-
高新沙水库是珠江三角洲水资源配置工程中一个重要的拟新建调节水库,目前正在挖土建设,库区土壤多为淤质黏土和微透水性,其中重金属具有难降解性、隐蔽性和毒性大等特点,在库区水体环境变化的情况下有可能释放到水体中,影响水质安全,威胁人体健康. 鉴于此,高新沙水库库底土壤重金属含量与形态分布及其对水质安全的影响研究,对保护水库环境与居民身体健康具有重要意义.
近年来,土壤重金属分布特征与生态风险在国内外开展了大量研究[1-3]. 研究内容主要集中在土壤重金属富集与污染评价[4-5]、重金属迁移转化过程[6]、重金属污染源解析[7]等方面,研究侧重农田[8-9]、城市[10-11]和采矿[12-13]等区域,对水库区域的研究逐渐引起研究者们的重视. 水库型水源地是我国重要的居民饮用水水源地,同时作为一类人工淡水生态系统,受人类活动影响较大,污染途径多和来源广[14]. 针对现有运行的水库,部分学者对密云水库周围矿区土壤[15-17]、三峡库区表层土壤[18-19]、丹江口水库周围土壤[20-21]、百花水库消落带土壤[22]等水库重金属分布特征与潜在生态风险进行研究,表明现行的水库土壤重金属具有不同程度的潜在生态风险,对水质安全可能存在一定的不利影响. 但是,在新建水库重金属污染风险评价中,针对水库库底土壤重金属含量与形态分布对水质安全的影响研究,鲜见报道.
本研究以高新沙水库土壤为研究对象,通过对8种重金属(Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Ni、Cr、Hg、As)含量与形态的测定,并采用单因子指数和潜在生态危害指数法对重金属的生态风险进行了评价,结合重金属浸出特征分析,来阐明水库库底土壤重金属含量、形态及浸出特征,评价土壤重金属对水质安全风险的影响,为高新沙水库水质安全管理提供科学依据.
-
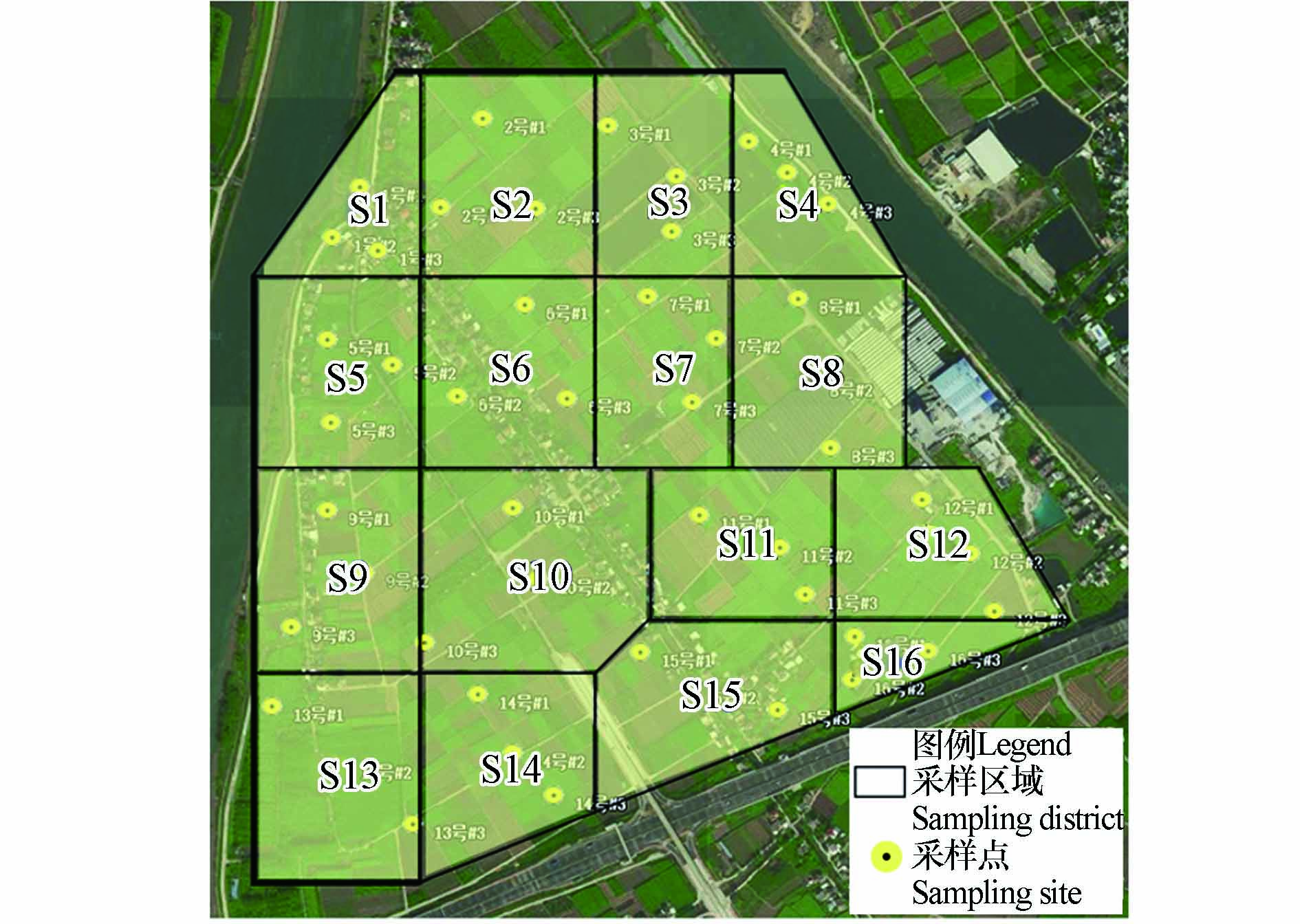
拟建高新沙水库库容达529.4万m3,库区约100万m2. 根据水库地理特点,采取改进棋盘式布点法布置16个采样区域,每个区域分别命名为S1—S16(图1),结合前期重金属总量测试结果,选取8个区域S1、S4、S5、S9、S10、S13、S15和S16进行重金属浸出风险评价. 在实际采样中,部分区域采用“S”或“X”形尽可能避开人为干扰,并设置3个平行样.
-
土壤样品采集后经过除杂、风干和过筛等前处理后,采用BCR四步提取法对土壤样品中Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Ni、Cr、Hg、As进行不同形态的提取[15-23]. 弱酸提取态采用0.1 mol·L−1 HOAc振荡16 h,可还原态是0.5 mol·L−1 NH2OH·HCl振荡16 h,可氧化态采用30% H2O2氧化完全和1 mol·L−1 NH4OAc振荡16 h,残渣态是通过将上一步的残渣转移至微波消解管中,添加2 mL HF与8 mL HNO3进行消解后,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)测定重金属Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Ni和Cr含量,采用原子荧光分光光度计(AFS)测定Hg和As含量.
-
地累计指数法可定量评价土壤重金属污染程度,它不但考虑到环境化学背景值和人为活动影响因素,而且考虑了自然成岩作用引起的背景值变动的影响. 计算公式如下[17]:
式中:Igeo是重金属i的地累计指数,Csi为样品中第i种重金属的实测浓度(mg·kg−1),K是可能引起背景值的变动而采用的系数,一般取值1.5,Cni是第i种重金属的地球化学背景值(mg·kg−1),本文以珠江三角洲地区土壤背景值(DB 44/T1415-2014)作为参考,Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Ni、Cr、Hg和As背景值分别取值32、97、0.11、60、28、77、0.13、25 mg·kg−1. 地累积指数评价标准划分如下(表1).
潜在生态风险指数是应用于土壤重金属污染的生态风险评价常用方法之一,其不但反映某一特定环境中单项重金属污染物的影响,还反映多种重金属污染物的综合影响,并定量划分出潜在生态危害程度. 计算公式如下[17]:
式中,RI是土壤中多种重金属综合潜在生态危害指数,Eri是第i种重金属的潜在生态危害指数;Csi为第i种重金属的实测浓度(mg·kg−1),Cni为第i种重金属的背景参考值(mg·kg−1);Tri为第i种重金属的毒性系数,Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Ni、Cr、Hg和As分别取值5、1、30、5、5、2、40、10. 潜在生态风险指数分级标准如下(表2).
-
土壤重金属浸出采用美国环保局1312方法SPLP(Synthetic Precipitation Leaching Procedure),按H2SO4:HNO3=3:2配制不同pH 1.0、3.6和5.6的浸提剂,固液比为1:10(kg·L−1),常温下放入摇床中180 r·min−1连续振荡24 h后,经4000 r·min−1离心10 min、0.45滤膜过滤得到土壤浸出溶液,通过电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)测定浸出液中的Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Ni、Cr6+、Hg和As含量,同时设置去离子水pH=(6.34±0.16)为空白对照(CK).
在模拟水库水体pH情况下,考察库区土工膜不同破损程度对重金属浸出特性及其对水质安全的影响. 设置4个处理组:土工膜破损0%,20%,50%和100%,并置于分别装有50 g土壤样品的土柱底部. 根据南沙汛期降雨量计算(平均每月225.82 mm),设定pH=7.5±0.05的淋溶量为450 mL. 在淋溶24 h后,测定淋出液中8种重金属含量. 水质安全风险评价采用生活饮用水卫生标准(GB 5749-2022),Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Ni、Cr6+、Hg和As等重金属标准限值分别为1.0、1.0、0.005、0.01、0.02、0.05、0.001、0.01 mg·L−1.
-
测试过程中采用试样空白对照、平行样品测试和标准分析物质(GBW07385 GSS-29)进行质量保证和控制. 标准曲线的相关系数均大于0.999,标准土壤的回收率在94%—102%之间,符合相关检测标准的质控要求.
-
针对库区8个采样点位中3 m深处土壤,仅S13点位土壤中唯独As总量22.10 mg·kg−1轻微超出农用地土壤污染风险管控标准-重金属风险筛限值(GB15618-2018),超标系数为0.11,其余7个点位中Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Ni、Cr、Hg和As等8种重金属均未超出相应的标准限值100、250、0.6、140、100、300、0.6、20 mg·kg−1(表3). 张德举等[24]研究表明,北京密云水库内湖消落带5种重金属Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr和Ni含量均符合该区域土壤环境质量要求,说明高新沙库区土壤质量总体处于清洁水平.
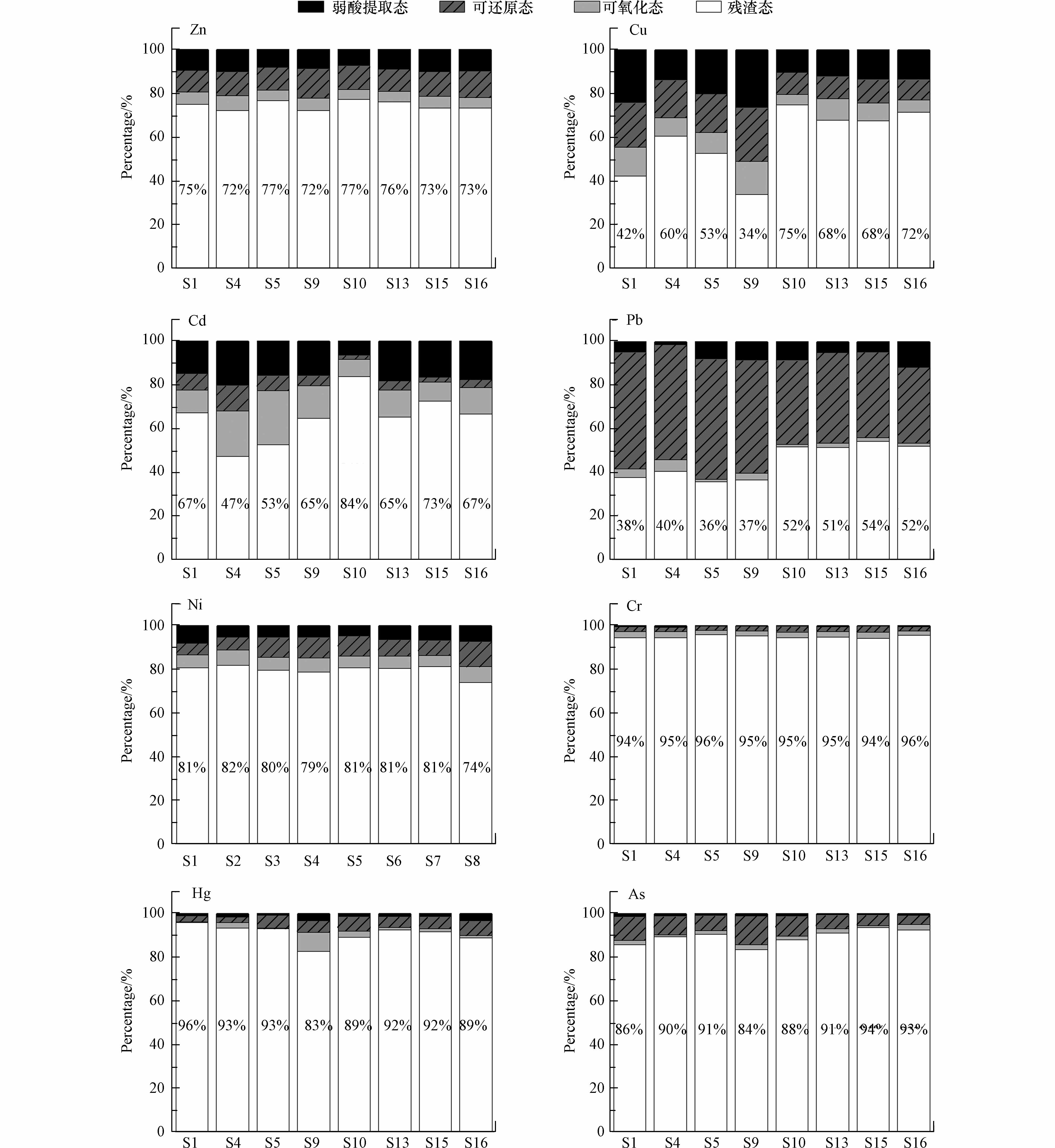
从重金属形态分布来看,绝大多数重金属以残渣态为主,其中Zn、Ni、Cr、Hg和As等5种重金属残渣态所占比例均达到70%以上(图2). 土壤中Cu大体上以残渣态为主(最高占比75%),各形态比例顺序为残渣态>弱酸提取态>可还原态>可氧化态. 类似地,土壤中Cd以残渣态为主(最高占比84%),其次弱酸提取态或可还原态,可氧化态占比最少. 值得注意地是,土壤中Pb主要以可还原态和残渣态为主(35%—54%),而且S1、S4、S5、S9点位中重金属可还原态占比超过残渣态,表明重金属稳定性相对减弱,迁移活性可能增强,对水库水质安全具有一定的潜在风险.
-
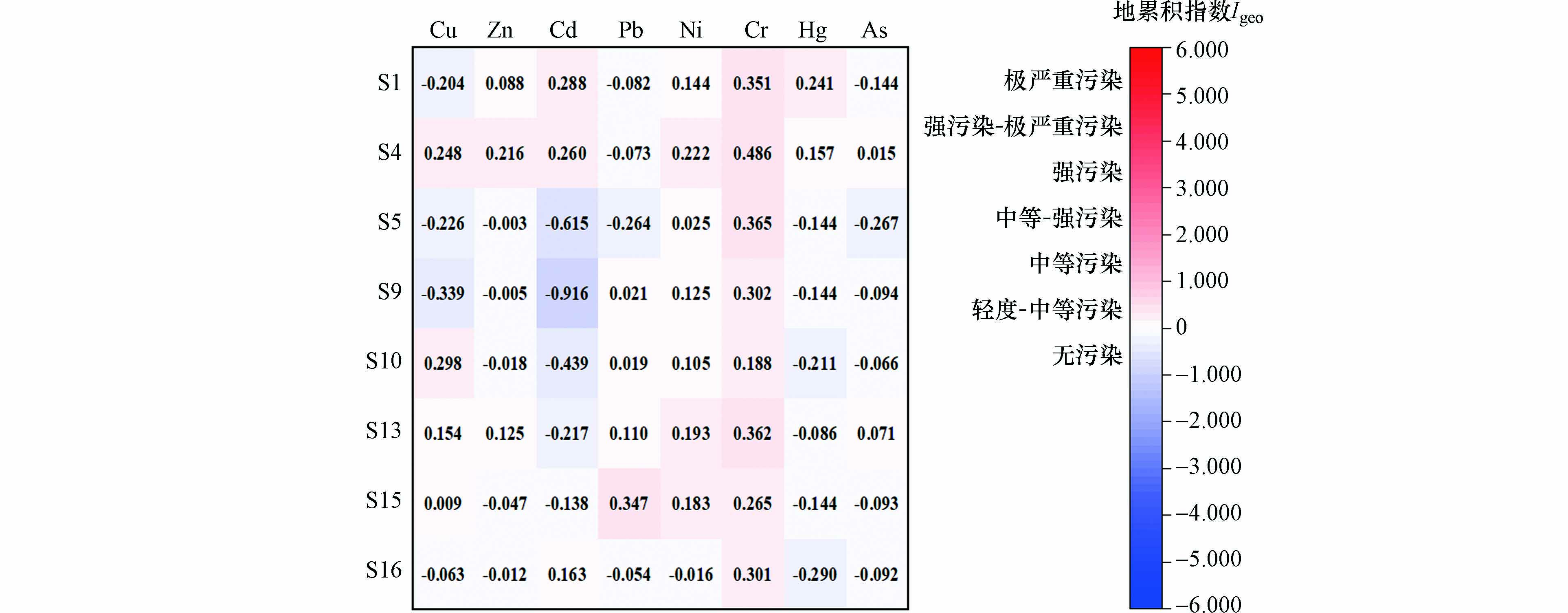
根据地累积指数法评价结果(图3),库区土壤8种重金属普遍属于极轻度污染水平. 重金属Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Ni、Cr、Hg和As的地累积指数范围分别是−0.063—0.298、−0.003—0.216、−0.916—0.288、−0.264—0.347、−0.016—0.222、0.188—0.486、−0.290—0.241和−0.144—0.071. 类似地,王剑等[20]采用地累积指数法评价丹江口水库新增淹没区土壤重金属生态危害,发现Cu、Zn、Pb、Ni、Cr、As等处于无污染水平,而Cd则是主要的污染元素.
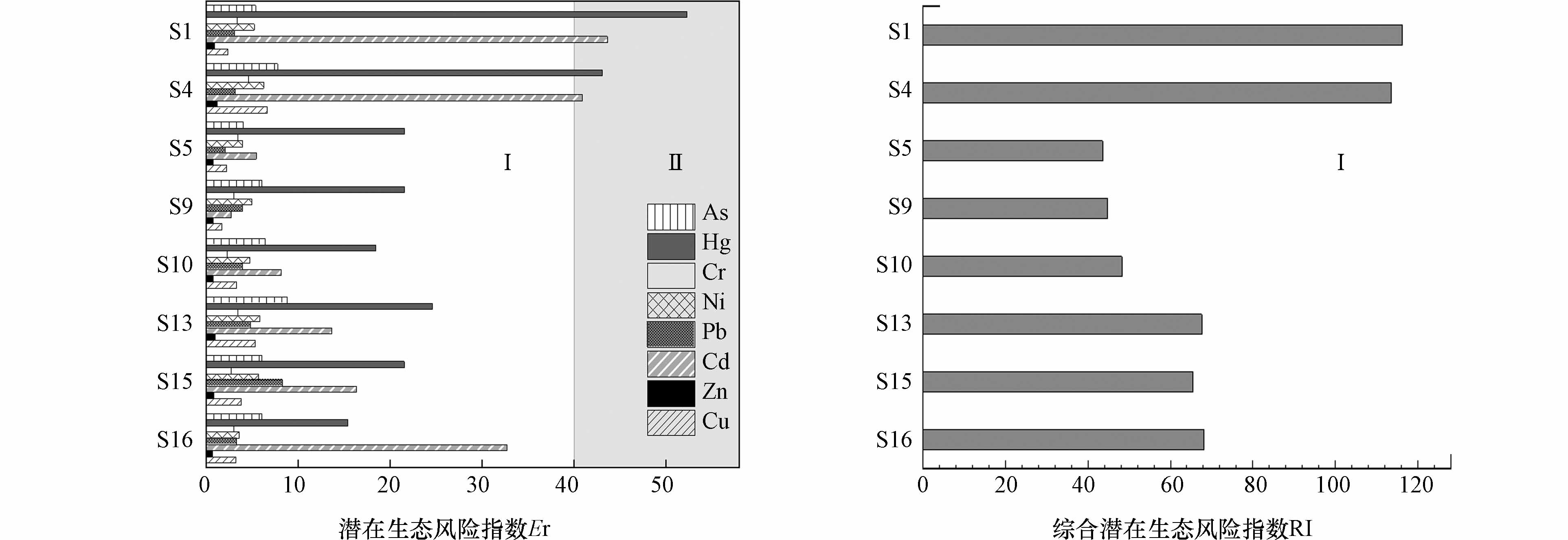
从单项潜在生态风险指数来看(图4),库区土壤8种重金属污染程度同样地普遍属于轻微水平(Er <40),除了在采样点S1和S4中Cd和Hg略微大于40,属于中等生态危害水平. 从综合潜在生态风险指数评价来看,库区土壤8种重金属生态风险水平均处于轻微水平. 类似地,乔敏敏[15]、辜敏[17]、傅杨武[18]等在研究三峡库区和密云水库土壤重金属污染风险中,绝大部分重金属生态危害属于轻微水平. 不同地是,孙婷等[22]通过地累积指数和潜在生态风险指数对贵阳市百花水库消落带土壤重金属生态风险进行评价,均表明水库消落带土壤Hg污染风险水平较高,生态风险不容忽视. 综合以上结果,表明高新沙库区土壤重金属生态风险总体处于轻微水平,对水质安全带来的环境风险可能非常有限.
-
当浸提液pH=3.6和pH=5.6时候(图5),绝大部分重金属均未有浸出,唯独As在土壤点位S1、S4、S5、S9、S10和S16中有少量浸出,但浸出浓度均未超出生活饮用水卫生标准限值10 μg·L−1(GB 5749-2022). 这些结果与土壤重金属总量分析结果保持一致(表1). 在浸提液pH=3.6条件下,水库土壤样品浸出液中重金属Pb浓度均超过标准限值0.01mg·L−1,这与重金属形态分布特征得到的结果类似(图2),反映土壤Pb可能会对水质造成一定污染风险. 除此之外,其余7种重金属均未有浸出或者浓度低于标准限值. 类似地,邱其俊等[25]在研究闽北新建水库周边土壤重金属生态与健康风险中,发现8种重金属总非致癌风险顺序为Pb>Zn>Cr>Cu>As>Ni>Cd>Hg. 此外,当浸提液pH=1.0时,5种重金属Zn、Cd、Pb、Ni和As在所有土壤点位浸出液中均出现超标现象,Cu在土壤点位S1和S9中轻微的超标,超标倍数分别为1.06和1.61. 值得注意地是,即是在极端情况下2种重金属Cr和Hg在所有土壤点位中均未超标,处于相对安全水平.
-
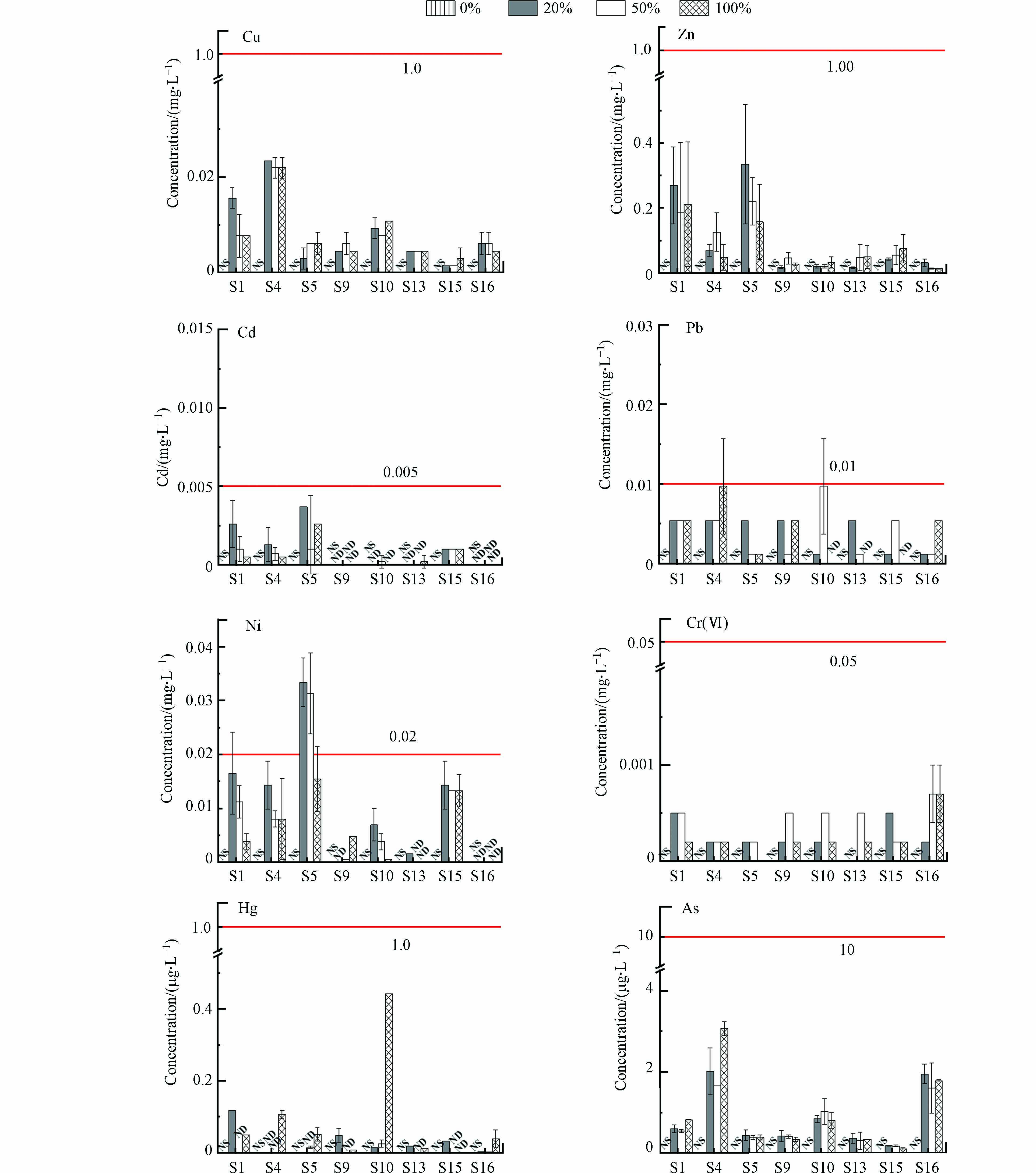
当土工膜完好的情况下(破损度0%),实际的西江水pH=7.50±0.05对库区所有8个土壤点位8种重金属均没有出现浸出液(图6),表明土工膜在实际情况下完全可以阻隔土壤重金属浸出,从而有效阻断重金属从土壤迁移至水体. 当土工膜破损20%和50%情况下,8个土壤点位浸出液中绝大多数重金属均低于标准限值(GB 5749-2022),除了S5土壤点位浸出液中Ni出现轻微超标现象. 当土工膜破损100%情况下,8个区域土壤点位中8种重金属均低于标准限值. 同样地,崔磊等[26]采用蒸馏水和模拟水分别研究瀑河水库库底土壤对水质影响,发现从整体上看土壤理化组分对水质未产生明显的不良影响. 以上这些结果表明,土壤重金属基本不会对水质安全风险造成影响,但在水库将来实际运行中加强水体Ni含量的监测与管理.
-
(1)高新沙库区3 m处土壤8种重金属均未超出农用地土壤污染风险管控标准-重金属风险筛选值(GB15618-2018),仅S13点位土壤中As轻微超出标准限值. 8种重金属普遍以残渣态为主,唯独Pb在部分土壤点位中以可还原态和残渣态为主,两者共占比35%—54%.
(2)根据地累积指数法和生态潜在风险指数评价结果,绝大部分重金属的Igeo和Er值范围分别为−1—1和0—4,表明库区土壤重金属生态风险总体处于轻微水平,对水质安全带来的环境风险非常有限.
(3)在不同pH浸提液条件作用下(pH=6.34、5.6、3.6),大部分重金属浸出浓度未超出生活饮用水卫生标准限值(GB 5749-2022),但在浸提液pH=1.0情况下,Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Ni和As出现不同程度的超标现象.
(4)在实际水库水体作用下,整体上来看土工膜破损程度没有对水质未产生显著的不良影响,但在水库实际运行中加强重金属含量的监测与管理,尤其是Pb和Ni.
高新沙水库土壤重金属形态分布、浸出特征及其对水质安全影响
Species and leaching characteristics of soil heavy metals in Gaoxinsha reservoir and its impact on water quality safety
-
摘要: 为了研究高新沙水库土壤重金属对水质安全风险的影响,本文通过8个采样区域3 m深处土壤重金属含量与形态的测定,采用地累积指数和生态风险指数法阐明重金属潜在生态风险,并通过浸提模拟试验来探究重金属浸出特性及对水质安全影响. 结果表明,8种重金属Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Ni、Cr、Hg和As含量范围分别为11—42.5、70.75—119.5、0.01—0.16、24.5—100、20.25—35、89—177、0.05—0.17、10.15—22.1 mg·kg−1,在8处区域普遍未超出农田土壤环境标准风险筛选值(GB 15618-2018),仅有1处As含量为22.10 mg·kg−1,超出筛选值20 mg·kg−1. 重金属主要以残渣态为主,其中Zn、Ni、Cr、Hg和As等5种重金属残渣态所占比例均达到70%以上,总体潜在生态风险处于轻微水平. 在不同pH浸提液模拟作用下(pH=6.34、5.6和3.6),绝大部分重金属浸出浓度未超出生活饮用水卫生标准限值(GB 5749-2022),但浸提液pH=1.0极端情况下,Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Ni和As出现了不同程度的超标现象. 在实际水体作用下,整体上库底土工膜破损程度对水质未产生不良影响,除了1处土壤点位中Ni出现轻微超标现象. 综合以上结果,水库土壤重金属污染风险处于较安全水平,对水质造成的环境风险非常有限,但在水库实际运行中加强重金属含量的监测与管理,尤其是Pb和Ni.Abstract: In order to evaluate the risk of heavy metals in Gaoxinsha reservoir for the water quality safety, the distribution characteristics and potential ecological risk of heavy metal were studied by the determination of heavy metal, the geo-accumulation index and ecological risk index. The leaching characteristics of heavy metals and their effects on water quality were also investigated by the leaching solutions. These results indicated that the contents of Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, Ni, Cr, Hg and As ranged from 11—42.5, 70.75—119.5, 0.01—0.16, 24.5—100, 20.25—35, 89—177, 0.05—0.17, 10.15—22.1 mg·kg−1, in which these heavy metals generally had not exceeded the standard (GB15618-2018), only the concentration of As slightly exceeded the standard. Heavy metals were mainly in the residue state, whose proportion of Zn, Ni, Cr, Hg and As were more than 70%, these suggested that their potential ecological risks were generally at slight level. In the leaching experiments (pH=6.34, 5.6 and 3.6), the concentration of most heavy metals had not exceeded the limit of drinking water (GB 5749-2022), while at the extreme pH of 1.0, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, Ni and As exceeded the standard at different degrees. In the case of actual water, the damage of the geomembrane generally had no significant adverse effect on the water quality, but only one soil sample that the Ni slightly exceeded the standard. Based on the above results, the risks of heavy metal pollution in the reservoir soil were at a relatively safe level, and the environmental risk was very limited, while the management of heavy metals in water, especially Pb and Ni, should be strengthened in the actual operation of the reservoir.
-
Key words:
- heavy metals /
- reservoir soil /
- risk assessment /
- leaching risk /
- water safety
-

-
表 1 地累积指数分级标准
Table 1. Ground accumulation index classification standard
Igeo 分级
Degree污染程度
Contamination degreeIgeo ≤ 0 0 无 0< Igeo ≤1 1 无-中等 1< Igeo ≤2 2 中等 2< Igeo ≤3 3 中等-强 3< Igeo ≤4 4 强 4< Igeo≤5 5 强-极严重 5< Igeo ≤10 6 极严重 表 2 潜在生态风险指数分级标准
Table 2. Potential ecological risk index classification standard
Eri 污染程度
Contamination degreeRI 污染程度
Contamination degreeEri < 40 轻度生态危害 RI < 150 轻度生态危害 40 ≤ Eri < 80 中等生态危害 150 ≤ RI < 300 中等生态危害 80 ≤ Eri < 160 强度生态危害 300 ≤ RI < 600 强度生态危害 160 ≤ Eri < 320 很强生态危害 600 ≤ RI < 1200 很强生态危害 Eri ≥ 320 极度生态危害 RI ≥ 1200 极度生态危害 表 3 库区深层土壤(3m)8种重金属含量(mg·kg−1)
Table 3. Contents of 8 heavy metals in deep soil (3m)(mg·kg−1)
pH Cu Zn Cd Pb Ni Cr Hg As S1 7.51±0.20 15.00±5.04 89.00±2.35 0.16±0.03 37.25±3.49 29.25±4.26 129.50±9.40 0.17±0.16 13.45±1.11 S4 7.91±0.53 42.50±1.80 119.50±8.17 0.15±0.01 38.00±3.74 35.00±3.08 177.00±5.83 0.14±0.01 19.43±0.58 S5 7.27±0.21 14.25±0.43 73.25±2.86 0.02±0.01 24.50±3.35 22.25±3.96 133.75±7.22 0.07±0.00 10.15±0.47 S9 7.69±0.11 11.00±3.00 72.00±6.16 0.01±0.00 47.25±3.70 28.00±1.41 115.75±13.29 0.07±0.01 15.10±1.61 S10 7.52±0.27 21.25±6.18 75.75±5.80 0.03±0.00 47.00±4.30 26.75±3.63 89.00±4.19 0.06±0.01 16.10±6.25 S13 7.72±0.10 34.25±2.38 97.00±4.69 0.05±0.01 58.00±1.58 32.75±2.28 133.00±8.80 0.08±0.01 22.10±2.62 S15 7.05±0.54 24.50±10.01 81.00±22.59 0.06±0.02 100.00±13.89 32.00±9.30 106.25±3.04 0.07±0.02 15.13±8.57 S16 8.35±0.17 20.75±2.17 70.75±6.14 0.12±0.01 39.75±4.82 20.25±5.07 115.50±10.45 0.05±0.00 15.18±1.05 标准限值(GB15618-2018) 100 250 0.6 140 100 300 0.6 20 -
[1] KIANPOOR KALKHAJEH Y, HUANG B, HU W Y, et al. Environmental soil quality and vegetable safety under current greenhouse vegetable production management in China [J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2021, 307: 107230. [2] 胡杰, 赵心语, 王婷婷, 等. 太原市汾河河岸带土壤重金属分布特征、评价与来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(5): 2500-2509. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202107258 HU J, ZHAO X Y, WANG T T, et al. Distribution characteristics, evaluation, and source analysis of heavy metals in soils of Fenhe riparian zone in Taiyuan City [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(5): 2500-2509(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202107258
[3] 赵梓霖, 王璋强, 王锐, 等. 电子垃圾拆解区不同用地类型土壤重金属空间分布特征与风险评价 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(4): 1294-1302. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202109159 ZHAO Z L, WANG Z Q, WANG R, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals for different land-use types in electronic waste disposal area [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2022, 16(4): 1294-1302(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202109159
[4] 王毛兰, 何昶, 赵茜宇. 江西某养殖场废水灌溉土壤重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试试, 2022, 41 (6): 1072-1081. WANG M L, HE C, ZHAO Q Y. Characteristics of heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of the long-term livestock wastewater irrigated soilsin Jiangxi Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(6): 1072-1081 (in Chinese).
[5] WU Y F, LI X, YU L, et al. Review of soil heavy metal pollution in China: Spatial distribution, primary sources, and remediation alternatives [J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2022, 181: 106261. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106261 [6] ANAMAN R, PENG C, JIANG Z C, et al. Identifying sources and transport routes of heavy metals in soil with different land uses around a smelting site by GIS based PCA and PMF [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 823: 153759. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153759 [7] 于旦洋, 王颜红, 丁茯, 等. 近十年来我国土壤重金属污染源解析方法比较 [J]. 土壤通报, 2021, 52(4): 1000-1008. doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2020101202 YU D Y, WANG Y H, DING F, et al. Comparison of analysis methods of soil heavy metal pollution sources in China in last ten years [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2021, 52(4): 1000-1008(in Chinese). doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2020101202
[8] YUAN X H, XUE N D, HAN Z G. A meta-analysis of heavy metals pollution in farmland and urban soils in China over the past 20 years [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 101: 217-226. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.08.013 [9] REN S Y, SONG C Q, YE S J, et al. The spatiotemporal variation in heavy metals in China's farmland soil over the past 20 years: A meta-analysis [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 806: 150322. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150322 [10] WANG J, GAO P, LI M Y, et al. Dermal bioaccessibility and cytotoxicity of heavy metals in urban soils from a typical plateau city: Implication for human health [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 835: 155544. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155544 [11] 彭驰, 何亚磊, 郭朝晖, 等. 中国主要城市土壤重金属累积特征与风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(1): 1-10. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202103054 PENG C, HE Y L, GUO Z H, et al. Characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in urban soils of major cities in China [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(1): 1-10(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202103054
[12] 崔雅红, 崔炜, 孟庆俊, 等. 陕西蒿坪石煤矿区重金属污染及生态风险评价 [J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2021, 41(2): 157-162. doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2021.02.022 CUI Y H, CUI W, MENG Q J, et al. Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment in haoping stone coal mine area of Shaanxi Province [J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021, 41(2): 157-162(in Chinese). doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2021.02.022
[13] LIU H B, QU M K, CHEN J, et al. Heavy metal accumulation in the surrounding areas affected by mining in China: Spatial distribution patterns, risk assessment, and influencing factors [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 825: 154004. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154004 [14] 陈汉, 王振峰, 梅琨, 等. 东南沿海某水源地水质健康风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(5): 1161-1170. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018102101 CHEN H, WANG Z F, MEI K, et al. Water quality health risk assessment in a drinking water source in southeast coastal area of China [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(5): 1161-1170(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018102101
[15] 乔敏敏, 季宏兵, 朱先芳, 等. 密云水库沉积物中重金属元素分布及形态研究 [J]. 首都师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 34(3): 59-67. doi: 10.19789/j.1004-9398.2013.03.013 QIAO M M, JI H B, ZHU X F, et al. Analysis on distribution and partition of heavy metal in sediments of Miyun Reservoir [J]. Journal of Capital Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 34(3): 59-67(in Chinese). doi: 10.19789/j.1004-9398.2013.03.013
[16] 魏静, 郑小刚, 王彩铃, 等. 官厅水库、密云水库上游流域土壤砷含量特征与环境质量评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(1): 71-77. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018071102 WEI J, ZHENG X G, WANG C L, et al. Soil arsenic content and environmental quality assessment in the upstream basin of Guanting Reservoir and Miyun Reservoir [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(1): 71-77(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018071102
[17] 辜敏, 赵靓, 陈倩, 等. 密云水库土壤重金属污染与生态风险评价 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(11): 1398-1404,1442. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.11.017 GU M, ZHAO L, CHEN Q, et al. Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment of soil in Miyun Reservoir [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2020, 42(11): 1398-1404,1442(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.11.017
[18] 傅杨武, 祁俊生, 陈书鸿, 等. 三峡库区苎溪河流域消落带土壤重金属污染调查及评价 [J]. 土壤通报, 2009, 40(1): 162-166. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2009.01.042 FU Y W, QI J S, CHEN S H, et al. Investigation and assessment of soil pollution by heavy metals in water-level-fluctuating zones of the Zhuxi River valleys [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2009, 40(1): 162-166(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2009.01.042
[19] 叶琛, 李思悦, 卜红梅, 等. 三峡水库消落区蓄水前土壤重金属含量及生态危害评价 [J]. 土壤学报, 2010, 47(6): 1264-1269. doi: 10.11766/trxb200904150174 YE C, LI S Y, BU H M, et al. Heavy metals in soil of the ebb-tide zone of the three-gorges reservoir and their ecological risks [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2010, 47(6): 1264-1269(in Chinese). doi: 10.11766/trxb200904150174
[20] 王剑, 尹炜, 强小燕, 等. 丹江口水库新增淹没区农田土壤重金属生态危害评价 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2015, 28(4): 568-574. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2015.04.11 WANG J, YIN W, QIANG X Y, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil from new submerged area around Danjiangkou Reservoir [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 28(4): 568-574(in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2015.04.11
[21] 韩培培, 谢俭, 王剑, 等. 丹江口水库新增淹没区农田土壤重金属源解析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(8): 2437-2443. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.08.025 HAN P P, XIE J, WANG J, et al. Source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soil from new submerged area in Danjiangkou Reservoir [J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(8): 2437-2443(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.08.025
[22] 孙婷, 李秋华, 唐黎, 等. 贵阳市百花水库消落带土壤汞形态分布及风险评价 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(4): 831-839. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2019.04.023 SUN T, LI Q H, TANG L, et al. Distribution and risk assessment of Hg species in soil of the water-level-fluctuating zone in baihua reservoir [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(4): 831-839(in Chinese). doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2019.04.023
[23] 郭杰, 王珂, 于琪, 等. 长江中游近岸表层沉积物重金属污染特征分析及风险评估 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(11): 4625-4636. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0317 GUO J, WANG K, YU Q, et al. Pollution characteristics of the heavy metals and their potential ecological risk assessment in nearshore sediments of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(11): 4625-4636(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0317
[24] 张德举, 张玉宝, 董艳艳, 等. 密云水库内湖土壤重金属含量分析 [J]. 北京水务, 2018(1): 11-16. doi: 10.19671/j.1673-4637.2018.01.003 ZHANG D J, ZHANG Y B, DONG Y Y, et al. Heavy metal accumulation in littoral zone soil of Miyun Reservoir inner lake [J]. Beijing Water, 2018(1): 11-16(in Chinese). doi: 10.19671/j.1673-4637.2018.01.003
[25] 邱其俊, 于瑞莲, 胡恭任, 等. 闽北某新建水库周边土壤重金属生态与健康风险评价 [J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(3): 348-355. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2017.03.014 QIU Q J, YU R L, HU G R, et al. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around a new reservoir in northern Fujian Province, China [J]. Earth and Environment, 2017, 45(3): 348-355(in Chinese). doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2017.03.014
[26] 崔磊, 郝芳华, 许嘉琳, 等. 水库蓄水初期库底土壤对水质影响的模拟实验研究 [J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 39(5): 688-693. CUI L, HAO F H, XU J L, et al. A simulative experimental study on the impact of submerged soil on water quality in reservoir [J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 2003, 39(5): 688-693(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: