-
高级氧化技术因其在反应过程中可产生具有强氧化能力的活性氧物质(ROS),常用于处理难生物降解的有机污染物[1-2]。基于过氧化单硫酸盐(PMS)活化的高级氧化技术,与传统的芬顿技术相比,具有更宽的pH适应范围及更高的氧化电位,近年来受到研究者们的广泛关注[3-4]。
过渡金属可有效活化PMS,其中Co离子在活化PMS过程中展现出最佳的催化性能,然而具有一定的生物毒性,限制了实际应用[5-6]。与其它过渡金属相比,Fe离子及其氧化物具有环境友好,成本低等优点,相关研究最为广泛。在均相高级氧化过程中,溶液中存在大量的过渡金属离子,易造成二次污染,同时存在催化剂回收困难等问题[7]。
Fe3O4中存在Fe(Ⅱ),可以作为催化剂的活性中心活化PMS,而且通过外部磁力可以实现回收利用,降低了催化剂的回收成本[8]。然而,Fe3O4催化氧化过程中也存在表面Fe(Ⅱ)的再生问题,表面Fe(Ⅱ)被氧化成Fe(Ⅲ)后失去对PMS的活化能力,导致其催化活性有所下降,影响其对有机污染物的降解效果[9]。
二硫化钼(MoS2)是由S—Mo—S层通过范德华力堆积在一起的过渡金属二卤化物,作为一种非贵金属催化剂在析氢反应、光电传感器件及消毒灭菌中显示出巨大的应用前景[10]。MoS2中的Mo(Ⅳ)易失去电子,转化为更高价态的Mo(Ⅴ)或Mo(Ⅵ),因此MoS2具有还原性,可将高价态金属还原为低价态。Xing等[11-12]在将MoS2引入Fe(Ⅱ)活化H2O2的体系中,发现MoS2可以还原过程中生成的Fe(Ⅲ),使其转化为Fe(Ⅱ)从而加速了H2O2的活化。
目前,MoS2常用作均相高级氧化过程中的助催化剂,可显著提升催化效果,然而其用于非均相催化过程中的助催化研究仍十分有限。因此,设想采用MoS2作为载体,负载Fe3O4纳米颗粒,可有效增强对PMS的活化性能,具有较大的催化潜力。
2,4-二氯苯氧乙酸(2,4-D)作为常见的除草剂,多用于控制阔叶杂草。它具有较高的溶解度,土壤吸附系数低,容易通过地表径流和雨水渗透的作用,进入地表和地下水[13]。研究表明2,4-D对人和哺乳动物具有毒害作用,是可能的致癌物质和诱变剂[14],故本研究选择了2,4-D作为模型污染物,以MoS2为载体,采取水热法合成了纳米Fe3O4/MoS2复合物,并将其用于活化PMS降解2,4-D。研究了反应过程中的影响因素、催化性能和PMS的活化机理,此外,还考察了催化剂的稳定性。
-
试剂:硫酸亚铁(国药,99%),氯化铁(国药,99%),硫化钼(阿拉丁,99.5%),2,4-二氯苯氧乙酸(安谱,99%),过硫酸氢钾(>95%,阿拉丁),实验用水均为去离子水。仪器:高效液相色谱仪(Ultimate 3000,赛默飞),TOC测定仪(Multi N/C 3100,德国耶拿),紫外分光光度计(TU-1810,Purkinje),pH计(PE-28,梅特勒-托利多)等。
-
将1 g FeSO4·7H2O和0.32g FeCl3·6H2O加入40 mL去离子水中,搅拌均匀后加入0.35 g MoS2 至上述溶液,搅拌30 min后,逐滴加入20 mL NaOH溶液(10 mmol)搅拌60 min。随后将混合溶液转入水热反应釜中,200 ℃ 下保持8 h。冷却至室温后分别用水和乙醇洗涤多次,60 ℃下真空干燥12 h得到所需催化剂,记为Fe3O4/MoS2。
-
将0.03 g的Fe3O4/MoS2加入到100 mL 0.1 mmol·L−1,4-D溶液中,机械搅拌使其分散均匀,30 min后向上述混合液中加入1 mmol·L−1的PMS启动反应。初始反应溶液pH=3.6(不调节pH的情况下)按照一定的时间间隔取样,将1.0 mL的样品通过0.45 μm滤膜,迅速注入含有0.1 mL甲醇的液相小瓶中以淬灭反应,然后使用高效液相色谱检测污染物浓度。实验中采用0.1 mol·L−1的NaOH溶液和0.1 mol·L−1的H2SO4溶液调节反应溶液的pH。淬灭实验时预先在反应液中加入一定量的淬灭剂,用于淬灭相应自由基。催化剂的循环:将使用后的催化剂用水和乙醇洗涤多次,60 ℃下真空干燥12 h。
-
采用配备有285 nm紫外检测器的高效液相色谱仪(Thermofisher,Ultimate 3000)测定2,4-D浓度,流速和柱温分别设置为1 mL·min−1和30 ℃,流动相由60%甲醇和40%水相乙酸(V / V)组成,其中水相乙酸中乙酸的含量为5%。使用紫外分光光度计(TU-1810,北京浦金野)测试溶液中Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)及PMS的浓度。采用N/C 3100分析仪(Analytikjena)测量溶液中的总有机碳(TOC).
-
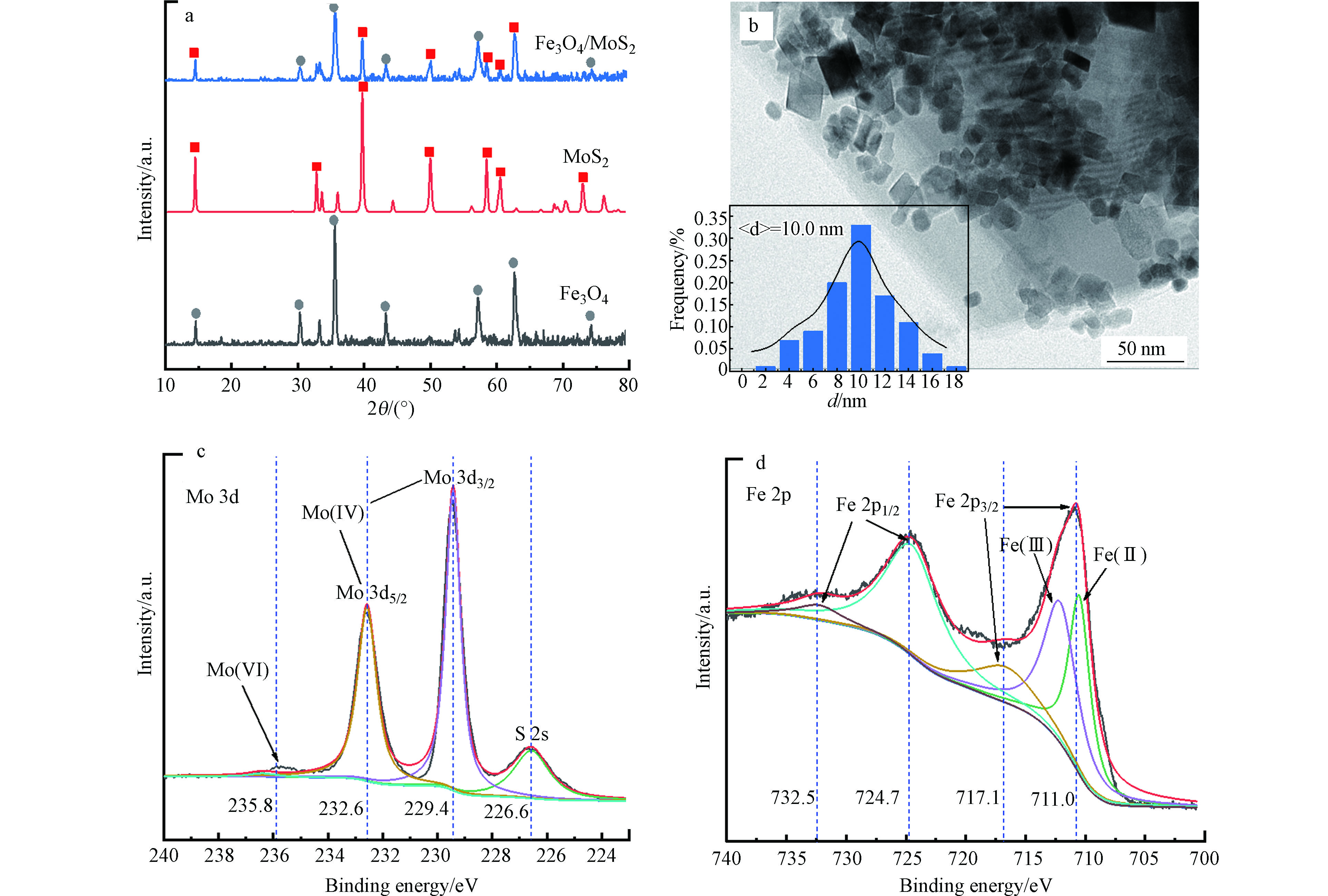
通过XRD表征对Fe3O4/MoS2样品的晶型结构进行分析,如图1a所示,Fe3O4/MoS2中同时具有MoS2和Fe3O4特征峰,表明经过沉淀沉积以及水热之后,Fe3O4与MoS2结合紧密且结晶度良好。通过透射电镜表征Fe3O4/MoS2样品的微观形貌,如图1b所示,纳米Fe3O4颗粒负载在MoS2表面上,同时粒径分布图显示Fe3O4粒径为10 nm左右。采用XPS分析Fe3O4/MoS2催化剂表面Mo、Fe元素化学价态,如图1c所示,在Mo 3d的XPS光谱中,229.4 eV和232.6 eV处的特征峰分别对应于Mo(Ⅳ) 3d3/2和Mo 3d5/2[15],235.8 eV处微弱的峰对应于Mo(Ⅵ)[16],表明Fe3O4/MoS2中,Mo主要以Mo(Ⅳ)存在,另外,226.6 eV处的峰属于S 2s。如图1d所示,在Fe 2p的XPS光谱中,711.0 eV和717.1 eV处的两个特征峰属于Fe 2p3/2,而在724.7 eV和732.5 eV处的两个峰属于Fe 2p1/2,这与材料中Fe3O4的Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)对应[17]。
-
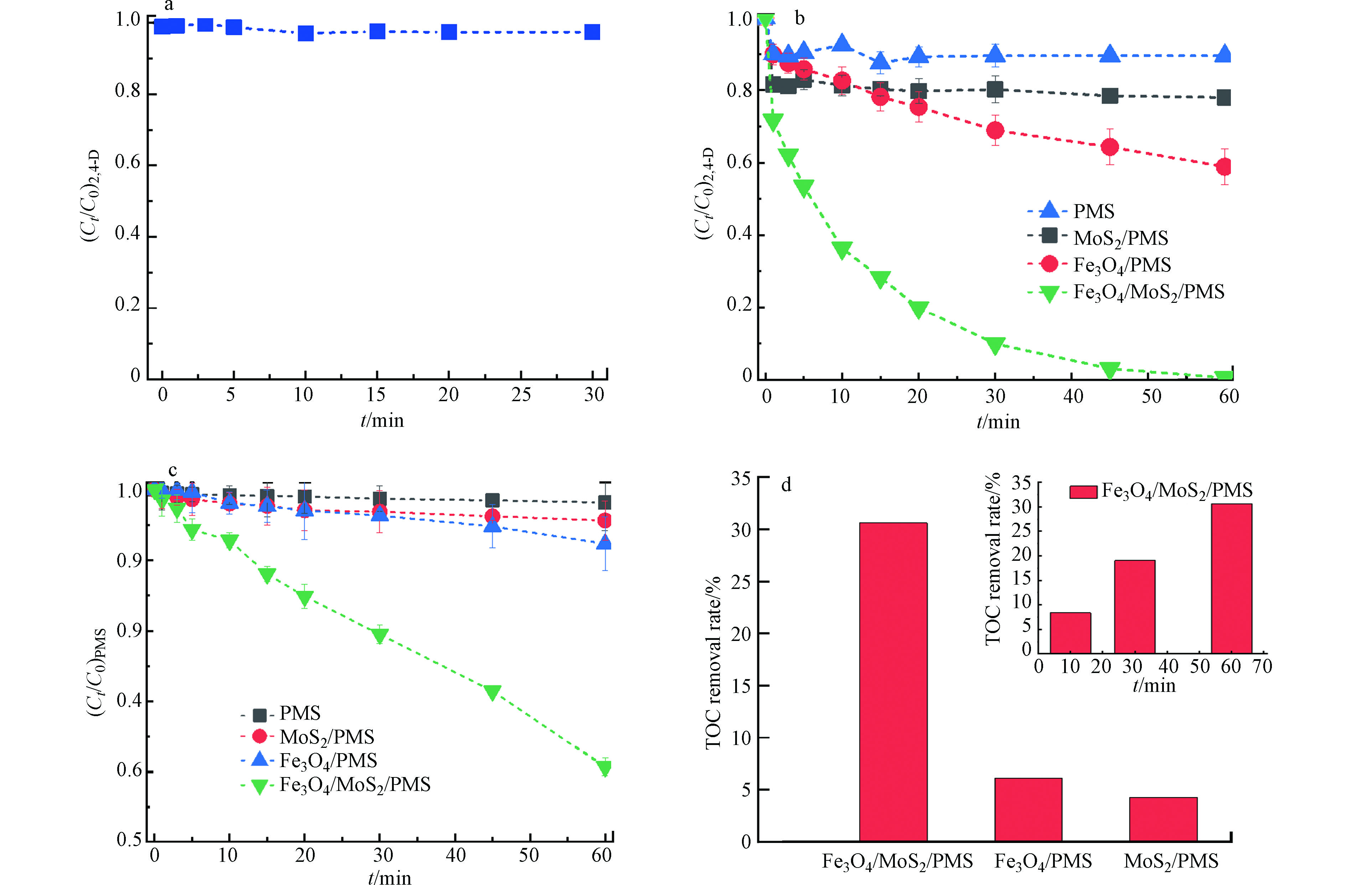
图2a显示了Fe3O4/MoS2对2,4-D的吸附效果,在30 min处实现吸附-解吸平衡,因吸附作用去除的2,4-D仅3%。从图2b可以看出,单独的PMS对2,4-D的降解效率低于10%,这表明单独PMS无法有效氧化 2,4-D。MoS2/PMS体系在30 min内对2,4-D的去除率仅为20.%,表明MoS2对PMS有一定的活化能力[18],但活化效率较低。Fe3O4/PMS体系在30 min对2,4-D的去除效率为31%,这是由于Fe3O4表面所含的Fe(Ⅱ)能活化PMS,但表面Fe(Ⅱ) 的含量有限。相比之下,Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS体系中2,4-D的去除速率显著提高,在30 min内可达100%。这表明Fe3O4负载在MoS2上更有利于活化PMS去除2,4-D。
为了进一步证明Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS体系对PMS的高效活化作用,检测了不同体系中PMS的浓度。图2c表明,PMS在溶液中的自分解可以忽略,MoS2/PMS和Fe3O4/PMS体系中,1 h内PMS浓度分别降低了5.7%和10.1%,明显低于Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS体系中的40%的分解率。
最后对比了不同体系中TOC的去除率,如图2d所示。可以发现Fe3O4/PMS和MoS2/PMS体系中反应1 h TOC的去除率仅4%,而Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS体系,TOC的去除可以达到30.5%,上述结果进一步表明Fe3O4/MoS2催化剂可以高效活化PMS降解2,4-D,表现出优异的催化活性。
-
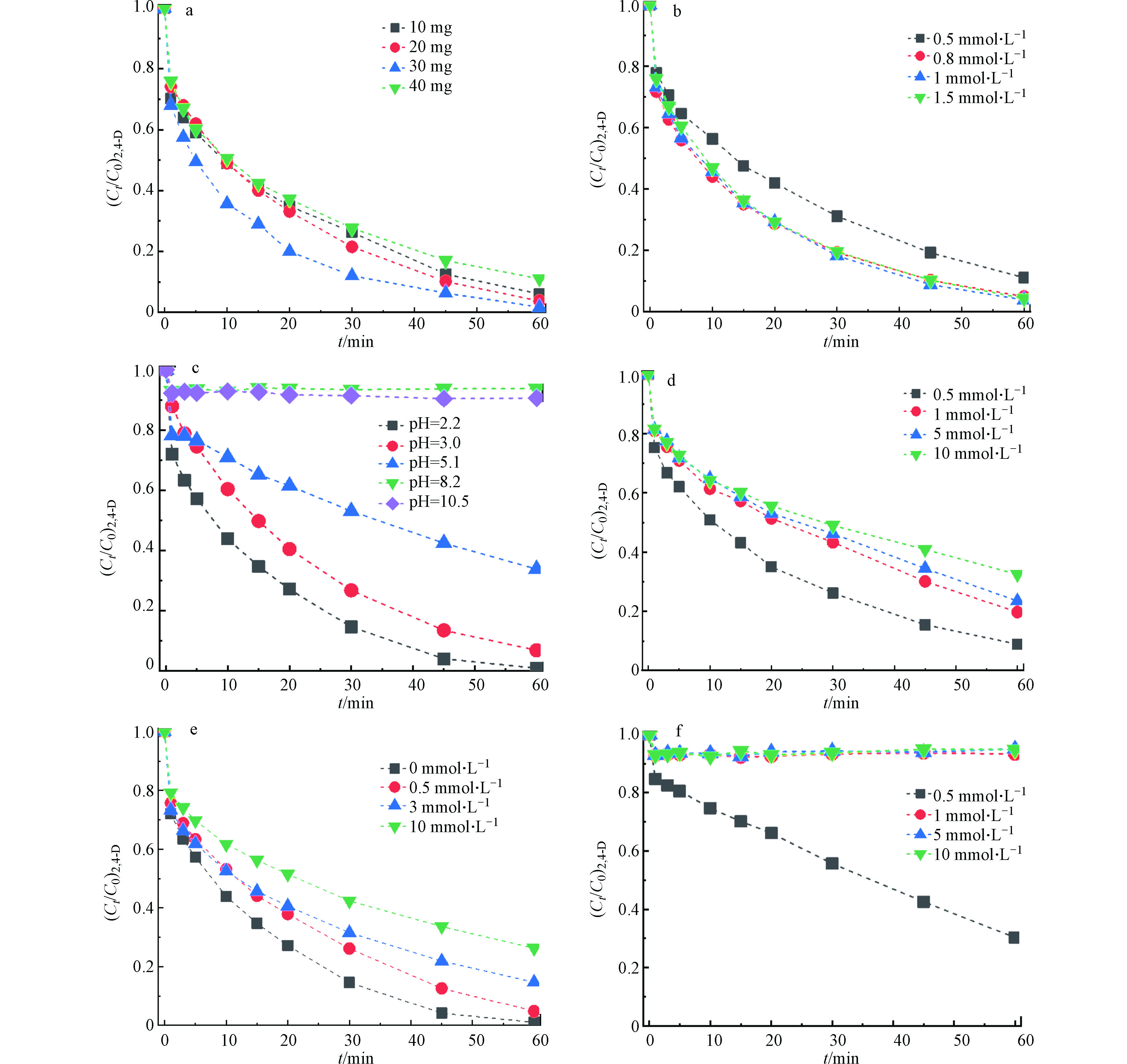
不同催化剂的投加量对2,4-D的降解的影响如图3a所示,当加入0.1 g·L−1 Fe3O4/MoS2,2,4-D的降解效率显著提高,在1 h内达到了80.7%。进一步将催化剂的投加量从0.1 g·L−1增加到0.4 g·L−1发现2,4-D的去除效果先增加后降低。可能是受材料磁性的影响,投加量过多会导致材料磁性团聚,从而导致催化剂暴露的活性位点减少,使其催化活性下降。在本实验中最佳催化剂的投加量为0.3 g·L−1,在1 h内可实现对2,4-D的完全去除。
高级氧化过程中,活性物种产生量主要由催化剂的量和PMS的量共同决定,因此考察了PMS的投加量对2,4-D降解的影响。如图3b所示,2,4-D的去除率随着PMS投加量的增加先升高后降低,在投加量为1 mmol·L−1时达到最佳去除效果。投加量过多可能会导致PMS与活性氧物种反应引起ROS的自淬灭[19]。此外,pH会影响有机污染物的去除效率。初始pH对2,4-D的去除效果如图3c所示,随着溶液pH的升高,2,4-D的去除效率逐渐下降。pH会影响PMS在溶液中的存在形态,H2SO5的pKa1≤0,pKa2=9.4[20], pH<7时,
$ {\rm{HSO}}_5^ -$ 是PMS在水溶液中的主要存在形态,而$ {\rm{SO}}_5^{2 - }$ 在pH>9.2时会急剧增加。酸性条件下,MoS2边缘上的不饱和硫原子与H+结合,生成H2S,导致暴露更多的Mo(Ⅳ)位点,加速Mo(Ⅳ)对Fe(Ⅲ)的还原,从而加速了PMS的活化,使2,4-D的去除效率增加[11]。此外,pH会影响材料表面的Zeta电位,Fe3O4/MoS2的等电点在6—7之间,当pH>7时Fe3O4/MoS2表面主要带负电,会与$ {\rm{HSO}}_5^ -$ 或$ {\rm{SO}}_5^{2 - }$ 发生静电排斥,导致碱性条件下2,4-D的降解效率下降。 在废水处理过程中, Cl−广泛存在,且含量大。因此,在Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS体系中,我们研究了0.5—10 mmol·L−1范围内氯离子对2,4-D降解的影响。如图3d所示,Cl−的增加导致去除效率的下降,这是因为氯离子可以和$ {\rm{SO}}_4^ {\cdot -} $ 反应,造成体系中活性物质的减少 [21]。 腐殖酸(HA)在水和土壤中普遍存在,因此进一步研究了HA对Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS体系的影响,如图3e所示,随着腐殖酸的含量从0增加到10 mg·L−1,60 min内体系中2,4-D的降解效率从100%下降到75.8%。这是因为腐殖酸中的有机组分会与2,4-D竞争ROS,导致2,4-D的降解效率有所下降[22]。最后还考察了水体中另一种常见组分$ {\rm{HCO}}_3^ -$ ,对Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS体系的影响,如图3f所示,可以发现其对Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS体系去除2,4-D的抑制作用较强,当反应体系中存在0.5 mmol·L−1的$ {\rm{HCO}}_3^ -$ 时,2,4-D的降解效率从100%降低到了70.2%。这主要是因为$ {\rm{HCO}}_3^ -$ 会与ROS反应,从而导致活性物种减少,2,4-D的去除效率下降。[23] -
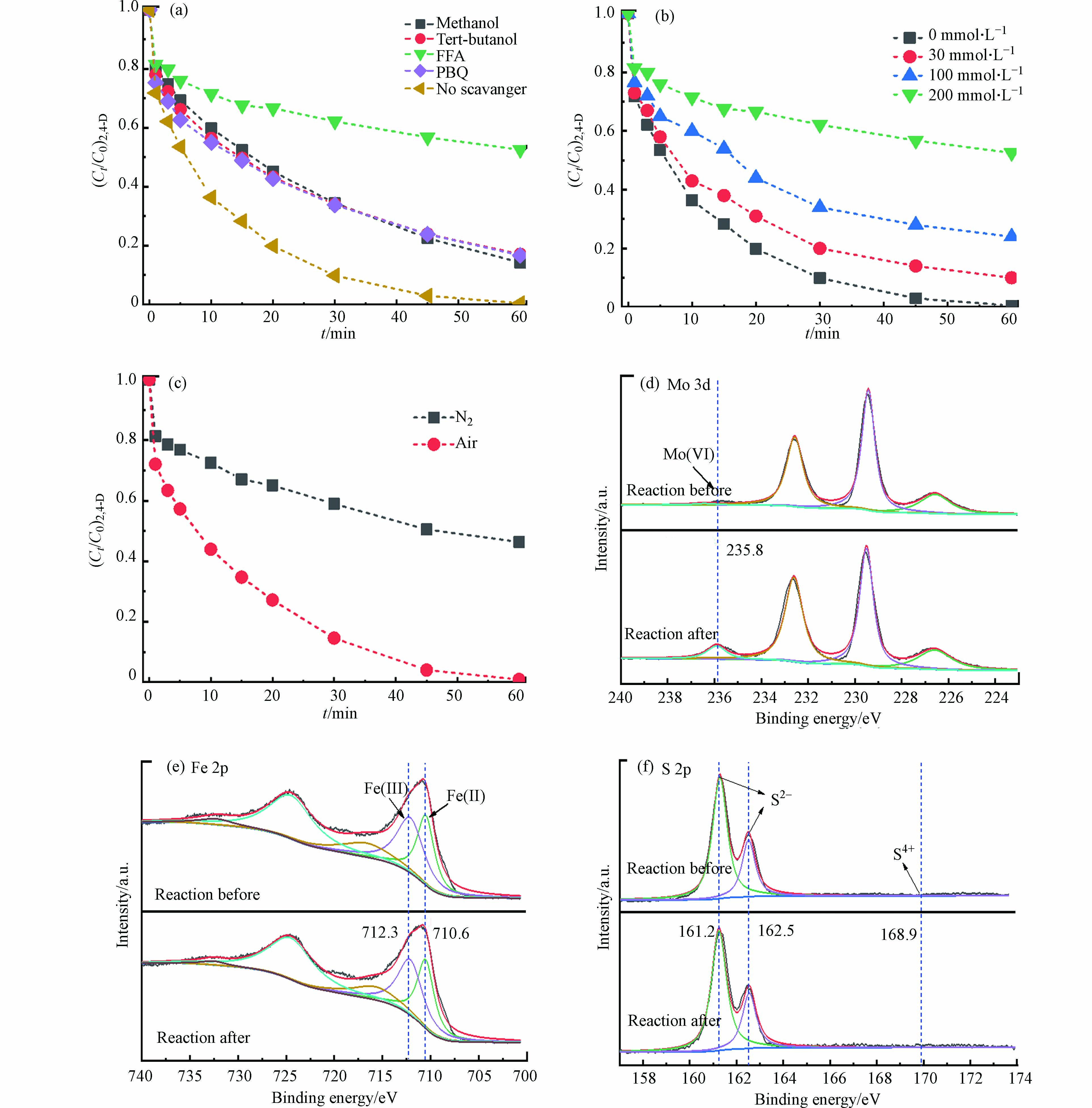
Fe3O4/MoS2催化剂的循环实验见图4a。在连续5次的循环过程中Fe3O4/MoS2对2,4-D的降解效率都能达到95.0%左右,表明该催化剂有较好的稳定性。此外测定了溶液中总Fe的浓度,铁的最大浸出量为0.3 mg·L−1,与初始铁含量0.17 g·L−1相比,过程中铁的溶出率为0.18%,铁的溶出可以忽略。
为了进一步评价Fe3O4/MoS2的稳定性对反应前后的Fe3O4/MoS2进行了XRD测试,如图4c。催化剂反应前后的特征峰并未发生变化,表明Fe3O4/MoS2具有良好的化学稳定性。反应过过程中溶出的Fe离子可能会引发均相的Fe(Ⅲ)的还原进而促进PMS的活化,因此模拟了溶液中溶出的Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)活化PMS降解2,4-D的效果。如图4d,溶出的Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)活化PMS在1 h内对2,4-D的降解效果低于10%,说明溶出的Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)对Fe3O4/MoS2活化PMS降解2,4-D的影响可以忽略。反应后材料的磁性如图4a所示,对于分散在水中的Fe3O4/MoS2催化剂,可以利用Fe3O4的磁性,将Fe3O4/MoS2催化剂进行回收。
-
使用甲醇作为·OH和
$ {\rm{SO}}_4^{ \cdot - }$ 的淬灭剂,叔丁醇作为·OH的清除剂[6],对苯醌(PBQ)作为$ \cdot {\rm{O}}_2^ -$ 的淬灭剂,糠醇(FFA)作的为1O2淬灭剂 [24]。如图5a所示,当反应体系存在叔丁醇和苯醌时,60 min内2,4-D的降解效率分别从100%降低到了82.6%和82.0%,表明·OH和$ \cdot {\rm{O}}_2^ -$ 参与了污染物的降解过程。当向反应体系中添加FFA时,60 min内降解效率从100%降至40%左右。为了进一步FFA对体系的抑制效果,考察了不同浓度的FFA对体系的影响。如图5b,随着FFA的浓度下降,体系中2,4-D的降解效果逐渐提高,表明1O2在反应过程中起着重要作用。相关研究表明,1O2可能来源于水中的溶解氧,因此,进行了氮气条件下的反应。如图5c所示,在氮气氛围下,体系对2,4-D的去除效果显著下降,反应1 h后去除率从100%降低为44.7%,表明该体系有氧气的参与。为考察MoS2中的Mo(Ⅳ)或S2−与Fe3O4中的Fe(Ⅲ)是否有发生氧化还原反应,对反应前后的催化剂进行了XPS表征,如图5d—f,结果显示反应后Fe3O4/MoS2催化剂Mo(Ⅵ)含量明显增加,S 2p谱图中并未出现S4+峰[25],说明主要是Mo(Ⅳ)发挥了还原作用。而Fe(Ⅱ)/Fe(Ⅲ)的比值在反应前后并无明显变化(反应前44.3%,反应后45.0%),这可能是由于材料中的Fe(Ⅱ)被PMS氧化生成Fe(Ⅲ),而Mo(Ⅳ)还原了其表面的Fe(Ⅲ),自身被氧化生成了 Mo(Ⅵ),由此实现体系中Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)循环,可持续高效的活化PMS并降解2,4-D。
根据实验结果,结合相关表征,提出了如下机理:首先Fe3O4表面的Fe(Ⅱ)与PMS反应生成
$ {\rm{SO}}_4^{ \cdot - }$ 和·OH(①②),过程中Fe(Ⅱ)被氧化为Fe(Ⅲ),紧接着Fe3O4表面的Fe(Ⅲ)被MoS2还原(③)实现了Fe(Ⅱ)的循环再生。同时Fe(Ⅱ)与溶解氧发生反应生成$ \cdot {\rm{O}}_2^ -$ (④),然后$ \cdot {\rm{O}}_2^ -$ 与Mo(Ⅵ)反应生成1O2和Mo(Ⅳ)(⑤)。①
${\rm{Fe}}\left( {{\rm{II}}} \right) + {\rm{HSO}}_5^ - \longrightarrow {\rm{Fe}}\left( {{\rm{III}}} \right) + {\rm{SO}}_4^{ \cdot - } + {\rm{O}}{{\rm{H}}^ - }$ ②
${\rm{Fe}}\left( {{\rm{II}}} \right) + {\rm{HSO}}_5^ - \longrightarrow {\rm{Fe}}\left( {{\rm{III}}} \right) + {\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } + \cdot {\rm{OH}}$ ③
${\rm{Mo}}\left( {{\rm{IV}}} \right) + 2{\rm{Fe}}\left( {{\rm{III}}} \right) \longrightarrow 2{\rm{Fe}}\left( {{\rm{II}}} \right) + {\rm{Mo}}\left( {{\rm{VI}}} \right)$ ④
${\rm{Fe}}\left( {{\rm{II}}} \right) + {{\rm{O}}_2} \longrightarrow {\rm{Fe}}\left( {{\rm{III}}} \right) + \cdot {\rm{O}}_2^ -$ ⑤
${\rm{Mo}}\left( {{\rm{VI}}} \right) + \cdot {\rm{O}}_2^ - { \longrightarrow ^1}{{\rm{O}}_2} + {\rm{Mo}}\left( {{\rm{IV}}} \right)$ -
(1)采用沉淀沉积法和水热法合成了Fe3O4/MoS2催化剂,将该催化剂用于活化PMS降解2,4-D发现,在1 h内可完全降解2,4-D。
(2)考察了一系列有关Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS体系的影响因素,表明该体系适合在酸性条件下进行反应,其中
$ {\rm{HCO}}_3^ -$ 对体系的影响较大,可能是因为$ {\rm{HCO}}_3^ -$ 与2,4-D竞争活性物种所致。(3)Fe3O4/MoS2催化剂在5个循环周期内都表现出对活化PMS去除2,4-D高效性和稳定性。由于引入了磁性材料Fe3O4可以轻松的实现对催化剂的回收。
(4)在Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS体系降解2,4-D的过程中,
$ {\rm{SO}}_4^{ \cdot - }$ 、·OH、1O2和$ \cdot {\rm{O}}_2^ -$ 均发挥了作用,起主要作用的是1O2。
Fe3O4/MoS2强化过氧化单硫酸盐活化去除2,4-二氯苯氧乙酸
Removal of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by Fe3O4/MoS2 enhanced PMS activation.
-
摘要: 以MoS2为载体,通过水热法合成Fe3O4/MoS2催化剂,采用X射线衍射、透射电子显微镜和X射线光电子能谱分析对材料进行表征,研究了Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS体系中2,4-二氯苯氧基乙酸(2,4-D)的降解效率并探究了其反应机理。结果表明,以Fe3O4、MoS2和Fe3O4/MoS2为催化剂,30 min内2,4-D的去除率分别为31%、20%和89%。表征结果发现,在MoS2的存在下,Fe3O4表面的Fe(Ⅲ)还原为Fe(Ⅱ),Mo(Ⅳ)被氧化为Mo(Ⅵ),Fe3O4和MoS2间的协同作用加强了PMS分解,提高了2,4-D去除效率。自由基淬灭实验表明,·OH、
$ {\rm{SO}}_4^ - \cdot $ 、$ {\rm{O}}_2^ - \cdot $ 和1O2均参与了2,4-D的降解过程,且1O2的作用比其他活性物质更显著。低浓度Cl−和腐殖酸(HA)对2,4-D的降解没有明显的抑制效果,而$ {\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ 对Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS体系有明显的抑制作用。此外,催化剂循环实验表明Fe3O4/MoS2在催化反应过程前后保持良好的稳定性。-
关键词:
- 过一硫酸盐 /
- 四氧化三铁 /
- 二硫化钼 /
- 2,4-二氯苯氧基乙酸
Abstract: Fe3O4/MoS2 catalyst was synthesized by hydrothermal method with MoS2 as support. The material was characterized by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis. The degradation efficiency and influencing factors of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid(2,4-D) in Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS system were studied, and the reaction mechanism was explored. The results showed that when Fe3O4, MoS2 and Fe3O4/MoS2 were used as catalysts, the removal rates of 2,4-D within 30 min were 31%, 20% and 89%, respectively. Characterization results showed that in the presence of MoS2, Fe(Ⅲ) on the surface of Fe3O4 was reduced to Fe(Ⅱ) accompanied by the oxidation of Mo(Ⅳ) to Mo(Ⅵ), and the synergistic effect between Fe3O4 and MoS2 enhanced PMS decomposition and improved the removal efficiency of 2, 4-D. The experiment of radical quenching showed that ·OH,$ {\rm{SO}}_4^ - \cdot $ ,$ {\rm{O}}_2^ - \cdot $ and 1O2 were all involved in the degradation process of 2,4-D, and the effect of 1O2 was more significant than that of other active substances. Low concentrations of Cl− and humic acid (HA) had no obvious inhibitory effect on the degradation of 2,4-D, while$ {\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ had obvious inhibitory effect on Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS system. In addition, XRD and catalyst cycling experiments show that Fe3O4/MoS2 maintains good stability before and after the catalytic reaction.-
Key words:
- permonosulfate(PMS) /
- Fe3O4 /
- MoS2 /
- 2, 4-D
-

-
图 2 (a) Fe3O4/MoS2对2,4-D的吸附效果,(b) Fe3O4/MoS2活化PMS降解2,4-D,(c) Fe3O4/MoS2活化PMS的效果,(d) Fe3O4/MoS2催化剂活化PMS降解2,4-D过程中TOC的去除率。
Figure 2. (a)Adsorption effect of Fe3O4/MoS2 on 2,4-D, (b) The Fe3O4/MoS2 activation of Fenton-like of PMS for catalytic degradation of 2,4-D, (c) Effect of Fe3O4/MoS2 activation on PMS, (d) Fe3O4/MoS2 catalyst activates the removal of TOC in the process of PMS degradation 2,4-D.
图 4 (a) Fe3O4/MoS2催化剂循环催化降解2,4-D的效果及反应后材料的磁性,(b) 体系中Fe和Mo的浓度,(c) Fe3O4/MoS2反应前和反应后的XRD图,(d) Fe2+及Fe3+活化PMS降解2,4-D,反应条件:[Fe2+]0=[Fe3+]0=0.3 mg·L−1 ,PMS=0.3 g·L−1,2,4-D= 0.1 mmol·L−1
Figure 4. (a) Effect of Fe3O4/MoS2 catalyst on cyclic degradation of 2,4-D, (b) Fe and Mo concentrations in the system, (c) XRD patterns of Fe3O4/MoS2 before and after reaction, (d) Fe3O4/MoS2 catalyst activated PMS to degrade 2,4-D, and the material was magnetic after the reaction
图 5 (a)Tert-butanol,PBQ,Methanol,L-histidine和FFA对2,4-D的去除的抑制效果,Tert-butanol= 200 mmol·L−1,PBQ=0.06 g·L−1, Methanol= 200 mmol·L−1, L-histidine= 0.06 g·L−1,(b) 不同浓度FFA对2,4-D降解的抑制效果,(c) Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS在不同气氛下去除2,4-D,(d)(e)(f) Fe3O4/MoS2反应前和反应后Mo 3d、Fe 2p和S 2p的XPS谱图。
Figure 5. (a) Inhibition effect of Tert-Butanol, PBQ, Methanol, L-Histidine, FFA on removal of 2,4-D, (b) Inhibitory effect of FFA at different concentrations on removal of 2,4-D, (c)Fe3O4/MoS2/PMS divided by 2, 4-D at different atmospheres, The XPS pattern of Mo 3d (c) Fe 2p (d) S 2p (e) before and after reaction
-
[1] LIU J, ZHAO Z W, SHAO P H et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate with magnetic Fe3O4–MnO2 core–shell nanocomposites for 4-chlorophenol degradation [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 262: 854-861. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.10.043 [2] AO X W, LIU W J. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole by medium pressure UV and oxidants: Peroxymonosulfate, persulfate, and hydrogen peroxide [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 313: 629-637. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.089 [3] LIU J, ZHOU J H, DING Z X, et al. Ultrasound irritation enhanced heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate with Fe3O4 for degradation of azo dye [J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2017, 34: 953-959. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.08.005 [4] GHANBARI F, MORADI M. Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants: Review [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 310: 41-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.064 [5] LISON D. Human toxicity of cobalt-containing dust and experimental studies on the mechanism of interstitial lung disease (hard metal disease) [J]. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 1996, 26(6): 585-616. doi: 10.3109/10408449609037478 [6] ZENG T, ZHANG X L, WANG S H, et al. Spatial confinement of a Co3O4 catalyst in hollow metal-organic frameworks as a nanoreactor for improved degradation of organic pollutants [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(4): 2350-2357. [7] 苏跃涵, 张利朋, 王枫亮, 等. Fe2+/单过氧硫酸氢盐(PMS)体系降解水体中酮洛芬的机制研究 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(9): 1753-1761. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.09.2016030301 SU Y H, ZHANG L P, WANG F L, et al. Degradation mechanism of ketoprofen by Fe2+/potassium peroxy monosulfate (PMS) oxidation process in aqueous [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(9): 1753-1761(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.09.2016030301
[8] TAN C Q, GAO N Y, DENG Y, et al. Radical induced degradation of acetaminophen with Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as heterogeneous activator of peroxymonosulfate [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 276: 452-460. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.05.068 [9] LI J, WAN Y J, LI Y J et al. Surface Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ) cycle promoted the degradation of atrazine by peroxymonosulfate activation in the presence of hydroxylamine [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2019, 256: 117782. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117782 [10] MERKI D, VRUBEL H, ROVELLI L et al. Fe, Co, and Ni ions promote the catalytic activity of amorphous molybdenum sulfide films for hydrogen evolution [J]. Chemical Science, 2012, 3(8): 2515-2525. doi: 10.1039/c2sc20539d [11] XING M Y, XU W J, DONG C C et al. Metal sulfides as excellent Co-catalysts for H2O2 decomposition in advanced oxidation processes [J]. Chem, 2018, 4(6): 1359-1372. doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2018.03.002 [12] ZHU L L, JI J H, LIU J et al. Designing 3D-MoS2 sponge as excellent cocatalysts in advanced oxidation processes for pollutant control [J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2020, 59(33): 13968-13976. doi: 10.1002/anie.202006059 [13] DING L, LU X, DENG H P, et al. Adsorptive removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D) from aqueous solutions using MIEX resin [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(34): 11226-11235. [14] SECK E I, DONA-RODRIGUEZ J M, FERNANDEZ-RODRIGUEZ C et al. Photocatalytic removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by using sol–gel synthesized nanocrystalline and commercial TiO2: Operational parameters optimization and toxicity studies [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2012, 125: 28-34. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.05.028 [15] MU D Z, CHEN Z, SHI H F, et al. Construction of flower-like MoS2/Fe3O4/rGO composite with enhanced photo-Fenton like catalyst performance [J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(64): 36625-36631. doi: 10.1039/C8RA06537C [16] LIN T R, WANG J, GUO L Q, et al. Fe3O4@MoS2 core-shell composites: Preparation, characterization, and catalytic application [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(24): 13658-13664. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b02516 [17] WANG Y, LI S, XING X et al. Self-assembled 3D flowerlike hierarchical Fe3O4@Bi2O3 core–shell architectures and their enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light [J]. Chemistry A European Journal, 2011, 17(17): 4802-4808. doi: 10.1002/chem.201001846 [18] ZHANG Y, NIU J, XU J. Fe(Ⅱ)-promoted activation of peroxymonosulfate by molybdenum disulfide for effective degradation of acetaminophen [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 381: 122718. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122718 [19] LUO H P, ZHOU X, GUO X J, et al. WS2 as highly active co-catalyst for the regeneration of Fe(Ⅱ) in the advanced oxidation processes [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 262: 128067. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128067 [20] REN Y, LIN L, MA J et al. Sulfate radicals induced from peroxymonosulfate by magnetic ferrospinel MFe2O4 (M=Co, Cu, Mn, and Zn) as heterogeneous catalysts in the water [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2015, 165: 572-578. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.10.051 [21] HUANG Y, SHENG B, WANG Z H et al. Deciphering the degradation/chlorination mechanisms of maleic acid in the Fe(ⅡI)/peroxymonosulfate process: An often overlooked effect of chloride [J]. Water Research, 2018, 145: 453-463. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.08.055 [22] XIE P C, MA J, LIU W et al. Removal of 2-MIB and geosmin using UV/persulfate: Contributions of hydroxyl and sulfate radicals [J]. Water Research, 2015, 69: 223-233. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.11.029 [23] LEI Y, CHEN C S, TU Y J, et al. Heterogeneous degradation of organic pollutants by persulfate activated by CuO-Fe3O4: Mechanism, stability, and effects of pH and bicarbonate ions [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(11): 6838-6845. [24] MA W J, WANG N, DU Y C et al. One-step synthesis of novel Fe3C@nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes/graphene nanosheets for catalytic degradation of Bisphenol A in the presence of peroxymonosulfate [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 356: 1022-1031. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.093 [25] ZHOU H Y, LAI L D, WAN Y J et al. Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2): A versatile activator of both peroxymonosulfate and persulfate for the degradation of carbamazepine [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 384: 123264. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123264 -









 下载:
下载: