-
硒元素(Se)近些年一直是学者们关注的微量元素,同时是人体及动物必需的微量营养元素之一,近些年来. 硒在地壳中含量为0.05 mg·kg−1,属于稀有分散元素[1],而我国硒含量分布极为不均匀[2]. 缺硒是发生克山病和大骨节病的重要原因. 而过量的硒可引起中毒[3-5]. 人体摄取硒的主要来源为粮食、水果和蔬菜,而大多数植物获取硒的来源是通过土壤途径,因此研究土壤硒元素对于人体健康及农产品安全有重要意义.
近年来,土壤硒元素的研究成为国内外众多学者的关注热点,杨忠芳等[6]对海南岛土壤研究表明,土壤中黏土矿物、有机质、铁锰氧化物及风化淋溶程度是影响土壤中硒含量变化的主控因素. 而土壤中的硒并无法完全被植物吸收,能被植物吸收的被称为有效硒,周菲等[7]提出了新型有效硒的测定办法,其计算方法所得的特征参数能较好得表征土壤硒生物有效性的可行性. 王锐等[8]基于回归方程对硒的生物有效性进行研究,表明硒生物有效性受到土壤中P和S的含量以及pH的共同影响. 结合前人研究成果[9-11],本文研究土壤硒的分布特征及其影响因素和有效硒的研究对区域土壤治理开发有重要意义.
龙山县有“湘鄂川之孔道”之称,其大面积的土壤属于典型的富硒地带[12]. 本次研究基于龙山县土地质量地球化学调查成果,研究区域内硒的空间分布、垂向迁移及影响因素,探讨土壤有效硒影响因素,以期为富硒土壤合理开发利用和特色农产品种植提供科学依据.
-
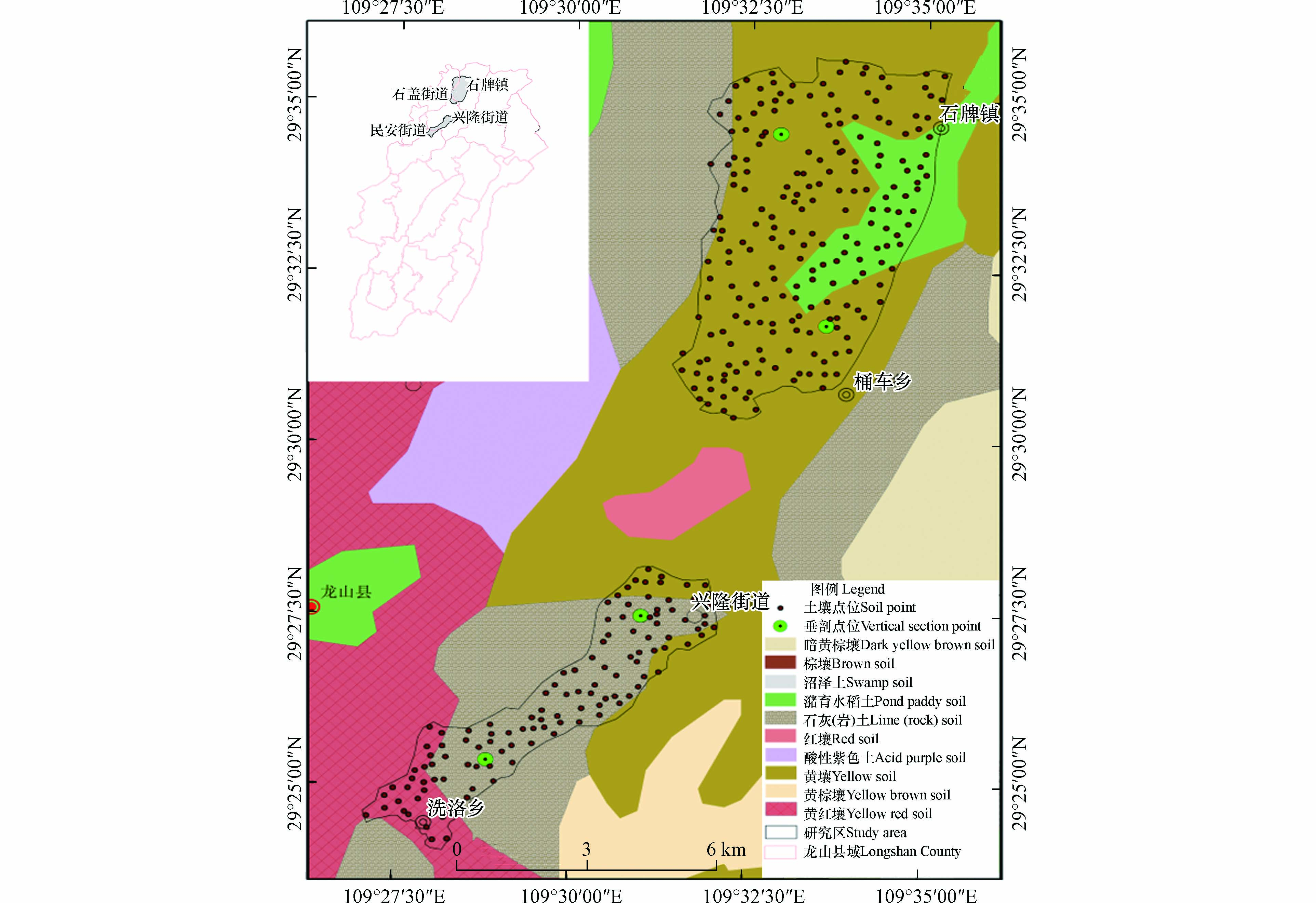
龙山县位于湖南西北部,与湖北省、重庆市交界,地处武陵山区腹地,本次选取龙山县部分耕地区作为研究区域(图1),其行政区域主要为石牌镇、洗洛乡大部分区域,区域内土地利用主要以水田、旱地为主,为主要农耕区,主要土壤类型是黄壤、水稻土和部分黄红壤. 研究区出露地层包括寒武系(高台组),奥陶系(大湾组),志留系(罗惹坪组、纱帽溪组),泥盆系(写经寺组、黄家磴组、云台观组)等,主要岩石类型多为石灰岩、板页岩、砂岩、白云岩、紫色砂页岩、第四纪红土及河流冲积物等. 地处亚热带季风湿润气候区,其气候较为温和,降雨量足,雨热同季.
-
2021年7—8月,依据土地质量地球化学调查规范[13],在1 km×1 km的网格内根据土地利用类型布设4—16个采集点位,采集0—20 cm的表层土壤样品,每个样品遵循多点结合,混合采样原则,从中心点位向四周辐射4个20—50 m的分样,分样与主样分布呈“X”或“S”型,采取四分法分样混合均匀后组成1 kg的总样,剔除样品中的枯枝落叶后,经过风干后过10目尼龙筛,过筛后混分300 g样品送实验室进一步处理.
垂向剖面布设于研究区四个土壤发生层发育完整或具有区域代表性的地段,将提取出的土壤样品按深度依次排放,按土壤发生层标准划分土壤层位,其样品加工处理方法与土壤样品一致.
-
土壤硒全量测定:称取 0.5000 g 样品于 50 mL 烧杯中,加入 10 mL(1+1)王水,电热板上加热分解,(1+1)盐酸提取,定容至 50 mL,放置过夜,分取 25 mL于比色管中,采用原子荧光光谱法(AFS) 测定 Se,检出限为0.01 mg·kg−1.
有机质、pH测定:有机质通过容量法测定,检出限为0.1%. pH值通过离子选择电极法测定,检出限为0.1(无量纲). 其步骤分别为:称取 0.5000 g 样品于三角烧杯中,加入 5 mL 0.8 mol·L−1 的重铬酸钾标准溶液、5 mL 浓硫酸,摇匀于电热板上消解,冷却后加入邻菲罗啉指示剂,硫酸亚铁滴定,测定有机质含量. 称取 10.0 g 样品,加无二氧化碳蒸馏水浸溶,使用pH 计测定.
硒的形态分析:采用氢化物发生原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS)分析各相态中的硒,严格根据《生态地球化学评价样品分析技术要求(试行)》(DD2005-03)[14]依次测定硒的水溶态、离子交换态、碳酸盐结合态、腐殖酸结合态、铁锰结合态、强有机结合态和残渣态.
本次研究分析测试承担单位为湖北省地质实验测试中心,分析测试准确度、精密度、重复分析、异常抽检、报出率等内部质量控制均符合要求,所有样品分析测试质量均通过了样品分析质量监控单位的验收,数据可靠.
-
采用Microsoft Excel 2019对表层土壤样品中硒含量进行描述性统计分析;采用ArcGIS 10.7进行Kriging差值分析并建立半方差变异函数模型,形成空间分布图;采用IBM SPSS 25软件进行相关性分析;采用Origin 2021绘制相关图件.
-
通过计算研究区内Se元素参数统计,结果表明,研究区内表层土壤中Se元素含量最大值为0.69 mg·kg−1,最小值为0.18 mg·kg−1,平均值为0.33 mg·kg−1(表1). 全国土壤背景值[15]中Se含量为0.22 mg·kg−1,研究区内Se元素含量为全国土壤背景值的1.48倍,说明该区域土壤中Se有较为显著的富集. 研究区内pH范围为4.01—8.18,其变化幅度较大,研究区内土壤以酸性土壤为主. 研究区内土壤中有机质(OM)范围为9.22—36.2 g·kg−1,平均值为20.7 g·kg−1. 根据变异系数(CV)划分等级依据[16](CV>36%为高度变异;16%<CV<36%为中度变异;CV<16%为低等变异),可以得出,研究区内Se元素、pH和有机质均为中度变异,表明龙山县主要耕地区这三类元素均受外来因素的影响较大.
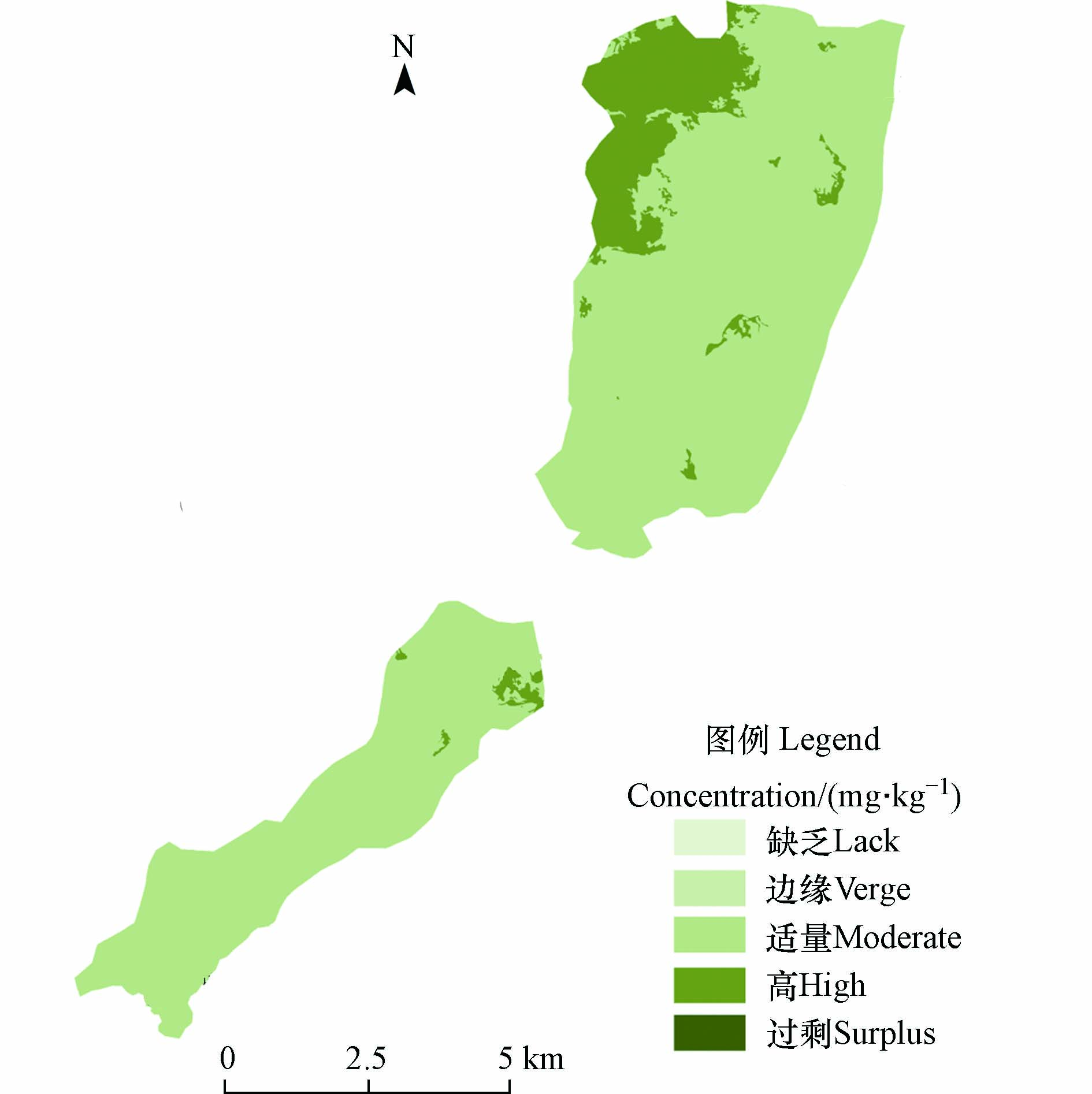
根据土壤硒含量等级划分标准(《土地质量地球化学评价规范》(DZ/T0295-2016)),结果显示,研究区内土壤硒含量整体较高,硒等级为过剩(一等)、富硒(二等)、适量(三等)、较缺乏(四等)、缺乏(五等)的土壤面积分别为0、7.26、48.82 km2、0、0,分别占调查面积的0.00%、12.94%、87.06%、0.00%和0.00%(表2),且通过图2可以明显看出,富硒地区主要分布在石牌镇西边区域,说明该区域表层土壤富硒,符合开发富硒资源的前提条件.
-
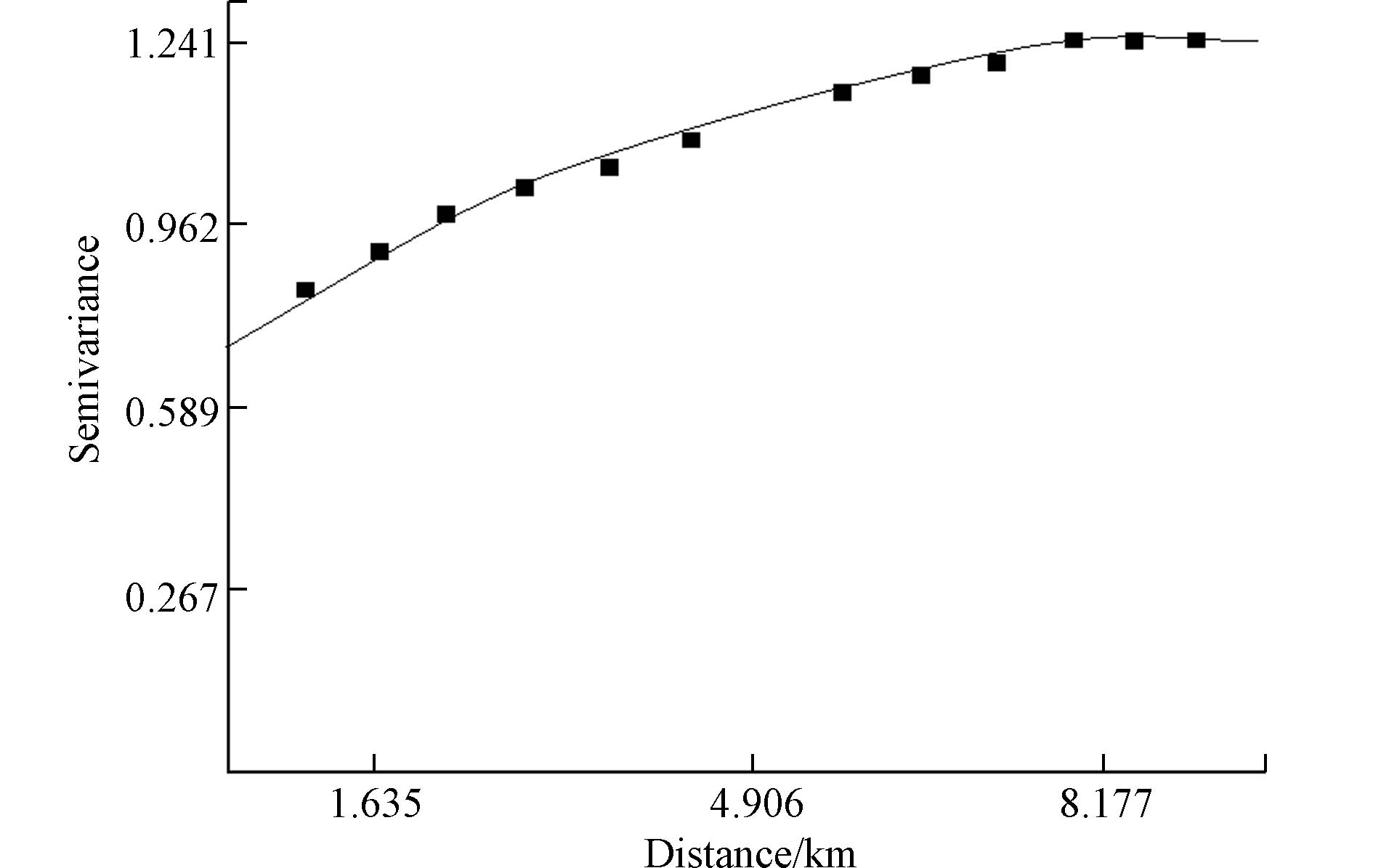
土壤中硒含量受成土母质、地形地貌、土壤类型及人类活动等各类因素影响不同而呈现其空间变异性[17],为定量刻画研究区内土壤中硒含量的独立性、随机性和结构性因素,使用ArcGIS软件对经自然对数化后的研究区内硒含量数据进行半方差函数拟合,根据标准方根预测误差RMSS趋向于1,标准平均值MS趋向于0,判断其最优模型为球面模型,得到变异函数理论模型的各项参数(表3)、输出其半变异函数(图3).
半方差函数中块金值C0为原点处的测量误差和微尺度变量之和,代表由非采样间隔所引起的随机性变异,基台值(C0+C)为半变异函数在首次呈现平稳状态下所达到的高度,代表空间系统包括随机性和结构性的总变异,块金系数代表由随机性引起的变异与空间总变异的比值,其能基本反映元素空间相关性的程度,其数值越大,空间变异性越强. 按照区域化空间变异性程度的划分标准[18],块金系数大于75%时,其空间变异性很强,受外来因素等影响程度大,当块金系数介于25%—75%时,空间变异性中等,均受结构性和随机性影响. 当块金系数小于25%时,其空间变异性弱,受结构性(自然因素)影响程度较大. 研究区内硒元素含量其块金系数为43.2%,属于中等空间变异,说明其既受自然因素(成土母质、土壤类型等)又受人为因素(人类活动)的影响[19].
-
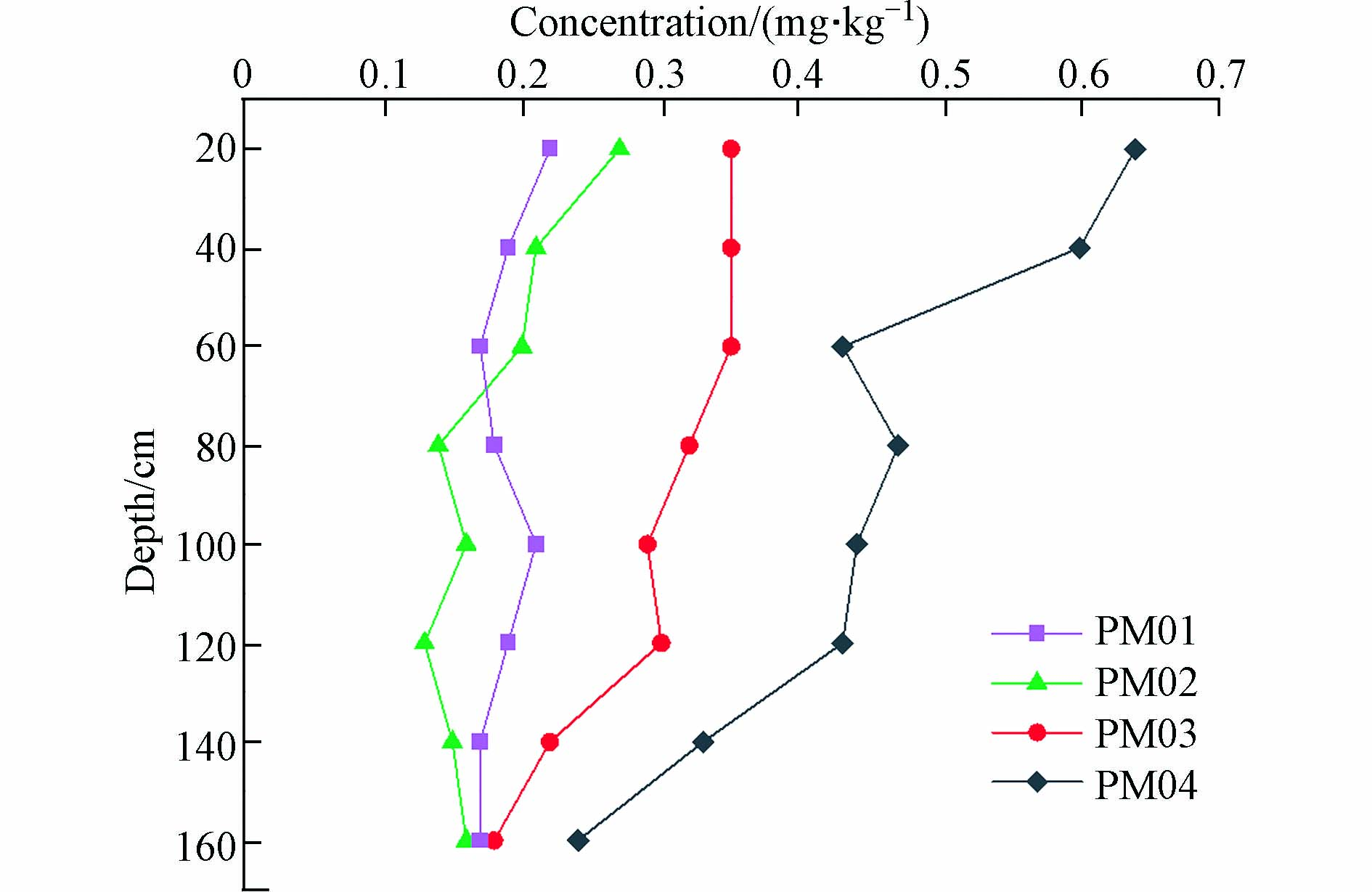
为探寻研究区内Se元素垂向分布特征,在区内布置了4条土壤剖面(图1),制作其含量特征分布图(图4).
4个剖面中PM01位于寒武系中统高台组上段,其Se含量变化范围为0.17—0.22 mg·kg−1,平均值为0.19 mg·kg−1;PM02位于志留系中统罗惹坪组,其Se含量变化范围为0.13—0.27 mg·kg−1,平均值为0.18 mg·kg−1;PM03位于奥陶系中下统大湾组,其Se含量变化范围为0.18—0.35 mg·kg−1,平均值为0.30 mg·kg−1;PM04位于志留系上统帽沙溪组,其Se含量范围为0.24—0.64 mg·kg−1,平均值为0.45 mg·kg−1;总体趋势来看,4个剖面在垂向变化的趋势几乎一致,变化趋势以PM04最明显,呈现出表聚性,即其在表层土壤中较为富集,向深层土壤中迁移能力较弱,深层土壤中Se元素含量较低. 根据王美珠等[20]对我国一些土壤剖面形式变化特征根据生物累积与淋溶相对强弱可分为三种,即①表层含量高于深层,生物累积作用大于淋溶作用;②表层含量低于深层,生物累积作用小于淋溶作用;③表层土壤与深层土壤含量相当,生物累积作用等于淋溶作用. 研究区内部四个剖面均显示其生物累积性大于淋溶作用,且由于地方差异不同,其向下渗透淋溶的能力有所差异. 这与表层土壤中腐殖质及氧化铁含量较为深层土壤中高,对硒具有更强的吸附作用有关[21].
-
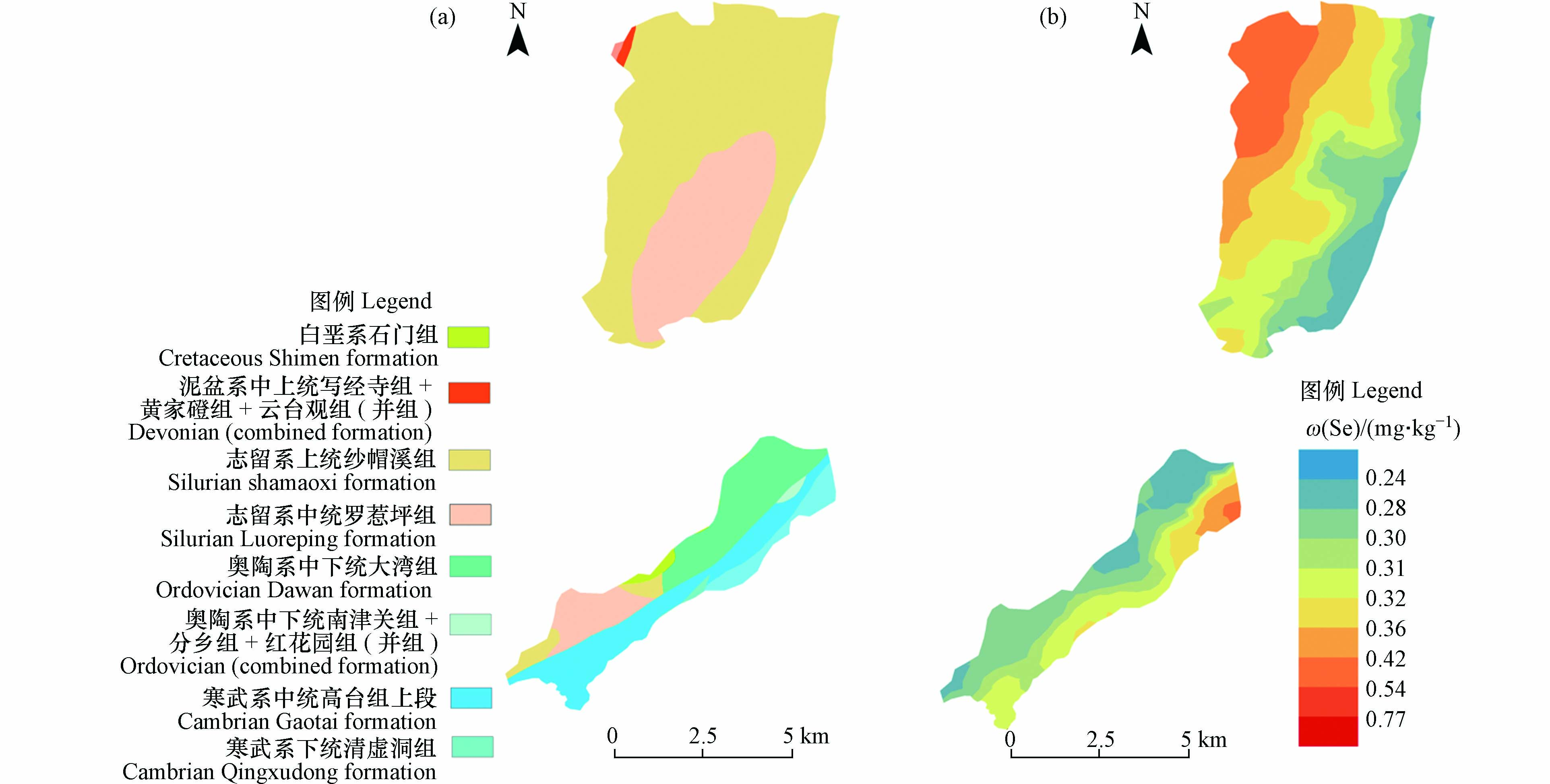
成土母质是大多数土壤形成的最初来源[22],由于不同成土母质之间的成分差异导致土壤中元素含量之间的差异. 研究区内共有五种地层分布,分别为寒武系中统高台组上段、下段、奥陶系中下统大湾组、志留系上统帽溪组和中统罗惹坪组,通过对比各成土母质发育形成的土壤Se统计参数(表4),研究区内寒武系地层其平均值和变化范围均高于奥陶系和志留系地层,这是因为寒武系地层发育白云质灰岩与白云岩,其本质为碳酸盐岩在风化过程中所产生的次生矿物和土壤溶液,造成容易让Se富集的表生生物环境,土壤 Se的淋滤流失减少[23],进而导致表层土壤中Se在一定程度的富集.
通过普通克里金差值法对研究区Se含量进行空间插值,形成空间分布图(图5),与研究区地质简图进行对比发现,研究区西南地区其Se含量空间分布与地层变化较为相似,在寒武系地层中Se含量整体高于奥陶系及志留系地层,表明土壤于母岩而言具有继承性[24],使得Se元素富集于相应的母质土壤中,而研究区石牌镇西边区域,其呈现出与地层变化不一致的富集能力,这代表研究区只是一定程度上的受成土母质控制,应还有其他控制源导致土壤中Se含量富集,与研究区选择大多都是耕地原因有关,较大程度上受外来即人为因素的影响.
-
研究表明,Se是受人类活动影响反应最大的元素之一[25],人类活动通常会对土壤中Se的变化产生较大影响,尤其是其表层土壤中Se. 研究区大部分为耕地、农田,因此,土地利用方式的改变是人类活动较为明显的表达形式之一,人类活动通过土地利用影响土壤环境从而影响土壤中Se的含量变化[26]. 研究区主要土地利用类型为水田、旱地和林地,对这几种土地利用类型表层土壤中Se含量进行统计(表5),可以发现研究区内旱地中Se含量高于水田和林地中,旱地土壤中Se含量最高,平均值为0.33mg·kg−1,这可能是因为研究区土壤主要为偏酸性的黄壤,其中含有较多的碎屑矿物和黏土矿物,在旱地中通气条件较好,在酸性土壤中Se元素较为容易以亚硒硝酸(Se4+)被黄壤中粘土矿物所吸附,从而导致土壤中Se的富集[27]. 水田中Se含量平均值为0.31 mg·kg−1,由于长期的水土耕作,导致土壤中有机结合态的Se迁移,同时水稻土在淹水条件下土壤中硒元素会发生流失,从而导致其Se含量较低于旱地. 林地中Se含量最低,为0.29 mg·kg−1,主要是因为林地受人为干预最少,其呈现的是母质中所继承的Se含量,因此土地利用方式对研究区Se含量变化的影响较为显著,人为因素是研究区Se含量变化的主要因素之一.
-
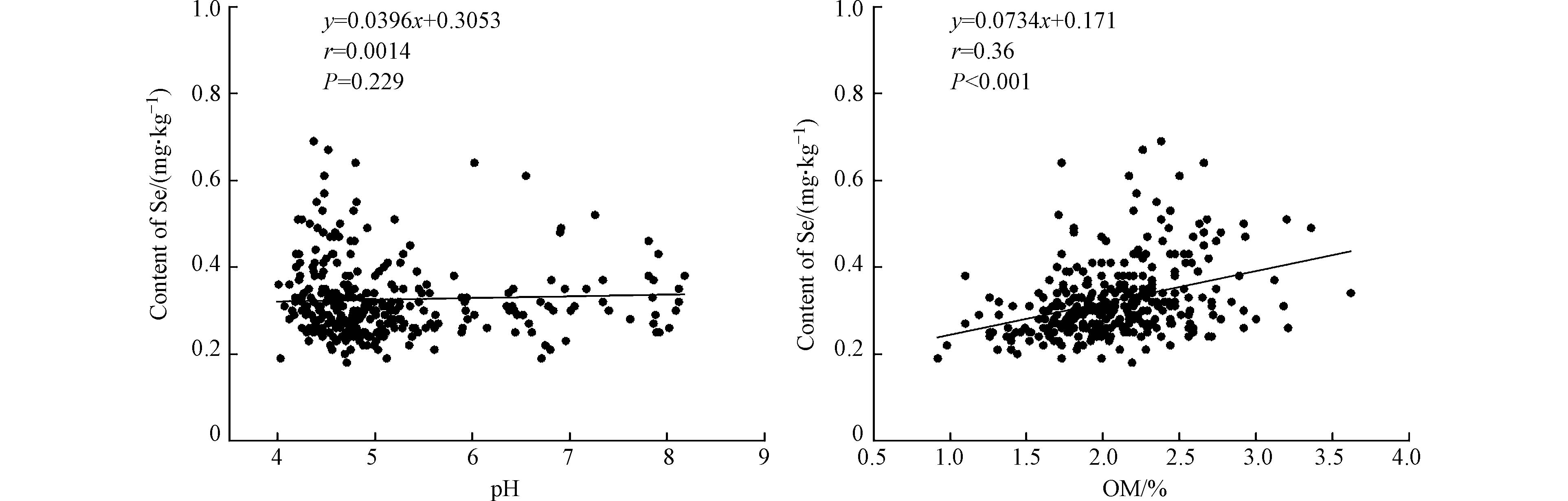
有研究表明,对土壤中Se含量产生重要影响有pH与有机质等理化性质[28],通过对研究区土壤Se含量与土壤pH和有机质含量进行相关性分析(图6),结果表明,土壤Se含量与pH值呈弱的正相关(无显著相关,P>0.05). 已有大量研究表明[29],在酸性土壤中,Se元素以亚硒酸盐的形式存在,其迁移能力较弱,较为容易与土壤中有机质和金属氧化物结合而成为稳定态,而在碱性土壤中,土壤中Se主要以硒酸盐的形式存在,其溶解度较高,不易被土壤中金属氧化物所结合,容易发生Se迁移[30]. 由于研究区内大部分土壤为酸性土壤,平均值为5.13,pH值变化波动范围较小,碱性土壤占比过低,而无法形成代表性的规律. 因此,本次研究并没有得出其pH与土壤中Se的明显规律.
土壤中有机质是动植物、微生物等生物残体在不同分解程度下的产物及产物的腐殖质组分[31],通过相关性分析表明有机质含量与Se含量呈显著的正相关(r=0.36,P<0.01),有机质对土壤中的Se起吸附和固定作用,在富含有机质的土壤中,Se能够以与腐殖质结合的形式存在,从而导致Se更容易富集于土壤中,呈现土壤Se与有机质正相关的关系[32].
-
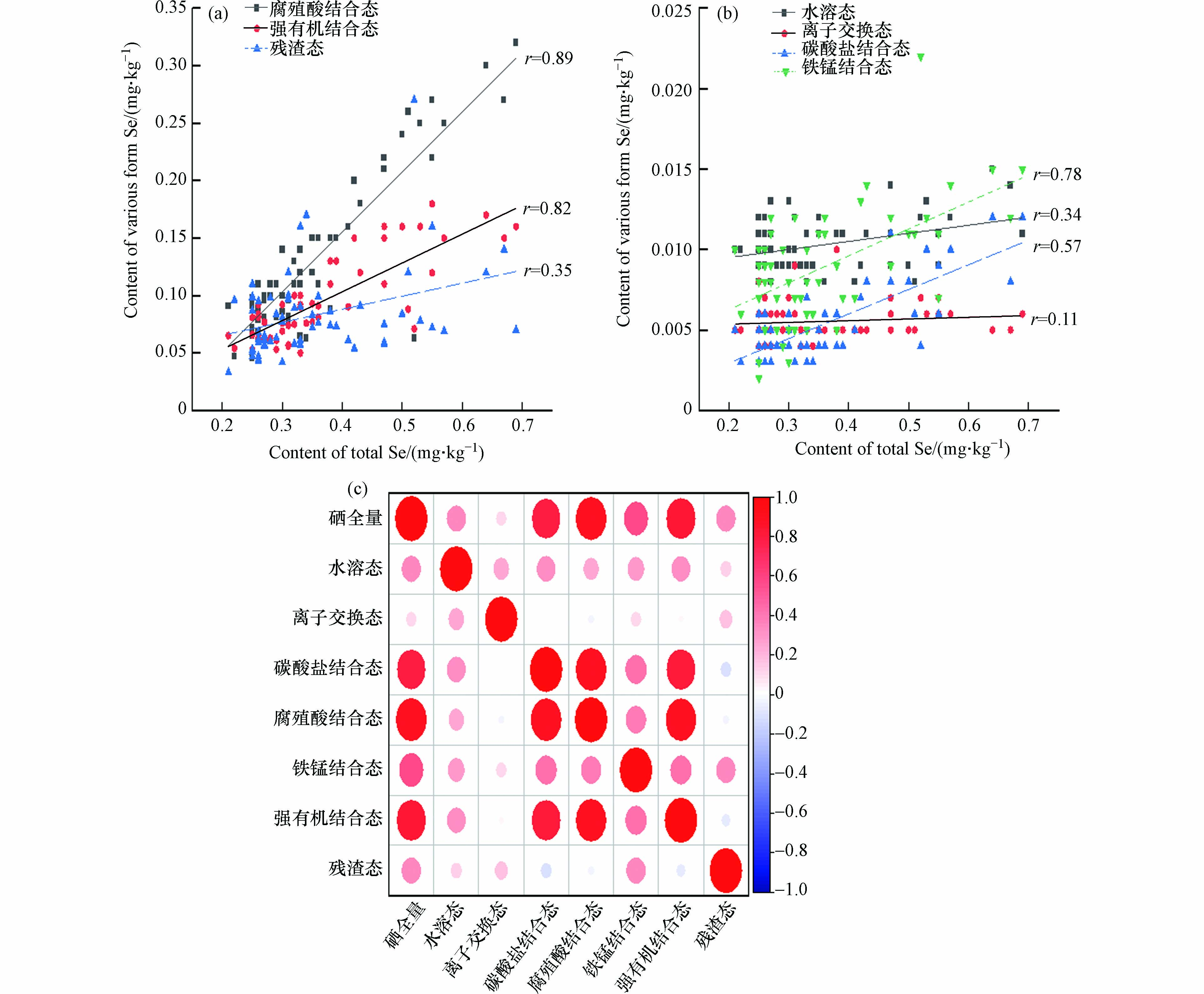
通过研究土壤中硒的赋存形式,来判断土壤中硒元素的生物活动性[33]. 土壤中硒元素赋存形式主要有七种形态(表6),通过对研究区土壤硒元素不同形态含量特征统计发现,其含量由高至低分别为腐殖酸结合态、强有机结合态、残渣态、水溶态、铁锰结合态、离子交换态和碳酸盐结合态,研究区内土壤中硒的赋存形式以腐殖酸结合态和强有机结合态为主,这与前人大多数的研究结果类似[34],主要是因为硒在土壤中的赋存形式主要受岩石风化、腐殖化过程和微生物运动的影响,其中,岩石风化所产生的的硒转化为碳酸盐和铁锰氧化物结合态,腐殖化和微生物作用会导致硒的形态转变或形成络合物,使得更多的无机结合态硒转化为有机结合态硒,因此土壤中的硒主要以有机结合态和腐殖酸结合态的形式存在[35]. 而通常能被植物所吸收的水溶态、离子交换态和碳酸盐结合态含量很低,占比较少. 通过相关性分析(图7)可知,腐殖酸结合态与强有机结合态硒与硒全量相关性极强,说明硒全量在一定程度上,受控于腐殖酸结合态与强有机结合态硒,而水溶态和离子交换态与硒全量相关性相对于较弱,因此提高土壤中硒全量并不一定能被农作物吸收,应对土壤中有效硒进行影响因素研究.
-
土壤中硒全量无法真实反映土壤硒的生物有效性,因此一般用土壤中有效硒的含量来体现土壤对农作物硒的供给需求能力[36]. 以往研究表明[37-39],通常能被植物所吸收的水溶态、离子交换态、碳酸盐结合态硒被称为有效硒. 土壤理化性质是影响硒有效性的重要因素,同时硒全量也是一项重要指标. 通过选取有效硒和pH与有机质等理化性质进行偏相关分析(表7),结果表明,当控制变量为有机质时,pH与有效硒相关系数为0.37,相关性较好. 当控制变量为pH时,有效硒与有机质的相关系数为0.08,无相关性. 所以,研究区内土壤有机质对硒有效性的影响程度小于pH值的影响程度. 对土壤中有机质与硒全量和有效硒进行偏相关分析,可得,当控制变量为硒全量时,有机质与有效硒的相关系数为0.42,相关性较低,当控制变量为有机质时,硒全量与有效硒的相关系数为0.68,相关性较高. 因此研究区内硒全量对硒的有效性的影响最大,影响硒有效性的主控因素是硒全量及pH.可以通过人为手段从而提高土壤硒的生物有效性,适当调整土壤 pH 值从而显著提高硒元素的生物有效性[40]
-
(1)湖南省龙山县主要耕地区表层土壤中硒平均含量为0.33 mg·kg−1,有机质平均含量为20.7 g·kg−1,土壤pH以酸性为主,硒含量等级适量和高的占比分别为87.06%和12.94%,富硒土壤地区主要分布在石牌镇西边区域,硒含量空间变异等级为中等空间变异,其含量变化受人为与自然双重影响,通过垂向剖面分析得其为表层富集,具有表聚性.
(2)对比硒含量空间分布图发现,硒含量受地层影响较大,老地层硒含量通常大于新地层,但石牌镇西部富硒地区呈现不一样的变化趋势. 硒含量位于旱地中含量最高,水田次之,林地最低,受人为因素显著影响. 土壤硒含量与有机质呈正相关关系,与pH值无显著相关.
(3)硒的赋存形态以腐殖酸结合态和强有机结合态为主,有效硒含量占比较低. 硒全量和pH是影响硒生物有效性的主要因素,适当提高土壤pH值,能提高土壤硒生物有效性.
湖南省龙山县耕地土壤硒含量特征及其影响因素
Characteristics and influencing factors of soil se content in cultivated land in Longshan County, Hunan Province
-
摘要: 硒是人体及动物必需的微量营养元素之一. 在龙山县耕地区系统地采集了326件表层土壤样品进行分析测试,研究了区域内土壤硒含量空间分布特征、空间变异特性、垂向分布特点及其影响因素,分析了土壤有效态硒的影响因素. 结果表明,研究区土壤硒平均含量为0.33 mg·kg−1,土壤有机质平均含量为20.7 g·kg−1,土壤呈酸性. 土壤硒含量呈中等空间变异,垂向分布呈表层富集的规律. 研究区内硒含量主要受成土母质与土地利用的双重影响,有机质含量与硒含量呈显著正相关关系(P<0.01). 土壤硒形态以腐殖酸结合态与强有机结合态为主,有效硒组分占比较低,土壤硒的生物有效性受硒全量和酸碱度影响较大,可以通过人为方式适当调整土壤酸碱度,提高硒生物有效性,有效提升土地利用价值.Abstract: Se is one of the essential micronutrients for human body and animals. 326 surface soil samples were systematically collected in the cultivated area of Longshan County for analysis and testing. The spatial distribution characteristics, spatial variation characteristics, vertical distribution characteristics and influencing factors of soil Se content in the region were studied, and the influencing factors of soil available Se were analyzed. The results showed that the average content of Se in the study area was 0.33 mg·kg−1, and the average content of soil organic matter was 20.7 g·kg−1. The soil was acidic. The soil of Se content showed medium spatial variation, and the vertical distribution showed the law of surface enrichment. Se content is mainly affected by soil forming parent material and land use in the study area, and there is a significant positive correlation between organic matter content and Se content (P < 0.01). The forms of soil Se are mainly humic acid bound and strong organic bound, and the effective Se components account for a relatively low proportion. The bioavailability of soil Se is greatly affected by the total amount of Se and pH. the soil pH can be adjusted artificially to improve the bioavailability of Se, effectively improve the value of land use.
-
Key words:
- top soil /
- Se /
- spatial distribution /
- influencing factors /
- Longshan, Hunan Province
-

-
表 1 研究区土壤硒含量参数统计
Table 1. Statistics of soil Se content parameters in the study area
元素/指标
Elements/Indicators平均值
Mean最大值
Maximum最小值
Minimum标准差
Standard deviation变异系数
Variation coefficient全国土壤背景值[15]
National soil background valueSe/(mg·kg−1) 0.33 0.69 0.18 0.10 0.30 0.22 pH — 8.18 4.01 0.94 0.18 — OM/(g·kg−1) 20.7 36.2 9.22 4.12 0.20 — 注:pH无量纲;“—”表示无数据. Note: pH is dimensionless; "—" means no data 表 2 研究区土壤硒划分标准
Table 2. classification standard of soil Se in the study area
含量等级
Content gradeSe含量/(mg·kg−1)
Se土壤中样品所占比例/%
Samples in soil Proportion面积/km2
Area缺乏 ≤0.125 0 0 边缘 0.125—0.175 0 0 适量 0.175—0.4 87.06 48.82 高 0.4—3.0 12.94 7.26 过剩 >3.0 0 0 表 3 研究区土壤硒理论半方差模型及其拟合参数
Table 3. theoretical semivariance model of soil Se and its fitting parameters in the study area
最优模型
Best Model块金值
C0基台值C0+C 块金系数C0/(C0+C) 变程/km
Range预测误差
Prediction ErrorMS RMSS Se 球面模型 0.534 1.236 0.432 8.159 0.0045998 1.0251987 表 4 不同成土母质土壤中Se元素参数统计
Table 4. statistics of Se element parameters in soils with different soil forming parent materials/mg·kg−1
时代
Times地层名称
Stratum name岩性
Lithology样本数
Sample size平均值/(mg·kg−1)
Mean变化范围/(mg·kg−1)
Variation
range标准差/
(mg·kg−1)
Standard
deviation变异系数
Variation
coefficient寒武系
Cambrian System高台组上段 灰岩、灰绿色页岩、白云岩 40 0.33 0.22—0.61 0.067 0.20 高台组下段 灰岩页岩互层 17 0.31 0.24—0.39 0.039 0.13 奥陶系
Ordovician System大湾组 灰岩、钙质页岩 38 0.26 0.18—0.43 0.045 0.17 志留系
Silurian system帽溪组 黄绿色页岩、泥质粉砂岩、页岩 158 0.35 0.19—0.69 0.099 0.28 罗惹坪组 泥岩、灰岩 73 0.29 0.19—0.46 0.055 0.19 表 5 不同土地利用类型土壤中Se含量参数统计(mg·kg−1)
Table 5. Statistics of Se content parameters in soils of different land use types
土地利用方式
Land use mode平均值
Mean样本数
Sample size变化范围
Variation range标准差
Standard deviation变异系数
Variation coefficient旱地 0.34 210 0.18—0.69 0.091 0.273 水田 0.31 94 0.19—0.55 0.117 0.375 林地 0.29 22 0.21—0.48 0.054 0.184 表 6 研究区土壤硒不同形态含量特征
Table 6. characteristics of different forms and contents of soil Se in the study area
元素形态
Elemental均值/
(mg·kg−1)
Mean最小值/
(mg·kg−1)
Minimum最大值/
(mg·kg−1)
Maximum标准偏差/
(mg·kg−1)
Standard deviation变异系数
Variation
coefficient占比
Proportion水溶态SOL-Se 0.010 0.007 0.015 0.002 16.81% 2.89% 离子交换态EX-Se 0.006 0.004 0.010 0.001 19.03% 1.57% 碳酸盐结合态CA-Se 0.005 0.003 0.012 0.002 42.62% 1.49% 腐殖酸结合态HA-Se 0.133 0.046 0.318 0.069 51.98% 37.36% 铁锰结合态FMO-Se 0.009 0.002 0.022 0.003 39.04% 2.49% 强有机结合态OM-Se 0.092 0.050 0.179 0.036 38.64% 25.87% 残渣态RES-Se 0.083 0.033 0.274 0.038 46.26% 23.38% 表 7 有效硒与硒全量、有机质、pH的偏相关分析结果
Table 7. partial correlation analysis results of Available Se and total Se, organic matter and pH
因变量
Dependent
variable控制变量
Control
variable自变量
Independent
variable相关系数
Correlation
coefficient控制变量
Control
variable自变量
Independent
variable相关系数
Correlation
coefficient有效硒
Available SepH 有机质 0.08 硒全量 有机质 0.42 有机质 pH 0.37 有机质 硒全量 0.68 -
[1] 黄冰霞, 支添添, 赵志刚, 等. 硒元素与人类健康 [J]. 宜春学院学报, 2019, 41(9): 95-101. HUANG B X, ZHI T T, ZHAO Z G, et al. The relationship between selenium and human heath [J]. Journal of Yichun University, 2019, 41(9): 95-101(in Chinese).
[2] 许月明, 张爽, 许凌凌, 等. 硒与人体健康 [J]. 科技视界, 2018(14): 135-136. XU Y M, ZHANG S, XU L L, et al. Selenium and human health [J]. Science & Technology Vision, 2018(14): 135-136(in Chinese).
[3] 王学求, 柳青青, 刘汉粮, 等. 关键元素与生命健康: 中国耕地缺硒吗? [J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(3): 412-423. WANG X Q, LIU Q Q, LIU H L, et al. Key elements and human health: Is China's arable land selenium-deficient? [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(3): 412-423(in Chinese).
[4] RAYMAN M P. Food-chain selenium and human health: Emphasis on intake [J]. The British Journal of Nutrition, 2008, 100(2): 254-268. doi: 10.1017/S0007114508939830 [5] 李军, 张忠诚. 微量元素硒与人体健康 [J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 2011, 28(5): 59-63. LI J, ZHANG Z C. Trace element selenium and human health [J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 2011, 28(5): 59-63(in Chinese).
[6] 杨忠芳, 余涛, 侯青叶, 等. 海南岛农田土壤Se的地球化学特征 [J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5): 837-849. YANG Z F, YU T, HOU Q Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in farmland of Hainan Island [J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5): 837-849(in Chinese).
[7] 周菲, 彭琴, 王敏, 等. 土壤-植物体系中硒生物有效性评价研究进展 [J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(6): 461-472. doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-1268 ZHOU F, PENG Q, WANG M, et al. Advances in the evaluation of selenium bioavailability in soil-plant system [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(6): 461-472(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-1268
[8] 王锐, 邓海, 严明书, 等. 基于回归方程的硒元素生物有效性研究 [J]. 土壤通报, 2020, 51(5): 1049-1055. WANG R, DENG H, YAN M S, et al. Bioavailability of selenium based on regression equation [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 51(5): 1049-1055(in Chinese).
[9] SKALNAYA M G, TINKOV A A, PRAKASH N T, et al. Selenium and other elements in wheat (Triticum aestivum) and wheat bread from a seleniferous area [J]. Biological Trace Element Research, 2019, 192(1): 10-17. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01776-6 [10] JIANG T Y, YU T, QI H B, et al. Analysis of phosphorus and sulfur effect on soil selenium bioavailability based on diffusive gradients in thin films technique and sequential extraction [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 302: 134831. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134831 [11] YANG H, YANG X F, NING Z P, et al. The beneficial and hazardous effects of selenium on the health of the soil-plant-human system: An overview [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 422: 126876. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126876 [12] 张永康, 刘红艳, 周亚林. 湘西地区土壤硒含量及其分布的调查 [J]. 长沙大学学报, 2009, 23(2): 16-17. ZHANG Y K, LIU H Y, ZHOU Y L. Investigation on soil selenium content and its distribution in Western Hunan [J]. Journal of Changsha University, 2009, 23(2): 16-17(in Chinese).
[13] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 土地质量地球化学评价规范: DZ/T 0295—2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. Determination of land quality geochemical evaluation: DZ/T 0295—2016[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016(in Chinese).
[14] DD2005-03生态地球化学评价样品分析技术要求(试行). [S]. 北京: 中国地质调查局地质调查技术标准, 27-30. DD2005-03 Technical requirements for analysis of ecological geochemical evaluation samples (Trial). [S]. Beijing: Geological Survey Technical Standard of China Geological Survey, 27-30.
[15] 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 余涛. 中国土壤地球化学参数[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2020. HOU Q Y, YANG Z F, YU T. Soil geochemical dataset of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020(in Chinese).
[16] 张仁铎. 空间变异理论及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005. ZHANG R D. Spatial variation theory and application [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005(in Chinese).
[17] 王锐, 邓海, 梁绍标, 等. 重庆市两不同地貌及地质背景区土壤Cd、Se元素含量空间插值方法研究 [J]. 土壤通报, 2020, 51(6): 1332-1341. WANG R, DENG H, LIANG S B, et al. Spatial interpolation method of soil Cd and Se element contents in two different landforms and geological background areas in Chongqing City [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 51(6): 1332-1341(in Chinese).
[18] 肖凯琦, 董好刚, 郭军, 等. 湖南省汨罗市耕地土壤养分空间变异特征研究 [J]. 华南地质, 2021, 37(4): 369-376. XIAO K Q, DONG H G, GUO J, et al. Study on spatial variability of farmland soil nutrients in Miluo City, Hunan Province [J]. South China Geology, 2021, 37(4): 369-376(in Chinese).
[19] 赵明松, 李德成, 张文凯, 等. 淮北平原农田土壤养分空间变异特征: 以安徽省蒙城县为例 [J]. 土壤通报, 2016, 47(3): 611-617. ZHAO M S, LI D C, ZHANG W K, et al. Spatial variability characteristics of soil nutrient in north plain of Anhui Province-A case study of Mengcheng County, Anhui Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(3): 611-617(in Chinese).
[20] 宋江涛, 林治家, 张锦煦, 等. 湖南隆回县土壤硒元素地球化学特征及其影响因素: 以石门-滩头镇为例 [J]. 华南地质, 2021, 37(1): 83-92. SONG J T, LIN Z J, ZHANG J X, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in soil and its influencing factors in Longhui County, Hunan Province: A case study of Shimen-tantou township [J]. South China Geology, 2021, 37(1): 83-92(in Chinese).
[21] 王美珠, 章明奎. 我国部分高硒低硒土壤的成因初探 [J]. 浙江农业大学学报, 1996(1): 89-93. WANG M Z, ZHANG M K. A discussion on the cause of high-Se and low-Se soil formation [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural University, 1996(1): 89-93(in Chinese).
[22] 张秀芝, 马忠社, 魏静, 等. 利用元素地球化学特征研究河北平原第四纪沉积环境的探讨与实践 [J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(4): 194-205. ZHANG X Z, MA Z S, WEI J, et al. The use of geochemical characteristics of elements in the study of Quaternary sedimentary environment in the Hebei Plain [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(4): 194-205(in Chinese).
[23] 张丽, 张乃明, 张玉娟, 等. 云南耕地土壤硒含量空间分布及其影响因素研究 [J]. 土壤, 2021, 53(3): 578-584. ZHANG L, ZHANG N M, ZHANG Y J, et al. Spatial distribution of Se content and its influencing factors in cultivated topsoil in Yunnan [J]. Soils, 2021, 53(3): 578-584(in Chinese).
[24] 王锐, 邓海, 贾中民, 等. 硒在土壤-农作物系统中的分布特征及富硒土壤阈值 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12): 5571-5578. WANG R, DENG H, JIA Z M, et al. Distribution characteristics of selenium in a soil-crop system and the threshold of selenium-rich soils [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(12): 5571-5578(in Chinese).
[25] 武芝亮, 李致坤, 侯青叶, 等. 四川省邻水县土壤及作物硒地球化学特征及其研究意义 [J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(6): 1752-1761. WU Z L, LI Z K, HOU Q Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in soils and crops and its research significance in Linshui County, Sichuan Province [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(6): 1752-1761(in Chinese).
[26] 余飞, 张风雷, 张永文, 等. 重庆典型农业区土壤硒地球化学特征及影响因素 [J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4): 830-838. YU F, ZHANG F L, ZHANG Y W, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influential factors of soil selenium in typical agricultural area, Chongqing [J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4): 830-838(in Chinese).
[27] 周亚龙, 郭志娟, 王乔林, 等. 雄安新区富硒土地资源分布特征及开发利用评价 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(8): 3913-3921. ZHOU Y L, GUO Z J, WANG Q L, et al. Distribution characteristics and utilization evaluation of selenium-rich land resources in Xiongan New District [J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(8): 3913-3921(in Chinese).
[28] 刘飞, 杨柯, 徐仁廷, 等. 广西都安县典型水田硒地球化学特征及影响因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(10): 4897-4907. LIU F, YANG K, XU R T, et al. Selenium geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of paddy fields in du. an County, Guangxi [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(10): 4897-4907(in Chinese).
[29] 黄春雷, 宋明义, 魏迎春. 浙中典型富硒土壤区土壤硒含量的影响因素探讨 [J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(11): 4405-4410. HUANG C L, SONG M Y, WEI Y C. Study on selenium contents of typical selenium-rich soil in the middle area of Zhejiang and its influencing factors [J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(11): 4405-4410(in Chinese).
[30] 刘永贤, 陈锦平, 潘丽萍, 等. 浔郁平原富硒土壤成因及其影响因素研究 [J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6): 1139-1144. LIU Y X, CHEN J P, PAN L P, et al. Studies on causes and influential factors of selenium-rich soil in Xunyu plain [J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6): 1139-1144(in Chinese).
[31] 彭琴, 李哲, 梁东丽, 等. 不同作物对外源硒动态吸收、转运的差异及其机制 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(4): 1667-1674. PENG Q, LI Z, LIANG D L, et al. Dynamic differences of uptake and translocation of exogenous selenium by different crops and its mechanism [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(4): 1667-1674(in Chinese).
[32] ZHANG Y, WU S Y, ZHENG H, et al. Modes of selenium occurrence and LCD modeling of selenite desorption/adsorption in soils around the selenium-rich core, Ziyang County, China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(15): 14521-14531. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1595-0 [33] 谢薇, 杨耀栋, 侯佳渝, 等. 天津市蓟州区土壤硒的有效性及影响因素 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(10): 2306-2316. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019042802 XIE W, YANG Y D, HOU J Y, et al. Bioavailability of selenium and its influencing factors in soil of Jizhou district, Tianjin [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(10): 2306-2316(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019042802
[34] YU T, HOU W L, HOU Q Y, et al. Safe utilization and zoning on natural selenium-rich land resources: A case study of the typical area in Enshi County, China [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2020, 42(9): 2803-2818. doi: 10.1007/s10653-020-00519-0 [35] 陈东平, 张金鹏, 聂合飞, 等. 粤北山区连州市土壤硒含量分布特征及影响因素研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(7): 2838-2848. CHEN D P, ZHANG J P, NIE H F, et al. Selenium distribution in soils of Lianzhou City, mountain area of northern Guangdong Province and its influencing factors [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(7): 2838-2848(in Chinese).
[36] LI C, ZHANG C S, YU T, et al. Use of artificial neural network to evaluate cadmium contamination in farmland soils in a Karst area with naturally high background values [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 304: 119234. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119234 [37] 侯佳渝, 杨耀栋, 谢薇, 等. 天津市西郊富硒土壤地球化学特征和成因分析 [J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(3): 618-625. HOU J Y, YANG Y D, XIE W, et al. The analysis of geochemical characteristics and genesis of selenium-rich soil in western suburb of Tianjin [J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(3): 618-625(in Chinese).
[38] DINH Q T, WANG M K, TRAN T A T, et al. Bioavailability of selenium in soil-plant system and a regulatory approach [J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 49(6): 443-517. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2018.1550987 [39] 陈锦平, 刘永贤, 潘丽萍, 等. 浔郁平原不同作物的硒富集特征及其影响因素 [J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6): 1155-1159. CHEN J P, LIU Y X, PAN L P, et al. Selenium accumulation characteristics and influential factors of different crops in Xunyu plain [J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6): 1155-1159(in Chinese).
[40] 余涛, 杨忠芳, 王锐, 等. 恩施典型富硒区土壤硒与其他元素组合特征及来源分析 [J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6): 1119-1125. YU T, YANG Z F, WANG R, et al. Characteristics and sources of soil selenium and other elements in typical high selenium soil area of Enshi [J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6): 1119-1125(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: