-
重金属污染是生物圈面临的最广泛、最严重的环境问题之一[1-2]。《2014全国污染调查公报》显示,我国土壤环境质量总体堪忧,以重金属为代表的无机污染物超标点位数占全部超标点位的82.8%,在耕地土壤系统中点位超标率为19.4%,污染情况最为严重,而主要污染物为Cd、Pb等[3]。随着重金属在土壤中不断地蓄积,重金属污染将会导致严重的农业损失,对动物和人类的健康产生严重威胁[4-6]。因此,重金属对人类健康和农业环境的潜在风险性在不断增加。
原位化学钝化修复技术因其经济、高效被广泛关注,而其使用关键在于依据土壤理化性质选择合适的钝化材料[7]。常用的钝化材料分为有机材料(有机肥、腐植酸、污泥、富里酸、粪便、秸秆等)、无机材料(含硅材料、含钙材料、含磷材料、黏土矿物、金属氧化物、生物炭等)和有机-无机复合材料等3种类型[8-9]。这些钝化材料一方面能够有效改善土壤理化性质,增加土壤营养元素含量[10];另一方面,钝化材料能够提高土壤pH,与重金属发生吸附、氧化还原、络合或沉淀作用,改变重金属在土壤中的赋存形态,使重金属的生物有效性下降,从而降低其生物毒性[11-14],这也是钝化修复土壤重金属污染的主要机制。梁妮等[15]研究表明,生物炭与腐殖土混合施入进行修复,Pb生物有效态含量显著降低,生物炭与腐殖土复合的修复效果更好;沈章军等[16]对的研究表明,海泡石、生石灰、鸡粪、秸秆腐殖质有效地钝化了Pb、Cd和Cu的活性,相对于单一材料处理,海泡石与鸡粪和秸秆腐殖质混合处理表现出更好的降低重金属活性;张彦娟等[17]的研究表明,在Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu污染土壤中,施用钙镁磷肥、坡缕石、生物炭组配钝化剂在治理重金属复合污染蔬菜地具有明显的优势,其对全方位修复重金属复合污染土壤的效果好于单一钝化剂;陈盾[18]的研究表明,羟基磷灰石+钙镁磷肥复配处理对Cd污染土壤钝化效果相较单一钝化剂最佳,黑麦草体内Cd含量分别为0.183 mg·kg−1和0.085 mg·kg−1,较对照分别降低了93.64%和91.77%;张新帅等[19]的研究表明,石灰、生物炭单施和配施均降低土壤Cd有效性和玉米Cd含量,提高玉米产量,具有明显的土壤改良效应,处理中石灰与生物炭配合施用最佳,处理效果最好。
长期使用单一钝化材料会对土壤环境造成负面影响,甚至可能加剧其他污染风险或出现污染反复的状况,所以多种钝化材料联合使用不仅对农田土壤环境更加友好,而且还可达到更好的修复效果。但目前对于无机钝化材料的联用以及与有机钝化材料的联用对重金属污染修复的复合效应研究较少。因此本研究通过选用生物炭熟、钙镁磷肥、石灰及猪粪为原位钝化修复材料进行单施、两两混施苗期玉米盆栽实验,对土壤中Cd、Pb化学形态分布、有效态含量及其在苗期玉米植株体内的分布和苗期玉米生长状况进行综合分析,为土壤重金属钝化修复材料的筛选及其应用提供科学依据。
-
本研究所采用的土壤为砂姜黑土,取自青岛市平度市某矿区农田0—20 cm表层土壤(表1),经碎化、风干处理后,添加CdCl2、Pb(NO3)2溶液,使土壤Cd、Pb浓度达到3.5 mg·kg−1、750 mg·kg−1,保持土壤田间持水量在60%左右培养30 d,经风干、磨碎、过20目筛处理后保存备用。
-
本研究所用生物炭、钙镁磷肥、熟石灰均为市售商品,猪粪为当地农户养殖所产,经风干、粉碎后装袋备用。供试材料基本性质如表2所示,生物炭以玉米秸秆为原材料,在450 ℃下热解2 h以完成生物炭的制备,有机质含量 ≥ 20%;熟石灰含钙95% ± 3%;钙镁磷肥有效磷P2O5 ≥ 12.0%。试验作物选用农大372,购于北京华奥农科玉育种开发有限公司。
-
盆栽实验用土每盆2 kg(塑料盆,h=10 cm,d=15 cm),生物炭单施处理(B) 每盆0.1 kg,钙镁磷肥单施处理(C) 每盆0.15 kg,熟石灰单施处理(L) 每盆0.075 kg,猪粪单施处理(P) 每盆0.5 kg;各处理均再设置两两混施处理,生物炭-钙镁磷肥混施处理(BC),生物炭-熟石灰混施处理(BL),生物炭-钙镁磷肥混施处理(BP),熟石灰-钙镁磷肥混施处理(LC),熟石灰-猪粪混施处理(LP),猪粪-钙镁磷肥混施处理(PC),混施施用量即为单施处理的一半,且每个处理均设置3次重复。盆栽在人工温室内进行培养,培养温度22—30 ℃,持水量保持在60%,三叶期后停止间苗,培养35 d后收获。
-
土壤理化指标:根据HJ 962—2018,采用电位法对土壤pH进行测定(土水比1:2.5);根据NY/T 1848—2010,采用联合浸提-比色法对土壤速效钾、有效磷进行测定;根据鲍士旦[20]《土壤农化分析》,分别采用碱解扩散法、重铬酸钾容量-外加热法测定土壤碱解氮、有机质 含量。
土壤/植物重金属含量:土壤、作物中Cd、Pb含量采用酸式消解法进行消解,根据GB/T 23739—2009采用DTPA法提取土壤中能被生物吸收利用或产生毒害效应的有效态Cd、Pb;土壤Cd、Pb化学形态均采用欧共体标准物质局提出的BCR连续浸提法将金属提取为弱酸提取态、可氧化态、可还原态、残渣态,最终消解液和提取液都通过电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(Optima 8000型,PE美国)进行测定,并用土壤标准物质(GBW07401a)对土壤重金属检测数据进行校准,测试Cd、Pb回收率分别为98.2%、99.2%;用植物标准物质(GBW10049)对植物重金属检测数据进行校准,测试Cd、Pb回收率分别为98.5%、98.8%。
植物生理生化指标:实验采用便携式叶绿素仪(SPAD-502Plus,KONICA MINOLTA美国)直接对植物叶绿素含量进行测定;根据刘新[21]《植物生理学实验指导》,采用双组分分光光度法测定丙二醛(MDA)含量,采用淡蓝四唑法测定超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性,采用愈创木酚比色法测定过氧化物酶(POD)活性;根据Cakmak等[22]的方法测定植物叶片过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性。植物生理生化指标均在收获前采取鲜样进行测定。
-
实验数据采用Excel 2019和SPSS 26.0进行差异显著性分析,使用Duncan法进行多重比较,在P<0.05条件下认为存在显著性差异,在 P<0.01条件下认为存在极显著差异。采用Origin 2021进行绘图。
-
由表3可知,与CK对比分析,生物炭单施、混施处理均能够有效提升土壤71.62%—150.85%的速效钾、98.91%—224.00%的有机质,且以生物炭单施提升效果最明显;所有处理均能够有效提高土壤21.93%—411.94%的有效磷,以生物炭、生物炭-熟石灰、熟石灰处理提高效果最差,仅提高了63.28%、65.42%、21.93%;猪粪单施、混施处理均能够有效提升土壤22.74%—62.08%的碱解氮,其他处理对土壤碱解氮含量几乎没有影响。
-
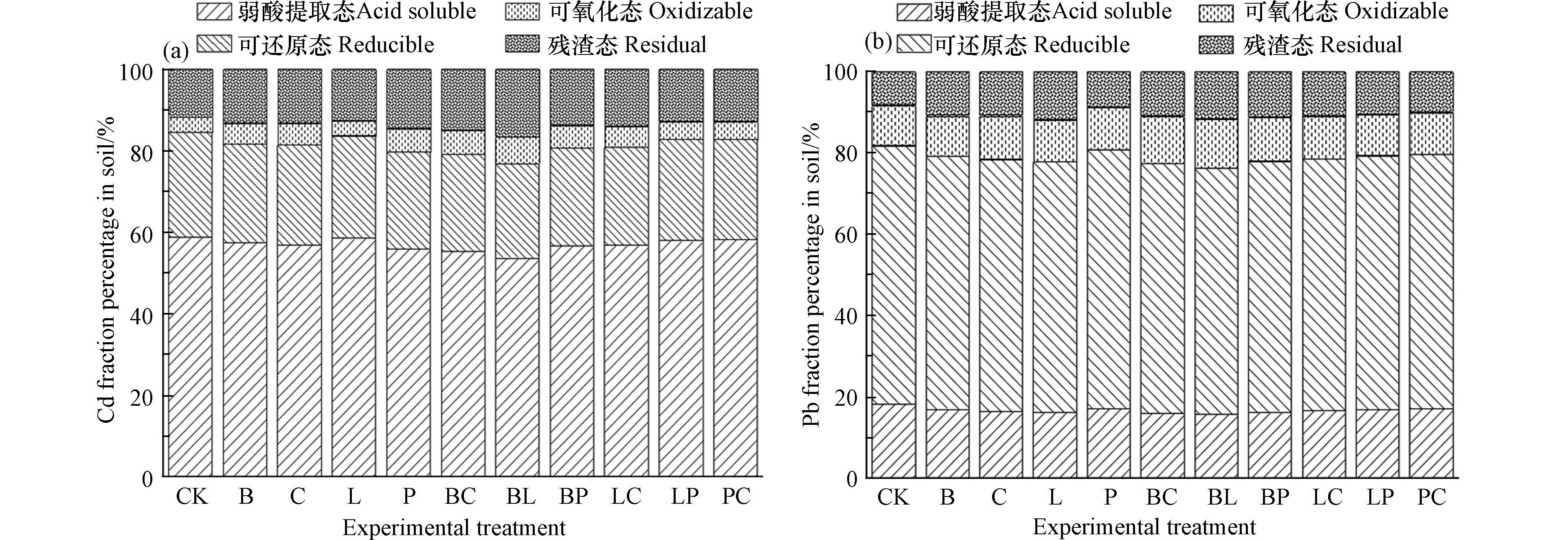
由图1可知,相对CK,生物炭、钙镁磷肥、熟石灰、生物炭-钙镁磷肥、生物炭-熟石灰处理下,有效降低土壤中5.83%—9.71%的弱酸提取态Cd含量,增加土壤中54.45%—72.73%的残渣态Cd含量,即可被植物直接利用态的Cd含量减少,且不可利用态的Cd含量增加,处理效果较为明显。所有处理均能够有效降低土壤中6.27%—14.48%的弱酸提取态Pb含量,增加土壤中4.36%—43.00%的残渣态Pb含量。整体来看,所有处理中猪粪对Cd、Pb的化学形态的影响较其他钝化材料的处理明显较差,而生物炭、熟石灰、钙镁磷肥单施、混施的处理能够有效影响土壤中Cd、Pb的赋存形态,使弱酸提取态、可还原态Cd、Pb更多地向可氧化态、残渣态转化,降低Cd、Pb在土壤中的流动性。不同钝化材料间对土壤Cd、Pb钝化效果存在极显著的差异,生物炭本身具备良好的孔性结构,而且对土壤孔性等土壤其他理化性质产生积极影响,土壤活动、固相-水相比例等发生变化[23-25],生物炭对重金属离子的钝化机制主要涉及4个过程:沉淀反应、表面络合、Cπ-阳离子相互作用(存在于π体系电子云与阳离子之间的相互作用,与物质结构的芳香程度有关)和氧化还原,引起土壤Cd、Pb的化学形态、有效态变化[26];钙镁磷肥、熟石灰能够提高土壤酶活性、改善微生物群落结构,促进一些耐Cd、Pb微生物的活动,有利于对土壤Cd、Pb的螯合固定,但过量施用钙镁磷肥、熟石灰可能会导致土壤健康状况的恶化,大量的磷积累会增加磷通过侵蚀和淋溶流失的风险,进而导致地表水富营养化[27-30];猪粪能够与重金属络合形成低溶解性的金属-有机配合物或黏土-金属-有机质,以此降低土壤中重金属的有效性,但其本身含有一定量的重金属,但其作为钝化材料,由于其有机质或腐殖酸含量较少,对土壤pH影响相对生物炭、钙镁磷肥、熟石灰较小,所以在合理施用的前提下,其钝化修复农田土壤Cd、Pb的效果并不好,长期或大量地施用反而可能会因猪粪携带外源重金属而造成重金属污染[31-33]。
-
由表4可知,土壤pH、有机质含量分别与可氧化态、残渣态Cd呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)、正相关,而土壤碱解氮、有效磷、有机质与可氧化态、残渣态Cd、Pb呈负相关,速效钾与残渣态Cd、Pb呈负相关。总的来说,Cd、Pb在土壤中与土壤营养指标的相关性具备相似性,其中pH是影响土壤中Cd、Pb的化学形态或活性的关键因素[34]。这与王逸群等[35]、王玉婷等[36]的研究结果不尽相同,分析其原因可能是土壤样品的质地不均一,以及钝化材料本身所含的物质或物质的量的差异导致的,对于同一质地土壤,不同钝化材料都能够一定程度提升土壤pH,但施用之后能够为土壤供给的养分不同,同一养分的量也不同,在此基础上,钝化材料的联用共同表现出pH为稳定的、主要的钝化土壤Cd、Pb的因素。
-
由图2可知,生物炭、钙镁磷肥、熟石灰、生物炭-钙镁磷肥、生物炭-熟石灰处理较其他处理存在差异或显著性差异,显著降低土壤16.81%—19.83%的有效态Cd、12.93%—20.61%有效态Pb。整体来看,生物炭-熟石灰处理效果最佳,有效降低土壤19.83%有效态Cd、20.61%有效态Pb;生物炭-钙镁磷肥处理效果次之,有效降低土壤18.53%有效态Cd、17.53%有效态Pb,而猪粪单施、混施处理效果明显较差,且以猪粪单施处理效果最差。结合表3、表4分析,生物炭、钙镁磷肥、熟石灰、猪粪的单施、混施处理均能够不同程度提高土壤pH,从而有效促进Cd2+、Pb2+的溶解[37-38];能够产生与Cd、Pb形成不溶性螯合物的大量的羰基、酚基、醌基、羧基、氨基等[39-40];能够产生的大量阳离子,与土壤中的酸性离子发生交换作用[41-42];能够促进碳酸盐、磷酸盐、氢氧化物沉淀的生成,共同影响土壤中Cd、Pb的化学赋存形态,降低其有效态含量,降低其生物有效性[43-46]。
-
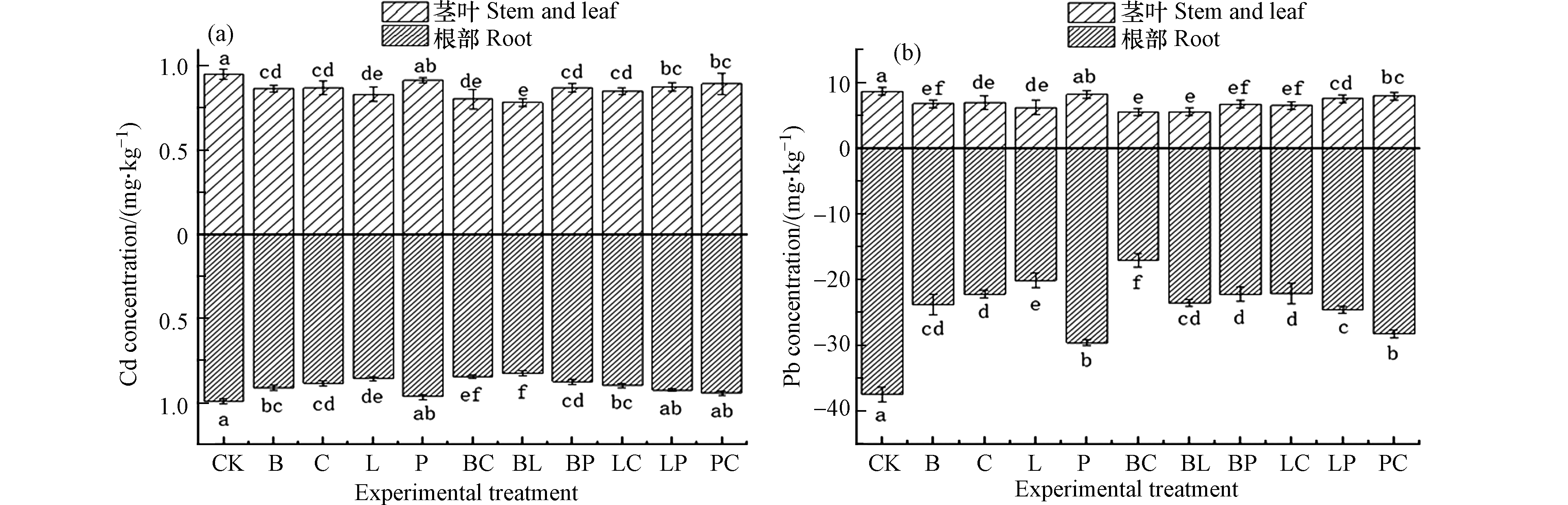
由图3(a)可知,除猪粪单施处理以外的其他处理下玉米植株根部、茎叶部Cd含量较CK均存在显著性差异(P<0.05),有效减少玉米植株根部、茎叶部Cd含量4.83%—7.14%、1.71% —6.65%。由图3(b)可知,除猪粪单施处理以外的其他处理下玉米植株根部、茎叶部Pb含量较CK存在显著差异(P<0.05),生物炭、钙镁磷肥、熟石灰、生物炭-钙镁磷肥、生物炭-熟石灰处理效果较好,有效减少玉米植株根部、茎叶部Pb含量36.42%—58.58%、21.86%—47.53%。总的来说,生物炭-熟石灰、生物炭-钙镁磷肥、生物炭处理能够有效降低Cd、Pb在玉米植株体内的富集,较猪粪单施、混施处理效果显著较好。综合分析出现这种状况可能是猪粪提升土壤pH的能力与其他3种材料相比较为有限,即钝化能力较差,但在该土壤环境下其促进玉米植株生长的效果较其他处理更为明显有效,在不能改变玉米植株转运能力的基础上,猪粪单施、混施处理下玉米植株体内富集、转运了相较其他钝化材料处理更多的Cd、Pb。
-
由图4(a)可知,所有处理下玉米株高较CK增高1.50%—20.28%,且以猪粪单施、混施处理处理下玉米增高6.47%—20.28%,在P<0.05水平上与其他处理存在显著差异或不显著差异。由图4(b)可知,猪粪、生物炭-猪粪处理下叶绿素含量较CK(38.5Spad)明显增多14.09%、11.26%,与其他处理(不包括生物炭-钙镁磷肥处理)间均存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。由图4(c)可知,相较于CK,猪粪单施、混施处理苗期玉米干重增加0.37—1.01倍,且以猪粪单施处理下,玉米植株增重效果最显著(P<0.05)。整体来看,猪粪单施、混施处理对玉米植株的生长状况的影响较其他处理更大,更有利于作物的生长。分析其差异来源于不同钝化材料基于其成分组成及含量不同,在施用到土壤中的同时还携带一定量的磷、氮、钾、有机质一起进入,由于磷、氮、钾对于作物生长的影响存在差异,玉米植株株高、叶绿素含量及地上部、地下部生物量也存在显著性差异,其中猪粪单施、混施处理对玉米植株的生长影响更大,这可能是因为猪粪的施入直接导致土壤有效氮含量的增加,而氮素相对磷素、钾素对玉米生长及叶绿素含量影响更大[47]。
-
由图5(a)可知,各处理中,猪粪、熟石灰-猪粪、猪粪-钙镁磷肥处理下植物叶片内MDA含量均极显著高于其他处理(P<0.01);生物炭-熟石灰处理下植物叶片内MDA含量极显著低于其他处理(P<0.01),降低玉米叶片MDA含量44.95%、58.43%。由图5(b)可知,猪粪、猪粪-钙镁磷肥处理下植物叶片SOD酶活极显著(P<0.01)高于其他处理,但较CK低;生物炭-熟石灰、生物炭-钙镁磷肥处理下植物叶片SOD酶活极显著低于其他处理(P<0.01),降低玉米植株SOD活性77.28%、80.56%。由图5(b)、(c)可知,各处理间植物叶片内CAT酶活、POD酶活差异性基本一致,猪粪、猪粪-钙镁磷肥处理下CAT、POD酶活极显著高,但较CK极显著低(P<0.01);而生物炭-熟石灰、生物炭-钙镁磷肥处理在P<0.01水平上极显著降低玉米植株CAT活性41.57%、43.28%,POD活性56.84%、58.23%。结合图2、图3分析,一方面由于不同的钝化材料基于其材质,经过土壤活动或直接为玉米提供一定的营养成分,从而促进玉米的生长,即玉米在更好的生长过程中会转运更多Cd、Pb;另一方面,不同钝化材料又具备一定的钝化土壤Cd、Pb的能力,能够确保玉米在有利生长的过程中更少的富集Cd、Pb,即降低Cd、Pb对玉米的胁迫,使各处理较CK叶片MDA含量减少及抗氧化酶活性降低,证明了此几种处理钝化土壤Cd、Pb的有效性及对玉米植株产生良性的影响。
-
(1)生物炭与钙镁磷肥、熟石灰混施处理钝化修复土壤Cd、Pb复合污染的效果更好,能够有效降低土壤6.31%、8.74%弱酸提取态Cd、7.13%、6.27%的弱酸提取态Pb,增加54.55%、75.76%残渣态Cd、26.42%、21.08%残渣态Pb。
(2)生物炭-钙镁磷肥、生物炭-熟石灰混施处理能够有效提高土壤pH,有效降低土壤有效态Cd 含量18.53%、19.83%,降低有效态Pb 含量17.53%、20.61%,有效降低作物地下部Cd 含量4.33%、Pb含量2.92%,54.46%、37.17%,作物地上部Cd含量6.41%、5.25%,地上部Pb含量36.25%、36.02%,降低玉米叶片MDA含量44.95%、58.43%,降低玉米植株SOD活性77.28%、80.56%,CAT活性41.57%、43.28%,POD活性56.84%、58.23%。生物炭-钙镁磷肥、生物炭-熟石灰混施处理效果最佳,能够有效钝化土壤Cd、Pb,并促进玉米生长,有效缓解玉米因受Cd、Pb胁迫造成的氧化物损伤。
不同钝化材料及其组合对Cd、Pb污染土壤的修复效果及玉米生长的影响
Effects of different passivation materials and combinations on the remediation of Cd and Pb polluted soil and the growth of Maize
-
摘要: 为高效钝化修复农田土壤重金属污染及促进作物生长,以生物炭、熟石灰、钙镁磷肥、猪粪作为钝化材料,采用盆栽实验研究了材料单施及两两混施对Cd、Pb复合污染土壤的修复效果,以及对苗期玉米生长状况的影响。结果表明,4种材料单施、两两混施处理均能不同程度提高土壤pH,有效降低土壤弱酸提取态Cd、Pb含量5.83%—9.71%、6.27%—14.48%,增加土壤残渣态Cd、Pb含量54.45%—72.73%、4.36%—43.00%。与对照相比,猪粪单施、混施处理苗期玉米株高增长6.47%—20.28%,干重增加0.37—1.01倍;生物炭-钙镁磷肥、生物炭-熟石灰混施处理能够显著提高土壤pH,分别降低土壤有效态Cd含量18.53%、19.83%,降低有效态Pb含量17.53%、20.61%,降低玉米叶片MDA含量44.95%、58.43%,降低玉米植株SOD活性77.28%、80.56%,CAT活性41.57%、43.28%,POD活性56.84%、58.23%。生物炭-钙镁磷肥、生物炭-熟石灰混施处理效果最佳,能够有效钝化土壤Cd、Pb,并促进玉米生长,有效缓解玉米因受Cd、Pb胁迫造成的氧化物损伤。Abstract: In order to effectively passivate and remediate heavy metal pollution in farmland soil and promote crop growth, biochar, hydrated lime, calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer and pig manure were used as passivation materials. A pot experiment was carried out to study the remediation effect of single application and mixed application of materials on Cd and Pb contaminated soil and the growth status of maize at seedling stage. The results indicated that both single and mixed application of passivation materials increased the soil pH in varying degrees, and effectively reduced acid extraction state of Cd and Pb by 5.83%—9.71%, 6.27%—14.48%, and increased residual state of Cd and Pb by 54.45%—72.73%, 4.36%—43.00%, respectively. Compared with the control treatment, the plant height of maize at seedling stage increased by 6.47%—20.28% and the dry weight increased by 0.37—1.01 times. The mixed application of biochar-calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer and biochar-hydrated lime could significantly increase soil pH, reduce the available Cd by 18.53% and 19.83%, the available Pb content by 17.53% and 20.61%, MDA in maize leaves by 44.95%, 58.43%, the activity of SOD by 77.28%, 80.56%, the activity of CAT by 41.57%, 43.28%, and the activity of POD by 56.84%, 58.23%, respectively. The mixed application of biochar-calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer and biochar-hydrated lime has the best treatment effect, which can effectively passivate soil Cd and Pb, promote maize growth, and effectively alleviate the oxide damage of maize caused by Cd and Pb stress.
-
Key words:
- passivation /
- heavy metals /
- effective state /
- MDA /
- antioxidant enzyme activity
-

-
表 1 供试土壤基本理化性质
Table 1. Basic physical and chemical properties of tested soil
土壤背景值
Soil background
valuepH 碱解氮
(mg·kg−1)
Available N有效磷/(mg·kg−1)
Available P速效钾/
(mg·kg−1)
Available K有机质/
(mg·kg−1)
OM全Cd/
(mg·kg−1)
Total Cd全Pb/
(mg·kg−1)
Total Pb7.42 13.52 0.37 141.21 31.71 0.24 4.46 表 2 供试材料基本性质
Table 2. Basic properties of tested materials
供试材料
Test materialpH 全Cd/(mg·kg−1)
Total Cd全Pb/(mg·kg−1)
Total Pb生物炭 10.12 0.01 9.25 钙镁磷肥 7.81 0.07 10.2 熟石灰 12.93 0.08 20.14 猪粪 7.28 0.52 35.24 表 3 不同处理对土壤pH、养分的影响
Table 3. Effects of different treatments on soil pH、nutrients
处理
TreatmentspH 碱解氮/
(mg·kg−1)
Available N有效磷/
(mg·kg−1)
Available P速效钾/
(mg·kg−1)
Available K有机质/
(g·kg−1)
OM对照CK 7.53±0.24 c 14.03±0.51 E 5.61±0.16 J 67.40±2.45 F 31.33±3.12 E 钙镁磷肥单施C 7.73±0.21 ab 14.94±0.48 DE 27.16±0.25 B 66.33±5.12 F 26.32±2.14 E 生物炭单施B 7.84±0.18 ab 14.54±0.21 DE 9.16±0.25 H 169.07±3.12 A 101.51±3.65 A 熟石灰单施L 7.90±0.11 a 14.84±0.31 DE 6.84±0.21 I 53.87±4.45 G 29.03±5.44 E 猪粪单施P 7.68±0.14 ab 22.74±0.65 A 22.68±0.34 D 125.13±8.23 CD 42.79±2.43 D 生物炭-钙镁磷肥混施BC 7.85±0.16 ab 14.74±0.45 DE 21.08±0.22 E 138.67±6.65 B 62.23±3.25 C 生物炭-熟石灰混施BL 7.88±0.13 ab 15.33±0.24 D 9.28±0.15 H 115.67±5.32 D 63.64±4.12 BC 生物炭-猪粪混施BP 7.86±0.23 ab 19.07±0.35 B 17.64±0.24 G 133.13±10.25 BC 70.95±2.54 B 熟石灰-钙镁磷肥混施LC 7.88±0.15 ab 14.94±0.26 DE 23.32±018 C 74.73±4.21 F 31.73±1.84 E 熟石灰-猪粪混施LP 7.87±0.11 ab 17.65±0.18 C 18.24±0.13 F 64.27±5.12 F 41.79±2.12 D 猪粪-钙镁磷肥混施PC 7.60±0.24 b 17.22±0.13 C 28.72±0.33 A 87.80±7.14 E 41.08±3.14 D 注:大写字母表示在P<0.01水平上的差异极显著,小写字母表示在P<0.05水平上的差异显著.
Note: Capital letters indicate significant difference at P < 0.01 level,and lowercase letters indicate significant difference at P < 0.05 level.表 4 土壤理化性质与Cd、Pb化学形态的相关性分析
Table 4. Correlation Analysis between chemical forms of Cd、Pb and soil properties
Cd、Pb化学形态
Chemical speciation of Cd、 PbpH 碱解氮
Available N有效磷
Available P速效钾
Available K有机质
OM弱酸提取态Cd −0.871** 0.222 0.209 0.044 −0.128 可还原态Cd −0.820** 0.071 0.142 0.054 −0.071 可氧化态Cd 0.968** −0.168 −0.229 −0.121 0.058 残渣态Cd 0.828** −0.147 −0.135 −0.001 0.140 弱酸提取态Pb −0.917** 0.016 0.039 0.007 −0.107 可还原态Pb −0.976** 0.084 0.189 0.075 −0.202 可氧化态Pb 0.957** −0.060 −0.227 −0.039 0.170 残渣态Pb 0.971** −0.107 −0.155 −0.006 0.128 注:** 表示达到极显著相关性(P<0.01)水平.
Note:** indicate the level of P<0.01. -
[1] HAMID Y, TANG L, YASEEN M, et al. Comparative efficacy of organic and inorganic amendments for cadmium and lead immobilization in contaminated soil under rice-wheat cropping system [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 214: 259-268. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.113 [2] O'CONNOR D, PENG T Y, ZHANG J L, et al. Biochar application for the remediation of heavy metal polluted land: A review of in situ field trials [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 619/620: 815-826. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.132 [3] 环境保护部, 国土资源部. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[R]. 北京, 2014. Ministry of Environment of the People's Republic of China, Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. National survey bulletin on soil pollution[R]. Beijing, 2014.
[4] XU X J, HUANG Q, HUANG Q Y, et al. Soil microbial augmentation by an EGFP-tagged Pseudomonas putida X4 to reduce phytoavailable cadmium [J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2012, 71: 55-60. [5] KIRAN, BHARTI R, SHARMA R. Effect of heavy metals: An overview[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2022, 51(1): 880-885. [6] WANG Q, PAN F S, XU X M, et al. Cadmium level and soil type played a selective role in the endophytic bacterial community of hyperaccumulator Sedum alfred Hance [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 263: 127986. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127986 [7] 丁园, 敖师营, 陈怡红, 等. 4种钝化剂对污染水稻土中Cu和Cd的固持机制 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(8): 4037-4044. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202010260 DING Y, AO S Y, CHEN Y H, et al. Immobilization mechanism of four types of amendments on Cu and Cd in polluted paddy soil [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(8): 4037-4044(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202010260
[8] 吴霄霄, 曹榕彬, 米长虹, 等. 重金属污染农田原位钝化修复材料研究进展 [J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2019, 36(3): 253-263. doi: 10.13254/j.jare.2018.0101 WU X X, CAO R B, MI C H, et al. Research progress of in situ passivated remedial materials for heavy metal contaminated soil [J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2019, 36(3): 253-263(in Chinese). doi: 10.13254/j.jare.2018.0101
[9] 纪艺凝, 王农, 徐应明, 等. 无机-有机复配材料对Cd污染土壤的修复效应 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(11): 2333-2340. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017060804 JI Y N, WANG N, XU Y M, et al. Effect of inorganic-organic compound mixtures on the immobilization remediation of Cd contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(11): 2333-2340(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017060804
[10] 陈炳睿, 徐超, 吕高明, 等. 6种固化剂对土壤Pb Cd Cu Zn的固化效果 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(7): 1330-1336. CHEN B R, XU C, LV G M, et al. Effects of six kinds of curing agents on lead, cadmium, copper, zinc stabilization in the tested soil [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(7): 1330-1336(in Chinese).
[11] 李英, 商建英, 黄益宗, 等. 镉砷复合污染土壤钝化材料研究进展 [J]. 土壤学报, 2021, 58(4): 837-850. doi: 10.11766/trxb201912170575 LI Y, SHANG J Y, HUANG Y Z, et al. Research progress on passivation materials for cadmium-arsenic co-contamination in soil [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2021, 58(4): 837-850(in Chinese). doi: 10.11766/trxb201912170575
[12] WAN Y N, HUANG Q Q, WANG Q, et al. Accumulation and bioavailability of heavy metals in an acid soil and their uptake by paddy rice under continuous application of chicken and swine manure [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121293. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121293 [13] 刘勇, 刘燕, 朱光旭, 等. 石灰对Cu、Cd、Pb、Zn复合污染土壤中重金属化学形态的影响 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(2): 158-164. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201902030 LIU Y, LIU Y, ZHU G X, et al. Effects of lime on chemical forms of heavy metals under combined pollution of Cu, Cd, Pb and Zn in soils [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(2): 158-164(in Chinese). doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201902030
[14] 闫家普, 丁效东, 崔良, 等. 不同改良剂及其组合对土壤镉形态和理化性质的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(9): 1842-1849. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0187 YAN J P, DING X D, CUI L, et al. Effects of several modifiers and their combined application on cadmium forms and physicochemical properties of soil [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(9): 1842-1849(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0187
[15] 梁妮, 净婷菲, 李中文, 等. 不同钝化剂对土壤环境中重金属有效性和微生物群落的影响 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2021, 16(1): 177-187. LIANG N, JING T F, LI Z W, et al. Effects of different amendments on the availability of heavy metals and microbial communities in contaminated soils [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2021, 16(1): 177-187(in Chinese).
[16] 沈章军, 侯万青, 徐德聪, 等. 不同钝化剂对重金属在土壤-油菜中迁移的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(12): 2779-2788. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0397 SHEN Z J, HOU W Q, XU D C, et al. Effects of different immobilization materials on heavy metal migration in contaminated soil-rape [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(12): 2779-2788(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0397
[17] 张彦娟, 章明奎. 组配钝化剂对复合污染蔬菜地土壤重金属的钝化效果 [J]. 江西农业学报, 2020, 32(10): 121-124,130. doi: 10.19386/j.cnki.jxnyxb.2020.10.23 ZHANG Y J, ZHANG M K. Inactivation effect of mixed amendments on heavy metals in complex polluted vegetable soil [J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2020, 32(10): 121-124,130(in Chinese). doi: 10.19386/j.cnki.jxnyxb.2020.10.23
[18] 陈盾. 生物炭复配及硫改性对Cd污染农田土壤的修复效果研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2020. CHEN D. Study on the remediation effect of biochar compounding and sulfur modification on Cd contaminated farmland soil[D]. Yangzhou, China: Yangzhou University, 2020(in Chinese).
[19] 张新帅, 张红宇, 黄凯, 等. 石灰与生物炭对矿山废水污染农田土壤的改良效应[J]. 农业环境科学学报: 2021, 41(3): 481-491. ZHANG X S, ZHANG H Y, HUANG K, et al. Beneficial effects of lime and biochar application on farmland soil polluted by mine wastewater[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2022, 41(3): 481-491(in Chinese).
[20] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. BAO S D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis[M]. Beijing: Chinese Agriculture Press, 2000(in Chinese).
[21] 刘新. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2015. LIU X. Experimental guidance of Plant Physiology [M]. Beijing: Chinese Agriculture Press, 2015(in Chinese).
[22] CAKMAK I, STRBAC D, MARSCHNER H. Activities of hydrogen peroxide-scavenging enzymes in germinating wheat seeds [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 1993, 44(1): 127-132. doi: 10.1093/jxb/44.1.127 [23] HAMID Y, TANG L, HUSSAIN B, et al. Adsorption of Cd and Pb in contaminated gleysol by composite treatment of sepiolite, organic manure and lime in field and batch experiments [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 196: 110539. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110539 [24] BOLAN N, KUNHIKRISHNAN A, THANGARAJAN R, et al. Remediation of heavy metal(loid)s contaminated soils - To mobilize or to immobilize? [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 266: 141-166. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.12.018 [25] 黄连喜, 魏岚, 刘晓文, 等. 生物炭对土壤-植物体系中铅镉迁移累积的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(10): 2205-2216. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0740 HUANG L X, WEI L, LIU X W, et al. Effects of biochar on the migration and accumulation of lead and cadmium in soil-plant systems [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(10): 2205-2216(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0740
[26] ZHOU Z, XU Z H, FENG Q J, et al. Effect of pyrolysis condition on the adsorption mechanism of lead, cadmium and copper on tobacco stem biochar [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 187: 996-1005. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.268 [27] 安梅, 董丽, 张磊, 等. 不同种类生物炭对土壤重金属镉铅形态分布的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(5): 892-898. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1388 AN M, DONG L, ZHANG L, et al. Influence of different kinds of biochar on Cd and Pb forms in soil [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(5): 892-898(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1388
[28] WU W C, WU J H, LIU X W, et al. Inorganic phosphorus fertilizer ameliorates maize growth by reducing metal uptake, improving soil enzyme activity and microbial community structure [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 143: 322-329. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.05.039 [29] LU H L, WU Y X, LIANG P X, et al. Alkaline amendments improve the health of soils degraded by metal contamination and acidification: Crop performance and soil bacterial community responses [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 257: 127309. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127309 [30] WANG C R, HUANG Y C, ZHANG C B, et al. Inhibition effects of long-term calcium-magnesia phosphate fertilizer application on Cd uptake in rice: Regulation of the iron-nitrogen coupling cycle driven by the soil microbial community [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 416: 125916. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125916 [31] 马国泰, 杜红艳, 刘芝妨, 等. 猪粪施用量对土壤和辣椒中Cd和Pb积累的影响 [J]. 甘肃农业科技, 2021, 52(1): 28-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1463.2021.01.006 MA G T, DU H Y, LIU Z F, et al. Effect of pig manure application on Cd and Pb accumulation in soil and pepper [J]. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 52(1): 28-34(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1463.2021.01.006
[32] 曾凡健. 畜禽粪便堆肥钝化修复Pb/Cd污染土壤的潜力与强化研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020. ZENG F J. The study on the capacity and enhancement of immobilizing remediation of Pb/Cd contaminated soil using livestock manure composts[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2020(in Chinese).
[33] ZHOU W J, REN L W, ZHU L Z. Reducement of cadmium adsorption on clay minerals by the presence of dissolved organic matter from animal manure [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 223: 247-254. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.01.019 [34] LIU P, HU W Y, TIAN K, et al. Accumulation and ecological risk of heavy metals in soils along the coastal areas of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea: A comparative study of China and South Korea [J]. Environment International, 2020, 137: 105519. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105519 [35] 王逸群, 许端平, 薛杨, 等. Pb和Cd赋存形态与土壤理化性质相关性研究 [J]. 地球与环境, 2018, 46(5): 451-455. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2018.46.118 WANG Y Q, XU D P, XUE Y, et al. Correlation between fractionation content of pb, Cd and physico-chemical properties of contaminated soils [J]. Earth and Environment, 2018, 46(5): 451-455(in Chinese). doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2018.46.118
[36] 王玉婷, 王紫玥, 刘田田, 等. 钝化剂对镉污染土壤修复效果及青菜生理效应影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(9): 2395-2403. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020032505 WANG Y T, WANG Z Y, LIU T T, et al. Effects of amendments on remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil and physiological characteristics of pakchoi [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(9): 2395-2403(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020032505
[37] KRIKA F, AZZOUZ N, NCIBI M C. Adsorptive removal of cadmium from aqueous solution by cork biomass: Equilibrium, dynamic and thermodynamic studies [J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2016, 9: S1077-S1083. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2011.12.013 [38] HE Y B, HUANG D Y, ZHU Q H, et al. A three-season field study on the in situ remediation of Cd-contaminated paddy soil using lime, two industrial by-products, and a low-Cd-accumulation rice cultivar [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 136: 135-141. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.11.005 [39] PURAKAYASTHA T J, BERA T, BHADURI D, et al. A review on biochar modulated soil condition improvements and nutrient dynamics concerning crop yields: Pathways to climate change mitigation and global food security [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 227: 345-365. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.170 [40] HAMID Y, TANG L, HUSSAIN B, et al. Organic soil additives for the remediation of cadmium contaminated soils and their impact on the soil-plant system: A review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 707: 136121. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136121 [41] BARROW C J. Biochar: Potential for countering land degradation and for improving agriculture [J]. Applied Geography, 2012, 34: 21-28. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2011.09.008 [42] 杨淑颐. 生物炭对水稻土和黑土中Cd和Pb的生物有效性的影响[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2019. YANG S Y. Effect of biochar on bioavailability of Cd and Pb in paddy and black soil[D]. Yaan, China: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2019(in Chinese).
[43] 袁金华, 徐仁扣. 稻壳制备的生物质炭对红壤和黄棕壤酸度的改良效果 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2010, 26(5): 472-476. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2010.05.013 YUAN J H, XU R K. Effects of rice-hull-based biochar regulating acidity of red soil and yellow brown soil [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2010, 26(5): 472-476(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2010.05.013
[44] XU X Y, CAO X D, ZHAO L. Comparison of rice husk- and dairy manure-derived biochars for simultaneously removing heavy metals from aqueous solutions: Role of mineral components in biochars [J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 92(8): 955-961. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.03.009 [45] ZHAI X Q, LI Z W, HUANG B, et al. Remediation of multiple heavy metal-contaminated soil through the combination of soil washing and in situ immobilization [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 635: 92-99. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.119 [46] ALBERT H A, LI X, JEYAKUMAR P, et al. Influence of biochar and soil properties on soil and plant tissue concentrations of Cd and Pb: A meta-analysis [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 755: 142582. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142582 [47] 朱启东, 鲁艳红, 廖育林, 等. 施氮量对双季稻产量及氮磷钾吸收利用的影响 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(2): 183-188. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2019.02.029 ZHU Q D, LU Y H, LIAO Y L, et al. Effects of nitrogen application rates on yield and nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium uptake of double cropping rice [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(2): 183-188(in Chinese). doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2019.02.029
-



 下载:
下载: