-
Bare BPs是一种新型二维材料,具有高载流子迁移率[1]、强大的光吸收特性[2]、高比表面积以及各向异性[1, 3]等特性,目前已经应用于多个领域,如太阳能电池[4-5]、场效应晶体管[6-8]、传感器[9]和环境[10]。随着Bare BPs的广泛应用,Bare BPs的环境风险和潜在危害需要进行系统研究。目前有研究报道了Bare BPs的暴露导致各种类型哺乳类动物细胞的损伤[11-12]和死亡[13]。此外,Bare BPs还显示出了对环境生物的毒性,例如,Bare BPs对大肠杆菌和枯草芽孢杆菌的毒性[14] 、嗜热链球菌生长的抑制[15]以及对正常藻类生长的干扰[16]。由于Bare BPs具有高的理论比表面积和疏水表面进入到水环境后Bare BPs可能与有机污染物发生吸附作用,从而改变两者的迁移规律和环境风险,因此,探究Bare BPs对有机污染物的吸附行为对Bare BPs的环境风险评估有重要意义。
迄今为止,Bare BPs在水性环境中对有机污染物吸附的研究有限。Zhao等[10]报道了两种染料在Bare BPs的吸附行为,研究发现Bare BPs由于其褶皱机制具有高效吸附能力。然而,Bare BPs对其他种类有机污染物的吸附行为未见报道。
双酚A(BPA)是一种内分泌干扰物,主要用作生产聚碳酸酯塑料和环氧树脂的中间体[17-18]。 从2013年到2019年,全球BPA产量预计将以4.6%的年增长率增长[19]。 BPA的大量生产和频繁使用导致其在自然环境中的持续释放和广泛分布[18, 20]。
因此,本文以Bare BPs作为吸附剂,以BPA作为模型吸附质,利用吸附动力学模型和吸附等温模型,研究了Bare BPs对BPA的吸附行为,研究了不同的环境因素,包括pH、温度对Bare BPs吸附BPA的影响,结合透射电镜和原子力显微镜等手段进行了机制探讨。
-
BPA购自Maya Reagent公司,纯度≥99%,物理性质见表1。实验室用水为 18.25 MΩ·cm的超纯水。
-
黑磷的制备:将600 mg的红磷、136 mg的Sn和44 mg的SnI4添加到石英管底部,然后使用氢氧喷枪边抽真空边密封。将石英管放置马弗炉中加热至600 ℃,并在此温度下保持24 h后降温冷却。获得具有金属光泽的块状黑色晶体,净化去除未反应完的红磷、Sn和SnI4。
Bare BPs的制备:将长度约1 cm的块状黑磷晶体通过铜胶带电连接至高压电源设备。将Pt丝用作对电极,并与黑磷平行放置,固定距离为2 cm。剥离在1 mol·L−1 H2SO4中进行,通过向阳极施加+5 V电压。在剥离过程始终通入氩气,可以通过从晶体中缓慢释放细颗粒溶液并将溶液从透明的白色逐渐着色为黄色、橙色来显现剥离。收集剥落的材料,使用真空过滤用超纯水洗涤至中性。
Bare BPs表面形态分析采用透射电子显微镜(TEM,jeol2100f);采用原子力显微镜观察(AFM,布鲁克)观察Bare BPs的形貌以及尺寸大小。
-
吸附实验在带有特氟隆衬里的螺帽的40 mL棕色玻璃小瓶中进行。将100 mg·L−1的BPA原液溶解在用200 mg·L−1的NaN3(抑制微生物生长)和0.02 mol·L−1的NaCl(控制吸附过程中离子强度)配制成的背景液中,稀释一系列浓度,范围从1—50 mg·L−1,然后加入2mL Bare BPs悬浮液(浓度为50 mg·L−1)。实验中所需要的背景液、BPA溶液和Bare BPs悬浮液均通入氩气保护。然后于(25±1)°C和160 r·min−1条件下避光振荡,直至24 h后吸附达到平衡。平衡后,将所有小瓶以3000 r·min−1离心10 min,取1 mL上清液,通过孔径为0.22 μm的膜过滤,采用高效液相色谱检测。包括空白在内的所有实验均一式两份进行。
吸附动力学实验,选择初始浓度为50 mg·L−1的BPA,分别在5、10、20、40、60、120、240、360 min内取样测BPA浓度, Bare BPs悬浮液浓度为80 mg·L−1。pH影响实验采用0.1mol·L−1的HCl或NaOH调节pH值为2—11,BPA初始浓度为10 mg·L−1,Bare BPs悬浮液浓度为80 mg·L−1。温度影响实验考察5 ℃(Bare BPs悬浮液浓度为50 mg·L−1)、15 ℃(Bare BPs悬浮液浓度为100 mg·L−1)和25 ℃的3个梯度。
-
使用高效液相色谱(Agilent 1260)测定BPA的浓度。检测条件为,色谱柱采用Agilent C-18柱(100 mm×4.6 mm,3.5 μm);流动相为甲醇:水=70:30(体积比),等度洗脱,流速:1 mL·min−1;柱温25 ℃;进样量10 μL;检测波长:280 nm。
-
吸附动力学过程通常使用拟一级动力学、拟二级动力学和粒子内扩散模型描述(采用Origin2019拟合)。
拟一级动力学方程(PFOM):
拟二级动力学方程(PSOM):
粒子内扩散模型(IPDM):
初始特性曲线(IPDM)[21]:
初始吸附因子(IPDM)[21]:
式中,k1为拟一级动力学速率常数;q1为平衡吸附量;k2为拟一级动力学速率常数;q2为平衡吸附量;kp为粒子扩散速率常数;C是常数;qref为最终吸附量;q0为初始吸附量.
本实验用Sigmaplot 14.0 数据统计软件对实验数据进行拟合,用Freundlich模型(1)和Langmuir模型(2)拟合吸附等温线,两个模型的方程为:
式中,Qe 为固相平衡浓度;Ce 为液相平衡浓度;Kf为 Freundlich 亲和系数,n 为非线性指数(无量纲); KL为 Langmuir 亲和系数,Q0为最大吸附量。
对吸附温度依赖性的研究为吸附过程中的能量变化提供了有价值的信息。 获得了BPA在278 K、288 K和298 K下在Bare BPs上的吸附等温线,以确定热力学参数。 吸附系数K0定义为:
标准吉布斯自由能变化(∆G0),标准焓变(∆H0)和标准熵变(∆S0)由K0通过以下公式确定:
等式(4)和(5)的重排:
式中,∆H0和∆S0从lnK0对1 / T的线性图的斜率和截距获得。
吸附能与平衡水溶质浓度之间的关系可描述如下:
其中E *是Ce和Cs处的吸附能之差。 对等式1和等式7的重新排列产生:
F(E *)由Freundlich模型(1)推导为:
相对于E *区分方程(8)并将其与方程(9)组合可得出:
公式(10)用于本研究中获得的吸附数据的现场吸附能分布分析。
-
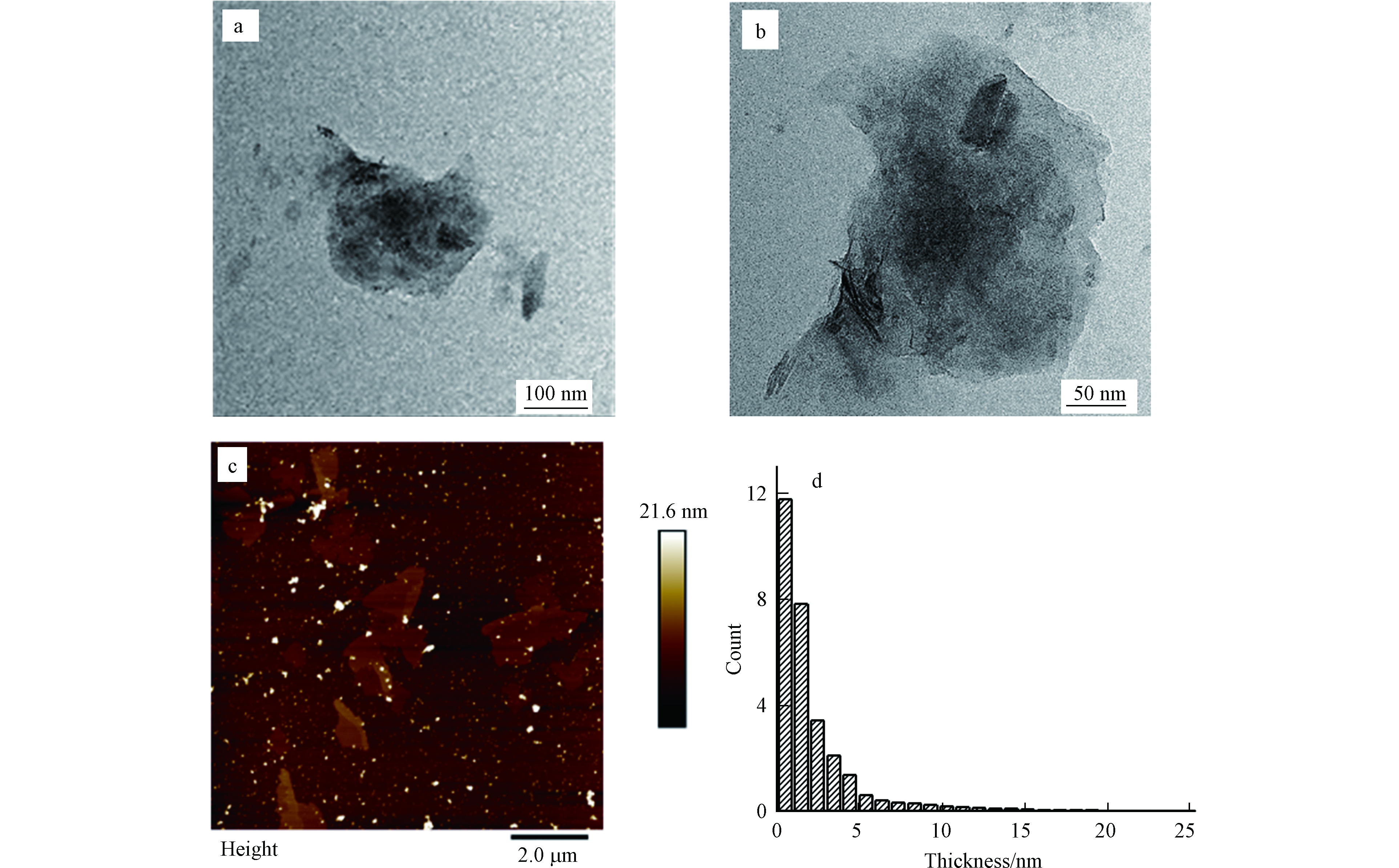
图1a、b为Bare BPs的透射电镜图。由图1可知,电化学剥离得到的Bare BPs具有明显的片层结构,横向尺寸约为150 nm。图1c、d Bare BPs的原子力显微镜图,可以得出,Bare BPs尺寸大小不一,约为100 nm—2 μm,而Bare BPs的厚度主要分布5 nm(大约10层)以下。
-
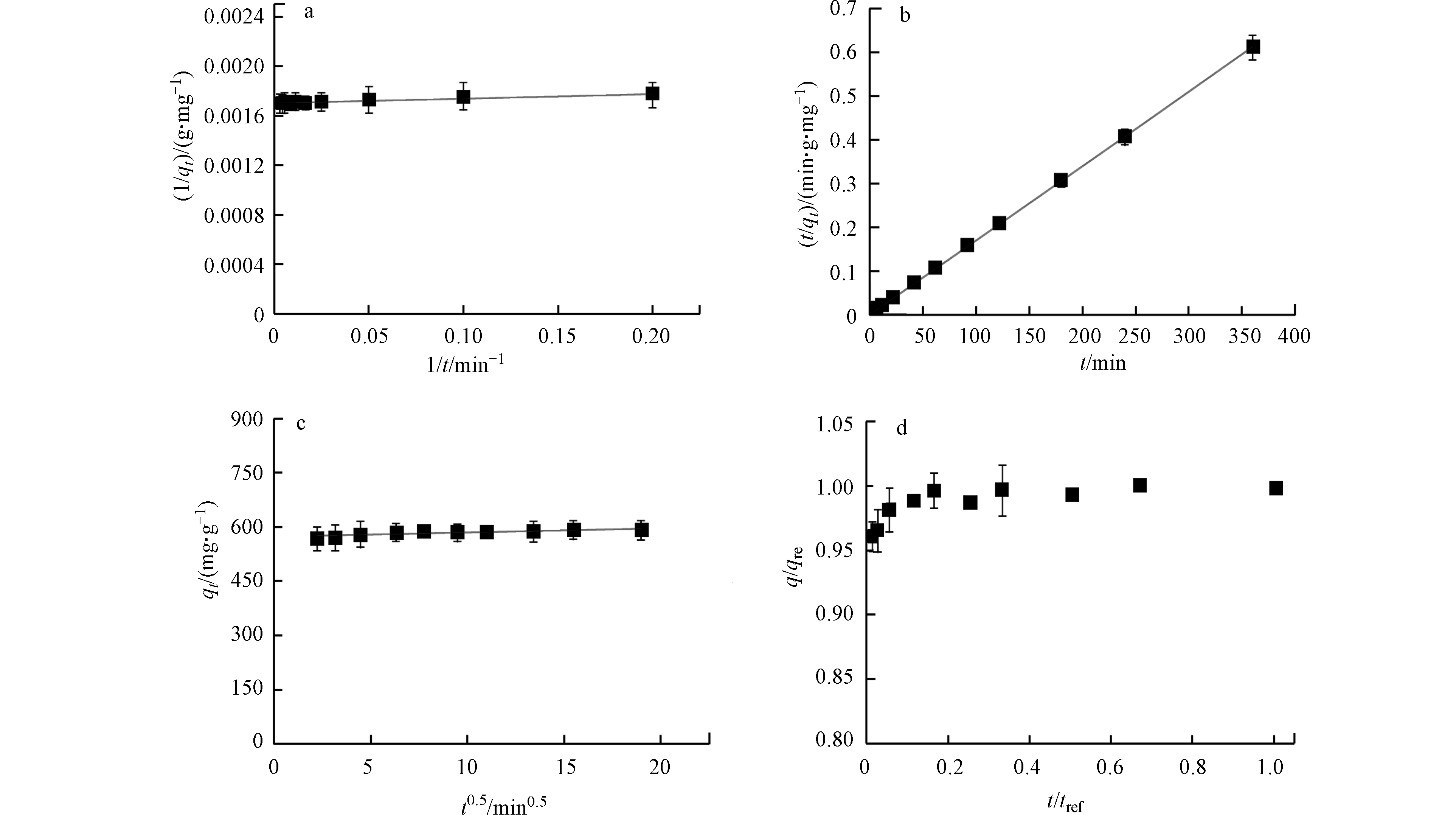
由表2可知,拟一级动力学的相关系数(R2=0.835)低于拟二级动力学(R2=0.999),说明拟二级动力学模型能更好地拟合Bare BPs吸附BPA的过程(图2a、b)。由此可推测,可能包含外部液膜扩散、表面吸附和颗粒内扩散等。此外,吸附速率常数较小(<<0.3),预示着Bare BPs可快速吸附水中BPA [22]。然而,上述两种模型无法识别扩散机理和吸附的初始行为。为此使用粒子内扩散模型[23]以及粒子内扩散模型下的初始特性曲线和初始吸附因子[21]进行描述。如果是颗粒内扩散参与吸附过程则动力学曲线过原点,反之曲线未过原点,表明受到边界层影响,而且截距越大,边界层影响越大[23]。BPA在Bare BPs的吸附动力学曲线未过原点且截距大(图2c),说明受边界层影响大。粒子内扩散模型中初始因子Ri通常被用于描述吸附动力学中的初始行为。当1 > Ri >0.9时,认为是弱初始吸附;当0.9 > Ri > 0.5时,认为是中度初始吸附;当0.5 > Ri > 0.1时,认为是强初始吸附;当Ri < 0.1时称之为接近完全初始吸附。而BPA在Bare BPs的吸附Ri=0.01(图2d,表2),表明BPA在Bare BPs上的吸附动力学非常接近完全初始吸附行为,初始吸附达到了99%。同时,Wu等[21]认为,活性炭的颗粒粒径和孔径分布会显著影响其初始吸附行为,颗粒粒径越大,初始行为越不显著,而孔径分布越大则会有强烈的初始吸附。通过表征分析可以看出,Bare BPs颗粒较小且不存在孔隙,这可能是BPA在Bare BPs上初始行为显著的主要原因。Adnan等[23]报道的DEDMA-海泡石吸附酸性蓝193出现类似的吸附动力学行为,在短时间内吸附迅速达到吸附平衡并且吸附动力学数据符合拟二级动力学模型。
-
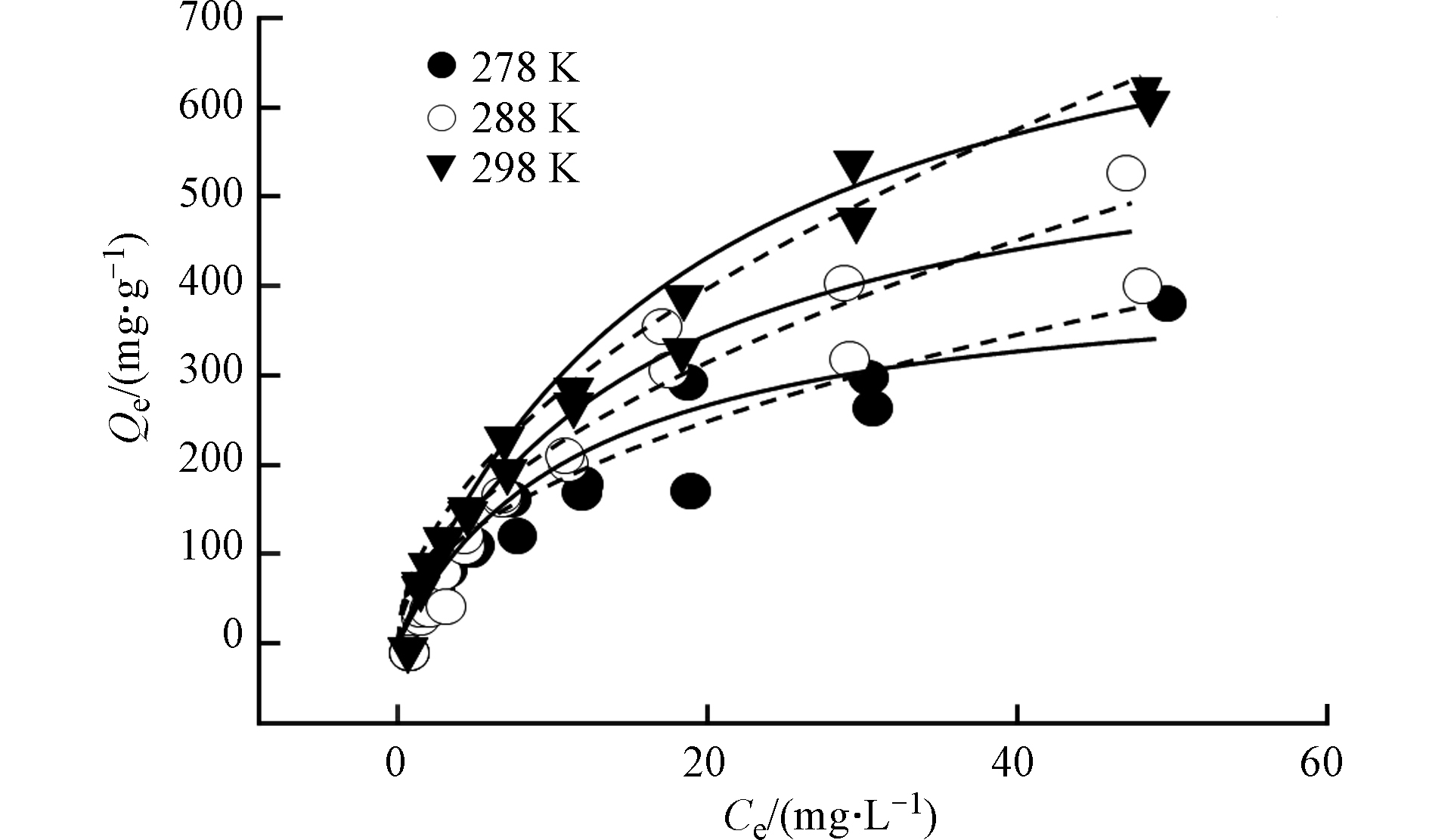
Bare BPs对BPA的吸附等温线如图3所示。采用Freundlich模型和Langmuir 模型对BPA的吸附等温线进行了拟合(图3、表3),通过比较R2可知,两种模型均可较好的描述Bare BPs对BPA的吸附,其中Freundlich 模型的拟合效果相对更佳,说明BPA在Bare BPs上的吸附以多层吸附为主[24]。n值为0.535<1,非线性程度较高,说明了BPA在Bare BPs上易于吸附且吸附能量分布异质程度较高。根据Langmuir模型计算出的最大吸附容量Q0高达839.3 mg·g−1,证明了Bare BPs高效吸附的性能。
-
从图4a可知,在初始pH 2—11的范围内,pH对Bare BPs对BPA的吸附行为影响显著。通过离子色谱检测磷酸根仅在pH10和11检测到微量磷酸根(0.29 mg·L−1和0.76 mg·L−1),表明在pH>10会对Bare BPs的降解略微有影响。可以看到,在酸性pH范围内(pH值为2—6)吸附量变化不明显,当pH>7,吸附量随着pH的增加而逐渐增加,并在pH=9时达到最大值,随后吸附量逐渐降低。这种现象与Bare BPs在不同pH下所带电荷(图4b)以及BPA在不同pH下的解离度(图4a)有关。Bare BPs在整个实验的pH范围内带负电,而BPA在pH<7时主要以分子形式存在,在pH 7左右开始去质子化并在pH=9时趋于具有第二种去质子形式(图4a)。Bare BPs具有疏水表面,吸附在pH范围2—6内BPA以分子形式存在,表面不带电荷,疏水性作用是主要吸附机制。由于Bare BPs表面带负电[25],在pH >7产生带负电的BPA−吸附量反而有所上升,说明静电排斥不是主要作用。释放的氢氧化物是由观察到的pH变化确定的,Bare BPs自身消耗的氢氧化物的量是pH的函数,这是通过在不存在有机溶质的情况下通过酸碱滴定来独立确定的。而Bare BPs吸附BPA则是在24h吸附后在测量的结果(图5)。从图5可见,在pH 7—9时Bare BPs吸附BPA的pH高于Bare BPs ,表明氢氧化物的释放,证明(-)CAHB可能参与pH 7—9条件下Bare BPs对BPA的吸附[26]。(-)CAHB是在质子接受基团上的负电荷的辅助下形成的氢键,它是一种强于普通氢键、具有与共价键相当特性的作用力。(-)CAHB能较好地解释吸附实验中出现的不能用静电作用解释的一些异常现象[27]。Wang等[28]曾报道了BPA在还原氧化石墨烯(RGO)吸附pH研究中出现相似现象,BPA的羟基与RGO的羟基或羰基形成H键,并用DFT计算证明出是(-)CAHB 的作用。Bare BPs的表面是存在-OH和O键[29],可与BPA−形成H键或者(-)CAHB。在pH>10范围内, Bare BPs的降解是微弱的,忽略降解的影响,此时BPA主要存在形式BPA−和BPA2-,并且Bare BPs表面负电性更强(图4b),因此静电排斥在pH>9范围内占主导作用。
-
研究了在278 、288 、298 K温度下Bare BPs对BPA的吸附情况,由表3可知,在298 K计算出的最大吸附量(Q0= 839.3 mg·g−1)最高,且随着温度降低吸附量减小。并且从单点Kd值分配来看,无论是高浓度(Ce=0.1Cs)还是低浓度(Ce=0.01Cs)298 K温度下Kd值均高于278 K和288 K,与不同温度下最大吸附容量比较现象一致。说明室温环境相对于低温环境更有利于Bare BPs对BPA的吸附。
热力学数据提供了BPA吸附的内部能量变化的深层信息。根据上文中提供吉布斯方程计算得到了标准吉布斯自由能变化(∆G0),标准焓变(∆H0)和标准熵变(∆S0)(表4)。所得焓变为正值,表明BPA在Bare BPs上的吸附是吸热过程。∆H0绝对值小于60 kJ·mol−1,说明BPA在Bare BPs上的吸附具有物理吸附特性[30] 。∆G0均为负值,表明这是一个自发的过程。∆G绝对值更大说明吸附越有利,可以看出298 K的∆G绝对值较高,表明高温有利于吸附。计算了BPA的平均吸附能(E *),298 K>288 K>278 K,同样表明较高温度有利于BPA的吸附。这可能是由于温度升高时,BPA分子(离子)与Bare BPs表面的碰撞机率增加,因此吸附量增加。也可能是由于随着温度的升高BPA溶液的黏度降低更容易进入到Bare BPs的内部层间[31]。
-
通过TEM和AFM对吸附前后Bare BPs的形貌进行了表征(图6),TEM可以看出NaCl加入后Bare BPs的透明程度下降,并且对应的AFM结果显示厚度增加。这是可能是由于NaCl的加入诱导Bare BPs出现团聚(图6 b、e、h)。而吸附BPA后的Bare BPs的TEM可以观察到不仅透明度低而且周围存在流动的有机物,并且AFM图像所显示的横向尺寸和厚度增加(图6 c、f、i)。这可能由于溶液中的NaCl诱导Bare BPs发生团聚,而BPA在Bare BPs表面的吸附加剧了Bare BPs的团聚,最终BPA吸附在了Bare BPs的表面与层间,形成类似于团簇的聚集体。
进一步分析吸附机制,Bare BPs具有疏水性表面[32],Zhao等[10]曾提到Bare BPs的疏水性作用,BPA是一种疏水性有机分子(lgKow=3.32(表1)),因此,疏水性作用可能是Bare BPs吸附BPA的一种机制。同时,在pH实验的研究中,不同pH条件下主导吸附机制并不一致。本实验发现在pH值范围2—6内疏水性作用为主导机制,而pH7—9静电作用在Bare BPs吸附BPA中是微弱的,并且主导机制可能是H键或者是(-) CAHB作用在pH10—11静电排斥占据主导作用。机理示意图如图7。
-
实验研究表明,Bare BPs对BPA吸附的动力学是快速的且符合拟二级动力学模型同时,Bare BPs对BPA吸附量较高(Q0=839.3 mg·g−1),因此,BPA在Bare BPs的吸附更应该引起高度重视,这会影响Bare BPs颗粒和BPA在水环境中的运输。同时,探究了BPA在Bare BPs上的吸附环境行为。结果表明,在酸性pH范围(pH=2—6)吸附量基本不受影响,而在碱性pH范围内(pH=7—11)吸附量先上升后下降与BPA−的形态规律基本保持一致,猜测是(-)CAHB作用致使此现象的发生。BPA在Bare BPs的吸附受温度影响,温度越高越容易吸附,证实吸附是一个自发且吸热的过程。从吸附前后的表征分析可以看出,在盐的诱导下,吸附了BPA的Bare BPs会出现团聚现象,而BPA在Bare BPs的快速吸附可能是疏水性、H键或(-)CAHB的共同作用。
黑磷纳米片对水中双酚A的吸附
Sorption of bisphenol A in water by bare black phosphorus nanosheets
-
摘要: 由于独特的理化性质,黑磷纳米片(Bare BPs)成为一种新型的二维纳米材料。Bare BPs有望在光电器件、催化和生物医学等领域得到广泛应用。目前,对于Bare BPs的环境风险研究不足。Bare BPs具有超高的理论比表面积和大量的疏水表面,理论上会与有机物污染物相结合形成复合污染,改变两者原有的环境行为和危害性,因此对Bare BPs与有机污染物的吸附行为和机制的系统研究尤为重要。本文采用电化学阳极剥离法制备了少层Bare BPs,以双酚A(BPA)作为模型污染物,系统研究了Bare BPs对BPA的吸附行为。结果表明,Bare BPs对BPA的吸附符合拟二级动力学模型,并且Bare BPs对BPA具有高吸附能力(Q0=839.3 mg·g-1),等温吸附呈非线性,符合Freundlich 模型。在酸性pH范围内,Bare BPs吸附量基本不变,而在碱性pH范围内吸附量波动较大,猜测存在负电辅助氢键((-)CAHB)机制。另外,热力学结果分析表明,在5—25 ℃范围内BPA在Bare BPs上的吸附行为是吸热的,高温有利于BPA在Bare BPs上的吸附。能量分布与非线性等温线一致,表明Bare BPs存在吸附BPA的异质位点。采用透射电镜(TEM)、原子力显微镜(AFM)等手段观察到Bare BPs吸附前后的形貌变化,吸附BPA了的Bare BPs存在聚集现象。Abstract: Due to the unique physical and chemical properties, bare black phosphorous nanosheets (Bare BPs) have become a new type of two-dimensional nanomaterials. Bare BPs is expected to be widely used in the fields of optoelectronic devices, catalysis and biomedicine. At present, there is insufficient research on the environmental risks of Bare BPs. Bare BPs have an ultra-high theoretical specific surface area and a large number of hydrophobic surfaces, which can theoretically combine with organic pollutants to form compound pollution, and changing the original environmental behavior and hazards of the two. Therefore, it is particularly important to systematically study the adsorption behavior and mechanism of Bare BPs with organic pollutants. In this paper, few-layer Bare BPs were prepared by electrochemical anode exfoliation method, and bisphenol A (BPA) was used as a model pollutant. The adsorption behavior of Bare BPs to BPA was systematically studied. The results show that the kinetic adsorption process of BPA on Bare BPs conform to the pseudo-kinetic model, and the Bare BPs have high adsorption capacity for BPA (Q0 = 839.3 mg·g-1), and the adsorption isotherm is nonlinear, which conforms to the Freundlich model. In the range of acidic pH, the adsorption capacity of Bare BPS was basically unchanged, while in the range of alkaline pH, the adsorption capacity fluctuated greatly, which suggested that the mechanism of negative electricity-assisted hydrogen bond ((-) CAHB) existed. In addition, the analysis of thermodynamic results shows that the adsorption behavior of BPA on Bare BPs was endothermic in the range of 5—25 ℃, and the high temperature was beneficial to the adsorption of BPA on Bare BPs. The energy distribution is consistent with the non-linear isotherm, indicating that the Bare BPs have heterogeneous sites for BPA adsorption. Using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM) and other means to observe the morphological changes before and after the absorption of Bare BPs, the Bare BPs that have adsorbed BPA had aggregation phenomenon.
-
Key words:
- bare black phosphorous /
- bisphenol A /
- sorption /
- pH /
- thermodynamics
-

-
图 2 (a) 拟一级动力学吸附曲线图;(b) 拟二级动力学吸附曲线图;(c) 粒子内扩散吸附曲线图;(d) 粒子内扩散模型初始特性曲线
Figure 2. (a) pseudo first-order kinetic adsorption curve diagram; (b) pseudo-secondary kinetic adsorption curve diagram; (c) intra-particle diffusion adsorption curve diagram; (d) intra-particle diffusion model initial characteristic curve
图 6 (a)Bare BPs的低倍TEM图;(b)加入NaCl后Bare BPs的低倍TEM图像;(c)吸附后Bare BPs的低倍TEM图像。(d)Bare BPs的AFM图;(e)加入NaCl后Bare BPs的AFM图像;(f)吸附后Bare BPs的AFM图像;(g—i)是对应的厚度分布。
Figure 6. (a)Low power TEM image of Bare BPs. (b)Low magnification TEM image of Bare BPs after adding NaCl. (c) Low magnification TEM image of Bare BPs after adsorption. (d)AFM image of Bare BPs. (e)AFM image of Bare BPs after adding NaCl. (f)AFM image of b Bare BPs after adsorption. (g—i)is the corresponding thickness distribution.
表 1 BPA基本理化参数
Table 1. Physicochemical properties of BPA
吸附质
SorbatespKa 分子量/ (g·mol−1)
Molecular weight溶解度/(mg·L−1)
SolubilitylgKow 分子结构 双酚A 9.59/11.3 228.3 129 3.32 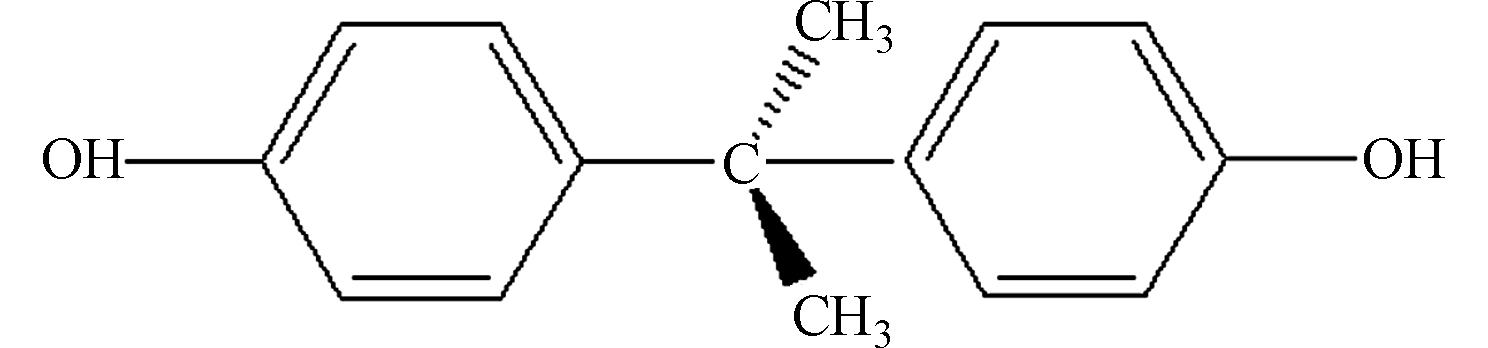
表 2 BPA在Bare BPs的动力学参数
Table 2. Kinetic parameters of BPA in black phosphorus nanosheets
吸附质
AdsorbatePFOM PSOM IPDM K1(×10−3)
/min−1q1/
(mg·g−1)R2 K2(×10−3)
/min−1q2/
(mg·g−1)R2 Kp /
(mg·g−1 ·min−1)C/
(mg·g−1)R2 Ri BPA 2.28 588 0.835 7.47 588 0.999 1.10 574 0.543 0.01 表 3 Bare BPs吸附BPA的等温吸附参数
Table 3. Isothermal adsorption parameters of black phosphorus nanosheets adsorption of BPA
温度/K
TemperatureLM FM Kd/(L·g−1) KL Q0/(mg·g−1) R2 Kf n R2 0.01Cs 0.1Cs 278 0.0858 422.2 0.9120 50.9 0.475 0.9498 44.5 13.3 288 0.0649 611.8 0.9535 62.3 0.521 0.9440 55.2 18.3 298 0.0529 839.3 0.9741 80.1 0.535 0.9892 71.1 24.4 表 4 Bare BPs吸附BPA热力学参数
Table 4. black phosphorus nanosheets adsorption thermodynamic parameters of BPA
温度/K Temperature lnKf ∆G0/(kJ mol-−1) ∆H0/(kJ mol-−1) ∆S0/(J mol-−1 K-−1) 278K 3.93 -9.08 15.59 88.62 288K 4.13 -9.89 298K 4.38 -10.86 -
[1] QIAO J S, KONG X H, HU Z X, et al. High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus [J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4475. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5475 [2] LI B S, LAI C, ZENG G M, et al. Black phosphorus, a rising star 2D nanomaterial in the post-graphene era: Synthesis, properties, modifications, and photocatalysis applications [J]. Small (Weinheim an Der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2019, 15(8): e1804565. doi: 10.1002/smll.201804565 [3] XIA F N, WANG H, JIA Y C. Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics [J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4458. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5458 [4] CHEN W, LI K W, WANG Y, et al. Black phosphorus quantum dots for hole extraction of typical planar hybrid perovskite solar cells [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2017, 8(3): 591-598. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b02843 [5] YANG Y, GAO J, ZHANG Z, et al. Black phosphorus based photocathodes in wideband bifacial dye-sensitized solar cells [J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(40): 8937-8944. doi: 10.1002/adma.201602382 [6] LI L K, YU Y J, YE G J, et al. Black phosphorus field-effect transistors [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2014, 9(5): 372-377. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.35 [7] BUSCEMA M, GROENENDIJK D J, BLANTER S I, et al. Fast and broadband photoresponse of few-layer black phosphorus field-effect transistors [J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(6): 3347-3352. doi: 10.1021/nl5008085 [8] DU Y C, LIU H, DENG Y X, et al. Device perspective for black phosphorus field-effect transistors: Contact resistance, ambipolar behavior, and scaling [J]. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(10): 10035-10042. doi: 10.1021/nn502553m [9] MAYORGA-MARTINEZ C C, SOFER Z, PUMERA M. Layered black phosphorus as a selective vapor sensor [J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2015, 54(48): 14317-14320. doi: 10.1002/anie.201505015 [10] ZHAO Q, MA W, PAN B, et al. Wrinkle-induced high sorption makes few-layered black phosphorus a superior adsorbent for ionic organic compounds [J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2018, 5(6): 1454-1465. doi: 10.1039/C8EN00266E [11] MU X Y, WANG J Y, BAI X T, et al. Black phosphorus quantum dot induced oxidative stress and toxicity in living cells and mice [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(24): 20399-20409. [12] ZHANG X, ZHANG Z, ZHANG S, et al. Size effect on the cytotoxicity of layered black phosphorus and underlying mechanisms [J]. Small, 2017, 13(32): 1701210. doi: 10.1002/smll.201701210 [13] FOJTŮ M, BALVAN J, RAUDENSKÁ M, et al. Black phosphorus cytotoxicity assessments pitfalls: Advantages and disadvantages of metabolic and morphological assays [J]. Chemistry (Weinheim an Der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2019, 25(1): 349-360. [14] XIONG Z Q, ZHANG X J, ZHANG S Y, et al. Bacterial toxicity of exfoliated black phosphorus nanosheets [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 161: 507-514. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.008 [15] WU Q, YAO L L, ZHAO X C, et al. Cellular uptake of few-layered black phosphorus and the toxicity to an aquatic unicellular organism [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(3): 1583-1592. [16] LI P, ZENG L, GAO J, et al. Perturbation of normal algal growth by black phosphorus nanosheets: The role of degradation [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2020, 7(1): 35-41. [17] HUANG Y Q, WONG C K C, ZHENG J S, et al. Bisphenol A (BPA) in China: A review of sources, environmental levels, and potential human health impacts [J]. Environment International, 2012, 42: 91-99. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2011.04.010 [18] KARALIUS V P, HARBISON J E, PLANGE-RHULE J, et al. Bisphenol A (BPA) found in humans and water in three geographic regions with distinctly different levels of economic development [J]. Environmental Health Insights, 2014, 8: 1-3. [19] WANG Z, LIU H Y, LIU S J. Low-dose bisphenol A exposure: A seemingly instigating carcinogenic effect on breast cancer [J]. Advanced Science (Weinheim, Baden Wurttemberg, Germany), 2017, 4(2): 1600248. [20] XIAO C Y, WANG L H, ZHOU Q, et al. Hazards of bisphenol A (BPA) exposure: A systematic review of plant toxicology studies [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121488. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121488 [21] WU F C, TSENG R L, JUANG R S. Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2009, 153(1/2/3): 1-8. [22] 温元波, 张陆军, 王宁宁, 等. 水化氯铝酸钙去除水中氟及其动力学研究 [J]. 应用化工, 2021, 50(2): 311-315. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.02.008 WEN Y B, ZHANG L J, WANG N N, et al. Study on the removal of fluorine in water by hydrated calcium chloroaluminate and its kinetics [J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(2): 311-315(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.02.008
[23] ÖZCAN A, ÖNCÜ E M, ÖZCAN A S. Adsorption of Acid Blue 193 from aqueous solutions onto DEDMA-sepiolite [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 129(1/2/3): 244-252. [24] PARK Y, SUN Z M, AYOKO G A, et al. Bisphenol A sorption by organo-montmorillonite: Implications for the removal of organic contaminants from water [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 107: 249-256. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.12.050 [25] ZHANG L, GAO L F, LI L X, et al. Negatively charged 2D black phosphorus for highly efficient covalent functionalization [J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2018, 2(9): 1700-1706. doi: 10.1039/C8QM00237A [26] GAO B Q, LI P, YANG R, et al. Investigation of multiple adsorption mechanisms for efficient removal of ofloxacin from water using lignin-based adsorbents [J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 637. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37206-1 [27] 王朋, 肖迪, 梁妮, 等. 电荷辅助氢键的形成机制及环境效应研究进展 [J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(5): 812-818. doi: 10.11896/cldb.201905013 WANG P, XIAO D, LIANG N, et al. Advances in formation mechanism and environmental effects of charge-assisted hydrogen bonds [J]. Materials Reports, 2019, 33(5): 812-818(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/cldb.201905013
[28] WANG P, ZHANG D, TANG H, et al. New insights on the understanding of the high adsorption of bisphenol compounds on reduced graphene oxide at high pH values via charge assisted hydrogen bond [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 371: 513-520. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.012 [29] LIN Y J, CHEN J J, CAO W Z, et al. Novel materials for Cr(VI) adsorption by magnetic titanium nanotubes coated phosphorene [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 287: 110826. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.04.103 [30] 陈素清, 梁华定, 邱昀芳. 碳纳米管吸附水溶液中双酚A的热力学 [J]. 应用化学, 2009, 26(5): 571-575. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0518.2009.05.016 CHEN S Q, LIANG H D, QIU Y F. Thermodynamics of adsorption of carbon nanotubes for bisphenol A [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2009, 26(5): 571-575(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0518.2009.05.016
[31] WANG Z Y, YU X D, PAN B, et al. Norfloxacin sorption and its thermodynamics on surface-modified carbon nanotubes [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(3): 978-984. [32] ZHANG S Y, ZHANG X J, LEI L, et al. pH-dependent degradation of layered black phosphorus: Essential role of hydroxide ions [J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2019, 58(2): 467-471. doi: 10.1002/anie.201809989 -



 下载:
下载: