-
四溴双酚A(TBBPA)是最常用的溴代阻燃剂,已广泛分布于各种环境基质中,并引起了人们对其内分泌干扰,细胞致死性和难降解性的广泛关注[1-4]。为了去除TBBPA,微生物[5]、δ-MnO2[6]、臭氧[7]、漆酶[8]、硫酸根自由基[9-10]等氧化方法以及低价金属还原技术被开发出来[11-12]。然而,这些方法存在能源成本高且会有毒性更强的产物生成(如:双酚A和溴酸盐)的弊端[6-7]。本课题组最近的研究发现,在碱性条件下(如pH 10),FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系可以在1 min内实现TBBPA的完全去除以及部分脱溴和矿化[13-14]。
FeⅢ-TAML活化剂由于其高效和低毒性而被归属于新型绿色催化剂。反应中,FeⅢ-TAML需要先被氧化剂,如:H2O2和过硫酸盐等[15],活化形成高价铁-氧配合物,即FeIV-TAML[16]或FeⅤ-TAML[17])。FeⅣ-TAML或FeV-TAML作为芳香类有机污染物的主要氧化活性物种具有很强的氧化能力和选择性[14, 18-19]。因此,FeⅢ-TAML已被用于降解多种芳香族有机污染物,包括染料[20]、雌激素性化学品[21-22]、软体动物杀虫剂[23]、磷酸盐农药[24]以及持久性卤代酚类物质[15, 18-19]。FeⅢ-TAML的局限性之一是FeⅢ-TAML(分子结构如图1)的反应活性具有很强的pH依赖性,在碱性条件下活性高,而在中性或酸性条件下会急剧降低[25-26]。
FeⅢ-TAML分子结构:

研究发现,FeⅢ-TAML除了反应活性具有很强的pH依赖性之外,污染物的降解路径也会发生改变。用FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系催化氧化双酚A,发现双酚A在碱性条件下可以很快被降解,而在中性条件下去除速率显著降低且会生成胶状物质[27]。TBBPA是双酚A的结构类似物,很有可能发生相似的现象。此外,以前的研究仅仅针对FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系对TBBPA不同pH条件下的降解效率,尚未对TBBPA在不同pH条件下的转化路径进行研究。
在这项工作中,本课题组探究了pH 7.5和10条件下FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系对TBBPA的降解动力学,分析了不同pH条件下TBBPA的降解产物,并结合理论计算推导了FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系在不同pH条件下降解TBBPA的反应路径。此外,本研究测定了TBBPA及其不同pH条件下的降解产物对发光菌的发光抑制率,采用定量结构活性相关性模型预测了降解产物对不同营养级生物的急性和慢性毒性.
-
分析纯的TBBPA、碳酸钠、碳酸氢钠和其他试剂均购自Sigma-Aldrich,由于TBBPA的解离平衡常数(pKa)为pKa1=7.4和pKa2=8.5[13],提高溶液pH可以使得分子态的TBBPA发生酚羟基解离作用,提高TBBPA在水中的溶解度。因此将TBBPA溶解在10 mmol·L−1 NaOH溶液得到浓度为1.0 g·L−1的TBBPA储备液。FeⅢ-TAML由GreenOx Catalysts, Inc.(Mellon Institute, Pittsburgh, PA, USA)提供,根据FeⅢ-TAML的摩尔吸光系数(6600(mol·L−1)−1 ·cm−1)以及366 nm吸光度定量FeⅢ-TAML储备液的浓度。H2O2(30% 质量百分比)由Fisher Scientific提供。实验使用Milli-Q水(18.2 MΩ·cm)配置溶液。
-
在100 mL锥形瓶中进行降解实验。将TBBPA储备溶液添加到100 mL FeⅢ-TAML溶液中,TBBPA和FeⅢ-TAML的初始浓度分别为10 mg·L−1和0.1 μmol·L−1。通过加入1.0 mol·L−1 NaOH和HClO4,调节5.0 mmol L−1磷酸盐缓冲液至pH 7.5和pH 10。通过添加10 μL的H2O2(30%)储备溶液(H2O2:FeⅢ-TAML的物质的量比= 10000:1)启动反应。在预定的反应时间取样500 μL,与10 μL高氯酸(7 mol·L−1)混合以终止反应,然后加入1 mL甲醇萃取TBBPA。
-
将1.2节中的样品通过0.22 μm的聚四氟乙烯针式滤头,使用高压液相色谱法(HPLC,Waters Alliance 2695,Milford,MA)分析TBBPA的浓度。HPLC系统由SunFire C18色谱柱(5 μm,120Å;4.6 mm×250 mm)和波长为210 nm的UV检测器组成。流动相是甲醇和水(85:15,V/V)的混合物,流速为1.0 mL·min−1。TBBPA降解动力学采用伪一级动力学模型拟合(式1):
式中:C0为TBBPA的初始浓度(μmol·L−1),Ct为反应时间t时的TBBPA浓度(单位μmol·L−1),kobs为TBBPA伪一级降解速率常数(min−1),t为反应时间(min)。
-
使用配备电导检测器和AS23阴离子柱的离子色谱仪(Dionex ICS900,Dionex Co.,美国)测量反应过程中释放的溴离子浓度,将3.5 mmol·L−1 Na2CO3/1.0 mmol·L−1 NaHCO3混合溶液用作淋洗液,淋洗液流速设为1.0 mL·min−1。TBBPA脱溴动力学也采用伪一级动力学模型拟合(式2):
式中:C0Br为TBBPA分子上Br的初始浓度(μmol·L−1),Ct为反应时间t时的TBBPA分子上Br的浓度(μmol·L−1),kBr为TBBPA伪一级脱溴速率常数(min−1),t为反应时间(min).
-
为了鉴定反应产物,使用Waters Oasis HLB柱通过固相萃取(SPE)方法浓缩了在不同pH下反应特定时间后的样品。萃取前,先加入5 mL甲醇,再加入5 mL Milli-Q水,流速为5 mL·min−1,以活化SPE小柱。然后将25 mL反应溶液通过小柱。用5 mL甲醇洗脱HLB柱保留的提取液。通过在负离子模式下运行的Orbitrap Fusion Lumos质谱仪(Thermo Scientific,美国加利福尼亚州圣何塞)鉴定降解产物。使用电喷雾电离源在100—1000(m/z)范围内以60000的分辨率进行全扫描MS分析。离子传输管温度设定为300 ℃。电离电势和RF分别设置为-4500 V和60%。将样品以5 μL·min−1的流速注入质谱仪。
-
参照水质急性毒性的测定-发光细菌试验国家标准(GB/T 15441—1995)分析TBBPA降解产物对发光细菌的急性毒性。实验用发光细菌T3小种冻干粉从中国科学院南京土壤研究所购得,为同一批次密封保存。不同反应时间点的TBBPA反应液采用加入过氧化氢酶中止反应获得,加入3%的NaCl保证发光菌生存的离子强度,并加入0.1 mol·L−1的HCl和NaOH调节pH值至7.8±0.1。将发光菌菌液与TBBPA不同反应时间的溶液按9:1体积比混合,于20 ℃振荡培养15 min后使用酶标仪(Tecan Infinite M200,Switzerland)测定发光菌的发光强度。以标准的黑色不透明96孔板(Corning,USA)为样品载体,为避免96孔板在酶标仪中的边缘效应,周围的36个孔分别加入200 µL的Milli-Q水。发光菌的发光抑制率按照式(3)计算得到,其中Lblank和Lsample分别表示发光菌在空白对照和实验样品溶液中培养15 min后的发光信号强度,高抑制率对应高毒性。
ECOSAR程序进行FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系降解TBBPA产物的定量结构活性相关性(QSAR)分析。QSAR可以提供TBBPA降解产物对不同营养级生物的急性和慢性毒性预测,包括大型溞的48 h半数致死浓度(LC50)和鱼的96 h半数致死浓度。根据我国环境保护行业保护标准《新化学物质危害评估导则》对TBBPA降解产物进行毒性分级:低毒(LC50>100 mg·L−1)、中毒(10 mg·L−1<LC50≤100 mg·L−1)、高毒(1 mg·L−1<LC50≤10 mg·L−1)、极高毒(LC50≤1 mg·L−1)。
-
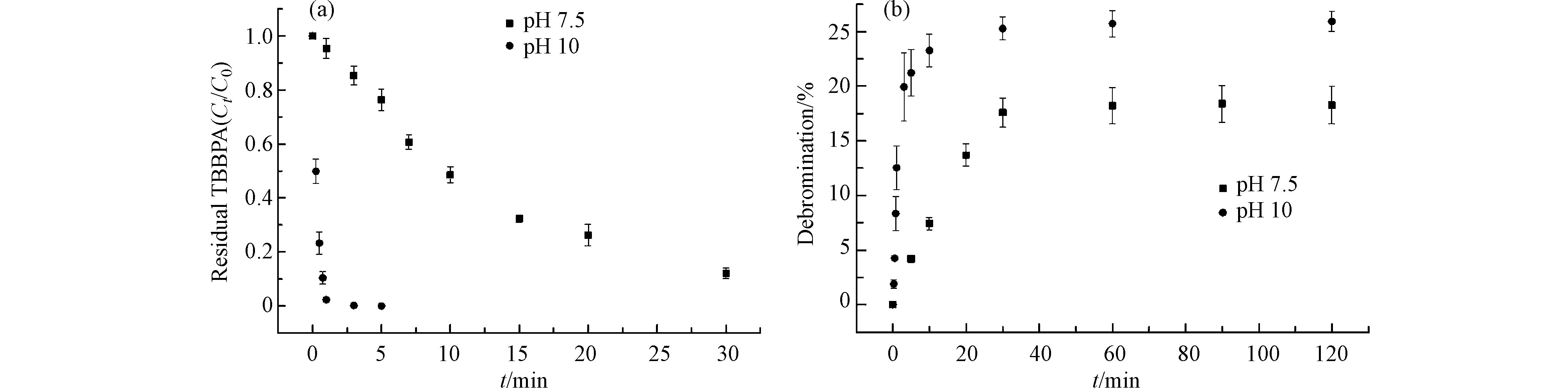
如图1a所示,在pH 7.5和pH10条件下,FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系降解TBBPA的kobs为分别为6.5×10−2 min−1和3.3 min−1。除了TBBPA分子的去除,FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系还可以打断C—Br键,释放溴离子。图1b所示,TBBPA在pH 7.5和pH10条件下反应120 min后脱溴率分别为18.3%和25.9%,伪一级脱溴速率常数kBr分别为1.2×10−3 min−1和9.1×10−2 min−1。在碱性条件下(pH 10)TBBPA的降解和脱溴速率都高出其在近中性条件下的结果50倍,这可能归因于去质子化的FeⅢ-TAML比例随pH的升高而增加,而去质子化的FeⅢ-TAML对H2O2的活化更敏感[13]。
-
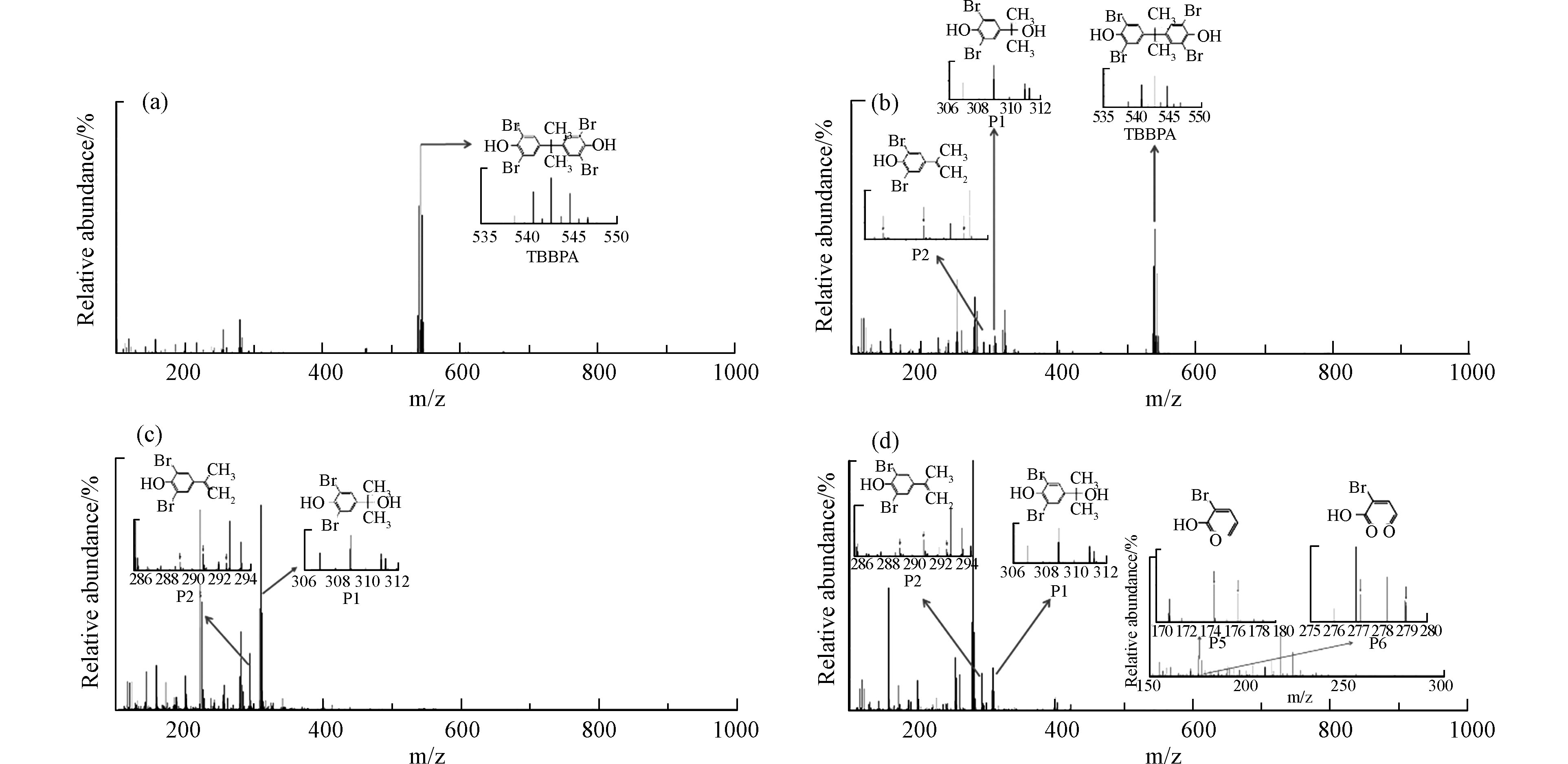
如图2a和3a所示,反应初始时只检测到TBBPA母体的质谱信号(质荷比为538.75/540.75/542.75/544.74/546.74)。在pH 7.5条件下,TBBPA被FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系降解10 min检测到了裂解产物4-(2-羟基异丙基)-2,6-二溴苯酚(P1,质荷比为306.90/308.89/310.89)和2,6-二溴-4-(异丙烯基)苯酚(P2,质荷比为288.89/290.89/292.89)以及耦合产物4-(2-(4-(3,5-二溴-4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二溴苯基)丙-2-基)-2,6-二溴苯酚(P3,质荷比为786.60/788.60/790.59/792.59/794.59/796.59/798.58)(图2b)。随着反应进行,在反应30 min和60 min检测到了另一个耦合产物4-(2-(3,5-二溴-4-羟基苯氧基)丙-2-基)-2,6-二溴苯酚(P4,质荷比为554.74/556.74/558.74/560.74/562.74)或其同分异构体4-(2,6-二溴-4-(2-羟基丙-2-基)苯氧基)-2,6-二溴苯酚(P4’,质荷比为554.74/556.74/558.74/560.74/562.74)(图2c和d)。除P1和P2之外,TBBPA及其中间产物P3和P4/P4’在120 min后质谱信号全部消逝,生成溴代的小分子有机酸2-溴戊-2,4-二烯酸(P5,质荷比为174.91/176.91)和2-溴-3-甲酰基丙烯酸(P6,质荷比为177.09/179.09)(图2e)。P1、P2、P5和P6作为TBBPA在pH 7.5条件下的最终降解产物也可以解释不完全脱溴的原因。TBBPA在pH 10条件下降解的最终产物与pH 7.5类似,但是降解中间产物未检测到耦合产物P3和P4/P4’(图3b—d),表明TBBPA的降解存在明显的pH依赖性。
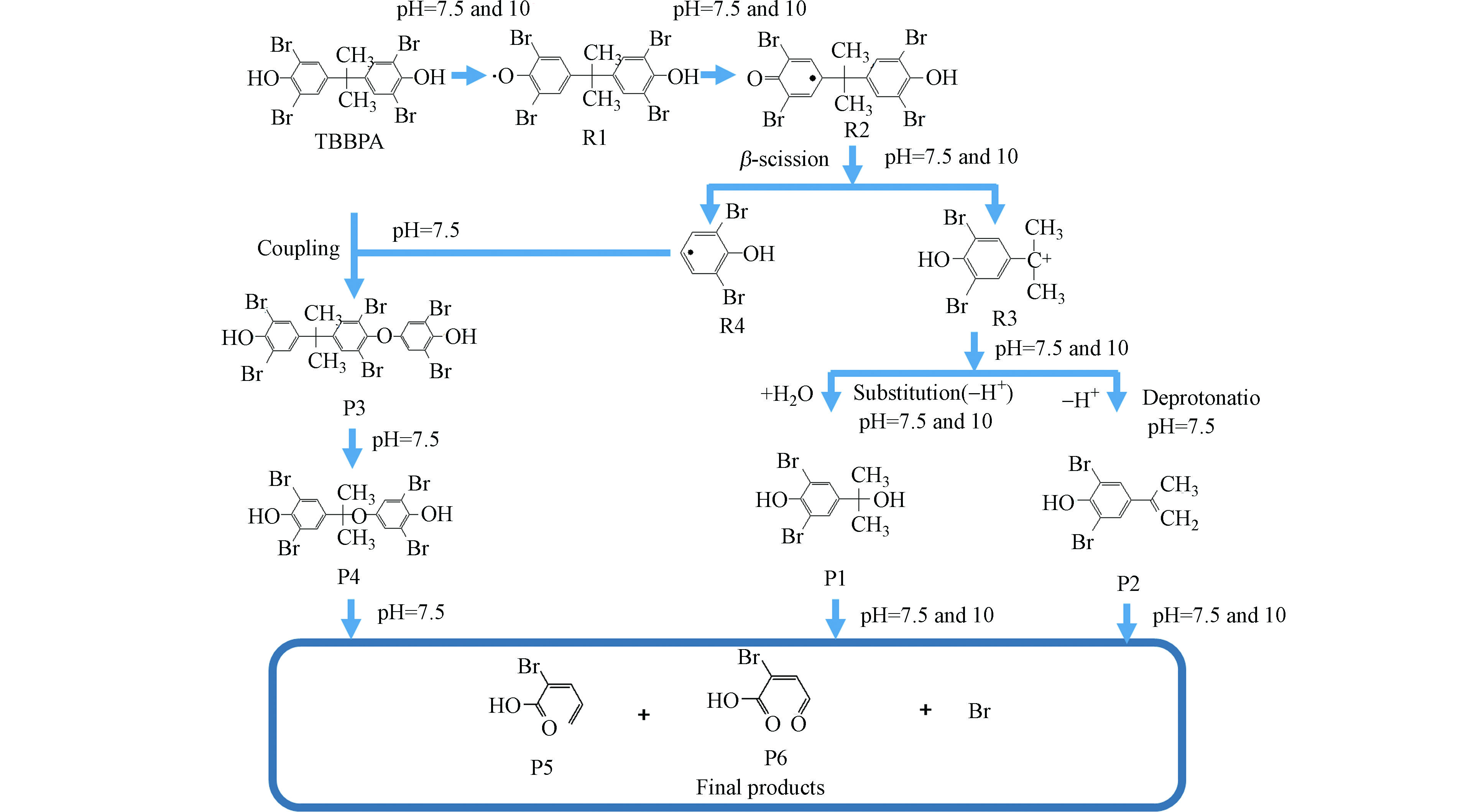
根据已鉴定的pH 7.5和pH10的TBBPA反应产物,推导了TBBPA的降解路径。如图4所示,TBBPA降解是通过从酚羟基中剥夺电子生成苯氧基自由基(R1)开始,该自由基可以通过未配对电子的自旋共振转变为更稳定的自由基R2。随后,自由基R2经历β-断裂,形成碳阳离子中间体R3和新的自由基R4。通过取代和去质子化,R3将进一步转化为P1和P2。本课题组以前的研究也发现了相同的降解产物和反应路径[13]。经过氧化态Fe-TAML氧化后,P1和P2最终分解为溴取代的小分子有机羧酸P5和P6。但是,通过与pH 10条件下TBBPA的降解产物进行比较,在pH 7.5时降解TBBPA可以检测到新的耦合产物P3和P4/P4’。由于FeⅢ-TAML在低pH条件下反应活性比pH条件下低几个数量级[28],所以近中性条件下氧化态Fe-TAML无法高效去除R4自由基。此外,低pH条件下TBBPA解离程度较低,不完全解离态的TBBPA对亲电试剂FeⅣ-TAML/FeⅤ-TAML的反应活性相比于完全解离态的TBBPA更低,从而导致偶联反应的发生产生P3和P4/P4’[19, 27]。
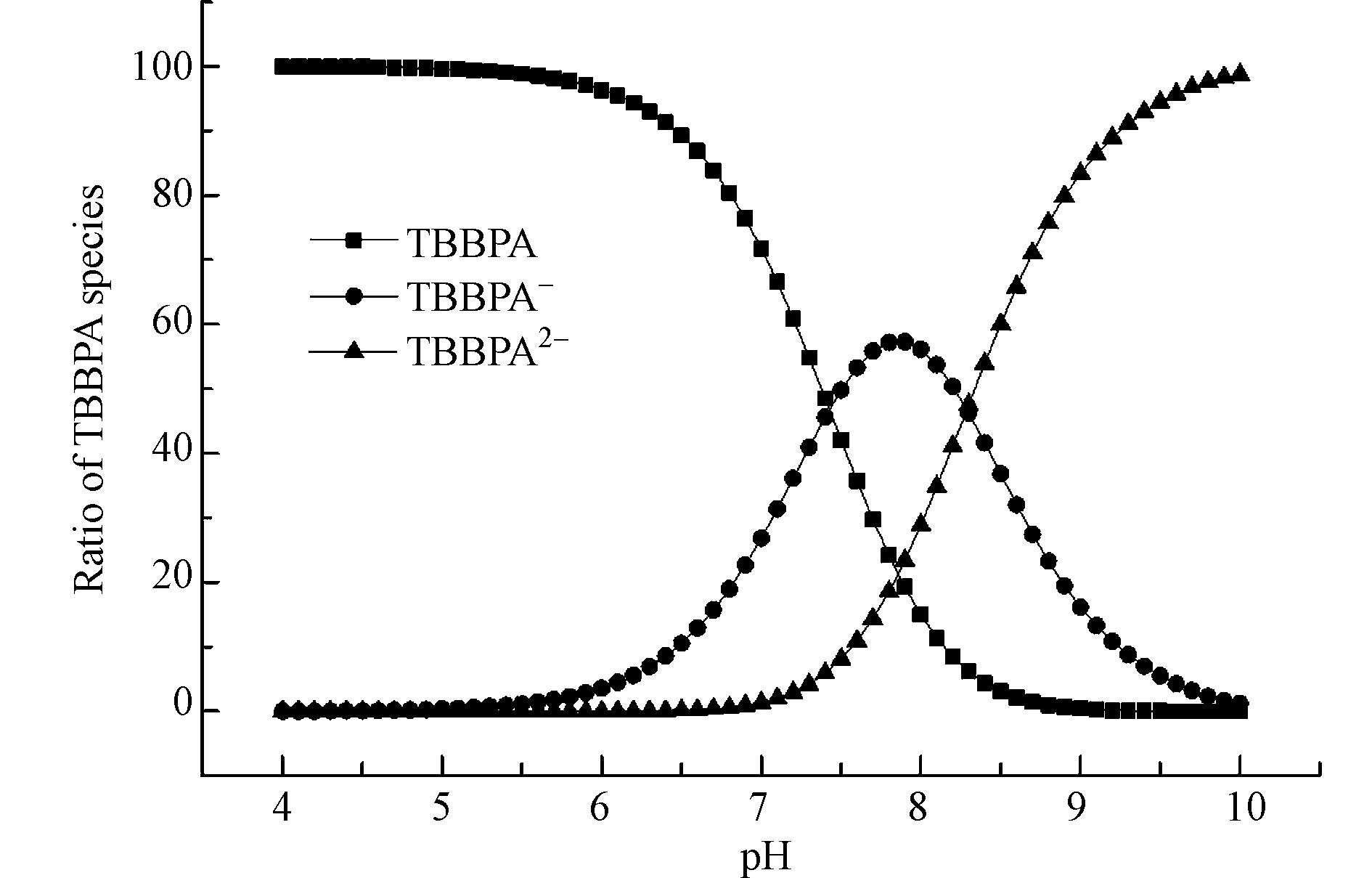
理论计算的结果也为TBBPA不同pH条件下降解路径的不同提供了理论支撑。根据TBBPA两个解离平衡常数7.4和8.5,使用Visual MINTEQ软件模拟了TBBPA形态随pH的变化。如图5所示,随着pH的升高,分子态的TBBPA逐渐减少,不完全解离态TBBPA(TBBPA−)先增加后降低,在pH 8左右出现最大值,完全解离态的TBBPA(TBBPA2−)比例随pH升高而逐渐增多。在pH 7.5条件下,TBBPA、TBBPA−和TBBPA2−的比例分别为46.94%、47.95%和5.11%。当pH升高到10时,TBBPA、TBBPA−和TBBPA2−的比例分别为0.01%、2.65%和97.34%。Qu等研究了不同pH条件下TBBPA的臭氧氧化,发现解离态的TBBPA酚羟基的氧原子最高占用分子轨道的前线电子密度显著高于分子态TBBPA,更高的前线电子密度表明更容易被亲电试剂进攻发生氧化还原反应[7]。因此,随着pH的升高,解离态TBBPA含量增加,更容易被FeⅤ-TAML或FeⅣ-TAML氧化。
-
如图6所示,TBBPA在pH 7.5条件下降解的发光抑制率随反应时间先升高后降低,在反应0、0.5、5、10、30、60、120 min的发光抑制率分别为65.9%、65.1%、74.0%、82.6%、73.5%、48.9%和26.1%。发光抑制率变化趋势与TBBPA降解过程中耦合产物基本一致,说明耦合产物P3和P4/P4’相比于TBBPA母体具有更强的发光抑制作用。相比于TBBPA及其产物在近中性条件下的毒性变化,FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系在pH 10条件下可以将TBBPA溶液的发光抑制率降到10%以下,反应最终产物的发光抑制率为~1%。高pH条件下毒性的急剧降低归因于FeⅢ-TAML的高反应活性[13],将TBBPA快速分解为小分子有机酸等低毒性降解产物。
为进一步评估TBBPA在FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系中降解产物的毒性,ECOSAR程序被用来预测TBBPA及其中间产物对水蚤和鱼的急性、慢性毒性效应。如表1所示,除TBBPA外,其降解产物P2、P3和P4/P4’的毒性分级也为极高毒,其中P4的预测毒性与母体TBBPA相当。对于慢性毒性的预测结果,降解产物P3的慢性毒性比TBBPA的母体高2个数量级,这与急性毒性的预测规律不同(表1)。因此,FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系在近中性条件下降解TBBPA很可能由于反应不完全而产生具有强慢性毒性的中间产物,从而增加环境风险。
-
本研究测定了FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系对TBBPA在pH 7.5和pH 10条件下的降解,发现TBBPA的降解动力学和反应路径具有显著的pH依赖性。pH 7.5和pH 10条件下的降解动力学表明FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系对TBBPA的降解速率随着pH升高而升高。与碱性条件不同,TBBPA在中性条件下的降解产物中可以检测到耦合产物的生成,这可能是由于FeⅢ-TAML的反应活性随pH的降低急剧下降,从而无法快速去除TBBPA裂解产生的自由基中间产物。此外,TBBPA在不同pH条件下的存在形态存在差异,不同解离形态的TBBPA与氧化态的Fe-TAML反应活性不同,这可能会造成TBBPA的降解路径的差异。本研究进而对TBBPA及其不同pH条件下的降解产物进行了毒性评估,发现近中性条件下生成的耦合产物具有更高的急性毒性和慢性毒性。本研究测定了FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系在不同pH条件下对TBBPA催化氧化活性,推导了不同pH条件下降解路径,评估了TBBPA及其降解产物的毒性,为FeⅢ-TAML的实际应用提供理论支撑。
FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系催化氧化四溴双酚A的pH依赖性
pH-dependent catalytic oxidation of tetrabromobisphenol A by the FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2 system
-
摘要: 四酰胺基六甲基苯基环铁配合物(FeⅢ-TAML)因其对芳香类有机污染物的高活性和选择性而备受关注。在这些芳香类有机污染物中,FeⅢ-TAML对酚类化合物表现出很高的降解效率。然而,以前的研究表明,FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系对酚类物质的降解除了反应活性具有很强的pH依赖性之外,酚类物质的降解路径和产物也会随pH变化而产生差异。本研究通过FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系在近中性和碱性条件下对四溴双酚A(TBBPA)的降解,发现TBBPA的降解速率具有显著的pH依赖性,并随着pH升高而升高。与碱性条件不同,在中性条件下可以检测到耦合产物,表明FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2体系对TBBPA的降解路径也表现出显著的pH依赖性。此外,本研究对TBBPA及其不同pH条件下的降解产物也进行了毒性评估,发现近中性条件下生成的耦合产物具有更高的急性毒性和慢性毒性。这项工作揭示了高价铁配合物催化氧化有机污染物的反应机理,评估了有机污染物及其降解产物的毒性,为FeⅢ-TAML的实际应用提供理论指导。
-
关键词:
- 四溴双酚A /
- 四酰胺基六甲基苯基环铁 /
- 催化氧化 /
- pH依赖性 /
- 毒性评估
Abstract: Iron(Ⅲ)-tetraamidomacrocyclic ligand (FeⅢ-TAML) has attracted great attention due to its high activity and selectivity for the degradation of aromatic organic pollutants. Among these aromatic contaminants, FeⅢ-TAML shows high efficiency for the removal of phenolic compounds. However, as reported in previous literatures, the degradation of phenols by the FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2 system is strongly pH-dependent, and the degradation pathways and products of phenols will also vary with pH changes. In this study, the FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2 system is used to decompose tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) under near neutral and alkaline conditions. It is found that the degradation rate of TBBPA was pH-dependent and increased with increasing pH levels. Unlike the reaction under alkaline conditions, coupling products can be detected for TBBPA after degradation by the FeⅢ-TAML/H2O2 system under near neutral pH conditions. This suggests that the degradation path of TBBPA also exhibits a significant pH-dependence. In addition, this study also evaluates the toxicities of TBBPA and its degradation products generated under different pH conditions, finding that the coupling products generated under near-neutral conditions exhibit higher acute and chronic toxicity. This study reveals the reaction mechanism of the catalytic oxidation of organic pollutants by high-valent iron complexes, evaluates the toxicity of organic pollutants and their degradation products, and provides theoretical guidance for the practical application of FeⅢ-TAML. -

-
表 1 TBBPA及其降解产物的ECOSAR毒性预测.
Table 1. Toxicity of TBBPA and its degradation intermediates predicted by the ECOSAR program.
化合物 Compound 急性毒性/(mg L−1)Acute toxicity 慢性毒性/(mg L−1)Chronic toxicity 毒性分级Hazard category 水蚤(LC50)Daphnid 鱼(LC50)Fish 水蚤Daphnid 鱼Fish TBBPA 0.023 0.023 0.006 0.006 极高毒 P1 3.188 6.078 0.605 0.736 高毒 P2 0.426 0.418 0.081 0.063 极高毒 P3 0.167 0.555 0.038×10−3 0.088×10−3 极高毒 P4 0.022 0.022 0.006 0.006 极高毒 P4’ 0.115 0.058 0.022 0.011 极高毒 P5 48.618 359.240 7.842 39.438 中毒 P6 179.049 1961.876 29.659 205.323 低毒 -
[1] 熊美昱, 夏雨琪, 彭程. 典型类雌激素的降解方法及其影响因素研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(3): 610-623. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019101303 XIONG M Y, XIA Y Q, PENG C. Degradation methods and influence factors of typical estrogen-like substances [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(3): 610-623(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019101303
[2] COVACI A, VOORSPOELS S, ABDALLAH M A E, et al. Analytical and environmental aspects of the flame retardant tetrabromobisphenol-A and its derivatives [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2009, 1216(3): 346-363. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2008.08.035 [3] 孙国新, 王杰琼, 周成智, 等. 四溴双酚A在近岸海水中的光降解动力学研究 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(8): 1683-1690. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018010602 SUN G X, WANG J Q, ZHOU C Z, et al. Photodegradation kinetics of tetrabromobisphenol A in coastal water [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(8): 1683-1690(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018010602
[4] 吴玉丽, 肖羽堂, 王冠平, 等. 多溴联苯醚、六溴环十二烷和四溴双酚A在环境中污染现状的研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(2): 384-403. WU Y L, XIAO Y T, WANG G P, et al. Research progress on status of environmental pollutions of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, hexabromocyclodocane, and tetrabromobisphenol A: A review [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(2): 384-403(in Chinese).
[5] 张静, 严静娜, 郭悦宁, 等. 阻燃剂四溴双酚A的厌氧-好氧生物降解 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(9): 1776-1784. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.09.2016013001 ZHANG J, YAN J N, GUO Y N, et al. Anaerobic and aerobic biodegradation of flame retardant tetrabromobisphenol A [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(9): 1776-1784(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.09.2016013001
[6] LIN K D, LIU W P, GAN J. Reaction of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) with manganese dioxide: Kinetics, products, and pathways [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(12): 4480-4486. [7] QU R J, FENG M B, WANG X H, et al. Rapid removal of tetrabromobisphenol A by ozonation in water: Oxidation products, reaction pathways and toxicity assessment [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(10): e0139580. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139580 [8] FENG Y P, COLOSI L M, GAO S X, et al. Transformation and removal of tetrabromobisphenol A from water in the presence of natural organic matter via laccase-catalyzed reactions: Reaction rates, products, and pathways [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(2): 1001-1008. [9] DING Y B, ZHU L H, WANG N, et al. Sulfate radicals induced degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A with nanoscaled magnetic CuFe2O4 as a heterogeneous catalyst of peroxymonosulfate [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 129: 153-162. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.09.015 [10] GUO Y G, ZHOU J, LOU X Y, et al. Enhanced degradation of Tetrabromobisphenol A in water by a UV/base/persulfate system: Kinetics and intermediates [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 254: 538-544. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.143 [11] LIU G B, ZHAO H Y, THIEMANN T. Zn dust mediated reductive debromination of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 169(1/2/3): 1150-1153. [12] LIU G B, DAI L, GAO X, et al. Reductive degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in aqueous medium [J]. Green Chemistry, 2006, 8(9): 781. doi: 10.1039/b605261d [13] WANG C, GAO J, GU C. Rapid destruction of tetrabromobisphenol A by iron(III)-tetraamidomacrocyclic ligand/layered double hydroxide composite/H2O2 system [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(1): 488-496. [14] WANG C, XIAN Z Y, DING Y H, et al. Self-assembly of FeIII-TAML-based microstructures for rapid degradation of bisphenols [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 256: 127104. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127104 [15] LI H C, SHAN C, LI W, et al. Peroxymonosulfate activation by iron(III)-tetraamidomacrocyclic ligand for degradation of organic pollutants via high-valent iron-oxo complex [J]. Water Research, 2018, 147: 233-241. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.10.015 [16] KUNDU, ANNAVAJHALA M, KURNIKOV I V, et al. Experimental and theoretical evidence for multiple Fe(IV) reactive intermediates in TAML-activator catalysis: Rationalizing a counterintuitive reactivity order [J]. Chemistry (Weinheim an Der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2012, 18(33): 10244-10249. [17] KUNDU S M, THOMPSON J V K, SHEN L Q, et al. Activation parameters as mechanistic probes in the TAML iron(V)-oxo oxidations of hydrocarbons [J]. Chemistry - A European Journal, 2015, 21(4): 1803-1810. doi: 10.1002/chem.201405024 [18] GUPTA S S, STADLER M, NOSER C A, et al. Rapid total destruction of chlorophenols by activated hydrogen peroxide [J]. Science, 2002, 296(5566): 326-328. doi: 10.1126/science.1069297 [19] SU H R, YU C Y, ZHOU Y F, et al. Quantitative structure-activity relationship for the oxidation of aromatic organic contaminants in water by TAML/H2O2 [J]. Water Research, 2018, 140: 354-363. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.04.062 [20] CHAHBANE N, POPESCU D L, MITCHELL D A, et al. FeIII-TAML-catalyzed green oxidative degradation of the azo dye Orange II by H2O2 and organic peroxides: Products, toxicity, kinetics, and mechanisms [J]. Green Chemistry, 2007, 9(1): 49-57. doi: 10.1039/B604990G [21] CHEN J L, RAVINDRAN S, SWIFT S, et al. Catalytic oxidative degradation of 17α-ethinylestradiol by FeIII-TAML/H2O2: Estrogenicities of the products of partial, and extensive oxidation [J]. Water Research, 2012, 46(19): 6309-6318. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.09.012 [22] SHAPPELL N W, VRABEL M A, MADSEN P J, et al. Destruction of estrogens using Fe-TAML/peroxide catalysis [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(4): 1296-1300. [23] SHEN L Q, BEACH E S, XIANG Y, et al. Rapid, biomimetic degradation in water of the persistent drug sertraline by TAML catalysts and hydrogen peroxide [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(18): 7882-7887. [24] CHANDA A, KHETAN S K, BANERJEE D, et al. Total degradation of fenitrothion and other organophosphorus pesticides by catalytic oxidation employing Fe-TAML peroxide activators [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128(37): 12058-12059. doi: 10.1021/ja064017e [25] GHOSH A, RYABOV A D, MAYER S M, et al. Understanding the mechanism of H+-induced demetalation as a design strategy for robust iron(III) peroxide-activating catalysts [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(41): 12378-12379. doi: 10.1021/ja0367344 [26] GHOSH A, MITCHELL D A, CHANDA A, et al. Catalase−Peroxidase activity of iron(Ⅲ)−TAML activators of hydrogen peroxide [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(45): 15116-15126. doi: 10.1021/ja8043689 [27] ONUNDI Y, DRAKE B A, MALECKY R T, et al. A multidisciplinary investigation of the technical and environmental performances of TAML/peroxide elimination of Bisphenol A compounds from water [J]. Green Chemistry, 2017, 19(18): 4234-4262. doi: 10.1039/C7GC01415E [28] DENARDO M A, MILLS M R, RYABOV A D, et al. Unifying evaluation of the technical performances of iron-Tetra-amido macrocyclic ligand oxidation catalysts [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(9): 2933-2936. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b13087 -



 下载:
下载: