-
近年来,随着“退二进三”“退城进园”等政策的实施,产生大量的遗留地块,土壤和地下水污染严重,其中不乏1,2-二氯乙烷(1,2-DCA)污染地块[1]。1,2-DCA是一种重要的有机溶剂和产品中间体,属于典型的“三致”化合物[2-3]。此外,1,2-DCA具有迁移性强、不易自然降解等特点,能长久地存在于地下水环境中,有较大的生态环境风险[4]。因此,如何高效去除1,2-DCA等氯代烃类污染物成为地下水污染治理领域亟待解决的问题。
地下水常用的修复技术包括抽出-处理、原位化学氧化/还原、可渗透性反应墙等技术(PRB)[5-8]。可渗透性反应墙技术作为一种原位地下水修复技术,在国内外氯代烃污染地下水修复中得到广泛研究和应用[9-10]。传统的PRB介质主要为零价铁材料,但零价铁存在易团聚、易氧化等问题[11]。因此,寻找一种环境友好、结构稳定和性能优异的介质材料对提升PRB性能具有重要意义。
介孔硅材料是一类通过自组装形成的孔道规则的无机多孔材料[12],孔径为2~50 nm。相较于传统多孔材料,介孔硅材料具有比表面积较大、孔道结构规则、可调、表面易修饰等特点[13-14]。MCM-41具有六方堆积结构,易于污染物扩散[15]。已有研究[12]表明,MCM-41对重金属、小分子有机物及染料等污染物具有良好的吸附效果。但MCM-41存在表面基团单一、内部晶格缺陷较少的弊端[16]。目前,常采用有机改性和金属掺杂等方式增加MCM-41表面基团和内部活性位点,进而提升其吸附和催化性能[16-17]。已有研究[18]表明,氨基的引入会增加MCM-41的活性位点。目前MCM-41材料的应用研究集中于工业废水中重金属和染料的去除[18-19],而在地下水修复中的应用研究鲜有报道。利用介孔硅材料比表面积大、孔道规则可调、表面易修饰等优点,研发高效介孔硅材料,将其作为PRB吸附介质或载体材料,对提升PRB传统介质材料吸附性差、易团聚失效等问题具有重要意义。
本研究采用共聚法制备氨基改性MCM-41材料,采用多种表征技术对材料微观形貌和结构进行表征;以NH2-MCM-41为1,2-DCA吸附剂,模拟地下水环境,探究其吸机理及影响因素,阐明NH2-MCM-41结构与吸附行为之间的关系,为改性MCM-41材料作为可渗透性反应墙介质提供基础参数,为介孔硅材料在氯代烃污染地下水修复中的应用提供技术支持。
-
1) 实验试剂。1,2-二氯乙烷(1,2-DCA),购自上海凌峰化学试剂有限公司;盐酸和氢氧化钠,购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司;乙醇、正硅酸乙酯(TEOS)、十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB)、氨水和3-氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷(APTES),购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司。以上试剂均为分析纯。实验用水为超纯水,电导率为0.055 μS·cm−1。
2) 实验仪器。7890B-5977A型气相色谱质谱联用仪(美国安捷伦公司);BSA124S型电子分析天平(德国赛多利斯公司);SX2-2.5-10箱式电炉(上海苏达实验仪器有限公司);DHG-9023A电热恒温鼓风干燥箱(上海精宏实验设备有限公司);THZ-82A数显水浴恒温振荡器(常州普天仪器制造有限公司);85-2A恒温磁力搅拌器(江苏科析仪器有限公司);HWCL-3集热式恒温磁力搅拌浴(郑州长城科工贸有限公司)。
-
称取1 g CTAB溶于130 mL去离子水中,加入90 mL浓氨水,60 ℃下搅拌至混合均匀;再缓慢滴加5 mL TEOS,持续搅拌3 h后,室温晶化48 h,所得产物经抽滤洗涤后于60 ℃烘干;最后在马弗炉中550 ℃煅烧6 h,得纯MCM-41。
称取1 g CTAB溶于130 mL去离子水中,60 ℃下搅拌至澄清,加入90 mL浓氨水,60 ℃下搅拌至混合均匀,缓慢滴加5 mL TEOS,搅拌1 h后,加入1 mL APTES;继续搅拌6 h后,室温晶化48 h,所得产物经抽滤洗涤后于60 ℃下烘干;最后经无水乙醇萃取6 h后,烘干得NH2-MCM-41。
-
利用X射线衍射仪(Bruker D8 Advance)分析材料的晶格结构(扫描范围为2°~5°,扫描速度为 0.5(°)·min−1);利用扫描电子显微镜(德国ZEISS GeminiSEM 300)分析材料表面形貌;利用透射电子显微镜 (FEI Talos F200s) 分析材料微观形貌;利用全自动比表面及孔隙度分析仪(康塔Autosorb-IQ-MP)测定材料的比表面积和孔径分布(吸附气体N2,脱气温度200 ℃,脱气时间8 h);利用傅里叶红外光谱(Thermo Scientific Nicolet iS5)分析材料表面基团(波数为400~4 000 cm−1)。
-
1) 批量吸附实验。配制若干份20 mg·L−1 1,2-DCA溶液于250 mL锥形瓶中,分别投加0.1 g材料并置于恒温水浴振荡器中,在10、20、30和40 ℃下,以250 r·min−1的转速振荡120 min后,取样,过0.22 μm有机滤膜,利用气相色谱质谱联用仪测定1,2-DCA浓度,并计算吸附容量。初始pH、阴离子浓度、腐殖酸浓度的探究方法与之类似。
2) 吸附动力学实验。配制2份20 mg·L−1 1,2-DCA溶液于250 mL锥形瓶中,分别投加0.1 g MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41,于20 ℃恒温振荡器中以250 r·min−1的转速振荡,在设定的时间(0、5、10、15、30、60、90和120 min)取样,检测方法同上。
3) 吸附等温线实验。配制若干份20 mg·L−1 1,2-DCA溶液于250 mL锥形瓶中,分别投加0.1 g MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41,于20 ℃恒温振荡器中以250 r·min−1的转速振荡,于120 min后取样,检测方法同上。
吸附量计算方法见式(1)。
式中:qe为吸附量,mg·g−1;C0和Ce分别为1,2-DCA初始浓度和吸附平衡时质量浓度,mg·L−1;V为溶液体积,L;m为吸附剂的质量,g。
-
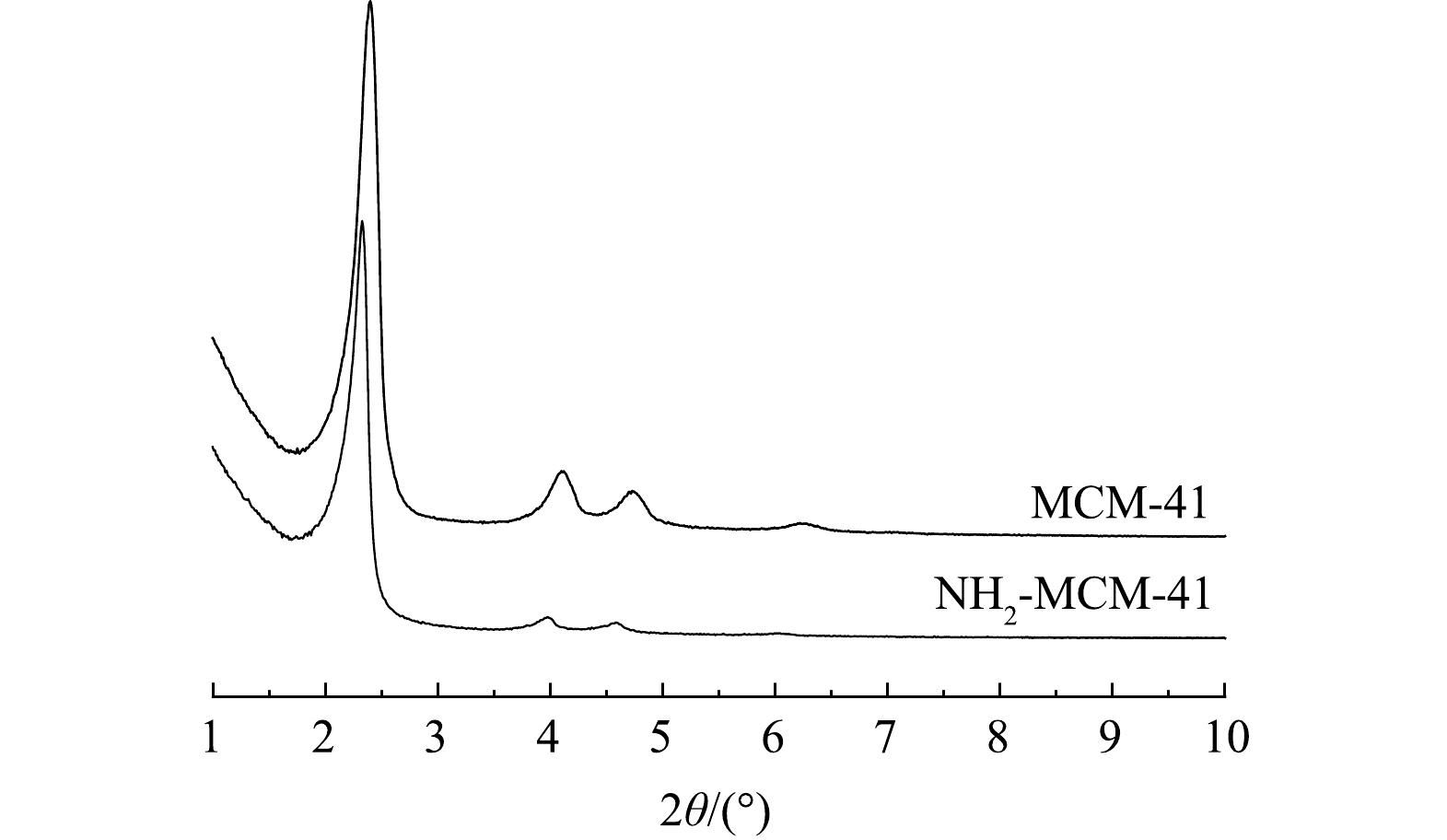
图1为MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41的小角度XRD谱图。可以看出,MCM-41材料在2θ为2.2°、4.1°、4.4°和6.3°存在4个强度不一的衍射峰,分别对应于材料晶胞的(100)、(110)、(200)和(210)晶面,说明MCM-41呈现有序的六方堆积结构,与已有研究结果[20-21]一致,属于典型的介孔二氧化硅结构。NH2-MCM-41材料(100)、(110)和(200)晶面所产生的衍射峰仍然存在,强度有所降低,(210)晶面的衍射峰消失。说明氨基的引入使得材料结晶度和有序度略有下降,但并未改变基本晶格结构,仍保持规则的六方堆积结构,与ENSHIRAH等[14]的研究结果一致。
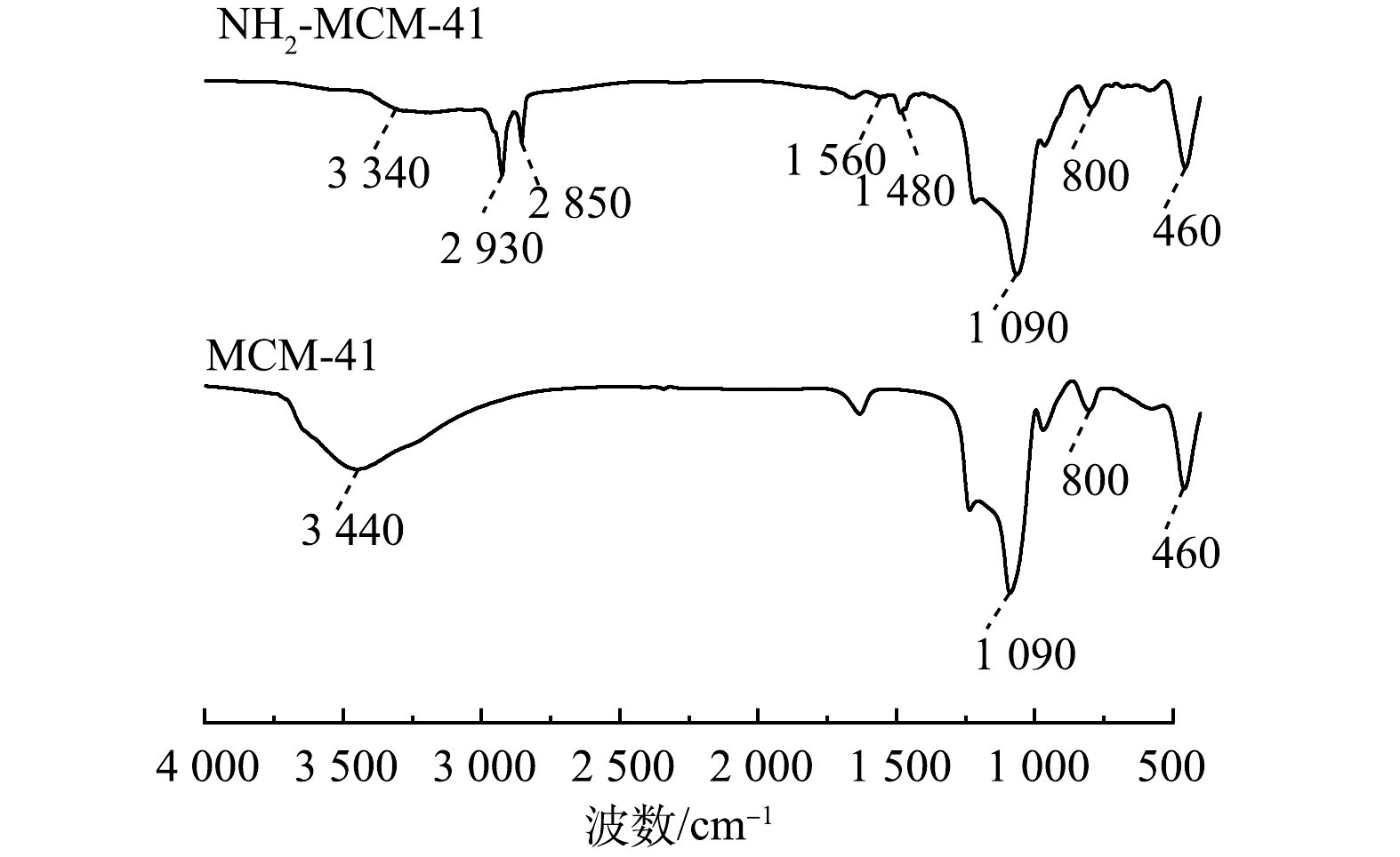
图2为MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41在波数为400~4 000 cm−1的FT-IR谱图。可以看出,MCM-41在3 440 cm−1处存在一个宽吸收峰,该峰由Si—OH的伸缩振动及吸附水分子所产生[18,22];1 090 cm−1处为Si—O—Si的不对称伸缩振动峰,800 cm−1处为Si—O—Si伸缩振动峰;460 cm−1处为Si—O—Si的弯曲振动峰,上述均为介孔SiO2的典型特征峰。NH2-MCM-41在3 340 cm−1处吸收峰的强度较MCM-41处的有明显下降,这归因于Si—OH与APTES反应后羟基数量减少[23-24]。此外,相较于MCM-41,NH2-MCM-41在1 480、1 560、2 850和2 930 cm−1处出现了新的吸收峰,其中1 480 cm−1和1 560 cm−1处为—NH2的变形振动峰;2 850 cm−1和2 930 cm−1处为亚甲基—CH2的伸缩振动峰。该结果表明,材料表面的Si—OH与APTES成功发生反应,氨基成功引入至材料中[24-26]。
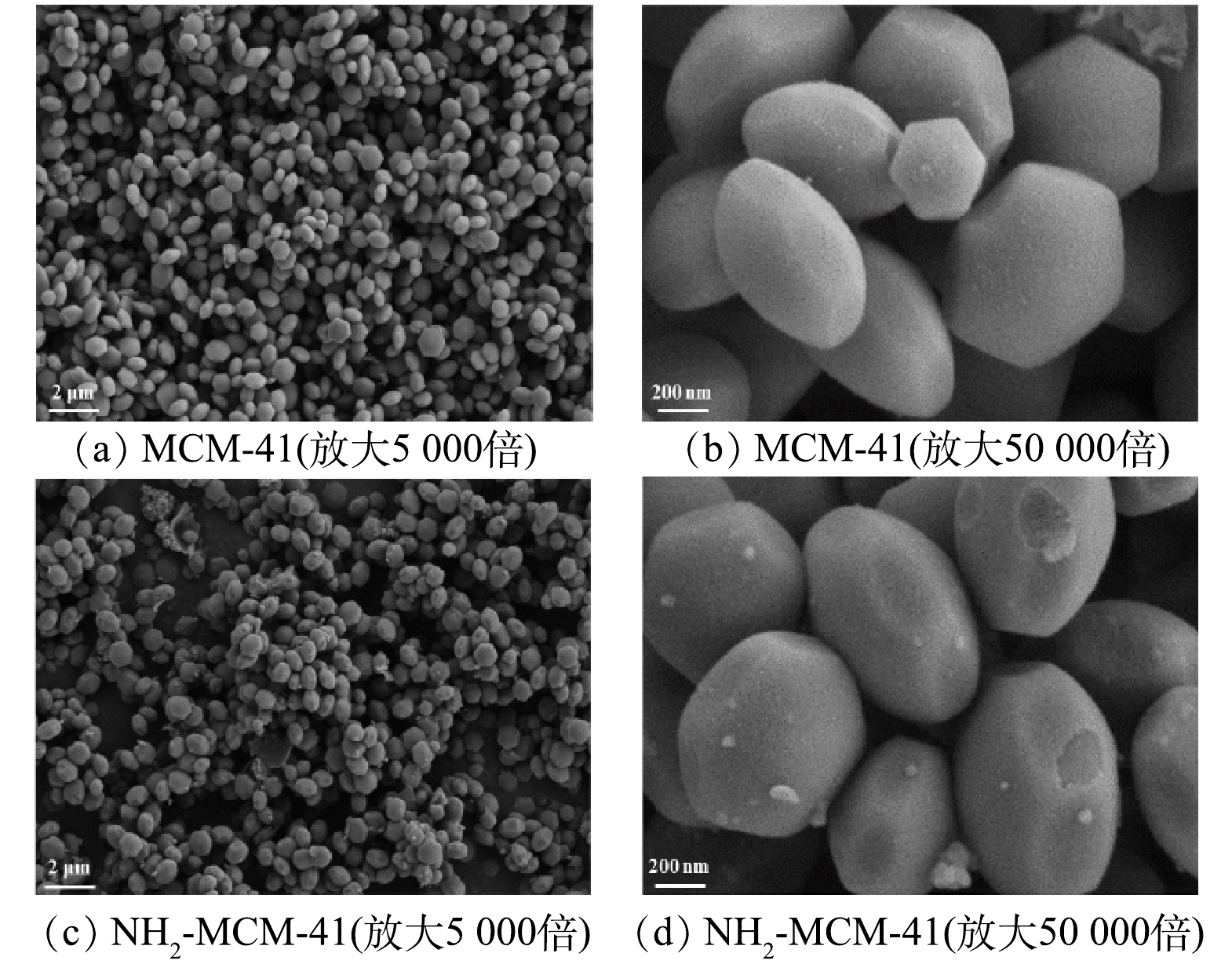
图3为MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41的SEM图。图3(a)和图3(c)显示MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41由大量六边形颗粒堆积而成,晶粒结晶度好,未出现明显的团聚现象,颗粒直径介于200~700 nm,这与已有研究结果[27]一致,表明氨基的引入未破坏材料的颗粒形态。此外,大量六边形颗粒具有良好的分散性,有利于污染物分子的扩散[20]。图3(d)显示NH2-MCM-41颗粒周围存在絮状物,推断是改性后接入的氨基。部分氨基附着在颗粒附近,对材料颗粒形态造成一定的影响[28]。已有研究[20,28]表明,氨基的引入会使材料表面活性位点增多,有利于材料对污染物分子的吸附。
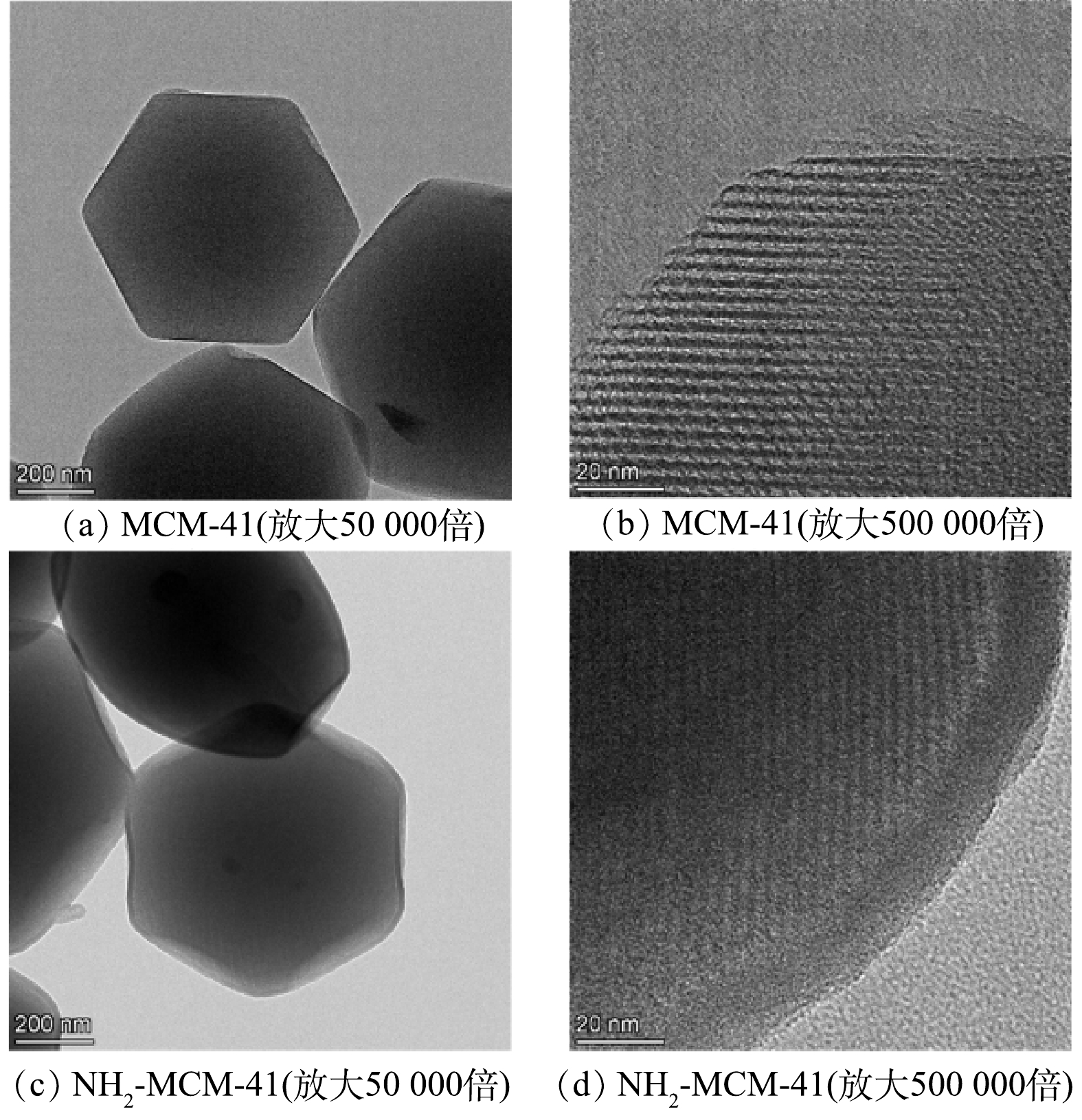
图4为MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41的TEM图。图4(a)和图4(c)显示改性前后材料的微观切面均为六边形,形状规整,氨基的引入使材料表面毛糙。图4(b)和图4(d)为MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41孔道横截面。可以看出,两者均具有规整的孔道结构,孔径为3~4 nm,孔道连通性好,未出现孔道堵塞情况,该结构有利于污染物分子的扩散。但NH2-MCM-41材料孔道壁变得模糊,原因是氨基引入孔道内部,影响了孔道连通性。由两者TEM图的对比结果可知,氨基并未改变材料的基本结构,这进一步验证了XRD及SEM的分析结果。
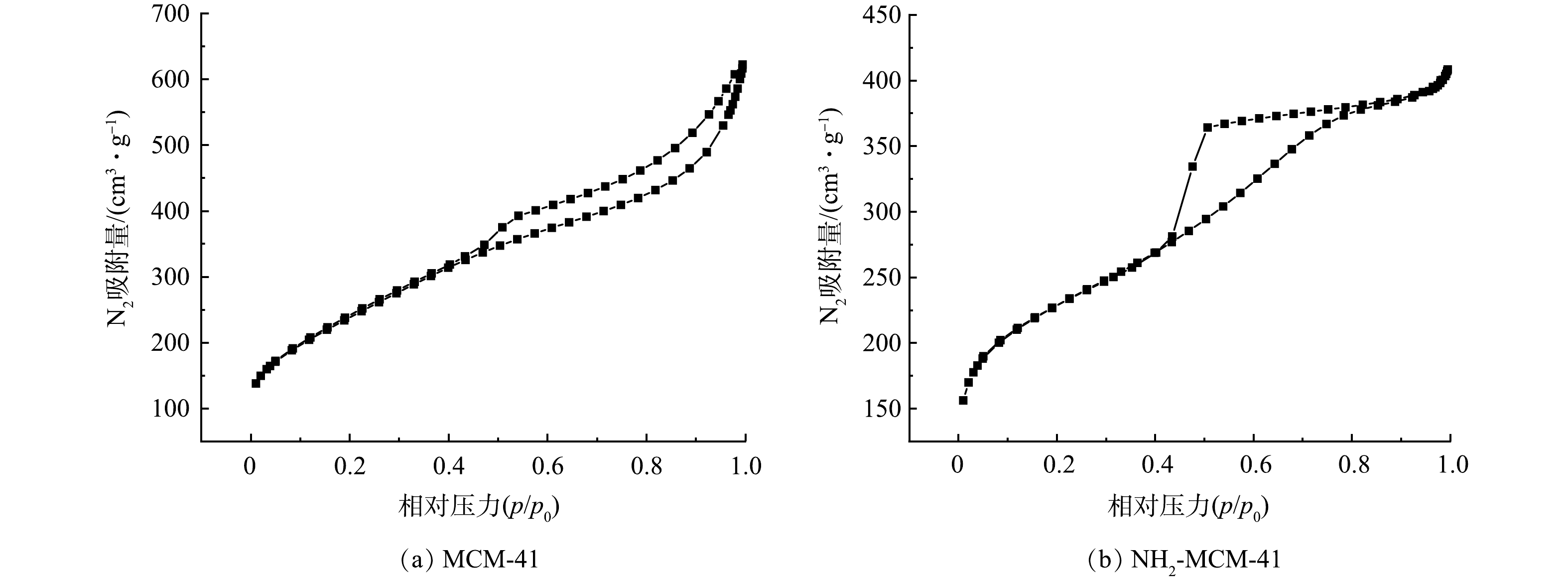
图5为MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41的氮气吸附-脱附等温线及孔径分布图,表1为MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41的比表面积及孔的相关参数。由图5(a)和图5(b)可知,改性前后材料的N2吸附脱附曲线均属于IUPAC分类中的IV型吸附等温线,存在明显的滞后环,说明2种材料均具有明显的介孔特性[29],该结果与XRD分析结果相吻合。MCM-41属于H4型回滞环,说明材料含有狭窄裂隙。NH2-MCM-41属于H2型回滞环,说明材料存在密堆积球形颗粒间隙孔。其原因是氨基的引入,使孔道连通性下降,导致脱附支较为陡峭[18,20]。
表1显示NH2-MCM-41比表面积、孔容以及孔径较MCM-41分别减小了约10%、25%和26%。这说明氨基的引入使材料孔道变粗糙、变窄,孔径变小,降低了孔道有序度[27],进而使其比表面积、孔容减小。NH2-MCM-41比表面积达到776.37 m2·g−1,优于已有研究结果(597.83 m2·g−1) [30]。
-
在材料投加量为0.4 g·L−1,1,2-DCA质量浓度为20 mg·L−1,实验温度为20 ℃,溶液pH分别为3、5、7、9和11的条件下,探究pH对吸附过程的影响,实验结果见图6。可以看出,酸性条件下pH的变化对MCM-41吸附1,2-DCA无显著影响,碱性条件下,随着pH的升高,吸附量逐渐降低。这是因为MCM-41在碱性条件会发生水解[31],材料Si—O—Si键断裂[32],结构受到破坏。强碱性(pH>11)条件下,MCM-41的XRD图见图6(b)。可以看出,MCM-41(100)晶面所产生的主峰强度大幅下降,说明强碱性环境会破坏MCM-41系列材料基本结构。对于NH2-MCM-41而言,酸性条件下,pH的变化对吸附过程的影响较为大。pH越低,NH2-MCM-41对1,2-DCA的吸附容量越低。其原因是,在酸性环境下,溶液中存在的H+易接受N的孤电子对[33]。此外,H+浓度过高,NH2-MCM-41表面氨基质子化,降低材料表面π电子云密度,削弱NH2-MCM-41与1,2-DCA间的色散力和偶极-偶极作用等分子间作用力[23,31]。在碱性条件下,吸附量随pH的增加而逐渐降低,这是因为NH2-MCM-41属于MCM-41系列材料,在强碱性条件下易发生水解[34]。综上,pH对材料吸附1,2-DCA有较大影响。酸性条件下,H+浓度影响NH2-MCM-41对1,2-DCA的吸附过程;碱性条件下,MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41结构发生分解,吸附能力降低。
-
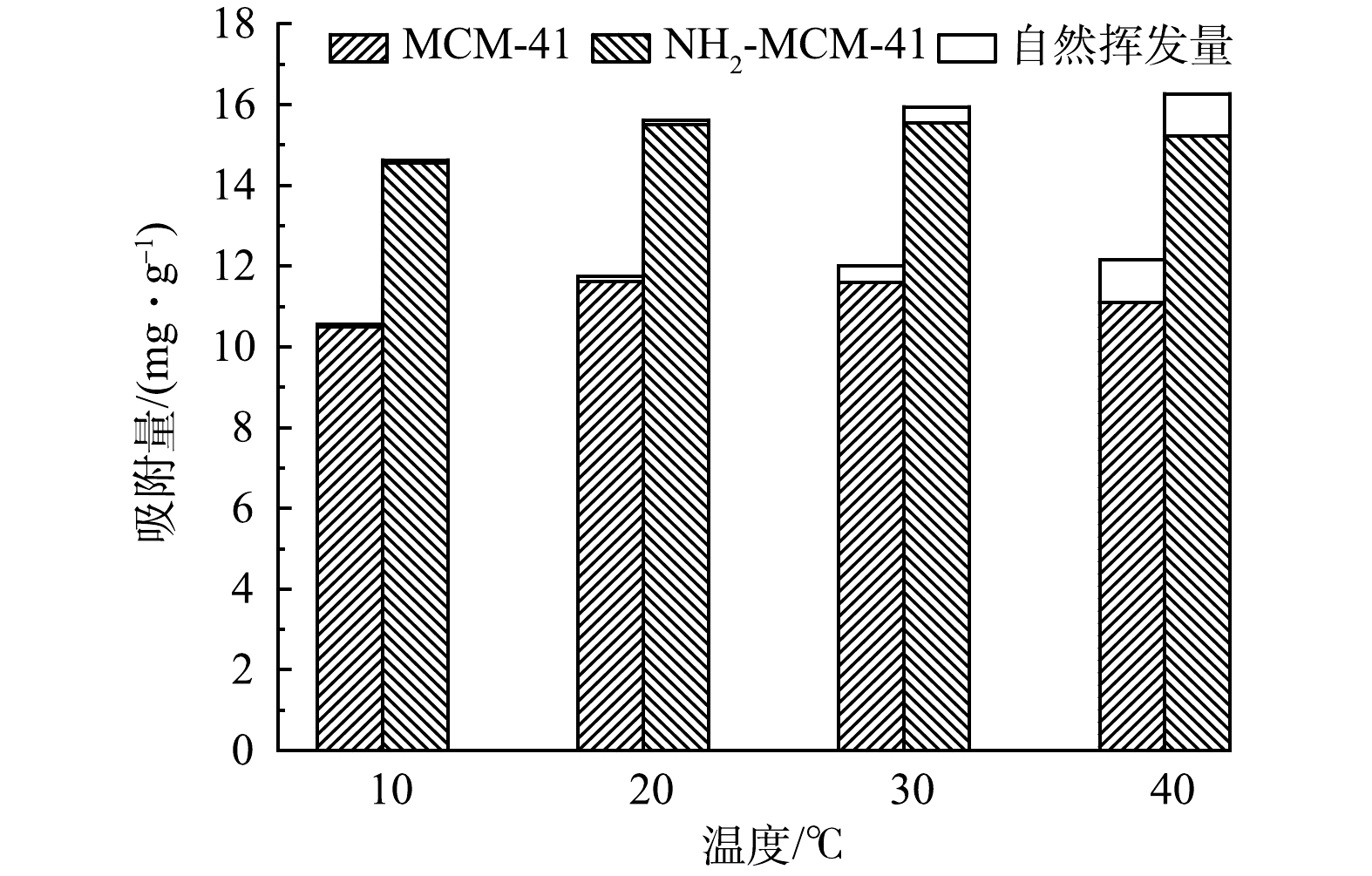
在材料投加量为0.4 g·L−1,1,2-DCA质量浓度为20 mg·L−1,实验温度分别为10、20、30和40 ℃的条件下,探究温度对吸附过程的影响,实验结果见图7。可以看出,不同温度下NH2-MCM-41对1,2-DCA的平衡吸附量均高于MCM-41。随着温度的升高,2种材料对1,2-DCA的吸附量均呈现波动的趋势,即平衡吸附量在10~20 ℃略有升高,20 ℃之后吸附量逐渐降低。由变化量看出,温度对于2种材料吸附水中1,2-DCA能力的影响较小,归因于水中吸附热较小[31]。10 ℃时,温度限制了1,2-DCA分子在水中的扩散速率,影响材料与吸附剂表面活性位点的接触,导致材料吸附容量低。温度高于20 ℃时,吸附容量逐渐下降。这是因为高温会导致1,2-DCA的挥发及解吸量增加,该现象在已有研究中[35-36]也有类似的报道。
-
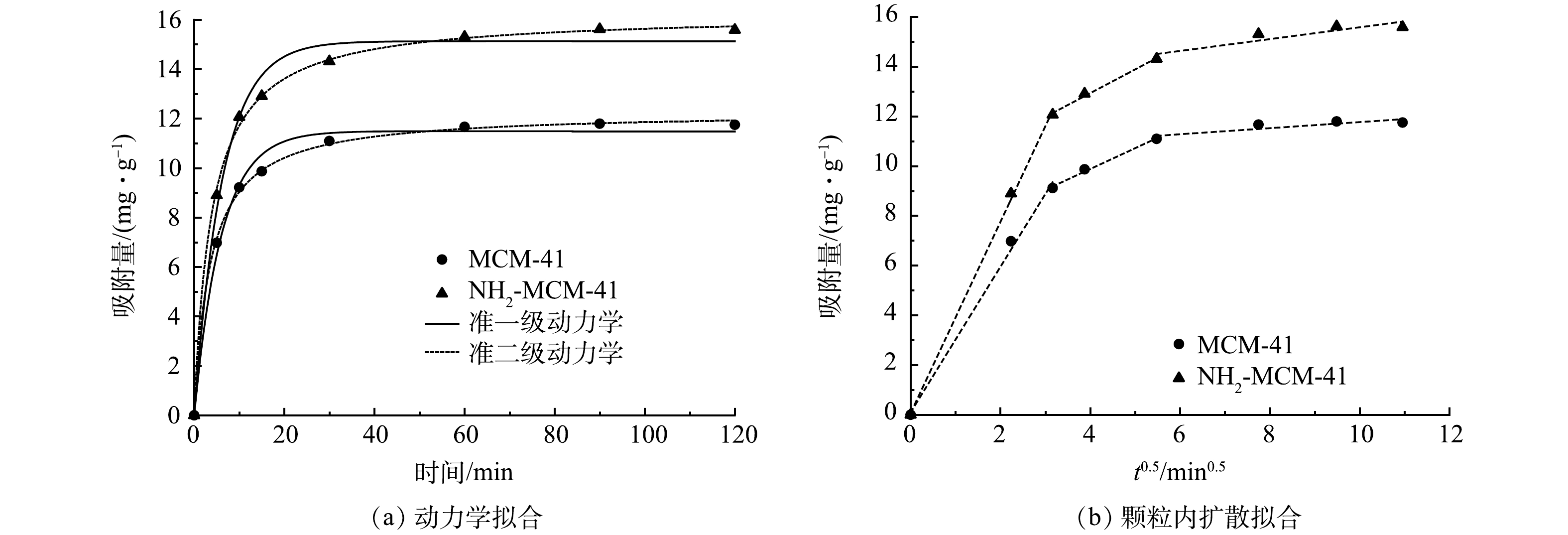
图8为MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41吸附1,2-DCA的动力学拟合结果。准一级动力学和准二级动力学拟合结果见图8(a)。可以看出,前10 min属于快速吸附阶段,2种材料对于1,2-DCA的吸附量迅速达到9.11 mg·g−1和12.07 mg·g−1,说明两者对1,2-DCA具有较强的亲和力[23]。随后,进入缓慢吸附阶段和吸附平衡阶段。这是因为吸附初始阶段,污染物分子迅速占据材料的活性位点,随着活性位点的减少,吸附速率逐渐减缓并趋于平衡。此外,NH2-MCM-41初期吸附速率明显大于MCM-41,说明氨基的引入增强了材料对1,2-DCA的亲和力。
为探究MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41的吸附机制,采用准一级动力学模型和准二级动力学模型对吸附数据进行拟合,准一级动力学方程见式(2),准二级动力学方程见式(3)。
式中:t为时间,min;qt和qe分别为t时刻、吸附平衡时的吸附量,mg·g−1;k1和k2分别为准一级动力学模型和准二级动力学模型吸附速率常数。
动力学相关拟合参数见表2。可以看出,2种模型均能较好地拟合吸附过程,但2种材料准二级动力学模型拟合系数均略大于准一级动力学模型拟合系数。这说明吸附过程更符合准二级动力学模型,该结果与已有研究结果[26,33]一致。准一级动力学模型仅能拟合吸附的初始阶段,此阶段是污染物分子向吸附剂表面扩散的过程[34,37],后续过程符合准二级动力学模型。说明吸附过程初始阶段受物理吸附控制,后续过程主要受化学吸附控制,推测材料与污染物之间存在电子供给关系[23,38]。
为进一步探究1,2-DCA分子在材料中的扩散过程及吸附过程的主要限速步骤,采用颗粒内扩散模型对吸附数据进行拟合,颗粒内扩散方程见式(4)。
式中:t为时间,min;qt为t时刻的吸附量,mg·g−1;kp为颗粒内扩散模型吸附速率常数;C为吸附剂边界层数的常数。
颗粒内扩散拟合结果见图8(b),相关拟合参数见表3。可以看出,NH2-MCM-41和MCM-41对1,2-DCA的吸附过程均分为3个阶段:在表面吸附阶段,1,2-DCA迅速扩散并吸附到材料外表面;在孔道内吸附阶段,1,2-DCA逐步由材料表面向孔道内部扩散;在吸附-解吸阶段,同时存在1,2-DCA的吸附和解吸,并逐渐达到吸附-解吸平衡[39]。第1阶段拟合曲线斜率最大,说明该阶段是吸附过程的次要限速阶段;第2阶段斜率变小,吸附量稳步增加,表明该阶段是吸附过程的主要控速步骤[23]。由MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41不同阶段kp对比结果可以看出,NH2-MCM-41在各个阶段吸附速度更快,说明氨基的引入增强了材料对1,2-DCA的亲和力,这与动力学分析结果一致。
由此可知,氨基的引入使材料孔容、孔径和比表面积分别减少了约10%、25%和26%,而吸附容量却提升了32.68%。这是因为:一方面,氨基属碱基基团,其中N原子含有孤电子对,可分配π电子,使得材料表面的π电子云密度增加,增强了NH2-MCM-41与1,2-DCA之间的作用力[40];另一方面,1,2-DCA属于非极性分子,氨基取代了材料表面部分硅羟基,降低了NH2-MCM-41的极性,进而提高了材料对1,2-DCA的亲和力。
-
为进一步探究MCM-41以及NH2-MCM-41吸附水中1,2-DCA的行为,采用Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附模型对实验数据进行拟合,Langmuir方程见式(5),Freundlich方程见式(6)。
式中:Ce为平衡质量浓度,mg·L−1;qe和qm为平衡吸附量和理论最大吸附量,mg·g−1;b、kf和n分别为Langmuir吸附常数、Freundlich吸附常数和Freundlich经验常数。
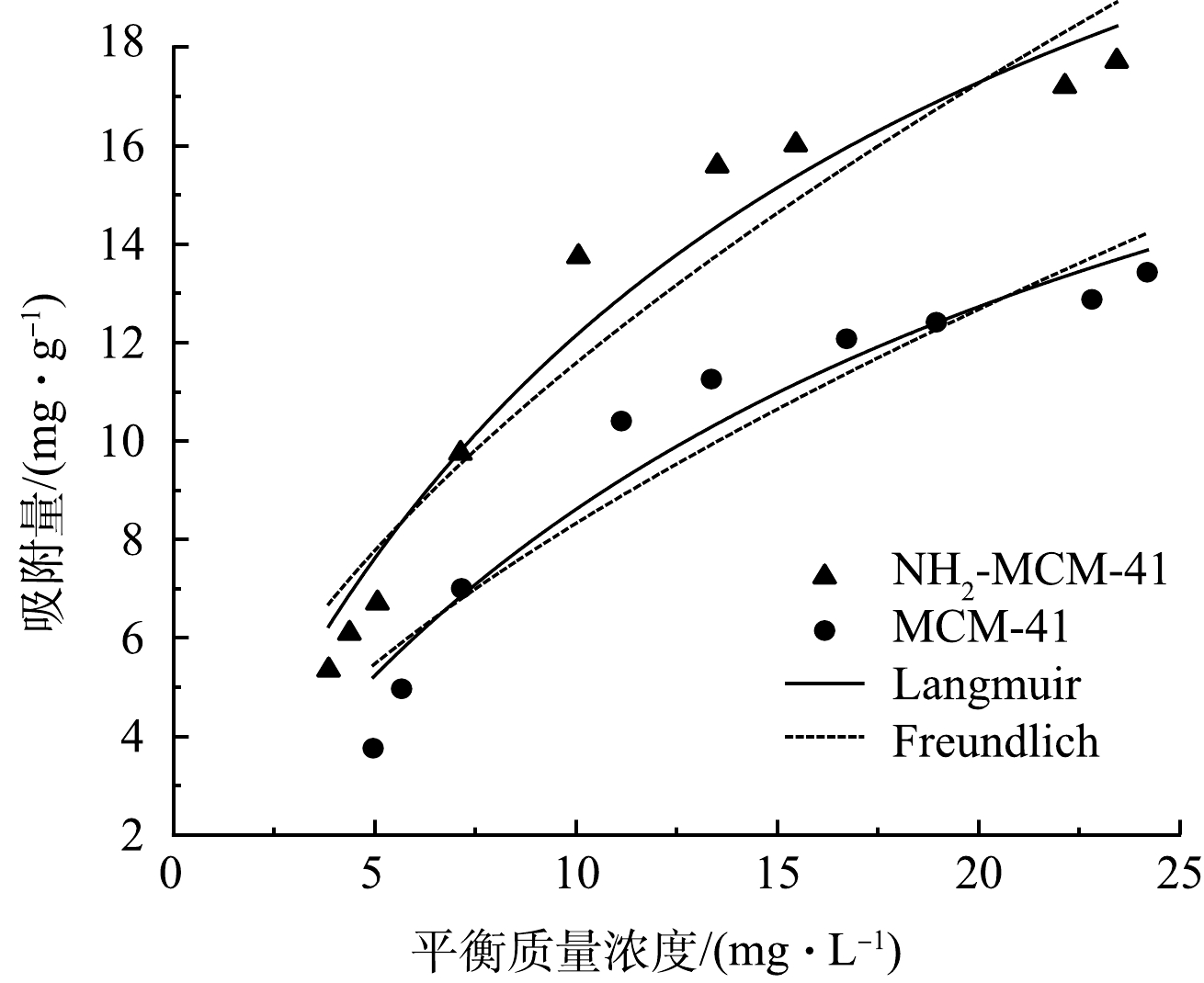
由图9可以看出,2种材料对于1,2-DCA的等温吸附趋势一致,吸附量随着平衡浓度的增加而增加,吸附量增长速度随平衡浓度的增加逐渐降低,均一定程度符合Langmuir和Freundlich模型,说明吸附过程中单层与多层吸附共存[41]。MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41对1,2-DCA等温吸附Langmuir拟合R2分别为0.936和0.956,Freundlich拟合R2分别为0.894和0.909。实测值分布于拟合曲线两侧,当吸附接近饱和时,最大吸附量实测值小于拟合值,说明2种模型拟合程度均不是很理想。这是因为实际吸附过程为单层吸附和多层吸附共存,不是只存在理想单层吸附或多层吸附,故实测值与拟合值略有差距。
由表4可以看出,NH2-MCM-41吸附1,2-DCA的Langmuir拟合常数b大于MCM-41,说明NH2-MCM-41对1,2-DCA有更强的亲和力[42],与颗粒内扩散拟合一致。此外,2种材料吸附1,2-DCA的Freundlich方程拟合指数n均大于1,说明改性前后材料对于1,2-DCA的吸附是易发生的。
-
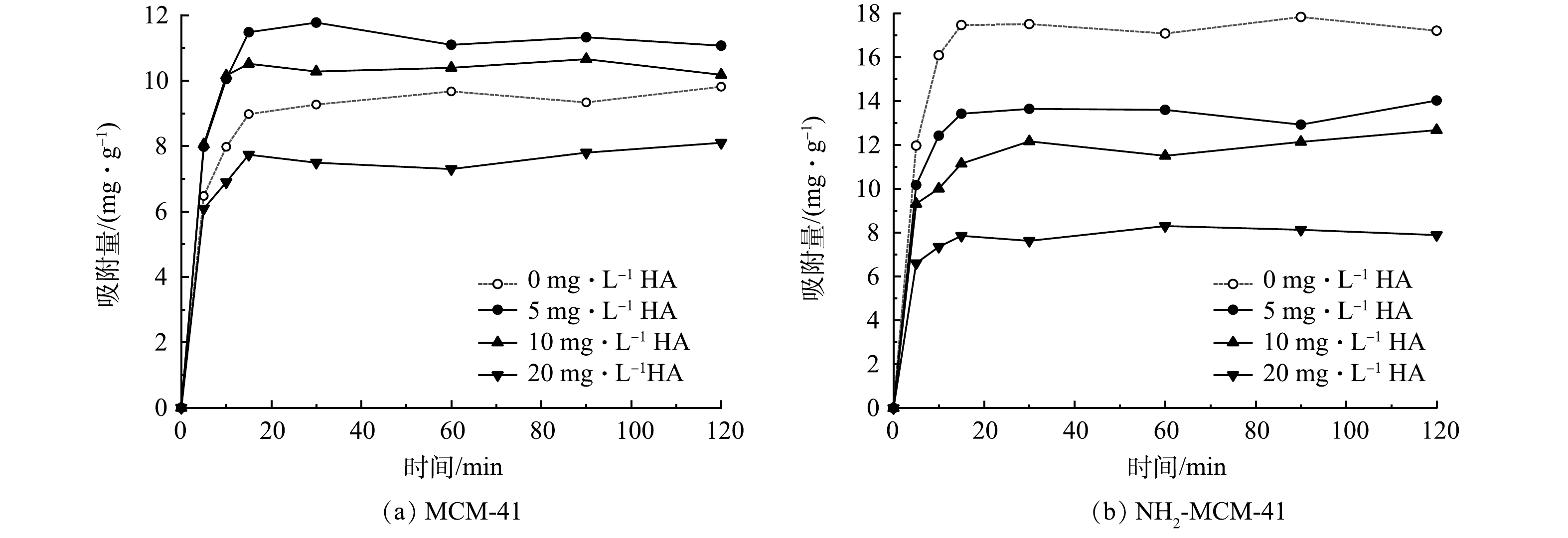
天然地下水环境中普遍存在着溶解性有机质,腐殖酸(HA)占50%~90%,腐殖酸分子结构复杂,对地下水中污染物的去除有一定的影响[43]。通过改变水中HA质量浓度,探究其对材料吸附1,2-DCA的影响,实验结果见图10。可以看出,低质量浓度HA对于MCM-41吸附1,2-DCA有一定的促进作用。这可能是HA分子分散在材料表面,其表面存在的活性基团促进了MCM-41对于1,2-DCA的吸附[44]。随着HA质量浓度的增加,促进作用逐渐减弱,抑制作用逐渐加强。这是因为大量HA分子的存在堵塞孔道,覆盖材料表面吸附位点,不利于1,2-DCA分子的扩散与吸附[43]。对于NH2-MCM-41而言,不同质量浓度的HA均表现出很强的抑制作用,且随着质量浓度的增加,抑制作用不断增强。吸附120 min后,3个体系中HA的质量浓度均降低到0.5 mg·g−1以下,说明NH2-MCM-41对于HA分子具有较强的吸附能力。一方面HA分子会使得材料表面氨基质子化,削弱其给电子能力,不利于其对1,2-DCA的吸附;另一方面HA分子通过含氧官能团与氨基反应,与1,2-DCA分子产生竞争吸附,导致材料对1,2-DCA的吸附量减少[45]。地下水环境中HA浓度普遍为0~5 mg·L−1,处于低质量浓度水平,NH2-MCM-41在该环境下表现出优于MCM-41的吸附性能,故在地下水环境中有一定的优势。
-
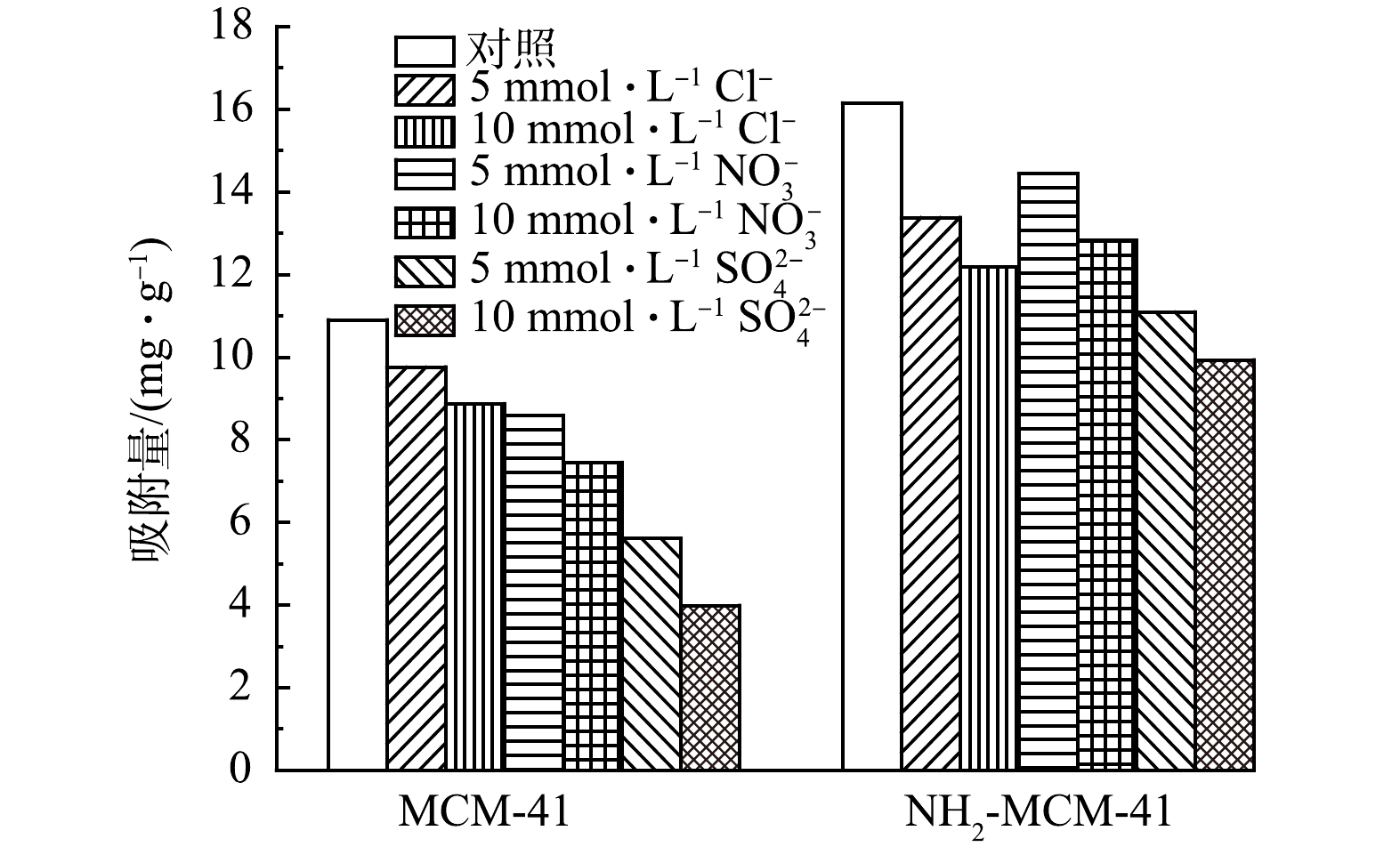
天然地下水成分复杂,存在大量的阴离子,会对材料吸附1,2-DCA造成一定的影响。故配制多种典型阴离子(Cl−、NO32−和SO42−)溶液,以探究共存阴离子对于吸附过程的影响,实验结果见图11。可以看出,3种典型阴离子对吸附过程均存在明显的抑制作用。这是因为共存阴离子进入材料孔道内部,占据吸附位点,导致吸附量有所降低[46]。对于MCM-41而言,抑制能力大小顺序为Cl−<NO32−<SO42−,与离子半径大小成正相关。说明离子半径较大的SO42−离子更易进入材料孔道,与1,2-DCA分子形成竞争关系,导致抑制作用大[47]。而对于NH2-MCM-41而言,Cl−和NO32−的抑制能力相近,SO42−抑制能力最大。且SO42−对NH2-MCM-41的抑制作用明显低于MCM-41,这是因为氨基的引入增强了材料与1,2-DCA间的π-π电子供体-受体相互作用,进而减少了SO42−竞争影响[48]。综上,氨基的引入增强了材料对共存阴离子的抗干扰能力。
-
1) 以共聚法成功制备NH2-MCM-41,改性后材料比表面积、孔容和孔径略有下降。氨基取代表面部分硅羟基,造成孔道毛糙,未破坏材料的基本结构,仍保持规则的六方堆积结构。
2) 温度对NH2-MCM-41吸附1,2-DCA影响较小,温度升高会加快1,2-DCA的挥发和解吸。酸性条件下,氨基质子化影响其给电子能力;碱性条件下,材料结构易分解;两者均不利于材料对1,2-DCA的吸附。
3) 氨基的引入提高了材料表面π电子云密度,降低了材料极性,提升了材料对于1,2-DCA的亲和力和吸附能力。动力学拟合结果显示,NH2-MCM-41对1,2-DCA的吸附初始阶段为物理吸附,后续阶段则以化学吸附为主;等温吸附模型拟合结果表明,材料表面吸附位点分布均匀,吸附过程中单层与多层吸附共存;颗粒内扩散模型拟合结果表明内扩散过程是吸附的主要控速步骤。
4) 低质量浓度的HA对MCM-41吸附1,2-DCA有一定的促进作用;而不同质量浓度的HA均会抑制NH2-MCM-41对于1,2-DCA的吸附。共存阴离子均会对吸附过程表现出抑制作用,SO42−抑制作用最强,氨基引入增强了材料对于共存阴离子的抗干扰能力。
氨基改性MCM-41对水中1,2-二氯乙烷的吸附
Adsorption of 1,2-dichloroethane in water by amino modified MCM-41
-
摘要: 为治理地下水中氯代烃污染,以3-氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷(APTES)为改性试剂,采用共聚法制备NH2-MCM-41。利用XRD、SEM、TEM、BET和FT-IR对材料结构进行表征,并研究材料对水中1,2-二氯乙烷(1,2-DCA)的吸附行为。结果表明:氨基取代部分硅羟基,造成孔道毛糙,未改变材料的六方堆积结构;改性后材料比表面积、孔容、孔径分别减小了约10%、25%和26%。氨基的引入增强了材料对1,2-DCA的亲和力和吸附能力,吸附容量由11.75 mg·g−1增加到15.59 mg·g−1,提升32.68%;NH2-MCM-41对1,2-DCA吸附初始阶段受物理吸附控制,后续过程主要受化学吸附控制;颗粒内扩散拟合表明颗粒内扩散过程是主要控速步骤;等温吸附拟合说明材料吸附位点分布均匀,吸附过程中单层与多层吸附共存;在温度为20 ℃,pH为7时NH2-MCM-41对1,2-DCA的吸附效果最佳;腐殖酸(HA)和共存阴离子对 NH2-MCM-41吸附1,2-DCA起抑制作用。由此可知,NH2-MCM-41能够有效地吸附水中1,2-DCA。该研究成果可为地下水氯代烃污染治理提供相关参考。Abstract: In order to control the pollution of chlorinated hydrocarbons in groundwater, NH2-MCM-41 was prepared by copolymerization with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) as the modifier. The structure of NH2-MCM-41 was characterized by XRD, SEM, TEM, BET and FT-IR, and its adsorption behavior towards 1,2-DCA in water was studied. The results showed that amino groups substituted part of silicon hydroxyl groups, resulting in the rough pores, while slight change on the hexagonal stacking structure of NH2-MCM-41 occurred. After modification, the specific surface area, pore volume and pore diameter decreased by about 10%, 25% and 26%, respectively. The introduction of amino groups enhanced the affinity and adsorption capacity of NH2-MCM-41 toward 1,2-DCA, and the adsorption capacity increased from 11.75 mg·g−1 to 15.59 mg·g−1 with an increase rate of 32.68%. The kinetic fitting showed that at the initial stage, NH2-MCM-41 adsorbing 1,2-DCA was controlled by physical adsorption, and it was mainly controlled by chemical adsorption during the subsequent process. The fitting of particle internal diffusion showed that the particle internal diffusion process was the main speed control step. Isothermal adsorption fitting showed that the adsorption sites of NH2-MCM-41 were evenly distributed, and monolayer and multilayer adsorption coexisted in the adsorption process. At 20 ℃ and pH 7, NH2-MCM-41 presented the best adsorption toward 1,2-DCA. Humic acid (HA) and coexisting anions inhibited the adsorption of 1,2-DCA on NH2-MCM-41. Thus, NH2-MCM-41 could effectively adsorb 1,2-DCA in water. The research results can provide a relevant reference for the treatment of polluted groundwater by chlorinated hydrocarbon.
-
Key words:
- MCM-41 /
- amino /
- functionalization /
- adsorption /
- 1,2- dichloroethane
-

-
表 1 MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41的比表面积以及孔的相关参数
Table 1. Specific surface area of MCM-41 and NH2-MCM-41 and related parameters of pores
样品 比表面积/
(m2·g−1)孔容/
(cm3·g−1)孔径/
nmMCM-41 860.17 0.85 4.78 NH2-MCM-41 776.37 0.64 3.53 表 2 MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41吸附1,2-DCA的动力学拟合参数
Table 2. Kinetic model parameters for the adsorption of 1,2-DCA on MCM-41 and NH2-MCM-41
样品 qe
/(mg·g−1)准一级动力学 准二级动力学 k1 qe
/(mg·g−1)R2 k2 qe
/(mg·g−1)R2 MCM-41 11.75 0.17 11.37 0.989 0.023 11.79 0.997 NH2-MCM-41 15.59 0.16 15.13 0.988 0.016 15.73 0.998 表 3 MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41吸附1,2-DCA的颗粒内扩散模型拟合参数
Table 3. Intra-particle diffusion model parameters for 1,2-DCA adsorption on MCM-41 and NH2-MCM-41
样品 第1阶段 第2阶段 第3阶段 kp1 C1 R2 kp2 C2 R2 kp3 C3 R2 MCM-41 2.93 0.098 0.992 0.84 6.533 0.986 0.12 10.547 0.667 NH2-MCM-41 3.85 0.067 0.998 0.95 9.116 0.989 0.24 13.205 0.762 表 4 MCM-41和NH2-MCM-41吸附1,2-DCA的等温拟合曲线参数
Table 4. Parameters of isothermal fitting curves for the adsorption of 1,2-DCA on MCM-41 and NH2-MCM-41
样品 Langmuir Freundlich qm
/(mg·g−1)b R2 kf n R2 MCM-41 24.38 0.055 0.936 2.06 1.65 0.894 NH2-MCM-41 29.97 0.069 0.956 3.07 1.74 0.909 -
[1] 范婷婷, 夏菲洋, 孔令雅, 等. 场地地下水中氯代甲烷烃自然衰减机制[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(12): 3934-3945. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202108083 [2] CHEN S, BEDIA J, LI H, et al. Nanoscale zero-valent iron@mesoporous hydrated silica core-shell particles with enhanced dispersibility, transportability and degradation of chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 343: 619-628. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.011 [3] 张凤君, 刘哲华, 苏小四, 等. 土壤类型及组分对热活化过硫酸盐氧化降解土壤中挥发性氯代烃的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2018, 48(4): 1212-1220. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.20170240 [4] JEONG W G, KIM J G, BAEK K. Removal of 1, 2-dichloroethane in groundwater using Fenton oxidation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 428: 128253. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128253 [5] 孙军亮, 宫志强, 李璐, 等. 某氯代烃污染场地地下水抽出方案优化[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(11): 172-178. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202111023 [6] SANTOSH P G, SAROHA A K. Catalytic ozonation for the treatment of synthetic and industrial effluents: Application of mesoporous materials: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 211: 83-102. [7] 王泓泉. 污染地下水可渗透反应墙(PRB)技术研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2020, 10(2): 251-259. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190129 [8] 孟宪荣, 葛松, 许伟, 等. 原位电阻热脱附修复氯代烃污染土壤[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(2): 669-676. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202009077 [9] ANNE W, AKI S R, RICHARD T A. Investigating dominant processes in ZVI permeable reactive barriers using reactive transport modeling[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2013, 151: 68-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2013.05.001 [10] 崔海炜, 孙继朝, 张英, 等. 可渗透反应墙原位修复垃圾渗滤液污染地下水[J]. 环境工程学报, 2012, 6(8): 2698-2704. [11] 张永祥, 王晋昊, 井琦, 等. 地下水修复中纳米零价铁材料制备及应用综述[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(8): 4486-4496. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2020-1852 [12] COSTA J A S, JESUS R A, SANTOS D O, et al. Synthesis, functionalization, and environmental application of silica-based mesoporous materials of the M41S and SBA-n families: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(3): 105259. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105259 [13] 李美元, 白金, 杨丽娜, 等. 金属改性硅基介孔材料及其加氢脱硫研究进展[J]. 化学通报, 2017, 80(5): 448-453. doi: 10.14159/j.cnki.0441-3776.2017.05.006 [14] ENSHIRAH D N. Adsorption of heavy metals on functionalized-mesoporous silica: A review[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017, 247: 145-157. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.03.050 [15] ALARDHI S M, ALBAYATI T M, ALRUBAYE J M. Adsorption of the methyl green dye pollutant from aqueous solution using mesoporous materials MCM-41 in a fixed-bed column[J]. Heliyon, 2020, 6(1): e03253. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03253 [16] 旦辉. 硅基介孔材料的控制合成及其核素吸附性能研究[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2020. [17] GETKESH E M, YOUNESI H, SHAHBAZI A. Nitrate removal from aqueous solution using nanoporous MCM-41 silica adsorbent functionalized with diamine group[J]. Journal of Water and Wastewater, 2014, 25: 69-76. [18] RUMMAN G A, MUSAWI T J, SILLANPAA M, et al. Adsorption performance of an amine-functionalized MCM-41 mesoporous silica nanoparticle system for ciprofloxacin removal[J]. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 2021, 16: 100536. [19] 周丽枫, 王韧, 冯伟, 等. 巯基改性磁性介孔二氧化硅的制备及其对重金属Cd2+的吸附研究[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2018, 37(10): 1035-1041. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2018.10.005 [20] OTALVARO J O, AVENA M, BRIGANTE M. Adsorption of organic pollutants by amine functionalized mesoporous silica in aqueous solution. Effects of pH, ionic strength and some consequences of APTES stability[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2019, 7(5): 103325. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2019.103325 [21] ILIADE P, MILETTO I, COLUCCIA S, et al. Functionalization of mesoporous MCM-41 with aminopropyl groups by co-condensation and grafting: A physico-chemical characterization[J]. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 2012, 38: 785-794. doi: 10.1007/s11164-011-0417-5 [22] 刘佳, 隋铭皓, 盛力. Mn-MCM-41介孔分子筛的制备、表征及催化性能研究[J]. 现代化工, 2018, 38(7): 93-97. doi: 10.16606/j.cnki.issn0253-4320.2018.07.021 [23] LU D W, XU S, QIU W, et al. Adsorption and desorption behaviors of antibiotic ciprofloxacin on functionalized spherical MCM-41 for water treatment[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 264: 121644. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121644 [24] WONG T C, WONG N B, TANNER P A. A Fourier transform IR study of the phase transitions and molecular order in the hexadecyltrimethylammonium sulfate/water system[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1997, 186(2): 325-331. doi: 10.1006/jcis.1996.4674 [25] 曹渊, 王晓, 白英豪, 等. 氨丙基修饰MCM-41的制备及载药释药性能研究[J]. 功能材料, 2010, 41(5): 833-836. [26] NICOLAS F, FRANCISCO J P A, MARTIN P P, et al. Chromium (VI) removal from water by means of adsorption-reduction at the surface of amino-functionalized MCM-41 sorbents[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017, 239: 138-146. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.10.012 [27] 徐彦芹, 秦钊, 王烨, 等. NH2-MCM-41的改性及其pH响应性释药的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(10): 4783-4791. [28] SOUZA A P N, LICEA Y E, COLACA M V, et al. Green iron oxides/amino-functionalized MCM-41 composites as adsorbent for anionic azo dye: Kinetic and isotherm studies[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(2): 105062. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105062 [29] YOKOI T, KUBOTA Y, TATSUMI T. Amino-functionalized mesoporous silica as base catalyst and adsorbent[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2012, 421-422: 14-37. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.02.004 [30] ZHANG B, WU T, SUN D J, et al. NH2-MCM-41 supported on nitrogen-doped graphene as bifunctional composites for removing phenol compounds: Synergistic effect between catalytic degradation and adsorption[J]. Carbon, 2019, 147: 312-322. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.02.084 [31] QIN Q D, XU Y. Enhanced nitrobenzene adsorption in aqueous solution by surface silylated MCM-41[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016, 232: 143-150. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.06.018 [32] BROYER M, VALANGE S, BELLAT J P, et al. Influence of aging, thermal, hydrothermal, and mechanical treatments on the porosity of MCM-41 mesoporous silica[J]. Langmuir, 2002, 18(13): 5083-5091. doi: 10.1021/la0118255 [33] 王英. 功能化MCM-41介孔材料的制备及其吸附稀土离子的性能研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2017. [34] EDER S, MULLER K, AZZARI P, et al. Mass transfer mechanism and equilibrium modelling of hydroxytyrosol adsorption on olive pit-derived activated carbon[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 404: 126519. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126519 [35] PASTI L, MARTUCCI A, NASSI M, et al. The role of water in DCE adsorption from aqueous solutions onto hydrophobic zeolites[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2012, 160(36): 182-193. [36] 史琳. 多孔吸附材料对水中氯代烃的吸附性能研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019. [37] GIRISH C R, RAMACHANDRA M V. Mass transfer studies on adsorption of phenol from wastewater using lantana camara, forest waste[J]. International Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 2: 1-11. [38] 陈星, 王小丽, 冉谷, 等. 氨基改性的MCM-41吸附水溶液中亚甲基蓝的研究[J]. 精细化工, 2016, 33(2): 188-194. doi: 10.13550/j.jxhg.2016.02.014 [39] 秦庆东. 功能化介孔材料MCM-41选择性吸附水中污染物的性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2009. [40] ALMAZAN M C, MENDOZA M P, GARCIA M D, et al. The role of the porosity and oxygen groups on the adsorption of n-alkanes, benzene, trichloroethylene and 1, 2-dichloroethane on active carbons at zero surface coverage[J]. Carbon, 2007, 45(9): 1777-1785. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2007.05.003 [41] 梁志杰. 功能化介孔硅吸附剂的制备及其选择吸附特性与作用机制[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017. [42] LIN R Y, LIANG Z J, YANG C, et al. Selective and enhanced adsorption of the monosubstituted benzenes on the Fe-modified MCM-41: Contribution of the substituent groups[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 237: 124546. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124546 [43] 袁放. 腐殖酸和硝酸盐对铁屑去除地下水中六价铬的影响研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014. [44] PAN B, ZHANG D, LI H, et al. Increased adsorption of sulfamethoxazole on suspended carbon nanotubes by dissolved humic acid[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(14): 7722-7728. [45] 梁喜花. 腐殖酸对零价铁处理地下水中三氯乙烯影响的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013. [46] 刘华秋, 付融冰, 温东东, 等. 颗粒活性炭对尾渣污染地下水中氰化物的吸附去除效能[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(12): 3531-3541. [47] 朱立超, 刘元元, 李伟民, 等. 施氏矿物的化学合成及其对含Cr(Ⅵ)地下水吸附修复[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(2): 629-639. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201608044 [48] ZHANG X T, LIU M Y, HAN R P. Adsorption of phosphate on UiO-66-NH2 prepared by a green synthesis method[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(6): 106672. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.106672 -



 下载:
下载: