-
由于人类活动的影响,大量工业废水、生活污水以及农田径流中的氮、磷营养物质排入湖泊、水库、河口和海湾等缓流水体,引起了不同程度的水体富营养化,进而导致了蓝藻水华的暴发[1-3]。漂浮在水面的大量蓝藻会遮蔽阳光,使水体动植物因光合作用受阻碍而死亡,导致水体透明度降低,溶解氧减少,产生恶臭气味,感官性状急速下降。而死去的动植物腐败后释放出的大量氮、磷营养物质会进一步被蓝藻利用,使其大量繁殖,造成恶性循环[4-5]。此外,蓝藻的生长代谢过程中所释放的多种蓝藻毒素在极低剂量下就会对人体的肝脏、肾脏等多处器官的健康产生不利影响,情况严重的会引发癌症,导致死亡[6-7]。因此,水体中尤其是饮用水水源地中的有害蓝藻及其释放的蓝藻毒素会对环境和人类健康造成严重威胁,是水处理工艺中需要解决的关键问题之一。
光催化氧化技术是一种利用光辐照激发半导体材料,使其催化产生具有极强氧化能力的活性氧自由基,从而有效降解微生物与有机物等污染物的高级氧化技术[8]。其中,UV/TiO2高级氧化技术因其自然环境无毒、化学性能稳定、使用成本低廉和光催化活性高的优点,得到了广泛的研究与应用。UV/TiO2高级氧化技术在蓝藻治理方面的应用同样具有广阔的前景[9-10],例如PINHO et al[11]的研究表明在紫外光照下,50 mg/L TiO2能在15~20 min内快速灭活水体中的铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa)并有效降解其释放的微囊藻毒素(Microcystins,MCs),证明了UV/TiO2在蓝藻治理中应用的可行性。然而,目前有关UV/TiO2降解蓝藻的研究大多以铜绿微囊藻为研究对象。
近年来,另一种常见的产毒蓝藻——颤藻(Oscillatoria sp.)在水源地的频繁暴发使其受到广泛关注。与在水体中均匀分散的单细胞铜绿微囊藻不同,颤藻为丝状蓝藻,且在水体中易发生团聚现象,进而形成颤藻藻垫,对颤藻细胞具有更强的保护作用[12-13]。此外,颤藻分泌的蓝藻毒素更为复杂,不仅分泌微囊藻毒素,还会产生柱孢藻毒素(Cylindrospermopsin,CYN)以及异嗅物质[14]。由于与铜绿微囊藻的生理性状以及行为特征明显不同,颤藻在UV/TiO2降解过程中的变化规律也可能有很大差别。然而,作为一种急需针对治理的水华蓝藻,有关光催化氧化技术尤其是UV/TiO2对颤藻及其分泌毒素降解效果与机理的研究尚未有报道。
因此,本研究主要针对UV/TiO2降解过程中颤藻细胞的裂解机制、微囊藻毒素与柱孢藻毒素的降解效率以及胞外有机物的变化规律进行研究,并与同等条件下铜绿微囊藻的降解过程进行比较。该研究可以为治理水体中不同生理特征的有害蓝藻提供经验技术,也可以为光催化氧化技术处理团聚型蓝藻提供理论参考。
-
受试蓝藻藻种分别为颤藻(Oscillatoria sp.)和铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa),由中国科学院典型培养物保藏委员会淡水藻种库(FACHB)提供,采用BG11培养基,培养温度为20 ℃ ,可见光照强度为2 000 lux,培养至对数生长期时进行实验。
-
实验所用原水取自南四湖,经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后用于稀释藻液。
-
将分析纯TiCl4溶液20 mL,在搅拌时加入200 mL的去离子水中,使其形成乳浊液,然后再取40 mL浓H2SO4一边搅拌一边慢慢地加到上述体系中,然后放在内层衬有聚四氟乙烯的不锈钢高压釜中加热,反应温度为200 ℃,加热10 h,取出反应物先后用去离子水和丙酮洗涤3次,然后在100 ℃烘l h,即得锐钛矿相结构的TiO2粉末[15]。制备过程中所使用的化学试剂均购置于国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
-
实验所配置的模拟水源中蓝藻浓度为106 cells/mL。将铜绿微囊藻培养液与原水直接混合,通过光学显微镜计数调整比例,即可得到浓度为106 cells/mL含铜绿微囊藻水源(叶绿素a: 3 mg/L, COD: 14.2 mg/L, pH 8.6)。而对于颤藻,如果采用上述直接混合法配置106 cells/mL的含颤藻水源,则会使水体中的颤藻因浓度过高而出现团聚现象,形成藻垫,从而无法在显微镜下计数,也无法调整到所需要的藻浓度。因此,在本实验中,我们先将颤藻培养液与去离子水混合,配置10 L, 104 cells/mL的颤藻溶液(此时颤藻在水体中呈丝状均匀分散),然后用0.45 μm 滤膜将其过滤,取滤膜上的颤藻加入到100 mL原水中,则得到藻浓度为106 cells/mL的含颤藻水源(叶绿素a: 0.52 mg/L, COD: 12.5 mg/L, pH 8.3)。取若干组20 mL含蓝藻水源,分别加入0、50和100 mg/L TiO2,放置于紫外光下匀速搅拌,分别在反应0、5、10、15、20、25和30 min以及1、2、3、4、5和6 h后进行检测。为保证数据的准确性,每个时间点取不同浓度TiO2的蓝藻水源组进行检测,每个20 mL水源组仅进行一次检测,每个浓度每个时间点设置3组平行。对照组的含蓝藻水源放置在培养箱中培养(20 ℃,2 000 lux)。
-
(1) 叶绿素a
取2 mL的样品置于高速离心机(Eppendorf 5810R),转速10 000 r/min离心10 min后弃上清并加入2 mL无水甲醇溶液。混合均匀后放置在黑暗条件下45 ℃恒温孵化24 h后,用荧光分光光度计(日本日立公司,F-7100)测定液体在652.4和665.2 nm波长下的吸光度。叶绿素a浓度的计算公式为[16]:叶绿素a(μg/mL)=16.72 × OD665.29.16 × OD652.4 。
(2) 微囊藻毒素与柱孢藻毒素
MCs与CYN采用酶联免疫法测定,样品经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后,取滤液按照藻毒素试剂盒操作步骤进行测定,所用试剂盒分别均来自美国Beacon公司。
(3) 有机物测定
利用荧光分光光度计(F-7000,日本日立公司)分析样品中有机物种类及含量的变化。取0.45 μm滤膜过滤后的样品滤液进行分析。激发波长以5 nm为间隔,200~450 nm扫描,在250~550 nm间以1 nm为间隔测量发射光谱,扫描速度为12 000 nm/min,电压为700 V。
-
为消除实验环境等因素对实验结果的影响,所有实验均设置3组平行实验,数据表示为各自的平均值±标准偏差(SD)。处理后的数据采用origin2021进行作图。
-
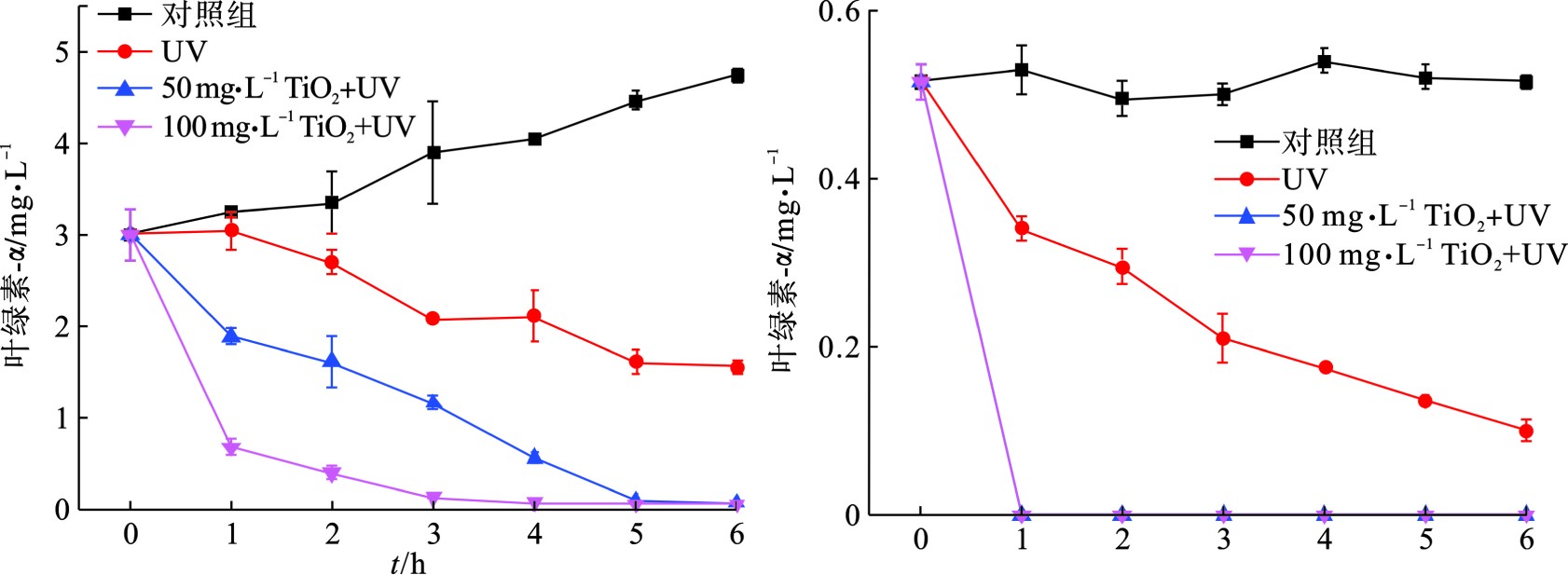
为了更直观地研究UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术对颤藻的作用效果,我们比较了相同紫外光催化条件下,不同剂量TiO2对颤藻细胞与铜绿微囊藻细胞的降解效率,通过测定降解过程中叶绿素a浓度的大小可以近似表征体系内蓝藻细胞数量的变化规律,见图1。
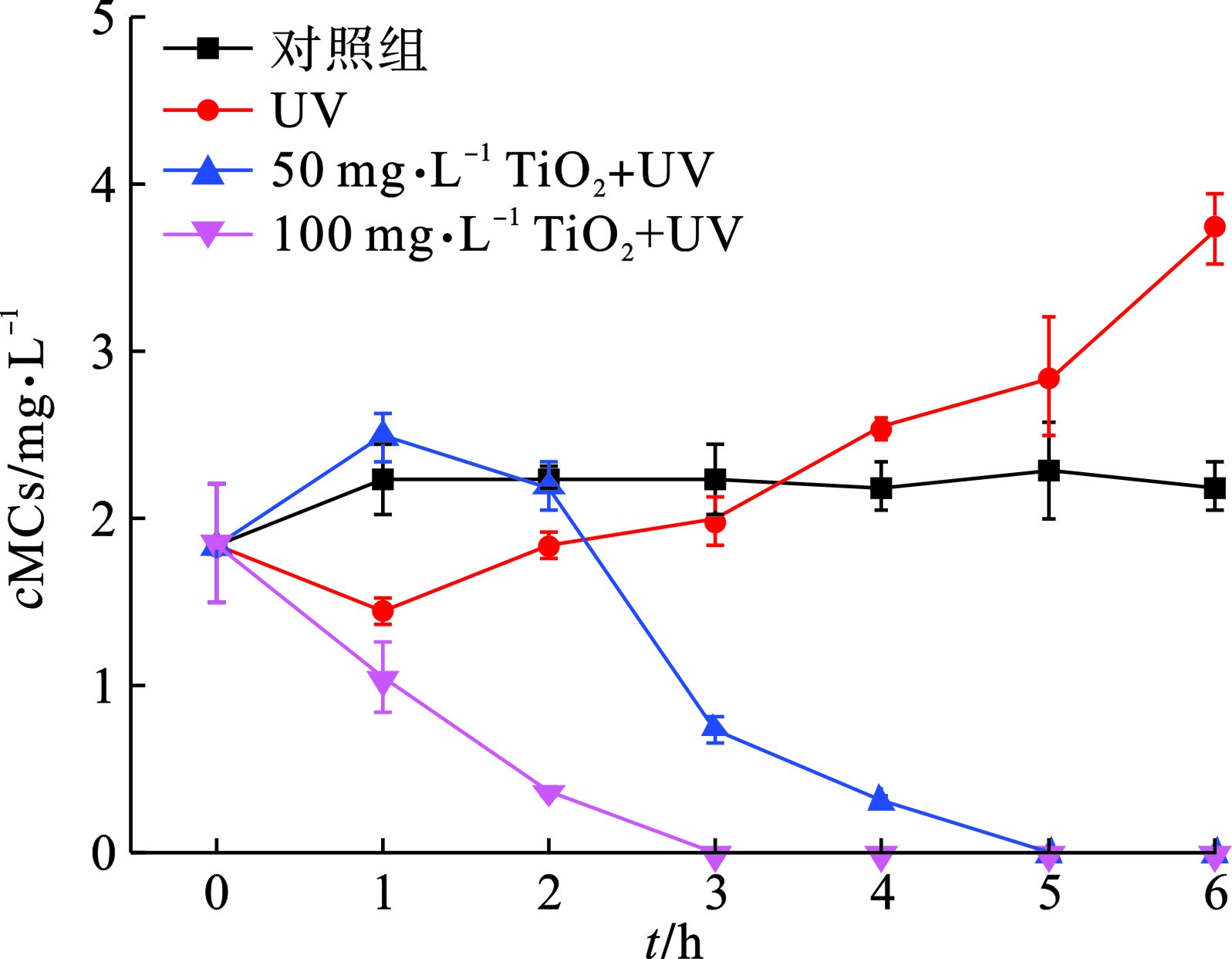
图1(b)可知,在紫外光照射下,50 mg/L TiO2可以在25 min之内将体系中106 cells/mL的铜绿微囊藻完全降解,而当TiO2剂量提到0 mg/L,降解时间可缩至5 min,结果与PINHO et al[11]的研究相符。此外,为了排除紫外光对藻细胞的单独作用效果,我们在不投加TiO2的情况下用相同条件的紫外光照射蓝藻细胞,结果表明,紫外光对铜绿微囊藻具有一定的灭活作用,在15和25 min时,降解贡献率分别为15.5%和24.2%。相比于铜绿微囊藻,UV/ TiO2对颤藻细胞的降解效率明显降低,见图1(a)。在30 min紫外光照射下,100 mg/L TiO2仍无法将体系内的颤藻细胞的完全降解,降解效率仅为70%,而当TiO2为50 mg/L时,仅有约33%的颤藻细胞得以降解。此外,UV实验组与对照组中叶绿素a浓度在反应过程中均没有明显变化,说明在反应30 min内紫外光对颤藻细胞基本没有破坏效果。为了进一步研究UV/ TiO2对颤藻的降解效能,我们将反应时间从30 min延长到6 h,见图2。
图2可知,在紫外光照3 h后,100 mg/L TiO2可以降解体系内90%以上的颤藻细胞,而对于50 mg/L的TiO2,这一过程需要5 h。值得注意的是,对照组中的颤藻细胞在培养6 h后出现了明显的增殖现象,而铜绿微囊藻的数量没有明显变化。这与文献[17]的研究结果相符,即颤藻具有极强增殖能力,其数量可以在短时间内大量增长。由此可推断,相比于铜绿微囊藻,颤藻强大的繁殖能力也可能是其能够抵御活性氧自由基(ROS)等外界伤害的原因之一。此外,随着反应时间延长,紫外光对于颤藻的损伤作用逐渐显现,在UV实验组中,紫外照射6 h后,体系中约50%的颤藻细胞破裂。而对于铜绿微囊藻,仅施加6 h的紫外光照射下,细胞降解率可达约80%。
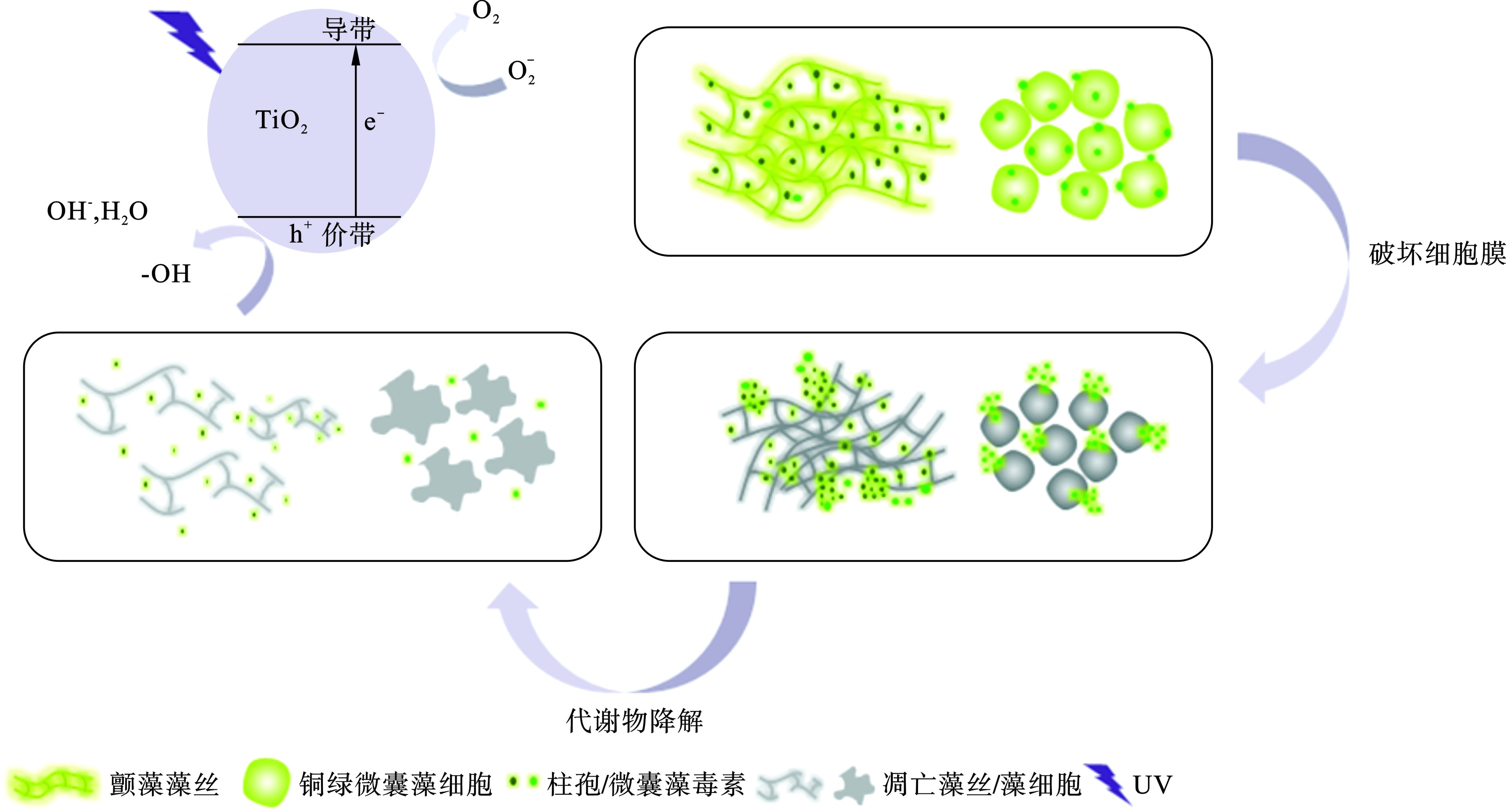
由此可见,UV/ TiO2光催化氧化技术虽然能有效降解颤藻细胞,但降解效率与单细胞蓝藻铜绿微囊藻相比明显不足,主要原因是:(1)颤藻容易在水体中形成藻垫[18],这种团聚体结构能有效包裹颤藻藻丝,大大减少了颤藻与TiO2催化形成的ROS的接触面积,从而抑制了ROS对颤藻的氧化降解作用;(2)颤藻藻垫会削弱紫外光的透射效果,这一方面使水体中的TiO2颗粒无法接受足够的紫外光照射从而抑制了ROS的生成,另一方面也阻碍了紫外光对颤藻的直接伤害作用,这也可以解释紫外光对铜绿微囊藻细胞有更强损伤作用的原因:单细胞的铜绿微囊藻在水体中相对分散不聚集从而与紫外光有更大的接触面积,见图3。
-
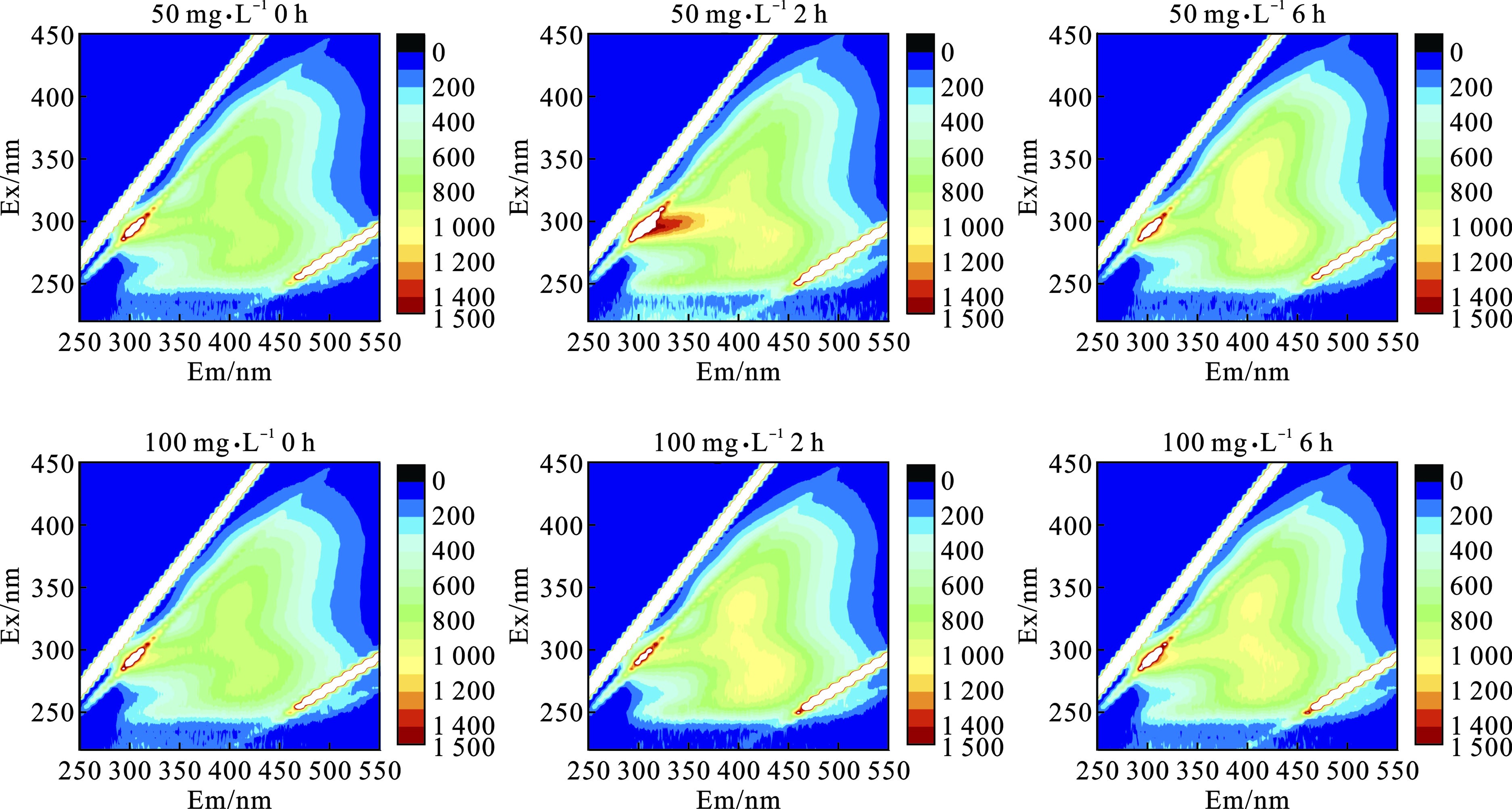
UV/ TiO2光催化氧化技术对蓝藻的有效处理不仅体现在对蓝藻细胞的破坏作用,更体现在对蓝藻代谢物的高效降解,而胞外有机物种类和含量的变化可以反映降解过程中蓝藻代谢物的去除情况。EEM荧光光谱图可以直观反映有机物种类和含量的变化[19]。其中Ex/En: 280/335 nm为蛋白质类物质的特征峰,Ex/Em: 355/445 nm与Ex/Em: 275/450 nm均属于腐殖酸类物质的特征峰[20],见图4。
图4可知,在 UV/TiO2降解颤藻之前,颤藻悬浮液中EOM主要为少量的蛋白质类物质。这可能与培养过程中颤藻细胞增值代谢向水体中释放了部分蛋白质类物质有关[20]。TiO2投加量为50 mg/L处理一段时间后,由于UV/TiO2光催化氧化的作用,颤藻细胞破裂,胞外蛋白质类物质显著增多。当处理6 h后,蛋白质类物质出现减少的情况,腐殖酸类物质明显增加。这可能是氧化过程中死细胞和蛋白质类物质的分解造成的。TiO2投加量为100 mg/L处理2 h后,腐殖酸类物质增多,未观察到蛋白质类物质的出现。这可能是由于催化剂的剂量增大导致氧化性能进一步加强,使得颤藻在2 h内完成了细胞破裂和蛋白质类物质向腐殖酸类物质的转化。最后,在2种剂量处理下的颤藻悬浮液中EOM腐殖酸类物质逐渐降解,最终与蛋白质物质等其他产物一起降低到低浓度水平。
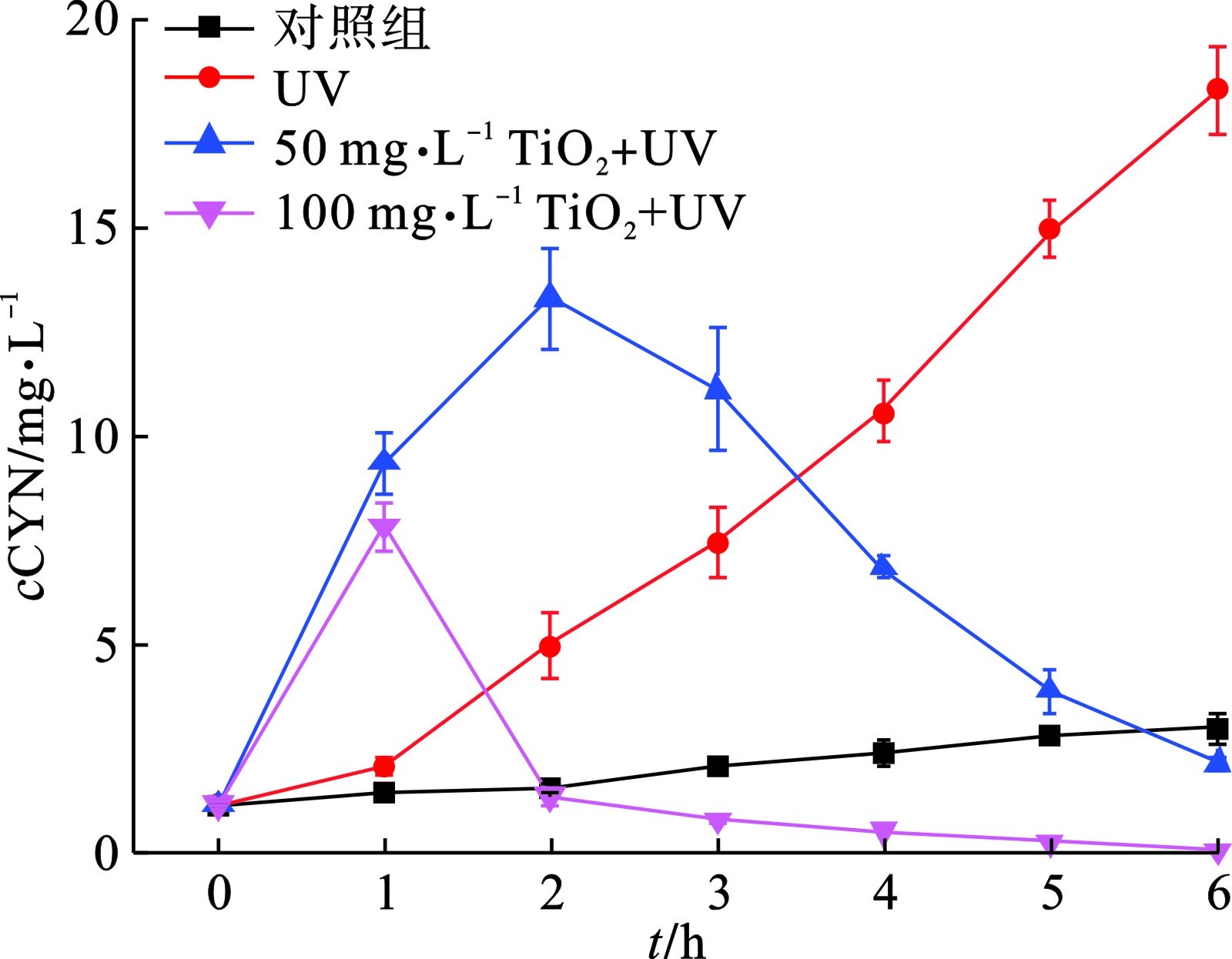
在自然水体中,颤藻所分泌的蓝藻毒素主要有CYN和MCs,且大多存在于颤藻细胞内部。UV/TiO2能否快速降解颤藻细胞破裂后释放的大量蓝藻毒素是衡量其有效性的关键指标。在UV/TiO2降解CYN的过程中,CYN浓度的变化规律与胞外有机物相似,见图5。
颤藻细胞破裂释放胞内藻毒素,藻毒素浓度达到峰值后,随着UV/TiO2光催化反应的进行迅速降低。这主要是因为,与其他蓝藻细胞相似[21],TiO2在紫外光照下催化形成的ROS对颤藻细胞造成的破坏作用使细胞内的CYN在短时间内大量释放,而在反应初期细胞破裂释放的CYN量超出了ROS的降解能力,因此使得体系内CYN浓度在反应初期迅速升高。而随着反应进行,胞内CYN逐渐完全释放,水体中没有新增的CYN,而TiO2仍在不断催化产生ROS,从而使体系内CYN浓度迅速降低。当TiO2投加量为100 mg/L时,水体中CYN浓度在反应1 h内迅速从1.2升到7.9 μg/L,此过程中大量颤藻细胞破裂或受损,使得CYN释放量大于ROS的降解量。反应1 h后,随着颤藻细胞内CYN完全释放,水体中剩余的CYN被迅速降解,在反应6 h后基本实现了胞内、胞外CYN的完全去除。而对于50 mg/L TiO2,在反应2 h后水体中CYN浓度才达到峰值,峰值浓度为13.4 μg/L,远高于100 mg/L TiO2实验组的峰值浓度。这主要是因为50 mg/L TiO2催化产生ROS量相对较小,对CYN的降解效率低于100 mg/L TiO2,因此无法快速控制水体内CYN浓度的上升。随着胞内CYN完全释放,50 mg/L TiO2实验组体系内CYN浓度也迅速下降,但反应6 h后,水体中CYN仍无法完全去除。值得注意的是,UV实验组中的CYN浓度在6 h的反应过程中一直上升,这是因为仅施加紫外光照射对于体系中颤藻伤害作用相对较弱,导致颤藻细胞逐渐损伤或破裂,胞内CYN不是在短时间内大量释放而是在整个反应过程中逐渐释放。而另一方面紫外光对CYN的降解作用有限,因此也无法控制水体中CYN浓度的持续上升。对照组中CYN浓度也有轻微的上升,这可能与培养过程中颤藻细胞增殖所导致的CYN常规代谢有关。UV/TiO2降解颤藻过程中MCs浓度变化情况,见图6。
MCs的降解趋势与CYN基本相似。但值得注意的是,100 mg/L TiO2实验组中并未出现MCs浓度的上升,在反应过程中MCs浓度持续下降,并在3 h后被完全降解,这一方面因为本实验所使用的颤藻分泌的MCs量要远低于CYN,另一方面是CYN化学结构比MCs稳定[18],从而使MCs比CYN更易降解。因此,当投加100 mg/L TiO2时,体系中颤藻释放的MCs量始终未超过ROS的降解能力,在反应3 h后体系内的MCs被完全降解。而当TiO2浓度为50 mg/L时,MCs的变化趋势仍为先上升后下降,并最终在反应5 h后完全降解。
-
本实验研究了UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术对丝状底栖蓝藻颤藻的去除效果,并与铜绿微囊藻的降解过程进行了比较。结果表明,颤藻细胞在UV/TiO2光催化下6 h内被完全破坏,并降解其释放出的蓝藻毒素CYN与MCs。然而其细胞破坏效率以及藻毒素降解效率要明显低于铜绿微囊藻。在相同光催化条件下,降解颤藻细胞需要更长的反应时间。此外,UV/TiO2在破坏颤藻细胞后,也能在反应6 h内有效降解其释放出藻类代谢物。综上所述,由于颤藻团聚形成的藻垫对其自身的保护作用,UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术对颤藻处理时间增长。但其依然是降解水体中颤藻的有效手段,对控制水源地颤藻水华的暴发有重要的参考价值。
UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术因其自然环境无毒、化学性能稳定、使用成本低廉和光催化活性高的优点,在水华治理方面的应用具有广阔的前景。光催化氧化技术在治理水华问题的实际应用过程中的影响因素十分复杂。首先,富营养化水体中包含多种物质且引起水华暴发的藻类多样;其次,TiO2光催化剂的性质、UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术在水厂中的反应条件也是限制其大规模实际应用的重要因素。针对以上问题开展相关研究是UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术能否有效治理水华问题的关键。
UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术降解颤藻及其毒素的研究
Degradation of Oscillatoria sp. and its toxins by UV/TiO2
-
摘要: UV/TiO2为非选择性高级氧化技术,对各类蓝藻均有降解能力,但其处理效果受蓝藻生理生化特性的影响。自然水体中往往存在多种有害蓝藻优势种,然而目前UV/TiO2降解有害蓝藻的研究大多以铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa)为对象,对其他具有不同生理生化特性的蓝藻优势种的处理效果与机制研究仍鲜有报道。近年来,另一种常见的产毒蓝藻——颤藻(Oscillatoria sp.)在水源地的频繁暴发使其受到广泛关注并急需找到具有针对性的治理方法。为探索UV/TiO2高级氧化技术治理水体中颤藻的可行性,针对UV/TiO2降解过程中颤藻细胞的裂解机制、微囊藻毒素与柱孢藻毒素的降解效率以及胞外有机物的变化规律进行研究,并与同等条件下铜绿微囊藻的降解过程进行比较。Abstract: UV/TiO2 is a non-selective advanced oxidation technology, which can degrade all kinds of cyanobacteria. However, its treatment effect is affected by the physiological and biochemical characteristics of the cyanobacteria. There are many dominant species of harmful cyanobacteria in natural water. The present research on the degradation of harmful cyanobacteria by UV/TiO2 is mostly focused on Microcystis aeruginosa, and there are still few reports on the treatment effect and mechanism of other dominant species of cyanobacteria with different physiological and biochemical characteristics. In recent years, the frequent outbreak of Oscillatoria sp., another common poisonous cyanobacteria, has attracted widespread attention and urgently needs to find a targeted treatment method. To explore the feasibility of UV/TiO2 advanced oxidation technology to treat Oscillatoria in water, this paper focuses on the lysis pattern of Chlamydomonas cells during UV/TiO2 degradation, the degradation efficiency of microcystins and columnaris toxins, and the types and contents of extracellular organic matter. The changes of Microcystis aeruginosa under the same conditions are also analyzed.
-
Key words:
- UV/TiO2 /
- photocatalytic oxidation /
- Oscillatoria sp. /
- Microcystis aeruginosa /
- cyanotoxins
-
由于人类活动的影响,大量工业废水、生活污水以及农田径流中的氮、磷营养物质排入湖泊、水库、河口和海湾等缓流水体,引起了不同程度的水体富营养化,进而导致了蓝藻水华的暴发[1-3]。漂浮在水面的大量蓝藻会遮蔽阳光,使水体动植物因光合作用受阻碍而死亡,导致水体透明度降低,溶解氧减少,产生恶臭气味,感官性状急速下降。而死去的动植物腐败后释放出的大量氮、磷营养物质会进一步被蓝藻利用,使其大量繁殖,造成恶性循环[4-5]。此外,蓝藻的生长代谢过程中所释放的多种蓝藻毒素在极低剂量下就会对人体的肝脏、肾脏等多处器官的健康产生不利影响,情况严重的会引发癌症,导致死亡[6-7]。因此,水体中尤其是饮用水水源地中的有害蓝藻及其释放的蓝藻毒素会对环境和人类健康造成严重威胁,是水处理工艺中需要解决的关键问题之一。
光催化氧化技术是一种利用光辐照激发半导体材料,使其催化产生具有极强氧化能力的活性氧自由基,从而有效降解微生物与有机物等污染物的高级氧化技术[8]。其中,UV/TiO2高级氧化技术因其自然环境无毒、化学性能稳定、使用成本低廉和光催化活性高的优点,得到了广泛的研究与应用。UV/TiO2高级氧化技术在蓝藻治理方面的应用同样具有广阔的前景[9-10],例如PINHO et al[11]的研究表明在紫外光照下,50 mg/L TiO2能在15~20 min内快速灭活水体中的铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa)并有效降解其释放的微囊藻毒素(Microcystins,MCs),证明了UV/TiO2在蓝藻治理中应用的可行性。然而,目前有关UV/TiO2降解蓝藻的研究大多以铜绿微囊藻为研究对象。
近年来,另一种常见的产毒蓝藻——颤藻(Oscillatoria sp.)在水源地的频繁暴发使其受到广泛关注。与在水体中均匀分散的单细胞铜绿微囊藻不同,颤藻为丝状蓝藻,且在水体中易发生团聚现象,进而形成颤藻藻垫,对颤藻细胞具有更强的保护作用[12-13]。此外,颤藻分泌的蓝藻毒素更为复杂,不仅分泌微囊藻毒素,还会产生柱孢藻毒素(Cylindrospermopsin,CYN)以及异嗅物质[14]。由于与铜绿微囊藻的生理性状以及行为特征明显不同,颤藻在UV/TiO2降解过程中的变化规律也可能有很大差别。然而,作为一种急需针对治理的水华蓝藻,有关光催化氧化技术尤其是UV/TiO2对颤藻及其分泌毒素降解效果与机理的研究尚未有报道。
因此,本研究主要针对UV/TiO2降解过程中颤藻细胞的裂解机制、微囊藻毒素与柱孢藻毒素的降解效率以及胞外有机物的变化规律进行研究,并与同等条件下铜绿微囊藻的降解过程进行比较。该研究可以为治理水体中不同生理特征的有害蓝藻提供经验技术,也可以为光催化氧化技术处理团聚型蓝藻提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
1.1.1 蓝藻藻种
受试蓝藻藻种分别为颤藻(Oscillatoria sp.)和铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa),由中国科学院典型培养物保藏委员会淡水藻种库(FACHB)提供,采用BG11培养基,培养温度为20 ℃ ,可见光照强度为2 000 lux,培养至对数生长期时进行实验。
1.1.2 原水
实验所用原水取自南四湖,经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后用于稀释藻液。
1.1.3 TiO2的制备
将分析纯TiCl4溶液20 mL,在搅拌时加入200 mL的去离子水中,使其形成乳浊液,然后再取40 mL浓H2SO4一边搅拌一边慢慢地加到上述体系中,然后放在内层衬有聚四氟乙烯的不锈钢高压釜中加热,反应温度为200 ℃,加热10 h,取出反应物先后用去离子水和丙酮洗涤3次,然后在100 ℃烘l h,即得锐钛矿相结构的TiO2粉末[15]。制备过程中所使用的化学试剂均购置于国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 光催化降解实验
实验所配置的模拟水源中蓝藻浓度为106 cells/mL。将铜绿微囊藻培养液与原水直接混合,通过光学显微镜计数调整比例,即可得到浓度为106 cells/mL含铜绿微囊藻水源(叶绿素a: 3 mg/L, COD: 14.2 mg/L, pH 8.6)。而对于颤藻,如果采用上述直接混合法配置106 cells/mL的含颤藻水源,则会使水体中的颤藻因浓度过高而出现团聚现象,形成藻垫,从而无法在显微镜下计数,也无法调整到所需要的藻浓度。因此,在本实验中,我们先将颤藻培养液与去离子水混合,配置10 L, 104 cells/mL的颤藻溶液(此时颤藻在水体中呈丝状均匀分散),然后用0.45 μm 滤膜将其过滤,取滤膜上的颤藻加入到100 mL原水中,则得到藻浓度为106 cells/mL的含颤藻水源(叶绿素a: 0.52 mg/L, COD: 12.5 mg/L, pH 8.3)。取若干组20 mL含蓝藻水源,分别加入0、50和100 mg/L TiO2,放置于紫外光下匀速搅拌,分别在反应0、5、10、15、20、25和30 min以及1、2、3、4、5和6 h后进行检测。为保证数据的准确性,每个时间点取不同浓度TiO2的蓝藻水源组进行检测,每个20 mL水源组仅进行一次检测,每个浓度每个时间点设置3组平行。对照组的含蓝藻水源放置在培养箱中培养(20 ℃,2 000 lux)。
1.2.2 蓝藻生理指标测定
(1) 叶绿素a
取2 mL的样品置于高速离心机(Eppendorf 5810R),转速10 000 r/min离心10 min后弃上清并加入2 mL无水甲醇溶液。混合均匀后放置在黑暗条件下45 ℃恒温孵化24 h后,用荧光分光光度计(日本日立公司,F-7100)测定液体在652.4和665.2 nm波长下的吸光度。叶绿素a浓度的计算公式为[16]:叶绿素a(μg/mL)=16.72 × OD665.29.16 × OD652.4 。
(2) 微囊藻毒素与柱孢藻毒素
MCs与CYN采用酶联免疫法测定,样品经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后,取滤液按照藻毒素试剂盒操作步骤进行测定,所用试剂盒分别均来自美国Beacon公司。
(3) 有机物测定
利用荧光分光光度计(F-7000,日本日立公司)分析样品中有机物种类及含量的变化。取0.45 μm滤膜过滤后的样品滤液进行分析。激发波长以5 nm为间隔,200~450 nm扫描,在250~550 nm间以1 nm为间隔测量发射光谱,扫描速度为12 000 nm/min,电压为700 V。
1.2.3 统计分析与作图方法
为消除实验环境等因素对实验结果的影响,所有实验均设置3组平行实验,数据表示为各自的平均值±标准偏差(SD)。处理后的数据采用origin2021进行作图。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术降解颤藻细胞的研究
为了更直观地研究UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术对颤藻的作用效果,我们比较了相同紫外光催化条件下,不同剂量TiO2对颤藻细胞与铜绿微囊藻细胞的降解效率,通过测定降解过程中叶绿素a浓度的大小可以近似表征体系内蓝藻细胞数量的变化规律,见图1。
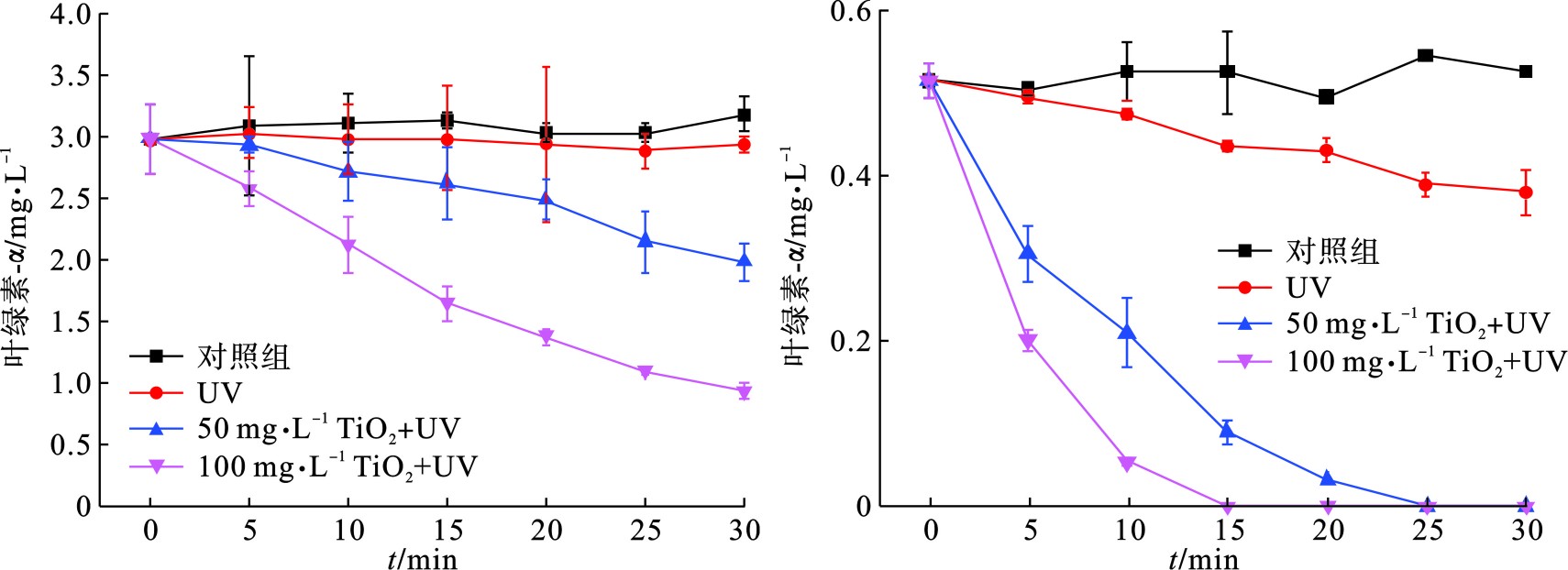 图 1 UV/TiO2降解颤藻(a)与铜绿微囊藻(b)30 min内叶绿素a浓度变化情况Figure 1. Changes of chlorophyll-a concentration in 30 min after UV/TiO2 degradation of Oscillatoria sp. (a) and Microcystis aeruginosa (b)对照组:不施加紫外光照,无TiO2投加,置于适宜条件下培养;UV:仅施加紫外光照,无TiO2投加;50 mg•L−1 TiO2 + UV:紫外光照下投加50 mg•L−1 TiO2;100 mg•L−1 TiO2 + UV:紫外光照下投加100 mg•L−1 TiO2
图 1 UV/TiO2降解颤藻(a)与铜绿微囊藻(b)30 min内叶绿素a浓度变化情况Figure 1. Changes of chlorophyll-a concentration in 30 min after UV/TiO2 degradation of Oscillatoria sp. (a) and Microcystis aeruginosa (b)对照组:不施加紫外光照,无TiO2投加,置于适宜条件下培养;UV:仅施加紫外光照,无TiO2投加;50 mg•L−1 TiO2 + UV:紫外光照下投加50 mg•L−1 TiO2;100 mg•L−1 TiO2 + UV:紫外光照下投加100 mg•L−1 TiO2图1(b)可知,在紫外光照射下,50 mg/L TiO2可以在25 min之内将体系中106 cells/mL的铜绿微囊藻完全降解,而当TiO2剂量提到0 mg/L,降解时间可缩至5 min,结果与PINHO et al[11]的研究相符。此外,为了排除紫外光对藻细胞的单独作用效果,我们在不投加TiO2的情况下用相同条件的紫外光照射蓝藻细胞,结果表明,紫外光对铜绿微囊藻具有一定的灭活作用,在15和25 min时,降解贡献率分别为15.5%和24.2%。相比于铜绿微囊藻,UV/ TiO2对颤藻细胞的降解效率明显降低,见图1(a)。在30 min紫外光照射下,100 mg/L TiO2仍无法将体系内的颤藻细胞的完全降解,降解效率仅为70%,而当TiO2为50 mg/L时,仅有约33%的颤藻细胞得以降解。此外,UV实验组与对照组中叶绿素a浓度在反应过程中均没有明显变化,说明在反应30 min内紫外光对颤藻细胞基本没有破坏效果。为了进一步研究UV/ TiO2对颤藻的降解效能,我们将反应时间从30 min延长到6 h,见图2。
图2可知,在紫外光照3 h后,100 mg/L TiO2可以降解体系内90%以上的颤藻细胞,而对于50 mg/L的TiO2,这一过程需要5 h。值得注意的是,对照组中的颤藻细胞在培养6 h后出现了明显的增殖现象,而铜绿微囊藻的数量没有明显变化。这与文献[17]的研究结果相符,即颤藻具有极强增殖能力,其数量可以在短时间内大量增长。由此可推断,相比于铜绿微囊藻,颤藻强大的繁殖能力也可能是其能够抵御活性氧自由基(ROS)等外界伤害的原因之一。此外,随着反应时间延长,紫外光对于颤藻的损伤作用逐渐显现,在UV实验组中,紫外照射6 h后,体系中约50%的颤藻细胞破裂。而对于铜绿微囊藻,仅施加6 h的紫外光照射下,细胞降解率可达约80%。
由此可见,UV/ TiO2光催化氧化技术虽然能有效降解颤藻细胞,但降解效率与单细胞蓝藻铜绿微囊藻相比明显不足,主要原因是:(1)颤藻容易在水体中形成藻垫[18],这种团聚体结构能有效包裹颤藻藻丝,大大减少了颤藻与TiO2催化形成的ROS的接触面积,从而抑制了ROS对颤藻的氧化降解作用;(2)颤藻藻垫会削弱紫外光的透射效果,这一方面使水体中的TiO2颗粒无法接受足够的紫外光照射从而抑制了ROS的生成,另一方面也阻碍了紫外光对颤藻的直接伤害作用,这也可以解释紫外光对铜绿微囊藻细胞有更强损伤作用的原因:单细胞的铜绿微囊藻在水体中相对分散不聚集从而与紫外光有更大的接触面积,见图3。
2.2 UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术降解颤藻代谢物的研究
UV/ TiO2光催化氧化技术对蓝藻的有效处理不仅体现在对蓝藻细胞的破坏作用,更体现在对蓝藻代谢物的高效降解,而胞外有机物种类和含量的变化可以反映降解过程中蓝藻代谢物的去除情况。EEM荧光光谱图可以直观反映有机物种类和含量的变化[19]。其中Ex/En: 280/335 nm为蛋白质类物质的特征峰,Ex/Em: 355/445 nm与Ex/Em: 275/450 nm均属于腐殖酸类物质的特征峰[20],见图4。
图4可知,在 UV/TiO2降解颤藻之前,颤藻悬浮液中EOM主要为少量的蛋白质类物质。这可能与培养过程中颤藻细胞增值代谢向水体中释放了部分蛋白质类物质有关[20]。TiO2投加量为50 mg/L处理一段时间后,由于UV/TiO2光催化氧化的作用,颤藻细胞破裂,胞外蛋白质类物质显著增多。当处理6 h后,蛋白质类物质出现减少的情况,腐殖酸类物质明显增加。这可能是氧化过程中死细胞和蛋白质类物质的分解造成的。TiO2投加量为100 mg/L处理2 h后,腐殖酸类物质增多,未观察到蛋白质类物质的出现。这可能是由于催化剂的剂量增大导致氧化性能进一步加强,使得颤藻在2 h内完成了细胞破裂和蛋白质类物质向腐殖酸类物质的转化。最后,在2种剂量处理下的颤藻悬浮液中EOM腐殖酸类物质逐渐降解,最终与蛋白质物质等其他产物一起降低到低浓度水平。
在自然水体中,颤藻所分泌的蓝藻毒素主要有CYN和MCs,且大多存在于颤藻细胞内部。UV/TiO2能否快速降解颤藻细胞破裂后释放的大量蓝藻毒素是衡量其有效性的关键指标。在UV/TiO2降解CYN的过程中,CYN浓度的变化规律与胞外有机物相似,见图5。
颤藻细胞破裂释放胞内藻毒素,藻毒素浓度达到峰值后,随着UV/TiO2光催化反应的进行迅速降低。这主要是因为,与其他蓝藻细胞相似[21],TiO2在紫外光照下催化形成的ROS对颤藻细胞造成的破坏作用使细胞内的CYN在短时间内大量释放,而在反应初期细胞破裂释放的CYN量超出了ROS的降解能力,因此使得体系内CYN浓度在反应初期迅速升高。而随着反应进行,胞内CYN逐渐完全释放,水体中没有新增的CYN,而TiO2仍在不断催化产生ROS,从而使体系内CYN浓度迅速降低。当TiO2投加量为100 mg/L时,水体中CYN浓度在反应1 h内迅速从1.2升到7.9 μg/L,此过程中大量颤藻细胞破裂或受损,使得CYN释放量大于ROS的降解量。反应1 h后,随着颤藻细胞内CYN完全释放,水体中剩余的CYN被迅速降解,在反应6 h后基本实现了胞内、胞外CYN的完全去除。而对于50 mg/L TiO2,在反应2 h后水体中CYN浓度才达到峰值,峰值浓度为13.4 μg/L,远高于100 mg/L TiO2实验组的峰值浓度。这主要是因为50 mg/L TiO2催化产生ROS量相对较小,对CYN的降解效率低于100 mg/L TiO2,因此无法快速控制水体内CYN浓度的上升。随着胞内CYN完全释放,50 mg/L TiO2实验组体系内CYN浓度也迅速下降,但反应6 h后,水体中CYN仍无法完全去除。值得注意的是,UV实验组中的CYN浓度在6 h的反应过程中一直上升,这是因为仅施加紫外光照射对于体系中颤藻伤害作用相对较弱,导致颤藻细胞逐渐损伤或破裂,胞内CYN不是在短时间内大量释放而是在整个反应过程中逐渐释放。而另一方面紫外光对CYN的降解作用有限,因此也无法控制水体中CYN浓度的持续上升。对照组中CYN浓度也有轻微的上升,这可能与培养过程中颤藻细胞增殖所导致的CYN常规代谢有关。UV/TiO2降解颤藻过程中MCs浓度变化情况,见图6。
MCs的降解趋势与CYN基本相似。但值得注意的是,100 mg/L TiO2实验组中并未出现MCs浓度的上升,在反应过程中MCs浓度持续下降,并在3 h后被完全降解,这一方面因为本实验所使用的颤藻分泌的MCs量要远低于CYN,另一方面是CYN化学结构比MCs稳定[18],从而使MCs比CYN更易降解。因此,当投加100 mg/L TiO2时,体系中颤藻释放的MCs量始终未超过ROS的降解能力,在反应3 h后体系内的MCs被完全降解。而当TiO2浓度为50 mg/L时,MCs的变化趋势仍为先上升后下降,并最终在反应5 h后完全降解。
3. 结论与展望
本实验研究了UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术对丝状底栖蓝藻颤藻的去除效果,并与铜绿微囊藻的降解过程进行了比较。结果表明,颤藻细胞在UV/TiO2光催化下6 h内被完全破坏,并降解其释放出的蓝藻毒素CYN与MCs。然而其细胞破坏效率以及藻毒素降解效率要明显低于铜绿微囊藻。在相同光催化条件下,降解颤藻细胞需要更长的反应时间。此外,UV/TiO2在破坏颤藻细胞后,也能在反应6 h内有效降解其释放出藻类代谢物。综上所述,由于颤藻团聚形成的藻垫对其自身的保护作用,UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术对颤藻处理时间增长。但其依然是降解水体中颤藻的有效手段,对控制水源地颤藻水华的暴发有重要的参考价值。
UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术因其自然环境无毒、化学性能稳定、使用成本低廉和光催化活性高的优点,在水华治理方面的应用具有广阔的前景。光催化氧化技术在治理水华问题的实际应用过程中的影响因素十分复杂。首先,富营养化水体中包含多种物质且引起水华暴发的藻类多样;其次,TiO2光催化剂的性质、UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术在水厂中的反应条件也是限制其大规模实际应用的重要因素。针对以上问题开展相关研究是UV/TiO2光催化氧化技术能否有效治理水华问题的关键。
-
-
[1] 罗晓春, 杭鑫, 曹云, 等. 太湖富营养化条件下影响蓝藻水华的主导气象因子[J]. 湖泊科学, 2019, 31(5): 1248 − 1258. doi: 10.18307/2019.0512 [2] 张兰婷. 富营养化蓝藻水华发生的主要成因与机制研究综述[J]. 水利发展研究, 2019, 19(5): 28 − 33.卷期. doi: 10.13928/j.cnki.wrdr.2019.05.008 [3] AGUILERA A, HAAKONSSON S, MARTIN M V, et al. Bloom-forming cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in Argentina: A growing health and environmental concern[J]. Limnologica, 2018, 69: 103 − 114. doi: 10.1016/j.limno.2017.10.006 [4] NYAKAIRU G, NAGAWA C B, MBABAZI J. Assessment of cyanobacteria toxins in freshwater fish: A case study of Murchison Bay (Lake Victoria) and Lake Mburo, Uganda[J]. Toxicon, 2010, 55(5): 939 − 946. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.07.024 [5] SCHINDLER D W, HECKY R E, MCCULLOUGH G K. The rapid eutrophication of Lake Winnipeg: Greening under global change[J]. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 2012, 38: 6 − 13. [6] ZAMYADI A, MACLEOD S L, FAN Y, et al. Toxic cyanobacterial breakthrough and accumulation in a drinking water plant: A monitoring and treatment challenge[J]. Water Research, 2012, 46(5): 1511 − 1523. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.012 [7] 姜锦林, 周军英, 刘仁彬, 等. 太湖重污染湖区和水源地水质概况及藻毒素污染环境风险[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2019, 14(3): 60 − 71. [8] 梁钊, 李子富, 周晓琴, 等. 氮掺杂二氧化钛光催化氧化降解污水中四环素[J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(3): 92 − 97. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201903017 [9] KAZUHITO H, HIROSHI I, AKIRA F, et al. TiO2 photocatalysis: A historical overview and future prospects[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 44(12): 8269 − 8285. [10] 李湄琳. 二氧化钛作为光催化剂的原理概述[J]. 生物化工, 2017(6): 94 − 96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0387.2017.06.029 [11] PINHO L X, AZEVEDO J, BRITO A, et al. Effect of TiO2 photocatalysis on the destruction of Microcystis aeruginosa cells and degradation of cyanotoxins microcystin-LR and cylindrospermopsin[J]. Chemical Eegineering Journal, 2015, 268: 144 − 152. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.12.111 [12] MIRANDA-BAEZA A, MARISCAL-LÓPEZ M D L A, LÓPEZ-ELÍAS J A, et al. Effect of inoculation of the cyanobacteria Oscillatoria sp. on tilapia biofloc culture[J]. Aquaculture Research, 2017, 48(9): 4725 − 4734. doi: 10.1111/are.13294 [13] MOHAMED Z A. Breakthrough of Oscillatoria limnetica and microcystin toxins into drinking water treatment plants - examples from the Nile River, Egypt[J]. Water SA, 2016, 42(1): 161 − 165. doi: 10.4314/wsa.v42i1.16 [14] World Health Organization(2008)Guidelines for drinking-water quality: incorporating the first and second addenda, [M] 3rd, vol. 1, World Health Organization, Geneva. [15] 汪国忠, 牟季美. 纳米TiO2的制备和性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 1997, 11(5): 527 − 530. [16] 金岩. 载体混凝耦合可见光催化氧化去除饮用水中有害蓝藻及其代谢物[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2019. [17] 孙炯明. 颤藻细胞及其代谢产物在聚合氯化铝铁混凝工艺中的行为特征[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2018. [18] SUN J, XU H, PEI H, et al. Worse than cell lysis: The resilience of Oscillatoria sp. during sludge storage in drinking water treatment[J]. Water Research, 2018, 142: 405 − 414. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.06.020 [19] LI L, SHAO C, LIN T, et al. Kinetics of cell inactivation, toxin release, and degradation during permanganation of Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(5): 2885 − 2892. [20] QU F S, LIANG H, HE J G, et al. Characterization of dissolved extracellular organic matter (dEOM) and bound extracellular organic matter (bEOM) of Microcystis aeruginosa and their impacts on UF membrane fouling[J]. Water Research, 2012, 46(9): 2881 − 2890. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.02.045 [21] JIN Y, ZHANG S S, XU H Z, et al. Application of N-TiO2 for visible-light photocatalytic degradation of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii —More difficult than that for photodegradation of Microcystis aeruginosa ?[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 245: 642 − 650. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.056 -






 下载:
下载: