-
核能作为当今新兴清洁能源,在实现“双碳”目标中发挥着不可或缺的作用[1]. 但核能的利用会大量累积高放射性核废物,目前处置高放废物的可行方案是深地质处置,建立高放废物处置库,减缓放射性核素的浸出和迁移[2 − 4],然而高放废物处置库中含有多种放射性核素,如铀、硒、镎、钚及锝等,包装容器在地下水多种作用耦合下易被腐蚀,使得上述放射性核素随地下水流动发生迁移,这些具有放射性和毒性双重污染的核素会严重影响和污染地下水[5 − 11]. 因此,抑制或减缓放射性核素的浸出和迁移对长期安全使用核能具有重要研究意义[12]. 高放废物中的U(Ⅵ)主要以铀酰离子(UO22+)和含铀络合物(UO22+与OH−和CO32−形成的溶解度较高的络合物,如UO2(CO3)22−、UO2OH+等)的形式存在,而长寿命的Se(Ⅳ)通常以SeO32−和H2SeO3(aq)为主要形式存在,以上形式的U(Ⅵ)和Se(Ⅳ)随地下水发生迁移后,会扩大污染范围,因此将U(Ⅵ)和Se(Ⅳ)还原成溶解度极低的UO2和Se(0)、Se(-Ⅰ)及Se(-Ⅱ)[13 − 15],能有效阻止U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)在地下水中的迁移,保障地下水安全[16]. 针对高放废物处置库周围地下水开展固定和净化U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)污染的研究,成为亟需解决的环境问题[17]. 近年来常用的固化/稳定化技术包括水泥基固化/稳定化技术,地质聚合物基固化/稳定化技术,化学药剂稳定化技术以及微生物诱导矿化稳定化技术等[18]. 已有报道表明[14 − 15],无机、有机、复合/纳米、框架类材料可用于去除U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ),其中,纳米零价金属材料(铁、镍、铜、铝等)具有无毒无害、还原性好、节能高效、绿色环保等优势,且对废水中的重金属有较好的去除效果而备受国内外学者的广泛关注[19 − 20]. 但传统的纳米金属具有易团聚、沉降、溶解及失活等局限性,且受限于自身理化性质和环境因素[21],严重影响其对污染物的处理效果,而对其改性处理可克服其自身缺陷并增加其对污染物的去除能力. 负载型纳米零价金属可以提高纳米金属自身的活性和回收率,减少对生态环境的二次污染[19 − 20]. 本课题组采用液相还原法制备的纳米零价镍(nZVNi),对U(Ⅵ)的去除率高达98.44%[22]. 维生素B12(VB12)对nZVNi还原重金属具有催化协同作用,VB12的加入增强了nZVNi的电子传递能力,提高了nZVNi对U(Ⅵ)的去除能力,VB12负载nZVNi(VB12@nZVNi)对U(Ⅵ)的去除率提高到98.54%[23].
本研究用液相还原法制备了VB12@nZVNi,并开展VB12@nZVNi固定地下水中U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的动态柱试验研究,该研究对高放废物处置库周围地下水修复具有一定的现实意义和应用价值.
-
主要试剂:硝酸、盐酸、亚硒酸钠、硝酸铀酰、硼氢化钾、氯化镍、氯化钙、氯化镁、氯化钾、硝酸钠、氟化钠、硫酸钠、碳酸钠、维生素B12,以上试剂均为市售分析纯,购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司及山西亨瑞达制药有限公司.
主要仪器:全温振荡箱(THZ-C-1),太仓市试验设备厂;原子吸收分光光度计(WFX-200),北京瑞利分析仪公司;数显恒温磁力搅拌器(85-2),杭州仪表电机有限公司;精密pH计(PHS-3C),智光仪器仪表公司;冷冻真空干燥箱(FD-1D-50),上海精若科学仪器公司;蠕动泵(BT1002J)保定兰格恒流泵有限公司;扫描电子显微镜(NNS-450),捷克FEI公司.
-
VB12负载纳米零价镍(VB12@nZVNi)的制备参考文献[23].
-
取等体积浓度均为100 mg·L−1的U(Ⅵ)溶液和Se(Ⅳ)溶液混匀后定容并校准,使得U(Ⅵ)和Se(Ⅳ)的浓度均达到10 mg·L−1,即得到试验所需的U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)溶液.
-
采用静态试验探究了VB12@nZVNi对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的去除效果,向3个锥形瓶中分别加入25 mL 10 mg·L−1的U(Ⅵ)溶液、Se(Ⅳ)溶液和U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)溶液,然后依次分别加入固液比(M/V,材料投加量与溶液体积的比)为0.2 g·L−1、0.3 g·L−1和0.3 g·L−1的VB12@nZVNi复合材料,用氢氧化钠和稀盐酸调节溶液pH值到试验所需值,在合适温度下振荡一定时间后,4000 r·min−1的速率离心2 min,用分光光度法测定上清液中U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的浓度,并根据公式(1)和(2)计算U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的去除率,探讨pH、反应温度和时间对去除效果的影响.
-
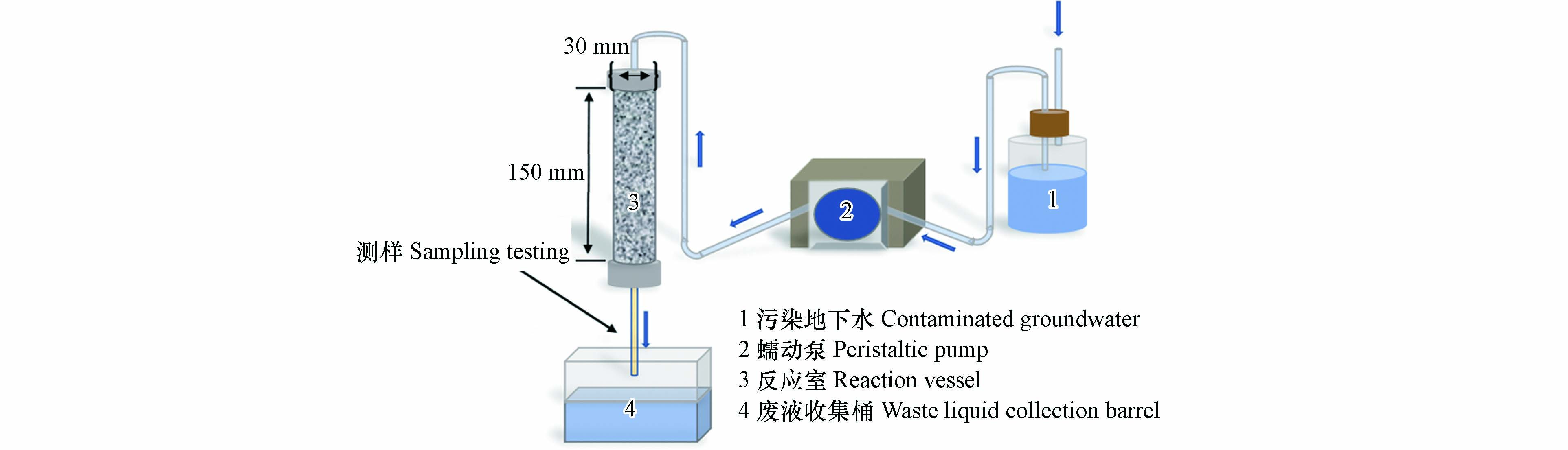
试验装置如图1所示,将5 g VB12@nZVNi复合材料与100 g粒径为0.25—0.50 mm的河砂混合均匀后填充至试验柱,试验用水选用去离子水配制模拟含U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)污染地下水,调节pH至3.5,离子含量见表1. 用蠕动泵调节流速为5.0 mL·min−1进行动态吸附试验,每间隔1 h取5 mL溶液测U(Ⅵ)、Se(Ⅳ)及Ni2+的浓度,当U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的出口浓度趋近初始浓度且保持稳定后,在226 h开始注入去离子水进行水洗,当U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的出口浓度趋近零且保持稳定后,采用pH=2.0的盐酸溶液对试验柱解析,探讨VB12@nZVNi固定模拟地下水中U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的效果.
-
样品表面形貌采用捷克FEI公司NNS-450型扫描电子显微镜(SEM-EDS)进行表征分析.
-
利用分光光度法测得溶液中U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的吸光度,按照下列公式计算U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的浓度、去除率、饱和吸附容量和浸出量. 通过原子吸收火焰法测得溶液中Ni2+的吸光度并计算其浓度和浸出量,探究VB12@nZVNi固定U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的性能. 计算公式如下:
式中:At—吸光度,Abs;Ct—浓度,mg·L−1;a,b—标准曲线线性方程参数;C0—初始浓度,mg·L−1; R—去除率,%;Q—流速,mL·min−1;q0—饱和吸附容量,mg·g−1; m—VB12@nZVNi材料用量,g;M—浸出量,mg.
-
Yoon-Nelson模型可以忽略材料用量、模拟地下水流速等情况,用来探究动态试验柱的吸附速率常数和半穿透率[24]. 计算公式如下:
式中:KYN—Yoon-Nelson速率常数,min−1;τ—半穿透率,min.
-
Thomas模型通常用于描述动态吸附试验的吸附曲线,并计算动态试验柱的饱和吸附容量以及吸附速率常数[24 − 25]. 计算公式如下:
式中:KTh—Thomas速率常数,mL∙min−1∙mg−1.
-
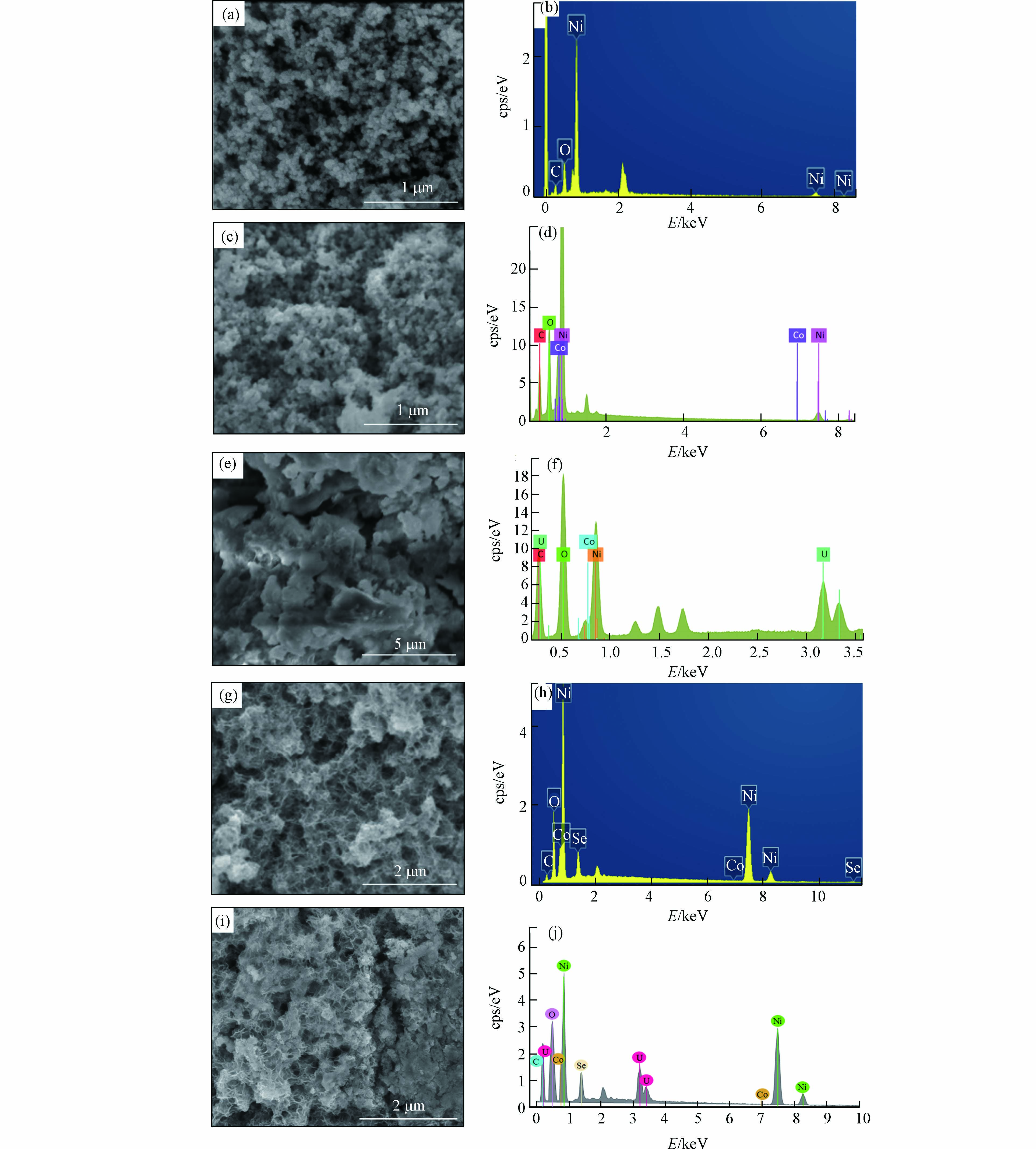
对纳米零价镍负载VB12前后,以及VB12@nZVNi材料吸附U(Ⅵ)、Se(Ⅳ)后的样品表面形貌变化和元素组成进行表征分析,结果如图2所示.
图2(a) 和(b) 是纳米零价镍的SEM和EDS图谱. 从图2可以看出,新制备的纳米零价镍颗粒呈链球状,发生了一定的团聚. 图2(c) 和(d) 是维生素B12负载后的纳米零价镍的SEM和EDS图谱,从图可以看出,维生素B12加入后纳米零价镍的团聚现象有所改善,但并不十分明显. 图2(e) 和(f) 是VB12@nZVNi吸附U(Ⅵ)后的SEM和EDS图谱,图2(g) 和(h) 是VB12@nZVNi吸附Se(Ⅳ)后的SEM和EDS图谱,图2(i) 和(j) 是VB12@nZVNi吸附U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)后的SEM和EDS图谱,从图可以看出,材料吸附U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)后,球状颗粒基本消失,表面分别呈不规则团状和疏松孔状,EDS图谱中分别出现了U和Se元素. 说明U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)被吸附在材料的表面,VB12@nZVNi复合材料可以应用于固定地下水中的U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ).
-
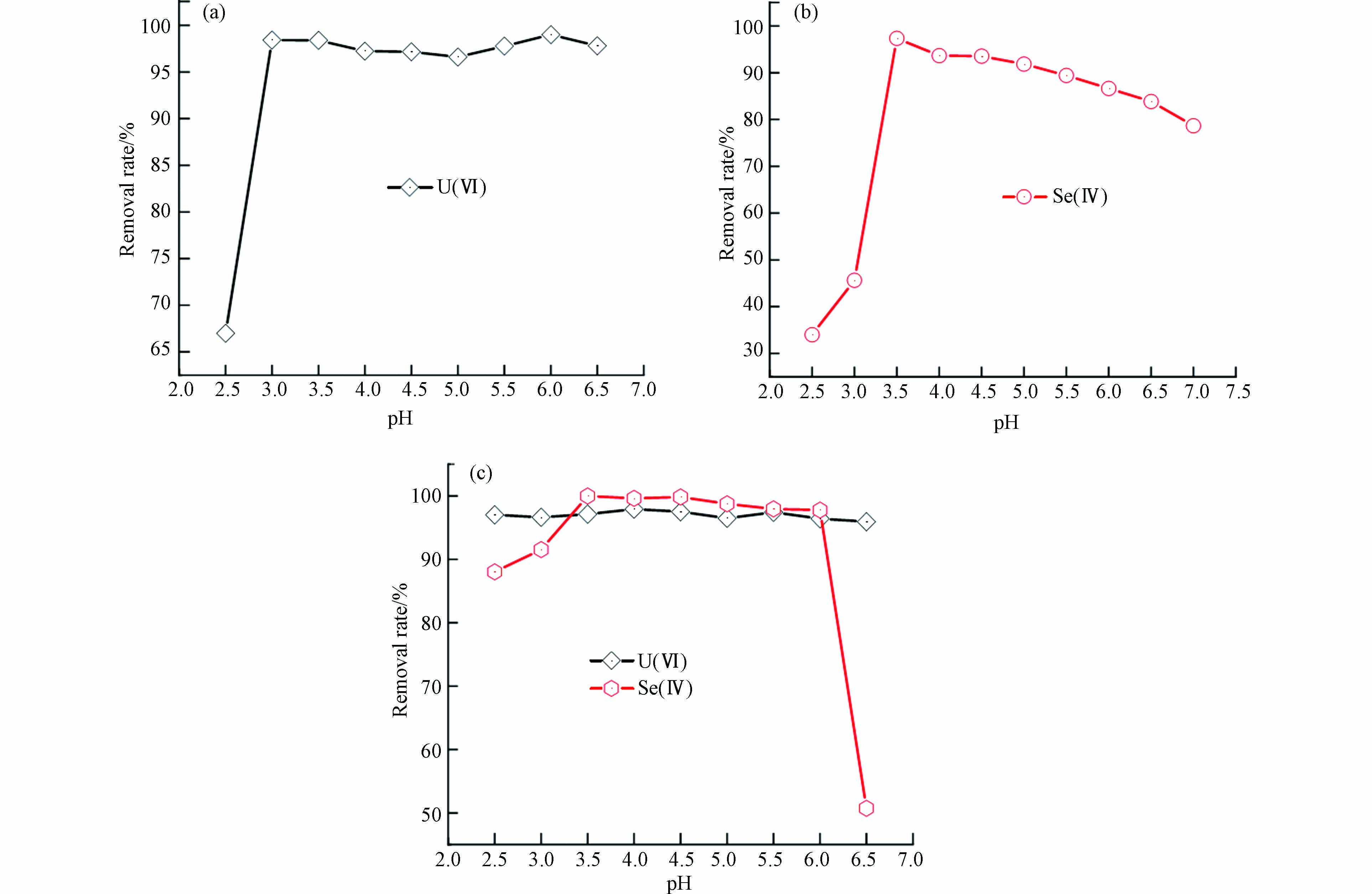
pH对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)去除效果的影响结果如图3所示. 从图3(a) 可以看出,当溶液pH=2.5时,U(Ⅵ)的去除率仅为66.99%,当pH≥3后,去除率急速上升到95.00%以上,并在pH=6.0时达到最大值99.00%,表明pH升高有利于材料去除U(Ⅵ). 原因可能是在酸性条件下材料被腐蚀,同时酸性溶液中H+与UO2+产生竞争效应,材料与UO2+发生反应的活性位点减少,导致U(Ⅵ)的去除效果较差[14,23]. 图3(b) 显示,在pH≤3时,Se(Ⅳ)的去除率较低,随着pH升高,材料的去除效果显著提高. 原因是在强酸下,溶液中Se(Ⅳ)主要以H2SeO3(aq)的形式存在,其表面电荷较少,与材料的静电作用较小,不易吸附在材料表面而被去除[15,23]. pH升高后,材料将部分H+转化为强还原性的原子态H,提高对Se(Ⅳ)的还原能力,所以Se(Ⅳ)的去除效果变好. 但pH的持续提高会导致材料表面电负性增强,材料与溶液中的HSeO3−发生静电排斥,去除效果逐渐降低. 图3(c) 显示,U(Ⅵ)和Se(Ⅳ)在同一溶液中材料对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的去除效果受pH影响与单一溶液[图3(a) 和(b)]较为接近,当pH=3.5时,VB12@nZVNi对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的去除率分别为97.13%、100.00%. 综合考虑,后续的动态试验选择pH=3.5进行原位固定U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的研究.
-
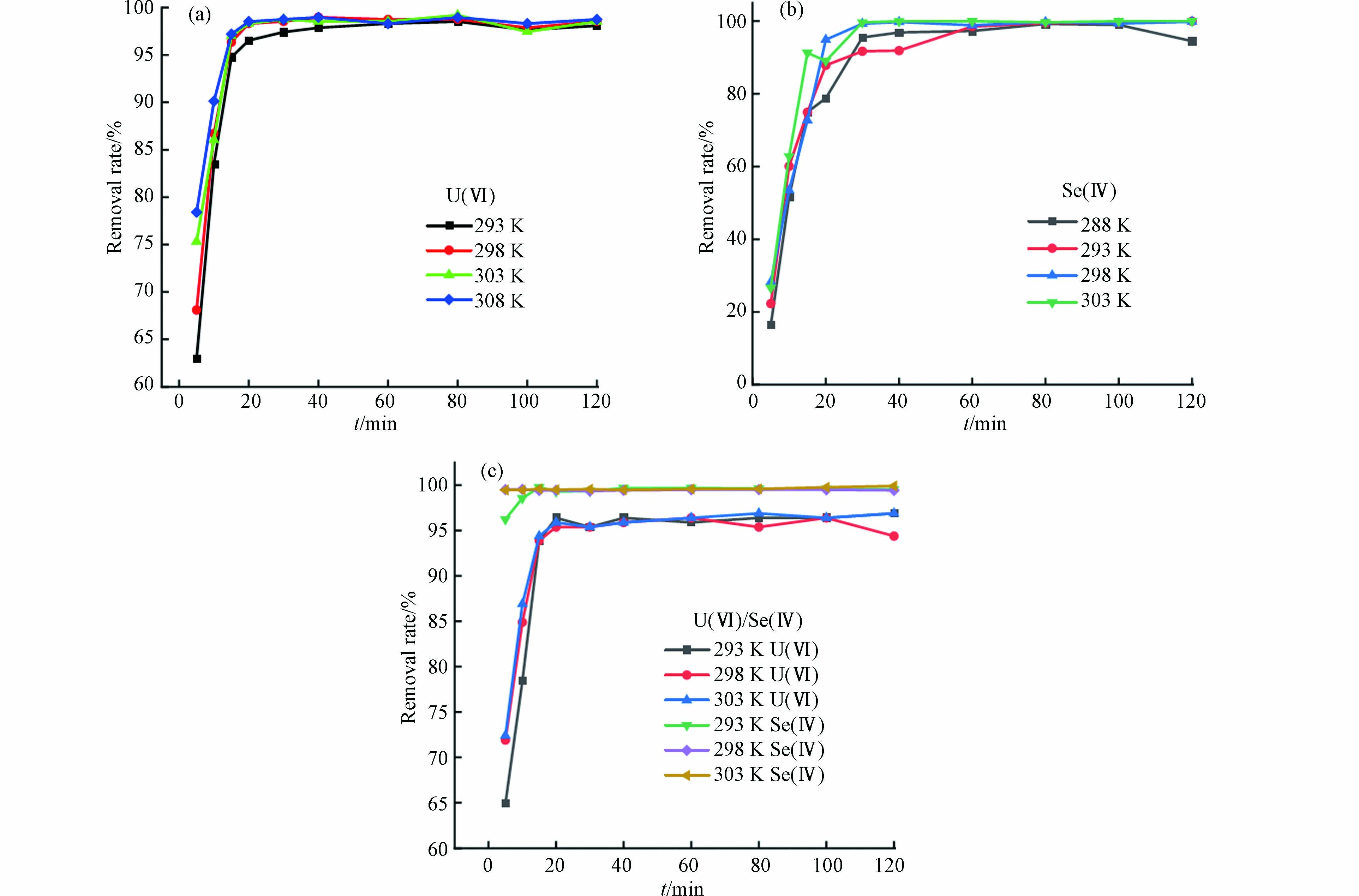
温度和时间对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)去除效果的影响结果如图4所示. 从图4可以看出,材料受温度影响较小,在293 K到303 K之间去除率接近,反应时间延长对材料的吸附性能有一定影响,但在20 min就可达到动态吸附平衡,表明材料对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的去除速度较快. 综合分析,后续动态试验中,选择室温(298 K)下进行动态试验.
-
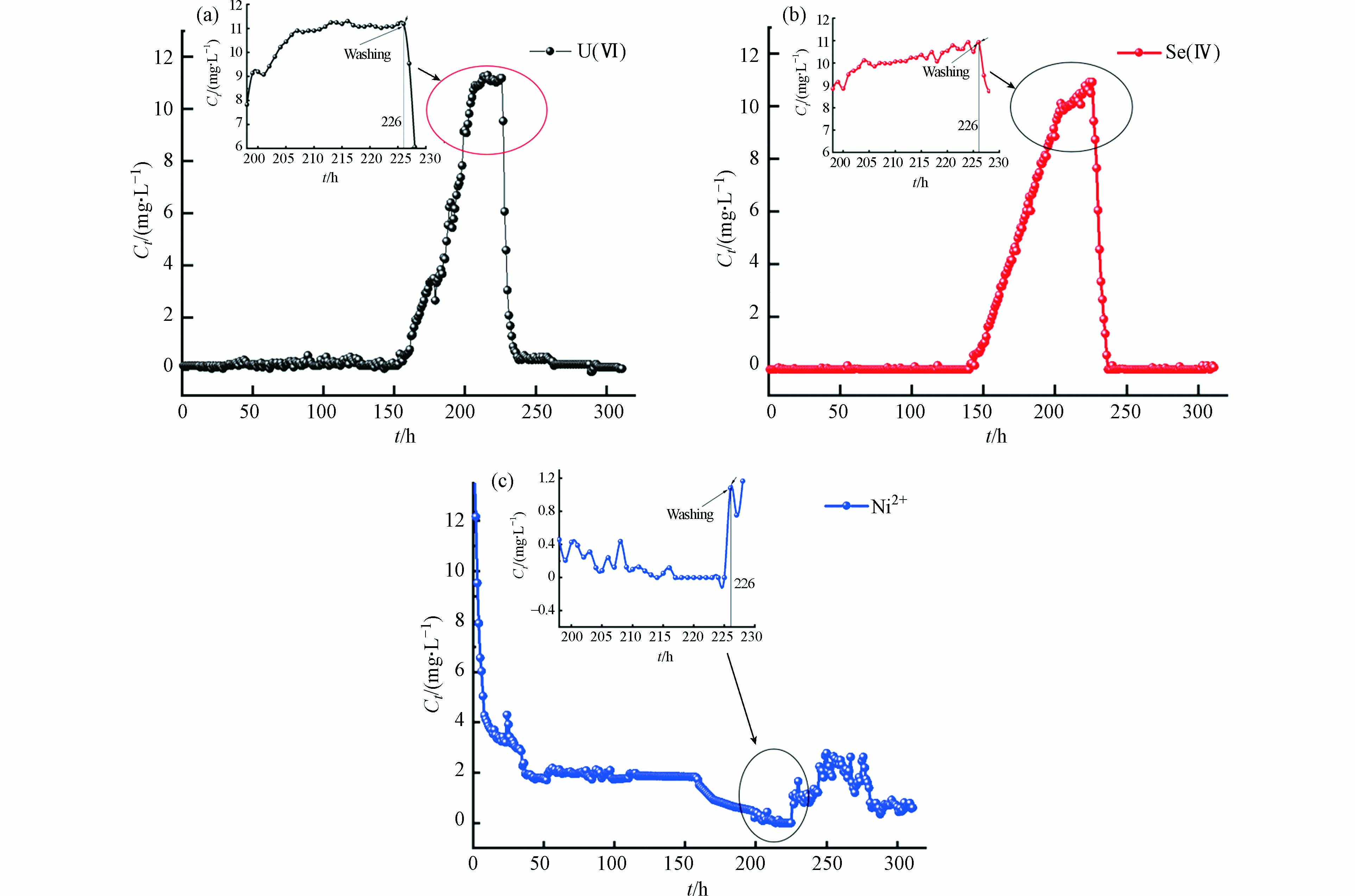
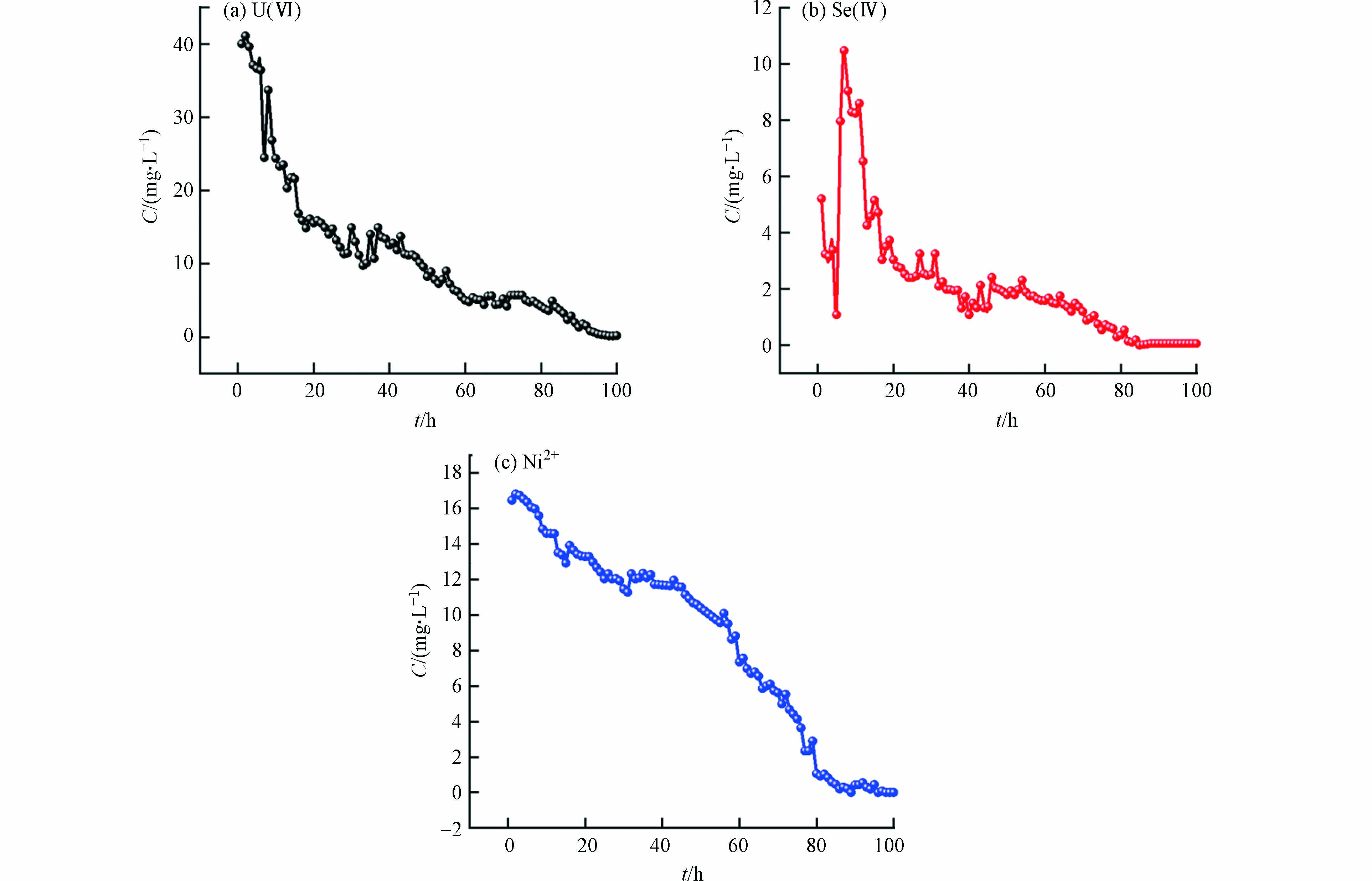
为了探究材料固定地下水中U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的效果,开展动态柱试验,试验柱流出液中U(Ⅵ)、Se(Ⅳ)及Ni2+的浓度随时间的变化如图5所示. 动态吸附试验数据如表2所示. 从图5(a) 可以看出,材料在前期对U(Ⅵ)的去除效果较好,能较长时间保持约100%的去除率. 柱体流出液U(Ⅵ)的浓度在204 h后与模拟地下水物质浓度接近并保持相对稳定,即U(Ⅵ)的穿透时间大概在204 h. 从图5(b) 可以看出,材料在前期对Se(Ⅳ)的去除效果明显,也能较长时间保持约100%的去除率. 柱体流出液Se(Ⅳ)的浓度在210 h后与模拟地下水物质浓度接近并保持相对稳定,即Se(Ⅳ)的穿透时间大概在210 h. 根据公式(3)计算得到U(Ⅵ)的饱和吸附容量q0,exp(U)为106.96 mg·g−1,Se(Ⅳ)的q0,exp(Se)=103.92 mg·g−1. 在穿透后柱体流出液U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)浓度有小幅度上涨,可能是模拟地下水pH为3.5呈酸性,对固定的U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)有一定的洗脱作用[23]. 图5(c) 流出液中Ni2+浓度在较长时间内能保持在大约2 mg·L−1以下,只有少部分镍元素被酸性污染地下水冲洗迁移,证明材料与污染物反应后浸出较少,说明材料有较强的浸出稳定性. 通过水洗试验证明材料对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)固定效果较好,模拟地下水对材料固定的U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)洗脱能力较弱,U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)能较好的固定在试验柱中.
-
(1) Yoon-Nelson模型
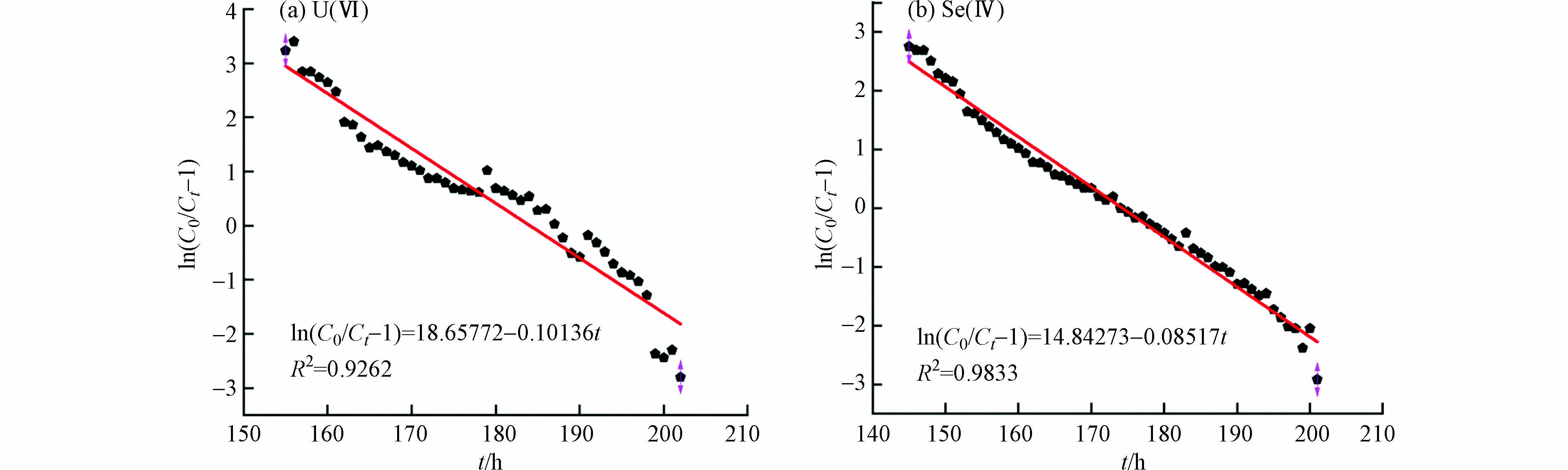
利用Yoon-Nelson模型对试验数据进行拟合,结果如图6和表3所示. 从图6和表3可以看出,Yoon-Nelson模型拟合曲线相关系数R2均超过0.94,模型适用于描述VB12@nZVNi材料对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)动态吸附过程[24]. KYN与τ根据公式(5)计算得到,半穿透率τ(U)、τ(Se)的理论半穿透率与实际值接近,说明VB12@nZVNi材料对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)污染地下水长期有较好的固定效果. 同时KYN(U)>KYN(Se),说明Se(Ⅳ)在试验柱的穿透能力更弱,材料吸附Se(Ⅳ)的活性位点更多,延长了Se(Ⅳ)在试验柱的穿透和吸附饱和时间.
(2)Thomas模型
利用Thomas模型对试验数据进行拟合,结果如图7和表4所示. 从图7和表4可以看出,Thomas模型拟合的相关系数R2>0.92,表明模型能用于模拟VB12@nZVNi对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的动态吸附. 根据公式(6)计算得到U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)对应的KTh(U)、q0(U)、KTh(Se)和q0(Se),q0(U)和q0(Se)与前文的q0,exp(U)=106.96 mg·g−1、q0,exp(Se)=103.92 mg·g−1相近. KTh(U)>KTh(Se),且Se(Ⅳ)的浸出量更低,再次验证了材料对Se(Ⅳ)的固定能力较强,与Yoon-Nelson模型分析一致[25]. 通过前文分析与Thomas模型拟合证实VB12@nZVNi材料对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)污染地下水有较好的固定能力.
-
为了进一步探究VB12@nZVNi固定地下水中U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的效果,采用解析试验来探究U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)在VB12@nZVNi上的稳定性,结果如图8所示. 从图8可以看出,pH=2.0的盐酸溶液对动态柱有较强的洗脱效果,酸性溶液的注入使得吸附材料表面固定的U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)被快速洗脱,随着溶液快速迁移,U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的浸出量分别为328.22 mg、63.00 mg,表明酸性环境不利于材料对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的固定.
-
本文通过动态试验柱,探究VB12@nZVNi材料对地下水中U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的固定效果,并用盐酸溶液进行了解析试验,得到以下结论:
1) 静态吸附试验表明:材料对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的去除易受pH的影响,当pH=3.5时,VB12@nZVNi对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的去除率分别为97.13%、100.00%,反应温度对材料影响较小,材料在20 min达到对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的吸附平衡.
2) 动态柱试验表明:VB12@nZVNi对地下水中U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的固定效果较好,对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的饱和吸附容量分别为106.96 mg·g−1、103.92 mg·g−1,且材料能在较长时间内保持稳定.
3) Yoon-Nelson、Thomas模型的拟合结果表明:Yoon-Nelson、Thomas模型能用于描述VB12@nZVNi对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的动态吸附过程. 理论参数与实际值相近,Se(Ⅳ)在试验柱的穿透能力更弱,材料对Se(Ⅳ)的固定能力更强. VB12@nZVNi动态柱的q0与试验值q0,exp相近,证实VB12@nZVNi对污染地下水中的U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)具有长期较好的固定效果.
4) 解析试验结果表明:pH=2.0的酸性条件下材料固定的U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的浸出量分别为328.22 mg、63.00 mg,U(Ⅵ)更易被洗脱且迁移能力较强.
VB12负载纳米零价镍固定地下水中U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的效能研究
Efficacy of VB12 loaded on nano-zero-valent nickel immobilizes U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ) in groundwater
-
摘要: 本研究用液相还原法制备了VB12负载纳米零价镍(VB12@nZVNi)复合材料,通过动态试验探讨了复合材料原位固定地下水中U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的固定效果. 运用Thomas、Yoon-Nelson模型对所得试验数据进行拟合,讨论VB12@nZVNi固定U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的性能. 结果表明,VB12@nZVNi材料对模拟U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)污染地下水有着较好的固定效果,对U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)的最大吸附量分别为106.96 mg·g−1、103.92 mg·g−1. Yoon-Nelson、Thomas模型符合其动态吸附过程,且理论吸附量和半穿透率与实际值比较接近. 因此,VB12@nZVNi可以作为一种有前景的固定材料,用于含U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)地下水的固定和净化处理.Abstract: In this study, a composite material consisting of nano-zero-valent nickel (nZVNi) loaded with VB12 (VB12@nZVNi) was synthesized using the liquid phase reduction method. This composite material was then utilized as a fixed material to investigate its effectiveness in immobilizing U(Ⅵ) and Se(Ⅳ) in groundwater through dynamic testing. The experimental data was analyzed using the Thomas and Yoon-Nelson models to evaluate the effectiveness of VB12@nZVNi in immobilizing U(Ⅵ) and Se(Ⅳ). The results indicate that VB12@nZVNi demonstrates excellent performance in fixing and removing U(Ⅵ) and Se(Ⅳ) from simulated groundwater contaminated with these elements. The maximum adsorption capacities of U(Ⅵ) and Se(Ⅳ) were determined to be 106.96 mg·g−1 and 103.92 mg·g−1, respectively. The Yoon-Nelson and Thomas models demonstrated consistent behavior with the dynamic adsorption process, indicating the accuracy of the models in predicting the theoretical adsorption capacity and semi-penetration rate. These results suggest that VB12@nZVNi holds great promise as an effective material for immobilizing and purifying U(Ⅵ) and Se(Ⅳ)-containing groundwater.
-
Key words:
- Vitamin B12 /
- nano zero-valent nickel /
- load /
- U(Ⅵ) /
- Se(IV) /
- groundwater.
-

-
图 2 不同样品的SEM和EDS图 (a)和(b) nZVNi、(c)和(d) VB12@nZVNi、(e)和(f) VB12@nZVNi吸附U(Ⅵ)后、(g)和(h) VB12@nZVNi吸附Se(Ⅳ)后、(i)和(j) VB12@nZVNi吸附U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)后
Figure 2. SEM and EDS of different samples (a) and (b) nZVNi, (c) and (d) VB12@nZVNi, (e) and (f) VB12@nZVNi after adsorption U(Ⅵ), (g) and (h) VB12@nZVNi) after adsorption Se(Ⅳ)、(i) and (j) VB12@nZVNi) after adsorption U(Ⅵ)/Se(Ⅳ)
表 1 污染地下水的组成
Table 1. The composition of contaminated groundwater
离子组成
Ionic composition初始浓度/(mg·L−1)
Initial concentration C0Se(Ⅳ) 10.0 U(Ⅵ) 10.0 Na+ 68.5 K+ 50.4 Ca2+ 69.4 Mg2+ 24.0 F− 0.75 NO3− 25.4 CO32− 127.5 SO42− 96.0 表 2 动态吸附试验数据
Table 2. Dynamic adsorption experimental data
污染物
Contaminant进水流速Q/(mL·min−1)
Inlet velocity Q进水浓度C0/(mg·L−1)
Influent concentration C0穿透时间t/h
Penetration time饱和吸附容量
q0,exp/(mg·g−1)
Saturated sorption capacity q0,expU(Ⅵ) 5 10 204 106.96 Se(Ⅳ) 5 10 210 103.92 表 3 Yoon-Nelson模型拟合曲线各参数
Table 3. The Yoon-Nelson model fits the parameters of the curve
污染物
Contaminant进水流速Q/(mL·min−1)
Inlet velocity Q进水浓度C0/(mg·L−1)
Influent concentration C0Yoon-Nelson 相关系数
R2KYN/ min−1 半穿透率τ /h U(Ⅵ) 5 10 0.08625 185.9 0.94291 Se(Ⅳ) 5 10 0.08393 174.4 0.98611 表 4 Thomas模型拟合曲线各参数
Table 4. The Thomas model fits the parameters of the curve
污染物
Contaminant进水流速Q/(mL·min−1)
Inlet velocity Q进水浓度C0/(mg·L−1)
Influent concentration C0Thomas 相关系数
R2KTh/(mL∙min−1∙mg−1) q0/(mg·g−1) U(Ⅵ) 5 10 0.16890 110.444 0.9262 Se(Ⅳ) 5 10 0.14195 104.563 0.9833 -
[1] 屈凡玉, 李言瑞, 杨彬. 积极安全有序发展核电 助力“双碳”目标顺利实现[J]. 能源, 2022(12): 38-43. QU F Y, LI Y R, YANG B. Actively, safely and orderly developing nuclear power to help achieve the goal of “double carbon”[J]. Energy, 2022(12): 38-43 (in Chinese).
[2] KONDO Y, GOTO T, SEKINO T. Sr2+ sorption property of seaweed-like sodium titanate mats: Effects of crystallographic properties[J]. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(30): 18676-18684. doi: 10.1039/D1RA03088D [3] 肖雨生. 中国核电发展与乏燃料贮存及后处理的关系[J]. 电工技术, 2020(18): 24-25,57. XIAO Y S. Relationship between China’s nuclear power development and spent fuel storage and reprocessing[J]. Electric Engineering, 2020(18): 24-25,57 (in Chinese).
[4] 孙学智, 罗朝晖. 全球乏燃料后处理现状与分析[J]. 核安全, 2016, 15(2): 13-16. SUN X Z, LUO Z H. Status of global spent fuel reprocessing[J]. Nuclear Safety, 2016, 15(2): 13-16 (in Chinese).
[5] 王驹, 陈伟明, 苏锐, 等. 高放废物地质处置及其若干关键科学问题[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(4): 801-812. WANG J, CHEN W M, SU R, et al. Geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste and its key scientific issues[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(4): 801-812 (in Chinese).
[6] ANDERSSON J, ROBINSON P, IMPEY M. Implications of rock structure on the performance in the near field of a nuclear waste repository[J]. Engineering Geology, 1998, 49(3/4): 195-200. [7] CASTAING R. Un modele simple pour la migration de radionucleides par transport colloidal dans un milieu fracture[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1991, 125(1/2): 55-92. [8] WANG L T, CHENG J F, BAO C Y, et al. Simulation of nuclide migration in a middle- and low-level radioactive waste repository based on GMS[J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2022, 331(5): 2159-2167. doi: 10.1007/s10967-022-08260-x [9] WEI G L, HAN W H, SHU X Y, et al. Heavy-ion irradiation effects on uranium-contaminated soil for nuclear waste[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 405: 124273. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124273 [10] LI L N, MA W, SHEN S S, et al. A combined experimental and theoretical study on the extraction of uranium by amino-derived metal–organic frameworks through post-synthetic strategy[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(45): 31032-31041. [11] KOU J S, WEI X Y, WU H, et al. Efficient adsorptive and reductive removal of U(VI) and Se(IV) using porous hexagonal boron nitride supported nanoscale iron sulfide: Performance and mechanism[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 359: 119355. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2022.119355 [12] WINTHER K H, RAYMAN M P, BONNEMA S J, et al. Selenium in thyroid disorders—Essential knowledge for clinicians[J]. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 2020, 16(3): 165-176. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0311-6 [13] CUI D, LOW J, RONDINELLA V V, et al. Hydrogen catalytic effects of nanostructured alloy particles in spent fuel on radionuclide immobilization[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2010, 94(1/2): 173-178. [14] JUN B M, LEE H K, PARK S, et al. Purification of uranium-contaminated radioactive water by adsorption: A review on adsorbent materials[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 278: 119675. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119675 [15] LICHTFOUSE E, MORIN-CRINI N, BRADU C, et al. Methods for selenium removal from contaminated waters: A review[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2022, 20(3): 2019-2041. doi: 10.1007/s10311-022-01419-8 [16] HU B W, YE F, REN X M, et al. X-ray absorption fine structure study of enhanced sequestration of U(Ⅵ) and Se(Ⅳ) by montmorillonite decorated with zero-valent iron nanoparticles[J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2016, 3(6): 1460-1472. doi: 10.1039/C6EN00421K [17] ZHAO B, SUN Z X, LIU Y J. An overview of in situ remediation for nitrate in groundwater[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 804: 149981. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149981 [18] 曾映达, 程银汉, 瞿广飞, 等. 固体废物中重金属的固化/稳定化技术研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(6): 2032-2047. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021122704 ZENG Y D, CHENG Y H, QU G F, et al. Review on solidification/stabilization of heavy metals in solid waste[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(6): 2032-2047 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021122704
[19] 王杨. 岩棉负载纳米零价金属去除溶液中U(Ⅵ)的性能与机理研究[D]. 抚州: 东华理工大学, 2022. WANG Y. Study on the performance and mechanism of removing U(Ⅵ) from solution by nano-zero-valent metal loaded on rock wool[D]. Fuzhou: East China Institute of Technology, 2022 (in Chinese).
[20] CURCIO G M, LIMONTI C, SICILIANO A, et al. Nitrate removal by zero-valent metals: A comprehensive review[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(8): 4500. doi: 10.3390/su14084500 [21] 韩泽蓉, 缪爱军. 金属纳米颗粒的环境行为及其与藻类的相互作用概述[J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(5): 1466-1483. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021112302 HAN Z R, MIAO A J. Environmental behavior of metal nanoparticles and their interactions with planktonic algae: A review[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(5): 1466-1483 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021112302
[22] 陈玉洁, 李小燕, 刘学, 等. 纳米零价镍去除溶液中U(Ⅵ)的研究[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2019(2): 71-75. CHEN Y J, LI X Y, LIU X, et al. Study on removal of U(Ⅵ)in aqueous solution with nano-zero-valent nickel[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2019(2): 71-75 (in Chinese).
[23] 付晓辉, 王昱莹, 何登武, 等. 维生素B12改性纳米零价镍去除溶液中U(Ⅵ)的性能[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2021(10): 90-95. FU X H, WANG Y Y, HE D W, et al. Removal of U(Ⅵ)from solution by nano-zero-valent nickel modified by vitamin B12[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2021(10): 90-95 (in Chinese).
[24] LI S, WU Y, NIE F Y, et al. Remediation of nitrate contaminated groundwater using a simulated PRB system with an La–CTAC–modified biochar filler[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2022, 10: 986866. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.986866 [25] LI S, YANG M X, WANG H, et al. Dynamic characteristics of immobilized microorganisms for remediation of nitrogen-contaminated groundwater and high-throughput sequencing analysis of the microbial community[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 267: 114875. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114875 -



 下载:
下载: