-
稀土元素(REE)是指在元素周期表中原子序数为57—71的15个镧系元素. 基于原子质量和有效离子半径,稀土元素通常可分为两类,即轻稀土元素(LREE: La—Eu)和重稀土元素(HREE: Gd—Lu)[1-2]. 稀土元素具有相似且相对稳定的地球化学性质,在成岩、变质、风化、搬运和沉积等过程中具有不易迁移的特点[3-4],因而被广泛应用于内生和外生地质过程中矿物和岩石的形成条件、物质来源、地球化学分异作用以及其气候变化等领域[5-8].
在土壤形成过程中,由于受到溶解、沉淀、氧化还原和络合作用等影响,REE的地球化学行为发生变化,导致REE总量变化、内部元素分馏或元素异常[1,3]. REE地球化学特征可用于判定成土物源[9]、反映风化成土过程[10-11]、揭示土壤发育程度[5,12]、判断土壤氧化还原环境[13]和人类活动对土壤环境的影响等[14-15]. 然而,由于成土母质的多样性、成土环境的复杂性以及人类活动的叠加影响,对于土壤发育过程中REE迁移、富集及分馏的认识还十分有限且存在不少分歧与争议[5,7,16],需要通过更多的调查以揭示土壤中REE的分布和分异规律.
本文以安徽省无为市南部长江冲积物形成的沿江平原为研究区,在构建土壤时间序列的基础上,对比不同成土时间和不同利用方式下REE地球化学特征,以期揭示土壤发育过程和集约化利用对REE的分布和分异的影响.
-
研究区位于安徽省无为市南部(图1)(31.08°—31.27°N,117.90°—118.01°E),地处长江北岸,面积约为160 km2. 在长江河道演变过程中,研究区因处于凸岸而持续接受长江沉积物的堆积,形成不断淤长的冲积平原. 在随后千余年的开垦利用和定居过程中,当地不断修建江堤以保护圩区内的居民和土地. 早期江堤建成后,由于江岸和冲积平原继续南移扩张,又陆续修建新江堤并形成新的圩区. 新江堤建成后其保护的圩区不再接受长江冲积物沉积,土壤即开始形成发育. 研究区各圩区的形成时间由南向北逐渐增加,根据《无为县志》和《无为大堤志》等记载的境内主要江堤的修建史,可以确定新、老江堤间各圩区形成和土壤发育的大致起始时间,建立母质均为长江冲积物的土壤时间序列,用以分析土壤形成和利用过程中REE的地球化学特征及其演变.
研究区土壤类型为长江冲积物母质上发育的潮土及由此经人为培育的水稻土. 气候属亚热带季风区,四季分明,光照充足,雨量充沛,温暖湿润,无霜期长,适宜农业生产,土地利用集约化程度高. 水田通常稻/麦(油菜)轮作,旱地除小麦和油菜外,还种植蔬菜等经济作物.
-
样品主要采自图1所示的6个片区,其中1片区为现江堤外的河漫滩,样品为代表成土母质的长江沉积物,1片区27个样品分别采自光滩、草地和林地. 2—6片区分别位于形成时间大致为60 a、160 a、280 a、1000 a和1500 a的圩区,样品主要采自林地、旱地和水旱轮作的稻田.
采集0—15 cm的表层土壤,在每个点位采用五点法采集土壤或沉积物样品. 共采集土壤和沉积物样品101个. 样品自然风干,剔除植物根茎后轻轻碾碎,过10目筛,用于测定pH和土壤机械组成等. 取部分过10目筛样品置于玛瑙研钵中研磨,至全部通过200目筛后供测试REE含量.
土壤pH、质地、有机碳和无机碳等基本理化性质测定方法参照鲁如坤等(1999)[17]. 常量元素含量采用X射线荧光光谱法测定. 过200目筛样品加入浓硝酸和氢氟酸消解后, REE等微量元素含量采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测定. 经插入美国USGS地球化学标准样品BHVO-2和W-2控制,REE最大相对误差为4.15%.
-
经球粒陨石标准化后计算REE特征参数,包括(La/Yb)N、(La/Sm)N、(Gd/Yb)N、δEu和δCe等. 计算公式参照田景春(1990)[18]:
式中,下标带N的元素为经过球粒陨石标准化后的元素.
-
研究区土壤和沉积物样品REE总量范围在140—215 mg·kg− 1之间,平均值为194 mg·kg− 1(表1),无论是单个元素还是REE总量都高于中国土壤平均值(163 mg·kg− 1)和地壳中稀土元素平均值(150 mg·kg− 1). LREE和HREE含量范围分别为124—193 mg·kg− 1和15.3—23.0 mg·kg− 1,平均值分别为174 mg·kg− 1和20.0 mg·kg− 1,分别占稀土总量的89.7%和10.3%,表明REE总量以LREE为主. 14个REE中,La、Ce和Nd元素含量之和占比较大,为80.9%. 表层土壤REE含量从大到小依次为Ce>La>Nd>Pr>Sm>Gd>Dy>Er>Yb>Eu>Ho>Tb>Tm>Lu,遵循Odd-Harkins规则,即原子序数为偶数的稀土元素含量普遍高于相邻两个原子序数为奇数的稀土元素含量. 区内各REE的变异系数普遍较小,均低于8.5%.
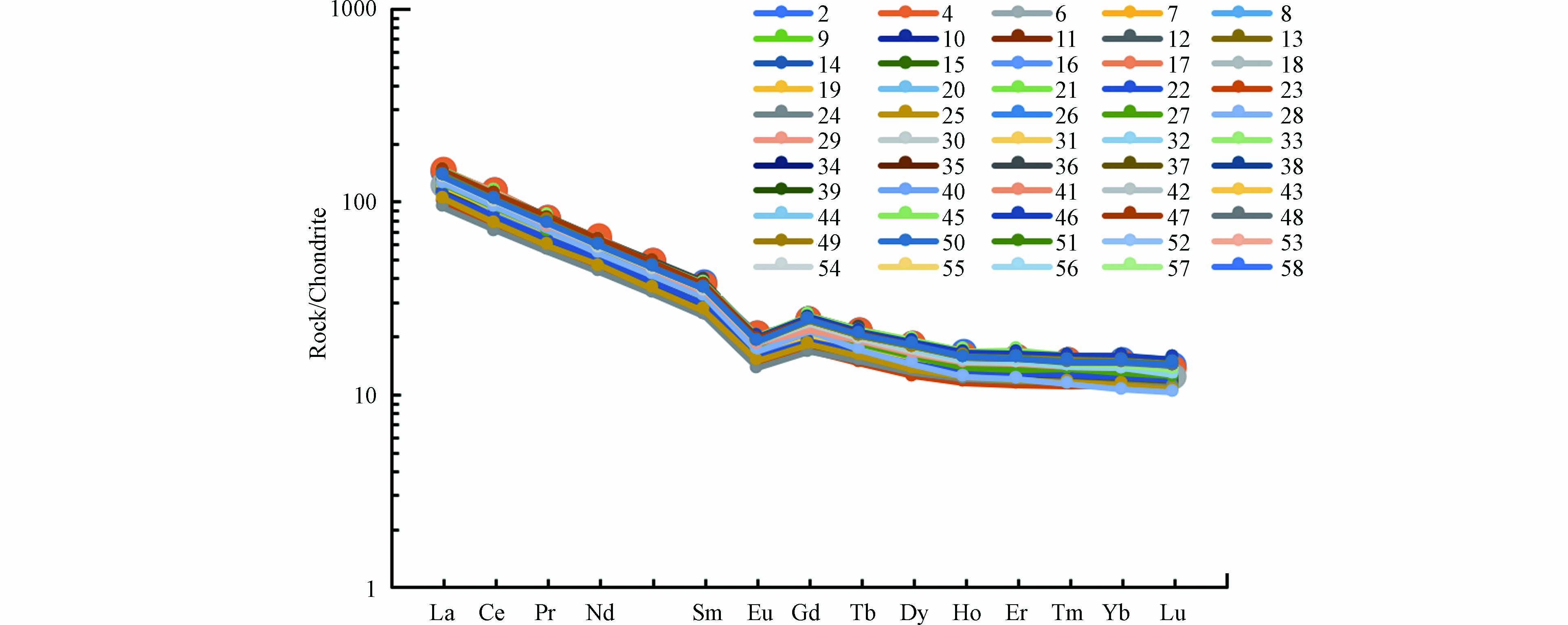
采用Boynton等 [20]球粒陨石标准值对研究区内土壤中的稀土元素含量进行标准化后,得到研究区土壤稀土元素球粒陨石标准化分配曲线. 从图2可知,101个土壤样品的稀土元素分配模式大致相同,均表现出整体向右倾斜的负斜率模式,轻稀土相对富集,重稀土相对亏损. 轻、重稀土的比值在7.94—9.48之间,平均值为8.71(表2),说明研究区轻稀土元素在总量中占优势,且轻重稀土元素分异程度较大.
稀土元素球粒陨石标准化曲线的斜率参数(La/Yb)N变化范围为8.22—11.7,平均值为9.50,表明土壤发育过程中轻重稀土之间发生明显分异,导致(La/Yb)N值较大,轻稀土相对富集. 表示轻稀土之间分馏程度的(La/Sm)N值的范围为3.66—4.11,平均值为3.91,表明轻稀土元素之间具有明显的分馏. 表示重稀土之间分馏程度的(Gd/Yb)N值的范围为1.42—2.00,平均值为1.61,表明重稀土元素之间存在较弱的分馏现象.
δEu和δCe值是用来表征稀土元素Eu和Ce的异常程度,是反映土壤环境的重要参数. 研究区土壤中的δEu值的范围为0.61—0.68(表2),平均值为0.65,表现出明显的Eu负异常,这表明土壤中的稀土元素相对于球粒陨石已经发生明显的分异. δCe在0.94—1.00之间,平均值为0.97,接近于中国土壤δCe值的0.99,表现出微弱的Ce负异常.
-
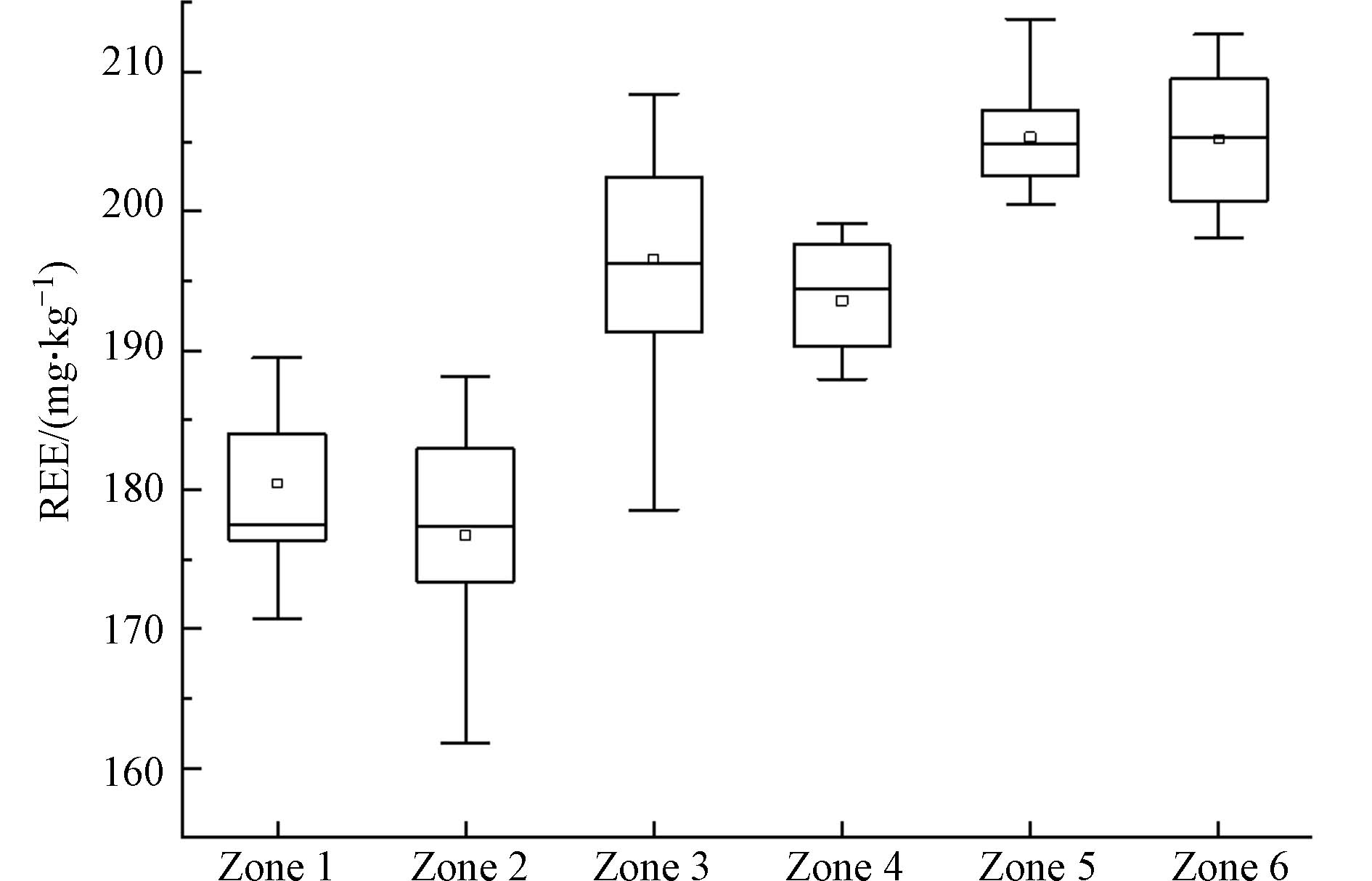
通过对不同片区土壤稀土元素做方差分析得到,不同片区的REE、LREE、HREE和LREE/HREE表现出明显的差异(P<0.05). 围垦后长江冲积物母质开始成土过程,在最新江堤外的1片区和围垦60 a的2片区,沉积物和土壤样品的∑REE平均含量分别为198.1 mg·kg− 1和176.7 mg·kg− 1,说明围垦后的土壤发育过程中REE含量有所下降. 之后随着围垦时间的增加,土壤REE含量总体上呈增加的趋势(图3),∑REE平均含量在围垦时间最长的5、6片区均达到200 mg·kg−1以上. 围垦初期REE含量下降应该与土壤碳酸钙的含量降低有关,次生碳酸钙中通常含有较多的REE[21],表层土壤失去碳酸钙的过程中REE不可避免随之淋溶. 研究区围垦60 a后表层土壤碳酸钙平均含量由沉积物母质的45.3 g·kg− 1迅速下降至1片区的18.2 g·kg− 1,平均每年减少达0.45 g·kg− 1.
长期围垦后土壤REE的富集既有自然因素,也有人为原因. REE含量随着成土时间增加而不断提高的现象较为普遍[5],主要与次生矿物和有机质对REE有较强的捕获和吸附固定能力有关,成土过程中迁移能力较强的组分失去后,次生矿物和有机质的富集作用导致REE含量相对升高[21-22]. 研究区REE总量与黏粒和粉粒含量具有显著的正相关关系(r=0.64**,P<0.01; r=0.69**, P<0.01)与砂粒之间存在负相关关系(r=-0.73**,P<0.01),与有机质含量也呈正相关关系(r=0.54**,P<0.01). 研究区土壤类型为潮土和由潮土水耕熟化形成的水稻土,这类土壤含有较多对REE有较强结合能力的晶质和无定形氧化铁[23],也是REE含量随成土时间增加而富集的原因.
磷肥的长期施用被普遍认为是耕作土壤中REE含量的升高的重要原因[24-25]. REE与磷酸盐有较强的结合能力,导致磷矿石中REE普遍含量较高[26]. 根据已有的报道,磷肥中∑REE可高达2.6 g·kg− 1 [27],是土壤中∑REE平均含量的100倍以上,长期施用磷肥可能会引起土壤REE的富集. Cheng等利用地方志记载的海堤修建历史资料,在浙东沿海根据滩涂围垦年代建立了超过千年尺度的土壤时间序列[28]. Chen等在这一研究区发现REE总量随水稻种植年限的增加而升高,作者把磷肥的长期施用列为重要原因之一[16].
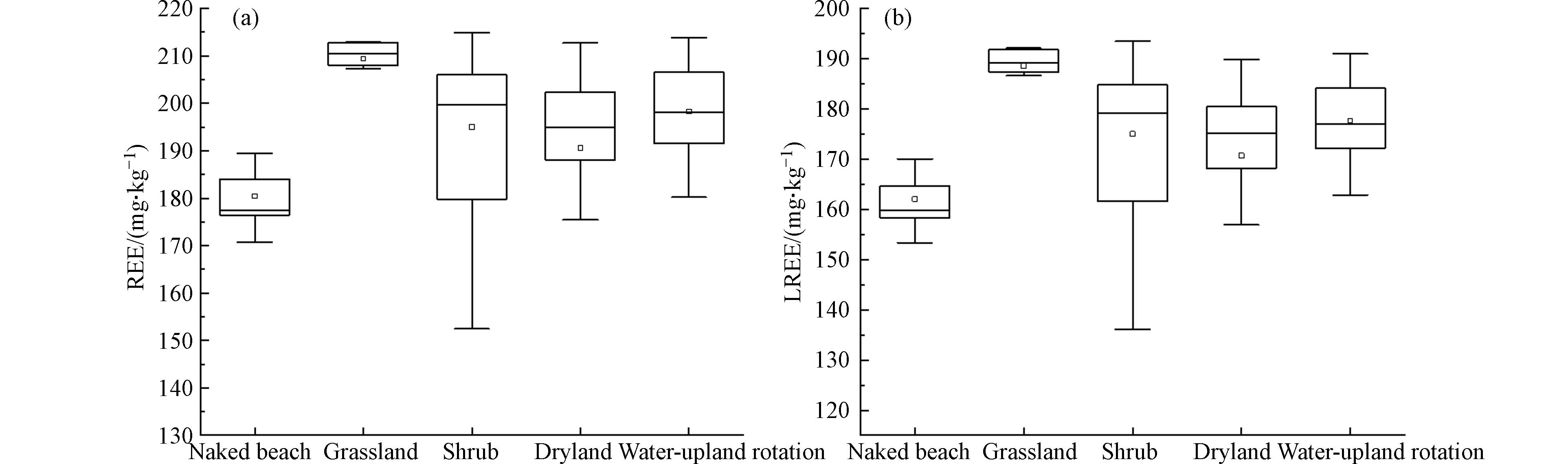
对不同土地利用方式下土壤REE特征参数做方差分析,显示草地的REE和LREE含量显著高于林地、旱地和水旱轮作等其它利用类型(图4),这可能与草地土壤有机质含量高于其它土地利用类型有关,研究区草地土壤有机质平均含量比全区平均含量高9.68%. 旱作和水旱轮作是区内两种主要农用方式,结果表明无论是单个REE含量还是∑REE,两种利用方式下的差异并不显著(P>0.05).
-
由于稀土元素在物理和化学性质上存在着某些差异,成土过程中各种物理、化学和生物过程导致其在相对含量上发生变化而发生分馏[21]. 由表3可见,LREE/HREE、δCe和δEu值总体上呈随围垦年限增加而减小的趋势,说明在REE逐渐富集的同时,HREE的增幅更大,同时Ce和Eu的亏缺在增加. 其原因之一是围垦年代较久的片区水稻种植更为普遍. 围垦初期以旱作为主,后期水稻种植面积增加导致土壤氧化还原电位普遍下降. Eh较低的情况下,Eu3+ 和Ce4+易被还原形成迁移能力更强的Eu2+和Ce3+而淋失[29-30],导致二者的负异常更为明显.
为进一步分析研究区REE的分布和分馏特征及其控制因素,利用主成分分析方法对所获得的REE和其它理化性质数据降维. 所得前3个主成分的方差贡献分别为57.5%、14.2%和8.0%,累计方差贡献达79.8%,以这3个成分进行最大化旋转,得到结果见表4.
第一主成分包含全部REE、Al、Fe、Ti、黏粒和OM,进一步说明黏土矿物、氧化铁和OM对REE的富集作用. 通常认为成土母质中REE的主要来源是含Ti和Zr的原生重矿物,如锐钛矿、钛铁矿、金红石和锆石等[31-32]. Ti的高载荷和Zr的低载荷表明,长江冲积物母质中REE的主要来源为含Ti的重矿物,Ti对∑REE的决定系数达65%(∑REE = 0.026Ti + 60.0,R2 = 0.65,P<0.01),而含Zr矿物的影响不明显. Ca和pH的负载荷应该是成土过程两个不同方向演变的结果,即随成土时间的增加REE发生富集,而同时土壤中发生碳酸钙淋溶和pH降低的过程.
第二主成分的高载荷主要包括δCe、δEu、Mn、Fe、(Si)、Ca、pH和Zr,显示Ce和Eu异常与Mn、Fe之间存在的密切联系. 无论是无定形还是晶质铁、锰氧化物都会选择性地捕获Ce,从而导致其出现正异常[33-34]. 在本研究区,铁、锰氧化物含量随围垦年代增加呈下降趋势(表3),间接导致Ce亏缺的增加. Si和Zr的负载荷和Al的中等正载荷说明土壤质地在一定程度上影响Ce和Eu异常,这一现象不是因为化学分馏,主要与特定细粒级黏土矿物对某些REE的选择性富集有关[33]. Ca和pH与Ce、Eu异常不一定有成因上的联系,其原因如前节所述.
第三主成分的高载荷只有LREE/HREE比值,其余指标的载荷均低于0.3,说明依据现有指标不能揭示轻重REE分馏的内在机制. 非环境因素,如植物的选择吸收可能是影响REE分馏的原因[21].
-
研究区土壤REE含量高于长江下游沉积物平均值和中国土壤平均值. 围垦初期REE含量有所下降,后期随着围垦时间的增加,土壤REE含量总体上呈增加的趋势. 次生矿物和有机质对REE较强的捕获和吸附固定能力是土壤REE富集的主要原因,磷肥的长期施用也可能是REE在土壤中不断积累的重要原因. 旱作和水旱轮作两种主要农用方式对单个REE含量和∑REE差异的影响不显著.
REE富集的同时,土壤中轻、重REE的分馏和Ce、Eu的亏缺也在增加. 水稻种植导致土壤氧化还原电位下降,Ce、Eu易被还原为易迁移的低价态而导致其相对含量降低,Eh降低造成的铁、锰氧化物含量减少是Ce亏缺增加的间接原因. 土壤质地的变化也在一定程度上影响Ce和Eu的异常.
长江下游冲积平原区土壤稀土元素富集与分馏特征
Enrichment and fractionation of rare earth elements in alluvial plain soils at the lower reaches of the Yangtze River
-
摘要: 在长江下游冲积平原区建立了一个跨度约1500 a的土壤时间序列,通过对比稀土元素(REE)含量和分馏的变化,分析其在成土过程中的演变特征与控制因素. 研究结果表明,REE含量经过成土初期的略有下降后,随着时间推移总体上呈增加的趋势. 次生矿物和有机质对REE较强的捕获和吸附固定能力是土壤REE富集的主要原因,磷肥的长期施用可能也是REE在土壤中不断积累的重要原因. 旱作和水旱轮作两种主要农用方式对单个REE含量和总量差异的影响不显著. 土壤中轻、重REE的分馏和Ce、Eu的亏缺也随成土时间推移变化. 水稻种植导致土壤氧化还原电位下降,直接和间接增加了Ce和Eu的亏损.Abstract: A soil chronosequence with a span of about 1500 years was established in the alluvial plain area of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River. By comparing the changes of rare earth element (REE) contents and fractionations, their evolution characteristics and control factors in the pedological process were analyzed. The results show that after a slight decrease in the initial stage of soil formation, the content of REE generally increases with the passage of time. The strong scavenging and fixing ability of secondary minerals and organic matter on REE is suggested as the main reason for the enrichment of REE in soil. The long-term application of phosphorus fertilizer might also lead to the continuous accumulation of REE in soil. Dry farming and paddy dry rotation had no significant effect on the contents of single REE and ∑REE. The fractionation of light and heavy REE and the deficiency of Ce and Eu also changed with the time of soil formation. Rice planting led to the decrease of soil redox potential, which directly and indirectly increased the negative anomalies of Ce and Eu.
-
Key words:
- Lower Yangtze Plain /
- soil chronosequence /
- pedological process /
- rare earth elements /
- fractionation.
-

-
表 1 研究区土壤的稀土元素含量(mg·kg− 1)
Table 1. Contents of rare earth elements in soil of the study area(mg·kg− 1)
最小值
Minimum value最大值
Maximum value均值
Average value变异系数/%
Coefficient of variation中国土壤[19]
Soil in China地壳[1]
CrustLa 29.0 45.5 40.9 7.93 39.7 30.0 Ce 57.0 90.9 81.4 8.07 68.4 60.0 Pr 6.71 10.2 9.20 7.76 7.17 8.20 Nd 25.7 38.8 35.0 7.44 26.4 28.0 Sm 4.98 7.55 6.59 7.80 5.22 6.00 Eu 1.01 1.52 1.34 7.49 1.03 1.20 Gd 4.34 6.69 5.80 8.60 4.60 5.40 Tb 0.682 1.02 0.913 7.91 0.630 0.900 Dy 4.02 6.21 5.39 8.46 4.13 3.00 Ho 0.825 1.21 1.08 7.91 0.870 1.20 Er 2.35 3.55 3.06 8.29 2.54 2.80 Tm 0.359 0.520 0.460 7.93 0.370 0.480 Yb 2.23 3.33 2.91 8.05 2.44 3.00 Lu 0.333 0.493 0.431 8.06 0.360 0.500 ∑REE 140 215 194 7.79 163 150 LREE 124 193 174 7.83 148 133 HREE 15.3 23.0 20.0 8.15 15.9 17.3 LREE/HREE 7.94 9.48 8.71 3.52 9.28 7.72 注:中国土壤稀土元素数据参考魏复盛1991年,地壳稀土元素数据参考刘英俊1984年.
Note: Chinese soil rare earth element data refer to Wei Shengfu 1991, crustal rare earth element data refer to Liu Yingjun 1984.表 2 研究区土壤稀土元素特征参数
Table 2. Characteristic parameters of rare earth elements in soil of the study area
LREE/HREE (La/Yb)N (La/Sm)N (Gd/Yb)N δEu δCe 范围 7.94—9.48 8.22—11.7 3.66—4.11 1.42—2.00 0.610—0.680 0.940—1.00 均值 8.71 9.50 3.91 1.61 0.650 0.970 表 3 部分指标在各片区的平均值
Table 3. The average value of some indicators in each area
片区号
Area codepH CaO/% Fe2O3/% MnO/% LREE/HREE δCe δEu 1 7.92 3.83 6.17 0.128 8.90 0.977 0.656 2 7.88 2.71 4.50 0.077 8.82 0.961 0.648 3 7.47 2.13 5.58 0.098 8.81 0.983 0.647 4 7.45 1.87 5.77 0.087 8.68 0.982 0.654 5 7.15 1.25 5.78 0.083 8.38 0.953 0.630 6 6.24 1.06 5.49 0.067 8.41 0.951 0.636 表 4 主成分分析结果
Table 4. Principal component analysis results
指标
Index主成分
Principal componentP1 P2 P3 La 0.94 0.09 0.29 Ce 0.92 0.20 0.26 Pr 0.95 0.06 0.26 Nd 0.93 0.14 0.25 Sm 0.96 0.01 0.22 Eu 0.94 0.15 0.18 Gd 0.97 −0.05 0.14 Tb 0.98 0.07 0.02 Dy 0.99 0.00 −0.09 Ho 0.97 0.08 −0.17 Er 0.97 −0.03 −0.18 Tm 0.95 0.01 −0.24 Yb 0.95 −0.03 −0.27 Lu 0.93 −0.07 −0.29 HREE 0.97 0.05 −0.16 LREE 0.93 0.16 0.27 LREE/HREE −0.15 0.18 0.87 δCe 0.05 0.70 −0.09 δEu −0.41 0.57 −0.14 Al 0.78 0.47 0.03 Si −0.45 −0.83 −0.19 Fe 0.69 0.67 0.13 Mn 0.11 0.86 0.18 Ca −0.55 0.57 0.16 Ti 0.73 0.34 0.27 Zr −0.26 −0.52 −0.22 P −0.17 −0.38 −0.03 黏粒 0.76 0.23 −0.05 OM 0.56 0.10 0.11 pH −0.51 0.54 0.09 -
[1] 刘英俊. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984. LIU Y J. Elemental geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1984(in Chinese).
[2] LOELL M, ALBRECHT C, FELIX-HENNINGSEN P. Rare earth elements and relation between their potential bioavailability and soil properties, Nidda catchment (Central Germany) [J]. Plant and Soil, 2011, 349(1-2): 303-317. doi: 10.1007/s11104-011-0875-y [3] 马英军, 刘丛强. 化学风化作用中的微量元素地球化学: 以江西龙南黑云母花岗岩风化壳为例 [J]. 科学通报, 1999, 44(22): 2433-2437. doi: 10.1360/csb1999-44-22-2433 MA Y J, LIU C Q. Trace element Geochemistry in chemical weathering: A case study of biotite granite crust in Longnan, Jiangxi Province [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44(22): 2433-2437(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb1999-44-22-2433
[4] LIU F W, MIAO L, CAI G Q, et al. The rare earth element geochemistry of surface sediments in four transects in the South China Sea and its geological significance [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 74(3): 2511-2522. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4265-2 [5] 黄成敏, 龚子同. 土壤发育过程中稀土元素的地球化学指示意义 [J]. 中国稀土学报, 2000, 18(2): 150-155. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.2000.02.015 HUANG C M, GONG Z T. Geochemical implication of rare earth elements in process of soil development [J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2000, 18(2): 150-155(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.2000.02.015
[6] 胡恭任, 于瑞莲, 余伟河. 泉州湾潮间带表层沉积物稀土元素地球化学特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2011, 30(12): 2086-2091. HU G R, YU R L, YU W H. Geochemistry of rare-earth elements in surface sediments of inter-tidal zone of Quanzhou Bay [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 30(12): 2086-2091(in Chinese).
[7] BOROWIAK K, LISIAK M, KANCLERZ J, et al. Relations between rare earth elements accumulation in Taraxacum officinale L. and land use in an urban area - A preliminary study [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2018, 94: 22-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.06.046 [8] YUAN Y Y, LIU S L, WU M, et al. Effects of topography and soil properties on the distribution and fractionation of REEs in topsoil: A case study in Sichuan Basin, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 791: 148404. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148404 [9] 张从伟, 韩孝辉, 龙根元, 等. 三亚近岸海域表层沉积物稀土元素地球化学特征及物源分析 [J]. 中国稀土学报, 2021, 39(4): 633-643. ZHANG C W, HAN X H, LONG G Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and provenance analysis of rare earth elements in surface sediments of Sanya offshore area [J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2021, 39(4): 633-643(in Chinese).
[10] 马英军, 霍润科, 徐志方, 等. 化学风化作用中的稀土元素行为及其影响因素 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2004, 19(1): 87-94. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.01.012 MA Y J, HUO R K, XU Z F, et al. Ree behavior and influence factors during chemical weathering [J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2004, 19(1): 87-94(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.01.012
[11] MIHAJLOVIC J, BAURIEGEL A, STÄRK H J, et al. Rare earth elements in soil profiles of various ecosystems across Germany [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2019, 102: 197-217. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.02.002 [12] 叶玮, 杨立辉, 朱丽东, 等. 中亚热带网纹红土的稀土元素特征与成因分析 [J]. 地理科学, 2008, 28(1): 40-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2008.01.008 YE W, YANG L H, ZHU L D, et al. Characteristics and origin of rare earth elements of vermicular red earth in middle sub-tropic zone [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2008, 28(1): 40-44(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2008.01.008
[13] CHANG C Y, LI F B, LIU C S, et al. Fractionation characteristics of rare earth elements (REEs) linked with secondary Fe, Mn, and Al minerals in soils [J]. Acta Geochimica, 2016, 35(4): 329-339. doi: 10.1007/s11631-016-0119-1 [14] 袁丽娟, 郭孝培, 魏益华, 等. 赣南典型稀土矿区周边土壤和动植物产品中稀土元素组成特征及其健康风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(8): 1850-1863. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019012401 YUAN L J, GUO X P, WEI Y H, et al. Compositions and health risk assessment of rare-earth elements in soil, animal and plant products around rare earth mining area in Southern Jiangxi Province [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(8): 1850-1863(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019012401
[15] 王祖伟, 刘雅明, 王子璐, 等. 中国北方典型设施菜地土壤稀土元素分布特征及环境意义 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(4): 2071-2080. WANG Z W, LIU Y M, WANG Z L, et al. Distribution and environmental significance of rare earth elements in typical protected vegetable soil, Northern China [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(4): 2071-2080(in Chinese).
[16] CHEN L M, ZHANG G L, JIN Z D. Rare earth elements of a 1000-year paddy soil chronosequence: Implications for sediment provenances, parent material uniformity and pedological changes [J]. Geoderma, 2014, 230/231: 274-279. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.03.023 [17] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 1999: 106-126. LU R K. Soil agrochemical analysis methods[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 1999: 106-126(in Chinese).
[18] 田景春, 张翔. 沉积地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990: 92-93. TIAN J C, ZHANG X. Sedimentary geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1990: 92-93(in Chinese).
[19] 魏复盛, 陈静生, 吴燕玉, 等. 中国土壤环境背景值研究 [J]. 环境科学, 1991, 12(4): 12-19. WEI F S, CHEN J S, WU Y Y, et al. Study on the background contents on 61 elements of soils in China [J]. Environmental Science, 1991, 12(4): 12-19(in Chinese).
[20] BOYNTON W V. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies[M] . Amsterdam: Developments in Geochemistry, 1984: 63-114. [21] LAVEUF C, CORNU S. A review on the potentiality of Rare Earth Elements to trace pedogenetic processes [J]. Geoderma, 2009, 154(1-2): 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.10.002 [22] 毛龙江, 郭爱鹏, 杜吉净, 等. 湖南澧水下游表层沉积物稀土元素特征 [J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2019, 41(3): 352-361. MAO L J, GUO A P, DU J J, et al. REE characteristics of the surface sediments in the lower reaches of Lishui River, Hunan, China [J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2019, 41(3): 352-361(in Chinese).
[23] 章海波, 骆永明. 水稻土和潮土中铁锰氧化物形态与稀土元素地球化学特征之间的关系研究 [J]. 土壤学报, 2010, 47(4): 639-645. ZHANG H B, LUO Y M. Relationship between geochemical characteristics of rear earth elements and speciation of iron/manganese oxides in paddy soil and Chao soil [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2010, 47(4): 639-645(in Chinese).
[24] HU Z Y, HANEKLAUS S, SPAROVEK G, et al. Rare earth elements in soils [J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2006, 37(9): 1381-1420. [25] BISPO F H A, de MENEZES M D, FONTANA A, et al. Rare earth elements (REEs): Geochemical patterns and contamination aspects in Brazilian benchmark soils [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 289: 117972. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117972 [26] RAMOS S J, DINALI G S, de CARVALHO T S, et al. Rare earth elements in raw materials and products of the phosphate fertilizer industry in South America: Content, signature, and crystalline phases [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 168: 177-186. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.06.009 [27] TODOROVSKY D S, MINKOVA N L, BAKALOVA D P. Effect of the application of superphosphate on rare earths' content in the soil [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 1997, 203(1): 13-16. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(97)00131-9 [28] CHENG Y Q, YANG L Z, CAO Z H, et al. Chronosequential changes of selected pedogenic properties in paddy soils as compared with non-paddy soils [J]. Geoderma, 2009, 151(1-2): 31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.03.016 [29] CONDIE K C, DENGATE J, CULLERS R L. Behavior of rare earth elements in a paleoweathering profile on granodiorite in the Front Range, Colorado, USA [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(2): 279-294. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)00280-Y [30] TOSTEVIN R, SHIELDS G A, TARBUCK G M, et al. Effective use of cerium anomalies as a redox proxy in carbonate-dominated marine settings [J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 438: 146-162. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.06.027 [31] AUBERT D, STILLE P, PROBST A. REE fractionation during granite weathering and removal by waters and suspended loads: Sr and Nd isotopic evidence [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(3): 387-406. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00546-9 [32] AIDE M T, PAVICH Z. Rare earth element mobilization and migration in a Wisconsin spodosol [J]. Soil Science, 2002, 167(10): 680-691. doi: 10.1097/00010694-200210000-00006 [33] COMPTON J S, WHITE R A, SMITH M. Rare earth element behavior in soils and salt pan sediments of a semi-arid granitic terrain in the Western Cape, South Africa [J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 201(3-4): 239-255. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(03)00239-0 [34] HUANG C, WANG C. Geochemical characteristics and behaviors of rare earth elements in process of vertisol development [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2004, 22(4): 552-557. -




 下载:
下载: