-
随着工业与农业的飞速发展,人类的生活水平得到了极大地提高。与此同时,人类生产生活中形成的污废水也对环境造成了相当的威胁。近年来,污废水中的微量有机污染物引起了人们的注意。由于其浓度低、毒性高、尺寸小等特点,这些微量有机污染物难以通过传统的水处理工艺有效去除[1]。吸附法和膜分离法虽然能够去除水中的微污染物,但该两种方法仅将微污染物转移至其他环境中,未能从根本上实现其消除[2]。高级氧化法是一种以自由基为活性物种的水处理方法,已经广泛应用于微污染物的降解去除[3]。其中,由于其产生的硫酸根自由基(
${\rm{SO_{4}^{-}}} \cdot$ )具有更高的氧化还原电位和更长的半衰期,过硫酸盐高级氧化法在对水中微量有机污染物的降解去除中更有优势[4]。众所周知,金属有机框架(MOFs)由于具有高比表面积、多活性位点及可调的组成与结构,已经广泛应用于催化过硫酸盐降解微量有机污染物中[5]。然而,由于其水稳定性较弱,在催化降解的过程中会造成水体的二次污染。最近,通过碳化MOFs衍生的复合纳米材料引起了研究人员的兴趣[6]。该复合材料不仅继承了MOFs的高比表面积和多活性位点等特点,还具有更稳定的物理化学结构与性质[7]。因此,将MOFs衍生复合纳米材料用于催化过硫酸盐降解有机微污染物具有显著的优势。然而,由于MOFs衍生复合纳米材料的粉体特性,将其直接用于水处理存在着易流失和易团聚的问题。利用廉价且环境友好的生物质作为载体对纳米材料进行负载是一种有效的途径[8]。陈潇等制备了生物质负载的纳米零价铁,并研究了其去除土壤中的十溴二苯乙烷的性能。结果表明,生物质的负载促进了纳米零价铁的均匀分布,使得其对十溴二苯乙烷的去除率达到了89.74%[9]。张婷婷利用生物质负载了TiO2-SnO2,并利用其处理焦化废水。结果显示,得益于生物质的微孔结构和TiO2-SnO2的催化活性,焦化废水的处理效果得到了较大的提升[10]。然而,利用生物质负载MOFs作为前驱体热解衍生复合材料催化过硫酸盐降解有机微污染物的相关研究尚未见报道。
本实验以禾本科植物狗尾巴草为生物质载体,利用原位生长的方法将ZIF-67负载于具有三维结构的狗尾巴草表面,随后通过高温热解制备了生物质负载MOFs衍生的复合材料,并研究其催化过硫酸盐降解典型有机微污染物双酚A(BPA)的性能。生物质狗尾草具有三维的空间结构,当其作为催化材料的载体时,有利于催化材料在其表面的均匀分布。同时,其三维的空间结构能够促进反应体系中催化材料与PMS的充分接触,有利于催化反应的高效进行。由于具有分散性良好的MOFs衍生纳米材料以及三维的空间结构,实验制备的复合材料表现出优异的催化性能。此外,实验考察了ZIF-67负载量、复合材料投加量、pH等参数对BPA降解效果的影响,确定了降解的最佳条件,并探究了催化降解的机理。
-
2-甲基咪唑(2-MeIm)、叔丁醇(TBA)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)和BPA采购自上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司,六水合硝酸钴(Co(NO3)2·6H2O)和甲醇(MeOH)采购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司,乙醇和盐酸(HCl)采购自上海凌峰化学试剂有限公司,过硫酸氢钾(PMS)采购自上海易恩化学技术有限公司。除MeOH为色谱纯(HPLC)外,其他试剂均为分析纯(AR)。生物质狗尾草采集自江苏省南通市崇川区南通大学。实验过程中所使用的水均为去离子水。
-
首先,利用去离子水和乙醇分别超声清洗采集的狗尾草3次,并于50℃烘干保存。称取5 g狗尾草(记为GW)于100 mL 2 mol·L−1的NaOH溶液中,在65℃温度下水解30 min。随后,利用去离子水清洗水解后的狗尾草3次,再将其浸泡于50 mL 0.1 mol·L−1的HCl溶液中10 min。最后,利用去离子水将HCl处理后的狗尾草清洗至中性,并于50℃烘干保存,所得水解后的狗尾草记为GWS。
称取一定量2-MeIm溶解于100 mL去离子水中,记为溶液A。将3 g水解狗尾草置于溶液A中,并搅拌10 min使其充分接触。称取一定量的Co(NO3)2·6H2O溶解于100 mL去离子水中,记为溶液B。随后,将溶液B迅速倒入溶液A中并搅拌3 h。所得紫色产物(狗尾草负载ZIF-67)用乙醇清洗3次后于50℃烘干保存。设定Co(NO3)2·6H2O的添加量分别0.14 g、0.42 g和0.7 g,对应2-MeIm的添加量为2.14 g、6.51 g和10.7 g,所得的狗尾草负载的ZIF-67分别记为GWS-Z1、GWS-Z2和GWS-Z3。
以上述制备的GWS、GWS-Z1、GWS-Z2和GWS-Z3为前驱体,以3℃·min−1的升温速度在管式炉中500℃下热解4 h,即可得复合催化材料。GWS、GWS-Z1、GWS-Z2和GWS-Z3热解所得材料分别记为BC、BC-1、BC-2和BC-3。复合催化材料的制备示意图如图1所示。
-
利用场发射扫描电子显微镜(Gemini SEM 300)对生物质负载ZIF-67及其衍生复合材料的表面形貌进行表征。采用傅里叶红外仪(Nicolet iS10)对生物质负载ZIF-67的化学基团进行表征。利用X射线衍射仪(Bruker 8D-Advance)对复合材料的晶体结构进行分析。测试前,将待测样品研磨至粉末状。
-
选取100 mL 20 mg·L−1的BPA溶液为目标降解对象。首先,配置100 mg·L−1的BPA母液1L。实验过程中,将BPA母液稀释5倍至20 mg·L−1使用。降解实验前,将一定量的复合催化材料加入BPA溶液中,在避光环境中暗吸附30 min以达到材料对BPA的吸附平衡。随后,将不同量的PMS添加至反应溶液中进行降解反应。在降解过程中,以一定时间间隔取2 mL反应溶液混合于2 mL的甲醇溶液中。测试时,所有样品均用0.22 mm水相滤头滤除混合液中的悬浮物。BPA的降解率(D)通过公式(1)计算。
其中,Ct为BPA在降解时间为t时的浓度(mg·L−1),C0为BPA的初始浓度(mg·L−1)。BPA的浓度利用高效液相色谱仪(HPLC,Ultimate 3000,Thermo-Fisher Scientific)测定。流动相由甲醇和水(75∶25,V/V)组成,流速为1.0 mL·min−1,双酚A的检测波长设置为276 nm。
-
为了研究水解前后生物质狗尾草的性质变化,利用红外光谱仪对其进行表征。如图2(a)所示,相比于未水解GW的红外图谱,水解后GWS的红外图谱中对应于羟基的特征吸收峰(1310 cm−1和3340 cm−1)有所增强。这是由于水解过程赋予了生物质表面更多的活性羟基基团。羟基基团能够通过共价键锚固Co2+,促进其在生物质表面均匀分布。在原位生长ZIF-67的过程中,均匀分布的Co2+能够诱导能够诱导ZIF-67在生物质表面均匀分散。为了证明ZIF-67衍生物在复合材料中的存在,实验进一步对比了负载前后催化材料的红外图谱(以BC-2为例)。从图2(b)中可以看出,与未负载的BC-0相比,BC-2的红外谱图在671 cm−1处出现了对应于Co—O键的特征峰。这可能是热解还原ZIF-67所得的单质Co部分发生了氧化所致[11]。这表明热解后复合材料活性催化中心ZIF-67衍生物的存在。此外,通过对比BC与BC-2的N2吸附脱附结果可以看出(图2c),在负载ZIF-67后,复合催化材料的比表面积从15 m2·g−1增加到165 m2·g−1。这可能是由于具有高比表面积ZIF-67衍生物的引入,使得所制备复合催化材料的比表面积得到了极大的提升。同时,从图2d中BC与BC-2的孔分布结果可以发现,相比于只有大孔的BC,BC-2中出现了较多的微孔和介孔。这些新孔结构的产生可能是由于负载ZIF-67热解形成的衍生物所致。
为了进一步证明复合材料活性催化中心的负载,利用XRD对其结构进行了表征。从图3可以看出,相比于空白的GWS,负载ZIF-67后的GWS-Z2的XRD图谱中在2θ为7.19°、10.34°和12.82°处出现3处较强的ZIF-67的特征衍射峰,这表明了ZIF-67的成功负载[12]。而经过碳化之后,GWS和ZIF-67都热解为无定形的炭基复合材料。因此,BC和BC-2的XRD图谱都未出现明显的特征峰。此外,相比于GWS热解形成的BC-0,GWS-Z2衍生的BC-2的XRD图谱中在2θ为37°附近出现了对应于Co3O4的特征峰[13]。Co3O4的出现可能是由于ZIF-67热解形成的Co0在空气中氧化而成。
为了评价水解过程对生物质狗尾草负载ZIF-67效果的影响,利用SEM研究了水解前后生物质负载ZIF-67的形貌。从图4a可以看出,空白的GW表面光滑且饱满。而经过水解后的GWS表面变成了粗糙的褶皱结构(图4b)。此外,对比图4(c)和(d)可以发现,GWS对ZIF-67的负载量要远高于GW,表明GWS对ZIF-67具有更强亲和力和更高的负载量。这是由于水解后生物质表面附带了更多的羟基基团,通过羟基的锚固作用,更多的Co2+被均匀地固定于GWS表面。在原位生长ZIF-67的过程中,GWS表面均匀分布的Co2+与溶液中的2-MeIm充分接触,从而使得形成的ZIF-67均匀地覆盖于GWS表面。
为了探究ZIF-67负载量对复合催化材料的影响,利用SEM进一步研究了不同负载量热解衍生复合材料的形貌。从图5(a和e)可以看出,经过碳化过程后,生物质表面发生收缩。由图5(b-d和f-h)所示,随着溶液中配体Co2+和2-MeIm浓度的增加,生物炭表面ZIF-67衍生材料的数量和颗粒尺寸都逐渐增加。其中,BC-1负载的ZIF-67衍生材料的尺寸较小,且负载量较低;BC-2负载的ZIF-67衍生材料的尺寸适中且分布均匀;而BC-3负载的ZIF-67衍生材料的尺寸过大,且发生了团聚现象。一般而言,催化材料的分散性和尺寸其催化性能具有重要影响[14]。良好的分散性和合适尺寸对催化剂的催化性能有促进作用。
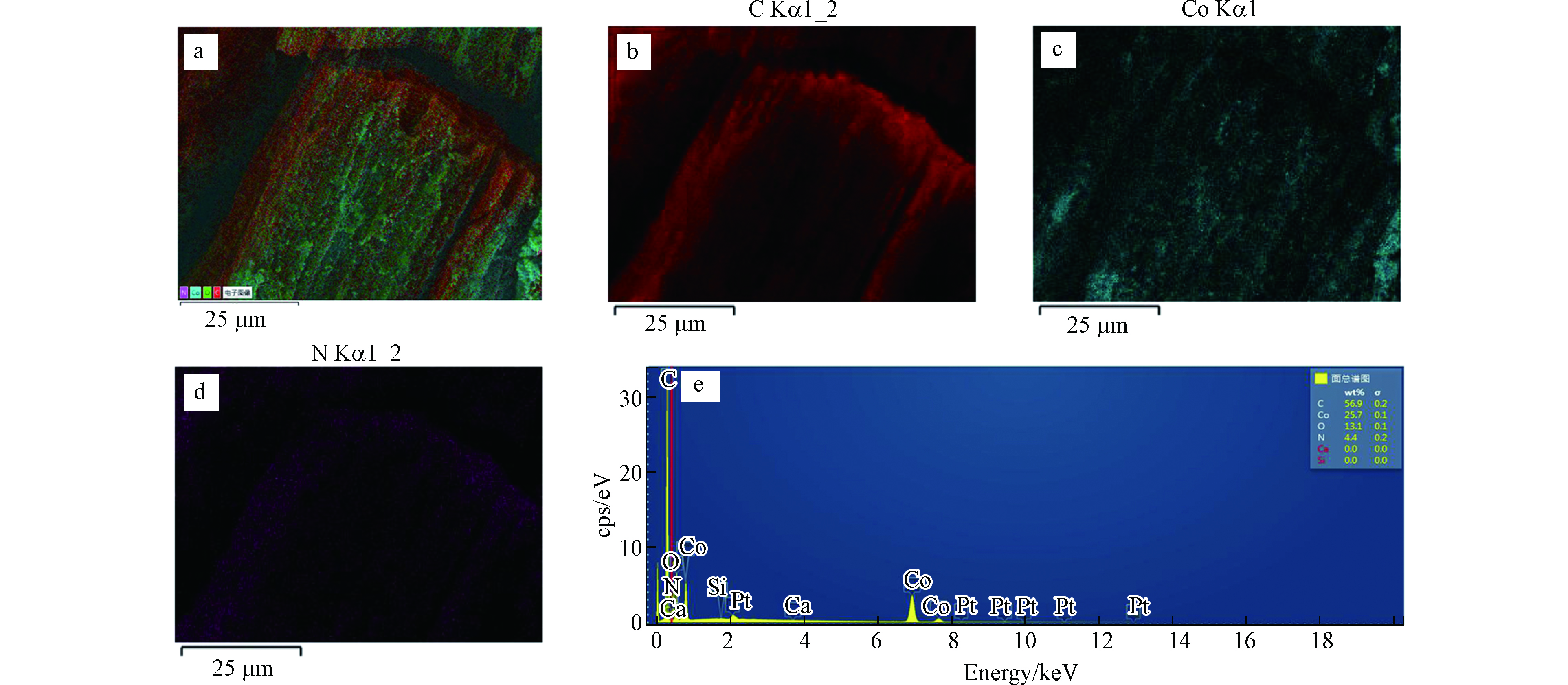
对于制备的复合催化剂而言,其有效活性物种为负载ZIF-67衍生的复合材料。该复合材料中Co是催化PMS降解有机污染物的活性中心。因此,利用mapping探究了Co在复合催化剂中的分布,结果如图6所示。热解生物质载体所衍生材料的主要成分为炭,因此,其对应区域中C元素的响应较强。相比之下,热解ZIF-67衍生的复合材料中含有大量的Co和N,因此,其对应区域中Co和N元素的响应较强。从图6c和d中可以看出,Co和N元素在复合催化材料中的分布较为均一,且与图6b中C元素的位置相匹配,这表明活性组分在复合催化材料中的均匀分布。此外,从图6e中还可以看出,复合催化材料中活性Co元素的含量较高,这有利于催化PMS降解有机污染物性能的提高。
-
ZIF-67衍生物中的Co为复合催化材料的活性中心,因此,实验首先考察不同ZIF-67衍生物负载量对复合材料催化PMS降解BPA性能的影响。如图7a所示,在反应时间为30 min时,相比于空白的PMS和未负载的BC,投加负载的BC-1、BC-2和BC-3时BPA的去除率分别高达84.64%、95.25%和90.22%。这表明负载纳米催化中心后,BPA的去除效率得到极大的提高。同时,从图7a中还可以发现,随着负载量的增加,BC-2活化过硫酸盐降解BPA的效率高于BC和BC-1。这是由于ZIF-67衍生物中的Co是催化反应的活性中心,负载量的提高增加了复合材料中Co的含量,从而促进了降解反应的进行[15]。而当负载量继续增加至BC-3时,BPA的降解效率有所下降。这是由于BC-3中负载的纳米材料尺寸过大且发生了团聚,导致了暴露的活性Co的数量减少,进而造成了催化效率的降低。因此,在后续实验中均选择BC-2为最优对象进行研究。
-
图7b为复合催化材料不同投加量对BPA降解性能的影响。当BC-2投加量从0.05 g·L−1增加到0.1 g·L−1时,BPA的降解率从71.44%提升至95.74%。这是由于复合材料添加量的增加提高了反应体系中活性位点的数量,从而促进了催化反应的进行[16]。然而,当BC-2投加量继续增加至0.125 g·L−1和0.15 g·L−1时,虽然其BPA去除率在降解初期比0.1 g·L−1投加量条件下的高,但最终BPA的降解率相差不大。这是由于过高的添加量使得BC-2发生了团聚,导致了暴露的有效活性位点减少,从而影响了BPA的降解效果[17]。因此,后续实验均在BC-2投加量为0.1 g·L−1的条件下进行。
-
PMS的投加量对降解反应具有重要影响。如图8a所示,在反应30 min时,当PMS的投加量从0.1 g·L−1增加至0.14 g·L−1时,BPA的降解率从94.55%提高至97.92%。这是由于反应体系中PMS的浓度越高,与BC-2接触的几率越高,从而产生的活性自由基就越多,这有利于BPA降解率的提高。而当PMS的投加量继续增加至0.16 g·L−1和0.18 g·L−1时,BPA的降解率分别为97.96%和97.99%。综合降解效率和经济性考虑,最终选择0.14 g·L−1为PMS的最优投加量。因此,后续实验均在PMS投加量为0.14 g·L−1的条件下进行。
-
反应溶液的pH是影响PMS降解过程的重要因素[18]。如图8b所示,当pH值为4.56和6.04时,BPA的降解效果都相对较差,降解率分别为89.2%和94.32%。这是由于在催化PMS产生
${\rm{SO_{4}^{-}}} \cdot$ 的过程中会生成大量的H+,导致降解体系的pH下降。因而,反应体系较低的pH会抑制降解反应的正向进行,导致降解效率的降低。当pH 8.03时,BPA的降解率高达98.65%。然而,当pH继续提高至10.08时,BPA的降解率降低至90.98%。这表明在强碱性条件下,BC-2催化过硫酸盐降解BPA的过程被抑制。这可能是由于强碱性环境中,${\rm{OH^{-}}} \cdot $ 会与${\rm{SO_{4}^{-}}} \cdot $ 发生反应,消耗了部分活性${\rm{SO_{4}^{-}}} \cdot $ ,从而导致降解率有所降低[19]。因而,实验选择8.03作为最优的pH值。 -
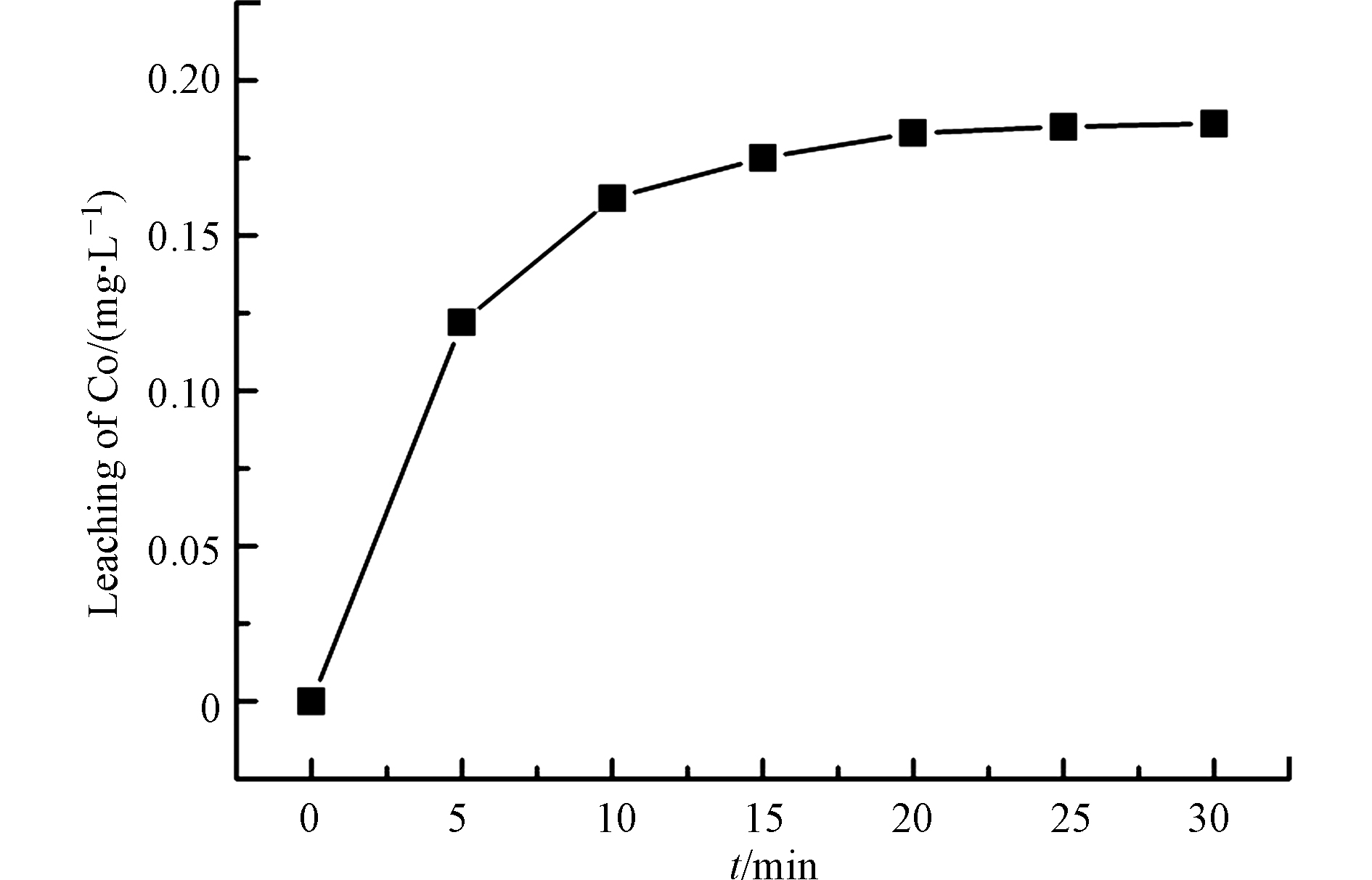
在复合催化材料催化PMS降解BPA的过程中,活性Co会溶出流失至反应溶液中。Co的流失不仅会造成催化剂中活性的降低,还会对水体造成二次污染。因此,在最优降解条件下,考察了BC-2反应溶液中溶出Co离子的浓度变化。如图9所示,在降解的初始阶段Co离子的溶出浓度增加较快。而随着时间的延长,Co离子的溶出浓度趋于平稳。最终,反应溶液中溶出Co离子的浓度为0.186 mg·L−1,达到了水质排放标准GB25467—2010。反应溶液中较低的Co离子浓度可能是由于ZIF-67衍生复合材料稳定的结构与性质以及生物质衍生碳材料对溶出Co离子的吸附所致。
-
为了探究复合催化材料的稳定性,考察了BC-2在上述最优降解实验条件下5次循环利用的性能。从图10中可以看出,随着循环利用次数的增加,BPA的降解率有所降低。这是由于在催化降解BPA的过程中,活性催化组分会逐渐流失,从而造成BPA降解效率的降低。然而,尽管经过了5次的循环,BPA的降解率依然高于85%,这表明制备的复合催化材料具有良好的稳定性。这可能是由于上述Co离子的流失较少,保证了复合催化材料中活性组分的含量,从而有利于其稳定性的提升。
-
实验对比分析了不同催化剂催化PMS降解BPA的性能,结果如表1所示。从表1中可以看出,在相对较低的催化剂和PMS投加量条件下,本实验制备的BC-2对催化PMS降解BPA具有一定的性能优势。这是由于BC-2的三维空间结构以及活性催化中心ZIF-67衍生复合材料在生物质上的均匀分散,促进了催化反应的高效进行。
-
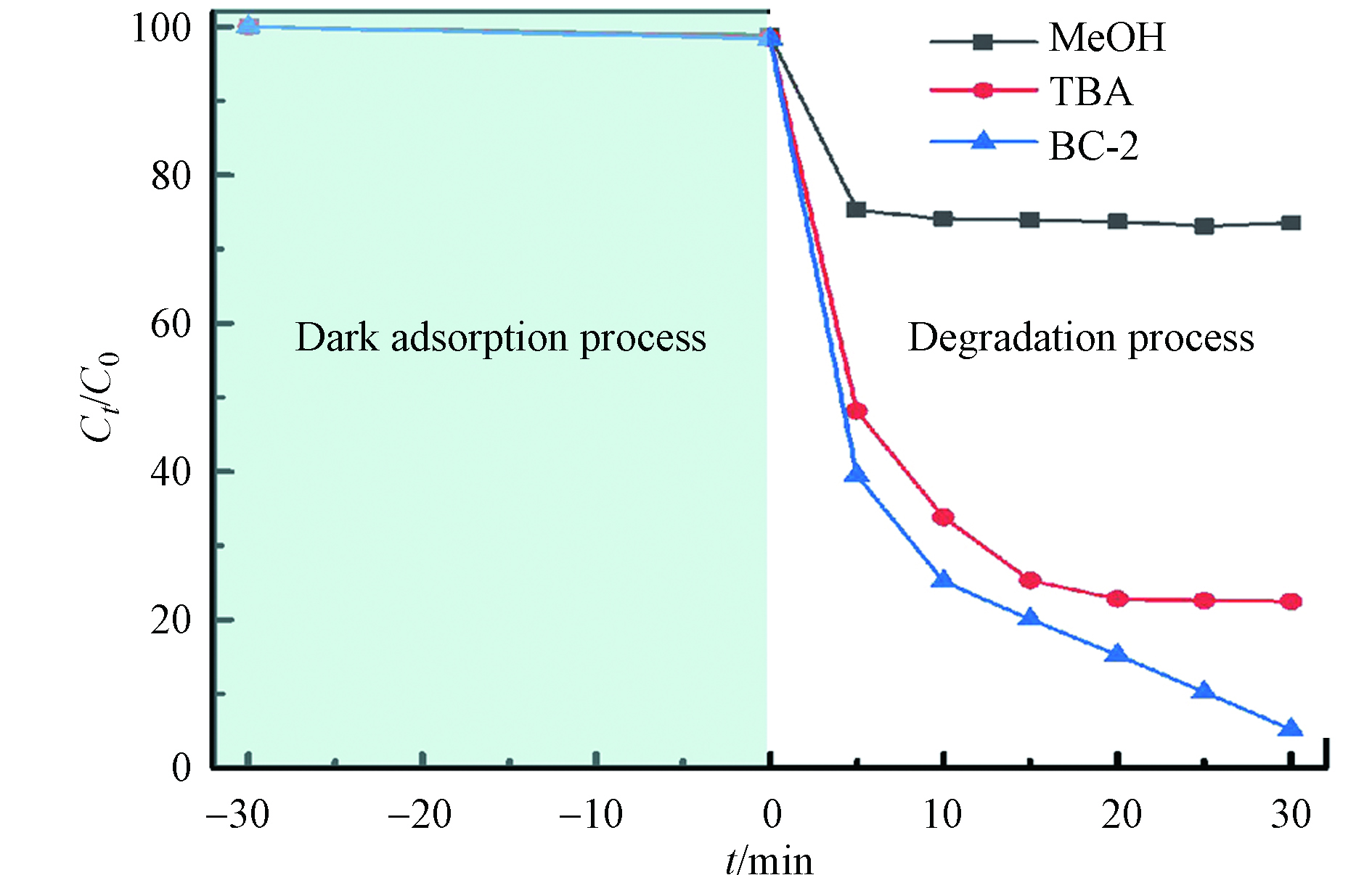
BPA的降解主要依靠催化形成的活性自由基实现[26]。为了探究复合材料催化PMS降解BPA的机理,利用TBA和MeOH进行了自由基淬灭实验[27-28]。一般而言,TBA可以淬灭反应体系中的羟基自由基(
${\rm{OH}} \cdot $ ),MeOH可以淬灭反应体系中的${\rm{OH}} \cdot $ 和SO${\rm{SO_{4}^{-}}} \cdot $ 。如图11所示,当向反应体系中分别加入1000∶1物质的量比的MeOH/PMS和TBA/PMS时,其对应BPA的去除率为26.34%和77.55%。该实验结果显示两种淬灭剂的添加都可以降低BPA的降解率,这表明${\rm{OH}} \cdot $ 和${\rm{SO_{4}^{-}}} \cdot $ 均参与了BPA的降解。而由于TBA的添加对BPA的降解率影响较小,这表明${\rm{OH}} \cdot $ 虽然参与了BPA的降解,但不是主要的活性自由基。相比之下,MeOH的添加对BPA的降解率影响较大,因此,可以得出${\rm{SO_{4}^{-}}} \cdot$ 是主导BPA降解的活性自由基。依据上述实验结果,分析研究了生物质狗尾草负载ZIF-67衍生复合材料催化PMS降解BPA的反应机理。如图12所示,首先,单质
${\rm{CO^0}} $ 与${\rm{HSO}}_{5}^- $ 反应产生${\rm{CO^{2+} }}$ 和${\rm{SO_{4}^{-}\cdot }} $ ;随后,生成的${\rm{CO^{2+} }}$ 与${\rm{HSO}}_{5}^- $ 反应产生${\rm{CO^{3+} }}$ 和${\rm{SO_{5}^{-}\cdot }} $ 。${\rm{CO^{3+} }}$ 进一步与${\rm{HSO}}_{5}^- $ 生成${\rm{CO^{2+} }}$ 和${\rm{SO_{4}^{-}\cdot }} $ 。最终,催化过程中形成的活性自由基将BPA氧化降解为二氧化碳和水(如图12所示)。生物质狗尾草负载ZIF-67衍生复合材料催化PMS降解BPA机理如下公式(2—5):
-
实验利用水解的生物质狗尾草原位负载ZIF-67,并以其为前驱体,通过高温热解制备了复合材料。以有机微污染物BPA为目标降解对象,探究了复合材料催化PMS的性能。主要结论如下:
(1)以水解生物质狗尾草负载ZIF-67为前驱体,通过热解法成功地制备了复合催化材料。表征结果显示ZIF-67的衍生物均匀地分布于生物炭表面。
(2)在最佳实验条件下,即复合催化材料投加量为0.1 g·L−1、PMS投加量为0.14 g·L−1、反应pH为8.03时,BPA的去除率高达98.65%。
(3)自由基淬灭实验表明,
${\rm{OH \cdot }} $ 和${\rm{SO_{4}^{-}\cdot }} $ 都参与了BPA的降解,但${\rm{SO_{4}^{-}\cdot }} $ 在降解过程中起主导作用。
生物质负载ZIF-67衍生复合材料催化过硫酸盐降解双酚A
Biomass immobilized ZIF-67 derived composites for degrading bisphenol A by activating peroxymonosulfate
-
摘要: 过硫酸盐(PMS)高级氧化法在降解新型有机微污染物中展现出独特的性能优势。本实验以生物质狗尾草原位负载ZIF-67为前驱体,高温热解制备了复合材料,并开展了其催化过硫酸盐降解微污染物双酚A(BPA)的性能研究。研究表明,ZIF-67均匀地负载于生物质狗尾草表面。分析优化了复合催化材料的负载量,并考察了降解实验参数如复合催化材料投加量、PMS投加量和反应溶液pH等对BPA去除率的影响。在本实验条件下,当复合催化材料投加量为0.1 g·L−1、PMS投加量为0.14 g·L−1、反应pH 8.03时,对20 g·L−1 BPA的降解效果最优,去除率高达98.65%。本研究为催化PMS降解水中有机微污染物的高性能催化材料提供了新的设计策略。Abstract: Peroxymonosulfate (PMS) based advanced oxidation technology has shown distinctive advantages in degrading emerging organic micropollutants. In this work, a composite material was fabricated by the pyrolysis of a precursor, which prepared by in situ growing ZIF-67 on the surface of biomass setaria. The catalytic performance of the obtained composite material for activating PMS toward degrading micropollutants Bisphenol A (BPA) was investigated. The results indicate that the ZIF-67 nanoparticles were uniformly dispersed on the surface of biomass setaria. The loading amount of composite material was optimized. Besides, the influence of experimental parameters i.e. catalyst and PMS dosage as well as the pH value on BPA degradation were investigated. The optimized degradation performance of 98.65% toward 20 mg·L−1 BPA was achieved, under the condition of catalyst dosage of 0.1 g·L−1, PMS dosage of 0.14 g·L−1 and the pH at 8.03. This work supplies a novel strategy of designing highly performed catalyst for PMS toward degrading organic micropollutants in water.
-
Key words:
- biomass /
- metal organic framework /
- peroxymonosulfate /
- micropollutants /
- advanced oxidation /
- bisphenol A
-

-
表 1 不同催化剂催化PMS降解BPA的性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of different catalyst for activating PMS to degrade BPA
催化剂
CatalystBPA浓度/(mg·L−1)
BPA concentrationPMS浓度/(g·L−1)
PMS concentration催化剂浓度/(g·L−1)
Catalyst concentration去除率
Removal efficiency降解时间/min
Degradation time文献
ReferenceFe3C@CN 20 0.3 0.2 99.1% 30 [20] Fe3O4-BC 20 5 mM 2 ~100% 120 [21] CA 10 0.34 0.4 91% 60 [22] FeCo-PBAs/PAN 20 0.5 0.233 67% 240 [23] FeAl-LDH 20 0.2 0.2 93% 60 [24] FexCo3-xO4 20 0.2 0.1 95% 60 [25] BC-2 20 0.14 0.10 98.65% 30 本研究 -
[1] LUO Y L, GUO W S, NGO H H, et al. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 473/474: 619-641. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.065 [2] LIAO Z P, NGUYEN M N, WAN G J, et al. Low pressure operated ultrafiltration membrane with integration of hollow mesoporous carbon nanospheres for effective removal of micropollutants [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 397: 122779. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122779 [3] LI R B, MANOLI K, KIM J, et al. Peracetic acid–ruthenium(Ⅲ) oxidation process for the degradation of micropollutants in water [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(13): 9150-9160. [4] CHENG X X, LI P J, LIU W C, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by metal oxide nanoparticles for mitigating organic membrane fouling in surface water treatment [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 246: 116935. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116935 [5] CHEN S S, LI M Q, ZHANG M, et al. Metal organic framework derived one-dimensional porous Fe/N-doped carbon nanofibers with enhanced catalytic performance [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 416: 126101. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126101 [6] LIU Y, XU X M, SHAO Z P, et al. Metal-organic frameworks derived porous carbon, metal oxides and metal sulfides-based compounds for supercapacitors application [J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 26: 1-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2019.12.019 [7] LUO H Z, ZENG Z T, ZENG G M, et al. Recent progress on metal-organic frameworks based- and derived-photocatalysts for water splitting [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 383: 123196. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123196 [8] ANAE J, AHMAD N, KUMAR V, et al. Recent advances in biochar engineering for soil contaminated with complex chemical mixtures: Remediation strategies and future perspectives [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 767: 144351. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144351 [9] 陈潇, 卢聪, 凌思源, 等. 生物炭负载零价纳米铁去除土壤中十溴二苯乙烷 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(12): 4524-4530. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0188 CHEN X, LU C, LING S Y, et al. Removal of decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE) by biochar doped with zero-valent-nano iron in a soil system [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(12): 4524-4530(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0188
[10] 张婷婷, 刘永军, 周成涛, 等. 竹制生物炭负载TiO2-SnO2电化学处理焦化废水 [J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(12): 5793-5801. ZHANG T T, LIU Y J, ZHOU C T, et al. TiO2-SnO2 coated bamboo biochar for electrochemical treatment of coking wastewater [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(12): 5793-5801(in Chinese).
[11] WU R B, QIAN X K, RUI X H, et al. Zeolitic imidazolate framework 67-derived high symmetric porous Co3O4 hollow dodecahedra with highly enhanced lithium storage capability [J]. Small, 2014, 10(10): 1932-1938. doi: 10.1002/smll.201303520 [12] LIN K Y A, CHANG H A. Ultra-high adsorption capacity of zeolitic imidazole framework-67 (ZIF-67) for removal of malachite green from water [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 139: 624-631. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.041 [13] SHAO J, WAN Z M, LIU H M, et al. Metal organic frameworks-derived Co3O4 hollow dodecahedrons with controllable interiors as outstanding anodes for Li storage [J]. J Mater Chem A, 2014, 2(31): 12194-12200. doi: 10.1039/C4TA01966K [14] LIN Y, WU S H, YANG C P, et al. Preparation of size-controlled silver phosphate catalysts and their enhanced photocatalysis performance via synergetic effect with MWCNTs and PANI [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2019, 245: 71-86. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.048 [15] LUO R, LIU C, LI J S, et al. Nanostructured CoP: An efficient catalyst for degradation of organic pollutants by activating peroxymonosulfate [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 329: 92-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.01.032 [16] ZHANG M, XIAO C M, YAN X, et al. Efficient removal of organic pollutants by metal-organic framework derived Co/C yolk-shell nanoreactors: Size-exclusion and confinement effect [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(16): 10289-10300. [17] HOU W X, HUANG Y, LIU X. Highly efficient and recyclable ZIF-67 catalyst for the degradation of tetracycline [J]. Catalysis Letters, 2020, 150(10): 3017-3022. doi: 10.1007/s10562-020-03210-2 [18] 张格红, 赵平歌, 廖志鹏, 等. 超声强化铋掺杂氧化铟降解偶氮染料废水 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(3): 526-532. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.03.2015080701 ZHANG G H, ZHAO P G, LIAO Z P, et al. Ultrasonic enhanced degradation of AZO dye wastewater by bismuth doped indium oxide [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(3): 526-532(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.03.2015080701
[19] ZHANG M, XIAO C M, ZHANG C, et al. Large-scale synthesis of Biomass@MOF-derived porous carbon/cobalt nanofiber for environmental remediation by advanced oxidation processes [J]. ACS ES& T Engineering, 2021, 1(2): 249-260. [20] GUO C Y, CHEN C F, LU J Y, et al. Stable and recyclable Fe3C@CN catalyst supported on carbon felt for efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 599: 219-226. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.04.092 [21] CUI X W, ZHANG S S, GENG Y, et al. Synergistic catalysis by Fe3O4-biochar/peroxymonosulfate system for the removal of bisphenol A [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 276: 119351. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119351 [22] ZHU M S, KONG L S, XIE M, et al. Carbon aerogel from forestry biomass as a peroxymonosulfate activator for organic contaminants degradation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 413: 125438. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125438 [23] WANG H Y, WANG C H, QI J W, et al. Spiderweb-like Fe-co Prussian blue analogue nanofibers as efficient catalyst for bisphenol-A degradation by activating peroxymonosulfate [J]. Nanomaterials, 2019, 9(3): 402. doi: 10.3390/nano9030402 [24] YE Q Y, WU J Y, WU P X, et al. Enhancing peroxymonosulfate activation of Fe-Al layered double hydroxide by dissolved organic matter: Performance and mechanism [J]. Water Research, 2020, 185: 116246. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116246 [25] LI X N, WANG Z H, ZHANG B, et al. FexCo3−xO4 nanocages derived from nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for removal of bisphenol A by activation of peroxymonosulfate [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 181: 788-799. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.08.050 [26] LIU J G, JIANG S J, CHEN D D, et al. Activation of persulfate with biochar for degradation of bisphenol A in soil [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 381: 122637. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122637 [27] ZHENG Z X, NG Y H, TANG Y M, et al. Visible-light-driven photoelectrocatalytic activation of chloride by nanoporous MoS2@BiVO4 photoanode for enhanced degradation of bisphenol A [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 263: 128279. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128279 [28] 李亚萍, 孙祥林, 陈晓, 等. 过硫酸盐增强ZnO@N, C-Co3O4光电催化降解四溴双酚A的性能研究 [J]. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 53(3): 43-53. LI Y P, SUN X L, CHEN X, et al. The photoelectrocatalytic degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A with persulfate-enhanced ZnO@N, C-Co3O4 [J]. Journal of South China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 53(3): 43-53(in Chinese).
-




 下载:
下载: