-
有机磷酸酯(OPEs)是近年来受到人们广泛关注的一类新有机污染物,其作为阻燃剂和增塑剂被应用于各类产品中,如建筑材料、家具、润滑剂、纺织品以及电子产品等[1-4]. OPEs是磷酸酯类衍生物,多具有磷酸三酯的共同骨架结构,根据取代基酯键的不同OPEs可大致分为烷基取代磷酸酯(Alkyl-OPEs),氯代磷酸酯(Cl-OPEs)和芳基取代磷酸酯(Aryl-OPEs)[5],其中,Cl-OPEs阻燃效率更高主要被用于生产阻燃剂,而非Cl-OPEs多用于生产增塑剂[6]. 据报道投入全球生产和使用的OPEs超过40种,而从2011年到2015年,仅作为阻燃剂的OPEs生产量已从50万吨增长到68万吨[7-8]. 由于部分OPEs对生态安全与人体健康造成了潜在的威胁,目前有一些传统的OPEs(如磷酸三氯乙基酯(TCEP))已经在产品生产中被禁止,进而导致对新型OPEs的需求持续增加,如基于磷酸三苯酯(TPHP)结构衍生出的双酚A双(磷酸二苯酯) (BPA-BDPP)和磷酸甲苯二苯酯(CDP)等[9-10]. 近年来,新型OPEs在环境中的污染也逐渐引起了环境学者的重视,表1列出了工业上应用的一些传统和新型OPEs及其理化性质和主要用途[9-13].
由于OPEs多是以简单的物理添加而非化学键合方式加于各类产品中,很容易通过磨损、渗滤、蒸发、溶解等途径扩散至大气、水以及土壤等环境介质中[14-15]. 大气中OPEs以干/湿沉降或者气-液/气-固交换进入水环境或者土壤,土壤中OPEs可通过地表径流或者灌溉等方式进入水体. 由于具有疏水性,大部分进入水中的OPEs会被悬浮物吸附而进入生物相以及沉积物中. 吸附在沉积物上的OPEs还可以再悬浮而再次进入到水相,成为流动的污染物. 目前,OPEs已在空气[16-19]、饮用水和表层水体[20-21]、沉积物[22-25]以及人体[26]等多种介质中频繁检出. 毒理学相关研究也逐渐报道OPEs具有神经毒性[27-29]、发育毒性[30-32]、生殖毒性[33-35]以及致癌性[36]等,从而对生态环境和人体健康造成潜在的危害.
现有的综述研究多集中于OPEs在环境中的检出方法、分布情况、毒性和部分介质中的风险评估等方面[37-40],有关OPEs迁移转化的报道非常有限. 而OPEs在环境中的归趋决定了其对生态环境以及人体健康的影响,是当今环境科学基础研究的热点之一. 基于此,本文综述了近年来OPEs在环境中可能发生的迁移转化过程,并就当前研究的不足和将来的研究方向提出一些思考和展望,旨在为今后OPEs的生态风险评估和污染管控提供支撑. 目前,环境中OPEs的迁移转化过程主要包括大气传输沉降、地表地下径流扩散、界面交换与吸附解吸、水解和光解,以及生物富集、植物吸收和代谢转化和微生物降解等.
-
大多数OPEs属于半挥发性物质,且以非化学键合方式添加于各类产品表面,导致OPEs在其使用过程中很容易挥发到周围大气中. 有研究评估过磷酸三(1,3-二氯-2-丙基)酯(TDCIPP)和磷酸三-氯(2-氯异丙基)酯(TCIPP)每天从全球地面建筑物以及交通工具等表面向大气的排放总量分别可达15.33 kg和89.56 kg[41]. OPEs具备潜在的长距离传输能力,可通过附着于大气中颗粒相而进行长距离传输,从而迁移至海洋以及极地环境中[42-46]. 据报道,在欧洲海域、公海和极地地区上空大气层中检测出多种OPEs,且浓度高于传统溴代阻燃剂[16,46-47]. 此外,Liu等[48]在其研究中也揭示了大气中–OH的氧化作用可延长附着于气溶胶颗粒上OPEs的半衰期,并预测了TPHP、磷酸三辛酯 (TEHP)和TDCIPP的半衰期分别为5.6 d、4.3 d和13 d. 该研究解释了OPEs发生长距离迁移的可能性,并指出由于Cl-OPEs的低活性可导致其更易发生长距离迁移. 随着OPEs在全球范围内的大气传输,其在各大洋上空大气中浓度水平大致表现为:北大西洋>南大西洋>北太平洋>南太平洋>印度洋,且低纬度地区含量高于高纬度地区[42,46].
随大气迁移至偏远地区的OPEs可进一步通过干沉降和湿沉降进入水体和土壤介质 [49-51],进而导致大气干湿沉降成为有些地区湖泊和土壤中OPEs的潜在来源 [52-53]. OPEs的干沉降过程主要受大气团、风速以及气压的影响,例如侯超[54]在探究极地大气OPEs的沉降中发现,白令海峡的高沉降通量主要归因于白令海峡夏季风速低和气压低,而北冰洋高纬度区沉降通量较高主要是受到大西洋北部气团的影响. OPEs的湿沉降主要受到大气中污染物浓度的影响,同时Mihajlovic和Fries[41]的研究发现,降雪对Cl-OPEs的沉降作用高于降雨. 一般情况下,OPEs的沉降作用会因其进一步迁移到深层土壤而被覆盖,但沉降作用对于气-土交换仍占重要地位. Rodgers等 [55]的研究发现,安大略湖中6种OPEs的负荷有13%来自于大气沉降.
-
污水处理厂排水被认为是天然水体中OPEs的重要来源之一[56]. 通常污水处理厂进水中检测的OPEs浓度水平可高至 µg·L−1水平 [49,57]. 由于传统污水处理厂的处理工艺对于OPEs的去除效果较差(平均约50%)[49],尤其Cl-OPEs的处理效率更低,导致OPEs随出水源源不断地进入到下游河流. 此外,大气干湿沉降、土气交换、污水灌溉以及污泥的土壤应用也会使得OPEs不断进入到土壤环境中[50,56-57]. 这些OPEs会随地表径流汇入附近河流,同时可以通过渗透作用进入临近含水层的地下水中[58-60]. 随着时间的累积以及降水渗透等过程有些地区的地下水中OPEs的检出浓度明显高于其在地表水中的浓度[61]. 进入地表水和地下水中的OPEs能够进一步随水流迁移,扩散至偏远地区 [61-63].
从陆地输出的OPEs主要通过水流转移至海洋表层水中,且速度受到风、气温变化以及潮流速度的影响[62,64],不同取代基OPEs表现的趋势相同. 来源于辽河,海河以及黄河河口的OPEs会随海洋流汇集于深海区,并且至洋流缓慢区浓度较高,与此同时OPEs也会随洋流进行再分布[64]. 此外,地表水和地下水中OPEs也会在流动中不断与表层土壤和沉积物发生交换,有研究评估了北太平洋(白令海)到北冰洋的海洋沉积物中的OPEs水平,发现OPEs总浓度随着纬度的增加而增加(0.16—4.66 ng·g−1),并指出偏远地区的海洋沉积物将是这些化合物的一个重要储存地[24].
-
OPEs在不同介质上的吸附/解吸不仅影响其在环境中的迁移和分布,同时也是影响其光解以及生物降解等过程的重要因素,且对OPEs在环境中的缓解和修复至关重要. 目前,有关OPEs的吸附过程的研究主要是基于液相-固相界面和气相-固相界面,表2总结了OPEs在不同环境介质中的吸附动力学模型和吸附等温线[65-72]. 一般情况下OPEs在不同介质上的吸附包含前期快速的物理吸附和化学吸附,本文中主要探讨化学吸附过程.
OPEs吸附动力学模型中一级动力学模型和准二级动力学模型的应用较为广泛[65-66,69,73],当OPEs的吸附满足准二级动力学模型时,说明吸附过程主要受化学作用控制[74]. OPEs的吸附速率与自身理化性质和结构紧密相关,疏水性越强(Kow越大)的化合物,在介质表面的吸附速率越快,如OPEs在活性炭表面吸附速率快慢表现为TEP < TCIPP < TCEP < TnBP < TPHP,基本与各化合物lgKow大小顺序一致(TCIPP除外),而当OPEs的疏水性接近时,Aryl-OPEs的吸附能力要明显高于Alkyl-OPEs,表明Aryl-OPEs结构中π-π相互作用对其吸附过程的影响也十分重要[70,73].
此外,OPEs吸附行为还受到吸附介质的特性、温度、pH值、盐度以及环境中共存物种等的影响[68,70,73,75-76]. 一般情况下,吸附介质的孔隙扩散以及膜扩散是控制有机污染物吸附过程快慢的控制步骤,因此,吸附剂的尺寸对OPEs的吸附动力学和吸附能力具有重要的影响,如粉末状活性炭表面的吸附速率和吸附能力明显高于颗粒状活性炭[73]. 土壤介质对OPEs的吸附受到土壤有机碳含量(organic carbon, OC)的影响,OC含量越高,其吸附能力越强[50]. 而当吸附介质中含有含氧官能团能够通过氢键与水分子发生作用,可减少自身有效的吸附位点而降低介质的吸附性能[76]. 溶液pH值不仅影响吸附介质的表面活性,也影响被吸附物的物种形成,随着pH值的升高,OPEs在介质表面的吸附量越大[73].
当介质(土壤或沉积物)上被吸附的OPEs通过解吸作用释放出来时,能够对环境造成二次污染,而带来潜在的生态风险. 目前,有研究指出OPEs解吸作用会出现解吸滞后现象,且该过程受到其自身理化性质的影响[67,76]. 例如Wang等[67]研究表明化合物分子大小对于OPEs在沉积物上解吸速度的影响高于化合物疏水性,因此,TPHP的解吸滞后现象相对于磷酸二苯酯(DPHP)和磷酸苯酯更明显. Cristale等[76]指出水溶性较高的TCEP、TCIPP和TBEP在土壤表面发生吸附后,可以有一定程度的解吸,而水溶性较低的TnBP、磷酸2-乙基己基二苯基酯(EHDPP)和TPHP的则未发生解吸过程,可能是由土壤OC的高亲和力导致的.
-
OPEs的水解是其自然消减的一个重要过程,与其在水环境中的稳定性紧密相关. 基于OPEs的三酯结构,其在水解过程容易发生酯键的断裂,形成二酯和单酯结构的产物,并且水解过程通常受水环境的pH值和自身结构的影响. 在酸性或中性条件下,OPEs容易发生C—O键的断裂,而碱性条件下则会造成P—O键的断裂[77]. 在pH值相同的情况下,OPEs水解形成的二酯化合物相较母化合物更稳定,随着pH值的增加,OPEs的水解速率明显加快,且稳定性表现为:Alkyl-OPEs>Cl-OPEs>Aryl-OPEs[78]. 目前,有关二酯结构的OPEs的毒性研究还非常有限,Su等[79]探究了TPHP和其二酯结构水解产物DPHP对细胞毒性和RNA基因表达的影响,并发现尽管两者的细胞毒性较低,但在基因表达过程中DPHP改变的基因数量明显高于TPHP. 由此可见,有关OPEs的转化产物的相关毒性研究还需继续深入开展.
水环境中溶解的金属离子以及矿物表面可以催化OPEs的水解过程[80-81]. Fang等[81]探究了不同矿物质催化OPEs的水解过程,发现当pH = 6时,大多数OPEs的水解半衰期超过10 年,但加入矿物质后其相应的半衰期则小于10 d,表明矿物质的加入对于OPEs半衰期的影响非常显著. 在加入的矿物质中,相比于铝氧化物和硅氧化物,铁(Ⅲ)氧化矿物质对于OPEs的水解促进效果更为明显,但由于其表面的—OH基团的限制,二氧化锰的存在时其水解速率相比铁(Ⅲ)氧化矿物质的水解速率快约一个数量级[82],该结果表明富含锰、铁矿物质的土壤和沉积物等体系能够发生促进OPEs水解的过程.
-
水环境和表层土壤中OPEs能够在光照条件下发生光解反应. 通常情况下OPEs在环境中的光解过程可以分为直接光解和间接光解[83-85]. 在直接光解过程中,OPEs可直接吸收太阳光能而发生化学键的断裂,而间接光解过程则是环境中光敏性物质吸收光后生成的氧化活性物种(ROS, 如羟基自由基–OH、单线态氧1O2,超氧自由基ROO–)而引发OPEs的降解. 有研究表明OPEs中只有Aryl-OPEs和磷酸三(2-丁氧乙基)酯(TBOEP)能够吸收220—400 nm的光,而Cl-OPEs和Alkyl-OPEs因没有发色团而不吸收全波段的光[86],从而导致环境介质中OPEs不易发生直接光解过程. 因此,有关OPEs直接光解的研究较少,我们课题组通过实验室模拟光照探究了不同光强条件下TCP的直接光解过程,并推断了OPEs直接光解的两种可能反应路径:(1) 吸光后直接发生P—O键断裂,与H2O反应后生产磷酸二酯;(2) 吸光后发生抽氢反应,进而与环境中–OH 发生反应而形成羟基化产物[85].
目前,有关OPEs间接光解的相关研究主要集中于探究不同结构OPEs的降解速率、光解产物以及转化机制等[82-85]. 尽管大部分OPEs在纯水中不易发生光降解,但可以作为光敏化剂转化为高能量激发态OPEs*而发生共同降解,且OPEs的光降解受其自身结构、光照强度以及环境组分的影响[82-84]. Cristale等[86]在实验室模拟光照条件下研究发现多种OPEs共存时降解速率表现为Aryl-OPEs>Alkyl-OPEs>Cl-OPEs. 此外,OPEs可在天然介质(湖水等)中发生光降解[87],可见湖水中的溶解性有机质以及无机离子等能够促进OPEs的降解,例如Xu等在实验室条件下[88]的研究探究了多种典型阴离子对OPEs光解的影响,结果发现,对TCEP的光降解速率的影响表现为HCO3->NO3->Cl->HPO42-.
此外,环境介质中溶解性金属或金属氧化物能够作为催化剂诱发OPEs的间接光降解作用[83,89]. 近年来高级氧化技术除采用UV-H2O2-、UV-SO4–-、UV-O3/H2O2[88, 90-93]作为催化体系探究水中OPEs的去除效果外,还应用金属氧化物(如TiO2)和金属离子(Fe2+)等作为用催化剂[83,94-95],探究其在紫外光照射条件下加快OPEs降解的过程及影响因素. 催化剂产生的ROS能够诱导OPEs发生P—O键断裂或卤素原子的脱离而形成二酯和单氯乙酸,进一步降解为甲酸、乙酸和磷酸根等小分子化合物[96]. Zhang等[84]总结了OPEs间接光解过程可能发生的3种路径:(1) –OH加成到苯环上形成加合物;(1) P—O间断裂后,–OH加成到中心磷原子上;(3) 抽氢反应后,与大气中O2形成过氧化物最终形成具有高活性而分子量较低的羰基产物和烷烃自由基.
光解过程是有机物在环境中发生的重要转化过程之一,它不可逆的改变了分子结构,通常情况下污染物光解产物的毒性相较于母化合物降低 [97],但也有可能在光照过程中生成毒性更强的中间产物或终产物[98],从而对生态环境以及人体产生潜在危害. 有关OPEs光解过程中生成中间产物和终产物及相关毒性的研究较少,还需继续深入探究.
-
自1979年Saeger等[99]发现OPEs能够在生物体内累积后,越来越多研究学者开始探究OPEs在不同生物体的潜在富集效应. 目前,OPEs已经被发现在啮齿类、鱼类、两栖类以及鸟类等生物体内可以发生富集,可进一步对生态系统以及人体健康造成潜在的威胁[100-103]. OPEs的富集行为受到其自身理化性质、生理生化过程以及代谢过程等因素的影响.
(1)理化性质的影响
前面提到OPEs疏水性越强,越容易发生吸附作用,同样的,其疏水性越强,越容易在生物体内发生富集[100-101]. 例如Wang 等[100]和Hou等[101]的研究发现lgBAF与OPEs的lgKow值具有显著相关性, Kow值越高,在同一物种中其生物富集因子(BAF)值越大,验证了OPEs的疏水性在其生物富集过程起到重要作用. 但研究学者在Nakdong河[104]和北部湾[105]等区域的生物体内却没有发现类似的规律,如Zhang等[105]的研究中发现,在小虾和螃蟹体内富集OPEs的lgBAF与lgKow呈现抛物线型关系,在lgKow=7时达到峰值,由此说明OPEs的生物富集不仅受到自身机构的影响,暴露方式、环境介质中浓度、生物种类及生活习惯、代谢途径等因素也会影响OPEs的生物富集行为.
(2)生理生化过程的影响
进入生物体内的OPEs会与组织细胞中的脂肪、蛋白以及酶等发生非特异性结合,进而导致其在生物体内不同组织和器官中富集规律具有明显差异性. Bekele等[106]在其研究中发现,OPEs在斑马鱼体内不同器官富集的BCFs值大小表现为肝脏>肾脏>>肠>>肌肉. Wang等[107]发现生物性别也会导致TDCPP富集行为的差异,仅在雌性斑马鱼体大脑内检出,而雄性斑马鱼未检出. 一方面部分学者表明生物体内OPEs的分布与组织中脂肪的含量有明显相关性[108-111],是影响OPEs生物富集的重要因子;另一方面也有研究表明OPEs的生物富集与组织脂肪含量没有明显相关性[112-114],可见不同生物的生理生化过程错综复杂,需综合多方面因素探究OPEs在生物体内的富集行为.
(3)代谢过程的影响
进入生物体内的OPEs可进一步被代谢转化,从而影响其生物富集效应[103,111,115-121]. 一些体外研究发现OPEs能够在在鱼类[115]、鸟类[84,116]、海洋哺乳动物[117]和人类[118]肝脏微粒体中可以发生快速代谢. 例如,有机磷三酯(tri-OPEs)可以在生物体内通过氧化脱烷基和羟化作用代谢成相应的二酯(di-OPEs)和羟化代谢物[83,116,118]. 有研究指出TDCIPP和TPHP在斑马鱼肝脏和肠道内的二酯代谢产物检出量为其母体化合物的1.2倍和2.0倍,且这两种OPEs的转化率分别为42.3%和13.7%,说明该转化过程消耗了富集于生物体内的OPEs [108]. 在生物体内转化过程中取代基的不同导致OPEs的转化效果明显不同,长链Cl-OPEs或Aryl-OPEs的转化比例明显高于Alkyl-OPEs和短链Cl-OPEs[118]. 值得注意的是OPEs的一些代谢产物比其母体化合物的毒性更强,例如羟基化产物5-OH-EHDPP比母体化合物EHDPP引起雄性激素受体拮抗活性强3.1倍[104],说明OPEs的部分代谢产物也具有潜在的威胁. 可见,代谢转化对于OPEs的生物富集行为至关重要,现有研究多采用计算代谢产物生成量的方式来表征化合物的转化效率,但对于不同代谢产物的定量以及二级代谢产物的表征是非常复杂的过程,难于准确获得OPEs的转化比例,且组织特异性代谢对其在生物体内的残留物也有不同的影响,因此还需进一步研究不同生物体和不同组织内OPEs的转化机制,有助于掌握其生物富集行为.
此外,前文提到疏水性 (lgKow>5) 强的OPEs容易发生生物富集,可能在食物网中发生放大[100,109,119-120],如异癸磷酸二苯酯(IDPP)被发现能够在红树林生态系统食物链中发生生物放大作用[109]. 但生物体内OPEs的代谢转化也会削弱其在食物链及食物网中的放大效应. Wang等[100]的研究中发现,尽管EHDPP的lgKow=5.73,但富集于体内后由于降解作用综合效应测定的营养级放大因子TMF仅为3.61. 目前有研究发现OPEs在部分流域食物网中具有生物放大效应,如中国莱州湾海峡 [119],安大略湖、伊利湖[121]、Nakdong River[104]以及西方斯凯尔特河河口淡水区[104],但也有研究指出菲律宾马尼拉湾海峡食物网[111]中未发现OPEs具有放大效应,这主要与生物种类以及区域环境因子紧密相关. 例如Ding等[120]研究中7种OPEs在热带地区水生食物网中的 TMFs值低于温带和寒带地区. 目前,关于 OPE 生物放大的研究主要集中于水生生物食物网,研究结果有限而尚无定论[122]. 因此,为全面掌握OPEs的生物富集过程应继续开展陆生生物食物网的相关研究.
目前,针对OPEs在生物体内的富集多基于水生生物,如斑马鱼、鲈鱼等. 用于斑马鱼体内的毒代动力学模型(PBPK)表明,尽管富集于体内的部分OPEs发生了代谢转化,但是母体化合物仍有超过50%的剩余,而OPEs的分配过程则主导其富集作用. 有研究计算了斑马鱼组织内TDCIPP,TPHP和TnBP的分配系数为0.03—0.91,同时OPEs的lgBCF与lgKow具有明显的相关性(P<0.01),表明OPEs的疏水性在分配以及体腔沉积过程至关重要[108].再者,沉积物作为水生系统中OPEs的重要储存库,也是底栖生物的主要暴露源. OPEs的有机碳-水分配系数范围较广,进而在水和颗粒物之间的分配差异性较大,也会影响OPEs在生物体内的利用性及随后的富集行为. 如Zhang等[123]在珠江三角洲区域的研究发现OPEs在不同采样点水样中的主要检出同类物具有明显差异性,但OPEs在水体和颗粒物之间的分配导致了不同采样点中悬浮颗粒物中OPEs的组成相似. 同时该计算TNBP、TCEP和TCIPP的沉积物富集因子lgBSAF均小于1,说明其具有较低的生物体潜在富集性.
-
OPEs一旦通过植物进入食物链将逐级积累,可能产生生物放大效应,最终危害人类健康. 近年来,对于OPEs的植物吸收研究主要集中于实验室的水培试验,野外暴露试验较少. 植物吸收主要包括根、茎、叶对OPEs的吸附、节流以及吸收分解等. 一般情况下,根的吸收能力高于茎和叶.
(1) 植物吸收
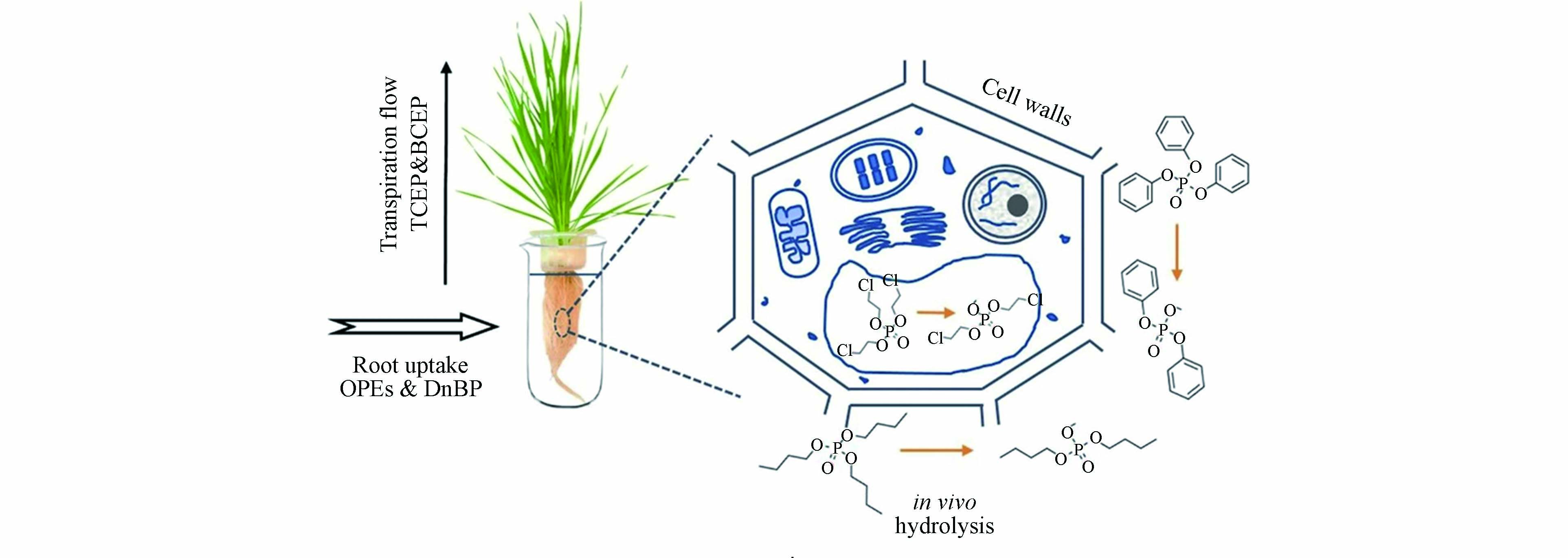
OPEs自身的理化性质(疏水性)是影响植物吸收的重要因素,疏水性越高的OPEs越容易被根部吸收,疏水性越弱的OPEs更易向顶部转移[124-125]. Liu等[126]发现小麦根部吸收中蒸腾作用是疏水性化合物吸收的动力,4种OPEs的吸收速率表现为TCIPP> TBOEP>TPHP>TEHP,与其lgKow呈正相关(P<0.05),并指出疏水性是决定OPEs在植物根部(尤其是根脂质部位)吸收中的重要性. 而Gong等[127]则继续深入探究了小麦对水解产物磷酸二酯的植物吸收机制,探究了其在小麦体内的吸收机制,并指出该类水解产物可进一步发生根吸收主要分布于细胞壁间隙且难以发生跨膜运输,能够稳定存在于植物体内(图1). 此外,植物的特性、植物根系的脂质和蛋白质含量、微生物群落等因素也直接影响植物对污染物的吸收行为,涉及到植物叶面积、蒸腾系数等因素. Liu等[126]的研究指出根部和植物细胞液中蛋白质的含量在OPEs的吸收中扮演重要角色,蛋白质含量越高,吸收速率越快,并指出吸收机理包括两个方面,一方面对于疏水性低的化合物主要是通过蒸腾流作用,而对于高疏水性OPEs则是与nsLTP蛋白质相结合进入根部脂质部位而被富集.
与先前的研究不同,Wang等[128]探究了沿海地带典型植被翅碱蓬对OPEs的吸附作用,发现OPEs的lgRCF与Kow,以及不同取代基OPEs的lgTF与Kow之间无明显相关性,说明不同植被对OPEs吸附过程具有不同的影响. 与室内实验相比,野外采样监测主要体现了植物对OPEs吸附的长期动态平衡过程.
(2) 代谢转化及机制
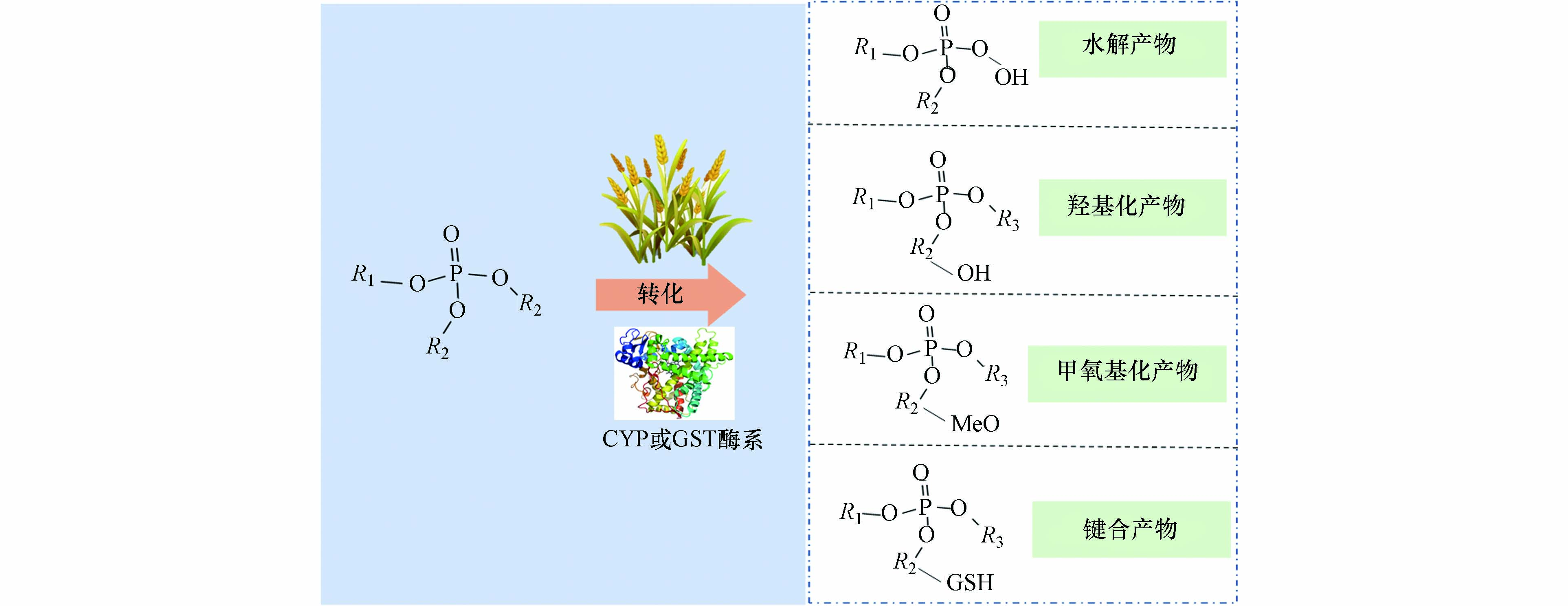
进入植物体内的OPEs可能发生代谢和水解反应. Wan等[125]在小麦的代谢产物中发现了包含脱氯、羟基化、脱烷基、谷胱甘肽以及葡萄苷酸键合等产物的生成(图2),且脱烷基生成的二酯类化合物为主要产物. 研究还发现,小麦体内OPEs的代谢产物与母体化合物相较具有更强的极性,lgKow值更低,因此更容易发生迁移. 同时,该研究首次在小麦体内发现了羟基化OPEs的代谢产物. 而值得注意的是,部分OPEs的羟基化代谢产物的内分泌干扰效应比母体化合物更强[129].
进入植物体后,OPEs能够与植物大分子发生键合,例如反应活性酶CYP酶系和基因表达酶系GST酶系. 这些反应活性酶具有疏水性,含有活性空穴,易与OPEs通过范德华力而完成对接. 同时,OPEs与植物大分子发生键合的能力与其疏水性呈正相关,进一步验证了植物吸收OPEs的主要途径是疏水分配. 与植物大分子键合反应受到OPEs自身结构影响,其中,卤代OPEs容易与GSH酶系键合,而非卤代OPEs更容易与CYP酶系键合生成反应产物.
-
微生物降解是环境中污染物有效的去除方式之一,能够避免因化学降解以及焚烧等处理方式产生的二次污染. 土壤以及海洋环境中有多种微生物能够将OPEs作为碳源、磷源等使其降解. 生物降解过程中P—O—烷基和P—O—芳基的水解是微生物降解的主要步骤[130]. 前人指出微生物利用磷酸水解酶可以将OPEs的支链水解,断裂酯键而快速降解OPEs[130]. 因此,筛选能够有效降解OPEs的微生物菌群可为土壤中污染物的去除提供有效支撑.
目前,已有研究筛选出多种具有降解OPEs能力的菌种,如Serratia odorifera [131]、 Sphingobium[132], Aspergillus niger [133]、Trichoderma hazianmum [134]、 Bacillus cereus [135] 等. Berne等[131,136]在受TnBP污染的土壤中分离出Serratia odorifera和Rhodopseudomonas palustris菌株,能够有效降解TnBP,且光照条件更有利于菌株的降解效率,21 d的去除率达80%. 近年来,研究学者开始逐渐探究海洋和沉积物中生物降解的相关基因和酶系,用以确认生物降解的机制. Takahashi等[130]用TCEP和TDCIPP作为唯一磷源来筛选能够降解Cl-OPEs的菌种,分离纯化后得到两种菌株并纯化克隆出两种卤代烷基磷水解酶(TCM-HAD和TDK-HAD),能够应用于土壤修复.
-
OPEs在环境中的迁移转化途径主要包括大气传输/沉降、吸附/解吸、光解、生物富集和转化、植物吸收以及微生物降解等,其中光转化和生物转化能够有效的将OPEs去除,但实际环境中光转化强度较弱,降解去除速率缓慢,导致OPEs会不断在环境介质中积累进而对生态环境和人体健康产生潜在的危害. 本文综述了OPEs环境中可能发生的物理、化学和生物过程,重点论述了OPEs的生物转化过程中吸收富集和代谢转化过程及机制,为后续环境中OPEs的归驱和生态风险评估等相关研究提供理论依据. 目前,有关环境介质中OPEs的检测以及迁移转化机制的研究有限,建议未来OPEs的研究可继续考虑以下几个方面:
(1)现有对OPEs迁移转化的研究多集中于两种介质之间,对于全面评估和掌握实际环境中OPEs的归驱具有一定局限性,应结合小型流域或小型生态系统中多种介质(如水-沉积物-生物体)的迁移转化过程进行深入分析,探究其过程及机制.
(2) 针对生物过程中OPEs生物富集的研究多集中室内养殖小型生物实验,鉴于受试生物的有限性和“3R”原则,应考虑结合不同生物体内OPEs的检出水平和自身理化学特性,建立该类化合物的定量构效关系(QASR)模型预测和评估OPEs在生物体内的富集和代谢过程及转化机制,一方面可以与实验测定结果相互验证,另一方面可补充缺少的其他物种富集信息,进而更全面的掌握生物富集过程.
(3)目前有关OPEs代谢转化的研究多集中于追踪其自身的变化,尚缺乏针对该过程中产生中间体及终产物的相关特性(如疏水性,持久性和毒性等)研究,特别是这些产物的环境行为以及其对环境伤害的风险评估和对人体的安全性评估,建议进一步开展这方面相关研究,有助于评估OPEs的应用前景和管理措施的制定.
新污染物有机磷酸酯生物地球化学过程的研究进展
Research progress on biogeochemical process of emerging contaminants organophosphate esters
-
摘要: 有机磷酸酯(organophosphate esters,OPEs)作为阻燃剂和增塑剂广泛应用于建筑材料和电子产品等材料,随着生产和使用量的增加,导致其普遍存在于各种环境介质中. 作为一类新污染物,OPEs的环境行为及归趋引起了越来越多环境学者的关注. 本文系统阐述了OPEs在环境中可能发生的物理、化学和生物过程. 现有研究表明:(1) OPEs自身理化性质和结构(疏水性和π-π效应)是影响其迁移转化过程的重要因素;(2) 复杂的介质环境 (温度、pH值、溶解性有机质、氧化活性物种等)能够影响OPEs的大气传输/沉降、吸附/解吸、水解、光解、生物富集和植物吸收等过程;(3) OPEs在迁移转化中能生成二酯或单酯类产物(化学键断裂)、羟基化产物、甲氧基化产物以及其他小分子化合物等. 针对目前的研究现状建议未来可重点关注OPEs在小型生态系统中多介质中的迁移转化过程与机制以及在迁移转化过程中生成产物的理化特性与生物效应等.Abstract: Organophosphate esters (OPEs) are the most widely used flame retardants and plasticizers in building materials and electronic products, etc. The increasing widespread use and production have resulted in their ubiquitous occurrence in the environment. As emerging contaminants, the environmental behaviors and fates of OPEs are attracting the attention of more and more scholars. In this article, the physical, chemical and biological processes of OPEs that may occur in the environment are systematically reviewed. Firstly, the physicochemical properties and structure of OPEs (hydrophobicity and π-π interaction) are important factors that influence their migration and transformation processes. Secondly, the complex media environment including temperature, pH, dissolved organic matter, oxidatively active species, etc. will affect the atmospheric transport/ deposition, adsorption/desorption, hydrolysis, photolysis, bioconcentration and plant uptake of OPEs. Thirdly, diester or monoester products from breakage of chemical bonds, hydroxylation products, methoxylation products, and other small molecule compounds can be generated by OPEs in the processes of migration and transformation. The study puts forward a prospect for future research on the migration and transformation processes and mechanisms of OPEs in multi-media of microecosystems as well as the physicochemical properties and biological effects of the products generated during the migration and transformation.
-

-
表 1 环境介质中常见和新型OPEs的理化性质和主要用途[9-13]
Table 1. Physicochemical properties and main application of traditional and emerging organophosphate esters in environments
化合物
Compounds简称
AbbreviationCAS 25 ℃时水
中溶解度/
( mg·L−1)
Solubility25 ℃时
蒸气压/
(mm Hg )
Vapor pressure正辛醇-
水分配
系数lg Kow正辛醇-空
气分配系数
lg Koa主要用途
Main
application传统
OPEs磷酸三乙酯(Triethyl phosphate) TEP 78-40-0 — 3.93 × 10−1 0.80 5.6 阻燃剂 磷酸三丙酯
(Tri-n-propyl phosphate)TPP 513-08-6 6.43× 103 2.31 × 10−2 2.35 6.42 阻燃剂、增塑剂 磷酸三丁酯
(Tri-n-butyl phosphate)TnBP 126-73-8 7.36 3.49 × 10−3 3.82 8.24 消泡剂、增塑剂 磷酸三-(2-氯乙基)酯
(Tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate)TCEP 115-96-8 7.00 × 103 3.91 × 10−4 1.63 7.42 阻燃剂 磷酸三-氯(2-氯异丙基)酯
(Tris(2-chloroisopropyl) phosphate)TCIPP 13674-84-5 1.20 × 103 5.64 × 10−5 2.89 8.20 阻燃剂 磷酸三(1,3-二氯-2-丙基)酯
(Tris(1,3-dichloroisopropyl) phosphate)TDCIPP 13674-87-8 7.00 2.86 × 10−7 3.65 10.6 阻燃剂 磷酸三(2-丁氧乙基)酯
(Tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate )TBOEP 78-51-3 1.10 × 103 1.23 × 10−6 3.00 13.0 增塑剂、消泡剂 磷酸三苯酯(Triphenyl phosphate) TPHP 115-86-6 1.90 4.72 × 10−7 4.70 8.45 消泡剂、增塑剂 新型
OPEs磷酸三异癸酯 triisodecyl phosphate TiDeP 29733-20-8 — 2.74 × 10−6 12.4 14.1 阻燃剂 磷酸三壬基酚酯
Trisnonylphenol phosphateTNPP 26523-78-4 — 2.74 × 10−6 18.1 20.8 阻燃剂 双酚A双(磷酸二苯酯)
(Bisphenol A bis(diphenyl phosphate))BPA-BDPP 5945-33-5 阻燃剂 磷酸甲酚二苯酯
(Cresyl diphenyl phosphate)CDP 26444-49-5 增塑剂、阻燃剂 磷酸三(2,4-二-叔-丁基苯基)酯 (tris(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphate) AO168 95906-11-9 — 2.74 × 10−6 16.2 19.5 阻燃剂 双(2,4-二叔丁基苯基)异戊四醇磷酸二酯(bis(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl) pentaerythritol diphosphate) AO626 97994-11-1 — 2.74 × 10−6 9.8 19.9 阻燃剂 表 2 不同介质上OPEs的吸附
Table 2. Adsorption of OPEs on different media
吸附介质
Adsorption medium模型化合物
Model compounds吸附动力学模型
Adsorption dynamic model吸附等温线
Adsorption isotherm气-固 不锈钢介质[65] TCEP Freundich等温式 液-固 沸石吸附剂[66] TCEP Langmuir等温式 沉积物[67] TPHP 准二级动力学模型 Langmuir等温式 微塑料[68] TnBP, TCEP 准二级动力学模型 Freundich等温式 TCEP 准二级动力学模型 Langmuir等温式 石墨烯纳米材料[69] TCP 准二级动力学模型 Langmuir等温式 碳纳米管[70] TnBP, TCEP, TPHP Dubinin–Ashtakhov 模型 树脂[71] TPHP 准二级动力学模型 Langmuir等温式 土壤[72] TDCP, TCIPP 准二级动力学模型 -
[1] 高小中, 许宜平, 王子健. 有机磷酸酯阻燃剂的环境暴露与迁移转化研究进展 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(2): 56-68. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20150103001 GAO X Z, XU Y P, WANG Z J. Progress in environment exposure, transport and transform of organophosphorus flame retardants [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(2): 56-68(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20150103001
[2] MIYAKE Y, TOKUMURA M, WANG Q, et al. Identification of novel phosphorus-based flame retardants in curtains purchased in Japan using orbitrap mass spectrometry [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2018, 5(7): 448-455. [3] ISETUN S, NILSSON U, COLMSJÖ A. Evaluation of solid-phase microextraction with PDMS for air sampling of gaseous organophosphate flame-retardants and plasticizers [J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2004, 380(2): 319-324. doi: 10.1007/s00216-004-2760-5 [4] ISETUN S, NILSSON U, COLMSJÖ A, et al. Air sampling of organophosphate triesters using SPME under non-equilibrium conditions [J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2004, 378(7): 1847-1853. doi: 10.1007/s00216-003-2489-6 [5] GREAVES A K, LETCHER R J. A review of organophosphate esters in the environment from biological effects to distribution and fate [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2017, 98(1): 2-7. doi: 10.1007/s00128-016-1898-0 [6] ANDRESEN J A, GRUNDMANN A, BESTER K. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticisers in surface waters [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2004, 332(1/2/3): 155-166. [7] WEI G L, LI D Q, ZHUO M N, et al. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers: Sources, occurrence, toxicity and human exposure [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2015, 196: 29-46. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2014.09.012 [8] van der VEEN I, de BOER J. Phosphorus flame retardants: Properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis [J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 88(10): 1119-1153. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.067 [9] LIU X T, CHEN D, YU Y J, et al. Novel organophosphate esters in airborne particulate matters: Occurrences, precursors, and selected transformation products [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(21): 13771-13777. [10] TAN H L, CHEN D, PENG C F, et al. Novel and traditional organophosphate esters in house dust from South China: Association with hand wipes and exposure estimation [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(19): 11017-11026. [11] CAO Z G, ZHAO L C, ZHANG Y C, et al. Influence of air pollution on inhalation and dermal exposure of human to organophosphate flame retardants: A case study during a prolonged haze episode [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(7): 3880-3887. [12] SUN Y, LIU L Y, SVERKO E, et al. Organophosphate flame retardants in college dormitory dust of northern Chinese cities: Occurrence, human exposure and risk assessment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 665: 731-738. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.098 [13] WANG Y, SUN H W, ZHU H K, et al. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs) in soil and outdoor settled dust from a multi-waste recycling area in China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 625: 1056-1064. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.013 [14] ABDALLAH M A E, COVACI A. Organophosphate flame retardants in indoor dust from Egypt: Implications for human exposure [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(9): 4782-4789. [15] WANG G G, LIU Y, ZHAO X D, et al. Geographical distributions and human exposure of organophosphate esters in college library dust from Chinese cities [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 255: 113332. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113332 [16] RAUERT C, SCHUSTER J K, ENG A, et al. Global atmospheric concentrations of brominated and chlorinated flame retardants and organophosphate esters [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(5): 2777-2789. [17] SALAMOVA A, MA Y N, VENIER M, et al. High levels of organophosphate flame retardants in the great lakes atmosphere [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2014, 1(1): 8-14. [18] SHOEIB M, AHRENS L, JANTUNEN L, et al. Concentrations in air of organobromine, organochlorine and organophosphate flame retardants in Toronto, Canada [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 99: 140-147. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.09.040 [19] WONG F, de WIT C A, NEWTON S R. Concentrations and variability of organophosphate esters, halogenated flame retardants, and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in indoor and outdoor air in Stockholm, Sweden [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 240: 514-522. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.086 [20] KHAN M U, LI J, ZHANG G, et al. First insight into the levels and distribution of flame retardants in potable water in Pakistan: An underestimated problem with an associated health risk diagnosis [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 565: 346-359. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.173 [21] GUO J H, ROMANAK K, WESTENBROEK S, et al. Current-use flame retardants in the water of lake Michigan tributaries [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(17): 9960-9969. [22] CRISTALE J, ARAGÃO BELÉ T G, LACORTE S, et al. Occurrence and human exposure to brominated and organophosphorus flame retardants via indoor dust in a Brazilian City [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 237: 695-703. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.110 [23] GIULIVO M, CAPRI E, KALOGIANNI E, et al. Occurrence of halogenated and organophosphate flame retardants in sediment and fish samples from three European River basins [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 586: 782-791. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.056 [24] MA Y X, XIE Z Y, LOHMANN R, et al. Organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in ocean sediments from the north Pacific to the Arctic ocean [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(7): 3809-3815. [25] SUTTON R, da CHEN, SUN J, et al. Characterization of brominated, chlorinated, and phosphate flame retardants in San Francisco Bay, an urban estuary [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 652: 212-223. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.096 [26] MEEKER J D, COOPER E M, STAPLETON H M, et al. Urinary metabolites of organophosphate flame retardants: Temporal variability and correlations with house dust concentrations [J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2013, 121(5): 580-585. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1205907 [27] DISHAW L V, HUNTER D L, PADNOS B, et al. Developmental exposure to organophosphate flame retardants elicits overt toxicity and alters behavior in early life stage zebrafish (Danio rerio) [J]. Toxicological Sciences, 2014, 142(2): 445-454. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu194 [28] JAREMA K A, HUNTER D L, SHAFFER R M, et al. Acute and developmental behavioral effects of flame retardants and related chemicals in zebrafish [J]. Neurotoxicology and Teratology, 2015, 52: 194-209. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2015.08.010 [29] HAN Z H, WANG Q W, FU J, et al. Multiple bio-analytical methods to reveal possible molecular mechanisms of developmental toxicity in zebrafish embryos/larvae exposed to tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2014, 150: 175-181. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.03.013 [30] BEHL M, HSIEH J H, SHAFER T J, et al. Use of alternative assays to identify and prioritize organophosphorus flame retardants for potential developmental and neurotoxicity [J]. Neurotoxicology and Teratology, 2015, 52: 181-193. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2015.09.003 [31] DU Z K, WANG G W, GAO S X, et al. Aryl organophosphate flame retardants induced cardiotoxicity during zebrafish embryogenesis: By disturbing expression of the transcriptional regulators [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2015, 161: 25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.01.027 [32] FARHAT A, CRUMP D, CHIU S, et al. In ovo effects of two organophosphate flame retardants—TCPP and TDCPP—on pipping success, development, mRNA expression, and thyroid hormone levels in chicken embryos [J]. Toxicological Sciences, 2013, 134(1): 92-102. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft100 [33] KOJIMA H, TAKEUCHI S, ITOH T, et al. In vitro endocrine disruption potential of organophosphate flame retardants via human nuclear receptors [J]. Toxicology, 2013, 314(1): 76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2013.09.004 [34] WANG Q W, LAM J C W, HAN J, et al. Developmental exposure to the organophosphorus flame retardant tris(1, 3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate: Estrogenic activity, endocrine disruption and reproductive effects on zebrafish [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2015, 160: 163-171. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.01.014 [35] ZHU Y, MA X F, SU G Y, et al. Environmentally relevant concentrations of the flame retardant tris(1, 3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate inhibit growth of female zebrafish and decrease fecundity [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(24): 14579-14587. [36] European Commission, 2014. Commission directive 2014/79/EU of 20 June 2014 amending appendix C of annex II to directive 2009/48/EC of the European Parliament and of the council on the safety of toys, as regards TCEP, TCPP and TDCP. Off. J. Eur. Union 182, 49–51. [37] WANG X, ZHU Q Q, YAN X T, et al. A review of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in the environment: Analysis, occurrence and risk assessment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 731: 139071. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139071 [38] YANG J W, ZHAO Y Y, LI M H, et al. A review of a class of emerging contaminants: The classification, distribution, intensity of consumption, synthesis routes, environmental effects and expectation of pollution abatement to organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs) [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(12): 2874. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122874 [39] PATISAUL H B, BEHL M, BIRNBAUM L S, et al. Beyond cholinesterase inhibition: Developmental neurotoxicity of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers [J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2021, 129(10): 105001. doi: 10.1289/EHP9285 [40] HOU R, XU Y P, WANG Z J. Review of OPFRs in animals and humans: Absorption, bioaccumulation, metabolism, and internal exposure research [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 153: 78-90. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.003 [41] MIHAJLOVIĆ I, FRIES E. Atmospheric deposition of chlorinated organophosphate flame retardants (OFR) onto soils [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2012, 56: 177-183. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.03.054 [42] CASTRO-JIMÉNEZ J, GONZÁLEZ-GAYA B, PIZARRO M, et al. Organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in the global oceanic atmosphere [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(23): 12831-12839. [43] SÜHRING R, DIAMOND M L, SCHERINGER M, et al. Organophosphate esters in Canadian Arctic air: Occurrence, levels and trends [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(14): 7409-7415. [44] SÜHRING R, WOLSCHKE H, DIAMOND M L, et al. Distribution of organophosphate esters between the gas and particle phase-model predictions vs measured data [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(13): 6644-6651. [45] NA G S, HOU C, LI R J, et al. Occurrence, distribution, air-seawater exchange and atmospheric deposition of organophosphate esters (OPEs) from the Northwestern Pacific to the Arctic Ocean [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 157: 111243. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111243 [46] MÖLLER A, STURM R, XIE Z Y, et al. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in airborne particles over the Northern Pacific and Indian Ocean toward the Polar Regions: Evidence for global occurrence [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(6): 3127-3134. [47] SALAMOVA A, HERMANSON M H, HITES R A. Organophosphate and halogenated flame retardants in atmospheric particles from a European Arctic site [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(11): 6133-6140. [48] LIU Y C, LIGGIO J, HARNER T, et al. Heterogeneous OH initiated oxidation: A possible explanation for the persistence of organophosphate flame retardants in air [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(2): 1041-1048. [49] MARKLUND A, ANDERSSON B, HAGLUND P. Traffic as a source of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in snow [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(10): 3555-3562. [50] REGNERY J, PÜTTMANN W. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in rain and snow from middle Germany [J]. CLEAN - Soil, Air, Water, 2009, 37(4/5): 334-342. [51] LI J, XIE Z Y, MI W Y, et al. Organophosphate esters in air, snow, and seawater in the north Atlantic and the Arctic [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(12): 6887-6896. [52] FRIES E, MIHAJLOVIĆ I. Pollution of soils with organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers [J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring:JEM, 2011, 13(10): 2692-2694. doi: 10.1039/c1em10538h [53] MIHAJLOVI I, MILORADOV M V, FRIES E. Application of Twisselmann extraction, SPME, and GC-MS to assess input sources for organophosphate esters into soil [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(6): 2264-2269. [54] 侯超. 极地大气有机磷酸酯介质分配机制研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2020. HOU C. Research on the medium partitioning mechanism of atmospheric organophosphate esters in polar regions[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2020(in Chinese).
[55] RODGERS T F M, TRUONG J W, JANTUNEN L M, et al. Organophosphate ester transport, fate, and emissions in Toronto, Canada, estimated using an updated multimedia urban model [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(21): 12465-12474. [56] WANG X L, ZHU L Y, ZHONG W J, et al. Partition and source identification of organophosphate esters in the water and sediment of Taihu Lake, China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 360: 43-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.07.082 [57] SCHREDER E D, la GUARDIA M J. Flame retardant transfers from US households (dust and laundry wastewater) to the aquatic environment [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(19): 11575-11583. [58] DENG M J, KUO D T F, WU Q H, et al. Organophosphorus flame retardants and heavy metals in municipal landfill leachate treatment system in Guangzhou, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 236: 137-145. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.042 [59] WOUDNEH M B, BENSKIN J P, WANG G H, et al. Quantitative determination of 13 organophosphorous flame retardants and plasticizers in a wastewater treatment system by high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2015, 1400: 149-155. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.04.026 [60] FRIES E, PÜTTMANN W. Monitoring of the three organophosphate esters TBP, TCEP and TBEP in river water and ground water (Oder, Germany) [J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 2003, 5(2): 346-352. doi: 10.1039/b210342g [61] FRIES E, PUTTMANN W. Occurrence of organophosphate esters in surface water and ground water in Germany [J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 2001, 3(6): 621-626. doi: 10.1039/b105072a [62] ZHENG H Y, CAI M H, YANG C, et al. Terrigenous export and ocean currents' diffusion of organophosphorus flame retardants along China's adjacent seas [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 299: 118873. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.118873 [63] FANG L D, LIU A F, ZHENG M G, et al. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate flame retardants in seawater and sediment from coastal areas of the East China and Yellow Seas [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 302: 119017. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119017 [64] ZHANG L J, WANG Y, TAN F, et al. Tidal variability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organophosphate esters in the coastal seawater of Dalian, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 708: 134441. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134441 [65] LIANG Y, LIU X, ALLEN M R. Measuring and modeling surface sorption dynamics of organophosphate flame retardants on impervious surfaces [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 193: 754-762. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.080 [66] GRIECO S A, RAMARAO B V. Removal of TCEP from aqueous solutions by adsorption with zeolites [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2013, 434: 329-338. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.04.042 [67] WANG P F, LI D D, FAN X L, et al. Sorption and desorption behaviors of triphenyl phosphate (TPhP) and its degradation intermediates on aquatic sediments [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 385: 121574. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121574 [68] CHEN S P, TAN Z R, QI Y S, et al. Sorption of tri-n-butyl phosphate and tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate on polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride microplastics in seawater [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 149: 110490. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110490 [69] LIU J, XIA S Y, LÜ X, et al. Adsorption of tricresyl phosphate onto graphene nanomaterials from aqueous solution [J]. Water Science and Technology, 2017, 76(6): 1565-1573. doi: 10.2166/wst.2017.317 [70] YAN W, YAN L, DUAN J M, et al. Sorption of organophosphate esters by carbon nanotubes [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 273: 53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.03.030 [71] WANG W, DENG S B, LI D Y, et al. Adsorptive removal of organophosphate flame retardants from water by non-ionic resins [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 354: 105-112. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.002 [72] ZHENG C L, FENG S S, WANG Q R, et al. Application of SPME-GC/MS to study the sorption of organophosphate esters on peat soil [J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2016, 227(7): 1-12. [73] WANG W, DENG S B, LI D Y, et al. Sorption behavior and mechanism of organophosphate flame retardants on activated carbons [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 332: 286-292. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.085 [74] HO Y S, MCKAY G. The sorption of lead(II) ions on peat [J]. Water Research, 1999, 33(2): 578-584. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00207-3 [75] PANG L, LIU J F, YIN Y G, et al. Evaluating the sorption of organophosphate esters to different sourced humic acids and its effects on the toxicity to Daphnia magna [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2013, 32(12): 2755-2761. doi: 10.1002/etc.2360 [76] CRISTALE J, ÁLVAREZ-MARTÍN A, RODRÍGUEZ-CRUZ S, et al. Sorption and desorption of organophosphate esters with different hydrophobicity by soils [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2017, 24(36): 27870-27878. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0360-0 [77] BLUMENTHAL E, HERBERT J B M. The mechanism of the hydrolysis of trimethyl orthophosphate [J]. Transactions of the Faraday Society, 1945, 41: 611. doi: 10.1039/tf9454100611 [78] SU G Y, LETCHER R J, YU H X. Organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in aqueous solution: PH-dependent hydrolysis, kinetics, and pathways [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(15): 8103-8111. [79] SU G Y, CRUMP D, LETCHER R J, et al. Rapid in vitro metabolism of the flame retardant triphenyl phosphate and effects on cytotoxicity and mRNA expression in chicken embryonic hepatocytes [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(22): 13511-13519. [80] SMOLEN J M, STONE A T. Divalent metal ion-catalyzed hydrolysis of phosphorothionate ester pesticides and their corresponding oxonates [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1997, 31(6): 1664-1673. [81] FANG Y D, KIM E, STRATHMANN T J. Mineral- and base-catalyzed hydrolysis of organophosphate flame retardants: Potential major fate-controlling sink in soil and aquatic environments [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(4): 1997-2006. [82] BALDWIN D S, BEATTIE J K, COLEMAN L M, et al. Hydrolysis of an organophosphate ester by manganese dioxide [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2001, 35(4): 713-716. [83] LIU Q F, LIGGIO J, LI K, et al. Understanding the impact of relative humidity and coexisting soluble iron on the OH-initiated heterogeneous oxidation of organophosphate flame retardants [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(12): 6794-6803. [84] ZHANG Q Y, WANG Y, ZHANG C, et al. A review of organophosphate esters in soil: Implications for the potential source, transfer, and transformation mechanism [J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 204: 112122. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112122 [85] SUN S B, JIANG J Q, ZHAO H X, et al. Photochemical reaction of tricresyl phosphate (TCP) in aqueous solution: Influencing factors and photolysis products [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 241: 124971. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124971 [86] CRISTALE J, DANTAS R F, de LUCA A, et al. Role of oxygen and DOM in sunlight induced photodegradation of organophosphorous flame retardants in river water [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 323: 242-249. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.019 [87] REGNERY J, PÜTTMANN W. Occurrence and fate of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in urban and remote surface waters in Germany [J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(14): 4097-4104. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.05.024 [88] XU X X, CHEN J, QU R J, et al. Oxidation of Tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate in aqueous solution by UV-activated peroxymonosulfate: Kinetics, water matrix effects, degradation products and reaction pathways [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 185: 833-843. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.090 [89] 刘佳. 有机磷酸酯阻燃剂污染现状及降解过程研究进展 [J]. 应用化工, 2018, 47(12): 2705-2710,2714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2018.12.036 LIU J. Review of contamination status and degradation processes of organophosphate ester(OPE) flame retardants [J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(12): 2705-2710,2714(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2018.12.036
[90] ANTONOPOULOU M, KARAGIANNI P, KONSTANTINOU I K. Kinetic and mechanistic study of photocatalytic degradation of flame retardant Tris (1-chloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TCPP) [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 192: 152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.03.039 [91] RUAN X C, AI R, JIN X, et al. Photodegradation of tri (2-chloroethyl) phosphate in aqueous solution by UV/H2O2 [J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2012, 224(1): 1-10. [92] WATTS M J, LINDEN K G. Advanced oxidation kinetics of aqueous trialkyl phosphate flame retardants and plasticizers [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(8): 2937-2942. [93] YUAN X J, LACORTE S, CRISTALE J, et al. Removal of organophosphate esters from municipal secondary effluent by ozone and UV/H2O2 treatments [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2015, 156: 1028-1034. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2015.09.052 [94] ANTONOPOULOU M, GIANNAKAS A, BAIRAMIS F, et al. Degradation of organophosphorus flame retardant tris (1-chloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TCPP) by visible light N, S-codoped TiO2 photocatalysts [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 318: 231-239. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.124 [95] KONSTAS P S, HELA D, GIANNAKAS A, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of organophosphate flame retardant TBEP: Kinetics and identification of transformation products by orbitrap mass spectrometry [J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 99(4): 297-309. doi: 10.1080/03067319.2019.1593399 [96] LIU J, YE J S, CHEN Y F, et al. UV-driven hydroxyl radical oxidation of tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate: Intermediate products and residual toxicity [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 190: 225-233. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.111 [97] KIM T S, KIM J K, CHOI K, et al. Degradation mechanism and the toxicity assessment in TiO2 photocatalysis and photolysis of parathion [J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 62(6): 926-933. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.05.038 [98] ZHAO H X, JIANG J Q, WANG Y L, et al. Monohydroxylated polybrominated diphenyl ethers (OH-PBDEs) and dihydroxylated polybrominated biphenyls (di-OH-PBBs): Novel photoproducts of 2, 6-dibromophenol [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(24): 14120-14128. [99] SAEGER V W, HICKS O, KALEY R G, et al. Environmental fate of selected phosphate esters [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1979, 13(7): 840-844. [100] WANG X L, ZHONG W J, XIAO B W, et al. Bioavailability and biomagnification of organophosphate esters in the food web of Taihu Lake, China: Impacts of chemical properties and metabolism [J]. Environment International, 2019, 125: 25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.018 [101] HOU R, LIU C, GAO X Z, et al. Accumulation and distribution of organophosphate flame retardants (PFRs) and their di-alkyl phosphates (DAPs) metabolites in different freshwater fish from locations around Beijing, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 229: 548-556. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.06.097 [102] ROBINSON S A, YOUNG S D, BRINOVCAR C, et al. Ecotoxicity assessment and bioconcentration of a highly brominated organophosphate ester flame retardant in two amphibian species [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 260: 127631. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127631 [103] HALLANGER I G, SAGERUP K, EVENSET A, et al. Organophosphorous flame retardants in biota from svalbard, Norway [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 101(1): 442-447. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.09.049 [104] LI Y, KANG Q Y, CHEN R C, et al. 2-ethylhexyl diphenyl phosphate and its hydroxylated metabolites are anti-androgenic and cause adverse reproductive outcomes in male Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(14): 8919-8925. [105] ZHANG R J, YU K F, LI A, et al. Occurrence, phase distribution, and bioaccumulation of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in mariculture farms of the Beibu Gulf, China: A health risk assessment through seafood consumption [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 263: 114426. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114426 [106] BEKELE T G, ZHAO H X, WANG Y, et al. Measurement and prediction of bioconcentration factors of organophosphate flame retardants in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 166: 270-276. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.089 [107] WANG Q W, LAM J C W, MAN Y C, et al. Bioconcentration, metabolism and neurotoxicity of the organophorous flame retardant 1, 3-dichloro 2-propyl phosphate (TDCPP) to zebrafish [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2015, 158: 108-115. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.11.001 [108] WANG G W, SHI H H, DU Z K, et al. Bioaccumulation mechanism of organophosphate esters in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 229: 177-187. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.075 [109] XIE J L, PEI N C, SUN Y X, et al. Bioaccumulation and translocation of organophosphate esters in a mangrove nature reserve from the Pearl River Estuary, South China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 427: 127909. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127909 [110] LIU Y E, LUO X J, ZAPATA CORELLA P, et al. Organophosphorus flame retardants in a typical freshwater food web: Bioaccumulation factors, tissue distribution, and trophic transfer [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 255: 113286. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113286 [111] KIM J W, ISOBE T, CHANG K H, et al. Levels and distribution of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in fishes from Manila Bay, the Philippines [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(12): 3653-3659. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.07.020 [112] da CHEN, LETCHER R J, CHU S G. Determination of non-halogenated, chlorinated and brominated organophosphate flame retardants in herring gull eggs based on liquid chromatography-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2012, 1220: 169-174. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.11.046 [113] BRANDSMA S H, LEONARDS P E G, LESLIE H A, et al. Tracing organophosphorus and brominated flame retardants and plasticizers in an estuarine food web [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 505: 22-31. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.08.072 [114] SUNDKVIST A M, OLOFSSON U, HAGLUND P. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in marine and fresh water biota and in human milk [J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 2010, 12(4): 943-951. doi: 10.1039/b921910b [115] HOU R, HUANG C, RAO K F, et al. Characterized in vitro metabolism kinetics of alkyl organophosphate esters in fish liver and intestinal microsomes [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(5): 3202-3210. [116] GREAVES A K, SU G Y, LETCHER R J. Environmentally relevant organophosphate triesters in herring gulls: in vitro biotransformation and kinetics and diester metabolite formation using a hepatic microsomal assay [J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2016, 308: 59-65. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.08.007 [117] STROBEL A, LETCHER R J, WILLMORE W G, et al. Structure-dependent in vitro metabolism of alkyl-substituted analogues of triphenyl phosphate in east Greenland polar bears and ringed seals [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2018, 5(4): 214-219. [118] ZHANG Q, JI S J, CHAI L H, et al. Metabolic mechanism of aryl phosphorus flame retardants by cytochromes P450: A combined experimental and computational study on triphenyl phosphate [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(24): 14411-14421. [119] BEKELE T G, ZHAO H X, WANG Q Z, et al. Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of emerging organophosphate flame retardants in the marine food webs of Laizhou Bay, North China [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(22): 13417-13426. [120] DING Y, HAN M W, WU Z Q, et al. Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of organophosphate esters in tropical marine food web, South China Sea [J]. Environment International, 2020, 143: 105919. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105919 [121] GREAVES A K, LETCHER R J, da CHEN, et al. Retrospective analysis of organophosphate flame retardants in herring gull eggs and relation to the aquatic food web in the Laurentian Great Lakes of North America [J]. Environmental Research, 2016, 150: 255-263. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2016.06.006 [122] FU J, FU K H, CHEN Y, et al. Long-range transport, trophic transfer, and ecological risks of organophosphate esters in remote areas [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(15): 10192-10209. [123] ZHANG Y, ZHENG X B, WEI L F, et al. The distribution and accumulation of phosphate flame retardants (PFRs) in water environment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 630: 164-170. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.215 [124] WAN W N, HUANG H L, LV J T, et al. Uptake, translocation, and biotransformation of organophosphorus esters in wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ) [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(23): 13649-13658. [125] WAN W N, ZHANG S Z, HUANG H L, et al. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphorus esters in soils and wheat plants in a plastic waste treatment area in China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 214: 349-353. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.038 [126] LIU Q, WANG X L, YANG R Y, et al. Uptake kinetics, accumulation, and long-distance transport of organophosphate esters in plants: Impacts of chemical and plant properties [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(9): 4940-4947. [127] GONG X Y, WANG Y, PU J, et al. The environment behavior of organophosphate esters (OPEs) and di-esters in wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ): Uptake mechanism, in vivo hydrolysis and subcellular distribution [J]. Environment International, 2020, 135: 105405. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105405 [128] WANG Q Z, ZHAO H X, BEKELE T G, et al. Organophosphate esters (OPEs) in wetland soil and Suaeda salsa from intertidal Laizhou Bay, North China: Levels, distribution, and soil-plant transfer model [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 764: 142891. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142891 [129] KOJIMA H, TAKEUCHI S, van den EEDE N, et al. Effects of primary metabolites of organophosphate flame retardants on transcriptional activity via human nuclear receptors [J]. Toxicology Letters, 2016, 245: 31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2016.01.004 [130] TAKAHASHI S, KAWASHIMA K, KAWASAKI M, et al. Enrichment and characterization of chlorinated organophosphate ester-degrading mixed bacterial cultures [J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2008, 106(1): 27-32. doi: 10.1263/jbb.106.27 [131] BERNE C, MONTJARRET B, GUOUNTTI Y, et al. Tributyl phosphate degradation by Serratia odorifera [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2004, 26(8): 681-686. doi: 10.1023/B:BILE.0000023030.69207.c0 [132] IYER R, IKEN B, DAMANIA A. A comparison of organophosphate degradation genes and bioremediation applications [J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2013, 5(6): 787-798. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12095 [133] ADELOWO F E, OLU-AROTIOWA O A, AMUDA O S. Biodegradation of glyphosate by fungi species [J]. Advances in Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2014, 2(1): 104-118. [134] ARFARITA N, DJUHARI D, PRASETYA B, et al. The application of Trichoderma viride strain frp 3 for biodegradation of glyphosate herbicide in contaminated land [J]. AGRIVITA Journal of Agricultural Science, 2016, 38(3): 275-281. [135] FIRDOUS S, IQBAL S, ANWAR S. Optimization and modeling of glyphosate biodegradation by a novel Comamonas odontotermitis P2 through response surface methodology [J]. Pedosphere, 2020, 30(5): 618-627. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60381-3 [136] BERNE C, ALLAINMAT B, GARCIA D. Tributyl phosphate degradation by Rhodopseudomonas palustris and other photosynthetic bacteria [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2005, 27(8): 561-566. doi: 10.1007/s10529-005-2882-7 -



 下载:
下载: