-
河口区是河流和海洋的交汇地带,在河流和海潮带来的养分汇合下,河口区生态系统具有丰富的生物多样性,提供了较高的生态系统服务价值。因此,河口区成为人类生存活动的密集区。而河口也是一个敏感、脆弱的生态系统,在自然和人为因素的影响下,河口区出现防潮泄洪能力减弱、鱼类洄游通道受阻、海洋环境质量下降、滩涂湿地生态退化、生物多样性下降等生态系统退化问题[1],直接导致降低生态服务价值,影响人类福祉。
2000年美国颁布的《河口恢复法案》(ERA)中将河口栖息地的恢复列为重要研究事项,倡议恢复数万公里的河流走廊和数十万公顷的湿地,大量的河口湿地生态恢复工作陆续开展。伴随2009年《美国经济复苏和再投资法案》(ARRA)的颁布以及2012年《恢复法案》的出台,美国政府对栖息地恢复的投资继续加大,计划到2040年投入数十亿美元用于恢复沿海和海洋栖息地。目前,国外对河口区生态修复的研究多集中在河口区盐藻植被修复、红树林修复、河口潮沟水动力改造、牡蛎礁恢复、河口重要生物物种修复等方面[2-4],以及从河口区域管理协作的角度制定修复框架,强调修复过程中要更加注重上层机构管理、合作伙伴及民众的支持和参与[5-7]。
国内针对河口生态修复方面的法律法规较少,但河口修复工作一直备受重视,从国家“863”计划的“渤海湾典型海岸带生境修复技术”到2018年开展的“渤海综合治理攻坚战行动计划”,单对渤海及其入海河口的治理就开展了30多年研究,期间取得了很多重要的理论研究和技术应用。近几年来,海岸修复项目更是成倍增长,据统计,仅3年时间(2016—2019年)中国的海岸带生态修复投资超过10亿美元[8]。河口区生态修复技术方面的研究,较多集中在河口渔业资源修复、河口湿地盐碱地问题修复、河口污染水质及富营养化水环境治理等方面研究成果[9-12]。
研究发现,针对河口生态修复技术方面,国内外研究多集中在单项指标修复,在河口区整体生态修复方面还缺少深层次的研究和相应的技术指导。为了更好地指导河口区整体生态修复工作,系统总结了我国河口区存在的生态环境问题以及相应的修复对策,提出河口区整体生态修复技术框架和可持续发展管理建议,为后续河口生态修复应用和河口生态修复标准制定奠定基础。
-
河口修复首先要明确河口的位置、范围。河口从不同角度有不同的定义,生物化学领域普遍认可的定义为:河口是部分封闭的,永久性或间歇性与开阔的海洋相通,由于海水和来源于陆地的淡水混合,从而盐度有一定程度变化的海岸水体[13]。水动力学、地理学角度认为河口是河流与海洋之间的通道,它向陆延伸到潮水的上限[14]。河口可划分为3段:河口下游段(海洋段),与开阔的海洋自由连通;河口中游段,淡盐水发生混合;河口上游段(河流段),主要为淡水控制,但每天经受潮汐的影响。海洋学术语[15]中对河口的定义为:河流终端与受水体(海)相结合的地段。根据水动力条件的不同,将入海河口分为河流近口段、河流河口段和口外海滨段。河口范围目前没有统一的划分方法,从水动力角度考虑,河口是一个受径流、潮汐相互影响的一个往复振荡变化的区域,范围从近口段的潮区界(潮差为0)至口外海滨段的淡水舌锋缘之间的永久性水域。从化学海水盐度角度,河口范围是盐度介于海水和淡水之间的区域。一般海水盐度在30%~35%,淡水盐度一般小于0.1%。从管理的角度一般以河海划界为上界,但该划分方法很多割裂了河口生态系统的完整性。河口生态系统是指在河流入海口,淡水与海水混合并相互影响的水域环境与生物群落组成的统一的自然整体[16]。因此,河口修复应以实际修复的各要素自然属性为依据、以修复河口环境和生物群落组成的生态系统为修复对象从而确定河口修复范围。
-
美国国家研究委员会(NRC)[17]对生态修复的定义为:将生态系统恢复到“干扰前的近似状态”,即生态恢复指的是重建干扰前的整个生态系统。在恢复实践者中,ARONSON et al[18]注意到“以干扰前作为恢复模板与恢复有明显区别。 MIDDLETON[19]总结了一种不断发展的恢复观点,即建立“恢复成一个在其现实状态中进行自我调节和整合的场地,并非不考虑当前开发活动和全球气候变化,重建一个不可能恢复到的干扰前的生态系统”。近年来,人们对生态恢复的定义有了更深的理解,许学工[20]认为“恢复”的含义是使一个受损的生态系统变回到具有干净的水环境、健康的栖息地以支持鱼类、野生动物的生存和人类对河口的利用这样一个可持续的、自维持的生态系统。
-
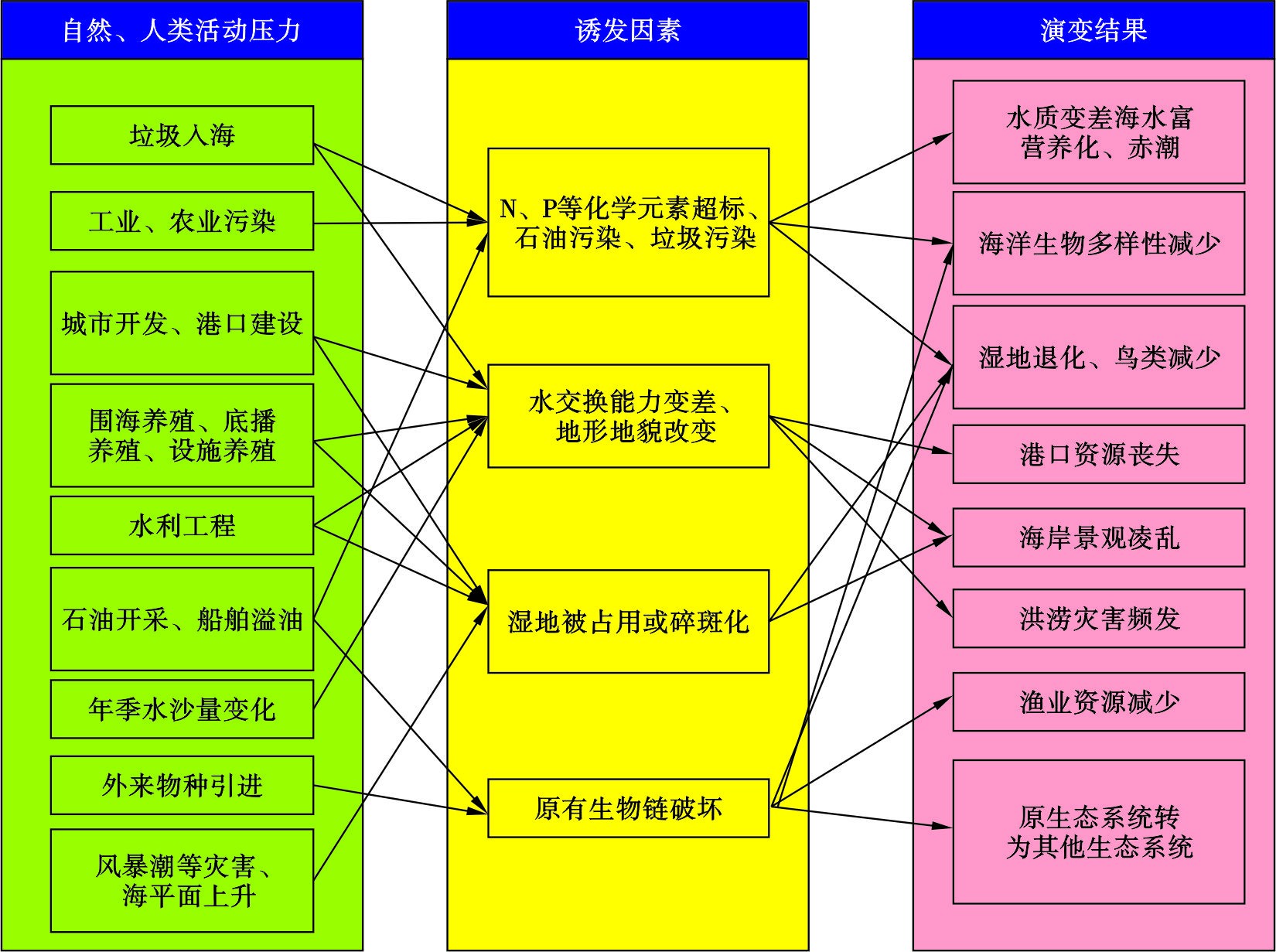
河口周边是人类活动的密集区,人类不合理的过度开发导致河口区生态环境恶化,如污染物和漂浮垃圾日渐累积导致河口区水质下降,岸滩视觉景观凌乱;不断扩大的围垦开发活动,导致河口区自由纳潮海域面积不断缩小,河口生境碎片化;生态系统产品以人工养殖水产品为主,生物多样性下降。河口区逐渐的演变结果为:河口不断淤浅,影响通航能力;水交换能力减弱,污染日益严重;生物群落改变,甚至对典型生态系统和特色渔业资源构成威胁。在自然灾害和人类高强度的开发下,河口区存在以下演变趋势,见图1。
根据2020年监测的7个河口生态系统统计[21],鸭绿江口、双台子河口、滦河口-北戴河、黄河口、长江口、闽江口、珠江口7个重要河口总监测面积27500 km2均处于亚健康状态,共有6点主要问题。
-
上游大型水利工程建设、 河口海岸围填海、台风风暴潮自然灾害等多种因素,导致防潮泄洪功能下降,很多河口区经常出现汛期河水漫滩、风暴潮时潮水涌入岸边等灾害,给当地村民造成大量损失。例如,珠江河口洪涝灾害、咸潮上溯问题突出,导致中山、顺德等多地水位抬升,给沿岸民众安全造成很大压力。因此,河口区的防潮泄洪功能是保障河口安全的首要任务。
-
近年来,随着河口周边工业、农业、垦区养殖规模化兴起,大量工业污水、生活污水、垃圾排入河口区,导致河口区水质氮磷超标,底泥污染,造成浮游动植物密度、生物量超出正常范围,底栖动物密度、生物量超出正常范围,生态系统自我调节作用和生态系统的稳定性大大降低,出现水质富营养化、赤潮灾害等。我国海域劣Ⅳ类水质海域面积为30070 km2,同比增加1730 km2,主要超标指标为无机氮和活性磷酸盐[21]。夏季富营养化状态海域面积为45330 km2,同比增加了2620 km2。劣Ⅳ类海域和重度富营养化海域主要集中在辽东湾、黄河口、江苏沿岸、长江口、杭州湾、珠江口等。2020年共发现赤潮31次,赤潮面积达到1748 km2,其中有毒赤潮2次,面积约81 km2。劣Ⅳ类水质海域面积增加,海水富营养化、赤潮频发,说明河口区水质污染严重。
-
随着人类围填海的加剧,河口局部区域淤积严重,造成原有航道淤浅、船只通航存在风险。长江口航道淤积问题一直是个世界性的难题,特别是台风等极端天气过后,航道骤淤量巨大,据统计某次台风过后造成长江口回淤量达750万m3。珠江口、辽河口、闽江口、瓯江口等很多河口都存在航道淤浅问题。
-
河口区由于工程建设如水闸、大坝的拦截,造成鱼类回游通道受阻,进而阻断了渔业资源的产卵场、索饵场、越冬场等,严重影响了海洋生物的繁殖生存。如双台河口由于拦海大堤的兴建,两侧联系被切断,天津厚蟹等生物量急剧减少[22]。黄河上游截至2020年建设了38座水电站,众多的水利工程造成下游断流、水源短缺、来泥量减少、鱼类洄游通道受阻、危及河口海域渔业资源。这些严重后果对大型水利工程的建设提出了警告[23]。
-
河口湿地具有清除河流入海污染物、调节气候等重大意义,也是很多生物群落生活、繁衍的重要场地。由于沿岸工程、盐田、滩涂养殖的占用,造成滩涂湿地面积减少,湿地生物量锐减、生物多样性下降,同时也间接影响到鸟类的觅食栖息。据统计,长江口湿地以每年至少200 km2的速度减少,已累计减少湿地57%,导致湿地生态服务功能下降50%。另外,气候变化、海平面上升等大环境因素也是造成滩涂湿地退化的重要原因之一。
-
海洋产业缺乏规划,追求短期利益,使得河口沿岸开发零乱,海岸人工化,河口区的防洪(潮)堤坝、工业填海、养殖围垦、盐业、港口码头等开发活动占用了原生的自然岸线,取而代之的是硬质化护岸,破坏了原有自然岸线生态功能,水土流失严重,对河口景观及旅游业也造成一定影响。
-
目前,生态修复对策主要从研究区存在的具体问题入手,采取单一修复方式或多种修复方式组合,最终以实现河口生态系统的健康、可持续发展为目标。河口生态修复过程中自然恢复的生态效益最佳,但可能不符合人类福祉要求,而人工促进修复或生态重建,需要投入的人力物力往往是无法承受的。因此,河口生态修复最好与防洪、排涝、防潮、通航、城市化景观提升等相结合。目前,针对河口区不同的问题主要修复方案,见表1。
-
由于河口区同时受河流和海洋的影响,尤其在雨季恰逢天文大潮,受高潮位顶托,潮水倒灌,致使洪水无法排泄,造成洪涝灾害。河口区的整治应以防洪防潮的安全需求为第一因素,在满足防洪防潮安全的前提下,开展生态功能修复才有意义。河口区常用的防洪防潮措施有河流上游蓄水、下游水系打通、退垦还滩、提高防洪闸、防浪堤标准等[24],生态修复方法则多采用生态护堤、种植水生植物等措施,形成河口区生态缓冲带,提高河口区的防洪防潮功能,同时提升生态景观。部分地方通过划定入海河口治导线[25],明确河口开发边界,保障河口防洪排涝安全,维持河口生态系统健康发展。
-
加强源头控制是杜绝河口区生态环境污染的关键一步。2020年,国家已对193个入海河流国控断面、442个污水日排放量大于100 t的直排海污染源开展了水质监测,建立“一口一档”的入海排污口动态台账,为后续污染防控提供溯源监测数据[21]。通过源头控制污水排放入海量、控制农业面源入海量,严禁流域垃圾入海,执行固定污染源排污许可制度、工业污染源稳定达标排放、严格执行养殖废水排放标准,控制养殖尾水排放量,采用离岸排放和生态化排放,严禁在重要、敏感和脆弱的河口生态区域进行排放等,这些都是解决河口区污染入海的重要举措。另外,可充分发挥人工湿地等生态工程的再净化作用,如红树林、湿地盐藻可对重金属污染起到净化作用,可以在适宜的河口区通过种植红树林、湿地盐藻植被,对入海污水进行生物降解处理。
-
水环境修复传统方法主要通过往海水中加载粘土、石灰等方法来缓解水体富营养化[26]。为避免造成二次污染,目前,水环境修复常用方法是通过微生物、生物等降解污染物从而达到水质标准。微生物修复通常利用溶藻微生物或称溶藻菌对付赤潮藻类[27-28],大型海藻如江蓠、凤眼莲[27]具有吸收富营养化水质中的氮磷作用,从而解决海水富营养化问题。还可通过生态养殖调节海洋水质,据研究在生态修复区进行贝类、大型藻类如条斑紫菜、龙须菜、海带及贝藻混养等[30-32],可大幅降低营养盐以及重金属含量,还可产生一定的经济效益。此外,非海洋植物如大麦秸和小麦秸具有控制赤潮生物的生长作用,在赤潮治理中也逐渐成为研究热点。文献[33]统计,烃类物质能够降解石油的微生物达200多种,在海洋生态系统中占主导地位,植被修复如翅碱蓬对石油烃污染的盐碱土壤具有一定修复作用[34]。
-
河口区底泥长期接受污染物、重金属沉淀累积,富营养化及污染化现象增加。通过退养还滩、清淤疏浚、疏通潮沟、改造微地形等措施,解决河口湿地生境基底退化。典型基底修复项目有盘锦市大凌河口东侧整治修复、滦河口北岸滨海湿地整治修复、永定新河入海口左岸滨海湿地修复项目[35]。底质环境改善还可以采用湿地生物修复,如种植红树林、盐藻植被等吸收部分底泥的重金属污染,或通过投放鱼礁来改善海底环境,为海洋生物提供更优质的栖息地,如海州湾修复采用投放人工鱼礁方式获得适宜生态养殖的底质环境[36]。
-
水动力修复常采取整治和疏浚拦门沙、疏通潮沟、退填还海、退垦还湿、拆除不合理的构筑物等工程方式进行水动力环境的改善,疏通鱼类洄游通道,提高泄洪能力和通航能力,还可通过营造微地形、控制水位等方式进行水动力环境改造。对由于海堤、闸门等工程影响水动力环境变差的,采取开口纳潮措施,如厦门高集海堤打开,很好地改善了西海域水动力条件[37]。
-
根据拟修复的生物群落、特殊物种、渔业资源品种的生长习性,进行重要物种或特殊物种的增殖修复,经过生态容量评估、科学确定适宜放流量,可通过人工鱼礁或增殖放流方式实现。如,连云港政府定期向海州湾放流大量中国对虾、梭子蟹、鱼类、贝类、刺参和鲍鱼等多种海珍品苗种,增加所在海域生物多样性。但要注意生态养殖的无害化,增殖放流的种类不得对其他生物种类造成生存压力,要以改善生物多样性,提高生态系统稳定性和成熟度为主要生态修复目的,还需通过实施严格的捕捞制度限制重要物种的减少。
-
河口湿地修复多采用“退养还湿”“退垦还滩”“拆除废弃构筑物”等措施恢复湿地面积,同时种植湿地植被,如翅碱蓬、芦苇、柽柳、红树林、海草床等滨海植被,达到提高河口湿地生物多样性、固碳、维持海岸稳定、减灾等生态功能。通过种植河口湿地植被进行湿地生境修复比较成功的案例有河北省滦南湿地人工岸线生态修复项目、寿光市老河入海口海岸带生态修复项目。
对影响生物多样性的外来物种,如大米草、护花米草等,可采取根系拔除、人工刈割等措施清除。如,泉州湾河口生态修复项目去除大米草、互花米草是河口湿地整治修复的一项重要工程。河口湿地是鸟类、水生动物等非常重要的栖息地,需营造好海洋生物栖息的良好环境。
-
从长远来看,人类工程生态系统没有自我维持的自然相互作用,不能提供生命支持服务[38]。因此,河口海岸尽可能是自然海岸,或通过种植滨海湿地植被获得良好的生态修复的海岸。对于必须通过建设海堤提高安全的河口区,河口海堤建设尽可能采用生态海堤,以利于植物生长和藻类、贝类附着,促进恢复生物多样性。护岸堤前沿水下可采用人工鱼礁等生态设计,为鱼类、贝类等提供繁殖、生长、索饵和庇敌场所,营造海洋生物栖息的良好环境。护坡可设置立体凹凸面营造生物附着环境,促进绿色植被生长。后方陆域配套绿化、生态防护带等措施,可提升防护能力又增强了岸线岸滩生态功能[39]。典型案例如昌邑市胶莱河入海口西岸海岸带生态修复项目(三期),通过建设生态化海堤,获得良好的生态修复效果。粤港澳大湾区河口海岸通过红树植物、半红树植物及其他滨海植物种植,有效恢复红树林生态系统[40]。
-
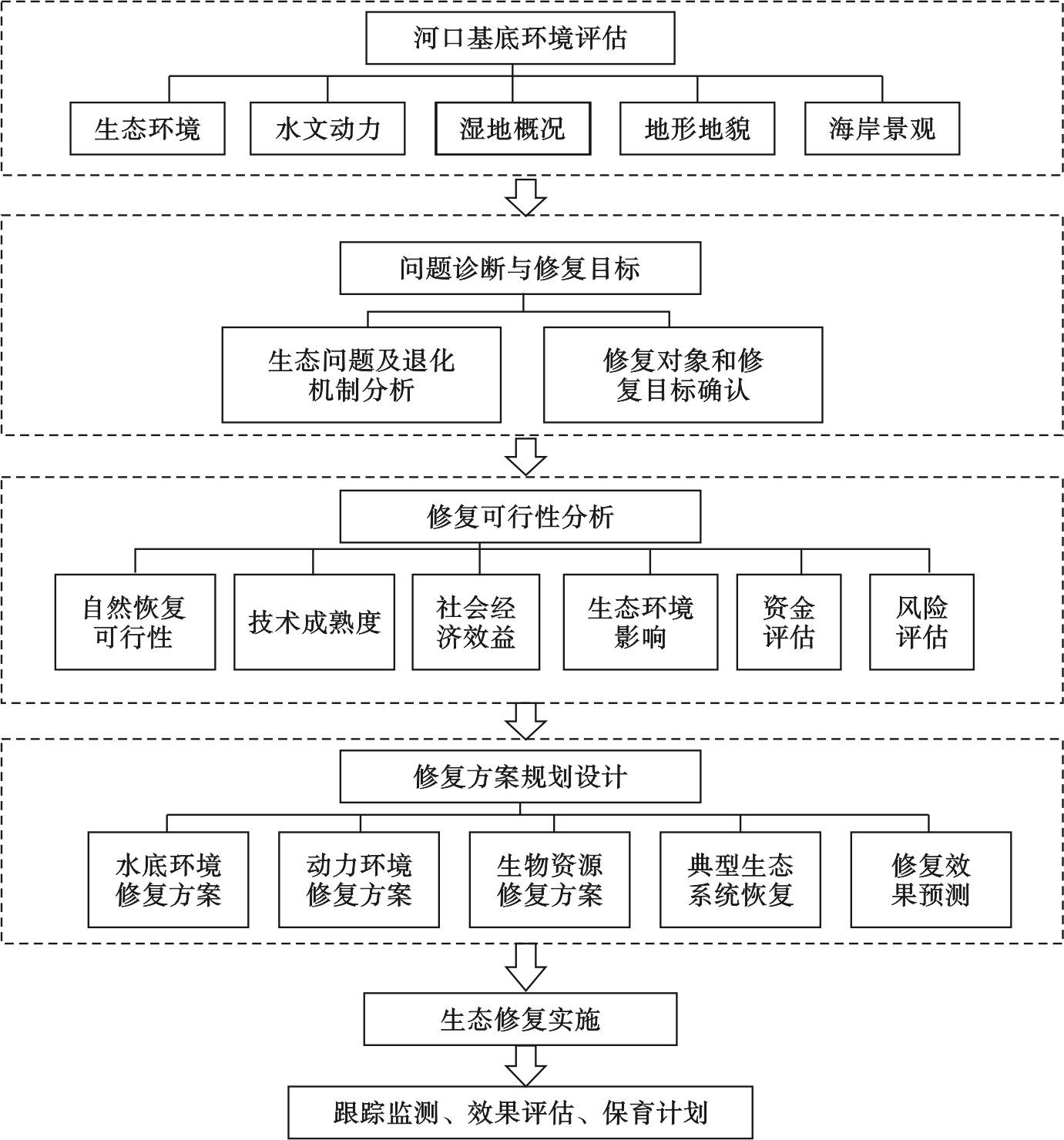
生态恢复的目标是重建自我维持的健康的生态系统,在没有人类额外投入的情况下,能够抵御未来的扰动[41]。河口生态系统结构与功能之间存在着复杂的相互作用关系,存在水动力环境-栖息地生境-生物群落之间的相互耦合反馈,同时河口是一个上下游联动的、河海陆相互影响的体系,要系统整体采取有序的修复策略,不要修复了某些问题又导致其他问题的出现,因此相对于单个问题的修复解决,需重点探讨河口区整体的修复方案规划、设计。文章遵循自然规律和生态学理论,充分利用生态系统的自然修复与恢复能力,自然生态恢复为主、人工促进生态修复为辅、避免或减少生态重建,确保生态修复效果持久发挥作用的原则,提出河口生态修复技术框架,见图2。
-
历史和现状资料是分析河口问题的基础,开展修复工作首先要清楚河口基底环境现状和历史,收集所在河口的水文动力、环境质量、生物生态、河口海岸状况、湿地生境等历史和现状资料,掌握现状和代表性历史时期的生态环境基础数据。
-
通过分析历史和现状数据,识别河口区存在的生态退化特征及其产生的原因,分辨生态退化的压力源是人类活动干扰还是自然灾害,或者两者叠加,进一步分析造成生态系统结构发生变化的控制因素,是围海湿地占用还是外来物种入侵,还是水动力受阻等其他原因。根据诊断结果,确定修复对象是水动力环境、水土生境、生物群落、特殊物种(渔业资源品种)、河口湿地、典型生态系统还是生态景观,并确定要达到的修复目标。修复目标可通过某些单项指标来反映,但最终目标是退化生态系统整体功能的提升,实现生态系统健康、可持续的发展。生态修复必须将人类的社会目标和生态系统的恢复紧密连接,而不是恢复到一个不受人类干扰的理想状态[42]。
-
首先根据修复对象的自然演替规律,分析自然恢复的可行性,是否符合人类福祉要求,对确实需要人工干预的要对其修复的可行性进行预判,现有的修复技术能否解决,是否有成功案例借鉴,会不会造成新的问题等。能够产生的经济社会生态效益有哪些,造成新的生态环境问题是否在可接受范围内。生态修复可行性除了从技术方案评估外,也应加入资金评估、风险评估,河口是一个不断受到干扰的区域,包括年际变化和偶然的极端事件,使得生态修复方案更具复杂性和挑战性,需要科学的评估恢复方案带来的不确定性和风险性,遵循最小风险与效益最大原则确定最终修复方案。
-
河口生态修复要从陆海统筹、河海共治视角统筹考虑,基于生态系统的系统战略性恢复方法,要兼顾河口各个因素之间的影响,不能顾此失彼,造成新的问题。根据修复对象的生态受损情况,以生态修复为目标,开展生态修复方案设计。明确修复尺度、修复时间长度,可提出短期、长期的分阶段实施方案。具体修复措施可依据生态服务功能区域分异,提出不同修复功能的空间分区方案,包括污染水体修复、污染底泥修复、特殊物种或生物群落恢复、特色渔业资源品种增殖、典型生态系统修复、人工海岸生态化,以及不合理的构筑物拆除、人工清淤、退垦还滩、退养还海等。根据河口区资源禀赋和生态适宜性,调整优化河口区开发利用布局,协调港口航道、渔业养殖、旅游观光、休闲娱乐的空间布局。合理控制养殖区域和面积,按照养殖容量控制养殖规模和养殖密度,推广生态养殖和碳汇渔业。最后对设计的修复方案开展效果预测,包括水质底质生境变化预测、水动力环境变化预测、泄洪防潮能力变化预测、典型生态系统变化预测等。根据预测结果进一步补充修正修复方案,最终给出一个合理可行可控的修复方案。
-
河口区的复杂性、敏感性以及修复过程中不确定性因素,决定了河口修复不可能一蹴而就,需要一个长达10年、20年的长期序列工作,生态修复效果才能慢慢显现出来。因此,河口修复项目恢复过程中必不可少地要有相应的责任管理机构监督负责,对其建立问责制度,防止修复工作功亏一篑。责任管理机构在项目实施过程中要进行有效和长期的监测管理,以便更好地修正修复方案。项目实施后,根据生态修复前后的监测信息,对项目实施后生态系统的结构和功能进行对比分析,评估生态修复效果,并提出改进措施。
-
生态系统恢复过程中,可根据河口区的特色资源、湿地生境、生物群落、海洋景观等自然资源状况,建立自然保护区、湿地公园、风景名胜区等,对河口生态系统进行保护。还可以建立以保护为核心的集生态涵养、科普教育、休闲游憩于一体的生态科普乐园。对于一些比较敏感脆弱的区域,可以实施周期性的“生态红线”管理,对典型生态系统划定“生态红线”,根据典型生态系统的自然演替特征,实施周期性自然保护,使其自然恢复,当生态系统结构和功能恢复稳定时,取消“生态红线”。
-
目前河口区存在以下几个主要生态环境问题:洪涝灾害、水质底泥污染、港口通航能力减弱、渔业资源减少、湿地退化及生物多样性减少、河口海岸生态功能下降等,针对这些问题可以采取的生态修复措施主要有加强生态海堤建设、控制污染源入海、水质底泥修复、生物资源修复、水动力修复、河口湿地修复、海岸生态景观修复等。除了以上修复措施外,文章重点从整体修复的角度提出构建一个整体的生态修复技术框架。开展河口基底调查、问题诊断和修复目标确定、生态修复可行性评估、生态修复方案规划设计、项目实施及监测评估、后期保育措施等整套修复过程,最终实现河口生态系统健康发展。
实际上要成功地全面整体恢复、提升河口生态系统,不仅要解决技术层面问题,法律规章制度的制定、各管理机构之间的协调管理、资金问题、责任监督管理机构、利益相关方、公众意识和参与等都是关系到生态修复能否成功的重要因素[43]。为了达到生态修复效果、保障河口区健康、可持续发展,建议采取以下3个措施。
(1)构建河口综合管理体制机制。法制上进一步完善河口保护修复等相关法规制度,做到有法可依,违法必究。行政上打破地域分割、部门分割、河海分割的界限,坚持流域统一规划、各部门联动、河海共治。政策上给予渔业、交通等利益相关方支持保障,发展与保护共存。资金保障上建立以政府为主体,社会企业多元化投入机制,加大拓宽投融资渠道,保障河口日常监测、生态保护、生态修复等资金需求。监测监管上构建业务化监测体系,打造“数字河口”,建立统一规范的河口生态环境基础数据库,实现对河口的实时监控、大数据管控。同时设立监督举报平台,强化社会公众参与和监督。通过以上制度改革,最终构建一个目标明确、有法可依、协调有度、监督有力、保护到位、可持续发展的河口综合管理体制机制。
(2)制定长期的、动态调整的河口保护修复计划。一个长期的、动态调整的河口保护修复计划可以为河口的可持续发展提供明确的发展方向。可以基于河口10年、20年甚至更长时间的演化方向、经济发展、人口增长及环境变化等制定一个长期的河口保护计划,计划实施过程中采用适应性管理方式,结合河口近期的安全问题、生态环境问题、产业发展协调等,进一步细化目标与决策,结合整治修复实践后的最新动态进一步调整更新河口保护修复计划。
(3)深入对河口基础学科交叉的研究。要加大对河口基础学科交叉的研究,深入研究河口区的地质过程、物理过程、化学过程、生物过程以及这些过程之间的相互作用,通过多学科交叉渗透,综合分析河口对全球变化及人类活动的响应过程和结果,揭示河口演变规律和发展趋势,为河口的健康、可持续发展提供科学指导。
河口区生态环境问题及生态修复对策探讨
Discussion on ecological environment problems and ecological restoration countermeasures in estuary area
-
摘要: 河口是一个生物多样性丰富又敏感的区域,在人类过度开发下,河口区生态环境问题日益明显,河口生态系统修复成为一项重要的研究课题。基于河口生态修复的基本概念,文章通过分析得出我国河口区普遍存在洪涝灾害、水质底泥污染、港口通航能力减弱、渔业资源减少、湿地退化及生物多样性减少、河口海岸生态功能下降等6个生态环境问题,以问题为导向系统总结了可以采取加强生态海堤建设、控制污染源入海、水质底泥修复、生物资源修复、水动力修复、河口湿地修复、海岸生态景观修复等生态修复措施,提出要构建一个河口基底调查、问题诊断和修复目标确定、生态修复可行性评估、生态修复方案规划设计、项目实施及监测评估、后期保育措施等一整套完整的系统修复技术框架。最后从河口可持续发展角度提出河口管理要构建河口综合管理体制机制、制定长期动态可调整的河口保护修复计划、加强对河口基础交叉学科的研究等措施,为后期河口区生态修复和管理提供借鉴。Abstract: The estuary, characterized by its abundant biodiversity and sensitivity, is increasingly experiencing ecological environmental issues due to excessive human development. The ecological environmental problems in the estuary area are becoming obvious, and the restoration of estuarine ecosystem has become an important research topic. Based on the basic concept of estuarine ecological restoration, six ecological and environmental problems such as flood disasters, water quality and sediment pollution, weakening of port navigation capacity, reduction of fishery resources, wetland degradation and biodiversity reduction, and decline of estuarine and coastal ecological functions were found in China's estuary area through analysis. Based on the problem, the ecological restoration measures that could be taken to strengthen the construction of ecological seawall, control pollution sources into the sea, water quality and sediment restoration, biological resources restoration, hydrodynamic restoration, estuarine wetland restoration, coastal ecological landscape restoration, estuarine wetland restoration and coastal ecological landscape restoration were summarized. It is proposed to construct a complete technical framework for ecological restoration and carry out a complete set of systematic restoration processes from the perspective of overall restoration, such as estuarine basement investigation, problem diagnosis and restoration target determination, ecological restoration feasibility assessment, ecological restoration program planning and design, project implementation, monitoring and evaluation, and late conservation measures. Finally, from the perspective of sustainable estuarine development, it is suggested that estuarine management should build an integrated estuarine management institutional mechanism, formulate a long-term dynamic and adjustable estuarine restoration plan, and strengthen research on basic estuarine cross-disciplines, which could provide a reference for the ecological restoration and management of estuarine areas in the future.
-
Key words:
- estuary /
- ecological environment /
- ecological restoration /
- technological frame
-

-
表 1 河口区常见问题整治修复对策
Table 1. Countermeasures for remediation and repair of common problems in estuary areas
生态环境问题 整治修复措施 应用案例举例 洪涝灾害、咸潮上溯等 打通河流各水系,使水流畅通;提高防潮防浪海堤标准,海堤生态化建设;通过退垦还湿、种植水生植物、修复河口湿地等措施,形成河口区生态缓冲带;通过水动力、数模等分析划定河口治导线,确保河口安全开发保护边界[24-25]。 钱塘江河口治理 上游污水排放、垃圾入海 加强源头控制、严格控制面源污染、点源污染达标排放;对上游垃圾进行拦截;采用离岸深海排放、严禁在敏感区、保护区排放等措施[21]。 2020年,国家已对主要河口的193个入海河流国控断面开展了水质监测 水质超标 水环境修复常用方法是通过微生物、植物等降解污染物、治理赤潮、修复石油污染;通过河口湿地植被吸附重金属、石油烃等;通过生态养殖调节水质、降低营养盐及重金属含量[26-36]。 天津滨海沿岸通过种植翅碱蓬吸附石油烃治理盐碱地、福建东山海域采用龙须菜来吸附超标的N、P 底质污染 通过退养还滩、清淤疏浚、改造微地形等措施,解决河口湿地生境基底退化[35-36]。 盘锦市大凌河口东侧整治修复、滦河口北岸滨海湿地整治修复、永定新河入海口左岸滨海湿地修复项目等 水动力环境受阻 整治和疏浚拦门沙、营造微地形、控制水位、疏通潮沟、退填还海、退垦还湿、拆除不合理构筑物等工程方式进行水动力环境的改善,疏通鱼类洄游通道,提高泄洪能力和通航能力[37]。 厦门高集海堤开口 重要生物资源减少 通过增殖放流及人工鱼礁和海藻场等栖息地营造方式实现重要物种的增加;通过禁渔期、严格控制捕获量来避免重要物种的减少[36]。 连云港政府定期向海州湾放流大量多种海珍品苗种,增加所在海域生物多样性 河口湿地生境遭受破坏 采用“退养还湿”、“退垦还滩”、“拆除废弃构筑物”等措施恢复湿地面积;通过种植湿地植被如翅碱蓬、芦苇、柽柳、红树林、海草床等滨海植被,提高河口湿地生物多样性、维持海岸稳定;清除破坏湿地生态系统如大米草、护花米草等外来物种[35]。 河北省滦南湿地人工岸线生态修复项目、寿光市老河入海口海岸带生态修复项目 河口海岸景观凌乱 重污染产业调出,合理规划产业布局;尽可能保留自然海岸;种植滨海湿地植被;生态海堤[35,38]。 昌邑市胶莱河入海口西岸海岸带生态修复项目(三期)、粤港澳大湾区河口海岸修复 -
[1] 丁德文, 吕吉斌, 杨建强, 等. 黄河河口—近海环境系统安全及修复对策[C]//中国水利学会,黄河研究会.黄河河口问题及治理对策研讨会专家论坛文集[A]. 东营: 黄河水利出版社,2003: 98-101. [2] BLOMBERG B N, POLLACK J B, MONTAGNA P A, et al. Evaluating the U. S. Estuary Restoration Act to inform restoration policy implementation: A case study focusing on oyster reef projects[J]. Marine Policy, 2018, 91(5): 161 − 166. [3] VANDENBRUWAENEA W , MEIRE P , TEMMERMAN S.Formation and evolution of a tidal channel network within a constructed tidal marsh[J].Geomorphology,2012,151:114-125. [4] NOWACKI D J , GROSSMAN E E . Sediment transport in a restored, river-influenced Pacific Northwest estuary[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020: 106869. [5] THAYER G W, KENTULA M E. Coastal restoration: where have we been, where are we now, and where should we be going?[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2005: 1-5. [6] DEANGELIS B M , SUTTON-GRIER A E , COLDEN A , et al. Social Factors Key to Landscape-Scale Coastal Restoration: Lessons Learned from Three U. S. Case Studies[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12. [7] CONNELLY A, KNUTH B, KAY D L. Public support for ecosystem restoration in the Hudson River Valley, USA[J]. Environmental management, 2002, 29(4): 467 − 476. [8] LIU Z, FAGHERAZZI S, LI J, et al. Mismatch between watershed effects and local efforts constrains the success of coastal salt marsh vegetation restoration[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 292(6): 126103. [9] 张婷婷, 赵峰, 王思凯, 等. 美国切萨比克湾生态修复进展综述及其对长江河口海湾渔业生态修复的启示[J]. 海洋渔业, 2017(6): 713 − 722. [10] 钱伟, 冯建祥, 宁存鑫, 等. 近海污染的生态修复技术研究进展[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(5): 1855 − 1866. [11] 柴召阳, 何培民. 我国海洋富营养化趋势与生态修复策略[J]. 科学, 2013(4): 48 − 52. [12] 罗育池, 陈瑜, 刘畅, 等. 水环境治理模式创新与关键对策——以广东省为例[J]. 环境保护科学, 2020, 46(1): 25 − 29. [13] DAVIS J L. A morphogenetic approach to world shorelines[J]. Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie, 1964(8): 127 − 142. [14] DIONNE J C. Toqards a more adequate definition of the St[J]. Lawrence estuary. Z. Geomorph., 1963, 7: 36 − 44. [15] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局、中国国家标准化管理委员会. 海洋学术语 海洋地质学:GB/T 18190—2017[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2017. [16] 国家海洋局. 近岸海洋生态健康评价指南: HY/T 087—2005[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2005. [17] National Research Council (NRC). Restoration of Aquatic Ecosystems—Science, Technology and Public Policy[M]. Washington: National Academy Press, 1992. [18] ARONSON J, FLORET C, FLOC'H E, et al. Restoration and Rehabilitation of Degraded Ecosystems in Arid and Semi-Arid Lands. II. Case Studies in Southern Tunisia, Central Chile and Northern Cameroon[J]. Restoration Ecology, 1993, 1(3): 168 − 187. [19] MIDDLETON B A . MIDDLETON, B. A. 1999. Wetland restoration, flood pulsing and disturbance dynamics. John Wiley & Sons, NY[M]. John Wiley & Sons, 1999. [20] 许学工, GABOURY B, 崔朝伟. “恢复美国的河口”的启迪[J]. 人民珠江, 2007(1): 35 − 38. [21] 中华人民共和国生态环境部.2020年中国海洋生态环境状况公报[EB/OL].(2021-05-26)[2022-05-25]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/jagb/202105/P020210526318015796036.pdf. [22] 黄桂林, 徐庆元. 双台河口自然保护区功能区划和管理对策-辽河三角洲湿地资源及其生物多样性的遥感监测系列论文之三[J]. 林业资源管理, 2000(6): 44 − 46. [23] 戴祥, 朱继业, 窦贻俭. 中外大河河口湿地保护与利用初探[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2001(增2): 11 − 14. [24] 章哲恺, 汤丽慧, 陈志刚, 等. 感潮河口平原防洪排涝的探索——以浙江省某河口为例[J]. 浙江水利科技, 2012(5): 18 − 20. [25] 韩曾萃, 潘存鸿. 钱塘江河口治导线探索[J]. 浙江水利科技, 2017, 209(1): 58 − 63. [26] 安鑫龙, 周启星. 水产养殖自身污染及其生物修复技术[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2006, 7(9): 1 − 6. [27] 舒阳, 刘振乾, 李丽君. 凤眼莲浸出液对东海原甲藻生长的抑制作用[J]. 生态科学, 2006, 25(2): 124 − 127. [28] 张福, 王思思. 我国近海水生生态系统的退化与修复[J]. 盐业与化工, 2006(6): 47 − 50. [29] 安鑫龙, 周启星, 邢光敏. 海洋微生物在海洋污染治理中的应用现状[J]. 水产科学, 2006, 25(2): 97 − 100. [30] 汤坤贤, 游秀萍, 林亚森, 等. 龙须菜对富营养化海水的生物修复[J]. 生态学报, 2005, 25(11): 3044 − 3051. [31] 沈淑芬, 魏婷, 孙琼花, 等. 海带对罗源湾养殖区海水的生物修复研究[J]. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 29(4): 103 − 108. [32] 林向阳, 钟晨辉, 唐隆晨, 等. 海带对大黄鱼网箱养殖区水质的生物修复[J]. 渔业研究, 2018, 40(4): 279 − 285. [33] 安鑫龙, 齐遵利, 李雪梅, 等. 中国海岸带研究II——海岸带生态环境问题及其解决途径[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2008(27): 11967 − 11969. [34] 许崇彦, 刘宪斌, 刘占广, 等. 翅碱蓬对石油烃污染的海岸带修复的初步研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2007, 7(1): 37 − 39. [35] 赵博, 张盼, 于永海, 等. 渤海海洋生态修复现状、不足及建议[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021(6): 975 − 980. [36] 符小明, 唐建业, 吴卫强, 等. 海州湾生态修复效果评价[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 2017, 32(1): 93 − 98. [37] 林毅辉, 潘伟然, 肖征, 等. 高集海堤开口后厦门湾潮流特征分析[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2020(6): 9 − 17. [38] 赵鹏, 朱祖浩, 江洪友, 等. 生态海堤的发展历程与展望[J]. 海洋通报, 2019, 38(5): 481 − 490. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2019.05.001 [39] MACCALLUM T , POYNTER J , BEARDEN D .Lessons learned from Biosphere 2: when viewed as a ground simulation/analog for long duration human space exploration and settlement[J]. SAE transactions, 2004: 1095-1104. [40] 王金华, 黄华梅, 贾后磊, 等. 粤港澳大湾区海岸带生态系统保护和修复策略[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(23): 8430 − 8439. [41] LLOYD M W, BURNETT R K, ENGELHARDT K A M, et al. Does genetic diversity of restored sites differ from natural sites? A comparison of Vallisneria americana (Hydrocharitaceae) populations within the Chesapeake Bay[J]. Conservation Genetics, 2012, 13(3): 753 − 765. doi: 10.1007/s10592-012-0324-3 [42] SIMENSTAD C, REED D, FORD M. When is restoration not?Incorporating landscape-scale processes to restore self-sustaining ecosystems in coastal wetland restoration[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2006, 26(1): 27 − 39. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2005.09.007 [43] SAPKOTA R P, STAHL P D, RIJAL K. Restoration Governance: An Integrated Approach Towards Sustainably Restoring Degraded Ecosystems[J]. Environmental Development, 2018, 27: 83 − 94. doi: 10.1016/j.envdev.2018.07.001 -



 下载:
下载: