-
双酚A(BPA)是工业生产中广泛使用的原材料之一,主要应用于各种塑料日用品的制造过程中. 近年来,在污水处理厂出水、再生水以及各类自然水体中,均检出了BPA等内分泌干扰物的存在[1],因容易“致畸致癌致突变”,BPA的存在带来了潜在的生态健康风险. 目前,吸附法[2]、膜分离法[3]等方法已被用于BPA废水的处理. 但上述方法通常存在去除速率低、再生污染较大等缺点. 因此研发针对BPA的高效环保的处理手段具有重要意义.
光催化技术的反应条件相对温和,可在常温常压下进行,且对有机物的降解比较完全,该技术已被证明可用于BPA的处理[4]. 在诸多可见光催化材料中,石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4,CN)作为一种二维非金属半导体,因其具有较好的可见光吸收能力、热稳定性、化学稳定性和独特的电子结构,受到越来越多的关注[5]. 为进一步提升CN的可见光催化活性,已发展出的改性手段包括金属负载[6]、掺杂改性[7]、形貌调控[8]和构建异质结[9]等.
目前,研究者们对CN的金属修饰已有诸多研究,其中金属钴(Co)以单原子掺杂、化学键键合、表面颗粒负载等多种方式应用于催化材料的构建中. Zhou等[10]通过实验和模拟研究了Co掺杂浓度对 g-C3N4光学性能的影响, 质量分数0.15 %Co掺杂g-C3N4在450—800 nm波长范围内具有较好的吸收特性,展现出优异的光吸收和电导性能. Bhagat等[11]引入Co和B共掺杂的g-C3N4,因Co—B间的作用力引起了电荷重排,改变了N位的电荷分布,使得该复合催化剂表现出较好的光催化性能. Zheng等[12]设计了一种新型的Co3O4@CoO/g-C3N4三元复合催化剂, g-C3N4超薄纳米片均匀地分散在钴氧化物的花状微米粒子上,促进了光诱导电荷的分离,使该复合催化剂具有良好的氧化还原活性,可作为光催化剂降解四环素.
虽然多种钴物种已被证实可用于CN的修饰,但目前的改性方式多为分步操作,且钴源多为无机钴盐类,如何利用有机钴源,结合有机官能团与CN碳氮前驱体的相互作用,调变CN的聚合过程,一步实现钴修饰CN材料的制备仍有待研究. 研究表明,乙酰丙酮铁在碳化后会在材料表面形成铁氧纳米颗粒[13],而金属氧化物颗粒往往可作为催化反应的活性位点,进而提高催化反应速率. 钴与铁同为第Ⅷ主族的过渡金属元素,常用于构建石墨相氮化碳材料的活性位点.
本研究以尿素和乙酰丙酮钴为原料,通过一步热聚合法成功制备出超分散钴修饰多孔石墨相氮化碳(xCoCN)催化剂,并将其用于模拟太阳光下催化降解BPA,其主要研究内容如下:
(1)制备出含有不同比例钴物种修饰的CN光催化剂(xCoCN),并对催化剂进行了化学结构与形貌、光电性质的表征和分析.
(2)研究xCoCN催化剂光催化降解BPA的性能,探讨光催化降解BPA的性能提升的原因以及钴物种作为助催化剂的作用. 探讨了催化剂用量、BPA的初始浓度和初始pH值对反应的影响,进一步研究了xCoCN光催化剂的稳定性. 揭示了xCoCN光催化降解BPA过程中的活性物种,探讨了可能的降解路径.
-
试剂:乙酰丙酮钴(分析纯,上海笛柏生物科技有限公司),乙醇(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司),双酚A(分析纯,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司),2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶-氮-氧化物(分析纯,Sigma-Aldrich),重铬酸钾(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司),异丙醇(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司),尿素(分析纯,上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司),草酸钠(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司),去离子水为实验室自制.
实验仪器:光催化反应仪(XPA-7型,南京胥江机电厂),台式低速离心机(LDS-10,北京京立离心机有限公司), 马弗炉(YFX150104,上海意丰电炉有限公司),电热恒温鼓风干燥箱(DHG-9240A,上海精宏实验设备有限公司),分析天平(ME104E/02,梅特勒托利多),高效液相色谱(e2685,沃特世科技有限公司).
-
将一定量的尿素加入带盖坩埚,放入马弗炉中,以2 ℃·min−1的速率升温至550 ℃,并在550 ℃下保持4.0 h,自然降温至室温后取出材料,用纯水和无水乙醇离心洗涤所得材料至中性,最后在50℃烘箱中过夜烘干,所得到的淡黄色粉末固体即为g-C3N4,记为CN.
-
称取一定量的乙酰丙酮钴和20.0 g的尿素研磨混合均匀,转移到带盖坩埚中,以2 ℃·min−1升温至550 ℃并保持4.0 h,自然降温至室温后取出材料. 用纯水和无水乙醇离心洗涤至中性,最后在50℃烘箱中过夜烘干. 所制备的粉末材料标记为xCoCN. 其中x表示加入乙酰丙酮钴的质量(x分别为0.5、 1.0 、3.0 、5.0 mg).
-
采用TECNAI G2 20 LaB6型透射电子显微镜(TEM)对样品进行结构观测;利用BRUKER D8 Advance型X射线衍射仪对样品进行晶相结构分析;利用ThermoFisher Nicolet iS5型傅立叶红外光谱仪对样品进行红外光谱分析;利用Thermo Scientific ESCALAB 250Xi型X射线光电子能谱仪对样品的元素组成和化学环境进行分析;利用辰华CHI760E型电化学工作站测试样品的光电化学性能;N2吸附脱附等温线使用日本贝尔公司的生产的BELSORP-MAX多站扩展式全自动比表面与孔隙分析仪测试分析得到;采用UV-3600Plus岛津紫外可见分光光度计测试材料的光学性能;使用Agilent (ICP-OES) 720型电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪测试材料中Co含量.
-
通过在模拟太阳光(500W氙灯)照射条件下降解BPA来分析催化剂的光催化性能. 首先称取20 mg催化剂,加入50 mL浓度为15 mg·L−1的BPA溶液中,超声处理使催化剂均匀分散. 接着将混合液在黑暗环境下搅拌30 min以达到吸附-解吸平衡,之后在光照条件下进行光催化实验. 每隔30 min定时取样,样品用0.45 μm的滤膜过滤,之后利用高效液相色谱测定溶液中BPA的浓度,所用紫外检测器波长为230 nm.
-
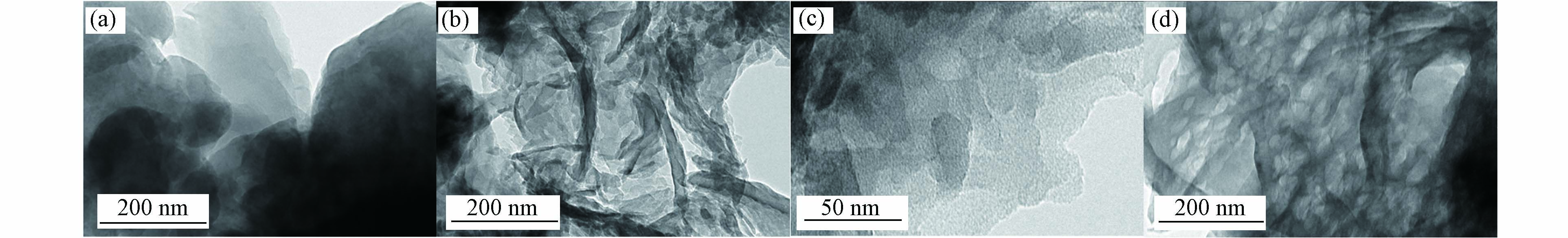
通过TEM研究了制得的CN和5CoCN的形貌. 图1(a)为CN图,表现为典型的层状叠加结构,而在相同的观察尺寸下,图1(b)中的5CoCN则呈现卷曲边界的褶皱状纳米片结构,这是因为纳米片层叠在一起导致的. 对5CoCN进行进一步观察,如图1(c)所示,可以看到其在边缘部分,呈现出二维的层状结构,表现了5CoCN的超薄结构. 同时在图1(d)中,清晰可见许多尺寸相近的孔道结构,这可能是因为乙酰丙酮钴与尿素在热聚合过程中产生了气体,气体逸出后在材料表面形成造孔作用. 而图中并未显示出明显的钴粒子,这可能是由于钴的尺寸过小且均匀分散在材料中. 如表1所示,通过EDS可以得到5CoCN的各元素分布情况,可以确认钴成功掺入CN中.
-
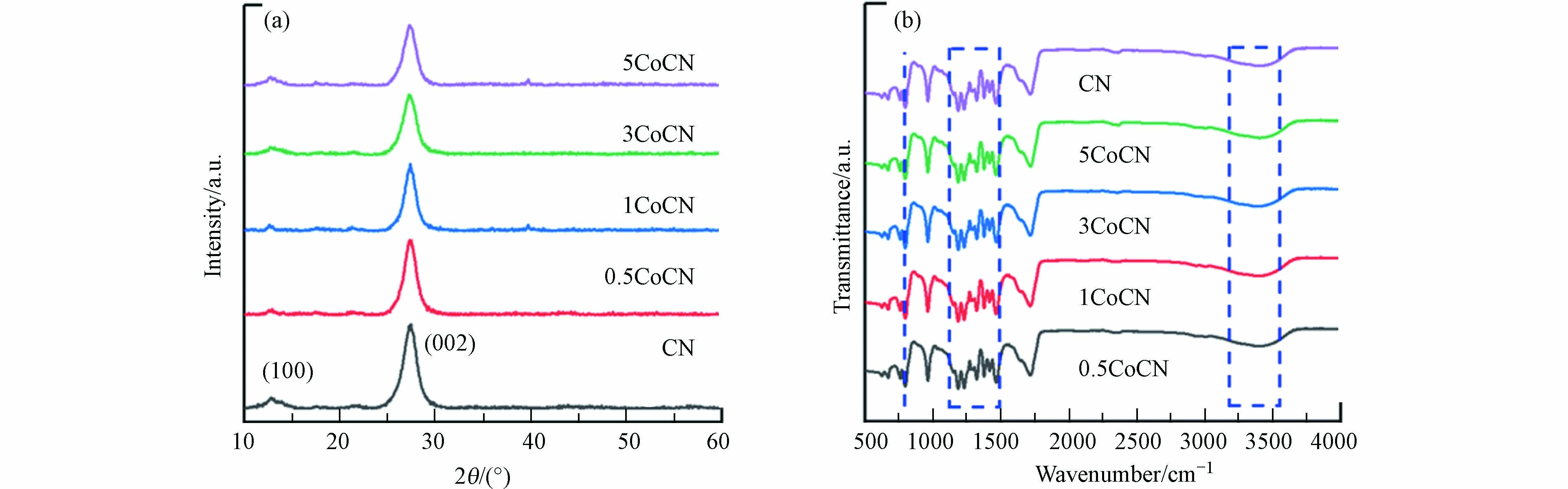
XRD谱图能够反映催化剂的晶面特性,结果如图2(a)所示. xCoCN样品的XRD谱图均显示出与CN相似的特征峰. 具体表现为两个特征峰位于13.2°和27.8°,分别对应CN的(100)和(002)晶面[14];(100)晶面代表CN面内三-s-三嗪单元的有序排列,而(002)晶面则是由CN的共轭芳香族体系的层间垛叠引起[15],这一结果表明了xCoCN复合催化剂总体上保持了CN的结构. 而随着乙酰丙酮钴含量的增加,xCoCN的特征峰逐渐变窄且强度减弱,这表明掺钴量的增加影响了材料的晶面结构,造成衍射峰强度的减弱. 此外,谱图中xCoCN并没有出现明显的钴化合物的特征峰,这可能是材料制备时乙酰丙酮钴的用量过低同时钴粒子的超分散特性所导致的.
-
利用 FT-IR研究了CN和xCoCN的表面化学结构,如图2(b)所示. 与XRD的结果类似,所有xCoCN样品的红外特征峰均与CN保持一致. 815 cm−1处出现的吸收峰代表氮化碳材料三嗪环的特征弯曲振动[16], 1100—1600 cm−1波数范围出现的吸收峰是典型的C—NH—C和N—C=N杂环单元伸缩振动峰[17], 3000—3600 cm−1处出现的宽吸收峰归因于材料表面物理吸收的H2O或边缘芳香环缺陷部位的N—H键的伸缩振动[18]. 这一现象表明钴物种的加入并没有显著改变CN结构的基本框架. 值得注意的是,在红外谱图上并没有观察到属于乙酰丙酮的特征峰,这可能是由于碳化后的乙酰丙酮被CN包裹住,或者钴元素的负载量较低,对红外响应的影响较小.
-
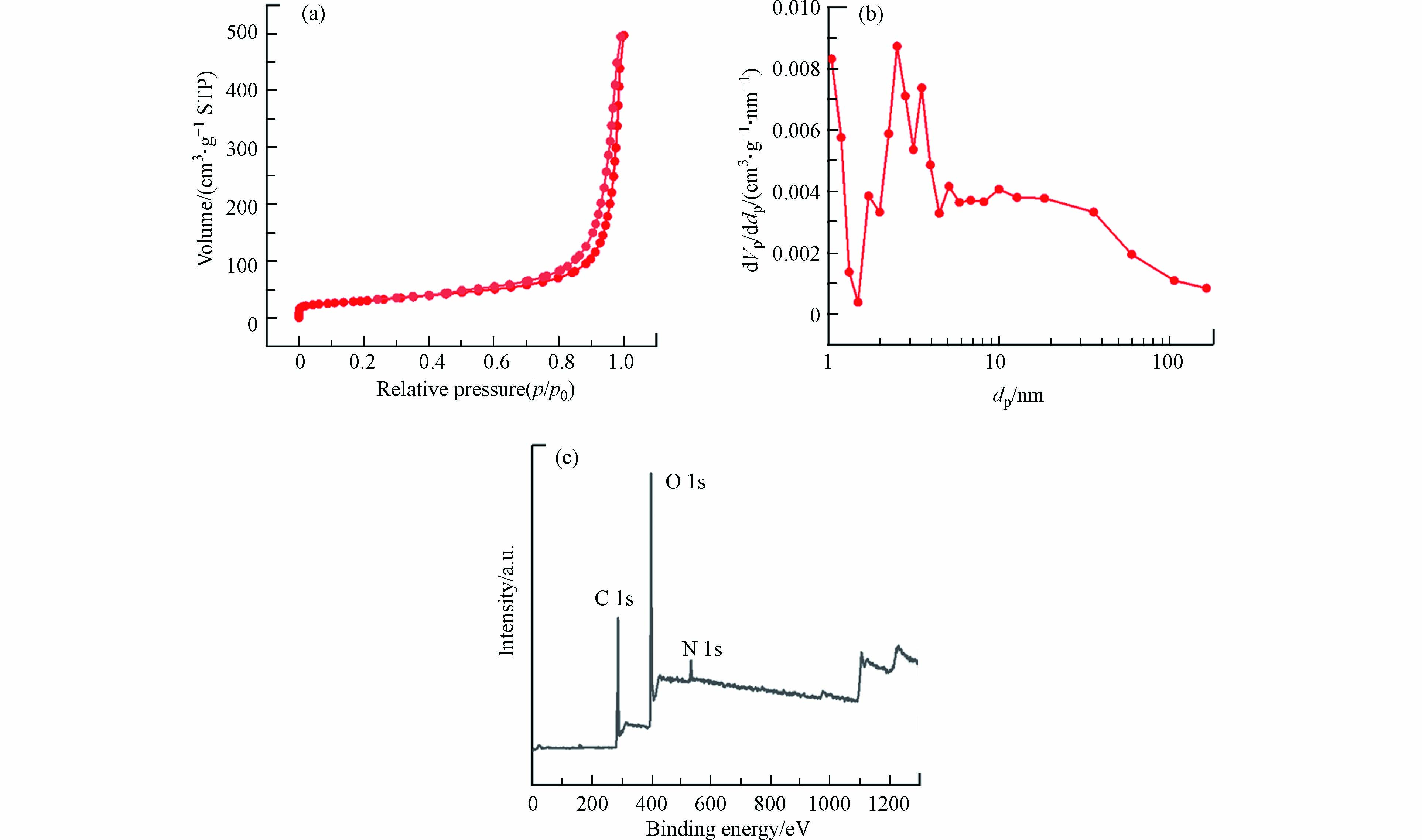
氮气吸附-脱附可用于分析催化剂的比表面积、孔径分布以及孔容. 本实验采用Brunauer-Emmett- Teller(BET)方法,利用N2吸附-脱附曲线研究CN和xCoCN催化剂的比表面积特性等,结果如图3(a)所示. CN与5CoCN样品均展示出典型的Ⅱ型等温线,说明在催化剂中存在中孔结构,图3(b)中的孔径分布图证实了这一结果,孔径大多位于2—40 nm范围内. 同时,5CoCN的比表面积为106.00 g·m−2,与CN(76.19 g·m−2)相比显著增大. 这是由于乙酰丙酮在热聚合过程中产生气体,气体逸出后在催化剂中形成了大量的多孔结构,这一结果与上述TEM结果一致. 而催化剂较大的表面积可提供更多的光催化位点,这有利于材料性能的提升.
-
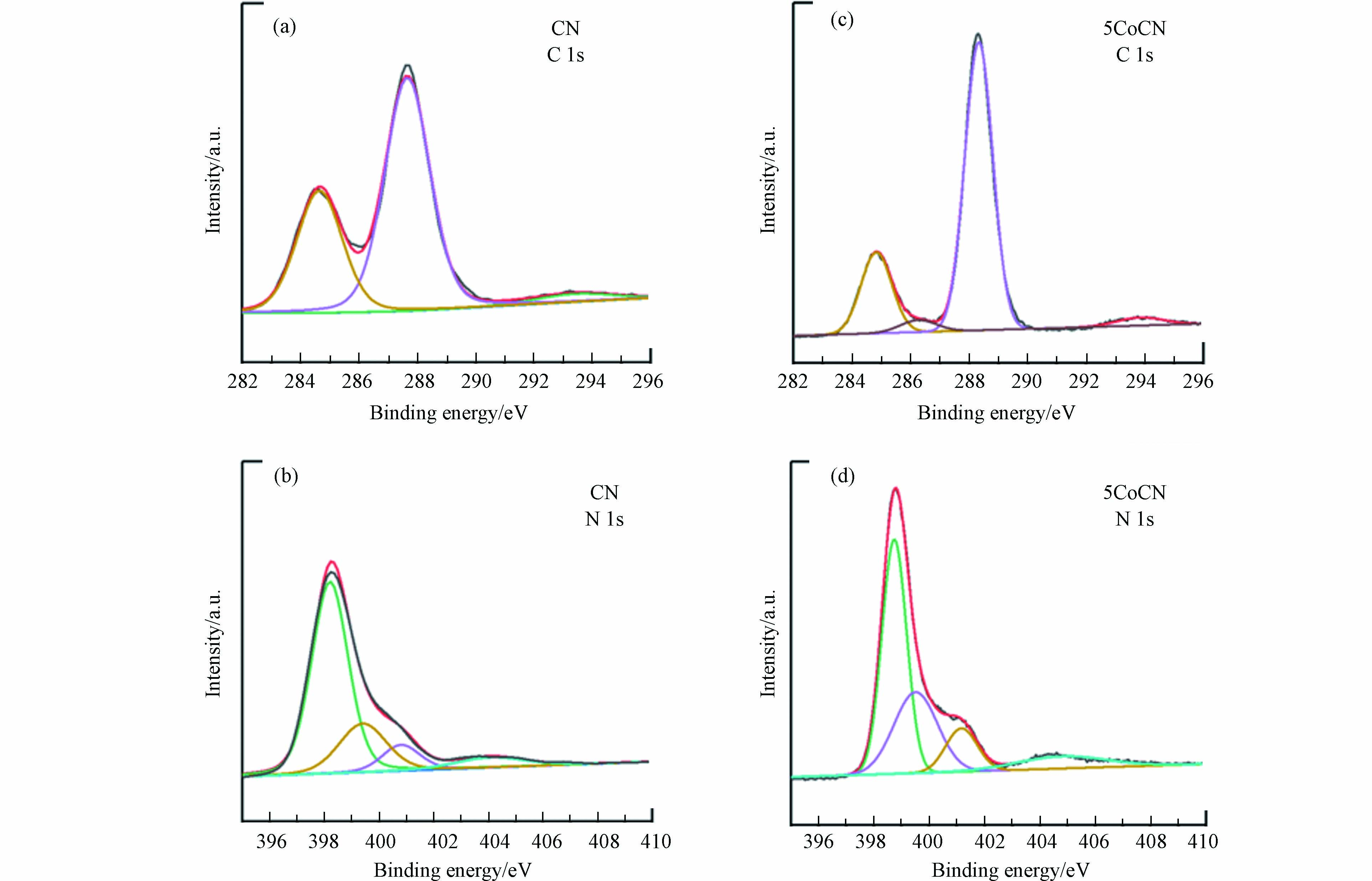
通过XPS对xCoCN的表面化学结构进行研究,图3(b)是xCoCN的XPS总谱图. xCoCN的XPS总谱图中并没有Co的特征峰,这可能是由于钴物种的超分散导致的. 图4是xCoCN的精细谱图,如图4(a)和(c)所示,CN和5CoCN的C 1s XPS精细谱图在284.6、288.0、293.5 eV处的3个峰分别对应石墨碳(C—C)、sp2杂化碳(N—C=N)和π-π*跃迁碳的特征峰[19-20].
利用C 1s的特征峰可以计算出不同形态的C的含量比例,其结果见表2. 结合5CoCN的C 1s谱图可以推测,在286.4 eV出现了C=O的新峰,这可能是因为乙酰丙酮在碳化后会在材料中形成含有C=O的碳层.
xCoCN的N 1s谱图在398.5、399.5、400.9、404.2 eV处出现4个峰,分别对应于xCoCN中的sp2杂化氮(C—N=C)、钴氮键(Co—N)、C—N—H氮和π激发的氮[21-22],这表明xCoCN材料在保留了基本CN结构的同时,钴物种与CN中七嗪结构中的N原子相连[23],这可以成为电子传输的有效途径.
与图4(b)中CN相比, xCoCN中C—N—H氮对应的特征峰向高结合能处偏移了0.4 eV,这表明与CN相比, xCoCN中C—N—H周围的N具有较低的电荷密度[24]. 这可能是因为钴原子的存在降低了C=O表面的电子密度,C=O倾向于从CN的吸取π电子,从而降低-NH2中氮原子周围的电子密度.
-
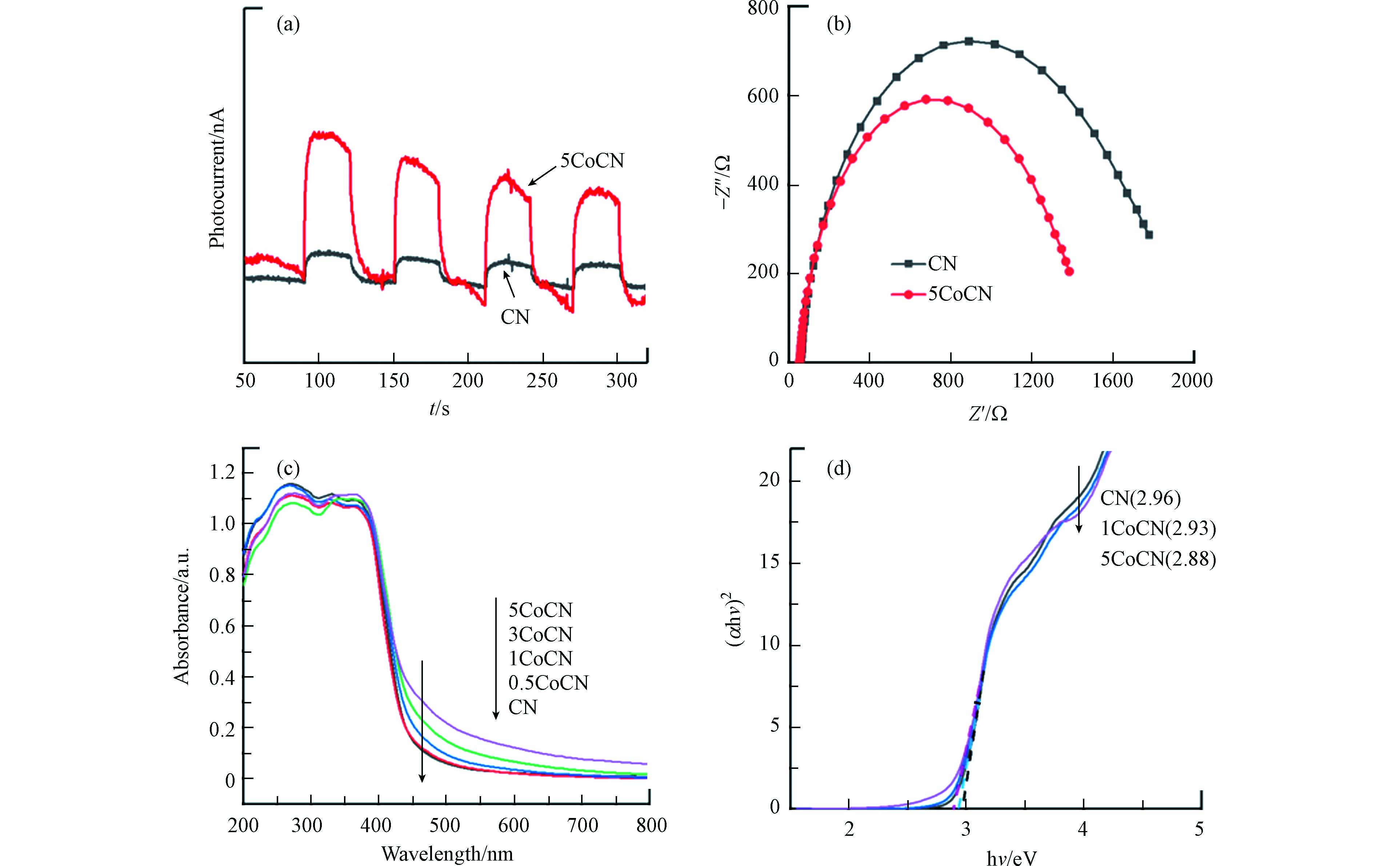
光生电子-空穴对的分离和迁移能力可通过光电流响应和电化学阻抗谱(EIS)来判断. 如图5(a)所示, CN和5CoCN在开灯条件下均显示出较为稳定的光电流响应,但5CoCN的瞬态光电流响应值明显高于CN,这表明前者的光生载流子的分离率高于CN. 由CN和5CoCN的电化学阻抗谱图(图5b)进一步证实了这一现象,EIS谱图中通常用奈奎斯特圆弧的曲率半径表征电荷转移过程,反映电极与电解质之间的电荷转移电阻(RCT). 圆弧半径越小,表明催化剂具有更快的电荷迁移速率和且更低的电子与空穴重组复合率[20]. 与CN相比, 5CoCN的EIS弧半径更小,表明其具有更优异的界面电荷转移性能. 综上,在前驱体中引入乙酰丙酮钴,由此引入的钴物种优化了催化剂的光生电子和空穴的传输路径,提高了载流子的分离效率.
通过UV-vis DRS对CN和xCoCN的光学响应进行了研究. 如图5(c)所示,所有的材料均在440 nm左右出现了本征吸收边,这正好对应CN的激发电子从价态到导带所需要的能量. 在引入钴之后,xCoCN的吸收边发生偏移,且在可见光区域,吸收强度也随着乙酰丙酮钴含量的增加而提高,5CoCN的光吸收阈值也得到了拓宽. 这个现象表明乙酰丙酮钴的加入对CN的本征带隙能产生了影响,这可能是由于尿素与其发生热聚合反应造成的,这一结果也间接证明了超分散钴进入CN的结构中.
通过Kubelka Munk公式对CN和xCoCN的禁带宽度进行了计算,结果如图5(d). 乙酰丙酮钴作为前驱体与尿素混合煅烧得到的5CoCN,其禁带宽度降低至2.88 eV,表明乙酰丙酮钴与尿素发生了共聚反应,钴物种镶嵌进入CN的结构中,有利于材料光催化性能的提升.
-
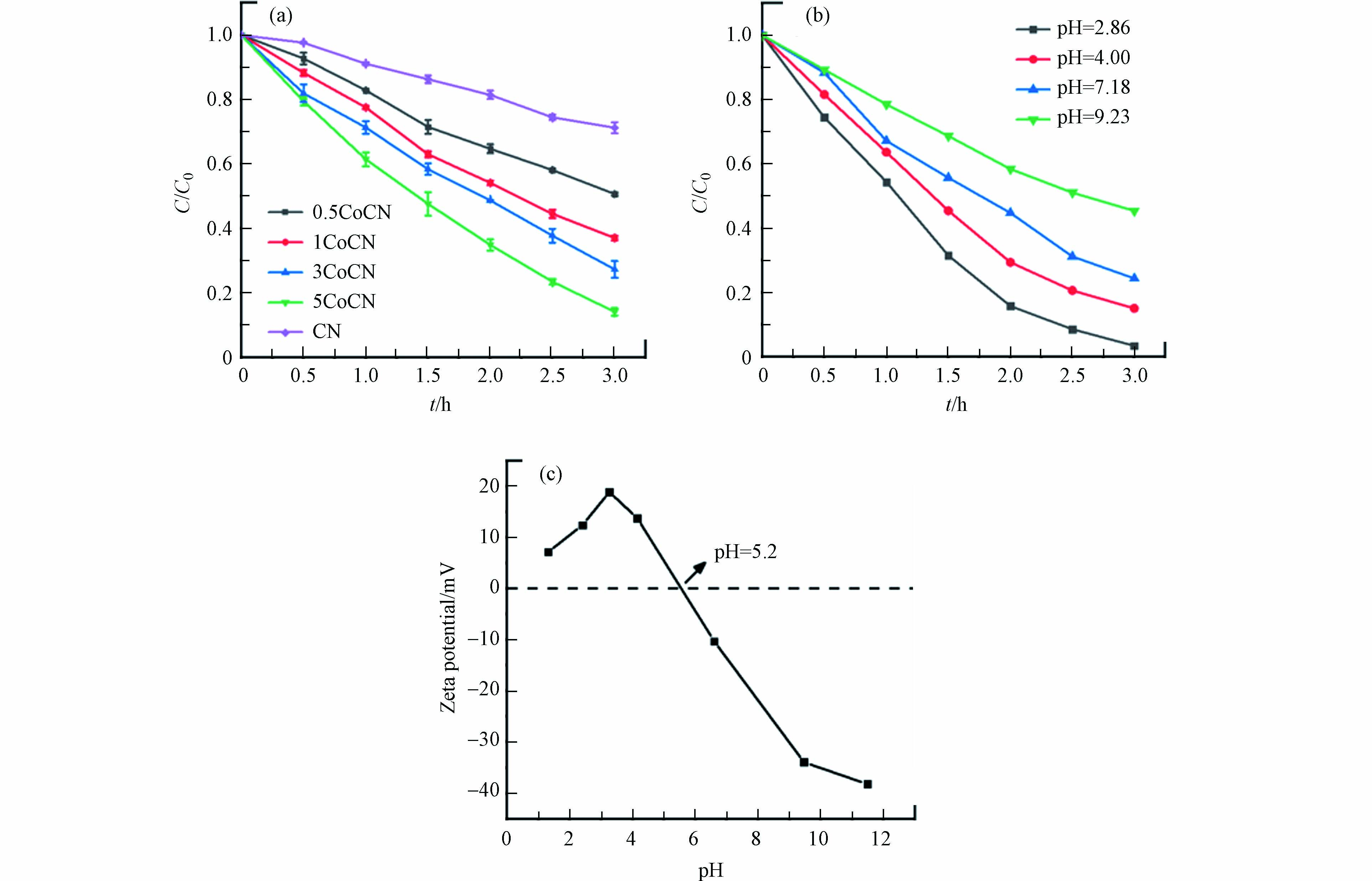
本研究以xCoCN对BPA的光降解效率验证其光催化性能,如图6(a). 结果表明,xCoCN系列材料中,随着Co掺杂量的提高,光催化剂对BPA的降解性能呈现出提高的趋势,5CoCN表现出最好的性能,3 h内0.4 g·L−1的催化剂对15 mg·L−1 的BPA的降解率达到85%以上. 这一现象是因为钴物种的引入,会拓宽催化剂的光吸收范围,促进载流子的分离效率. 而钴负载量过多时不易制备出均匀的材料,在后续研究中,以5CoCN为作为模型催化剂进行研究.
-
(1)pH值
考查了BPA污染物溶液的pH值在2.86—9.23范围内, 0.4 g·L−1的5CoCN催化剂对15 mg·L−1的BPA的降解效率,结果如图6(b)所示. 随着溶液的pH值提高,光催化剂对BPA的降解性能呈现出下降的趋势,这表明较低的pH有利于BPA的降解,而中性和碱性条件下BPA的降解速率受到抑制. 一般而言,光催化氧化过程发生在固液两相界面处[25],光催化剂与BPA的有效接触会影响BPA的降解效率. BPA的解离点为9.6,在碱性条件下BPA以Bis(O2)2-的形态存在,而Zeta电位测试表明(图c),催化剂的等电点在大概在5.2,说明当溶液pH值大于5.2时5CoCN表面带负电[26],静电排斥力使得BPA不易吸附在催化剂表面[27],从而抑制了BPA的降解速率.
(2) 催化剂用量的影响
对5CoCN光催化剂用量在BPA降解性能的影响进行了探究,结果如图7(a)和(b)所示. 如图7(a),随着催化剂用量的增加, 5CoCN对15 mg·L−1的 BPA的降解效率呈现出提升趋势;但超过0.4 g·L−1时提升效果有限,此时溶液中BPA的降解已经达到90%. 另外,从图7(b)中可以看出,随着催化剂用量的增加,反应速率常数也出现明显的提高,但是用量超过0.4 g·L−1时反应速率降低,说明此时催化剂的用量对反应速率的影响也开始减弱. 这是由于在催化剂用量较少时,催化剂用量是催化反应的主要限制因子,反应速率主要受其影响;而当催化剂量较多时,反应速率受到BPA和活性位点结合速率的限制[28-29]. 另一方面,大量催化剂分散在溶液中,增加了溶液的浊度,减弱了内部的光辐照强度,导致载流子与空穴的生成速率降低.
(3) BPA初始浓度的影响
对不同BPA初始浓度对降解效率的影响进行了探究,催化剂用量控制为0.4 g·L−1实验结果如图7(c)和(d). 随着BPA浓度升高,3 h内BPA的降解效率由98.9%下降到55.2%,这主要是反应速率下降导致的. 在图7(d)中可以看到,随着BPA初始浓度的升高,可能因为受到了催化剂活性位点数量的限制,使得k值出现下降,这归因于难以及时降解的中间产物吸附在催化剂表面,从而导致降解速率的降低;此外,初始高浓度BPA占据了催化剂的活性位点,阻碍了降解反应的快速进行[30].
-
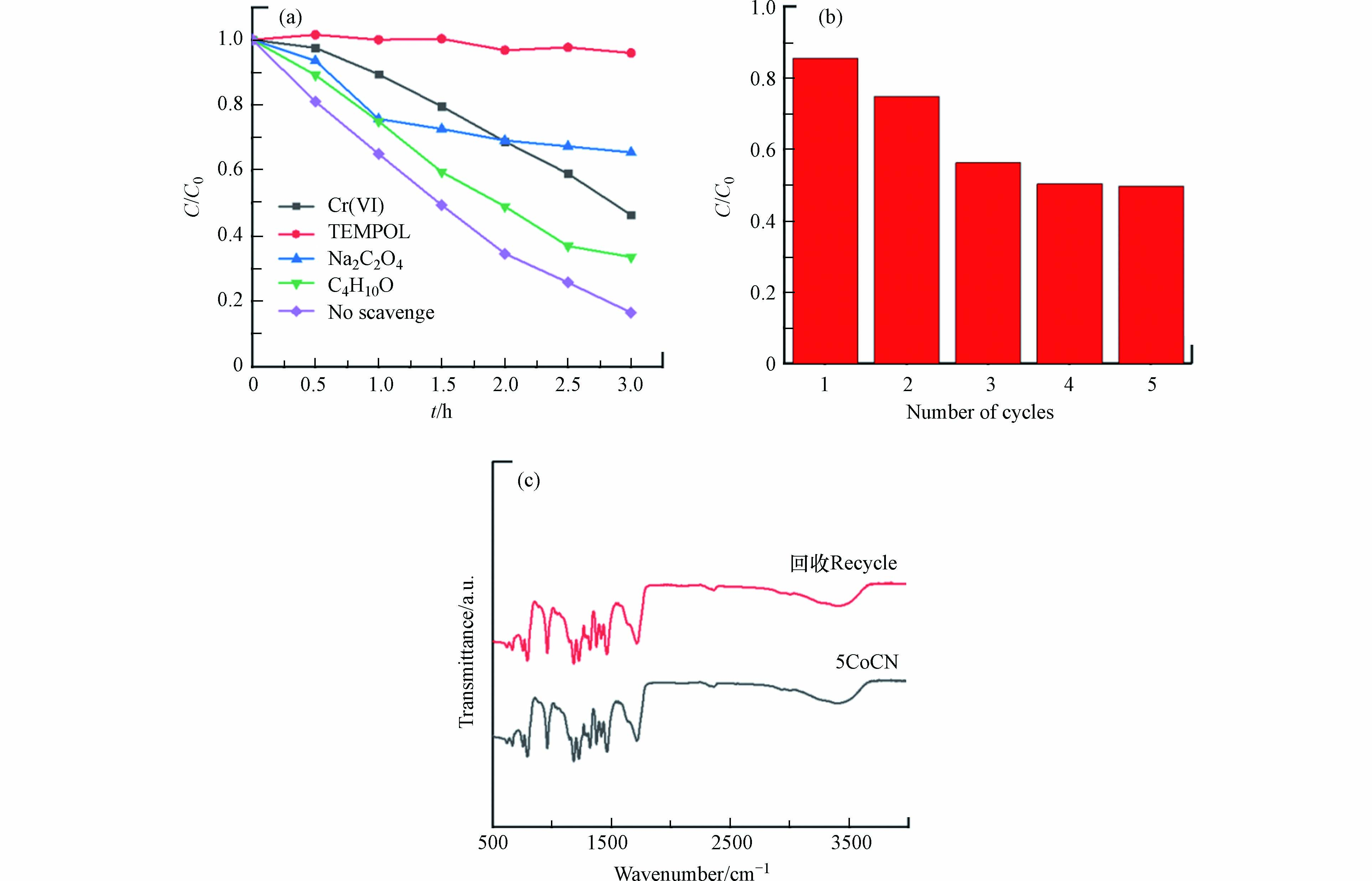
为研究5CoCN 光催化降解BPA的机理,本研究进行了自由基捕获实验来判断光催化降解BPA过程中的活性物种. 图8(a)为不同的自由基捕获剂对5CoCN可见光催化降解BPA的影响,分别用10 mmol·L−1重铬酸钾(K2Cr2O7)、异丙醇(C4H10O)、2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶-氮-氧化物(TEMPOL)和草酸钠(Na2C2O4)作为捕获剂,分别用于捕获电子(e−)、羟基自由基(·OH)、超氧自由基(·O2−)和空穴(h+). 结果表明,加入4种捕获剂均对BPA的降解产生了明显的抑制作用. 其中,加入TEMPOL几乎完全抑制了材料的催化性能,这表明超氧自由基是起主导作用的活性物种. 而在加入捕获剂Cr(VI)、草酸钠和异丙醇后,光催化降解BPA的效率也受到了一定的抑制,这说明e−、·OH和h+也是光催化降解BPA的活性物种. 综上所述,·O2-为该光催化体系的主要活性物种, e−、·OH和h+也参与到反应过程中. 各种活性自由基的重要性由高到低为·O2−>h+>e−>·OH.
根据以上结果,推测5CoCN光催化降解BPA的过程主要包括以下过程:
-
对5CoCN进行5次循环光催化降解15 mg·L−1 BPA来探究材料的稳定性,其实验结果如图8(b)所示. 循环实验前后,5CoCN对15 mg·L−1 BPA的降解率从86.6%降低到50.1%. 为了探究降解性能下降的原因,分析了5次循环实验结束前后5CoCN的FT-IR图谱,如图8(c)所示. 结果表明光催化剂在循环实验前后,其红外光谱没有发生显著变化. 进一步对反应前后Co含量进行测定,催化剂中Co的含量为1.388 mg·g−1,根据反应后溶液中Co的浓度,可得出Co的溶出率为25.2%,表明催化剂性能的下降是由于Co溶出导致催化剂活性位点减少,导致BPA降解效率降低.
-
本文以尿素和乙酰丙酮钴为原料,通过一步热聚合法成功制备出超分散钴物种修饰的xCoCN催化剂,通过一系列表征和光催化降解BPA实验. 得到以下结论:
(1)一步热聚合法成功制备出xCoCN光催化剂, 乙酰丙酮钴的加入将超分散钴物种引入到CN的结构中,且聚合过程产生的气体促使材料表面多孔结构的形成.
(2)xCoCN中钴物种与CN中七嗪结构中的N形成Co—N键,进而优化了光生电子和空穴的传输路径,提高了载流子的分离效率.
(3)在CN中引入钴物种,会增加催化剂暴露的活性位点,同时增强的电子传输作用促进了光催化降解BPA的效率.
超分散钴修饰多孔石墨相氮化碳光催化处理水中双酚A
Photocatalytic degradation of BPA in water by superdispersed cobalt-modified porous graphite phase carbon nitride
-
摘要: 本文通过一步热聚合法,以尿素和乙酰丙酮钴为前驱体,设计和制备了钴物种修饰的多孔石墨相氮化碳光催化剂(xCoCN). 利用透射电子显微镜(TEM)、X射线衍射(XRD)、傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)、BET比表面积测试、电化学阻抗(EIS)、紫外可见漫反射(UV-vis DRS)等手段对所得xCoCN催化剂进行表征分析,并以水中双酚A(BPA)为目标污染物,考察了xCoCN的光催化活性以及pH、催化剂用量、BPA浓度等实验条件对催化性能的影响. 通过活性物种捕获实验探究反应机制,实验结果表明,在模拟太阳光照射下,5CoCN用量为0.4 g·L−1时,3 h内对15 mg·L−1 双酚A的光催化降解率达86.6%,通过活性物种捕获实验确定了空穴和超氧自由基为主要的活性物种. xCoCN光催化活性较CN有明显提升,这归因于钴物种的引入在CN表面提供了更多的活性位点,提高了电子空穴对的分离效率.Abstract: In this paper, a cobalt species-modified porous graphite-phase carbon nitride photocatalyst (xCoCN) was designed and prepared by one-step thermal polymerization, using urea and acetylacetone cobalt as the precursor. The xCoCN catalysts were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectrum (XPS), BET ratio surface area test and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Bisphenol A (BPA) was used as the target pollutant, and the effects of the photocatalytic activity of xCoCN and pH, catalyst dosage and BPA concentration were investigated. The reaction mechanism was also explored through the active species capture experiments. The results showed that when the dosage of 5CoCN was 0.4 g·L−1 under simulated sunlight, the photocatalytic degradation rate of 15 mg·L−1 BPA reached 86.6% within 3 hours. h+ and ·O2- were identified as the major active species by active species capture experiments. The enhanced photocatalytic activity of xCoCN as compared to graphitic carbon nitride (CN) is attributed to the introduction of cobalt species in the CN surface modification that provided more active sites and improved the separation efficiency of electron hole pairs.
-
Key words:
- Graphitic carbon nitride /
- photocatalysis /
- bisphenol A /
- cobalt species modification.
-

-
图 7 (a)不同投加量的5CoCN对BPA光催化降解曲线(b)反应速率常数k变化曲线(c)不同初始浓度的BPA光催化降解浓度变化曲线(d)反应速率常数k变化曲线
Figure 7. (a) Photocatalytic degradation curve of BPA with different dosage of 5CoCN (b)Curve of reaction rate constant k (c) Photocatalytic degradation curve of photocatalytic degradation of BPA with different initial concentrations (d) Curve of reaction rate constant k
表 1 5CoCN各元素组分比例(%)
Table 1. Element proportion in 5CoCN from EDS analysis (%)
元素
Element质量
Mass原子
AtomC 45.78 50.42 N 50.53 46.93 O 3.10 2.52 Co 0.59 0.13 总计 100.00 100.00 表 2 基于C 1s谱图计算的不同形态C原子含量(%)
Table 2. The content of C atoms in different forms calculated based on the C 1s spectrum (%)
C=C C=O N=C—N π激发氮 CN 30.45 0 56.03 13.52 5CoCN 20.83 7.33 59.48 12.45 -
[1] 王培京, 胡明, 孙德智. 再生水补给河道中内分泌干扰物壬基酚变化特征分析 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(7): 1645-1652. WANG P J, HU M, SUN D Z. Analysis on the variation characteristic of endocrine disrupting chemicals nonylphenol in the reclaimed water supply river [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2019, 13(7): 1645-1652(in Chinese).
[2] 毕薇薇, 陈娅, 马晓雁, 等. 磁性有序介孔碳的制备及其对水中双酚A的吸附 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(11): 4762-4769. BI W W, CHEN Y, MA X Y, et al. Synthesis of magnetic ordered mesoporous carbon and its adsorption of bisphenol A in water [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(11): 4762-4769(in Chinese).
[3] 童浩, 王荣昌, 夏四清, 等. 膜分离技术处理水中内分泌干扰物的研究进展 [J]. 中国给水排水, 2009, 25(2): 5-9. TONG H, WANG R C, XIA S Q, et al. Research progress on removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals from waters by membrane separation technologies [J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2009, 25(2): 5-9(in Chinese).
[4] GARG A, SINGHANIA T, SINGH A, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol-A using N, Co codoped TiO2 catalyst under solar light [J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 765. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38358-w [5] JI H D, DU P H, ZHAO D Y, et al. 2D/1D graphitic carbon nitride/titanate nanotubes heterostructure for efficient photocatalysis of sulfamethazine under solar light: Catalytic “hot spots” at the rutile-anatase-titanate interfaces [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 263: 118357. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118357 [6] YIN Z, TIAN Y J, GAO P, et al. Photodegradation mechanism and genetic toxicity of bezafibrate by Pd/g-C3N4 catalysts under simulated solar light irradiation: The role of active species [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 379: 122294. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122294 [7] 彭小明, 罗文栋, 胡玉瑛, 等. 磷掺杂的介孔石墨相氮化碳光催化降解染料 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(8): 3277-3285. PENG X M, LUO W D, HU Y Y, et al. Study on the photocatalytic degradation of dyes by phosphorus doped mesoporous graphite carbon nitride [J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(8): 3277-3285(in Chinese).
[8] PAPAILIAS I, TODOROVA N, GIANNAKOPOULOU T, et al. Novel torus shaped g-C3N4 photocatalysts [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 268: 118733. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118733 [9] CHEN M, GUO C S, HOU S, et al. A novel Z-scheme AgBr/P-g-C3N4 heterojunction photocatalyst: Excellent photocatalytic performance and photocatalytic mechanism for ephedrine degradation [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 266: 118614. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118614 [10] ZHOU D F, QIU C Q. Study on the effect of Co doping concentration on optical properties of g-C3N4 [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2019, 728: 70-73. doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2019.04.060 [11] BHAGAT B R, DASHORA A. Understanding the synergistic effect of Co-loading and B-doping in g-C3N4 for enhanced photocatalytic activity for overall solar water splitting [J]. Carbon, 2021, 178: 666-677. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.03.049 [12] ZHENG J H, ZHANG L. Designing 3D magnetic peony flower-like cobalt oxides/g-C3N4 dual Z-scheme photocatalyst for remarkably enhanced sunlight driven photocatalytic redox activity [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 369: 947-956. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.131 [13] 孙宇翔. 木质素基铁氧物复合碳纳米纤维吸波材料的制备与应用[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2014. SUN Y X. Preparation and application of lignin-based carbon/iron oxide composite nanofibers as microwave absorption material[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2014(in Chinese).
[14] ONG W J, TAN L L, NG Y H, et al. Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)-based photocatalysts for artificial photosynthesis and environmental remediation: Are we a step closer to achieving sustainability? [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(12): 7159-7329. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00075 [15] GU J Y, CHEN H, JIANG F, et al. Visible light photocatalytic mineralization of bisphenol A by carbon and oxygen dual-doped graphitic carbon nitride [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 540: 97-106. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.01.023 [16] DU X Y, BAI X, XU L, et al. Visible-light activation of persulfate by TiO2/g-C3N4 photocatalyst toward efficient degradation of micropollutants [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 384: 123245. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123245 [17] DONG H J, ZHANG X X, LI J M, et al. Construction of morphology-controlled nonmetal 2D/3D homojunction towards enhancing photocatalytic activity and mechanism insight [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 263: 118270. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118270 [18] LV Q, CAO C B, LI C, et al. Formation of crystalline carbon nitride powder by a mild solvothermal method [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2003, 13(6): 1241. doi: 10.1039/b303210h [19] PHANG S J, WONG V L, TAN L L, et al. Recent advances in homojunction-based photocatalysis for sustainable environmental remediation and clean energy generation [J]. Applied Materials Today, 2020, 20: 100741. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100741 [20] YOON H S, OH J, PARK J Y, et al. Phonon-assisted carrier transport through a lattice-mismatched interface [J]. NPG Asia Materials, 2019, 11: 14. doi: 10.1038/s41427-019-0113-2 [21] FU Y S, ZHU J W, HU C, et al. Covalently coupled hybrid of graphitic carbon nitride with reduced graphene oxide as a superior performance lithium-ion battery anode [J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(21): 12555-12564. doi: 10.1039/C4NR03145H [22] ZHANG H J, LI H L, LI X T, et al. Pyrolyzing cobalt diethylenetriamine chelate on carbon (CoDETA/C) as a family of non-precious metal oxygen reduction catalyst [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(1): 267-276. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.09.084 [23] 张蓉, 柳璐, 马飞, 等. 过渡金属/氮掺杂石墨催化剂的制备及电催化氧还原 [J]. 分子催化, 2014, 28(6): 553-563. ZHANG R, LIU L, MA F, et al. Preparation and electrocatalytic activity of transition metal/nitrogen doped carbon catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction [J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis, 2014, 28(6): 553-563(in Chinese).
[24] 王彦娟, 孙佳瑶, 封瑞江, 等. 三元金属硫化物-石墨相氮化碳异质结催化剂的制备及光催化性能 [J]. 物理化学学报, 2016, 32(3): 728-736. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201511303 WANG Y J, SUN J Y, FENG R J, et al. Preparation of ternary metal sulfide/g-C3N4 heterojunction catalysts and their photocatalytic activity under visible light [J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2016, 32(3): 728-736(in Chinese). doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201511303
[25] AKPAN U G, HAMEED B H. Parameters affecting the photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2-based photocatalysts: A review [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 170(2/3): 520-529. [26] JIANG J J, WANG X Y, ZHANG C J, et al. Porous 0D/3D NiCo2O4/g-C3N4 accelerate emerging pollutant degradation in PMS/vis system: Degradation mechanism, pathway and toxicity assessment [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 397: 125356. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125356 [27] SAHU R S, SHIH Y H, CHEN W L. New insights of metal free 2D graphitic carbon nitride for photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 402: 123509. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123509 [28] XU P, WANG P, WANG Q, et al. Facile synthesis of Ag2O/ZnO/rGO heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity under simulated solar light: Kinetics and mechanism [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 124011. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124011 [29] ZHAO X, DU P H, CAI Z Q, et al. Photocatalysis of bisphenol A by an easy-settling titania/titanate composite: Effects of water chemistry factors, degradation pathway and theoretical calculation [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 232: 580-590. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.094 [30] TANG Y, YIN X H, MU M M, et al. Anatase TiO2@MIL-101(Cr) nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2020, 596: 124745. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124745 -



 下载:
下载: