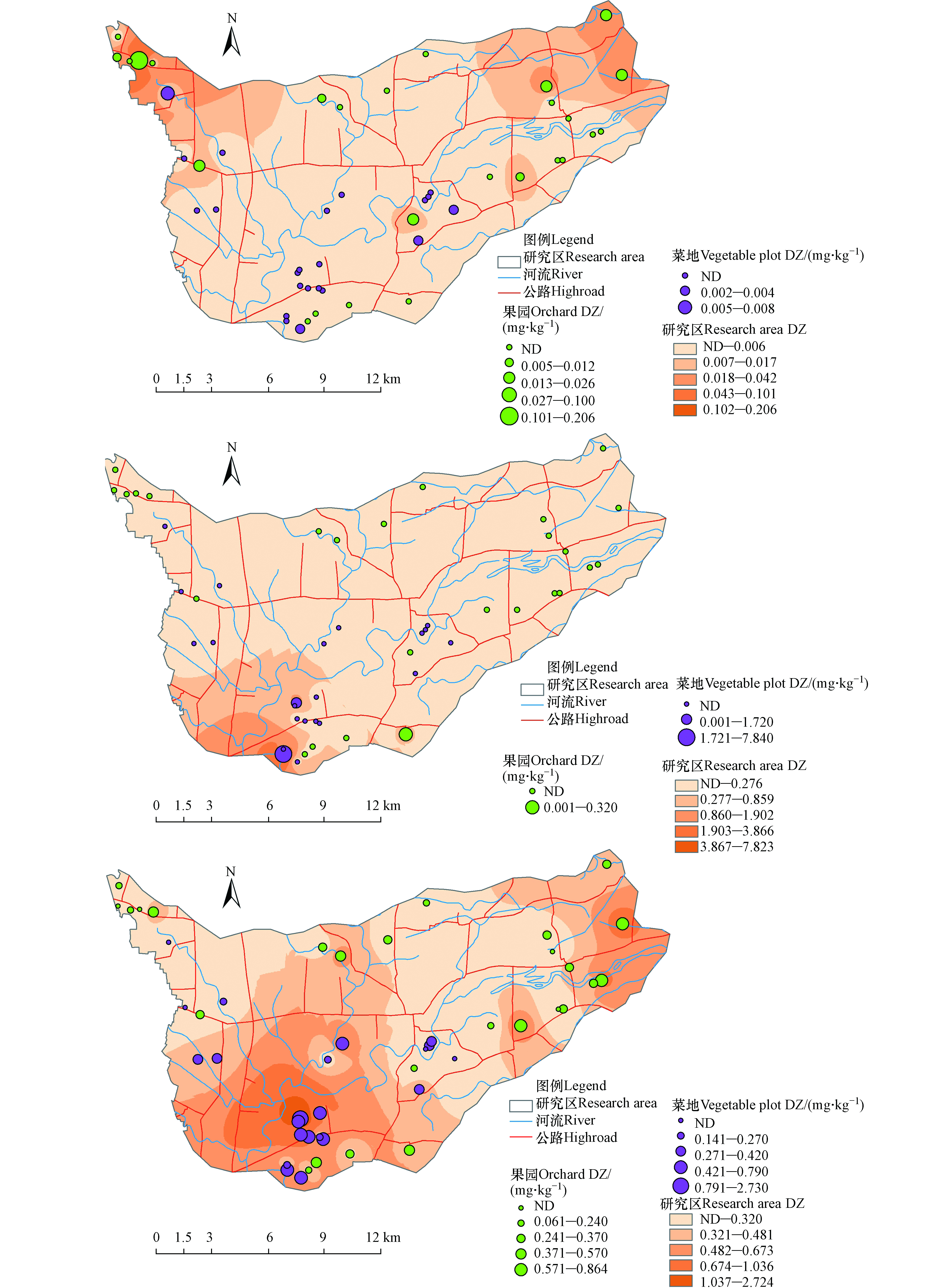
土壤中MLs类抗生素残留主要源于有机肥料(禽畜粪便堆)的使用,由于进入禽畜体内的抗生素不能完全被代谢和吸收,约20%—80%的抗生素会随着禽畜粪便或尿液排出体外[7]。由于果园和菜地主要施用的粪便种类不同,其抗生素残留也存在较大差异,由土壤中MLs类残留浓度显示(图2、表1),研究区菜地主要施用鸡粪,而果园有机肥料施用以羊粪为主。全区ERY检出率较低,仅3个点位检出ERY,分别位于菜地的9#、12#以及果园的26#。结合调查信息,其中9#、12#施用大量鸡粪,26#施用猪粪。菜地12#的MLs检出含量最高,为8.58 µg·kg−1,其中ERY含量为7.84 µg·kg−1,9#点位MLs检出含量为4.45 µg·kg−1,ERY含量为1.72 µg·kg−1。果园仅26#点位检出ERY,其残留量为0.32 μg·kg−1。区内检出ERY的点位主要集中在施用鸡粪的土壤中。
ROX的检出率高达93.88%,可知研究区主要选用ROX来预防或治疗禽畜的细菌感染,但区内ROX的检出含量较低,仅在菜地9#检出含量较高,为2.73 μg·kg−1,其余各点位含量均未超1.00 μg·kg−1。ROX在菜地土壤中的检出含量均值要高于果园土壤中,其中施用农家肥的土壤样点ROX检出含量均值最高,为0.66 μg·kg−1,施用羊粪的土壤样点检出含量均值最低,为0.27 μg·kg−1。ROX在果园土壤中不同施肥条件下,施用牛粪的土壤样点检出含量均值最高为0.45 μg·kg−1,检出含量均值最低为鸡粪土壤样点,含量为0.18 μg·kg−1。土壤中残留的MLs会逐渐转化为可提取态最终被植物吸收,对人类健康产生风险。
研究区DZ的残留浓度具有较大的差异性,区内DZ总体检出率为69.39%,且果园DZ检出率高于菜地,果园的平均残留浓度0.009 mg·kg−1远高于菜地残留浓度0.001 mg·kg−1。菜地中7#检出含量最高,为0.008 mg·kg−1,园地1#检出含量最高,为0.206 mg·kg−1,两个点位均出现在以鸡粪为主要施肥方式的区域,虽DZ与施肥方式无直接联系,但研究表明DZ的降解同土壤OM呈较强正相关,鸡粪又作为速效养分有易于分解、折合纯养量高等特点,故鸡粪的施用易造成DZ的残留。
-
对研究区49个土壤样品重金属测试结果进行描述性统计分析,得出6种重金属元素的算数平均数、最值、标准差、相对标准偏差等结果见表2。
由表2可见,研究区土壤pH均值为7.26,由《国家土壤环境质量》二级标准限值(6.5<pH<7.5)可知,研究区6项重金属均未超出限值,但Cr、Cu、Cd的平均值均高于当地土壤背景值,分别是当地土壤背景值的1.14、1.42、1.20倍,区内有一半以上的样品土壤Cu含量超过当地土壤背景值,说明研究区土壤环境总体呈以Cu为主及多种重金属共同富集的现象。区内Hg和Cu的相对标准偏差较高,Hg的相对标准偏差为80.29%,处于高度变异,Cu的相对标准偏差为36.80%,处于中度变异。表明研究区土壤部分重金属元素含量具有较大的差异性,连续性较差,区内贯穿多条公路、河流,受人为扰动可能性大。
-
为了解研究区不同用地类型土壤中DZ及MLs的残留特征,本研究利用ArcGIS在空间上将DZ、MLs的残留含量值进行划分,其残留含量及空间分布特征见图3。DZ作为一种高效广谱杀菌剂,可以有效防治蔬菜及果树的真菌性病害[16]。结果显示区内DZ整体呈东西部高中部低的趋势,从用地类型来看,研究区果园土壤残留浓度要明显高于菜地,菜地土壤DZ检出含量最高为0.008 mg·kg−1,而果园中近一半样点的DZ残留浓度高于0.008 mg·kg−1。经走访调查发现,菜地大多与居民住宅区距离较近,便于施肥、灌溉,菜地有机肥的施用频率及施用量要高于果园。许秀莹等研究发现,含水量及有机质含量高的土壤利于农药的降解[17],这可能是菜地土壤中DZ残留浓度低的原因。
MLs类抗生素能够有效抑制革兰氏阳性菌以及一些革兰氏阴性菌,被广泛地应用于人类以及畜禽兽细菌感染的治疗和预防,例如牛、羊、猪和家禽的呼吸道疾病、肠道感染和乳腺炎等,目前应用较为广泛的是ERY、ROX,由于禽畜粪便的大量施用,研究区土壤中ERY的衍生物ROX检出率较高。整体上研究区菜地与果园中ERY的检出率均较低,ERY高残留区主要分布与西南部,其余地区为轻度残留或无残留区域,且菜地土壤中MLs类抗生素残留浓度远高于果园。区内土壤ROX残留较为广泛在全区大部分区域均有分布,与ERY相同高残留区主要分布于西南部,另在东部也有少量分布,一定浓度的ROX残留会抑制土壤中脲酶及某些敏感微生物活性,从而导致土壤质量下降[18]。ERY及ROX残留会对研究区土壤产生一定的危害,并进一步通过生态系统对人体带来危害。
-
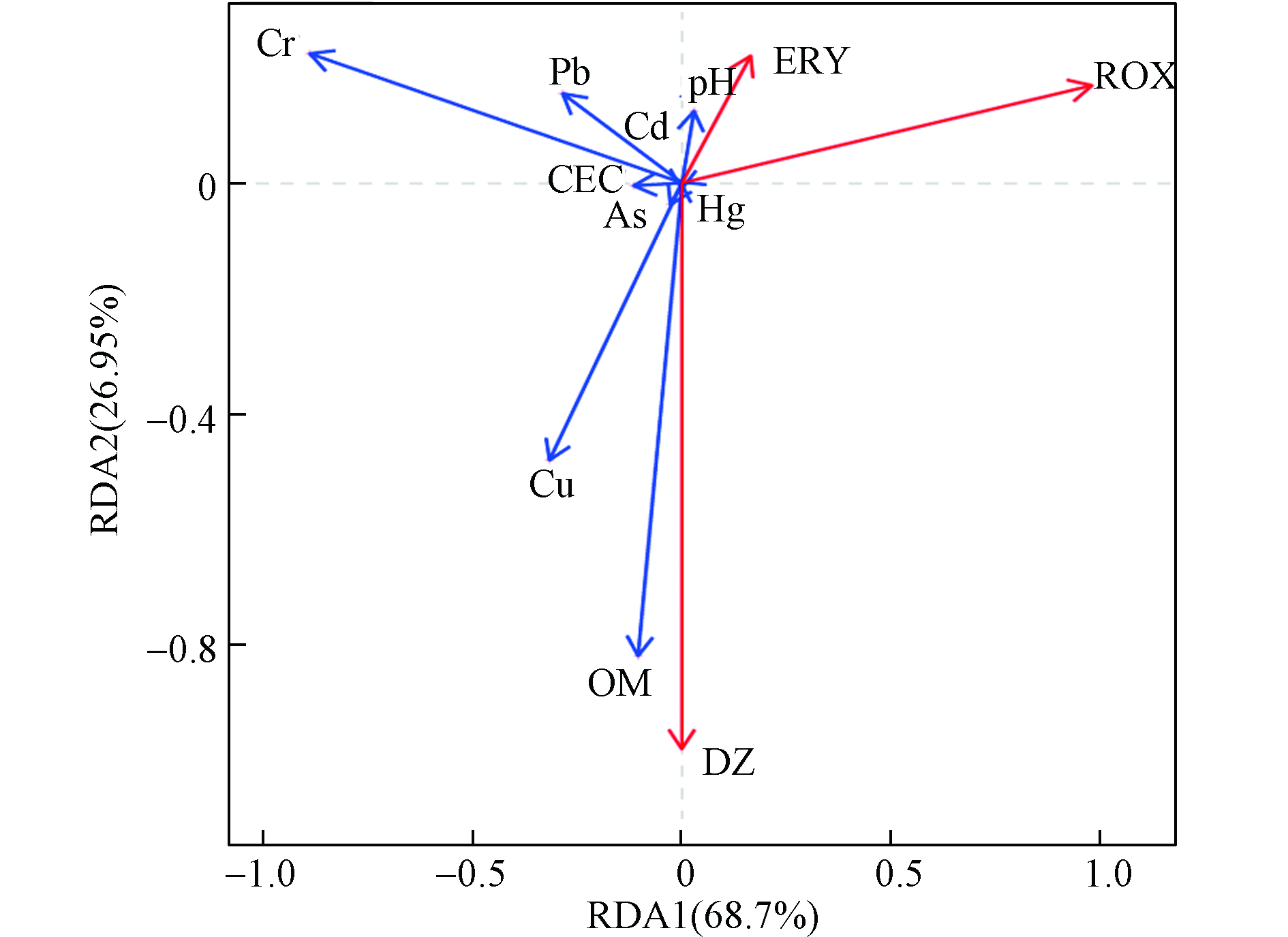
土壤中残留农药及抗生素的降解受到土壤环境(pH、有机质等)的影响,但同时农药与抗生素残留也会通过影响土壤中相关酶及微生物的生命活动来间接影响土壤环境。结合以上研究结果,本研究利用RDA冗余分析探究土壤中残留DZ及MLs对土壤环境的影响,RDA分析结果见图4。
整体上,MLs类抗生素与土壤中OM、Cu之间有较强的负相关性,其中对土壤OM有较强的影响。MLs类抗生素会抑制相关酶及微生物活性,进而影响有机物质的转化过程,而且已有相关研究发现土壤中残留的抗生素可以通过被OM中去质子化官能团吸附以及与极性官能团发生反应而被吸附[18],这可能是研究区MLs类抗生素与土壤OM呈现负相关的原因。禽畜养殖饲料通常会添加抗生素和含重金属的营养物质来促进禽畜生长和预防禽畜疾病[19]。ROX是ERY的衍生物,可与重金属Cr发生特定反应,喻倩曾利用罗红霉素荧光光度法测定重金属铬[20],这可能是ROX与土壤中的重金属Cr有一定的负相关性,但ERY与Cr几乎不存在相关性的原因。DZ与土壤中OM、Cu之间有较强的正相关性,土壤中的DZ残留会影响土壤微生物及相关酶的活性,从而影响其对OM的分解、代谢等相关生命活动,使残留浓度高的土壤OM含量低。在一定程度下,土壤pH高DZ更易降解,分析结果也表明DZ残留与土壤pH呈现出一定的负相关。DZ与铜制剂混用会降低其杀菌性能,因此要避免DZ与其他含铜农药施用。
-
由于农药、抗生素的种类较多,目前针对农药、抗生素的风险评价还没有具体的标准,但风险商(RQi)评价法在此类药品残留的风险评估上应用较为广泛[21-23]。风险商评价方法是某药品检测的环境浓度与预测无效应浓度的比值,其计算公式如下:
式中:RQi为抗生素i的风险商;MECi为抗生素i的测量浓度,mg·L−1;PNECi为抗生素i的无效应浓度,mg·L−1;Kd为抗生素的水土分配系数。根据RQ值评价:RQ<1,无明显风险;RQ≥1,表明有潜在的有害环境风险[24-25]。
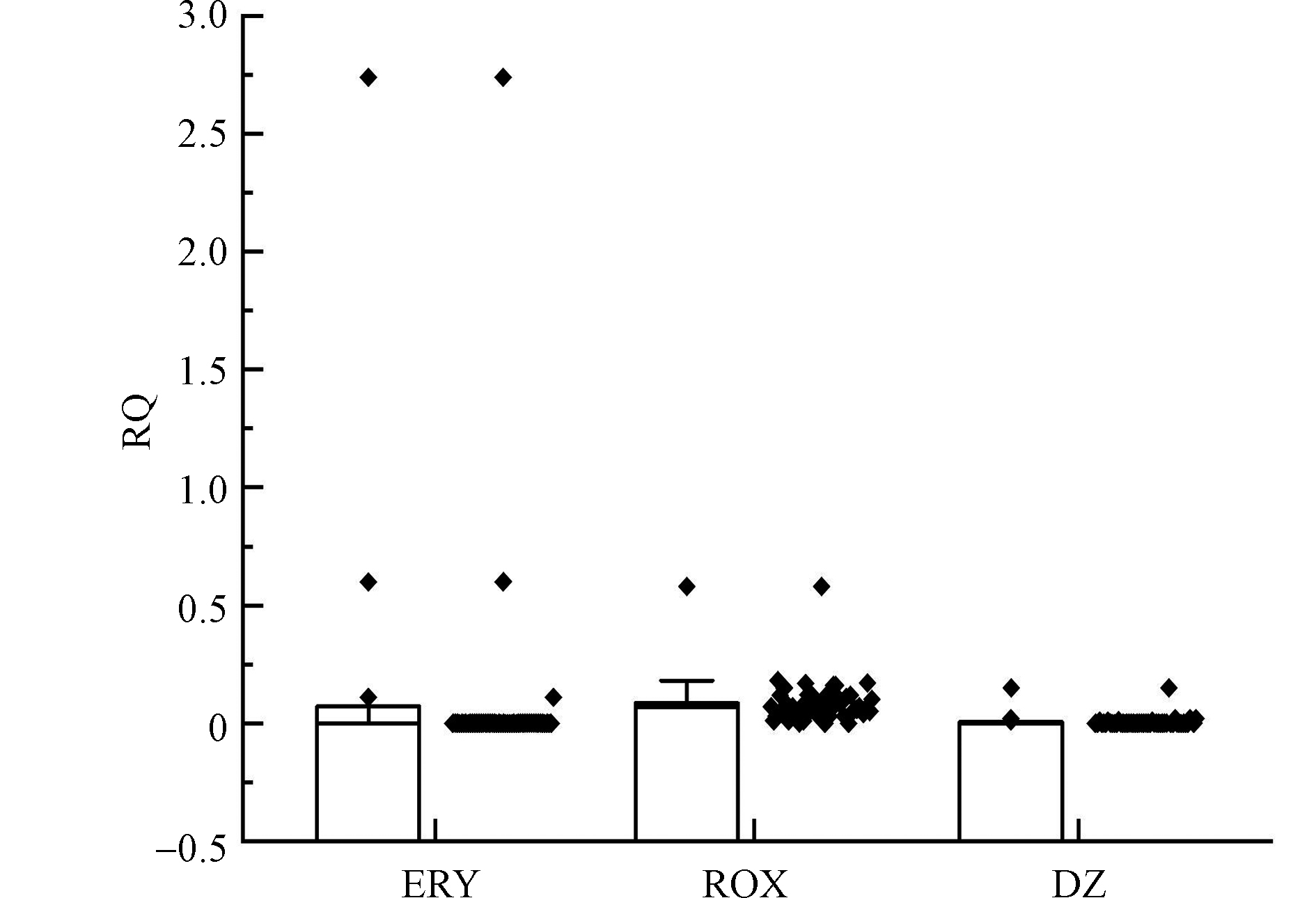
由计算公式得出ERY、ROX、DZ的土壤无效应浓度分别为2.86、4.70 、1386 μg·kg−1(表3)。研究区绝大多数土壤中MLs类抗生素及DZ不具有潜在风险(图5),仅在某一施用鸡粪的菜地土壤样点中检出ERY的RQ值为2.74,说明该点存在ERY潜在生态风险。研究区土壤中ROX和DZ的RQ值均小于1,表明研究区ROX和DZ残留在短期内均不构成潜在生态风险,但长期施用粪肥会导致土壤中抗生素含量累积,土壤中兽用抗生素和生物活性代谢物可持续存在数月至数年,并通过土壤-植物系统危害人类健康[26]。
-
对长期施用有机肥与农药的土壤,只针对抗生素及农药残留浓度进行简单的风险商评价不能够判断出其对土壤质量的影响。土壤中残留的药与抗生素会直接影响相关酶及生物的活性来影响土壤环境,图4冗余分析结果也表明MLs类抗生素、DZ与土壤pH、OM、重金属Cu等存在一定的相关性。为进一步了解研究区土壤环境质量,基于已有相关评价方法,对研究区土壤重金属进行综合污染评价,研究区土壤重金属综合评价方法采用内梅罗指数法,其计算公式为:
式中,PN为土壤重金属的内梅罗综合指数;(Ci /Si)max为土壤重金属单项污染指数最大值;(Ci /Si)ave为土壤重金属的单项污染指数的算数平均值。评价标准如表4所示[30]。
通过对研究区土壤重金属进行内梅罗综合污染评价发现,区内有4.08%的土壤样点重金属污染水平位于警戒线(0.7<PN≤1),77.55%的土壤样点属于轻度污染(1<PN≤2),18.37%的土壤重金属污染水达到中度污染水平(2<PN≤3)。
为进一步分析研究区土壤重金属潜在生态风险,采用潜在生态风险指数法进行预测评估,评价标准见表5,其计算方法为:
式中:RI为土壤重金属综合潜在生态风险指数;
$ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 单一重金属潜在生态风险系数;$ {T}_{r}^{i} $ 为土壤重金属的毒性响应系数;$ {C}_{s}^{i} $ 为土壤重金属元素的实测值,$ {C}_{n}^{i} $ 为土壤重金属元素的污染评价参比值。本次研究6种土壤重金属(Hg、As、Cr、Cu、Cd、Pb);重金属毒性系数分别为:40、40、2、5、30、5,土壤中重金属生态风险分析见表5[31]。研究区土壤重金属综合生态风险较高,RI为50.81—344.62,约75.50%的土壤样点属于轻微风险等级,22.45%属于中度风险,2.05%属于强风险。重金属的单一生态系数差距较大,研究区以轻微生态风险为主,Hg的风险系数范围最广且风险系数较高,范围为8.57—155.00,且有6.12%的点位风险等级为强。研究区土壤中重金属生态风险主要由Hg、As、Cd产生,虽Cr、Cu和Pb的单项污染指数高,但其重金属毒性系数低,故其潜在生态风险较小。
-
研究区是典型的农副产品基地,区内农业、养殖业协同发展,农业上产生的秸秆可粉碎成为禽畜饲料添加剂,禽畜粪便可作为有机肥施入土壤,然而农药与抗生素的大量使用也为这种发展模式带来危害。对区内土壤的MLs类抗生素进行残留统计分析发现,区内土壤中普遍存在ROX残留,ERY只有部分土壤样点检出,表明研究区养殖业主要选用ROX来治疗和预防禽畜疾病。结合走访调查信息及空间残留含量统计特征发现,区内抗生素残留含量高的样点大多靠近养殖场,养殖过程中药品残留可能是导致附近土壤样点抗生素含量高的直接原因。而DZ在果园与菜地中的残留特征有较大差异,菜地土壤中残留量要明显小于果园,结合调查信息猜测,含水量及有机质含量高的菜地土壤更利于DZ降解从而降低其残留量。土壤环境、农药及抗生素之间可相互影响,土壤pH、OM等会影响农药与抗生素的降解,农药与抗生素残留会影响土壤中微生物及相关酶的活性进而影响土壤质量[32]。通过冗余分析可知,研究区土壤中农药、抗生素残留会间接引起土壤OM、Cu等土壤环境的变化。
-
研究区土壤MLs类抗生素与DZ的残留浓度不高,总体上潜在生态风险较低。但土壤中残留抗生素、农药可被土壤吸附形成络合物或螯合物稳定存在土壤中[33-36]。因此尽管目前研究区内土壤中农药与抗生素残留浓度低,生态风险较小,但土壤综合环境质量较低,为了土壤持续稳定健康发展,需要控制向土壤中输入有害物质总量。有机肥与农药在农业上起着相关重要的作用,只能通过减少其使用量或降低危害后施用。目前针对禽畜粪便抗生素的消减处理,有好氧堆肥、厌氧消化、禽畜粪便炭化等,可有效使粪便中抗生素残留得到降解,但厌氧消化后的沼渣还田后仍可能造成潜在的生物毒性[37],粪便的炭化处理虽能高效去除抗生素,但其成本较高。综合考虑研究区养殖基地较多,采用成本较低的好氧堆肥处理施用可以使养殖厂产生的大量禽畜粪便得到有效利用。DZ作为杀菌剂在果园中应用广泛,其具有亲脂性、低生物降解性和在环境中易转移等特点,使其能够长期存在于土壤,长期使用不仅会使菌群产生抗药性,也会危害土壤内部环境[38]。草木灰作为植物燃烧后的残余物,含有植物生长所需的磷、钾、钙等元素,可作为作物肥料,同时草木灰也可以作为杀菌剂用以防止果树白粉病、根腐病、炭疽病、叶枯病等,合理利用草木灰杀虫杀菌功能可以减少区内土壤农药残留危害。
-
(1)研究区土壤抗生素及农药残留具有一定的空间差异性,MLs类抗生素在菜地的残留量高于果园,但果园的DZ残留量高于菜地。研究区DZ残留整体呈东、西部高,中部低的趋势;ERY的高残留区主要集中于西南部,其余地区为轻度残留或无残留区域;ROX残留较为广泛,在大部分区域均有分布,高残留区主要分布于西南部,另在东部也有少量分布。
(2)土壤中MLs类抗生素(ROX、ERY)的残留与土壤OM、Cu之间有较强的负相关性,ROX与重金属Cr之间存在一定负相关性;DZ的残留与OM、Cu之间有较强的正相关性,且与土壤pH有一定的负相关性。
(3)采用风险商评价法对区内土壤中残留MLs类抗生素及DZ进行评价,发现除某一施用鸡粪的菜地土壤样点ERY存在潜在生态风险,其余各样点土壤短期内不会构成生态风险。重金属内梅罗指数法得出区内77.55%的土壤重金属污染属于轻度污染水平,污染形势严峻,但重金属综合生态风险预测则显示75.50%的土壤样点属于轻微风险等级,22.45%属于中度风险等级,仅有2.05%的样点属强风险范围。
农用地大环内酯类抗生素与杀菌剂残留污染评价
Pollution assessment of macrolide antibiotics and fungicides residues in agricultural land
-
摘要: 土壤中农药与抗生素残留的污染问题引起了人们的广泛关注。研究选取我国华北地区典型农副产品基地,测定土壤中大环内酯类抗生素(macrolide antibiotics,MLs)中的红霉素(erythromycin,ERY)、罗红霉素(roxithromycin,ROX)与农药苯醚甲环唑(difenoconazole,DZ)的残留,分析不同种植模式及不同有机肥施用下土壤中抗生素残留差异,并从空间上分析研究区土壤中MLs类抗生素与DZ残留浓度特征,进一步的采用RDA冗余分析来探究土壤中残留DZ及MLs对土壤环境的影响。结果表明其对土壤中的OM、Cu等有一定的影响,这可能与土壤中酶与微生物的生命活动以及与其他药剂混用有关。DZ及MLs风险商(RQ)结果显示研究区土壤MLs类抗生素与DZ残留不具有潜在生态风险,但由土壤重金属综合污染评价得出区内有77.55%的土壤样点污染水平为轻度污染,潜在生态风险指数法预测区内土壤重金属75.50%的土壤样点属于轻微风险,22.45%属于中度风险等级,仅2.05%属于很强风险。本文对研究区土壤农药与抗生素残留特征及影响进行分析讨论,研究认为区内农药与抗生素污染短期内不存在潜在生态风险,但需注意与含金属药剂的混用问题。Abstract: The contamination of soil with pesticide and antibiotic residues has caused widespread concern. In this study, the residues of erythromycin (ERY) and roxithromycin (ROX) among macrolide antibiotics (MLs) and Difenoconazole (DZ) in soils of typical agricultural and sideline product bases in North China were determined, and the differences of antibiotic residues in soils under different planting patterns and different organic fertilizer application were analyzed, the characteristics of residual concentrations of MLS antibiotics and DZ in soil were analyzed spatially. RDA redundancy analysis was used to explore the effects of DZ and MLS on soil environment. The results showed that DZ and MLS had certain effects on OM and Cu in soil, which might be related to the life activities of enzymes and microorganisms in soil and the mixed use of other pesticides. The results of DZ and MLS risk quotient (RQ) showed that the residues of MLs and DZ in the soils of the study area were not potentially ecologically risky, but the comprehensive assessment of soil heavy metal pollution showed that 77.55% of the soil samples in the area were lightly contaminated, and the potential ecological risk index method for predicting soil heavy metals in the area indicates that 75.50% of the soil samples were at slight risk, 22.45% were at moderate risk level, and only 2.05% were at very strong risk. In this paper, the characteristics and effects of pesticide and antibiotic residues in the soil of the study area were analyzed and discussed. The results showed that there was no potential ecological risk in the short term of pesticide and antibiotic pollution in the area, but it was necessary to pay attention to the problem of mixing with metal containing pesticides.
-
Key words:
- soil /
- pesticides /
- antibiotic /
- residual characteristics /
- ecological risk
-

-
表 1 MLs及DZ残留情况
Table 1. Residual MLs and DZ
抗生素
Antibiotic浓度范围/(μg·kg−1)
Concentration range平均值/(μg·kg−1)
Mean标准差/(μg·kg−1)
Standard deviation检出率
Recall factorERY ND—7.84 0.20 1.14 6.12% ROX ND—2.73 0.40 0.41 93.88% DZ ND—206.00 9.94 32.43 69.39% 表 2 研究区土壤重金属残留情况
Table 2. Residual conditions of heavy metals in soil of the study area
项目
Project最小值/(mg·kg−1)
Maximum最大值/(mg·kg−1)
Minimum平均值/(mg·kg−1)
Mean标准差/(mg·kg−1)
Standard deviation相对标准偏差/%
Relative standard deviation土壤背景值/(mg·kg−1)
Background value of soilHg 0.02 0.27 0.06 0.05 80.29% 0.07 As 2.61 12.61 9.02 1.86 20.66% 11.20 Cr 50.07 154.53 69.42 22.28 32.10% 61.00 Cu 17.90 78.83 32.12 11.82 36.80% 22.60 Cd 0.08 0.38 0.18 0.06 33.89% 0.10 Pb 17.20 39.69 24.37 5.15 21.12% 26.00 表 3 预测土壤中抗生素无效应浓度
Table 3. Predicts the non-effective concentration of antibiotics in soil
表 4 土壤重金属污染指数分级标准
Table 4. Soil heavy metal pollution index classification standard
内梅罗污染指数
Nemerowindexofpollution潜在生态风险评估
PotentialecologicalriskassessmentPN 污染程度 $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 风险等级 RI 风险等级 PN≤0.7 安全 $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 轻微 RI<150 轻微风险 0.7<PN≤1 警戒线 40≤ $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 中等 150≤RI<300 中等 风险 1<PN≤2 轻度污染 80≤ $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 强 300≤RI<600 强风险 2<PN≤3 中度污染 160≤ $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 很强 600≤RI 很强风险 3<PN 重度污染 320≤ $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 极强 表 5 土壤重金属潜在生态风险分析
Table 5. Potential ecological risk analysis of heavy metals in soil
$ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 风险等级
Risklevel比例 Proportion RI 风险等级
Risklevel比例
ProportionHg As Cr Cu Cd Pb $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 轻微 77.55% 89.80% 100% 100% 18.37% 100% RI<150 轻微风险 75.50% 40≤ $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 中等 16.33% 10.20% 71.43% 150≤RI<300 中等风险 22.45% 80≤ $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 强 6.12% 10.20% 300≤RI<600 强风险 2.05% 160≤ $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 很强 600≤RI 很强风险 320≤ $ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 极强 -
[1] 高景峰, 孙丽欣, 樊晓燕, 等. 罗红霉素短期冲击对活性污泥中氨氧化微生物丰度和多样性的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(7): 2961-2971. GAO J F, SUN L X, FAN X Y, et al. Short-term effect of roxithromycin on abundance and diversity of ammonia oxidizing microorganisms in activated sludge [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(7): 2961-2971(in Chinese).
[2] 徐维海, 张干, 邹世春, 等. 香港维多利亚港和珠江广州河段水体中抗生素的含量特征及其季节变化 [J]. 环境科学, 2006, 27(12): 2458-2462. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.12.016 XU W H, ZHANG G, ZOU S C, et al. Occurrence and seasonal changes of antibiotics in the Victoria harbour and the Pearl River, South China [J]. Environmental Science, 2006, 27(12): 2458-2462(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.12.016
[3] 顾鑫, 余凯翔, 胡宏华, 等. 土壤中红霉素结合残留在菜心中生物有效性研究 [J]. 核农学报, 2020, 34(3): 601-609. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.03.0601 GU X, YU K X, HU H H, et al. Bioavailability of the bound residues of 14C-erythromycin in soil [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 34(3): 601-609(in Chinese). doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.03.0601
[4] 庄红娟, 周鹏飞, 陈弘扬, 等. 农田9种农药残留特征及对土壤环境指标影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(8): 2439-2449. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020113002 ZHUANG H J, ZHOU P F, CHEN H Y, et al. Characteristics of soil pesticide residues and their influence on soil environmental indicators [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(8): 2439-2449(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020113002
[5] 华乃震. 杀菌剂苯醚甲环唑的进展和应用 [J]. 世界农药, 2013, 35(6): 7-12,43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6485.2013.06.002 HUA N Z. Dvelopment and application of difenoconazole fungicide [J]. World Pesticides, 2013, 35(6): 7-12,43(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6485.2013.06.002
[6] 严虎. 多菌灵、氯霉素单一与复合条件下在土壤中的消解及其对土壤真菌细菌比和酶活性的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2011. YAN H. Dissipation of carbendazim and chloramphenicol alone and in combination, and their effects on soil fungi: Bacteria and soil enzyme activities[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2011(in Chinese).
[7] 封天佑. 苯醚甲环唑在稻田中的残留及降解动态研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2016. FENG T Y. Rearch on residues and dissipation dynamics of difenoconazole in rice field[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2016(in Chinese).
[8] PAN M, WONG C K C, CHU L M. Distribution of antibiotics in wastewater-irrigated soils and their accumulation in vegetable crops in the Pearl River Delta, Southern China [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2014, 62(46): 11062-11069. doi: 10.1021/jf503850v [9] 马亚培, 李宇轩, 谢欢, 等. 氮沉降与生物炭对土壤可溶性有机质的影响 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(10): 4514-4521. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.10.038 MA Y P, LI Y X, XIE H, et al. Effects of nitrogen deposition and biochar application on soil dissolved organic matter [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(10): 4514-4521(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.10.038
[10] 瞿程凯, 祁士华, 张莉, 等. 福建戴云山脉土壤有机氯农药残留及空间分布特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(11): 4427-4433. QU C K, QI S H, ZHANG L, et al. Distribution characteristics of organochlorine pesticides in soil from Daiyun mountain range in Fujian, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(11): 4427-4433(in Chinese).
[11] 赵方凯, 陈利顶, 杨磊, 等. 长三角典型城郊不同土地利用土壤抗生素组成及分布特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(12): 5237-5246. ZHAO F K, CHEN L D, YANG L, et al. Composition and distribution of antibiotics in soils with different land use types in a typical peri-urban area of the yangtze river delta [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(12): 5237-5246(in Chinese).
[12] 张涛, 郭晓, 刘俊杰, 等. 江西梅江流域土壤中四环素类抗生素的含量及空间分布特征 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(4): 1493-1501. ZHANG T, GUO X, LIU J J, et al. Concentration and spatial distribution of tetracycline antibiotics in soil of Meijiang river catchment, Jiangxi Province [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(4): 1493-1501(in Chinese).
[13] 陈莉, 贾春虹, 刘冰洁, 等. 超高效液相色谱-电喷雾串联质谱法同时测定土壤中四环素类抗生素及其降解产物 [J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(6): 1-6. CHEN L, JIA C H, LIU B J, et al. Determination of tetracyclines and their degradation products in soil using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(6): 1-6(in Chinese).
[14] 邰义萍. 珠三角地区蔬菜基地土壤中典型抗生素的污染特征研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2010. TAI Y P. The study on pollution characteristics of typical antibiotics in soil from vegetable fields of Pearl River Delta area[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2010(in Chinese).
[15] 王雅丽, 龚道新, 张春艳, 等. 气相色谱法对稻田水、土壤中的醚菌酯和苯醚甲环唑残留的检测 [J]. 湖北农业科学, 2014, 53(21): 5249-5252. WANG Y L, GONG D X, ZHANG C Y, et al. Simultaneous determination of kresoxim-methyl and difenoconazole residue in paddy water and soil with gas chromatography [J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 53(21): 5249-5252(in Chinese).
[16] 刘纲华. 苯醚甲环唑在几种果蔬中的残留降解行为研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2012. LIU G H. The residue and degradation behavior of difenoconazole in some fruits and vegetables[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2012(in Chinese).
[17] 许秀莹, 刘晓凤, 王鸣华. 氟啶胺的水解与土壤降解特性研究 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2014, 14(5): 252-256. XU X Y, LIU X F, WANG M H. On fluazinam hydrolysis and degradation features in the soil [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2014, 14(5): 252-256(in Chinese).
[18] GU C, KARTHIKEYAN K G, SIBLEY S D, et al. Complexation of the antibiotic tetracycline with humic acid [J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 66(8): 1494-1501. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.08.028 [19] 王瑞, 魏源送. 畜禽粪便中残留四环素类抗生素和重金属的污染特征及其控制 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(9): 1705-1719. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2013.09.002 WANG R, WEI Y S. Pollution and control of tetracyclines and heavy metals residues in animal manure [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(9): 1705-1719(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2013.09.002
[20] 喻倩. 罗红霉素荧光光度法测定铬(Ⅵ)的研究 [J]. 湖南城市学院学报(自然科学版), 2014, 23(1): 49-51. YU Q. Study on the determination of chromium(Ⅵ) with roxithromycin fluorescence spectrophotofluorimetry [J]. Journal of Hunan City University (Natural Science), 2014, 23(1): 49-51(in Chinese).
[21] 卢诚, 张俊, 王钊, 等. 河北潘家口水库氯霉素类抗生素检测及风险评估 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(6): 1843-1849. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.06.036 LU C, ZHANG J, WANG Z, et al. Determination and risk assessment of chloramphenicols in Panjiakou Reservoir, Hebei Province [J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(6): 1843-1849(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.06.036
[22] 涂棋, 徐艳, 李二虎, 等. 典型养鸡场及其周边土壤中抗生素的污染特征和风险评估 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(1): 97-107. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0823 TU Q, XU Y, LI E H, et al. Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in typical chicken farms and surrounding soils [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(1): 97-107(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0823
[23] NIETO A, BORRULL F, MARCÉ R M, et al. Selective extraction of sulfonamides, macrolides and other pharmaceuticals from sewage sludge by pressurized liquid extraction [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2007, 1174(1/2): 125-131. [24] CRISTALE J, KATSOYIANNIS A, SWEETMAN A J, et al. Occurrence and risk assessment of organophosphorus and brominated flame retardants in the River Aire (UK) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 179: 194-200. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.04.001 [25] SÁNCHEZ-AVILA J, TAULER R, LACORTE S. Organic micropollutants in coastal waters from NW Mediterranean Sea: Sources distribution and potential risk [J]. Environment International, 2012, 46: 50-62. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2012.04.013 [26] KARCı A, BALCıOĞLU I A. Investigation of the tetracycline, sulfonamide, and fluoroquinolone antimicrobial compounds in animal manure and agricultural soils in Turkey [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2009, 407(16): 4652-4664. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.04.047 [27] PAN M, CHU L M. Adsorption and degradation of five selected antibiotics in agricultural soil [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 545/546: 48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.040 [28] 王嘉玮. 渭河西安段表层水体中抗生素的分布特征及生态风险评价[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2018. WANG J W. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of antibiotics in surface water of xi’an section of Weihe river[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2018(in Chinese).
[29] 谭华东, 李勤奋, 张汇杰, 等. 南渡江农业土壤中农药分布特征与生态风险评估 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(1): 181-189. TAN H D, LI Q F, ZHANG H J, et al. Distribution and ecotoxicological risk of current-use pesticides in agricultural soil from nandu river basin in Hainan [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(1): 181-189(in Chinese).
[30] 郑睛之, 王楚栋, 王诗涵, 等. 典型小城市土壤重金属空间异质性及其风险评价: 以临安市为例 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6): 2875-2883. ZHENG J Z, WANG C D, WANG S H, et al. Spatial variation of soil heavy metals in Lin'an City and its potential risk evaluation [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6): 2875-2883(in Chinese).
[31] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [32] 张春秀. 农药污染对农作物土壤的影响及可持续治理对策 [J]. 现代农业, 2017(7): 39-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0708.2017.07.030 ZHANG C X. Effect of pesticide pollution on crop soil and sustainable management countermeasures [J]. Modern Agriculture, 2017(7): 39-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0708.2017.07.030
[33] SCHLÜSENER M P, BESTER K. Persistence of antibiotics such as macrolides, tiamulin and salinomycin in soil [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 143(3): 565-571. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.10.049 [34] 许天衡. 苯醚甲环唑在土壤中的消解及其对土壤微生物和烟曲霉敏感性的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. XU T H. Dissipation of difenoconazole in soil and its impacts on soil microorganism and sensitivity of A. Fumigatus[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018(in Chinese).
[35] 李云开, 刘世荣, 张克强, 等. 磺胺类药物在农田生态系统中迁移转化过程的研究进展 [J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2007, 34(12): 141-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7236.2007.12.051 LI Y K, LIU S R, ZHANG K Q, et al. Research progress on migration and transformation of sulfonamides in farmland ecosystem [J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2007, 34(12): 141-144(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7236.2007.12.051
[36] 王晓洁, 赵蔚, 张志超, 等. 兽用抗生素在土壤中的环境行为、生态毒性及危害调控 [J]. 中国科学:技术科学, 2021, 51(6): 615-636. doi: 10.1360/SST-2020-0337 WANG X J, ZHAO W, ZHANG Z C, et al. Veterinary antibiotics in soils: Environmental processes, ecotoxicity, and risk mitigation [J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2021, 51(6): 615-636(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/SST-2020-0337
[37] MOHRING S A I, STRZYSCH I, FERNANDES M R, et al. Degradation and elimination of various sulfonamides during anaerobic fermentation: A promising step on the way to sustainable pharmacy? [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(7): 2569-2574. [38] 初春, 王志华, 秦冬梅, 等. 苯醚甲环唑在芹菜及其土壤中的残留测定和消解动态研究 [J]. 中国科学:化学, 2011, 41(1): 129-135. doi: 10.1360/032010-100 CHU C, WANG Z H, QIN D M, et al. Study on determination and dynamics of difenoconazole residues in celery and soil [J]. Scientia Sinica (Chimica), 2011, 41(1): 129-135(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/032010-100
-



 下载:
下载: