-
大气颗粒物组分复杂,是影响环境空气质量、人体健康等的重要因素[1-3]。PM2.5是颗粒物的重要组成部分[4-5],主要由碳组分[6]、水溶性离子[7]、无机元素[8]等组成。碳组分作为PM2.5中首要组分,含量占PM2.5质量浓度的20%—80%[9-10],主要含碳组分为有机碳(organic carbon, OC)和元素碳(elemental carbon, EC)。有机碳可分为一次源直接排放的一次有机碳和部分经光化学反应生成的二次有机碳(SOC)[11],其中携带的多环芳烃等有毒物质,威胁人体健康[12]。元素碳具有较强的吸附性,常作为污染物转化的反应介质和触媒。有机碳的散射性、元素碳的吸收性,二者相互作用,影响大气能见度和辐射平衡[13-14]。
细颗粒物的污染机理存在着时空差异,因此需要开展多季节、多维度的研究[15]。目前,国内外学者对京津冀[16-17]、中国北方等城市[18-19]大气颗粒物成分及污染特征开展了大量的研究,但对于以盆地为主、地理气象条件复杂的西南成渝地区研究较少,尤其是成都平原地区。成都市作为特大中心城市,占四川省约3%的土地面积,承载了全省20%常住人口、36%GDP和30%机动车,大气污染物排放问题十分突出[20]。为打赢2020年蓝天保卫战,成都市从产业结构、能源结构、城市布局和机动车污染防治[21]等方面入手解决大气污染问题,环境空气质量得到显著提高。2019年,成都全年优良天数创下287 d的历史新高,但仍启动了7次污染天气预警,PM2.5年均质量浓度距国家二级标准(35 μg·m−3)仍有一定的差距。
本研究通过在线测定成都市2019年颗粒物(PM10、PM2.5、PM1)质量浓度和PM2.5中OC、EC质量浓度,分析颗粒物、OC、EC及碳组分质量浓度的变化规律,获得成都市颗粒物及PM2.5中OC、EC的污染特征,解析碳组分的潜在污染来源,可为成都市PM2.5碳组分综合治理提供科学依据。
-
采样站点位于成都市武侯区人民南路四段18号主楼楼顶(104.0728°E,30.6325°N),距地高度18 m,如图1。该站点位于交通主干道旁,车流量大,且居住区分布集中,能较好地反映成都市城区环境空气质量。PM10、PM2.5、PM1质量浓度测试数据分别来自3台美国Metone公司BAM-1020仪器,采样流量均为16.7 L·min−1。碳组分(OC、EC)质量浓度测试数据来源于美国Sunset公司的Model 4在线测试仪器,采样流量为8 L·min−1,时间分辨率为1 h。气象数据(如温度、相对湿度等)由美国DAVIS Vantage Pro2 Plus五参数气象监测仪在线仪器获得。测试时间为2019年全年。
-
BAM-1020测试仪器是利用β射线能量衰减的原理来测量周期内增加的颗粒物质量浓度。环境空气由采样泵吸入,经颗粒物切割器后进入采样管,颗粒物沉积在采样滤膜上,14C放射源发出的β粒子在穿过采集了颗粒物的滤膜后其能量会发生衰减,衰减程度与颗粒物的质量遵循公式(1)[22]。
式中,I为单位时间内β射线衰减强度,I0为未衰减的β射线强度,μ为单位PM2.5的截面积(cm2·g−1,已知),x为PM2.5的密度(g·cm−2),I、I0为仪器测试值,μ为常数,计算得出x的值,将密度进行换算即可得出PM2.5的质量。
-
Sunset OC EC分析仪采用美国职业安全与卫生研究所(NIOSH,The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health)认可的热学/光学方法测定在石英滤膜上的有机碳OC和元素碳EC。石英滤膜作为载体,收集环境空气中的PM2.5。在确定的阶梯升温程序下,仪器通过切换气体模式(He,He/O2)依次热脱附PM2.5中的有机碳和元素碳,相应的有机物和碳化产物进入MnO2氧化炉转化成CO2气体,通过非扩散红外检测器实现定量测定。
-
BAM-1020、Sunset OC EC在线监测仪器质量控制主要包括流量校准、标准比对两个方面。在线监测仪器的使用严格参照仪器操作规程,定期对仪器采样流量进行校准,保证流量维持在EPA指定范围设计值的±5%内。BAM-1020仪器自带参比膜,在每小时采样过程中会自动执行参比膜校准程序,并将测试值与标准值进行对比,确保误差在5%以内,保证仪器正常运行,测试数据可信。每季度,用蔗糖标准溶液对Sunset碳组分分析仪进行校准:测试至少3组不同浓度梯度的标准蔗糖溶液,将浓度与测试信号进行线性拟合,拟合曲线斜率乘以之前的校准常数,得到新的校准常数,替换校准常数后即完成仪器校准。
-
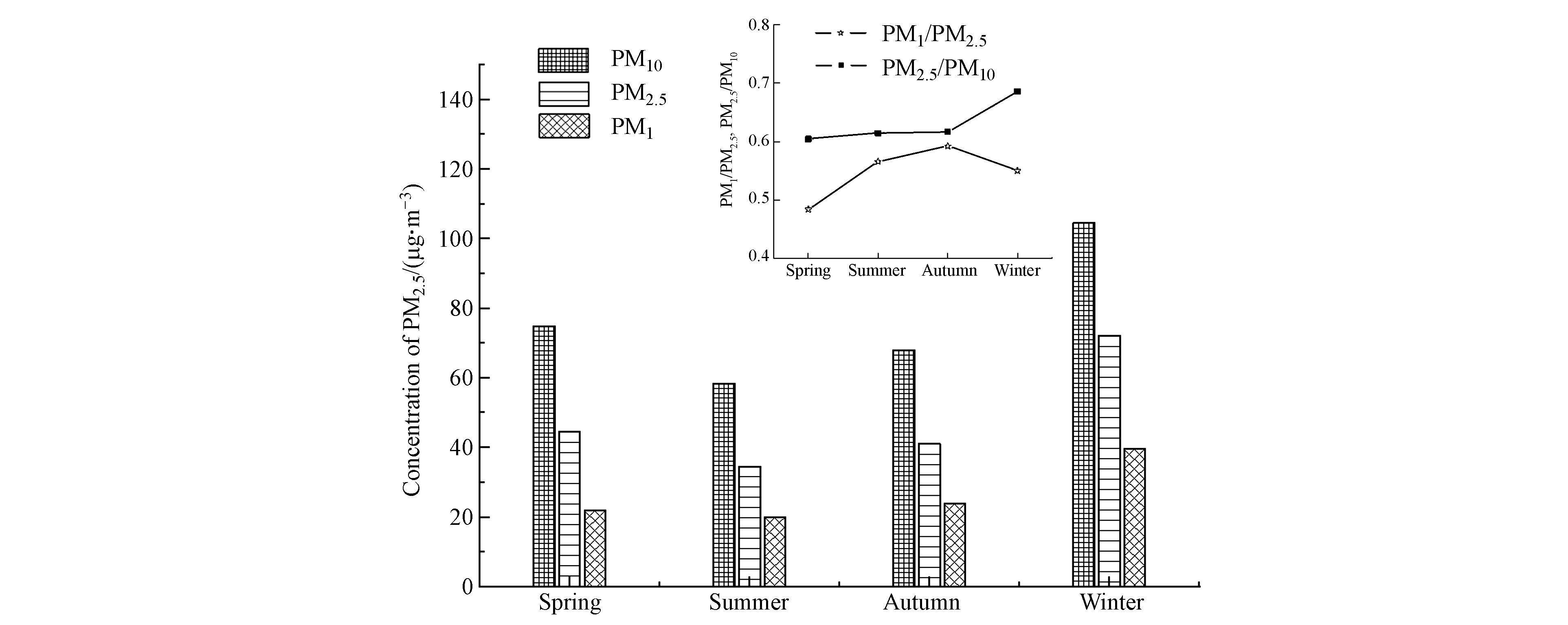
2019年成都市ρ(PM10)、ρ(PM2.5)、ρ(PM1)年均值分别为75.93、47.57、25.98 μg·m−3,季节均值如图2所示,颗粒物质量浓度均呈现春冬高夏秋低的趋势,原因在于盆地夏季雨水较多,大气扩散条件较好,颗粒物去除效率高,与文献[23]结论相同,冬季多静风少雨天气,污染物不易扩散,颗粒物易累积。PM2.5/PM10比值呈现春季至冬季逐渐上升的趋势,PM1/PM2.5比值呈春季至秋季上升,冬季降低的趋势,与冬季PM2.5浓度显著升高有关。在测试的350个有效数据中ρ(PM2.5)大于国家二级标准限值(75 μg·m−3)的污染天数为50 d,占比14.3%,其中中度污染天数为9 d,占比为2.6%。与2015年(ρ(PM10)、ρ(PM2.5)、ρ(PM1)分别为108、64[24]、51.97 μg·m−3[25])相比,2019年ρ(PM10)、ρ(PM2.5)、ρ(PM1)分别下降30%、26%、50%,说明成都市采取的一系列大气污染防治措施取得了较显著的成效。
-
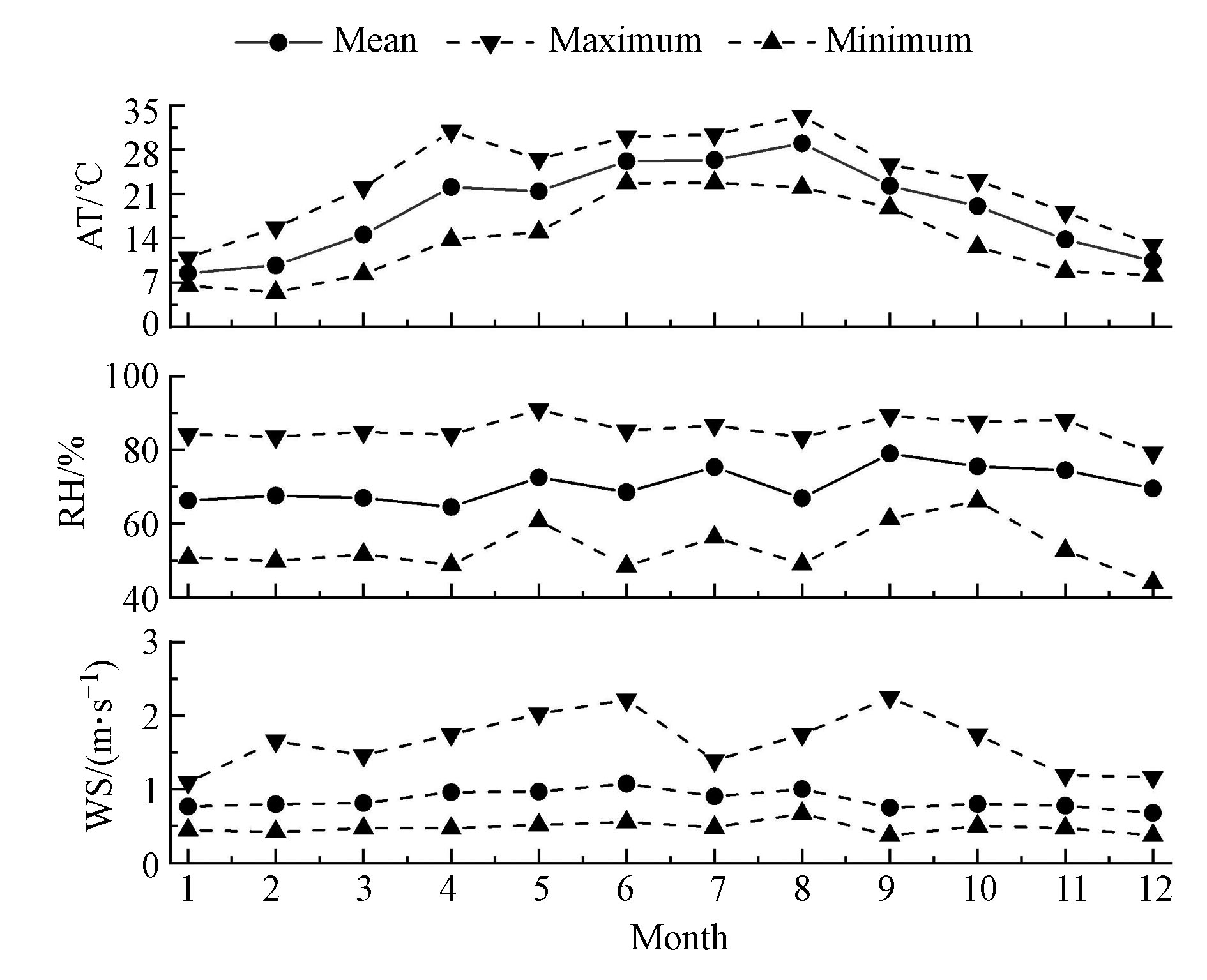
2019年观测点位气温(℃)、相对湿度(%)和风速( m·s−1)月变化和风玫瑰图如图3—4。由图3可得,1—2月气温最低,月均值分别为8.51 ℃和9.74 ℃,全年最低气温出现在2月,仅5.46 ℃。夏季气温明显较高,8月平均气温为29.04 ℃。成都市月均相对湿度在64.51%—79.03%之间,冬季均值为67.81%,秋季均值为76.36%,显著大于其它季节。成都市全年风速变化幅度较小,月均风速在0.68—1.08 m·s−1范围内变化,主导风向为东风,其次为西风(图4),冬季静小风(
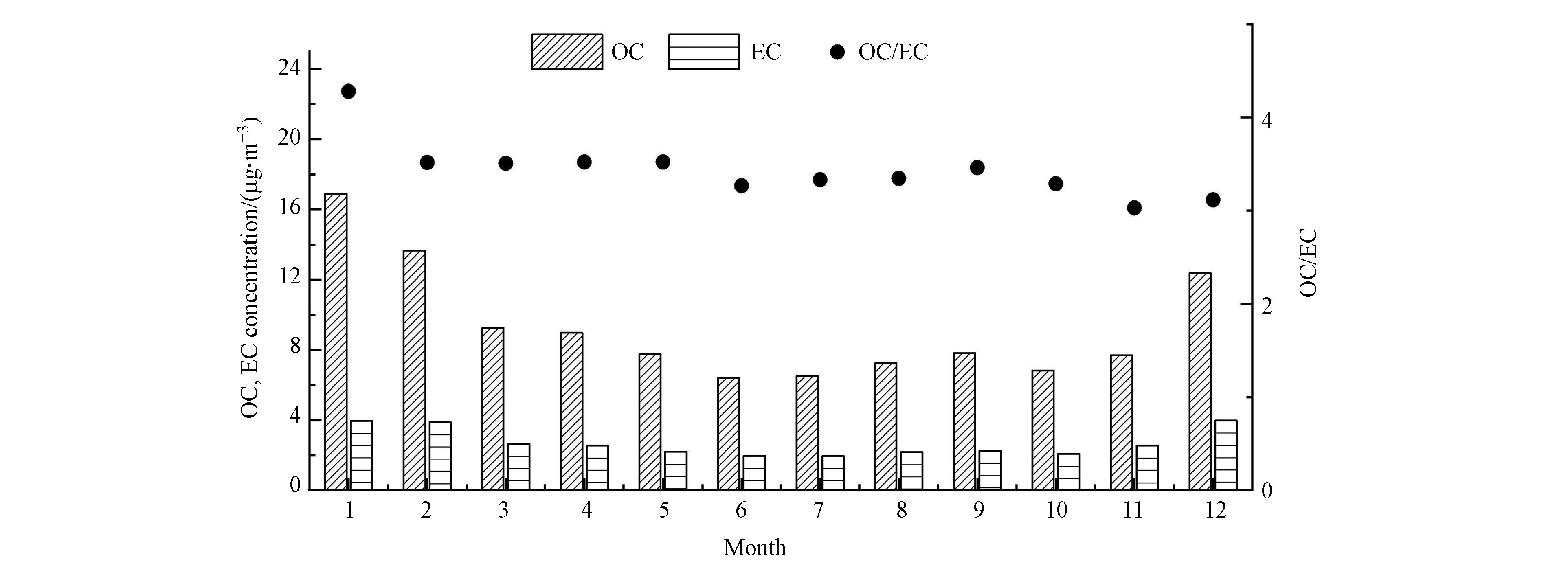
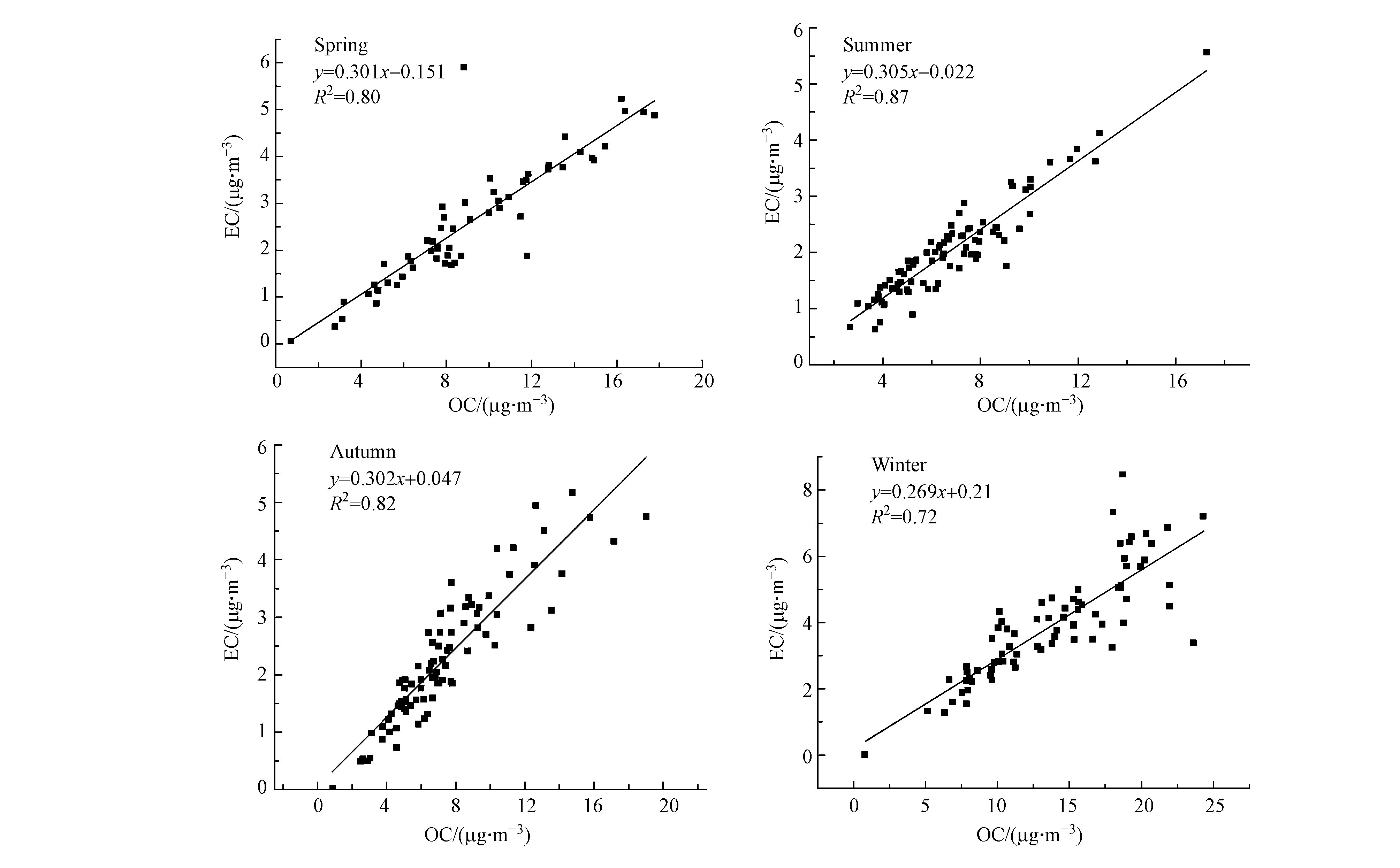
$ \leqslant$ 1.5 m·s−1)频率为93.79%。成都市冬季“低温高湿静风”的气象条件导致污染物难以扩散,且由于西侧青藏高原横断山脉阻挡,易造成输入源和本地源持续累积,引发重污染过程。2019年,成都市PM2.5中ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)年均值分别为9.29、2.68 μg·m−3,占比分别为20%、6%。ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)、OC/EC比值月变化见图5,1月至12月ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)呈先降低后增高的趋势,季节上呈冬高夏低,冬季ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)均值分别为14.30、3.93 μg·m−3,分别是夏季的2.1倍、1.9倍。OC、EC质量浓度与大气温度成反相关,主要原因是冬季温度低,大气层结构稳定,常会出现辐射逆温和锋面逆温,大气层在稳定状态下,大气湍流受到抑制,污染物容易富集难以稀释扩散[26],同时成都平原处于四川盆地,属于典型的盆地地形,盆地上空形成强的下沉气流,冬季尤为明显[27],污染物更易富集。OC/EC比值在3.02—4.28之间,比值均大于2,说明大气中存在二次有机碳[28],且比值介于机动车尾气源(1.0—4.2)和燃煤源(2.5—10.5)之间[29],表明OC与EC主要来源为机动车尾气和燃煤燃烧。OC、EC相关性可表征二者同源性[30-31],成都市不同季节OC、EC相关性分析结果如图6所示(春R2=0.80,夏R2=0.87,秋R2=0.82,冬R2=0.72),R2均大于0.7,说明两者来源相同,但冬季稍差,说明冬季含碳气溶胶来源较其它季节复杂,原因可能是受到气团运输以及二次碳气溶胶形成的影响[32],后续将对OC、EC来源做进一步讨论。
由于目前没有对有机碳和元素碳排放浓度限值的要求,对比2019年成都市与国内外城市ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)、OC/EC,判断成都市OC、EC排放水平,结果见表1。与北方及长三角城市相比,2019年成都市ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)处于相对较低的水平,但在PM2.5中占比处于中等水平,可能的原因是成都冬季未采暖,航空和公路线路密集程度不及北方和长三角等城市,燃料燃烧和交通污染相对较低。与本地区2013—2014年数据相比,ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)分别下降3.71、2.02 μg·m−3,这与成都市一系列大气污染防治工作如淘汰落后产能、优化产业、能源结构、机动车限行和加强非道路移动机械管理等措施密切相关。与伊朗德黑兰相比,成都市OC仍高于其2014—2015年的排放水平,说明成都市还应加强措施以降低OC排放浓度。
-
利用NIOSH协议,通过热学/光学方法在不同温度梯度下得到9种碳组分浓度(OC1、OC2、OC3、OC4、EC1、EC2、EC3、EC4、EC5),在一定程度上能够反应源谱特征,实现颗粒物中碳组分的来源解析,不同碳组分质量浓度见表2。不同碳组分年均质量浓度的分布顺序为OC4>OC2>OC1>OC3>EC4>EC3>EC1>EC5>EC2,有机碳中OC4浓度最高,冬季浓度高达5.91 μg·m−3,OC4是机动车污染源的标识组分之一[40],说明成都市冬季受机动车污染影响较大。季节分布上,OC1—EC3在春夏秋三季质量浓度变化并不明显,而冬季质量浓度显著上升。EC4和EC5春季质量浓度略高于其他季节,说明其来源与季节变化关联度不大。
-
目前SOC估算较多采用EC示踪法[41-42],但该方法未考虑非燃烧源对OC的贡献,会高估SOC含量[43],Cabada等[44]在此基础上对计算方法进行了改进,本研究采用改进后的计算方法,计算公式如下:
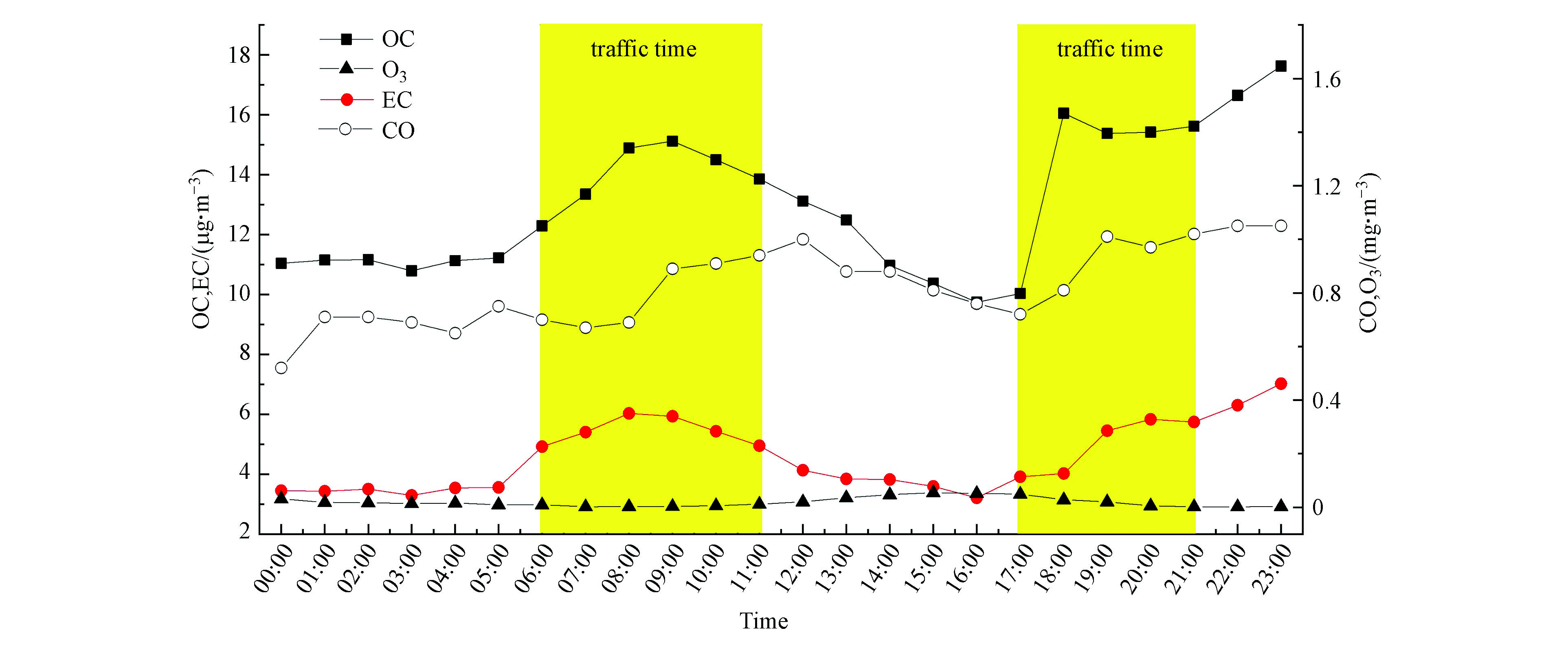
该方法将实测的污染物(OC、EC、O3、CO)小时数据结合起来,CO、EC为一次源排放重要指标,O3为二次成分的重要指标。对于SOC的计算,应选取O3浓度较低、CO和EC浓度较高时段对应的OC、EC数据进行线行拟合,得到的斜率(OC/EC)p表示一次源排放的OC与EC的浓度比。选取8:00—9:00时段的OC、EC浓度值数据进行线性拟合,得出斜率(OC/EC)p,如图7所示,此时段OC、EC、CO均处于较高值,但O3浓度并未上升,可以代表一次源的排放。通过计算,ρ(POC)四季均值依次为5.6、5.5、4.9、9.1 μg·m−3,ρ(SOC)四季均值依次为3.0、1.3、2.5、4.7 μg·m−3,在OC中占比,除夏季为19%外,其余季节均为34%,ρ(SOC)年均值为2.87 μg·m−3,在PM2.5中占比为6%。ρ(SOC)四季均值表现为冬季>春季>秋季>夏季,冬季OC排放增加的同时有机气态污染物也会增加,同时成都冬季频发的静稳天气、较低的温度和较高的相对湿度大大促进了SOC的生成和累积[45]。
-
根据《环境空气质量指数AQI技术规定》(HJ 633—2012)中PM2.5质量浓度划分空气质量等级,在有效测试的350 d中成都市无重度污染天气,其中优、良、轻度污染、中度污染天数分别为128、172、41、9 d,占比分别为36.6%、49.1%、11.7%、2.6%,可见2019年成都市以优良天气为主。碳组分质量浓度和OC、EC的变化特征见表3、表4,在不同空气质量等级下有机碳组分浓度均高于元素碳组分;有机碳中OC4、OC2浓度最高,随着污染等级从优向中度污染而逐渐增加,质量浓度变化范围分别为1.49—10.05 μg·m−3和1.82—5.12 μg·m−3。其中,OC2/OC随污染等级加重而下降,比值在0.32—0.22之间,OC4/OC随污染等级加重而小幅上升,比值在0.26—0.43之间;OC1、OC3浓度次之,其浓度随污染等级加重而增加。元素碳中EC3浓度较高,EC3/EC在0.18—0.30之间;EC1、EC2、EC4浓度较低,其质量浓度随污染等级加重而增加,其中EC2变化幅度较为明显,范围为0.08—0.50 μg·m−3;EC5变化幅度不大,良、轻度污染、中度污染均为0.24 μg·m−3,仅比优上升0.06 μg·m−3。随着污染等级的加重,OC总浓度显著上升,其变化范围为5.68—23.33 μg·m−3,而EC总浓度变化幅度较小,变化范围为0.85—2.65 μg·m−3,这主要与EC化学性质较稳定有关。PM2.5浓度随污染等级加重呈显著上升趋势,变化范围为25.05—129.13 μg·m−3,而OC、EC的增长速度较PM2.5低,OC/PM2.5和EC/PM2.5均随污染等级加重而呈小幅下降趋势,其变化范围分别为0.23—0.18和0.03—0.02,说明OC和EC并不是成都市污染天气的控制因子。
-
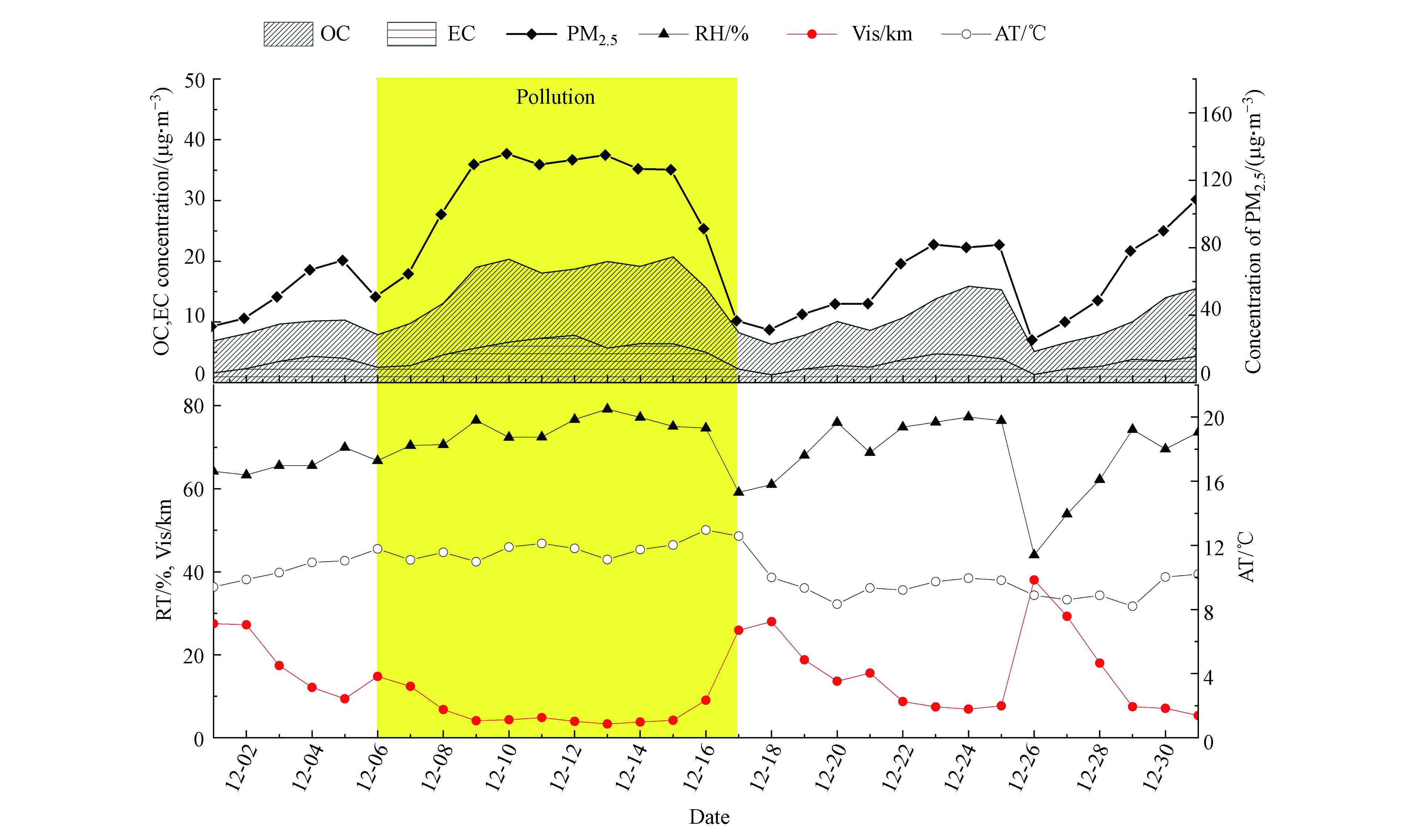
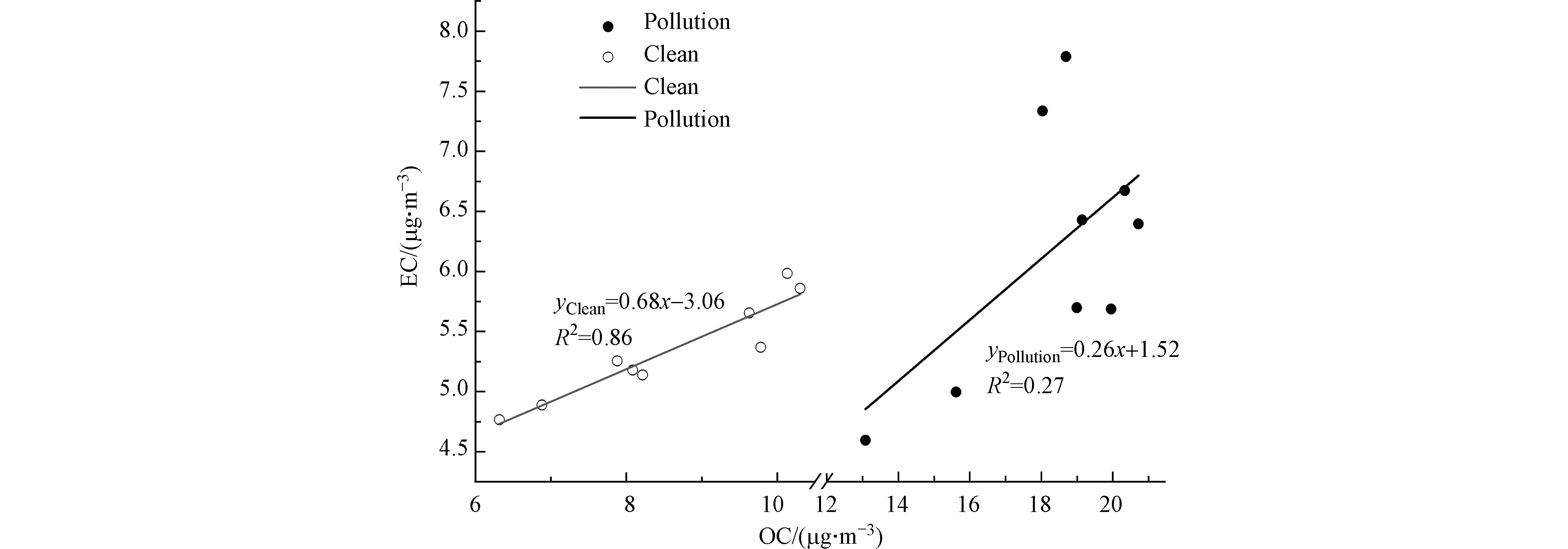
污染过程碳组分变化特征以成都市冬季一次中度污染过程为例,2019年12月9日—15日PM2.5质量浓度持续7 d超过115 μg·m−3,期间PM2.5、OC、EC质量浓度以及气象因素(相对湿度、温度、能见度)随时间变化如图8。ρ(PM2.5)在12月7日开始上升,12月9日达到平台值,温度和相对湿度有所上升,为后期持续的污染天气提供有利的气象条件,污染期间能见度明显降低。12月16日相对湿度、温度下降,气象条件转好,ρ(PM2.5)降低,污染天气显著缓解,17日ρ(PM2.5)降低至36.7 μg·m−3。污染期间ρ(PM2.5)最大值达到138.5 μg·m−3,ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)均值达到19.4 μg·m−3、6.5 μg·m−3较非污染天气质量浓度均增加了1.2倍。污染过程期间OC在PM2.5中的百分占比反而有所下降,EC占比波动不大,基本保持在5%左右,说明污染过程PM2.5中其它组分占比有所上升。污染天与非污染天OC、EC线性关系见图9,在非污染天R2达到0.86,说明两者具有相同的来源,而污染天R2仅为0.27,说明污染期间成都市碳组分来源更为复杂,污染治理措施应从多方面着手。
-
本研究应用SPSS statistic 24对监测期间PM2.5中碳组分质量浓度数据进行最大方差旋转因子分析,为解析组分来源提供依据。SPSS数据统计软件广泛应用自然科学领域,已被各领域研究学者普遍认可。因子分析为其功能之一,常用于环境领域污染物主要来源识别[46]。因子分析是根据变量之间的相关性强弱提取公因子,正交反差最大旋转使每一个主因子只与最少数的变量有相关关系,而使足够多的因子负荷均很小,以便对因子的意义做出更合理的解释[47]。碳组分因子分析结果见表5。
如表5结果所示,共提取3个因子作为有效主因子,前3种主因子因子载荷的累积方差贡献率为92.73%,能够反映主要的污染源信息。因子1载荷贡献率为44.49%,OC1、OC2、OC3、OC4和EC1贡献比例大,主要是易挥发的有机物。因子2载荷贡献率为26.35%,EC1—EC3贡献比例大。因子3载荷贡献率为21.89%,EC4和EC5,贡献比例最大,还有较小比例EC3。根据文献[48-50],含碳组分中OC1主要来源于生物质燃料燃烧,OC2主要来源于煤炭燃烧,OC3、OC4及EC1主要来源于汽油车尾气,故将因子1识别成生物质燃烧、燃煤及汽油车尾气排放。根据文献[51],EC1、EC2主要来源于汽油车尾气污染源,EC3来源于柴油车污染源,EC4—EC5来源于道路扬尘类污染源,故将因子2识别成机动车尾气排放源,因子3识别成道路扬尘类污染源。因此可以得出成都市碳组分污染物来源主要有机动车尾气排放、燃煤、生物质燃烧、道路扬尘类污染。
-
(1)2019年成都市ρ(PM10)、ρ(PM2.5)、ρ(PM1)分别为75.93、47.57、25.98 μg·m−3,较2015年分别下降30%、26%、50%,说明成都市采取的一系列大气污染防治措施取得了较显著的成效。
(2)2019年成都市ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)、ρ(SOC)分别为9.29、2.68、2.87 μg·m−3,OC/EC比值在3.02—4.28之间,表明机动车尾气和燃煤是主要的污染贡献源。不同季节OC与EC相关性R2>0.7,说明二者有着相同的来源。碳组分的平均浓度分布序列为OC4>OC2>OC1>OC3>EC4>EC3>EC1>EC5>EC2。
(3)随着污染等级的加重,OC总浓度呈现显著上升趋势,而EC总浓度变化幅度较小,但OC/PM2.5和EC/PM2.5均随污染等级的加重而呈小幅下降趋势,可见OC和EC并不是成都市污染天气的控制因子。冬季一次污染过程期间ρ(PM2.5)最大值达到138.5 μg·m−3,ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)均值分别为19.4、6.5 μg·m−3。与非污染天相比较,ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)均增加了1.2倍。
(4)来源解析结果表明,2019年成都市碳组分污染物来源主要有机动车尾气排放、燃煤、生物质燃烧、道路扬尘类污染源。
成都市主城区PM2.5碳组分污染特征分析
Pollution characteristics of carbonaceous components in PM2.5 in the Chengdu City
-
摘要:
为研究成都市2019年颗粒物(PM10、PM2.5、PM1)和细颗粒物(PM2.5)中碳组分的污染特征及潜在来源,采用BAM-1020、Sunset OCEC分析仪分别对成都市大气颗粒物和细颗粒物中碳组分开展了为期一年的在线观测,并利用因子分析对碳组分潜在来源进行解析。研究结果表明,2019年成都市ρ(PM10)、ρ(PM2.5)、ρ(PM1)年均值分别为75.93、47.57、25.98 μg·m−3,较2015年分别下降了30%、26%、50%,改善明显。PM2.5中ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)年均值分别为9.29、2.68 μg·m−3,PM2.5中占比分别为20%、6%,处于较低水平。采用Cabada改进方法,计算出ρ(SOC)春、夏、秋、冬四季均值分别为3.0、1.3、2.5、4.7 μg·m−3,季节分布明显,冬季高于其它季节。在不同空气质量等级下,质量浓度最高的碳组分均为OC4和OC2,两者质量浓度随污染等级的加重而增加。OC/PM2.5、EC/PM2.5比值均随污染等级加重而小幅下降,说明OC和EC并不是污染天气的控制因子。成都市冬季一次污染过程中ρ(PM2.5)最大值达到138.5 μg·m−3,ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)均值分别为19.4、6.5 μg·m−3,与非污染天气相比较,ρ(OC)、ρ(EC)均增加了1.2倍。来源解析结果表明2019年成都市碳组分主要来源于生物质燃烧、燃煤、机动车尾气排放、道路扬尘类源。
Abstract:To investigate the pollution characteristics and potential pollution sources of carbon components in atmospheric particles including PM10, PM2.5, PM1 in Chengdu, BAM-1020 and Sunset OCEC analyzer were used to analyze the variation of carbon components in atmospheric particles during 2019, and the factor analysis was applied to explore potential sources. The results demonstrated: (1) The annual average value of ρ(PM10), ρ(PM2.5), ρ(PM1) were 75.93, 47.57 and 25.98 μg·m−3. Compared with that in 2015, it has decreased by 30%, 26% and 50%, respectively, which showed the pollution of atmospheric particulates has improved significantly. (2) The annual average value of ρ(OC), ρ(EC) in PM2.5 were 9.29 μg·m−3 and 2.68 μg·m−3, accounting for 20%, 6%, respectively, at a low level. Based on the Cabada modified method, the calculation results of ρ(SOC) in four seasons were 3.0, 1.3, 2.5 ,4.7 μg·m−3.The seasonal distribution characteristics of carbon component and SOC were significant, and they were higher in winter than in other seasons. (3) The average mass concentrations of OC4, OC2 were the highest among the carbon components in the different air quality rating, and their mass concentrations increased with the aggravation of pollution grade. However, as the increase of pollution level, the ratio of OC/PM2.5 and EC/PM2.5 both showed a slight downward trend, suggesting that OC and EC were not the control factors for pollution weather. With analyzing the typical pollution process, it was found that the maximum value of ρ(PM2.5) was up to 138.5 μg·m−3, and the ρ(OC) and ρ(EC) were 19.4 μg·m−3 and 6.5 μg·m−3, respectively, which increased 1.2 times than that in un-pollution days. (4) Four major sources , apportioned by factor analysis, were biomass combustion, coal combustion, vehicle exhaust emissions, road dust.
-
Key words:
- PM2.5 /
- organic carbon /
- element carbon /
- seasonal characteristics /
- source apportionment /
- Chengdu
-

-
表 1 国内外城市环境空气PM2.5 中OC、EC质量浓度对比
Table 1. The concentration of OC and EC in PM2.5 at home and abroad
地区 Region OC/(μg·m−3) EC/(μg·m−3) OC/% EC/% OC/EC 西安[33](2017) 17.56±11.83 4.08±2.95 31 7 4.3 长春[34](2017) 21.7 1.85 — — 11.7 北京[35](2015—2016) 13.49±4.32 5.41±1.83 13.13 5.2 2.5 重庆[36](2014—2015) 12.37 3.65 16.2 4.8 3.4 伊朗德黑兰[37](2014—2015) 7.8±3.5 3.6±1.5 20 9 2.2 临安(长三角大气环境背景点)[38](2015) 21.93±11.69 6±3.6 17.7 4.9 3.6 成都[39](2013—2014) 13.0±7.5 4.7±3.6 — — 2.76 本研究 9.29 2.68 20 6 3.44 表 2 成都市OC1-EC5质量浓度季节变化(μg·m−3)
Table 2. Seasonal variation of mass concentration of OC and EC components in Chengdu(μg·m−3)
季节 Season OC1 OC2 OC3 OC4 EC1 EC2 EC3 EC4 EC5 春季 2.18 2.36 1.52 2.91 0.22 0.13 0.35 0.51 0.27 夏季 1.80 2.22 1.32 2.03 0.18 0.09 0.18 0.37 0.20 秋季 1.96 2.49 1.46 2.56 0.21 0.14 0.27 0.40 0.22 冬季 2.97 3.68 2.57 5.91 0.31 0.24 0.50 0.42 0.20 年均值 2.23 2.69 1.72 3.35 0.23 0.15 0.33 0.42 0.22 表 3 不同污染等级下的碳组分构成(μg·m−3)
Table 3. Composition of carbon components under different pollution levels(μg·m−3)
空气质量等级 Level PM2.5 OC1 OC2 OC3 OC4 EC1 EC2 EC3 EC4 EC5 OC EC 优 25.05 1.35 1.82 1.02 1.49 0.15 0.08 0.15 0.28 0.18 5.68 0.85 良 50.40 2.44 2.86 1.83 3.48 0.24 0.16 0.35 0.48 0.24 10.61 1.47 轻度污染 88.12 3.70 4.24 2.97 6.95 0.37 0.26 0.60 0.57 0.24 17.85 2.03 中度污染 129.13 4.56 5.12 3.59 10.05 0.51 0.50 0.80 0.61 0.24 23.33 2.65 表 4 不同污染等级下的碳组分变化特征
Table 4. Change characteristics of carbon components under different pollution levels
空气质量等级 Level OC2/OC OC4/OC EC3/EC OC/PM2.5 EC/PM2.5 优 0.32 0.26 0.18 0.23 0.03 良 0.27 0.33 0.24 0.21 0.03 轻度污染 0.24 0.39 0.29 0.20 0.02 中度污染 0.22 0.43 0.30 0.18 0.02 注:OC=OC1+OC2+OC3+OC4; EC=EC1+EC2+EC3+EC4+EC5. 表 5 2019年成都市碳组分因子分析结果
Table 5. Factor analysis for carbon component from Chengdu city during 2019
组分 Component 因子1 Factor 1 因子2 Factor 2 因子3 Factor 3 OC1 0.84 0.40 0.20 OC2 0.94 0.25 0.07 OC3 0.90 0.35 0.21 OC4 0.84 0.49 0.09 EC1 0.64 0.67 0.07 EC2 0.51 0.82 0.11 EC3 0.41 0.75 0.44 EC4 0.25 0.34 0.86 EC5 0.02 0.00 0.96 特征值 4.00 2.37 1.97 方差贡献率/% 44.49 26.35 21.89 累计方差贡献率/% 44.49 70.84 92.73 -
[1] LIU F, TAN Q, JIANG X, et al. Effects of relative humidity and PM2.5 chemical compositions on visibility impairment in Chengdu, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 86: 15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2019.05.004 [2] ZHAO L, WANG L, TAN J, et al. Changes of chemical composition and source apportionment of PM2.5 during 2013—2017 in Urban Handan, China [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2019, 206: 119-131. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.02.034 [3] 曾贤刚, 阮芳芳, 彭彦彦. 基于空间网格尺度的中国PM2.5污染健康效应空间分布 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(6): 2624-2632. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.06.046 ZENG X G, RUAN F G, PENG Y Y, et al. Health effects’ spatial distribution analysis of PM2.5 pollutions in China based on spatial grid scale [J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(6): 2624-2632(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.06.046
[4] XUE H, LIU G, ZHANG H, et al. Similarities and differences in PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations, chemical compositions and sources in Hefei city, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 220: 760-765. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.123 [5] XIE Y, LIU Z, WEN T, et al. Characteristics of chemical composition and seasonal variations of PM2.5 in Shijiazhuang, China: Impact of primary emissions and secondary formation [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 677: 215-229. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.300 [6] GOLLY B, WAKED A, WEBER S, et al. Organic markers and OC source apportionment for seasonal variations of PM2.5 at 5 rural sites in France [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2019, 198: 142-157. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.10.027 [7] XU W, LIU X, LIU L, et al. Impact of emission controls on air quality in Beijing during APEC 2014: Implications from water-soluble ions and carbonaceous aerosol in PM2.5 and their precursors [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2019, 210: 241-252. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.04.050 [8] TURAP Y, TALIFU D, WANG X, et al. Temporal distribution and source apportionment of PM2.5 chemical composition in Xinjiang, NW-China [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2019, 218: 257-268. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.12.010 [9] DAN M, ZHUANG G S, LI X X, et al. The characteristics of carbonaceous species and their sources in PM2.5 in Beijing [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2004, 38(21): 3443-3452. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.02.052 [10] HUANG H, ZOU C, CAO J J, et al. Carbonaceous aerosol characteristics in outdoor and indoor environments of Nanchang, China, during summer 2009 [J]. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association, 2011, 61(11): 1262-1272. doi: 10.1080/10473289.2011.604545 [11] WANG P, CAO J J, SHEN Z X, et al. Carbonaceous species in PM2.5 and PM10 in urban area of Zhengzhou in China seasonal variations and source apportionment [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2017, 191(7): 1-11. [12] 段凤魁, 贺克斌, 刘咸德, 等. 含碳气溶胶研究进展:有机碳和元素碳 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2007, 1(8): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9108.2007.08.001 DUAN F K, HE K B, LIU X D, et al. Review of carbonaceous aerosol studies: Organic carbon and elemental carbon [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2007, 1(8): 1-8(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9108.2007.08.001
[13] 谭吉华, 赵金平, 段菁春, 等. 广州典型灰霾期有机碳和元素碳的污染特征 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2009, 31(3): 105-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2009.03.027 TAN J H, ZHAO J P, DUAN J Q, et al. Characteristics of organic and elemental carbon during typical haze episode in Guangzhou [J]. Environmental Pollution and Control, 2009, 31(3): 105-108(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2009.03.027
[14] 刘珊, 彭林, 温彦平, 等. 太原市PM2.5中有机碳和元素碳的污染特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(2): 396-401. LIU S, PENG L, WEN Y P, et al. Pollution characteristics of organic and elemental carbon in PM2.5 in Taiyuan [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(2): 396-401(in Chinese).
[15] CHAN C K, YAO X. Air pollution in mega cities in China [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42(1): 1-42. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.09.003 [16] 索娜卓嘎, 谭丽, 周芮平, 等. 采暖期北京大气PM2.5中碳组分的分布特征及来源解析 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2018, 34(4): 54-59. SUO N Z G, TAN L, ZHOU R P, et al. Distribution characteristics and sources apportionment of carbonaceous components in PM2.5 during the heating periods in Beijing [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2018, 34(4): 54-59(in Chinese).
[17] 张俊峰, 韩力慧, 程水源, 等. 京津冀地区典型城市大气细颗粒物碳质组分污染特征及来源 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(8): 1729-1739. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.02.12 ZHANG J F, HAN L H, CHENG SY, et al. Characteristics and sources of carbon pollution of fine particulate matter in typical cities in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(8): 1729-1739(in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.02.12
[18] 张家营, 刘保双, 毕晓辉, 等. 菏泽市冬季大气PM2.5和PM10中碳组分来源解析 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2017, 30(11): 1670-1679. ZHANG J Y, LIU B S, BI X H, et al. Source apportionment of carbonaceous species in atmospheric PM2.5 and PM10 during winter in Heze city, China [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 30(11): 1670-1679(in Chinese).
[19] 张敬巧, 罗达通, 王涵, 等. 廊坊市开发区冬季颗粒物碳组分污染特征及来源分析 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(11): 1818-1825. ZHANG J Q, LUO D T, WANG H, et al. Characteristics and source of carbonaceous species in particulate matter during winter in Langfang city development zones [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(11): 1818-1825(in Chinese).
[20] 余娜. 235个蓝天背后 [J]. 四川党的建设, 2018, 313(1): 38-39. YU N. Behind the 235 blue sky [J]. Sichuan Party Building, 2018, 313(1): 38-39(in Chinese).
[21] 于会文. 成都平原大气治理的路径探索 [J]. 环境保护, 2018, 46(6): 43-45. YU H W. Exploration on the Path of air control in Chengdu plain [J]. Environmental Protection, 2018, 46(6): 43-45(in Chinese).
[22] 王永敏, 高健, 徐仲均, 等. 光散射法与β射线衰减-光散射联用法颗粒物在线测量方法对比 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2017, 30(3): 433-443. WANG Y M, GAO J, XU Z J, et al. Inter-comparison between light scattering and beta-attenuation-light scattering particulate matter on-line monitoring [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 30(3): 433-443(in Chinese).
[23] 陈源, 谢绍东, 罗彬, 等. 重庆市主城区大气细颗粒物污染特征与来源解析 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(7): 2420-2430. CHEN Y, XIE S D, LUO B, et al. Pollution characterization and source apportionment of fine particles in urban Chongqing [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(7): 2420-2430(in Chinese).
[24] 四川省人民政府. 2015成都环境质量公报出炉[EB/OL]. 2016-5-11[2019-12-27]. http://www.sc.gov.cn/10462/10464/10465/10595/2016/5/11/10379886.shtml. The People’s Government of Sichuan Province. 2015 Chengdu environmental quality bulletin released[EB/OL]. 2016-5-11[2019-12-27]. http://www.sc.gov.cn/10462/10464/10465/10595/2016/5/11/10379886.shtml (in Chinese).
[25] 林瑜, 叶芝祥, 杨怀金, 等. 成都市中心城区大气PM1的污染特征及来源解析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(9): 3220-3226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.09.003 LING Y, YE Z X, YANG H J, et al. Pollution level and source apportionment of atmospheric particles PM1 in downtown area of Chengdu [J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(9): 3220-3226(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.09.003
[26] 郭育红, 辛金元, 王跃思, 等. 唐山市大气颗粒物OC、EC浓度谱分布观测研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(7): 2497-2504. GUO Y H, XIN J Y, WANG Y S, et al. Observation of size distribution of atmospheric OC / EC in Tangshan, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(7): 2497-2504(in Chinese).
[27] 罗玉, 马振峰, 赵鹏国, 等. 近36a来四川盆地持续霾事件特征及环流分析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(9): 3604-3615. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.09.003 LUO Y, MA Z F, ZHAO P G, et al. Characteristics of persistent haze events and circulation analysis in Sichuan Basin in recent 36years [J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(9): 3604-3615(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.09.003
[28] CAO J J, LEE S C, HO K F, et al. Spatial and seasonal variations of atmospheric organic carbon and elemental carbon in Pearl River Delta Region, China [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2004, 38(27): 4447-4456. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.05.016 [29] CHOW J C, WATSON J G, LU Z Q, et al. Descriptive analysis of PM2.5 and PM10 at regionally representative locations during SJVAQS / AUSPEX [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 1996, 30(12): 2079-2112. doi: 10.1016/1352-2310(95)00402-5 [30] YE Z L, LIU J S, LI Q, et al. Characteristics and source identification of carbonaceous aerosols in PM2.5 Measurements during summer and fall in Changzhou [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(11): 4469-4477. [31] TURPIN B J, HUNTZICKER J J. Identification of secondary organic aerosol episodes and quantitation of primary and secondary organic aerosol concentrations during SCAQS [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 1995, 29(23): 3527-3544. doi: 10.1016/1352-2310(94)00276-Q [32] XU H H, XU J S, HE J, et al. Characteristics and source analysis of atmospheric carbonaceous aerosols in the cities of Hangzhou and Ningbo [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(8): 3511-3517. [33] 牟臻, 陈庆彩, 王羽琴, 等. 西安市PM2.5中碳质气溶胶污染特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(4): 1529-1536. MU Z, CHEN Q C, WANG YQ, et al. Characteristics of carbonaceous aerosol pollution in PM2.5 in Xi'an [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(4): 1529-1536(in Chinese).
[34] WANG J, YU A, YANG L, et al. Research on organic carbon and elemental carbon distribution characteristics and their influence on fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in Changchun city [J]. Environments, 2019, 6(2): 21. doi: 10.3390/environments6020021 [35] 张婷婷, 马文林, 亓学奎, 等. 北京城区PM2.5有机碳和元素碳的污染特征及来源分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(12): 2758-2766. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051701 ZHANG T T, MA W L, QI X K, et al. Characteristics and sources of organic carbon and element carbon in PM2.5 in the urban areas of Beijing [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(12): 2758-2766(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051701
[36] 余家燕, 王军, 许丽萍, 等. 重庆城区PM2.5化学组分特征及季节变化 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(12): 6372-6378. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201703096 YU J Y, WANG J, XU L P, et al. Characteristics of chemical components of PM2.5 and its seasonal variations in Chongqing urban area [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(12): 6372-6378(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201703096
[37] ARHAMI M, SHAHNE M Z, HOSSEINI V, et al. Seasonal trends in the composition and sources of PM2.5 and carbonaceous aerosol in Tehran, Iran [J]. Environmental pollution, 2018, 239: 69-81. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.03.111 [38] 康晖, 朱彬, 王红磊, 等. 长三角典型站点冬季大气PM2.5中OCEC污染特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(3): 961-971. KANG H, ZHU B, WANG H L, et al. Characterization and variation of organic carbon (OC) and elemental carbon (EC) in PM2.5 during the winter in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(3): 961-971(in Chinese).
[39] 吴明, 吴丹, 夏俊荣, 等. 成都冬季PM2.5化学组分污染特征及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(1): 76-85. WU M, WU D, XIA J R, et al. Analysis of pollution characteristics and sources of PM2.5 chemical components in Chengdu in Winter [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(1): 76-85(in Chinese).
[40] 国纪良, 姬亚芹, 马妍, 等. 盘锦市夏冬季PM2.5中碳组分污染特征及来源分析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(8): 3201-3206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.08.009 GUO J L, JI Y Q, MA Y, et al. Pollution characteristics and sources of carbon components in PM2.5 during summer and winter in Panjin city [J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(8): 3201-3206(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.08.009
[41] JI D, LI L, WANG Y, et al. The heaviest particulate air-pollution episodes occurred in northern china in January, 2013: insights gained from observation [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 92: 546-556. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.04.048 [42] 纪尚平, 王丽涛, 赵乐, 等. 邯郸市PM2.5中碳组分的浓度、来源及其变化 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(9): 2873-2880. JI S P, WANG L T, ZHAO L, et al. Concentrations, sources and changes of carbon fractions in PM2.5 in Handan [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(9): 2873-2880(in Chinese).
[43] 李恒庆, 丁椿, 潘光, 等. 济南市居住区采暖季大气PM2.5中碳组分构成及变化分析 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(9): 1810-1817. LI H Q, DING C, PAN G, et al. Analysis on the composition and change of carbon components in PM2.5 of residential area in Jinan during heating period [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(9): 1810-1817(in Chinese).
[44] CABABA J C, PANDIS S N, SUBRAMANIAN R, et al. Estimating the secondary organic aerosol contribution to PM2.5 using the EC tracer method special issue of aerosol science and technology on findings from the fine particulate matter supersites program [J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 2004, 38(S1): 140-155. [45] 程渊, 刘保双, 毕晓辉, 等. 天津市区夏冬季环境空气PM2.5中碳组分污染特征及来源研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(9): 3394-3405. CHENG Y, LIU B S, BI X H, et al. Character and source analysis of carbonaceous aerosol in PM2.5 during summer-winter period, Tianjin Urban Area [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(9): 3394-3405(in Chinese).
[46] 丁新航, 梁越, 肖化云, 等. 太原市采暖季清洁天与灰霾天PM2.5中水溶性无机离子组成及来源分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(6): 1356-1366. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018121102 DING X H, LIANG Y, XIAO H, et al. Composition and source analysis of water-soluble inorganic ions of PM2.5 in clean and haze days during heating season in Taiyuan City [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(6): 1356-1366(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018121102
[47] 翟航, 周俊, 李世梅, 等. 因子分析法在污染源解析方面的应用 [J]. 中国环境管理, 2014, 6(1): 20-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6252.2014.01.005 ZHAI H, ZHOU J, LI S M, et al. Factor analysis method is applied to analysis of the polluters [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Management, 2014, 6(1): 20-24(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6252.2014.01.005
[48] 古金霞, 白志鹏, 刘爱霞, 等. 天津冬季PM2.5与PM10中有机碳、元素碳的污染特征 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2009, 31(8): 33-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2009.08.009 GU J X, BAI Z P, LIU A X, et al. Pollution characteristics of OC and EC in PM2.5 and PM10 in Tianjin Winter [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2009, 31(8): 33-36(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2009.08.009
[49] CAO J J, WU F, CHOW J, et al. Characterization and source apportionment of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon during fall and winter of 2003 in Xi'an, China [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2005, 5: 3127-3137. doi: 10.5194/acp-5-3127-2005 [50] 张大宇, 刘效峰, 彭林, 等. 太原市PM2.5中含碳气溶胶特征分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(12): 2719-2727. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019010203 ZHANG D Y, LIU X F, PENG L, et al. Analysis of characteristics of carbonaceous aerosols in PM2.5 of Taiyuan [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(12): 2719-2727(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019010203
[51] 康宝荣, 刘立忠, 刘焕武, 等. 关中地区细颗粒物碳组分特征及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(8): 3431-3437. KANG B R, LIU L Z, LIU H W, et al. Estimation of secondary organic carbon in PM2.5 and PM10 in Guanzhong Area in autumn and winter [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(8): 3431-3437(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: