-
地下水演化主要研究地下水时空变化特征、发展规律和形成机理,通过对地下水水化学变化特征及演变规律进行研究,从而更好地揭示地下水与环境之间相互作用机制[1]。地下水在循环流动过程中,与含水层介质中化学物质和矿物组分发生一系列化学反应,决定其化学组分形成和演化过程,通过对研究区水文地球化学特征进行分析是研究其地下水演化规律的基础。国内外许多学者通过地球化学模拟及同位素示踪法等方法对地下水演化规律进行研究,建立地球化学模型反映地下水的演化过程。Radloff等[2]通过建立孟加拉盆地的地下水水量运输模型,得出地下水砷的存在显著阻碍了地下水运输,使得深层含水层受砷污染程度加大;Christofi等[3]利用水文地球化学模拟建立概念模型来研究断裂含水层辉长岩中地下水的水化学演化过程;Savage等[4]通过地球化学模型对加州主金脉区碱性坑湖高砷的化学演化规律进行分析;李义连等[5]在娘子关泉域水化学模拟中,考虑了CO2的分压对矿物饱和度的影响,得出区域地下水矿物溶解的合理条件;李长锁等[6]利用Piper三线图、相关性分析、离子比值法、矿物饱和指数法和反向地球化学模拟等方法对济北地热田地热水的水化学特征和地下水运移过程中所发生的水-岩作用及形成机理进行研究。
喀什地区是新疆主要的灌溉农业基地,但长期以来水资源分配不均、水质较差问题严重制约着喀什地区经济的发展。其中水质较差主要表现在地下水氯化物、硫酸盐和TDS普遍超标,地下水水质问题较为突出[7-8]。近几年来,许多专家学者在喀什地区西部开展了有关地下水的研究,主要是地下水水资源动态变化研究[9-10]、地下水污染[11-14]和地表水、地下水水化学特征[15-16]等方向,魏兴等[17]以喀什三角洲为研究区,运用水文地球化学与氢氧同位素分析水化学成因及演化过程。随着城镇化的进行,喀什地区西部经济发展迅速,工农业用水增加,随即产生的废水等污染物长期影响着地下水水质[18],而潜水含水层是农业活动的主要开采含水层。
本文在根据2014年和2016年潜水采样样品及岩土采集测试分析的基础上,通过Piper三线图、Gibbs图和离子比值法,借助PHREEQC软件模拟,通过两期数据进行对比分析,对喀什地区西部潜水水化学特征及演化规律进行研究,以期为其地下水利用提供科学依据。
-
喀什地区西部位于新疆塔里木盆地西南缘,具有南、北、西三面环山,向东面敞开的地形,为典型的半封闭盆地,地理坐标为75°00′—78°00′E,37°10′—40°10′N(图1),地势总体呈南、北、西部高,东部低趋势。研究区总面积约为1.78×104 km2,平原区面积1.71×104 km2,包括喀什市、疏勒县、疏附县、英吉沙县、岳普湖县、伽师县等6个县市。
该区为温带大陆性干旱气候,降水量少,垂直分带性明显,平原区降水量小且主要集中在春夏季,多年平均降水量为59.8 mm;山前带随地势升高降水量逐渐增大,主要集中在夏秋季,多年平均降水量为100 mm。蒸发强烈,呈明显垂直分带性,平原区蒸发量大,山前蒸发量随地势升高而逐渐减少。气温受地形地势因素影响,多年平均气温为11.7 ℃。地貌单元划分为构造剥蚀中高山、构造剥蚀低山丘陵、山麓斜坡堆积山前冲洪积平原、河流堆积冲积平原和风成沙丘五类[19]。
研究区主要含水层岩系为第四系松散层,赋存第四系松散岩类孔隙地下水,南部高山区和中山区主要分布基岩裂隙水,中低山区及低山丘陵区主要分布碎屑岩裂隙孔隙水[20]。第四系地下水类型主要划分为单一结构潜水和多层结构潜水-承压水含水层(上覆潜水含水层埋深为90—110 m,第一层承压水埋深为90—210 m,第二层承压水埋深为190—300 m)[21]。山麓斜坡堆积山前冲洪积平原地下水主要接受西部、北部和南部河流的引水渠水补给、大气降水入渗及山前侧渗等方式进行补给,中下游河流堆积冲积平原地势较为平坦,水系河网丰富,水平方向上受上游的侧向补给,垂直方向上通过地面径流入渗、灌溉用水入渗、水库等地表水渗漏等方式进行补给[17]。地下水流向由山前向平原区径流,西部呈由西向东径流,东部呈由南向北径流,总体趋势与地势走向基本一致。地下水排泄方式以人工开采、泉水溢出、潜水蒸腾蒸发及向下游侧向流出为主[20]。
-
依据中国地质调查局编制的《地下水污染调查评价规范(DD2008—01)》中的技术要求,对喀什地区进行了1:25万地下水污染调查工作,覆盖喀什市及周边县市,获得2014年及2016年地下水水质数据,其中2014年6月—7月潜水水化学样品21组,2016年6月—10月潜水水化学样品83组,研究区潜水水化学组分含量特征值见表1,取样前,用去离子水将聚乙烯塑料水样瓶润洗3遍,取样时用所取水样润洗3次,贴好标签密封保存,所取水样用0.45 μm醋酸纤维滤膜过滤,阳离子分析的水样加0.1 mL优级纯硝酸酸化至pH<2。
地下水水样严格按《地下水环境监测技术规范(HJ/T164—2004)》进行采集、保存和送样,水样检测由新疆地质矿产勘查开发局第二水文地质工程地质大队化验室完成,检测项目包括pH、水温、溶解氧(DO)、氧化还原电位(Eh)、电导率(EC)等5项现场必测指标,测试精度分别为0.01、0.01 ℃、0.01 mg·L−1、0.1 mV和0.01 μS·cm−1。K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−、SO42−、HCO3−、总硬度(TH)和溶解性总固体(TDS)等无机指标,其中,pH由哈纳(HANNA) HI98121笔式测定仪测定,K+和Na+使用火焰原子吸收分光光度法测定,Ca2+和Mg2+用乙二胺四乙酸二钠滴定法测定,Cl−用硝酸银容量法测定,SO42−用硫酸钡比浊法测定,HCO3−用盐酸滴定法测定。K+检测下限值为0.05 mg·L−1,Na+检测下限值为0.01 mg·L−1,Ca2+、Mg2+和Cl−检测下限值为1.0 mg·L−1,SO42−检测下限值为0.05 mg·L−1。
-
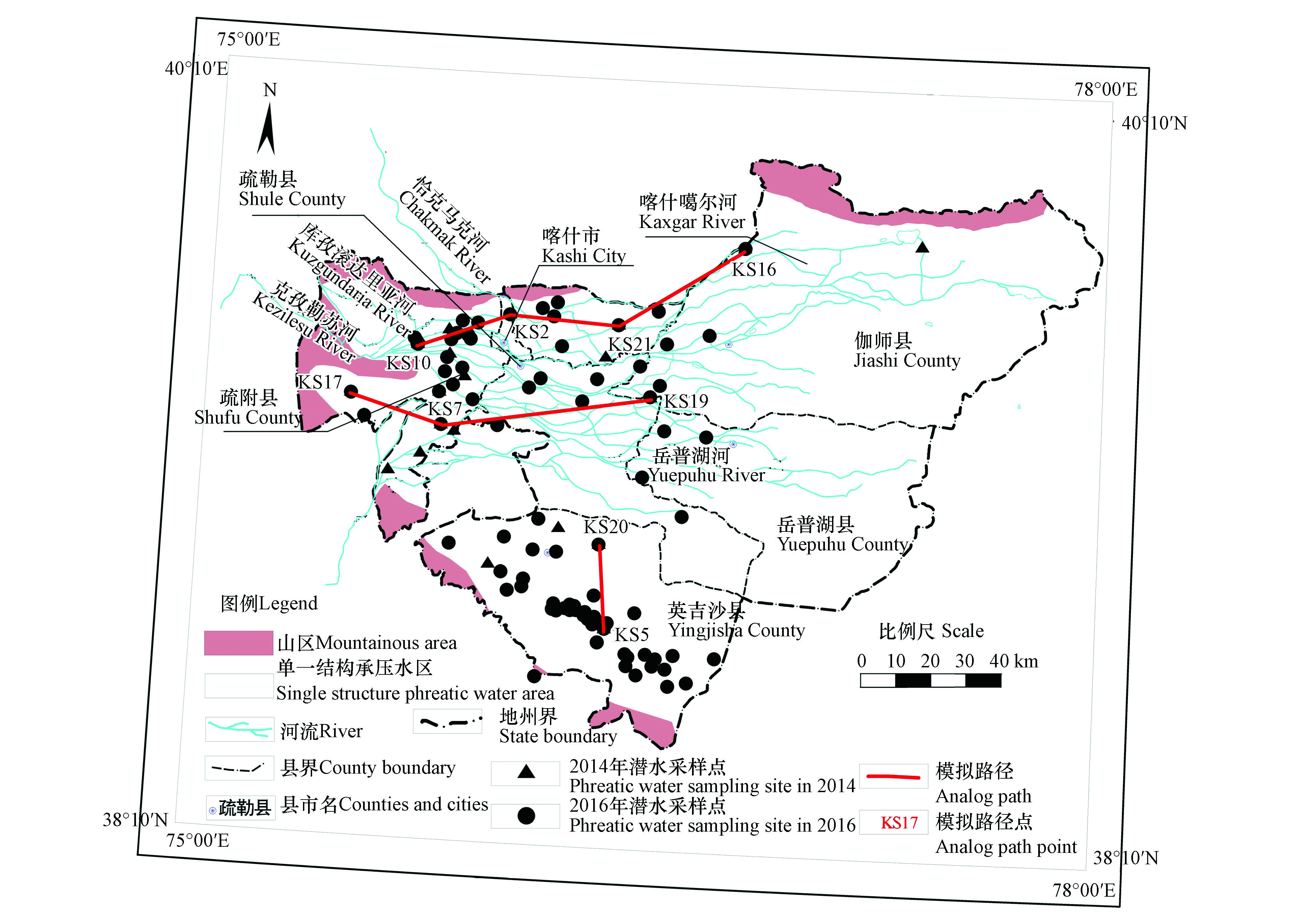
水文地球化学计算机模型PHREEQC可以模拟含水层中的溶质运移,定量分析模拟自然过程与人类活动影响下的水-岩相互作用[22],利用反向水文地球化学模拟对喀什地区西部潜水时空演化规律进行研究。通过地下水流场特征及潜水取样点分布情况,依据地下水流方向最终确定3条水流路径进行水文地球化学模拟,通过PHREEQC水文地球化学模拟软件建立数据较全的2014年及2016年两个时期的反应路径模型,分析各水化学组分变化特征,计算饱和指数及反向模拟,从而分析研究区潜水水化学特征及组分迁移演化规律。
-
根据表1知,2014年21组潜水水样中,Na++K+质量浓度范围为32.71—29909.95 mg·L−1,平均值为1790.04 mg·L−1,超标率为47.6%;Ca2+质量浓度范围为55.54—648.08 mg·L−1,平均值为258.80 mg·L−1;Mg2+质量浓度范围为18.06—4520.45 mg·L−1,平均值为852.93 mg·L−1;Cl−质量浓度范围为22.87—41586.1 mg·L−1,平均值为7176.08 mg·L−1,超标率为14.3%;SO42−质量浓度范围为96.24—19860.69 mg·L−1,平均值为4084.60 mg·L−1,超标率为23.8%;HCO3−质量浓度范围为72.85—652.70 mg·L−1,平均值为231.03 mg·L−1。潜水中主要阳离子毫克当量百分比关系为Na++K+>Ca2+>Mg2+,阴离子毫克当量百分比为SO42−>Cl−>HCO3−,Na++K+占阳离子总量的范围为18.3—76.1%(平均为40.6%),SO42−占阴离子总量的范围为26.0%—67.7%(平均为50.3%)。
2016年83组潜水水样中,Na++K+质量浓度范围为23.77—38168.11 mg·L−1,平均值为2158.01 mg·L−1,超标率为48.2%;Ca2+质量浓度范围为38.14—1707.15 mg·L−1,平均值为271.10 mg·L−1;Mg2+质量浓度范围为4.38—4185.80 mg·L−1,平均值为330.10 mg·L−1;Cl−质量浓度范围为28.39—54072.06 mg·L−1,平均值为2780.19 mg·L−1,超标率为47.0%;SO42−质量浓度范围为96.04—25857.83 mg·L−1,平均值为2161.80 mg·L−1,超标率为86.7%;HCO3−质量浓度范围为59.84—1294.92 mg·L−1,平均值为250.10 mg·L−1。潜水中主要阳离子浓度关系为Na++K+>Ca2+>Mg2+,阴离子毫克当量百分比为SO42−>Cl−>HCO3−,Na++K+占阳离子总量的范围为6.3%—87.2%(平均为40.9%),SO42−占阴离子总量的范围为13.3%—77.3%(平均为52.5%)。
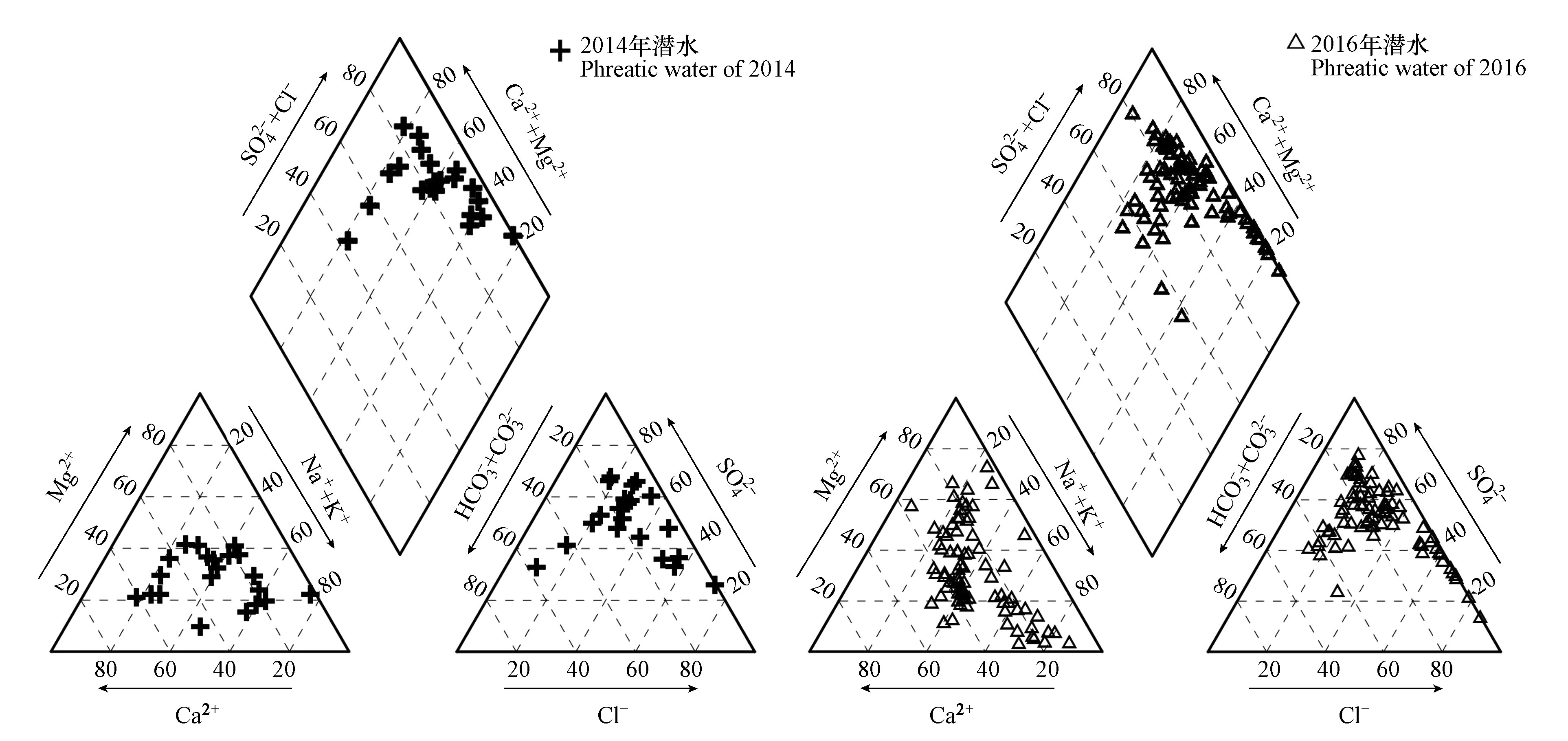
通过绘制2014年和2016年潜水Piper三线图,以表现潜水水样的一般化学特征及演化规律(图2),该图示法可直观看出各组分离子的相对含量,不受人为因素影响[23-24]。2014年研究区潜水水化学类型较复杂,主要为SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg型和SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型水,分别占23.8%和19.0%;2016年研究区潜水水化学类型总体也较复杂,主要为SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型和SO4·Cl-Na型水,分别占24.1%和13.3%。
2014年采集的21组潜水样品中,pH值范围为7.29—10.23,平均值为8.01,超标率为14.3%;TDS质量浓度范围为113.80—20032.84 mg·L−1,平均值为1424.08 mg·L−1,超标率为9.5%。2016年采集的83组潜水样品中,pH值范围为7.1—8.31,平均值为7.77,均未超标;TDS质量浓度范围为90.07—18686.62 mg·L−1,平均值为1908.55 mg·L−1,超标率为30.1%。两年的潜水均为弱碱性,pH从上游到下游变化不大,较为平缓,总体有减小趋势,由于出山口受岩石风化作用和水-岩相互作用有大量碱性物质随地面径流及冰川融雪等方式入渗补给地下水,使得出山口潜水pH相对较高;TDS含量从上游到下游为升高趋势,是由于潜水流向路径过程中不断有矿物质等盐类化合物溶解加入和下游水位降低,蒸发浓缩作用增强有关,且2016年潜水与2014年相比TDS升高较多,表明喀什地区西部潜水劣质水增多。
-
沿上游至下游分布选择3条模拟路径(图1),模拟路径控制点潜水水化学特征如表2所示。根据这3条模拟路径9个控制点的潜水样品水化学特征来判断潜水离子组分从上游到下游的变化情况。上游至下游,各条路径上潜水Na++K+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−、SO42−和HCO3−含量随地下水从上游到下游流动,含量普遍都升高,其中路径3的各组分含量均高于路径1和路径2。路径1由西北出山口穿过喀什主要居民居住地到下游河流冲积平原,潜水受人类活动影响,排泄大大增加,与地表水联系较为紧密,因此路径1控制点水化学组分变化波动较大。
-
潜水中化学组分之间存在一定的联系,通常用化学组分的相关关系来表明离子的联系程度及来源[25],利用SPSS 26.0软件对喀什西部潜水水化学组分进行Pearson分析,结果见表3和表4,TDS与Na++K+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−、SO42-、HCO3−均存在显著正相关关系,表明上述化学组分与TDS有明显联系,特别是与Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−、SO42-这几个组分,与HCO3−联系有所降低,说明Na++K+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−、SO42-、HCO3−是导致TDS含量增大的主要因素。Cl−与Na++K+、Ca2+、Mg2+,SO42-与Na++K+、Ca2+、Mg2+和HCO3−与Na++K+、Ca2+、Mg2+均有显著正相关关系,说明上述阴离子与阳离子存在同一来源,可能来自岩盐、硫酸盐岩、硅酸盐岩和碳酸盐岩的风化溶解,也可能来自盐岩蒸发溶解或大气降水。
研究区含水层主要矿物为岩盐、钙质粉砂岩、钙质细砂岩方解石、白云石、芒硝和石膏等[26],因此初步判定SO42-和Cl−主要来源是岩盐、石膏和芒硝的溶解,并且2016年的SO42-和Cl−浓度比例比2014年有所升高,而相关性降低,说明除了岩盐、石膏和芒硝风化溶解外,可能还有其他来源;Na++K+与Cl−和HCO3−为显著正相关关系,来源可能是岩盐和钠长石等硅酸盐类矿物的风化溶解;Ca2+和Mg2+为同源,可能是白云石的风化溶解。
-
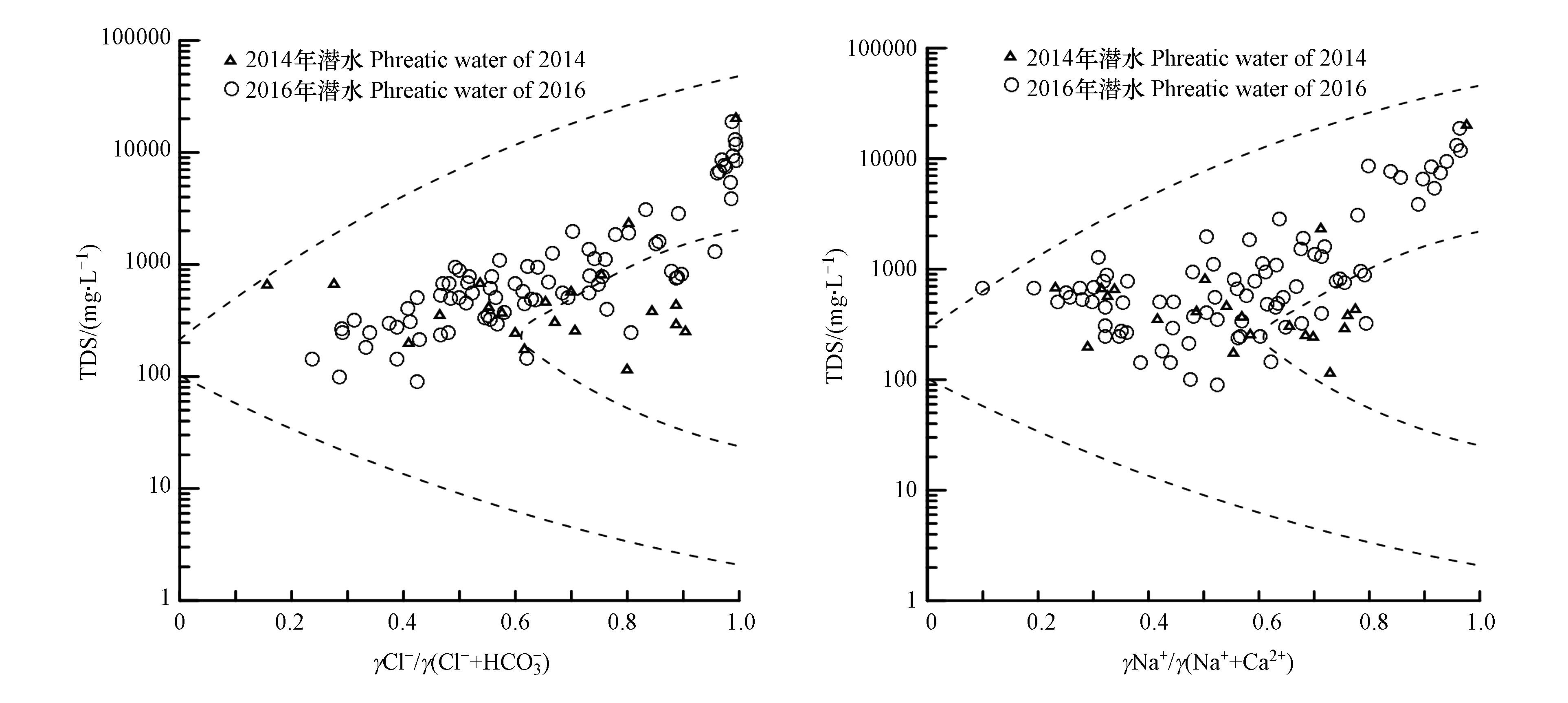
Gibbs图可以定性判断大气降水、岩石溶滤作用和蒸发浓缩所控制的水化学演化机制[27],该图反映Na+/(Na++Ca2+)和Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−)与TDS之间的关系。当水样落在TDS含量很高和较大比值范围里时,表明主要影响因素为蒸发浓缩控制,该区主要集中的是干旱区的水样,TDS含量中等和较低比值的水样化学组分主要影响因素为岩石溶滤控制,TDS含量较低和较大比值的水样化学组分主要影响因素为大气降水控制[28-30]。
研究区2014年和2016年潜水Gibbs图(图3)可看出,2014年潜水水样基本都落在TDS含量范围为110—2300 mg·L−1之间,Na+/(Na++Ca2+)比值基本分布在0.2—0.8之间,Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−)比值基本分布在0.2—0.9之间,表明2014年潜水绝大部分主要离子组分受岩石溶滤控制,极小部分受蒸发浓缩控制影响;2016年潜水水样基本落在TDS含量范围为100—10000 mg·L−1,Na+/(Na++Ca2+)比值基本分布在0.2—0.8之间,Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−)比值基本分布在0.2—1之间,表明2016年潜水大部分主要离子组分受岩石溶滤控制,部分受蒸发浓缩控制影响;2016年潜水较2014年蒸发浓缩控制影响增大,这表明研究区潜水水位降低,下游蒸发浓缩作用增强,大气降水控制对研究区潜水水化学组分影响较小。
-
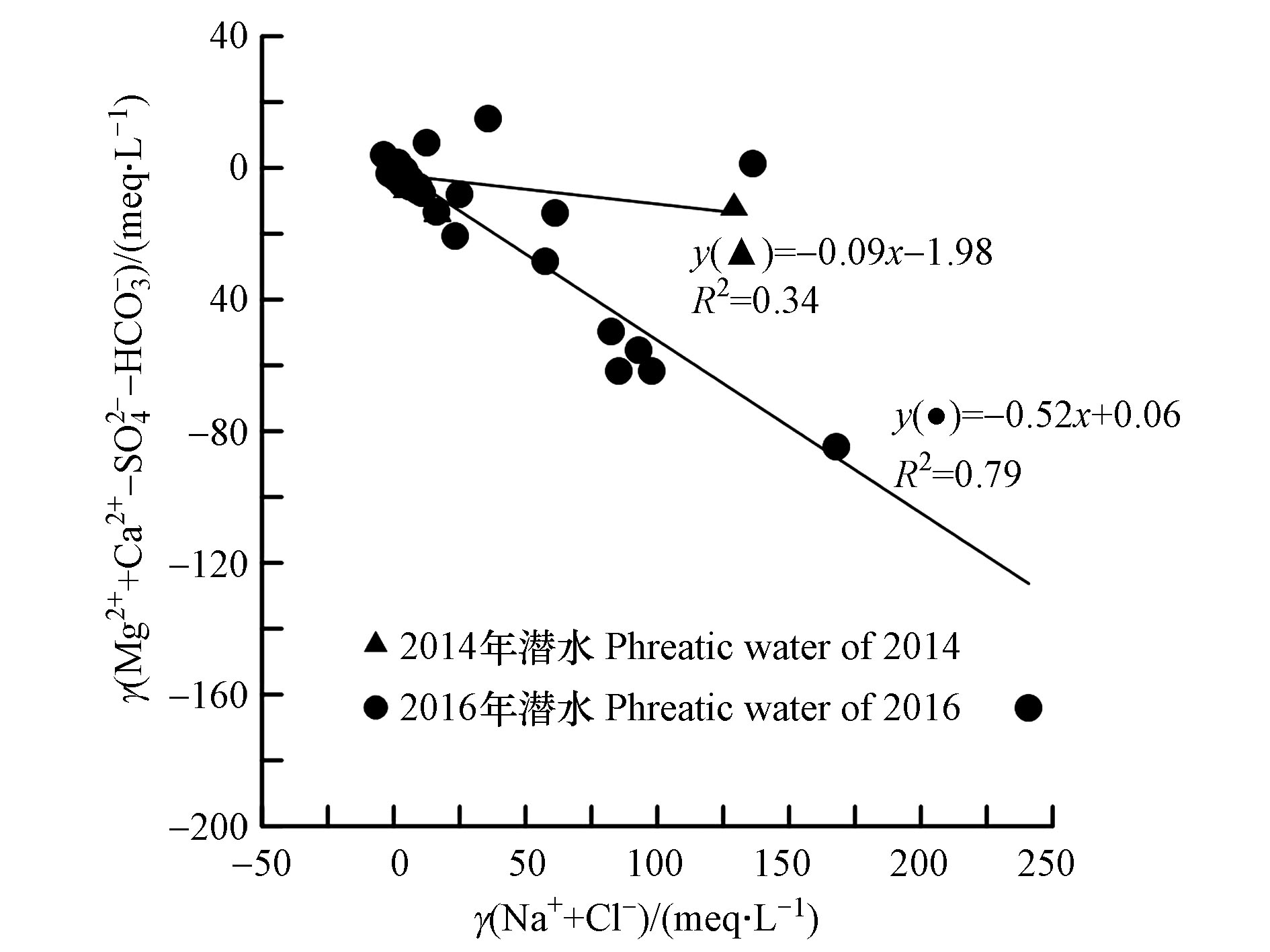
通常由(Na+-Cl−)与(Mg2++Ca2+-SO42−-HCO3−)的关系来判断是否发生阳离子交换作用,若发生阳离子交换作用,则两者的比值应该在−1左右[31]。2014年和2016年潜水样品γ(Na+-Cl−)与γ(Mg2++Ca2+-SO42−-HCO3−)的比值远离−1(图4),且相关关系较弱,说明研究区潜水阳离子交换作用不明显。
-
研究区潜水取样点几乎都落在γ(Cl−)/γ(Na++K+)=1的等值线上(图5(a)),说明潜水中Na+、K+和Cl−基本来自岩盐的溶解作用。
研究区潜水取样点均落在γ(HCO3−)/γ(Ca2++Mg2+)=1的上方(图5(b)),表明潜水除了白云石和方解石的溶解作用,还有其他Ca2+矿物的溶解参与。γ(Ca2++Mg2+)/γ(HCO3−+SO42−)呈线性关系(图5(c)),且大部分潜水样品落在γ(Ca2++Mg2+)/γ(HCO3−+SO42−)=1上,部分落在下方,表明潜水中Ca2+和Mg2+主要来自蒸发岩和硅酸盐的溶解作用[32]。γ(SO42−+Cl−)与γ(HCO3−)关系可判断碳酸岩和蒸发岩溶解对地下水化学组分的贡献程度,研究区2014年和2016年潜水样品均落在γ(SO42−+Cl−)/γ(HCO3−)=1的上方(图5(d)),表明离子主要来自蒸发岩的溶解。因此,潜水中Ca2+应该主要来源于蒸发岩的溶解。
由γ(Ca2+)与γ(SO42−)的关系可知(图5(e)),基本所有潜水样品中γ(Ca2+)/γ(SO42−)的值小于1,同样证明了地下水中Ca2+主要来源于石膏矿物的溶解。令γ(Ca2++Mg2+-HCO3−)表示潜水中石膏溶解后的Ca2+浓度,γ(SO42−+Cl−-Na+)表示石膏溶解后的SO42−浓度。若水样中SO42−全部来自石膏的溶解,那么γ(Ca2++Mg2+-HCO3−)/γ(SO42−+Cl−-Na+)的值应等于1[17],结合图5(f)可知,潜水取样点基本落在y=x上,表明潜水中的SO42−主要来自石膏的溶解,部分离群点主要位于农田附近,表明少量潜水中SO42−受灌溉及人类活动影响。
研究区潜水中Na+、K+、Cl−和SO42−主要来源于岩盐、芒硝和钠长石的风化溶解,Ca2+和Mg2+主要来源石膏和碳酸岩的风化溶解。综合图5(a)、图5(c)和图5(e)可看出,采样点中Na+和SO42−浓度偏高,这与表1数据相符。
-
研究区潜水共有3条模拟路径(图1),分别为路径1(KS10-KS2-KS21-KS16)、路径2(KS17-KS7-KS19)和路径3(KS5-KS20)。饱和指数SI是地下水水化学研究中应用最多的一个指标,它是表征矿物相对地下水饱和状态的参数,能够解释水化学成分如何变化。当地下水中某种矿物的SI>0时,这种矿物在地下水中处于过饱和状态;SI<0时,这种矿物处于未饱和状态;SI=0时,该矿物处于平衡状态[33]。利用PHREEQC软件计算饱和指数,2014年和2016年3条路径控制点结果如表5和表6所示,可知2014年和2016年研究区潜水中,方解石(CaCO3)和白云石[CaMg(CO3)2]的饱和指数均大于0,为饱和状态;硬石膏(CaSO4)、石膏(CaSO4·2H2O)和岩盐(NaCl)的饱和指数均小于0,为溶解状态。因此选择岩盐、方解石、白云石和石膏等作为“可能矿物相”,并且考虑潜水处于开放状态,在路径中将CO2作为“可能矿物相”。其中,KS10同位点2014年和2016年潜水Eh值降低,地下水偏向还原环境,方解石和白云石沉淀量降低幅度较大;KS2同位点2014年和2016年潜水pH值分别为10.23和8.21,变化较大,Eh值降低,地下水偏向还原环境,方解石和白云石沉淀量降低幅度大,CO2溶解量降低幅度大;KS20同位点2014年和2016年潜水pH值降低,Eh值降低,但变化幅度不大,地下水偏向还原环境,方解石沉淀量降低,CO2溶解量降低。
-
摩尔转移量的正数表明水-岩环境中含该组分矿物的溶解量大于沉淀量,负数表明该组分矿物含量沉淀量大于溶解量。根据喀什地区西部钻孔岩芯岩矿鉴定资料,研究区地层中富含石英、盐岩、白云石、石膏等矿物,利用PHREEQC软件对模拟路径进行反向模拟,得2014年和2016年各3条模拟路径摩尔转移量(表7和表8),进而定量分析该组分的迁移程度。该模型选择岩盐、方解石、白云石、石膏和CO2等作为“可能矿物相”,3条路径均不考虑阳离子吸附交换作用。结果表明:2014年和2016年路径1上石膏、白云石和岩盐一直发生溶解作用,从上游到中游,溶解作用降低,Ca2+含量降低,方解石沉淀量降低,到下游潜水埋深降低,由于蒸发浓缩作用增强,CO2溢出;2014年和2016年路径2上石膏、白云石和岩盐一直发生溶解作用,上游到下游溶解量增大,CO2溶解增大,白云石沉淀量增大;2014年和2016年路径3上石膏、白云石和岩盐一直发生溶解作用,白云石沉淀。3条路径上的溶解沉淀规律与表5和表6饱和指数变化规律也相符。
-
(1)2014年研究区潜水水化学类型比较复杂,主要以SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg型和SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型水为主;2016年研究区潜水水化学类型总体也较为复杂,主要是以SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型和SO4·Cl-Na型水为主。潜水阳离子主要以Na++K+为主,阴离子主要以
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 为主。2016年潜水与2014年相比TDS升高较多,表明喀什地区西部潜水劣质水增多。(2)研究区潜水水化学组分主要受岩石溶滤作用和蒸发浓缩作用影响,2016年潜水较2014年蒸发浓缩控制影响增大。研究区潜水中Na+、K+、Cl−和SO42−主要来源于岩盐、芒硝和钠长石的风化溶解,Ca2+和Mg2+主要来源石膏和碳酸岩的风化溶解。
(3)PHREEQC模拟表明,石膏、方解石、白云石和岩盐饱和矿物指数在沿潜水路径流向逐渐增加,潜水水化学组分含量呈递增趋势,矿物溶解沉淀规律为石膏、岩盐和白云石共同溶解,方解石沉淀。
(4)针对研究区潜水水质较差的现状,建议重视饮用地下水源和农业灌溉用水保护。
新疆喀什地区西部潜水水化学特征及演化规律分析
Analysis of chemical characteristics and evolution of phreatic water in Western Kashgar Prefecture, Xinjiang
-
摘要: 以2014年和2016年的潜水样品采集测试数据(分别为21组和83组)为基础,运用Piper三线图、相关性分析、Gibbs图、离子比值法、矿物饱和指数法及反向地球化学模拟等手段对新疆喀什地区西部潜水水化学特征及演化规律进行研究。结果表明,2014年潜水水化学类型主要以SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg型和SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型水为主;2016年潜水水化学类型主要以SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型和SO4·Cl-Na型水为主。潜水阳离子主要以Na++K+为主,阴离子主要以SO42−为主。2016年与2014年相比潜水TDS升高较多,研究区潜水劣质水增多。研究区潜水水化学组分主要受岩石溶滤作用和蒸发浓缩作用影响,2016年潜水较2014年蒸发浓缩控制影响增大,Na+、K+、Cl−和SO42−主要来源于岩盐、芒硝和钠长石的风化溶解,Ca2+和Mg2+主要来源石膏和碳酸岩的风化溶解。PHREEQC模拟表明,2014年和2016年石膏、方解石、白云石和岩盐饱和矿物指数在沿潜水路径流向逐渐增加,潜水水化学组分含量呈递增趋势,矿物溶解沉淀规律为石膏、岩盐和白云石共同溶解,方解石沉淀。Abstract: Basted on the data from testing phreatic water samples collected in 2014 and 2016 (21 groups and 83 groups, respectively), trilinear chart by Piper, correlation analysis, Gibbs plot, ion ratio method, mineral saturation index method and reverse geochemical simulation were used to study the hydrochemical characteristics and evolution pattern of phreatic water in western Kashgar Prefecture, Xinjiang. The results showed that the chemical types of phreatic water in 2014 were mainly SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg and SO4·Cl-Na·Mg water. As in 2016, the chemical types of phreatic water were mainly SO4·Cl-Na·Mg and SO4·Cl-Na type water. The main cations in phreatic water are Na++K+, while the main anion is SO42−. Compared with 2014, the phreatic water TDS increased significantly were and the phreatic water quality decreased in 2016. The dissolution of rocks and evaporation effect were the main controlling factors of the phreatic water in the study areas Evaporation effect had bigger effect on phreatic water in 2016 than in 2014. The main sources of Na+, K+, Cl− and SO42− were weathering and dissolution of halite, thenardite and sodium. The main sources of Ca2+ and Mg2+ were weathering and dissolution of gypsum and carbonate. PHREEQC simulations showed that the gypsum, calcite, dolomite, and rock salt mineral saturation indexes were all gradually increased along the phreatic water path both in 2014 and 2016. The chemical component content of the phreatic water showed an increasing trend. The mineral dissolution and precipitation pattern was that gypsum, rock salt and dolomite dissolved together while calcite precipitates.
-

-
表 1 喀什地区西部潜水水化学含量统计表
Table 1. Chemical composition content statistics of phreatic water in western Kashgar Prefecture
年份Year 统计值Statistics pH TDS Na++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− 2014(n=21) 最小值Minimum 7.29 113.8 32.71 55.54 18.06 22.87 96.24 72.85 最大值Maximum 10.23 20032.84 29909.95 648.08 4520.45 41586.1 19860.69 652.7 平均值Mean 8.01 1424.08 1790.04 258.8 852.93 7176.08 4084.6 231.03 超标率/%
Standard rate14.3 9.5 47.6 — — 14.3 23.8 — 2016(n=83) 最小值Minimum 7.1 90.07 23.77 38.14 4.38 28.39 96.04 59.84 最大值Maximum 8.31 18686.62 38168.11 1707.15 4185.8 54072.06 25857.83 1294.92 平均值Mean 7.77 1908.55 2158.01 271.1 330.1 2780.19 2161.8 250.1 超标率/%
Standard rate0 30.1 48.2 — — 47 86.7 — 注:n为样品数,pH无量纲,其余指标为mg·L−1;标准值根据《生活饮用水卫生标准》;“—”代表该指标无标准限值;下同.
Note: n is the number of samples, the pH is dimensionless, and the remaining indicators are mg·L−1; The standard values are according to the 《Sanitary Standards for Drinking Water》; “—”There is no standard limit for this indicator; Same as below.表 2 研究区模拟路径控制点水化学组分统计表
Table 2. The water chemical composition statistics of the control points on the simulation path in the study area
路径
Path样品编号
Sample serial number时间
TimepH 指标/(mg·L−1)
Index水化学类型
Water chemistry typeNa++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− TDS 1 KS10 2014 7.62 1137.98 287.9 187.4 1506 1317 327.8 428.60 SO4·Cl-Na 2016 7.74 87.84 160.61 26.79 74.52 461.30 122.11 450.27 SO4-Na KS2 2014 10.23 42.88 81.42 29.8 45.75 156.9 206.4 663.90 HCO3·SO4-Ca·Mg 2016 8.21 143.93 220.84 73.55 107.88 890.45 146.54 780.93 SO4-Na·Ca·Mg KS21 2014 7.47 336.00 289.79 36.86 273.72 892.67 153.86 798.47 SO4·Cl-Na·Ca 2016 7.50 351.54 83.72 222.15 325.36 1089.94 339.47 953.86 SO4-Na·Mg KS16 2014 7.65 29909.95 648.08 4520.45 41586.10 19860.69 390.61 20032.86 SO4·Cl-Na 2016 7.82 9831.86 658.20 1461.78 11705.52 10007.48 476.05 7423.39 SO4·Cl-Na 2 KS17 2014 7.72 35.42 75.67 18.06 55.17 181.24 136.77 194.91 HCO3·SO4-Na 2016 8.25 39.88 38.14 15.83 28.39 96.04 122.11 99.34 HCO3·SO4-Na·Ca·Mg KS7 2014 7.94 152.82 107 58.95 170.5 397.7 182.1 173.65 SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg 2016 8.13 57.31 88.25 43.79 63.82 225.92 268.92 266.14 HCO3·SO4-Na·Mg KS19 2014 7.57 923.91 325.23 406.71 837.46 2744.76 354.13 2309.38 SO4·Cl-Na·Mg 2016 7.80 1133.72 281.07 621.02 1171.02 3484.12 402.97 3057.01 SO4·Cl-Na·Mg 3 KS5 2014 8.07 269.75 123.6 127.9 272.7 746.3 230.7 304.45 SO4·Cl-Na·Mg 2016 7.56 213.90 102.61 96.90 262.38 520.32 207.68 551.29 SO4·Cl-Na·Mg KS20 2014 8.18 126.38 83.03 63.74 164.59 354.74 207.80 365.90 SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg 2016 7.26 5343.15 778.26 1218.17 7800.56 5991.37 476.43 6720.10 SO4·Cl-Na·Mg 表 3 研究区2014年潜水各化学组分相关系数统计表
Table 3. Statistical table of correlation coefficients of various chemical components of phreatic water in study area in 2014
指标Index pH TDS Na++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ pH 1.00 TDS −0.10 1.00 Na++K+ −0.13 0.99** 1.00 Ca2+ −0.54** 0.91** 0.88** 1.00 Mg2+ −0.20 0.99** 0.99** 0.89** 1.00 Cl- −0.20 0.99** 0.99** 0.88** 0.99** 1.00 SO42− −0.25 0.99** 0.99** 0.91** 0.99** 0.99** 1.00 HCO3− −0.26 0.75** 0.71** 0.82** 0.75** 0.70** 0.77** 1.00 注:*表示在0.05水平下,相关性显著;**表示在0.01水平下,相关性极显著;下同.
Note: * Indicates that the correlation is significant at the 0.05 level; ** indicates that the correlation is extremely significant at the 0.01 level; Same as below.表 4 研究区2016年潜水各化学组分相关系数统计表
Table 4. Statistical table of correlation coefficients of various chemical components of phreatic water in study area in 2016
指标Index pH TDS Na++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− pH 1.00 TDS −0.52** 1.00 Na++K+ −0.49** 0.89** 1.00 Ca2+ −0.49** 0.80** 0.73** 1.00 Mg2+ −0.49** 0.99** 0.87** 0.68** 1.00 Cl- −0.49** 0.85** 0.99** 0.72** 0.83** 1.00 SO42− −0.48** 0.98** 0.84** 0.74** 0.98** 0.79** 1.00 HCO3− −0.29** 0.45** 0.38** 0.44** 0.44** 0.35** 0.46** 1.00 表 5 喀什地区西部2014年潜水中矿物饱和指数
Table 5. Mineral saturation index of phreatic water in western Kashgar Prefecture in 2014
路径Path 硬石膏Anhydrite 方解石Calcite CO2 白云石Dolomite 石膏Gypsum 岩盐Halite CaSO4 CaCO3 CaMg(CO3)2 CaSO4·2H2O NaCl 1 KS10 −0.74 0.79 −2.12 1.74 −0.52 −4.48 KS2 −1.77 2.07 −5.64 4.09 −1.55 −7.3 KS21 −6.8 0.44 −2.26 0.32 −0.46 −5.69 KS16 −0.06 0.83 −2.33 2.91 0.11 −1.68 2 KS17 −1.59 0.28 −2.52 0.28 −1.37 −7.3 KS7 −1.29 0.66 −2.65 1.4 −1.07 −6.21 KS19 −0.5 0.73 −2.05 1.89 −0.28 −4.84 3 KS5 −1.11 0.85 −2.7 2.05 −0.89 −5.78 KS20 −1.43 0.85 −2.84 1.92 −1.21 −6.30 表 6 喀什地区西部2016年潜水中矿物饱和指数
Table 6. Mineral saturation index of phreatic water in western Kashgar Prefecture in 2016
路径Path 硬石膏Anhydrite 方解石Calcite CO2 白云石Dolomite 石膏Gypsum 岩盐Halite CaSO4 CaCO3 CaMg(CO3)2 CaSO4·2H2O NaCl 1 KS10 −1.03 0.47 −2.61 0.49 −0.81 −6.80 KS2 −0.77 1.03 −3.04 1.91 −0.55 −6.45 KS21 −1.21 0.23 −1.96 1.23 −0.99 −5.61 KS16 −0.15 1.12 −2.3 2.95 0.06 −2.78 2 KS17 −2.08 0.5 −3.1 0.97 −1.86 −7.52 KS7 −1.53 0.98 −2.66 2.01 −1.31 −7.04 KS19 −0.55 0.9 −2.25 2.47 −0.33 −4.62 3 KS5 −1.26 0.28 −2.21 0.88 −1.05 −5.89 KS20 −0.18 0.74 −1.7 2.02 0.04 −3.20 表 7 潜水路径反向模拟结果(2014)
Table 7. Reverse simulation results of phreatic water path in 2014
矿物相
Mineral facies化学式
Chemical formula摩尔转移量Molar transfer/(mmol·L−1) 路径1 Path1 路径2 Path2 路径3 Path3 KS10−KS2 KS2−KS21 KS21−KS16 KS17−KS7 KS7−KS19 KS5−KS20 石膏Gypsum CaSO4·2H2O 1.077×10−2 6.028×10−3 2.123×10−1 2.014×10−3 1.440×10−2 3.431×10−3 方解石Calcite CaCO3 −1.269×10−2 −1.109×10−3 −4.06×10−1 −2.914×10−3 −2.706×10−2 −5.062×10−1 白云石Dolomite CaMg(CO3)2 6.96×10−3 2.929×10−4 2.044×10−1 1.684×10−3 1.815×10−2 2.646×10−3 岩盐Halite NaCl 4.291×10−2 1.248×10−2 1.326 3.852×10−3 2.375×10−2 6.253×10−3 CO2 CO2 3.23×10−3 1.482×10−3 −1.077×10−2 3.894×10−4 1.927×10−3 2.42×10−4 注:正值表示溶解;负值表示沉淀;下同.
Note: Positive values indicate dissolution; Negative values indicate precipitation; Same as below.表 8 潜水路径反向模拟结果(2016)
Table 8. Reverse simulation results of phreatic water path in 2016
矿物相
Mineral facies化学式
Chemical formula摩尔转移量Molar transfer/(mmol·L−1) 路径1 Path1 路径2 Path2 路径3 Path3 KS10−KS2 KS2−KS21 KS21−KS16 KS17−KS7 KS7−KS19 KS5−KS20 石膏Gypsum CaSO4·2H2O 3.318×10−3 1.229×10−3 6.649×10−2 1.218×10−3 2.742×10−2 6.173×10−2 方解石Calcite CaCO3 −3.609×10−3 −1.124×10−3 −1.047×10−1 −1.061×10−3 −4.648×10−2 −9.167×10−2 白云石Dolomite CaMg(CO3)2 1.927×10−3 6.587×10−3 5.311×10−2 1.265×10−3 2.393×10−2 4.723×10−2 岩盐Halite NaCl 1.437×10−3 6.898×10−3 3.766×10−1 1.0×10−3 3.147×10−2 2.175×10−1 CO2 CO2 1.09×10−4 2.337×10−3 9.689×10−4 1.441×10−3 1.419×10−3 3.132×10−3 -
[1] 滕彦国, 左锐, 王金生, 等. 区域地下水演化的地球化学研究进展 [J]. 水科学进展, 2010, 21(1): 127-136. TENG Y G, ZUO R, WANG J S, et al. Progress in geochemistry of regional groundwater evolution [J]. Advances in Water Science, 2010, 21(1): 127-136(in Chinese).
[2] RADLOFF K A, ZHENG Y, MICHAEL H A, et al. Arsenic migration to deep groundwater in Bangladesh influenced by adsorption and water demand [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2011, 4(11): 793-798. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1283 [3] CHRISTOFI C, BRUGGEMAN A, KUELL C, et al. Hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in gabbro of the Troodos Fractured Aquifer. A comprehensive approach [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2020, 114: 104524-104543. [4] SAVAGE K S, ASHLEY R P, BIRD D K. Geochemical Evolution of a High Arsenic, Alkaline Pit-Lake in the Mother Lode Gold District, California [J]. Economic Geology, 2009, 104(8): 1171-1211. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.104.8.1171 [5] 李义连, 王焰新, 周来茹, 等. 地下水矿物饱和度的水文地球化学模拟分析-以娘子关泉域岩溶水为例 [J]. 地质科技情报, 2002, 21(1): 32-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2002.01.008 LI Y L, WANG Y X, ZHOU R L, et al. Hydrogeochemical modeling on saturation of minerals in groundwater: a case study at Niangziguan, Northern China [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2002, 21(1): 32-36(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2002.01.008
[6] 李常锁, 武显仓, 孙斌, 等. 济南北部地热水水化学特征及其形成机理 [J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(S1): 313-325. LI C S, WU X C, SUN B, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of geothermal water in northern Ji’nan [J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(S1): 313-325(in Chinese).
[7] 纪媛媛, 李巧, 周金龙. 新疆喀什地区地下水质量与污染评价 [J]. 节水灌溉, 2014(1): 50-53, 56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4929.2014.01.014 JI Y Y, LI Q, ZHOU J L. Assessment of groundwater quality and pollution in Kashgar region of Xinjiang [J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2014(1): 50-53, 56(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4929.2014.01.014
[8] 魏兴, 周金龙, 贾瑞亮, 等. 喀什地区不同TDS浅层地下水分布及资源量估算 [J]. 节水灌溉, 2017(9): 51-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4929.2017.09.012 WEI X, ZHOU J L, JIA R L, et al. Distribution and resource estimation of shallow groundwater with different TDS in Kashgar region of Xinjiang [J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2017(9): 51-54(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4929.2017.09.012
[9] 郎新文. 喀什地区2012-2015年地下水变化动态分析 [J]. 地下水, 2019, 44(4): 46-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2019.04.017 LANG X W. Dynamic analysis of groundwater changes in Kashi area from 2012 to 2015 [J]. Groundwater, 2019, 44(4): 46-48(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2019.04.017
[10] 热汗古丽·吾买尔, 满苏尔·沙比提, 陆吐布拉·依明. 喀什地区近10年地下水资源时空动态变化分析 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2011, 25(7): 63-68. REYANGUL U, MANSUR S, LOTPULLA E. Spatial dynamic changes of ground water resources in Kashghar prefecture during recent 10 years [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2011, 25(7): 63-68(in Chinese).
[11] 孙英. 新疆喀什地区西部地下水“三氮”空间分布特征及影响因素[C]. 北京: 中国环境科学学会, 2019. SUN Y. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of “Three-Nitrogen” in groundwater of the western area of Kashgar, Xinjiang[C]. Beijing: Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences, 2019(in Chinese).
[12] 魏兴, 周金龙, 曾妍妍, 等. 喀什地区西部地下水重金属空间分布特征及成因分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(8): 1802-1811. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016120802 WEI X, ZHOU J L, ZENG Y Y, et al. Spatial distribution and orign of heavy metals in groundwater in the western Kashgar Prefecture [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(8): 1802-1811(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016120802
[13] 栾凤娇, 周金龙, 曾妍妍, 等. 新疆南部典型地区地下水中氟的分布特征及其富集因素分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(6): 1203-1211. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.06.2015102703 LUAN F J, ZHOU J L, ZENG Y Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and enrichment factors of fluorine in groundwater in typical areas of southern Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(6): 1203-1211(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.06.2015102703
[14] 曾妍妍, 周殷竹, 周金龙, 等. 新疆喀什地区西部地下水质量现状评价 [J]. 新疆农业大学学报, 2016, 39(2): 167-172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8614.2016.02.015 ZENG Y Y, ZHOU Y Z, ZHOU J L, et al. Assessment of groundwater quality statusin western Kashgar, Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2016, 39(2): 167-172(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8614.2016.02.015
[15] 孙英, 周金龙, 乃尉华, 等. 新疆喀什噶尔河流域地表水水化学季节变化特征及成因分析 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019, 33(8): 128-134. SUN Y, ZHOU J L, NAI W H, et al. Seasonal variation characteristics and causes of surface water chemistry in Kashgar River Basin, Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2019, 33(8): 128-134(in Chinese).
[16] 陈小兵, 周宏飞, 张学仁, 等. 新疆喀什噶尔冲积平原区地下水水化学特征[J]. 干旱区地理, 2004(1): 75-79. ZHU H, ZHOU H F, CHEN X B, et al. Analysis on the characteristics of groundwater resources in Kashgar Prefecture, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2005, 22(2): 152-156(in Chinese).
[17] 魏兴, 周金龙, 乃尉华, 等. 新疆喀什三角洲地下水化学特征及演化规律 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(9): 4042-4051. WEI X, ZHOU J L, NAI W H, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the Kashgar Delta Area in Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(9): 4042-4051(in Chinese).
[18] 国家环境保护总局. HJ/T164—2004, 地下水环境监测技术规范[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2004. State Environmental Protection Administration. HJ/T164—2004, Groundwater environmental monitoring technical specifications[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2004(in Chinese).
[19] 乃尉华, 常志勇, 陆成新, 等. 新疆喀什经济开发区水文地质环境地质调查评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017. NAI W H, CHANG Z Y, LU C X, et al. Investigation and evaluation of hydrogeological environment and geology in economic development zone of Xinjiang Kashgar[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2017(in Chinese).
[20] 乃尉华, 常志勇, 李斌, 等. 新疆喀什三角洲1: 10万水文地质环境地质调查报告[R]. 新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产勘查开发局第二水文工程地 质大队, 2018. NAI W H, CHANG Z Y, LI B, et al. 1: 100, 000 hydrogeological environment geological survey report in Kashi Delta of Xinjiang[R]. Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Geological and Mineral Exploration and Development Bureau Second Hydrological Engineering Geology Brigade, 2018(in Chinese).
[21] 乃尉华, 史杰, 王文科, 等. 喀什平原区地下水同位素年龄特征及更新速率分析 [J]. 新疆地质, 2018, 36(3): 406-409. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2018.03.021 NAI W H, SHI J, WANG W K, et al. Isotopic age characteristics and renewal rate of groundwater in Kashgar Plain [J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2018, 36(3): 406-409(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2018.03.021
[22] LIPSON D S, MCCRAY J E, THYNE G D. Using PHREEQC to simulate solute transport in fractured bedrock [J]. Groundwater, 2007, 45(4): 468-472. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2007.00318.x [23] 周嘉欣, 丁永建, 曾国雄, 等. 疏勒河上游地表水水化学主离子特征及其控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(9): 3315-3324. ZHOU J X, DING Y J, ZENG G X, et al. Major Ion chemistry of surface water in the upper reach of Shule River Basin and the possible controls [J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(9): 3315-3324(in Chinese).
[24] 张涛, 何锦, 李敬杰, 等. 蛤蟆通河流域地下水化学特征及控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(11): 4981-4990. ZHANG T, HE J, LI J J, et al. Major ionic features and possible controls in the groundwater in the Hamatong River Basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(11): 4981-4990(in Chinese).
[25] HE J H, MA J Z, ZHANG P, et al. Groundwater recharge environments and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Jiuquan Basin, Northwest China [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2012, 27(4): 866-878. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.01.014 [26] 魏兴, 周金龙, 乃尉华, 等. 新疆喀什三角洲地下水SO42-化学特征及来源 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(8): 3550-3558. WEI X, ZHOU J L, NAI W H, et al. Chemical characteristics and sources of groundwater sulfate in the Kashgar Delta, Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(8): 3550-3558(in Chinese).
[27] MARANDI A, SHAND P. Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs Diagram [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2018, 97: 209-212. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.07.009 [28] XIAO J, JIN Z D, ZHANG F, et al. Solute geochemistry and its sources of the groundwaters in the Qinghai Lake catchment, NW China [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 52: 21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.02.006 [29] 赵辉. 三江平原蛤蟆通河流域地下水补、径、排特征及水化学演化规律[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017. ZHAO H. Groundwater recharge, discharge, runoff characteristics and hydrochemical evolution of hamatong river basin in Sanjiang Plain[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017(in Chinese).
[30] 张涛, 蔡五田, 李颖智, 等. 尼洋河流域水化学特征及其控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(11): 4537-4545. ZHANG T, CAI W T, LI Y Z, et al. Major ionic features and their possible controls in the water of the Niyang River Basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(11): 4537-4545(in Chinese).
[31] XIAO J, JIN Z D, ZHANG F. Hydrochemical characteristics, controlling factors and solute sources of groundwater within the Tarim River Basin in the extreme arid region, NW Tibetan Plateau [J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 380-381(5): 237-246. [32] REDWAN M, ABDEL M. Factors controlling groundwater hydrogeochemistry in the area west of Tahta, Sohag, Upper Egypt [J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2016, 118: 328-338. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2015.10.002 [33] 李霄, 林学钰, 都基众, 等. 齐齐哈尔市潜水水化学演化规律分析 [J]. 水利学报, 2014, 45(7): 815-827. LI X, LIN X Y, DU J Z, et al. Analysis of hydrochemical evolution of phreatic water in Qiqihar City [J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2014, 45(7): 815-827(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: